YAP Promotes Cell Proliferation and Stemness Maintenance of Porcine Muscle Stem Cells under High-Density Condition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Pig MuSCs Isolation
2.3. MuSCs Culture and Differentiation
2.4. Clone of the Full-Length Pig YAP1 CDS
2.5. Cell Transfection and Retroviral Infection
2.6. Gene Expression Analysis by Quantitative RT-PCR
2.7. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.8. Western Blot
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
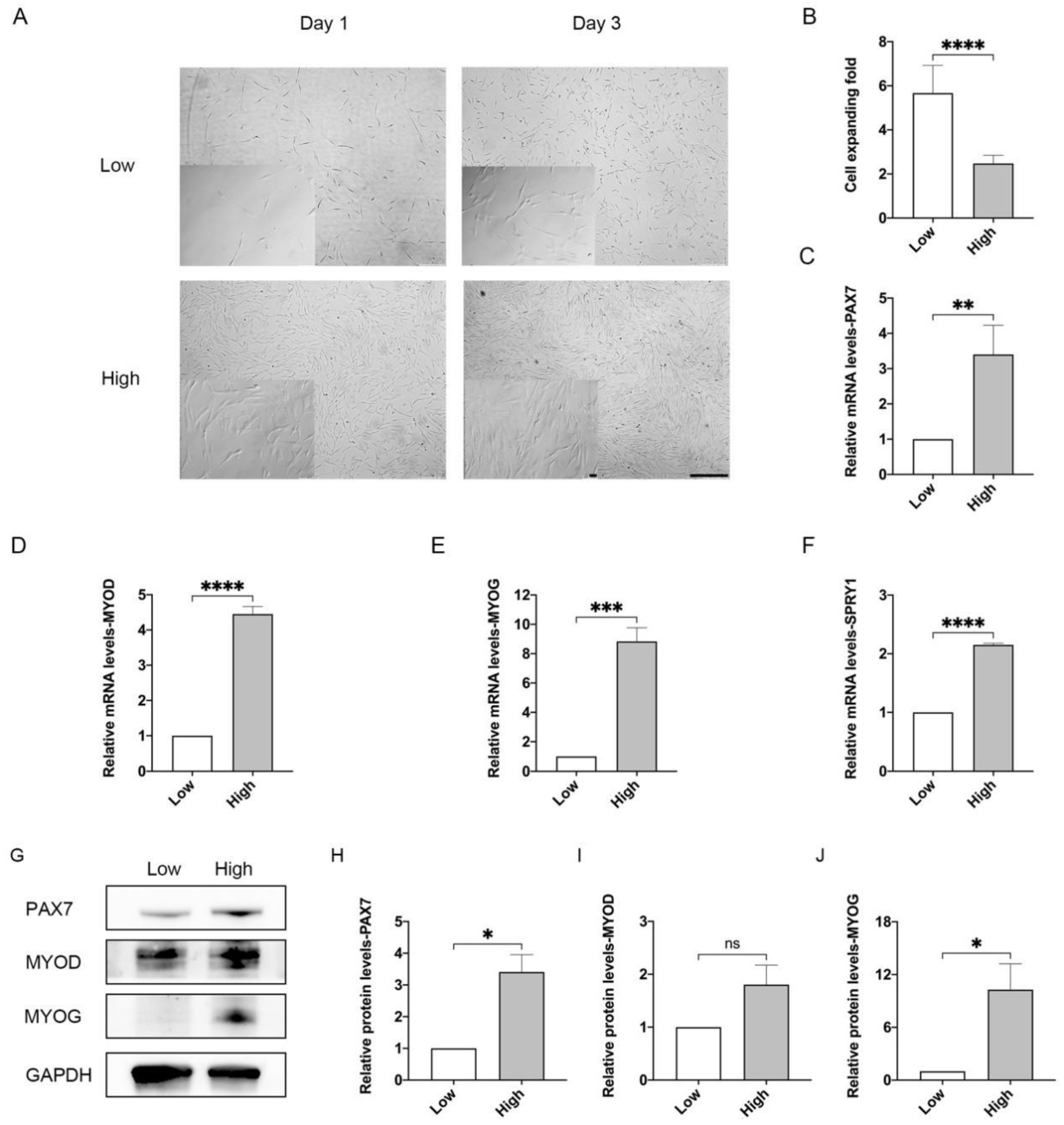
3.1. High-Density Cell Culture Impairs Proliferation and Differentiation Capacity of MuSCs
3.2. More YAP Is Phosphorylated and Located in Cytoplasm upon High-Density Culture
3.3. LPA Promotes Proliferation and Differentiation Potential of MuSCs
3.4. Phosphorylation Sites of YAP Are Highly Conserved among Various Species
3.5. Constitutively Active Porcine YAP Promotes Proliferation and Stemness Maintenance of MuSCs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pikaar, I.; Matassa, S.; Bodirsky, B.L.; Weindl, I.; Humpenöder, F.; Rabaey, K.; Boon, N.; Bruschi, M.; Yuan, Z.; Van Zanten, H.; et al. Decoupling livestock from land use through industrial feed production pathways. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7351–7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Aveyard, P.; Garnett, T.; Hall, J.W.; Key, T.J.; Lorimer, J.; Pierrehumbert, R.T.; Scarborough, P.; Springmann, M.; Jebb, S.A. Meat consumption, health, and the environment. Science 2018, 361, eaam5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eibl, R.; Senn, Y.; Gubser, G.; Jossen, V.; Van Den Bos, C.; Eibl, D. Cellular agriculture: Opportunities and challenges. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 12, 51–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, M.J.; Levenberg, S.; Kaplan, D.L.; Genovese, N.; Fu, J.; Bryant, C.; Negowetti, N.; Verzijden, K.; Moutsatsou, P. Scientific, sustainability and regulatory challenges of cultured meat. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, M.J. Cultured beef: Medical technology to produce food. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 1039–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Yoon, J.W.; Kim, M.; Lee, H.J.; Jeong, J.; Ryu, M.; Jo, C.; Lee, C. Muscle stem cell isolation and in vitro culture for meat production: A methodological review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 20, 429–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauro, A. Satellite cell of skeletal muscle fibers. J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 1961, 9, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wang, H.; Hu, P. Stem cell activation in skeletal muscle regeneration. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 1663–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chal, J.; Pourquié, O. Making muscle: Skeletal myogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Development 2017, 144, 2104–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Srutee, R.; Sowmya, S.R.; Uday, S.A. Clean meat: Techniques for meat production and its upcoming challenges. Anim. Biotechnol. 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, J.-J.; Rothrauff, B.B.; Alexander, P.G.; Tuan, R.S. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on chondrogenic differentiation of adipose and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng. Part A 2018, 24, 1432–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, S.; Kawashima, N.; Yamamoto, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Nara, K.; Sekiya, I.; Okiji, T. Effect of cell culture density on dental pulp-derived mesenchymal stem cells with reference to osteogenic differentiation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; De Mello, V.; Mohamed, A.; Quiroga, H.P.O.; Garcia-Munoz, A.; Al Bloshi, A.; Tremblay, A.M.; von Kriegsheim, A.; Collie-Duguid, E.; Vargesson, N.; et al. Common and distinctive functions of the Hippo effectors taz and yap in skeletal muscle stem cell function. Stem Cells 2017, 35, 1958–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, M.; Rikeit, P.; Knaus, P.; Coirault, C. YAP-mediated mechanotransduction in skeletal muscle. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judson, R.N.; Tremblay, A.M.; Knopp, P.; White, R.; Urcia, R.; De Bari, C.; Zammit, P.S.; Camargo, F.D.; Wackerhage, H. The Hippo pathway member Yap plays a key role in influencing fate decisions in muscle satellite cells. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 6009–6019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanconato, F.; Forcato, M.; Battilana, G.; Azzolin, L.; Quaranta, E.; Bodega, B.; Rosato, A.; Bicciato, S.; Cordenonsi, M.; Piccolo, S. Genome-wide association between YAP/TAZ/TEAD and AP-1 at enhancers drives oncogenic growth. Nature 2015, 17, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, T.; Murakami, H.; Fujii, M.; Ishiguro, F.; Tanaka, I.; Kondo, Y.; Akatsuka, S.; Toyokuni, S.; Yokoi, K.; Osada, H.; et al. YAP induces malignant mesothelioma cell proliferation by upregulating transcription of cell cycle-promoting genes. Oncogene 2012, 31, 5117–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen, C.G.; Moroishi, T.; Guan, K.-L. YAP and TAZ: A nexus for Hippo signaling and beyond. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shalhout, S.Z.; Yang, P.-Y.; Grzelak, E.M.; Nutsch, K.; Shao, S.; Zambaldo, C.; Iaconelli, J.; Ibrahim, L.; Stanton, C.; Chadwick, S.R.; et al. YAP-dependent proliferation by a small molecule targeting annexin A2. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2021, 17, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varelas, X. The Hippo pathway effectors TAZ and YAP in development, homeostasis and disease. Development 2014, 141, 1614–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, B.; Wei, X.; Li, W.; Udan, R.S.; Yang, Q.; Kim, J.; Xie, J.; Ikenoue, T.; Yu, J.; Li, L.; et al. Inactivation of YAP oncoprotein by the Hippo pathway is involved in cell contact inhibition and tissue growth control. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 2747–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gumbiner, B.M.; Kim, N.-G. The Hippo-YAP signaling pathway and contact inhibition of growth. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watt, K.; Judson, R.; Medlow, P.; Reid, K.; Kurth, T.B.; Burniston, J.G.; Ratkevicius, A.; De Bari, C.; Wackerhage, H. Yap is a novel regulator of C2C12 myogenesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 393, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, G.; Hu, P. Characterization and isolation of highly purified porcine satellite cells. Cell Death Discov. 2017, 3, 17003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, S.; Swennen, G.N.M.; Messmer, T.; Gagliardi, M.; Molin, D.G.M.; Li, C.; Zhou, G.; Post, M.J. Maintaining bovine satellite cells stemness through p38 pathway. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zammit, P.S.; Relaix, F.; Nagata, Y.; Ruiz, A.P.; Collins, C.; Partridge, T.A.; Beauchamp, J. Pax7 and myogenic progression in skeletal muscle satellite cells. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zammit, P.S. Function of the myogenic regulatory factors Myf5, MyoD, Myogenin and MRF4 in skeletal muscle, satellite cells and regenerative myogenesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 72, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Khalil, R.; Brack, A.S. Muscle stem cells and reversible quiescence: The role of sprouty. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 2575–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Schüler, S.C.; Hüttner, S.S.; Von Eyss, B.; Von Maltzahn, J. Adult stem cells at work: Regenerating skeletal muscle. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 2559–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, J.; Feldmann, G.; Huang, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, N.; Comerford, S.A.; Gayyed, M.; Anders, R.A.; Maitra, A.; Pan, D. Elucidation of a universal size-control mechanism in drosophila and mammals. Cell 2007, 130, 1120–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moolenaar, W.H. Lysophosphatidic acid, a multifunctional phospholipid messenger. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 12949–12952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, X.; Pfaff, S.L.; Gage, F.H. YAP regulates neural progenitor cell number via the TEA domain transcription factor. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 3320–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, N.; Zhang, C.; Dill, P.; Panasyuk, G.; Pion, D.; Koka, V.; Gallazzini, M.; Olson, E.N.; Lam, H.; Henske, E.P.; et al. Regulation of YAP by mTOR and autophagy reveals a therapeutic target of tuberous sclerosis complex. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 2249–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Xie, F.; Chu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, B.; Dai, T.; Gao, L.; Wang, L.; Ling, L.; Jia, J.; et al. YAP antagonizes innate antiviral immunity and is targeted for lysosomal degradation through IKKɛ-mediated phosphorylation. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattazzo, F.; Laurent, B.; Relaix, F.; Rouard, H.; Didier, N. Distinct phases of postnatal skeletal muscle growth govern the progressive establishment of muscle stem cell quiescence. Stem Cell Rep. 2020, 15, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shea, K.L.; Xiang, W.; LaPorta, V.S.; Licht, J.D.; Keller, C.; Basson, M.A.; Brack, A.S. Sprouty1 regulates reversible quiescence of a self-renewing adult muscle stem cell pool during regeneration. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 6, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ancel, S.; Stuelsatz, P.; Feige, J.N. Muscle stem cell quiescence: Controlling stemness by staying asleep. Trends Cell Biol. 2021, 31, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buikema, J.W.; Lee, S.; Goodyer, W.R.; Maas, R.G.; Chirikian, O.; Li, G.; Miao, Y.; Paige, S.L.; Lee, D.; Wu, H.; et al. Wnt activation and reduced cell-cell contact synergistically induce massive expansion of functional human iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 27, 50–63.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, N.; Bai, J.; Zhou, Q.; Mao, J.; Xu, L.; Liu, J.; Wei, H.; Ren, C.; Wu, X.; et al. Human telomerase reverse transcriptase is a novel target of Hippo—YAP pathway. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 4178–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, J.B.; Vankara, A.; Ettyreddy, A.R.; Bohning, J.D.; Gersbach, C.A. Myogenic progenitor cell lineage specification by CRISPR/Cas9-based transcriptional activators. Stem Cell Rep. 2020, 14, 755–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Genes | Primer Sequences (5′–3′) | Accession No. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| YAP | Forward | TATCAACCAAAGCACCCTACC | XM_021062706.1 |
| Reverse | CTCCTCTCCTTCTATGTTCATTCC | ||
| PAX7 | Forward | GTGCCCTCAGTGAGTTCGATT | XM_021095458.1 |
| Reverse | TCCAGACGGTTCCCTTTGTC | ||
| MYOD | Forward | GCTCCGCGACGTAGATTTGA | NM_001002824.1 |
| Reverse | GGAGTCGAAACACGGGTCAT | ||
| MYOG | Forward | AACCCCACTTCTATGACGGG | NM_001012406.1 |
| Reverse | TTATCTTCCAGGGGCACTCG | ||
| MYHC | Forward | CCGTGCTCCGTCTTCTTTCC | NM_001104951.2 |
| Reverse | CGCTCCTTCTCTGACTTGCG | ||
| SPRY1 | Forward | GCATAGACCTACCAGCCACC | NM_001267835.1 |
| Reverse | TCCGGATTGCCCTTTCAGAC | ||
| GAPDH | Forward | GTCGGAGTGAACGGATTTGGC | NM_001206359.1 |
| Reverse | CTTGCCGTGGGTGGAATCAT | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Lin, L.; Zhu, H.; Wu, Z.; Ding, X.; Hu, R.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, C.; Ding, S.; Guo, R. YAP Promotes Cell Proliferation and Stemness Maintenance of Porcine Muscle Stem Cells under High-Density Condition. Cells 2021, 10, 3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113069
Liu Z, Lin L, Zhu H, Wu Z, Ding X, Hu R, Jiang Y, Tang C, Ding S, Guo R. YAP Promotes Cell Proliferation and Stemness Maintenance of Porcine Muscle Stem Cells under High-Density Condition. Cells. 2021; 10(11):3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113069
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zheng, Ling Lin, Haozhe Zhu, Zhongyuan Wu, Xi Ding, Rongrong Hu, Yichen Jiang, Changbo Tang, Shijie Ding, and Renpeng Guo. 2021. "YAP Promotes Cell Proliferation and Stemness Maintenance of Porcine Muscle Stem Cells under High-Density Condition" Cells 10, no. 11: 3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113069






