MiR 208a Regulates Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Metabolically Challenged Cardiomyocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cells
2.3. Respiratory Studies in Cultured Cardiomyocytes
2.4. Gene Expression Analysis
2.5. Real-Time Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-PCR), and Quantitative PCR
2.6. Western Blot Experiments
2.7. Mitochondrial DNA
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. MicroRNA 208a in Human Cardiomyocytes under Metabolic Stress
3.2. Predicted Targets of MiR 208a
3.3. MiR 208a Suppression Protects against the Myosin Isoform Switch and Pathological Stress Markers Induced by Metabolic Challenges
3.4. MiR 208a, Mitochondrial Biogenesis, and Mitochondrial Markers
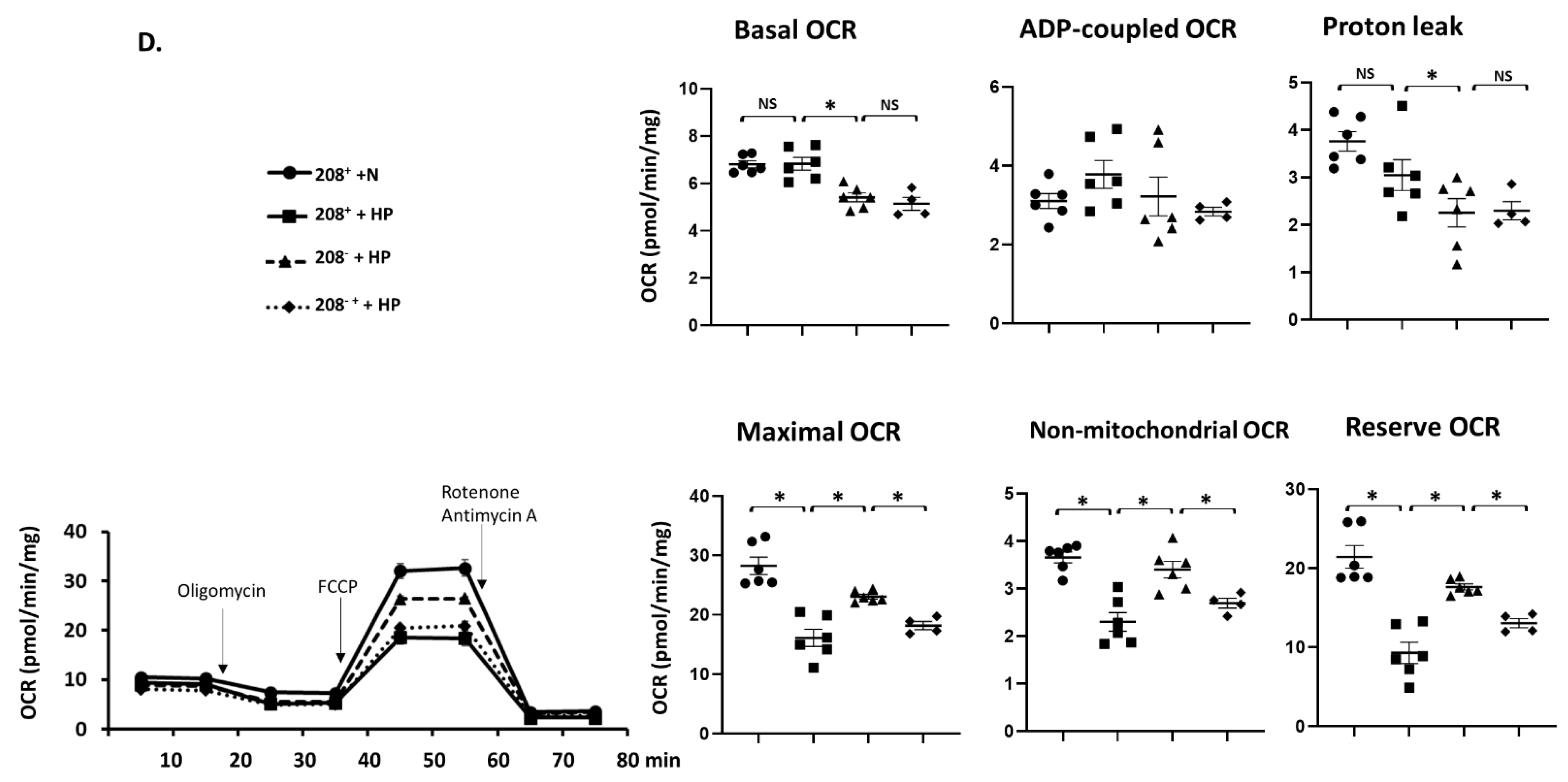
3.5. MiR 208a Suppression Protects against Mitochondrial Dysfunction Induced by the Metabolic Stress
4. Discussion
4.1. MiR 208a in Cardiomyocytes Exposed to Metabolic Stress
4.2. Predicted MiR 208a Targets
4.3. Cardiac Stress Markers
4.4. Mitochondrial Biogenesis
4.5. Mitochondrial Function
4.6. Fatty-Acid β-Oxidation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garcia, M.J.; McNamara, P.M.; Gordon, T.; Kannel, W.B. Morbidity and mortality in diabetics in the Framingham population. Sixteen year follow-up study. Diabetes 1974, 23, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannel, W.B.; Hjortland, M.; Castelli, W.P. Role of diabetes in congestive heart failure: The Framingham study. Am. J. Cardiol. 1974, 34, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beljic, T.; Miric, M. Improved metabolic control does not reverse left ventricular filling abnormalities in newly diagnosed non-insulin-dependent diabetes patients. Acta Diabetol. 1994, 31, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolino, A.; Longobardi, G.; Furgi, G.; Rossi, M.; Zoccolillo, N.; Ferrara, N.; Rengo, F. Left ventricular diastolic filling in diabetes mellitus with and without hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 1995, 8, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bugger, H.; Abel, E.D. Rodent models of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Disease Model Mechan. 2009, 2, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudina, S.; Abel, E.D. Diabetic cardiomyopathy, causes and effects. Rev. Endoc. Metab. Disord. 2010, 11, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rider, O.J.; Francis, J.M.; Ali, M.K.; Byrne, J.; Clarke, K.; Neubauer, S.; Petersen, S.E. Determinants of left ventricular mass in obesity; a cardiovascular magnetic resonance study. J. Cardiovasc. Magnet. Reson. Off. J. Soc. Cardiovasc. Magnet. Reson. 2009, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rider, O.J.; Lewis, A.J.; Lewandowski, A.J.; Ntusi, N.; Nethononda, R.; Petersen, S.E.; Francis, J.M.; Pitcher, A.; Banerjee, R.; Leeson, P.; et al. Obese subjects show sex-specific differences in right ventricular hypertrophy. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 8, e002454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de las Fuentes, L.; Waggoner, A.D.; Mohammed, B.S.; Stein, R.I.; Miller, B.V., 3rd; Foster, G.D.; Wyatt, H.R.; Klein, S.; Davila-Roman, V.G. Effect of moderate diet-induced weight loss and weight regain on cardiovascular structure and function. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 2376–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, P.; Bogaty, P.; Garneau, C.; Marois, L.; Dumesnil, J.G. Diastolic dysfunction in normotensive men with well-controlled type 2 diabetes: Importance of maneuvers in echocardiographic screening for preclinical diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiencke, S.; Handschin, R.; von Dahlen, R.; Muser, J.; Brunner-Larocca, H.P.; Schumann, J.; Felix, B.; Berneis, K.; Rickenbacher, P. Pre-clinical diabetic cardiomyopathy: Prevalence, screening, and outcome. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2010, 12, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bonito, P.; Cuomo, S.; Moio, N.; Sibilio, G.; Sabatini, D.; Quattrin, S.; Capaldo, B. Diastolic dysfunction in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus of short duration. Diabet. Med. A J. Br. Diabet. Assoc. 1996, 13, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouthoorn, S.; Valstar, G.B.; Gohar, A.; den Ruijter, H.M.; Reitsma, H.B.; Hoes, A.W.; Rutten, F.H. The prevalence of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in men and women with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Vasc. Disease Res. Off. J. Int. Soc. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. 2018, 15, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthiaume, J.M.; Kurdys, J.G.; Muntean, D.M.; Rosca, M.G. Mitochondrial NAD(+)/NADH Redox State and Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Antioxid. Redox. Sig. 2019, 30, 375–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koves, T.R.; Ussher, J.R.; Noland, R.C.; Slentz, D.; Mosedale, M.; Ilkayeva, O.; Bain, J.; Stevens, R.; Dyck, J.R.; Newgard, C.B.; et al. Mitochondrial overload and incomplete fatty acid oxidation contribute to skeletal muscle insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinti, M.V.; Fink, G.K.; Hathaway, Q.A.; Durr, A.J.; Kunovac, A.; Hollander, J.M. Mitochondrial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus: An organ-based analysis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 316, E268–E285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, L.L.; Wang, J.; Liew, O.W.; Richards, A.M.; Chen, Y.T. MicroRNA and Heart Failure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Nair, S. Role of microRNA in diabetic cardiomyopathy: From mechanism to intervention. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 2070–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, E.; Diao, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, R.; Hu, B. MicroRNAs involved in the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades pathway during glucose-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rooij, E.; Sutherland, L.B.; Qi, X.; Richardson, J.A.; Hill, J.; Olson, E.N. Control of stress-dependent cardiac growth and gene expression by a microRNA. Science 2007, 316, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawal, S.; Nagesh, P.T.; Coffey, S.; Van Hout, I.; Galvin, I.F.; Bunton, R.W.; Davis, P.; Williams, M.J.A.; Katare, R. Early dysregulation of cardiac-specific microRNA-208a is linked to maladaptive cardiac remodelling in diabetic myocardium. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grueter, C.E.; van Rooij, E.; Johnson, B.A.; DeLeon, S.M.; Sutherland, L.B.; Qi, X.; Gautron, L.; Elmquist, J.K.; Bassel-Duby, R.; Olson, E.N. A cardiac microRNA governs systemic energy homeostasis by regulation of MED13. Cell 2012, 149, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cousin, S.P.; Hugl, S.R.; Wrede, C.E.; Kajio, H.; Myers, M.G., Jr.; Rhodes, C.J. Free fatty acid-induced inhibition of glucose and insulin-like growth factor I-induced deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in the pancreatic beta-cell line INS-1. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.C.; Bovolenta, L.A.; Nachtigall, P.G.; Herkenhoff, M.E.; Lemke, N.; Pinhal, D. Combining Results from Distinct MicroRNA Target Prediction Tools Enhances the Performance of Analyses. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, E.J.; Berthiaume, J.M.; Kamath, V.; Achike, O.; Buchanan, E.; Montano, M.M.; Chandler, M.P.; Miyagi, M.; Rosca, M.G. Mitochondrial complex I defect and increased fatty acid oxidation enhance protein lysine acetylation in the diabetic heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 107, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorn, S.W.; Guo, H.; McGeary, S.E.; Rodriguez-Mias, R.A.; Shin, C.; Baek, D.; Hsu, S.H.; Ghoshal, K.; Villen, J.; Bartel, D.P. mRNA destabilization is the dominant effect of mammalian microRNAs by the time substantial repression ensues. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Bell, G.W.; Nam, J.W.; Bartel, D.P. Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. Elife 2015, 4, e05005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.L.; Suh, Y.; Cuervo, A.M. Deficient chaperone-mediated autophagy in liver leads to metabolic dysregulation. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, A.; Lingutla, R.; Mager, J. Expression analysis of mammalian mitochondrial ribosomal protein genes. Gene Expr. Patterns 2020, 38, 119147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulman, J.; Ruzzenente, B.; Bianchi, L.; Rio, M.; Boddaert, N.; Munnich, A.; Rotig, A.; Metodiev, M.D. Mutations in the MRPS28 gene encoding the small mitoribosomal subunit protein bS1m in a patient with intrauterine growth retardation, craniofacial dysmorphism and multisystemic involvement. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, 1445–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellard, J.P.; McCudden, C.R.; Tanega, C.; James, K.A.; Ratkovic, S.; Staples, J.F.; Wagner, G.F. The respiratory effects of stanniocalcin-1 (STC-1) on intact mitochondria and cells: STC-1 uncouples oxidative phosphorylation and its actions are modulated by nucleotide triphosphates. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2007, 264, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Yang, Y.; Qi, C.; Ju, H. Effects of porcine STC-1 on cell metabolism and mitochondrial function. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2020, 286, 113298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Shan, P.; Srivastava, A.; Li, Z.; Lee, P.J. Endothelial Stanniocalcin 1 Maintains Mitochondrial Bioenergetics and Prevents Oxidant-Induced Lung Injury via Toll-Like Receptor 4. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2019, 30, 1775–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Feng, L.X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H.S.; Tang, C.Y.; Cheng, W.; Deng, Y.H.; Wu, X.; Yan, P.; Duan, X.J.; et al. Stanniocalcin-1 Alleviates Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Regulating Mitochondrial Quality Control via the Nrf2 Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 1898213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verger, A.; Monte, D.; Villeret, V. Twenty years of Mediator complex structural studies. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2019, 47, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Tomomori-Sato, C.; Tsai, K.L.; Yu, X.; Sardiu, M.; Saraf, A.; Washburn, M.P.; Florens, L.; Asturias, F.J.; Conaway, R.C.; et al. Role for the MED21-MED7 Hinge in Assembly of the Mediator-RNA Polymerase II Holoenzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 26886–26898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callis, T.E.; Pandya, K.; Seok, H.Y.; Tang, R.H.; Tatsuguchi, M.; Huang, Z.P.; Chen, J.F.; Deng, Z.; Gunn, B.; Shumate, J.; et al. MicroRNA-208a is a regulator of cardiac hypertrophy and conduction in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2772–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.P. Factors controlling cardiac myosin-isoform shift during hypertrophy and heart failure. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2007, 43, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, R.L.; Hullinger, T.G.; Semus, H.M.; Dickinson, B.A.; Seto, A.G.; Lynch, J.M.; Stack, C.; Latimer, P.A.; Olson, E.N.; van Rooij, E. Therapeutic inhibition of miR-208a improves cardiac function and survival during heart failure. Circulation 2011, 124, 1537–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.K.; Calabrese, J.M.; Sharp, P.A. Quantitative analysis of Argonaute protein reveals microRNA-dependent localization to stress granules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18125–18130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojamaa, K.; Kenessey, A.; Klein, I. Thyroid hormone regulation of phospholamban phosphorylation in the rat heart. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 2139–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, J.G.; Fong, J.L.; Medeiros, D.M.; Finck, B.N.; Kelly, D.P. Insulin-resistant heart exhibits a mitochondrial biogenic response driven by the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha/PGC-1alpha gene regulatory pathway. Circulation 2007, 115, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, R.; Nogee, D.P.; Zechner, J.F.; Yea, K.; Gierasch, C.M.; Kovacs, A.; Medeiros, D.M.; Kelly, D.P.; Duncan, J.G. The transcriptional coactivators, PGC-1alpha and beta, cooperate to maintain cardiac mitochondrial function during the early stages of insulin resistance. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2012, 52, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huss, J.M.; Kelly, D.P. Nuclear receptor signaling and cardiac energetics. Circ. Res. 2004, 95, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, J.J.; Boudina, S.; Banke, N.H.; Sambandam, N.; Han, X.; Young, D.M.; Leone, T.C.; Gross, R.W.; Lewandowski, E.D.; Abel, E.D.; et al. The transcriptional coactivator PGC-1alpha is essential for maximal and efficient cardiac mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation and lipid homeostasis. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2008, 295, H185–H196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Blumensatt, M.; Fahlbusch, P.; Hilgers, R.; Bekaert, M.; Herzfeld de Wiza, D.; Akhyari, P.; Ruige, J.B.; Ouwens, D.M. Secretory products from epicardial adipose tissue from patients with type 2 diabetes impair mitochondrial beta-oxidation in cardiomyocytes via activation of the cardiac renin-angiotensin system and induction of miR-208a. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2017, 112, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mekala, N.; Kurdys, J.; Vicenzi, A.P.; Weiler, L.R.; Avramut, C.; Vazquez, E.J.; Ragina, N.; Rosca, M.G. MiR 208a Regulates Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Metabolically Challenged Cardiomyocytes. Cells 2021, 10, 3152. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113152
Mekala N, Kurdys J, Vicenzi AP, Weiler LR, Avramut C, Vazquez EJ, Ragina N, Rosca MG. MiR 208a Regulates Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Metabolically Challenged Cardiomyocytes. Cells. 2021; 10(11):3152. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113152
Chicago/Turabian StyleMekala, Naveen, Jacob Kurdys, Alexis Paige Vicenzi, Leana Rose Weiler, Carmen Avramut, Edwin J. Vazquez, Neli Ragina, and Mariana G. Rosca. 2021. "MiR 208a Regulates Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Metabolically Challenged Cardiomyocytes" Cells 10, no. 11: 3152. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113152
APA StyleMekala, N., Kurdys, J., Vicenzi, A. P., Weiler, L. R., Avramut, C., Vazquez, E. J., Ragina, N., & Rosca, M. G. (2021). MiR 208a Regulates Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Metabolically Challenged Cardiomyocytes. Cells, 10(11), 3152. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113152






