Arabidopsis SUMO E3 Ligase SIZ1 Interacts with HDA6 and Negatively Regulates HDA6 Function during Flowering
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.2. Gene Expression Analysis
2.3. Protein–Protein Interaction Assay
2.4. Histone Preparations
2.5. ChIP Assays
2.6. SUMOylation Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. SUMO E3 Ligase SIZ1 Interacts with HDA6 In Vitro and In Vivo
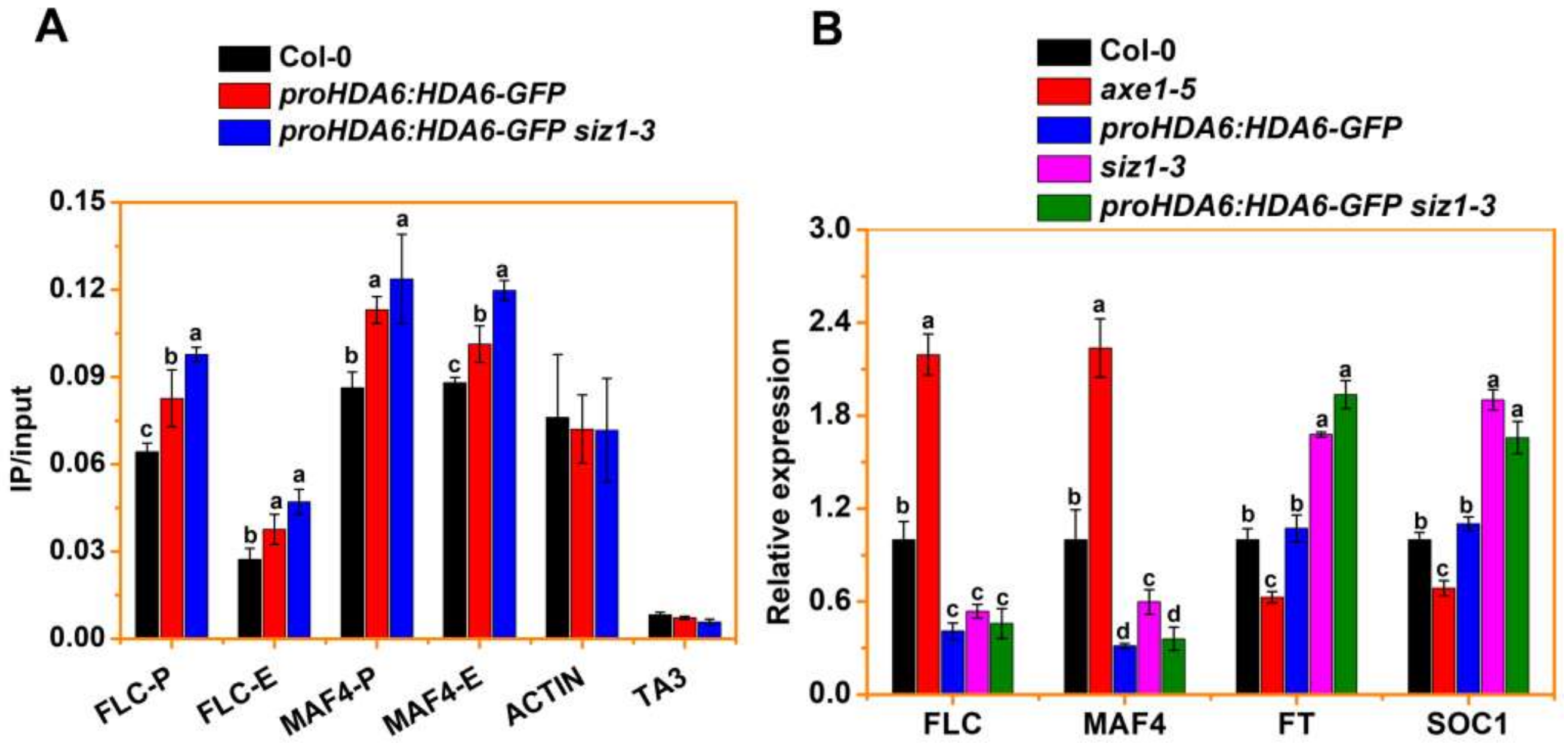
3.2. HDA6 Acts Downstream of SIZ1 to Repress FLC
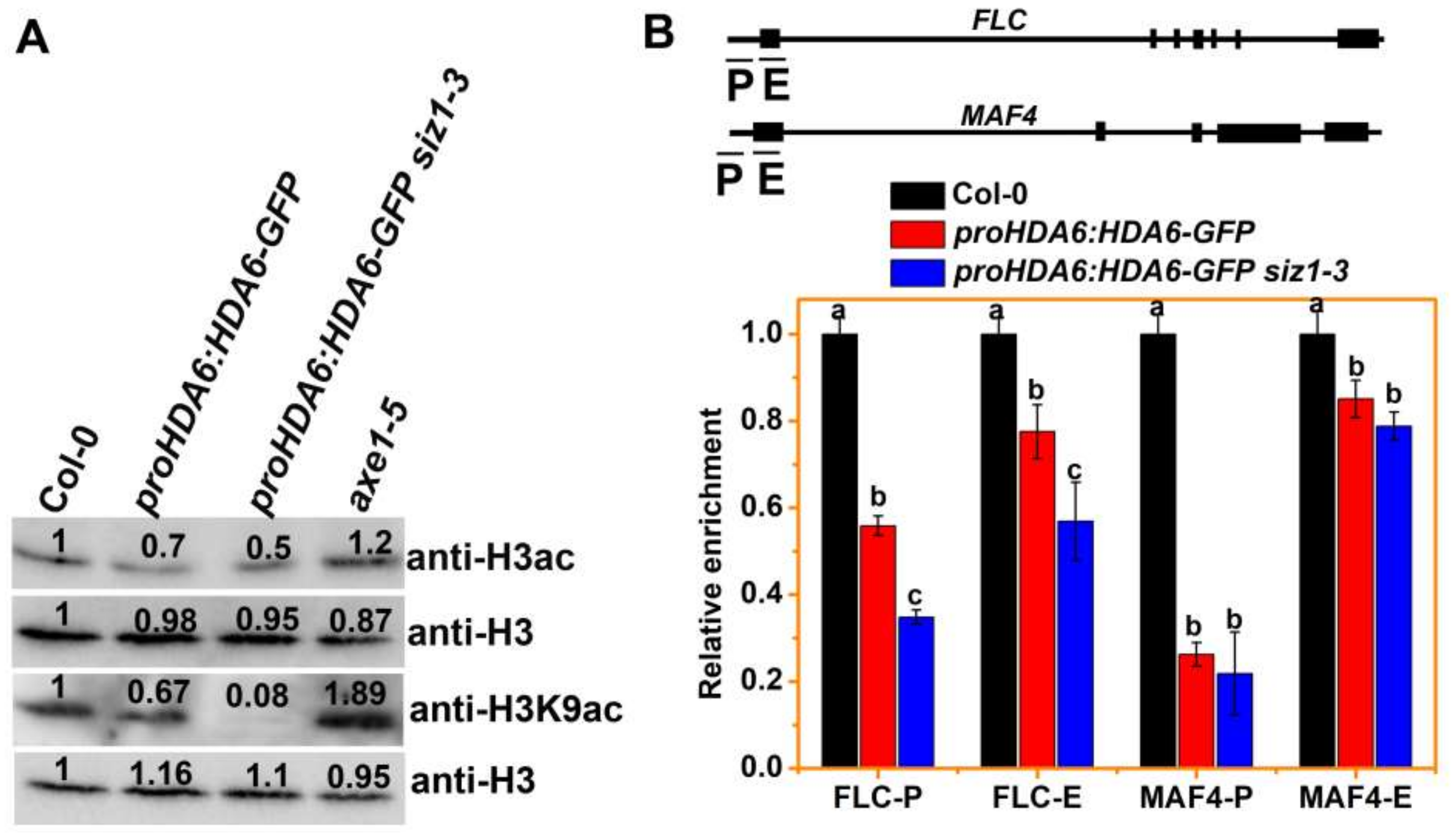
3.3. The H3ac and H3K9ac Levels of MAF4 and FLC Are Decreased in siz1-3 Plants
3.4. SIZ1 Represses HDA6 Binding to Its Target during Flowering
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kornberg, R.D. Chromatin structure: A repeating unit of histones and DNA. Science 1974, 184, 868–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luger, K.; Mader, A.W.; Richmond, R.K.; Sargent, D.F.; Richmond, T.J. Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 angstrom resolution. Nature 1997, 389, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, S.L. The complex language of chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature 2007, 447, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.J.; Wang, Z.X. Readout of Epigenetic Modifications. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82, 81–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kouzarides, T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell 2007, 128, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.J.; Seto, E. HATs and HDACs: From structure, function and regulation to novel strategies for therapy and prevention. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5310–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, R.T. Structure of chromatin containing extensively acetylated H3 and H4. Cell 1978, 13, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, C.; Sera, T.; Wolffe, A.P.; Hansen, J.C. Disruption of higher-order folding by core histone acetylation dramatically enhances transcription of nucleosomal arrays by RNA polymerase III. Mol. Cell Biol. 1998, 18, 4629–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, R.; Muller, A.; Napoli, C.A.; Selinger, D.A.; Pikaard, C.S.; Richards, E.J.; Bender, J.; Mount, D.W.; Jorgensen, R.A. Analysis of histone acetyltransferase and histone deacetylase families of Arabidopsis thaliana suggests functional diversification of chromatin modification among multicellular eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 5036–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.C.; Yang, S.G.; Zhao, M.L.; Luo, M.; Yu, C.W.; Chen, C.Y.; Tai, R.; Wu, K.Q. Transcriptional Repression by Histone Deacetylases in Plants. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.S.; Ding, A.B.; Zhong, X.H. Functions and mechanisms of plant histone deacetylases. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.; Ding, A.B.; Liu, F.; Zhong, X. Linking signaling pathways to histone acetylation dynamics in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 5179–5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.; Yu, C.W.; Chen, F.F.; Zhao, L.M.; Tian, G.; Liu, X.C.; Cui, Y.H.; Yang, J.Y.; Wu, K.Q. Histone Deacetylase HDA6 Is Functionally Associated with AS1 in Repression of KNOX Genes in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1003114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, C.W.; Liu, X.C.; Luo, M.; Chen, C.Y.; Lin, X.D.; Tian, G.; Lu, Q.; Cui, Y.H.; Wu, K.Q. HISTONE DEACETYLASE6 Interacts with FLOWERING LOCUS D and Regulates Flowering in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hung, F.Y.; Chen, F.F.; Li, C.L.; Chen, C.; Lai, Y.C.; Chen, J.H.; Cui, Y.H.; Wu, K.Q. The Arabidopsis LDL1/2-HDA6 histone modification complex is functionally associated with CCA1/LHY in regulation of circadian clock genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 10669–10681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hung, F.Y.; Chen, F.F.; Li, C.L.; Chen, C.; Chen, J.H.; Cui, Y.H.; Wu, K.Q. The LDL1/2-HDA6 Histone Modification Complex Interacts With TOC1 and Regulates the Core Circadian Clock Components in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.C.; Yu, C.W.; Duan, J.; Luo, M.; Wang, K.C.; Tian, G.; Cui, Y.H.; Wu, K.Q. HDA6 Directly Interacts with DNA Methyltransferase MET1 and Maintains Transposable Element Silencing in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, C.W.; Tai, R.; Wang, S.C.; Yang, P.; Luo, M.; Yang, S.G.; Cheng, K.; Wang, W.C.; Cheng, Y.S.; Wu, K.Q. HISTONE DEACETYLASE6 Acts in Concert with Histone Methyltransferases SUVH4, SUVH5, and SUVH6 to Regulate Transposon Silencing. Plant Cell. 2017, 29, 1970–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Segre, C.V.; Chiocca, S. Regulating the Regulators: The Post-Translational Code of Class I HDAC1 and HDAC2. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 690848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.; Chi, D.Y.; Yu, P.; Lu, J.J.; Xu, J.R.; Tan, P.P.; Wang, B.; Cui, Y.Y.; Chen, H.Z. Carbocisteine Improves Histone Deacetylase 2 Deacetylation Activity via Regulating Sumoylation of Histone Deacetylase 2 in Human Tracheobronchial Epithelial Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colby, T.; Matthai, A.; Boeckelmann, A.; Stuible, H.P. SUMO-conjugating and SUMO-deconjugating enzymes from Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saracco, S.A.; Miller, M.J.; Kurepa, J.; Vierstra, R.D. Genetic analysis of SUMOylation in arabidopsis: Conjugation of SUMO1 and SUMO2 to nuclear proteins is essential. Plant Physiol. 2007, 145, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miura, K.; Rus, A.; Sharkhuu, A.; Yokoi, S.; Karthikeyan, A.S.; Raghothama, K.G.; Baek, D.; Koo, Y.D.; Jin, J.B.; Bressan, R.A.; et al. The Arabidopsis SUMO E3 ligase SIZ1 controls phosphate deficiency responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 7760–7765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheong, M.S.; Park, H.C.; Hong, M.J.; Lee, J.; Choi, W.; Jin, J.B.; Bohnert, H.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Bressan, R.A.; Yun, D.J. Specific Domain Structures Control Abscisic Acid-, Salicylic Acid-, and Stress-Mediated SIZ1 Phenotypes. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 1930–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.X.; Yang, S.G.; Zhang, S.C.; Liu, M.; Lai, J.B.; Qi, Y.L.; Shi, S.F.; Wang, J.X.; Wang, Y.Q.; Xie, Q.; et al. The Arabidopsis SUMO E3 ligase AtMMS21, a homologue of NSE2/MMS21, regulates cell proliferation in the root. Plant J. 2009, 60, 666–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, T.; Fujiwara, S.; Miura, K.; Stacey, N.; Yoshimura, M.; Schneider, K.; Adachi, S.; Minamisawa, K.; Umeda, M.; Sugimoto, K. SUMO E3 Ligase HIGH PLOIDY2 Regulates Endocycle Onset and Meristem Maintenance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 2284–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomanov, K.; Zeschmann, A.; Hermkes, R.; Eifler, K.; Ziba, I.; Grieco, M.; Novatchkova, M.; Hofmann, K.; Hesse, H.; Bachmair, A. Arabidopsis PIAL1 and 2 Promote SUMO Chain Formation as E4-Type SUMO Ligases and Are Involved in Stress Responses and Sulfur Metabolism. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 4547–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elrouby, N. Analysis of Small Ubiquitin-Like Modifier (SUMO) Targets Reflects the Essential Nature of Protein SUMOylation and Provides Insight to Elucidate the Role of SUMO in Plant Development. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 1006–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Yu, H.; Li, L. SUMO modification of LBD30 by SIZ1 regulates secondary cell wall formation in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1007928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, J.B.; Jin, Y.H.; Lee, J.; Miura, K.; Yoo, C.Y.; Kim, W.Y.; Van Oosten, M.; Hyun, Y.; Somers, D.E.; Lee, I.; et al. The SUMO E3 ligase, AtSIZ1, regulates flowering by controlling a salicylic acid-mediated floral promotion pathway and through affects on FLC chromatin structure. Plant J. 2008, 53, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Son, G.H.; Park, B.S.; Song, J.T.; Seo, H.S. FLC-mediated flowering repression is positively regulated by sumoylation. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.L.; Niu, D.; Hu, Z.L.; Kim, D.H.; Jin, Y.H.; Cai, B.; Liu, P.; Miura, K.; Yun, D.J.; Kim, W.Y.; et al. An Arabidopsis SUMO E3 Ligase, SIZ1, Negatively Regulates Photomorphogenesis by Promoting COP1 Activity. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadanandom, A.; Adam, E.; Orosa, B.; Viczian, A.; Klose, C.; Zhang, C.J.; Josse, E.M.; Kozma-Bognar, L.; Nagy, F. SUMOylation of phytochrome-B negatively regulates light-induced signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11108–11113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niu, D.; Lin, X.L.; Kong, X.X.; Qu, G.P.; Cai, B.; Lee, J.; Jin, J.B. SIZ1-Mediated SUMOylation of TPR1 Suppresses Plant Immunity in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2019, 12, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gou, M.Y.; Huang, Q.S.; Qian, W.Q.; Zhang, Z.M.; Jia, Z.H.; Hua, J. Sumoylation E3 Ligase SIZ1 Modulates Plant Immunity Partly through the Immune Receptor Gene SNC1 in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2017, 30, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, B.S.; Song, J.T.; Seo, H.S. Arabidopsis nitrate reductase activity is stimulated by the E3 SUMO ligase AtSIZ1. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castro, P.H.; Verde, N.; Lourenco, T.; Magalhaes, A.P.; Tavares, R.M.; Bejarano, E.R.; Azevedo, H. SIZ1-Dependent Post-Translational Modification by SUMO Modulates Sugar Signaling and Metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 2297–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miura, K.; Jin, J.B.; Lee, J.; Yoo, C.Y.; Stirm, V.; Miura, T.; Ashworth, E.N.; Bressan, R.A.; Yun, D.J.; Hasegawa, P.M. SIZ1-mediated sumoylation of ICE1 controls CBF3/DREB1A expression and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rytz, T.C.; Miller, M.J.; McLoughlin, F.; Augustine, R.C.; Marshall, R.S.; Juan, Y.T.; Charng, Y.Y.; Scalf, M.; Smith, L.M.; Vierstra, R.D. SUMOylome Profiling Reveals a Diverse Array of Nuclear Targets Modified by the SUMO Ligase SIZ1 during Heat Stress. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 1077–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crozet, P.; Margalha, L.; Butowt, R.; Fernandes, N.; Elias, C.A.; Orosa, B.; Tomanov, K.; Teige, M.; Bachmair, A.; Sadanandom, A.; et al. SUMOylation represses SnRK1 signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2016, 85, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Schumaker, K.S.; Guo, Y. Sumoylation of transcription factor MYB30 by the small ubiquitin-like modifier E3 ligase SIZ1 mediates abscisic acid response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12822–12827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miura, K.; Lee, J.; Jin, J.B.; Yoo, C.Y.; Miura, T.; Hasegawa, P.M. Sumoylation of ABI5 by the Arabidopsis SUMO E3 ligase SIZ1 negatively regulates abscisic acid signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5418–5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miura, K.; Lee, J.; Gong, Q.Q.; Ma, S.S.; Jin, J.B.; Yoo, C.Y.; Miura, T.; Sato, A.; Bohnert, H.J.; Hasegawa, P.M. SIZ1 Regulation of Phosphate Starvation-Induced Root Architecture Remodeling Involves the Control of Auxin Accumulation. Plant Physiol. 2011, 155, 1000–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.I.; Park, B.S.; Kim, D.Y.; Yeu, S.Y.; Song, S.I.; Song, J.T.; Seo, H.S. E3 SUMO ligase AtSIZ1 positively regulates SLY1-mediated GA signalling and plant development. Biochem. J. 2015, 469, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Han, Q.; Xiong, J.; Zheng, T.; Han, J.; Zhou, H.; Lin, H.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, D. Sumoylation of BRI1-EMS-SUPPRESSOR 1 (BES1) by the SUMO E3 Ligase SIZ1 Negatively Regulates Brassinosteroids Signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019, 60, 2282–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.J.; Barrett-Wilt, G.A.; Hua, Z.H.; Vierstra, R.D. Proteomic analyses identify a diverse array of nuclear processes affected by small ubiquitin-like modifier conjugation in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16512–16517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, M.J.; Scalf, M.; Rytz, T.C.; Hubler, S.L.; Smith, L.M.; Vierstra, R.D. Quantitative Proteomics Reveals Factors Regulating RNA Biology as Dynamic Targets of Stress-induced SUMOylation in Arabidopsis. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2013, 12, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clough, S.J.; Bent, A.F. Floral dip: A simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1998, 16, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barth, C.; Jander, G. Arabidopsis myrosinases TGG1 and TGG2 have redundant function in glucosinolate breakdown and insect defense. Plant J. 2006, 46, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.; Jack, T. An intragenic suppressor of the Arabidopsis floral organ identity mutant apetala3-1 functions by suppressing defects in splicing. Plant Cell. 1998, 10, 1465–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gietz, R.D.; Woods, R.A. Transformation of yeast by lithium acetate/single-stranded carrier DNA/polyethylene glycol method. Methods Enzymol. 2002, 350, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Tang, X.; Tian, G.; Wang, F.; Liu, K.; Nguyen, V.; Kohalmi, S.E.; Keller, W.A.; Tsang, E.W.; Harada, J.J. Arabidopsis homolog of the yeast TREX-2 mRNA export complex: Components and anchoring nucleoporin. Plant J. 2010, 61, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.-D.; Cho, Y.-H.; Sheen, J. Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts: A versatile cell system for transient gene expression analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, T.; Peng, X.; Wu, K.; Yang, S. Identification and Characterization of Tomato SWI3-Like Proteins: Overexpression of SlSWIC Increases the Leaf Size in Transgenic Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jackson, J.P.; Johnson, L.; Jasencakova, Z.; Zhang, X.; PerezBurgos, L.; Singh, P.B.; Cheng, X.D.; Schubert, I.; Jenuwein, T.; Jacobsen, S.E. Dimethylation of histone H3 lysine 9 is a critical mark for DNA methylation and gene silencing in Arabidopsis thaliana. Chromosoma 2004, 112, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gendrel, A.V.; Lippman, Z.; Martienssen, R.; Colot, V. Profiling histone modification patterns in plants using genomic tiling microarrays. Nat. Methods. 2005, 2, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.L.; Yang, S.G.; Chen, C.Y.; Li, C.L.; Shan, W.; Lu, W.J.; Cui, Y.H.; Liu, X.C.; Wu, K.Q. Arabidopsis BREVIPEDICELLUS Interacts with the SWI2/SNF2 Chromatin Remodeling ATPase BRAHMA to Regulate KNAT2 and KNAT6 Expression in Control of Inflorescence Architecture. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, L.M.; Cao, X.F.; Jacobsen, S.E. Interplay between two epigenetic marks: DNA methylation and histone H3 lysine 9 methylation. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okada, S.; Nagabuchi, M.; Takamura, Y.; Nakagawa, T.; Shinmyozu, K.; Nakayama, J.; Tanaka, K. Reconstitution of Arabidopsis thaliana SUMO Pathways in E-coli: Functional Evaluation of SUMO Machinery Proteins and Mapping of SUMOylation Sites by Mass Spectrometry. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009, 50, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Lai, J.; Wang, F.; Yang, S.; He, Z.; Jiang, J.; Li, Q.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yu, M.; et al. A SUMO Ligase AtMMS21 Regulates the Stability of the Chromatin Remodeler BRAHMA in Root Development. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 1574–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Budhiraja, R.; Hermkes, R.; Muller, S.; Schmidt, R.; Colby, T.; Panigrahi, K.; Coupland, G.; Bachmair, A. Substrates Related to Chromatin and to RNA-Dependent Processes Are Modified by Arabidopsis SUMO Isoforms That Differ in a Conserved Residue with Influence on Desumoylation. Plant Physiol. 2009, 149, 1529–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Engelsberger, W.R.; Schulze, W.X. Nitrate and ammonium lead to distinct global dynamic phosphorylation patterns when resupplied to nitrogen-starved Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant J. 2012, 69, 978–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Q.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, W.; Mu, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Xue, Y.; Ren, J. GPS-SUMO: A tool for the prediction of sumoylation sites and SUMO-interaction motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W325–W330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Yuan, L.; Yen, M.R.; Zheng, F.; Ji, R.; Peng, T.; Gu, D.; Yang, S.; Cui, Y.; Chen, P.Y.; et al. SWI3B and HDA6 interact and are required for transposon silencing in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2020, 102, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, D.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Zhao, M.L.; Zhao, L.M.; Duan, X.W.; Duan, J.; Wu, K.Q.; Liu, X.C. Identification of HDA15-PIF1 as a key repression module directing the transcriptional network of seed germination in the dark. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 7137–7150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.M.; Peng, T.; Chen, C.Y.; Ji, R.J.; Gu, D.C.; Li, T.T.; Zhang, D.D.; Tu, Y.S.; Wu, K.Q.; Liu, X.C. HY5 Interacts with the Histone Deacetylase HDA15 to Repress Hypocotyl Cell Elongation in Photomorphogenesis. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 1450–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, I.U.; Ali, A.; Khan, H.A.; Baek, D.; Park, J.; Lim, C.J.; Zareen, S.; Jan, M.; Lee, S.Y.; Pardo, J.M.; et al. PWR/HDA9/ABI4 Complex Epigenetically Regulates ABA Dependent Drought Stress Tolerance in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, S.; Seto, E. Regulation of histone deacetylase activities and functions by phosphorylation and its physiological relevance. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 427–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, G.; Neptune, M.A.; DePinho, R.A. SUMO-1 modification of histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) modulates its biological activities. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 23658–23663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brandl, A.; Wagner, T.; Uhlig, K.M.; Knauer, S.K.; Stauber, R.H.; Melchior, F.; Schneider, G.; Heinzel, T.; Kramer, O.H. Dynamically regulated sumoylation of HDAC2 controls p53 deacetylation and restricts apoptosis following genotoxic stress. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 4, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wagner, T.; Kiweler, N.; Wolff, K.; Knauer, S.K.; Brandl, A.; Hemmerich, P.; Dannenberg, J.H.; Heinzel, T.; Schneider, G.; Krämer, O.H. Sumoylation of HDAC2 promotes NF-κB-dependent gene expression. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 7123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wils, C.R.; Kaufmann, K. Gene-regulatory networks controlling inflorescence and flower development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2017, 1860, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrona, S.; Hurtado, L.; March-Díaz, R.; Schmitz, R.J.; Florencio, F.J.; Turck, F.; Amasino, R.M.; Reyes, J.C. Brahma is required for proper expression of the floral repressor FLC in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hurtado, L.; Farrona, S.; Reyes, J.C. The putative SWI/SNF complex subunit BRAHMA activates flower homeotic genes in Arabidopsisthaliana. Plant Mol. Biol. 2006, 62, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.; Shen, L.; Wu, Y.; Chen, H.; Robertson, M.; Helliwell, C.A.; Ito, T.; Meyerowitz, E.; Yu, H. A repressor complex governs the integration of flowering signals in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell. 2008, 15, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujiwara, S.; Oda, A.; Yoshida, R.; Niinuma, K.; Miyata, K.; Tomozoe, Y.; Tajima, T.; Nakagawa, M.; Hayashi, K.; Coupland, G. Circadian clock proteins LHY and CCA1 regulate SVP protein accumulation to control flowering in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 2960–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, X.; Le, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Jiang, D.; Wang, Y.; He, Y. Arabidopsis FLC clade members form flowering-repressor complexes coordinating responses to endogenous and environmental cues. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, K.; Renhu, N.; Suzaki, T. The PHD finger of Arabidopsis SIZ1 recognizes trimethylated histone H3K4 mediating SIZ1 function and abiotic stress response. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Hong, T.; Walter, K.L.; Ewalt, M.; Michishita, E.; Hung, T.; Carney, D.; Pena, P.; Lan, F.; Kaadige, M.R. ING2 PHD domain links histone H3 lysine 4 methylation to active gene repression. Nature 2006, 442, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, K.; Lee, J.; Miura, T.; Hasegawa, P.M. SIZ1 Controls Cell Growth and Plant Development in Arabidopsis through Salicylic Acid. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010, 51, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, S.; Zeng, X.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Yu, C.; Huang, Y.; Wang, F.; Wu, K.; Yang, S. Arabidopsis SUMO E3 Ligase SIZ1 Interacts with HDA6 and Negatively Regulates HDA6 Function during Flowering. Cells 2021, 10, 3001. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113001
Gao S, Zeng X, Wang J, Xu Y, Yu C, Huang Y, Wang F, Wu K, Yang S. Arabidopsis SUMO E3 Ligase SIZ1 Interacts with HDA6 and Negatively Regulates HDA6 Function during Flowering. Cells. 2021; 10(11):3001. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113001
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Sujuan, Xueqin Zeng, Jianhao Wang, Yingchao Xu, Chunwei Yu, Yishui Huang, Feng Wang, Keqiang Wu, and Songguang Yang. 2021. "Arabidopsis SUMO E3 Ligase SIZ1 Interacts with HDA6 and Negatively Regulates HDA6 Function during Flowering" Cells 10, no. 11: 3001. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113001
APA StyleGao, S., Zeng, X., Wang, J., Xu, Y., Yu, C., Huang, Y., Wang, F., Wu, K., & Yang, S. (2021). Arabidopsis SUMO E3 Ligase SIZ1 Interacts with HDA6 and Negatively Regulates HDA6 Function during Flowering. Cells, 10(11), 3001. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113001





