Unexpected Pro-Fibrotic Effect of MIF in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis Is Linked to a Shift in NKT Cell Populations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Murine In Vivo Experiments and Determination of Hepatic Fibrosis
2.2. Hepatic Immune Cell Isolation and Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.3. Isolation and Cultivation of Murine NKT Cells
2.4. NAFLD Patient Cohort
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
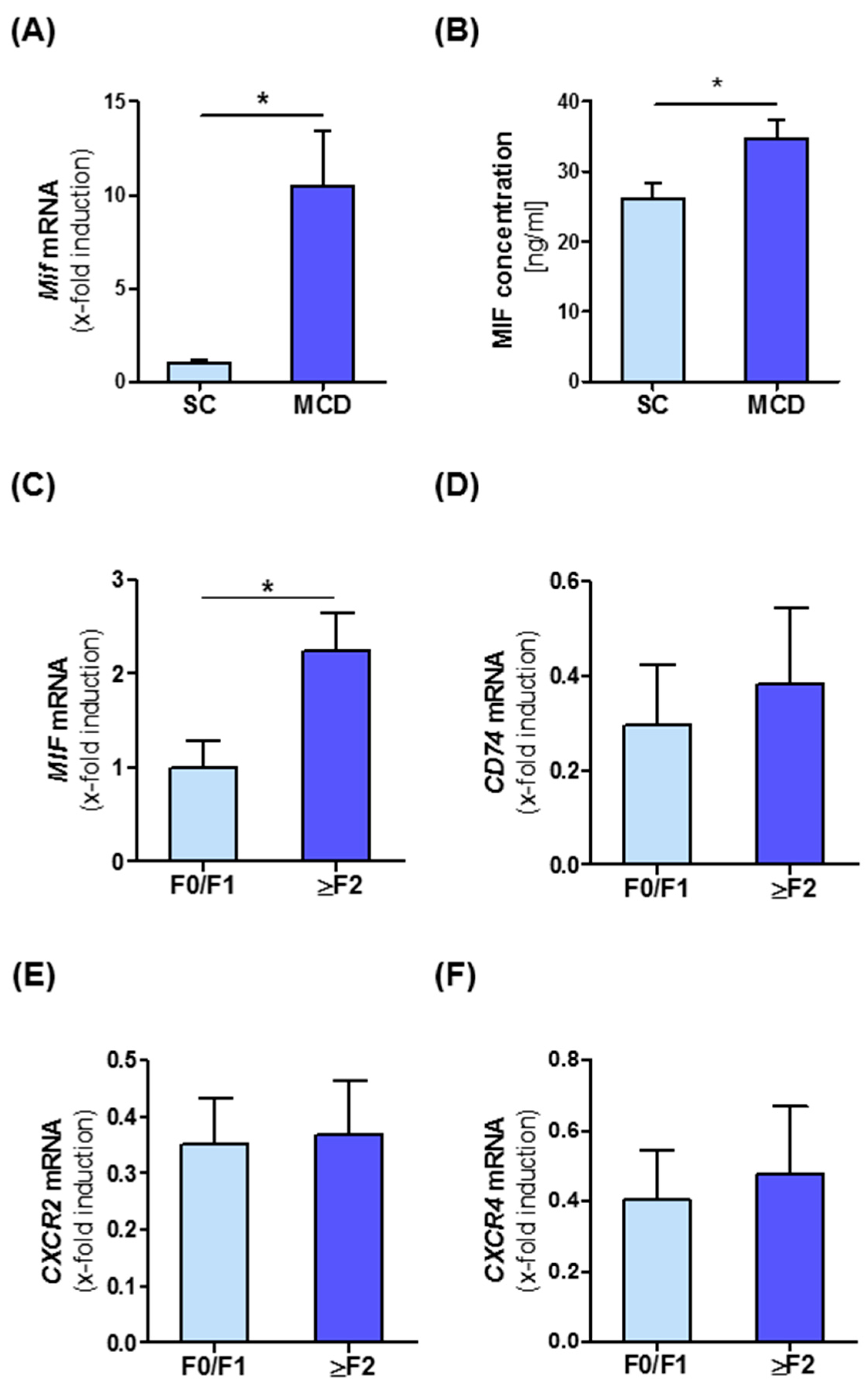
3.1. Intrahepatic Expression of MIF and Its Receptors Is Associated with NASH in Mice and Men
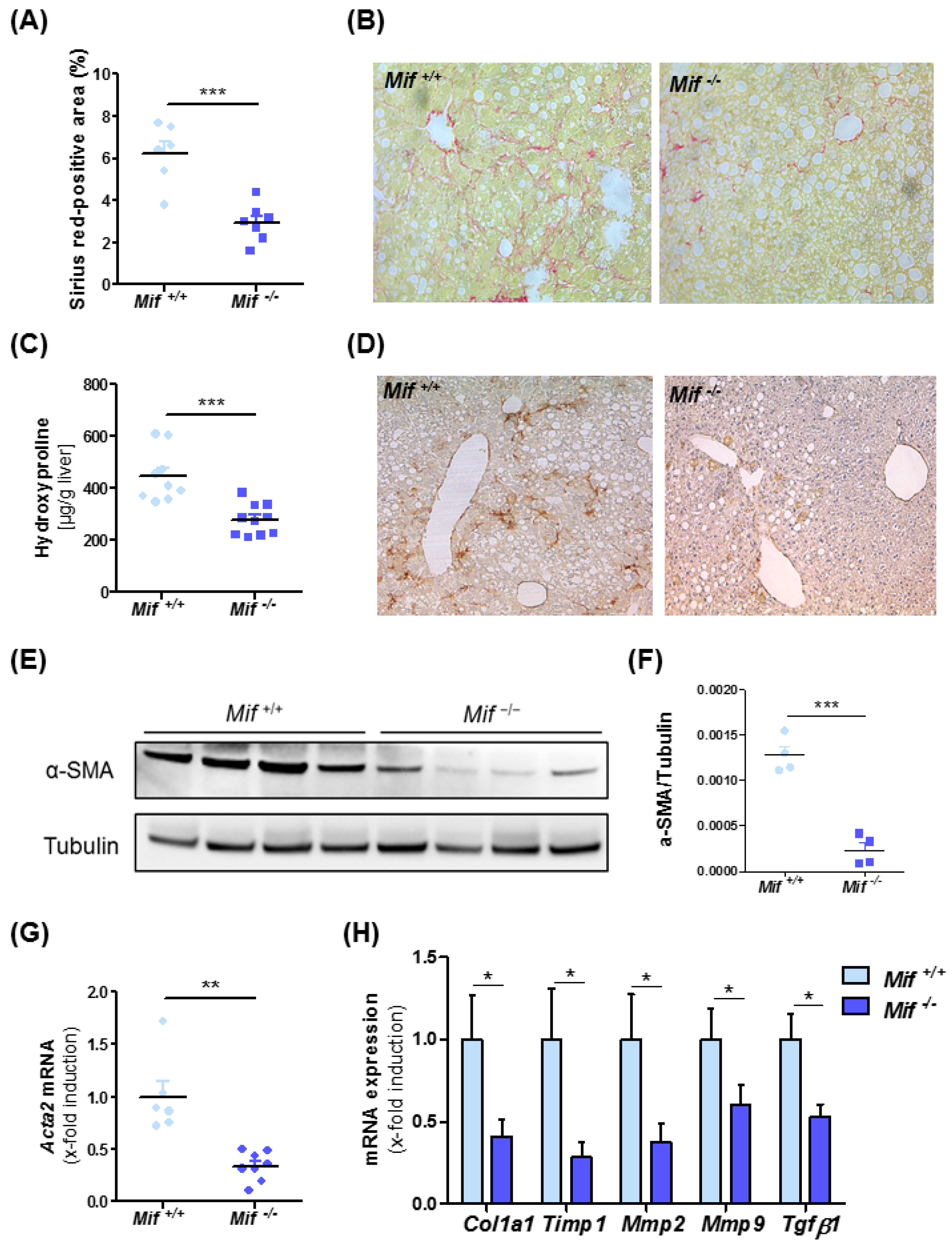
3.2. Mif−/− Mice Display Reduced Liver Fibrogenesis after Eight Weeks of MCD Diet
3.3. Reduced Liver Fibrosis in Mif−/− Mice Is Associated with Reduced Expression of Pro-Fibrotic Genes and a Reduction of Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells
3.4. Hepatocytes Are the Main Source of MIF within the Liver
3.5. Specific Deletion of Mif in Hepatocytes Results in Reduced NASH-Mediated Liver Fibrogenesis Similar to Effects Observed in Constitutive Mif-Deficient Mice
3.6. Hepatocyte-Specific Mif Deletion Leads to an Altered Pattern of Hepatic NKT Cell Polarization in MCD-Induced Liver Fibrogenesis
3.7. Intrahepatic Expression of Fibrosis-Related Genes Is Linked to NKT Cell Subset Marker Expression in Human NASH
3.8. MIF Directly Modulates NKT Cell Polarization
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MIF | Macrophage migration inhibitory factor |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| HSC | Hepatic stellate cells |
| NK cells | Natural killer cells |
| NKT cells | Natural killer T cells |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| CCl4 | Carbon tetrachloride |
| Hh | Hedgehog |
| FASL | FAS ligand |
| pDCs | Plasmacytoid DCs |
| MCD | Methionine- and choline-deficient |
| NASH | Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis |
| α-GalCer | α-Galactosylceramide |
References
- Tsochatzis, E.A.; Bosch, J.; Burroughs, A.K. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet 2014, 383, 1749–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iredale, J.P. Models of liver fibrosis: Exploring the dynamic nature of inflammation and repair in a solid organ. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsuchida, T.; Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymann, F.; Tacke, F. Immunology in the liver-from homeostasis to disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 88–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marra, F.; Tacke, F. Roles for chemokines in liver disease. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 577–594.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berres, M.L.; Koenen, R.R.; Rueland, A.; Zaldivar, M.M.; Heinrichs, D.; Sahin, H.; Schmitz, P.; Streetz, K.L.; Berg, T.; Gassler, N.; et al. Antagonism of the chemokine Ccl5 ameliorates experimental liver fibrosis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 4129–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calandra, T.; Roger, T. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: A regulator of innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, A.; Bernhagen, J.; Weber, C. Chemokine-like functions of MIF in atherosclerosis. J. Mol. Med. 2008, 86, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, S.; Bernhagen, J.; Noels, H. Arrest Functions of the MIF Ligand/Receptor Axes in Atherogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernhagen, J.; Krohn, R.; Lue, H.; Gregory, J.L.; Zernecke, A.; Koenen, R.R.; Dewor, M.; Georgiev, I.; Schober, A.; Leng, L.; et al. MIF is a noncognate ligand of CXC chemokine receptors in inflammatory and atherogenic cell recruitment. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, L.; Metz, C.N.; Fang, Y.; Xu, J.; Donnelly, S.; Baugh, J.; Delohery, T.; Chen, Y.; Mitchell, R.A.; Bucala, R. MIF signal transduction initiated by binding to CD74. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernhagen, J.; Calandra, T.; Mitchell, R.A.; Martin, S.B.; Tracey, K.J.; Voelter, W.; Manogue, K.R.; Cerami, A.; Bucala, R. MIF is a pituitary-derived cytokine that potentiates lethal endotoxaemia. Nature 1993, 365, 756–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baugh, J.A.; Chitnis, S.; Donnelly, S.C.; Monteiro, J.; Lin, X.; Plant, B.J.; Wolfe, F.; Gregersen, P.K.; Bucala, R. A functional promoter polymorphism in the macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) gene associated with disease severity in rheumatoid arthritis. Genes Immun. 2002, 3, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morand, E.F.; Leech, M.; Bernhagen, J. MIF: A new cytokine link between rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finucane, O.M.; Reynolds, C.M.; McGillicuddy, F.C.; Harford, K.A.; Morrison, M.; Baugh, J.; Roche, H.M. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor deficiency ameliorates high-fat diet induced insulin resistance in mice with reduced adipose inflammation and hepatic steatosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreih, A.; Ezzeddine, R.; Leng, L.; LaChance, A.; Yu, G.; Mizue, Y.; Subrahmanyan, L.; Pons-Estel, B.A.; Abelson, A.K.; Gunnarsson, I.; et al. Dual effect of the macrophage migration inhibitory factor gene on the development and severity of human systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 3942–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zernecke, A.; Bernhagen, J.; Weber, C. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2008, 117, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Djudjaj, S.; Lue, H.; Rong, S.; Papasotiriou, M.; Klinkhammer, B.M.; Zok, S.; Klaener, O.; Braun, G.S.; Lindenmeyer, M.T.; Cohen, C.D.; et al. Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Mediates Proliferative GN via CD74. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 1650–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assis, D.N.; Leng, L.; Du, X.; Zhang, C.K.; Grieb, G.; Merk, M.; Garcia, A.B.; McCrann, C.; Chapiro, J.; Meinhardt, A.; et al. The role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in autoimmune liver disease. Hepatology 2014, 59, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.A.; McMullen, M.R.; Roychowdhury, S.; Pisano, S.G.; Liu, X.; Stavitsky, A.B.; Bucala, R.; Nagy, L.E. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor contributes to ethanol-induced liver injury by mediating cell injury, steatohepatitis, and steatosis. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1980–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Djudjaj, S.; Martin, I.V.; Buhl, E.M.; Nothofer, N.J.; Leng, L.; Piecychna, M.; Floege, J.; Bernhagen, J.; Bucala, R.; Boor, P. Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Limits Renal Inflammation and Fibrosis by Counteracting Tubular Cell Cycle Arrest. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 3590–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, E.J.; Li, J.; Leng, L.; McDonald, C.; Atsumi, T.; Bucala, R.; Young, L.H. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor stimulates AMP-activated protein kinase in the ischaemic heart. Nature 2008, 451, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrichs, D.; Knauel, M.; Offermanns, C.; Berres, M.L.; Nellen, A.; Leng, L.; Schmitz, P.; Bucala, R.; Trautwein, C.; Weber, C.; et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) exerts antifibrotic effects in experimental liver fibrosis via CD74. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17444–17449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heinrichs, D.; Berres, M.L.; Coeuru, M.; Knauel, M.; Nellen, A.; Fischer, P.; Philippeit, C.; Bucala, R.; Trautwein, C.; Wasmuth, H.E.; et al. Protective role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 5136–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tajiri, K.; Shimizu, Y. Role of NKT Cells in the Pathogenesis of NAFLD. Int. J. Hepatol. 2012, 2012, 850836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Syn, W.K.; Oo, Y.H.; Pereira, T.A.; Karaca, G.F.; Jung, Y.; Omenetti, A.; Witek, R.P.; Choi, S.S.; Guy, C.D.; Fearing, C.M.; et al. Accumulation of natural killer T cells in progressive nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1998–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, O.; Jeong, W.I.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Lian, Z.X.; Gershwin, M.E.; Gao, B. Diverse roles of invariant natural killer T cells in liver injury and fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1683–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durante-Mangoni, E.; Wang, R.; Shaulov, A.; He, Q.; Nasser, I.; Afdhal, N.; Koziel, M.J.; Exley, M.A. Hepatic CD1d expression in hepatitis C virus infection and recognition by resident proinflammatory CD1d-reactive T cells. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 2159–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Syn, W.K.; Agboola, K.M.; Swiderska, M.; Michelotti, G.A.; Liaskou, E.; Pang, H.; Xie, G.; Philips, G.; Chan, I.S.; Karaca, G.F.; et al. NKT-associated hedgehog and osteopontin drive fibrogenesis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut 2012, 61, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V. NKT-cell subsets: Promoters and protectors in inflammatory liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 618–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, C.M.; Zimmer, M.I.; Wang, C.R. The functions of type I and type II natural killer T cells in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2013, 19, 1330–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fingerle-Rowson, G.; Petrenko, O.; Metz, C.N.; Forsthuber, T.G.; Mitchell, R.; Huss, R.; Moll, U.; Muller, W.; Bucala, R. The p53-dependent effects of macrophage migration inhibitory factor revealed by gene targeting. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9354–9359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brocks, T.; Fedorchenko, O.; Schliermann, N.; Stein, A.; Moll, U.M.; Seegobin, S.; Dewor, M.; Hallek, M.; Marquardt, Y.; Fietkau, K.; et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor protects from nonmelanoma epidermal tumors by regulating the number of antigen-presenting cells in skin. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 526–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hillebrandt, S.; Wasmuth, H.E.; Weiskirchen, R.; Hellerbrand, C.; Keppeler, H.; Werth, A.; Schirin-Sokhan, R.; Wilkens, G.; Geier, A.; Lorenzen, J.; et al. Complement factor 5 is a quantitative trait gene that modifies liver fibrogenesis in mice and humans. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhagen, J.; Mitchell, R.A.; Calandra, T.; Voelter, W.; Cerami, A.; Bucala, R. Purification, bioactivity, and secondary structure analysis of mouse and human macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF). Biochemistry 1994, 33, 14144–14155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nellen, A.; Heinrichs, D.; Berres, M.L.; Sahin, H.; Schmitz, P.; Proudfoot, A.E.; Trautwein, C.; Wasmuth, H.E. Interference with oligomerization and glycosaminoglycan binding of the chemokine CCL5 improves experimental liver injury. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.Y.; Chen, C.L.; Lin, Y.S.; Yeh, T.M.; Tsai, T.T.; Hong, M.Y.; Lin, C.F. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor triggers chemotaxis of CD74+CXCR2+ NKT cells in chemically induced IFN-gamma-mediated skin inflammation. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 3693–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doisne, J.M.; Bartholin, L.; Yan, K.P.; Garcia, C.N.; Duarte, N.; Le Luduec, J.B.; Vincent, D.; Cyprian, F.; Horvat, B.; Martel, S.; et al. iNKT cell development is orchestrated by different branches of TGF-beta signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1365–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, V.; Poulsen, K.; Odena, G.; McMullen, M.R.; Altamirano, J.; Sancho-Bru, P.; Tiribelli, C.; Caballeria, J.; Rosso, N.; Bataller, R.; et al. Hepatocyte-derived macrophage migration inhibitory factor mediates alcohol-induced liver injury in mice and patients. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Murphy, B.V.; Kominsky, D.J.; Orlicky, D.J.; Donohue, T.M., Jr.; Ju, C. Increased susceptibility of natural killer T-cell-deficient mice to acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.C.; Chen, P.; Maricic, I.; Inamine, T.; Hu, J.; Gong, S.; Sun, J.C.; Dasgupta, S.; Lin, H.C.; Lin, Y.T.; et al. Intestinal iNKT cells migrate to liver and contribute to hepatocyte apoptosis during alcoholic liver disease. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2019, 316, G585–G597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maricic, I.; Marrero, I.; Eguchi, A.; Nakamura, R.; Johnson, C.D.; Dasgupta, S.; Hernandez, C.D.; Nguyen, P.S.; Swafford, A.D.; Knight, R.; et al. Differential Activation of Hepatic Invariant NKT Cell Subsets Plays a Key Role in Progression of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 3017–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poulsen, K.L.; McMullen, M.R.; Huang, E.; Kibler, C.D.; Sheehan, M.; Leng, L.; Bucala, R.; Nagy, L.E. Novel Role of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor in Upstream Control of the Unfolded Protein Response after Ethanol Feeding in Mice. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 43, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heinrichs, D.; Brandt, E.F.; Fischer, P.; Köhncke, J.; Wirtz, T.H.; Guldiken, N.; Djudjaj, S.; Boor, P.; Kroy, D.; Weiskirchen, R.; et al. Unexpected Pro-Fibrotic Effect of MIF in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis Is Linked to a Shift in NKT Cell Populations. Cells 2021, 10, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020252
Heinrichs D, Brandt EF, Fischer P, Köhncke J, Wirtz TH, Guldiken N, Djudjaj S, Boor P, Kroy D, Weiskirchen R, et al. Unexpected Pro-Fibrotic Effect of MIF in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis Is Linked to a Shift in NKT Cell Populations. Cells. 2021; 10(2):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020252
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeinrichs, Daniel, Elisa F. Brandt, Petra Fischer, Janine Köhncke, Theresa H. Wirtz, Nurdan Guldiken, Sonja Djudjaj, Peter Boor, Daniela Kroy, Ralf Weiskirchen, and et al. 2021. "Unexpected Pro-Fibrotic Effect of MIF in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis Is Linked to a Shift in NKT Cell Populations" Cells 10, no. 2: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020252
APA StyleHeinrichs, D., Brandt, E. F., Fischer, P., Köhncke, J., Wirtz, T. H., Guldiken, N., Djudjaj, S., Boor, P., Kroy, D., Weiskirchen, R., Bucala, R., Wasmuth, H. E., Strnad, P., Trautwein, C., Bernhagen, J., & Berres, M.-L. (2021). Unexpected Pro-Fibrotic Effect of MIF in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis Is Linked to a Shift in NKT Cell Populations. Cells, 10(2), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020252








