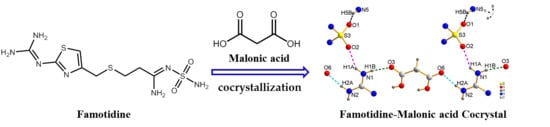
Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Solubility Analysis of a Famotidine Cocrystal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. General
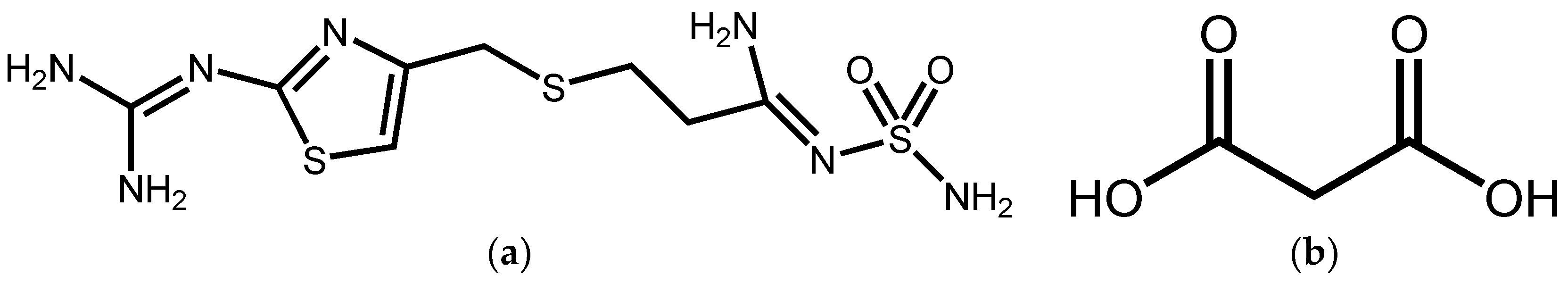
2.2. Synthesis of FMT-MAL Cocrystal
2.3. Single-Crystal X-ray Diffraction Analysis
2.4. Conductivity
2.5. High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
2.6. Solubility Determination
2.7. Stability Determination
3. Results and Discussion
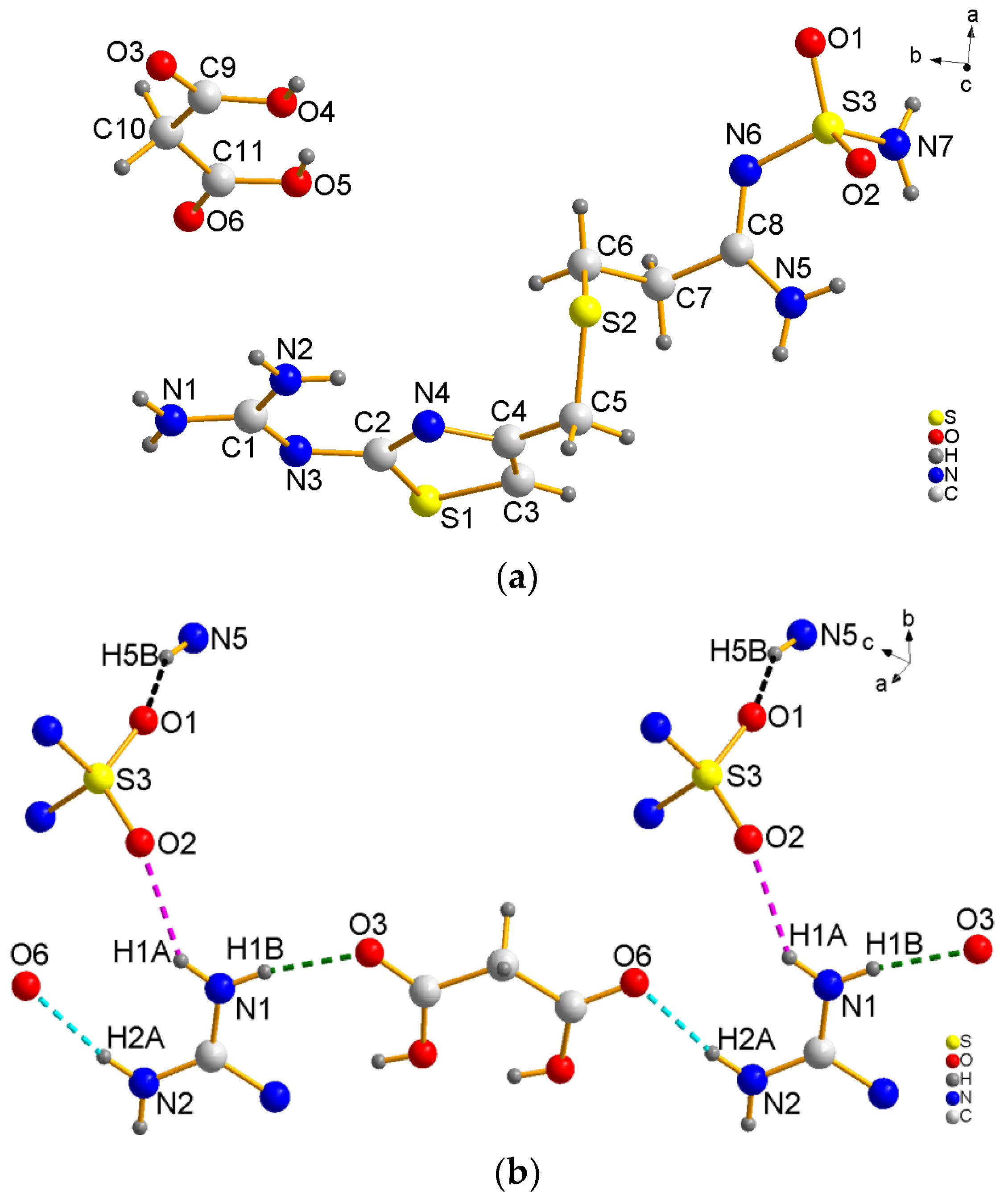
3.1. Crystal Strcture
3.2. Thermal Properties
3.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
3.4. Aqueous Solubility
3.5. Stability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kawabata, Y.; Wada, K.; Nakatani, M.; Yamadaa, S.; Onouea, S. Formulation design for poorly water-soluble drugs based on biopharmaceutics classification system: Basic approaches and practical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 420, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, H.D.; Trevaskis, N.L.; Charman, S.A.; Shanker, R.M.; Charman, W.N.; Pouton, C.W.; Porter, C.J.H. Strategies to address low drug solubility in discovery and development. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 65, 315–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittapalli, S.; Mannava, M.K.C.; Khandavilli, U.B.R.; Allu, S.; Nangia, A. Soluble salts and cocrystals of clotrimazole. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 2493–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Yoon, W.; Yun, J.; Ban, E.; Yun, H.; Kim, A. Emodin-nicotinamide (1:2) cocrystal identified by thermal screening to improve emodin solubility. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 557, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Zu, H.; Zhang, J. Enhanced dissolution and stability of adefovir dipivoxil by cocrystal formation. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 63, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcnamara, D.P.; Childs, S.L.; Giordano, J.; Iarriccio, A.; Cassidy, J.; Shet, M.S.; Mannion, R.; O’Donnell, E.; Park, A. Use of a glutaric acid cocrystal to improve oral bioavailability of a low solubility API. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 1888–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.Z.; Ouyang, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L. Structural characterization and dissolution profile of mycophenolic acid cocrystals. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 102, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavropoulos, K.; Johnston, S.C.; Zhang, Y.G.; Rao, B.G.; Hurrey, M.; Hurter, P.; Topp, E.M.; Kadiyala, I. Cocrystalline solids of telaprevir with enhanced oral absorption. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 3343–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyche, T.P.; Alvarenga, R.F.R.; Piotrowski, J.S.; Duster, M.N.; Warrack, S.R.; Cornilescu, G.; De Wolfe, T.J.; Hou, Y.; Braun, D.R.; Ellis, G.A.; et al. Chemical genomics, structure elucidation, and in vivo studies of the marine-derived anticlostridial ecteinamycin. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 2287–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowa, M.; Slepokura, K.; Matczakjon, E.; Sowa, M.; Ślepokura, K.; Matczak-Jon, E.J.C. Improving solubility of fisetin by cocrystallization. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2014, 16, 10592–10601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozd, K.V.; Manin, A.N.; Churakov, A.V.; Perlovich, G.L. Drug-drug cocrystals of antituberculous 4-aminosalicylic acid: Screening, crystal structures, thermochemical and solubility studies. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 99, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadha, R.; Bhandari, S.; Haneef, J.; Khullar, S.; Mandal, S. Cocrystals of telmisartan: Characterization, structure elucidation, in vivo and toxicity studies. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2014, 16, 8375–8389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, N.; Li, M.; Schlindwein, W.; Malek, N.; Davies, A.; Trappitt, G. Pharmaceutical cocrystals: An overview. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 419, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miroshnyk, I.; Mirza, S.; Sandler, N. Pharmaceutical co-crystals-an opportunity for drug product enhancement. Expert Opin. Drug Del. 2009, 6, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Childs, S.L.; Stahly, G.P.; Park, A. The salt-cocrystal continuum: The influence of crystal structure on ionization state. Mol. Pharm. 2007, 4, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerreia Vioglio, P.; Chierotti, M.R.; Gobetto, R. Pharmaceutical aspects of salt and cocrystal forms of APIs and characterization challenges. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 117, 86–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rad, T.S.; Khataee, A.; Kayan, B.; Kalderis, D.; Akay, S. Synthesis of pumice-TiO2 nanoflakes for sonocatalytic degradation of famotidine. J. Clean Prod. 2018, 202, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mady, F.M.; Abou-Taleb, A.E.; Khaled, K.A.; Yamasaki, K.; Iohara, D.; Ishiguro, T.; Hirayama, F.; Kaneto, U.; Otagiri, M. Enhancement of the aqueous solubility and masking the bitter taste of famotidine using drug/SBE-β-CyD/povidone K30 complexation approach. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 4285–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Német, Z.; Hegedűs, B.; Szántay, C.; Sztatisz, J.; Pokol, G. Pressurization effects on the polymorphic forms of famotidine. Thermochim. Acta 2005, 430, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karashima, M.; Kimoto, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Kojima, T.; Ikeda, Y. A novel solubilization technique for poorly soluble drugs through the integration of nanocrystal and cocrystal technologies. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 107, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT–Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. A Found. Adv. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, T.; In, Y.; Doi, M.; Inoue, M.; Yanagisawa, I. Structural study of histamine H2-receptor antagonists. Five 3-[2-(diaminomethyleneamino)-4-thiazolylmethylthio] propionamidine and-amide derivatives. Acta Crystallogr. B Struct. Sci. 1989, 45, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmerer, A.; Bernstein, J.; Kahlenberg, V. One-pot covalent and supramolecular synthesis of pharmaceutical co-crystals using the API isoniazid: A potential supramolecular reagent. CrystEngComm 2010, 12, 2856–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noonan, T.J.; Chibale, K.; Cheuka, P.M.; Bourne, S.A.; Caira, M.R. Cocrystal and salt forms of an imidazopyridazine antimalarial drug lead. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 2349–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimpi, M.R.; Alhayali, A.; Cavanagh, K.L.; Rodríguez-Hornedo, N.; Velaga, S.P. Tadalafil–malonic acid cocrystal: Physicochemical characterization pH-solubility, and supersaturation studies. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 4378–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, I.; Hirata, Y.; Ishii, Y. Studies on histamine H2 receptor antagonists. 2. Synthesis and pharmacological activities of N-sulfamoyl and N-sulfonyl amidine derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 1987, 30, 1787–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultheiss, N.; Newman, A. Pharmaceutical cocrystals and their physicochemical properties. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 2950–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Compound | FMT-MAL |
|---|---|
| Formula | C11H19N7O6S3 |
| Formula Weight | 441.51 |
| Temperature (K) | 296 (2) |
| Crystal System | Monoclinic |
| Space Group | P21/n |
| a (Å) | 7.0748 (3) |
| b (Å) | 26.6502 (9) |
| c (Å) | 9.9823 (4) |
| α ° | 90 |
| β ° | 104.2228 (12) |
| γ ° | 90 |
| Volume (Å3) | 1824.42 (12) |
| Z | 4 |
| Density calculated (g∙cm−3) | 1.607 |
| F (000) | 920 |
| Absorption coefficient (mm−1) | 0.453 |
| Reflection collected | 25641 |
| Unique Reflection | 8367 |
| Rint | 4189 |
| R1a, wR2b [I > 2σ(I)] | 0.0544/0.1477 |
| R1, wR2 (all data) | 0.0691/0.1586 |
| Goodness-of-fit on F2 | 1.049 |
| Δρmax, Δρmin, (e Å−3) | 0.617, −0.559 |
| FMT-MAL | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| S (1)-C (3) | 1.719 (3) | S (1)-C (2) | 1.723 (2) |
| S (2)-C (6) | 1.805 (3) | S (2)-C (5) | 1.814 (3) |
| S (3)-O (1) | 1.432 (2) | S (3)-N (6) | 1.613 (2) |
| S (3)-O (2) | 1.438 (2) | S (3)-N (7) | 1.609 (3) |
| C (9)-O (3) | 1.222 (4) | C (11)-O (5) | 1.300 (4) |
| C (9)-O (4) | 1.278 (4) | C (11)-O (6) | 1.215 (4) |
| N (3)-C (1) | 1.355 (3) | N (3)-C (2) | 1.391 (3) |
| N (4)-C (2) | 1.295 (3) | N (4)-C (4) | 1.391 (3) |
| O (1)-S (3)-N (7) | 109.30 (15) | C (1)-N (3)-C (2) | 125.2 (2) |
| O (2)-S (3)-N (7) | 105.97 (13) | C (18)-N (2)-C (21) | 108.02 (14) |
| O (1)-S (3)-N (6) | 105.50 (12) | N (2)-C (1)-N (1) | 122.0 (2) |
| O (2)-S (3)-N (6) | 113.49 (12) | N (2)-C (1)-N (3) | 121.0 (2) |
| N (7)-S (3)-N (6) | 106.09 (13) | N (1)-C (1)-N (3) | 117.0 (2) |
| O (1)-S (3)-N (6)-C (8) | −168.8 (2) | ||
| O (2)-S (3)-N (6)-C (8) | −40.7 (3) | ||
| N (7)-S (3)-N (6)-C (8) | 75.2 (2) | ||
| Hydrogen Bond | Distance a, Å | Distance b, Å | Angle c, ° |
|---|---|---|---|
| N1−H1A···O2 | 2.18 | 2.927 (1) | 145 |
| N1−H1B···O3 | 1.94 | 2.796 (1) | 171 |
| N2−H2A···O6 | 1.99 | 2.837 (1) | 167 |
| N5−H5B···O1 | 2.05 | 2.860 (1) | 157 |
| FMT | Inspection Item | 0 Day | 5 Day | 10 Day |
| 4500 lux | Content (%) | 99.8 | 99.4 | 98.9 |
| 60 °C | Content (%) | 99.8 | 99.2 | 98.2 |
| 25 °C, 92.5% RH | Increasing Weight (%) | 0 | 0.005 | 0.008 |
| Content (%) | 99.8 | 98.8 | 97.6 | |
| FMT-MAL | Inspection Item | 0 Day | 5 Day | 10 Day |
| 4500 lux | Content (%) | 99.5 | 99.3 | 99.0 |
| 60 °C | Content (%) | 99.5 | 98.2 | 97.5 |
| 25 °C, 92.5% RH | Increasing Weight (%) | 0 | 0.007 | 0.010 |
| Content (%) | 99.5 | 98.6 | 98.5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, X. Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Solubility Analysis of a Famotidine Cocrystal. Crystals 2019, 9, 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9070360
Zhang Y, Yang Z, Zhang S, Zhou X. Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Solubility Analysis of a Famotidine Cocrystal. Crystals. 2019; 9(7):360. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9070360
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yan, Zhao Yang, Shuaihua Zhang, and Xingtong Zhou. 2019. "Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Solubility Analysis of a Famotidine Cocrystal" Crystals 9, no. 7: 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9070360