Aging and Microglial Response following Systemic Stimulation with Escherichia coli in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Bacteria
2.3. Experimental Procedures
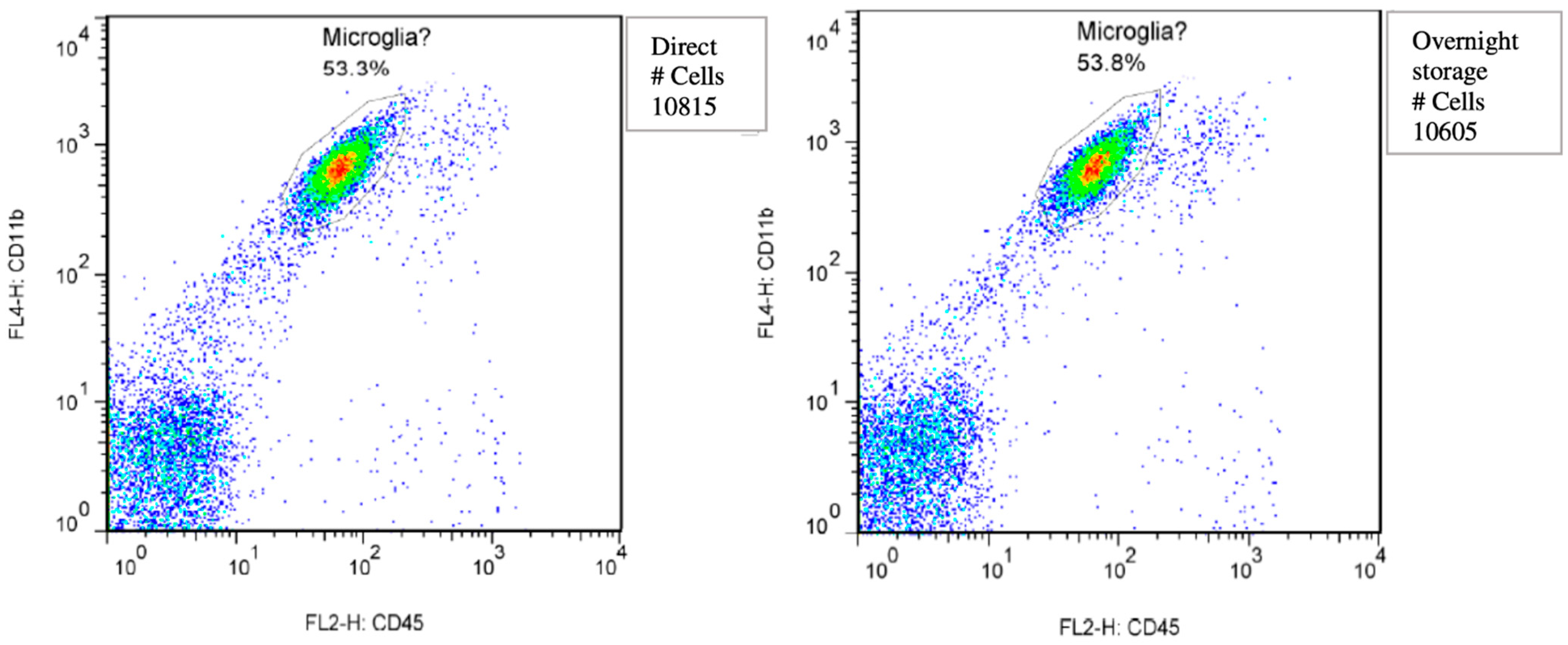
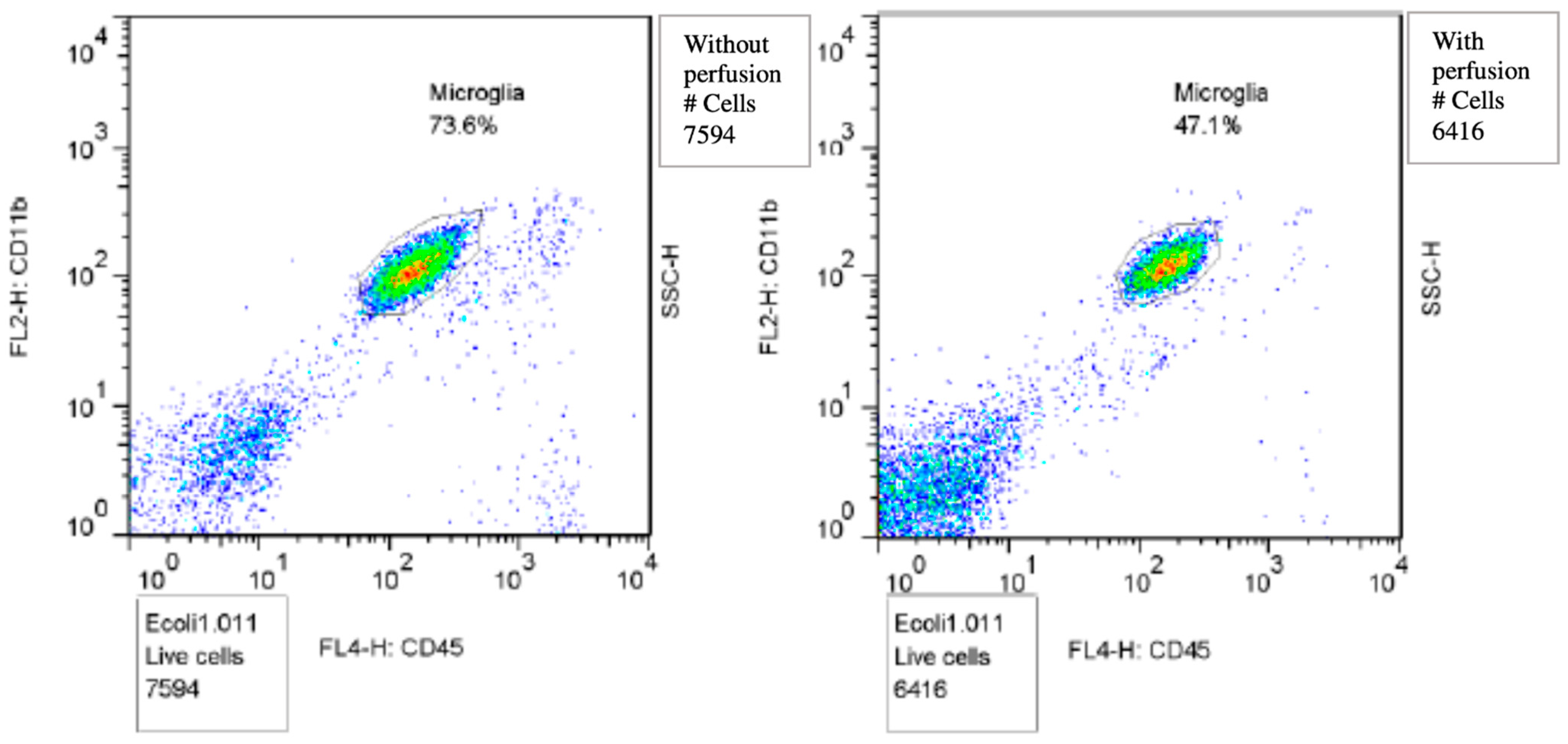
2.4. Isolating Microglia for Flowcytometry
2.5. Immunohistochemistry of Murine Brain
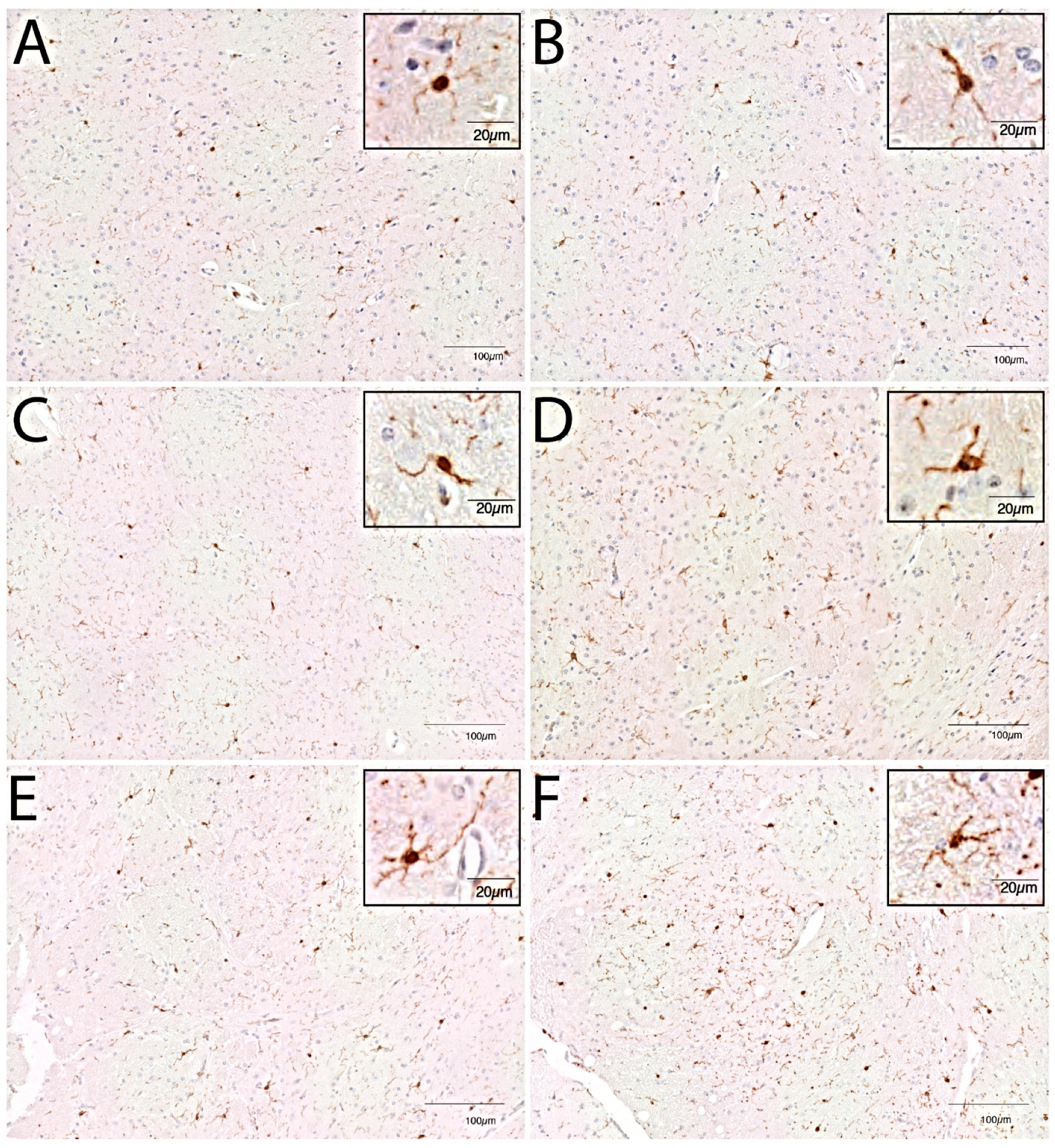
2.6. Quantification of Immunohistochemistry Images
2.7. Definition of Microglial Activation
2.8. RNA Extraction and Real Time PCR
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
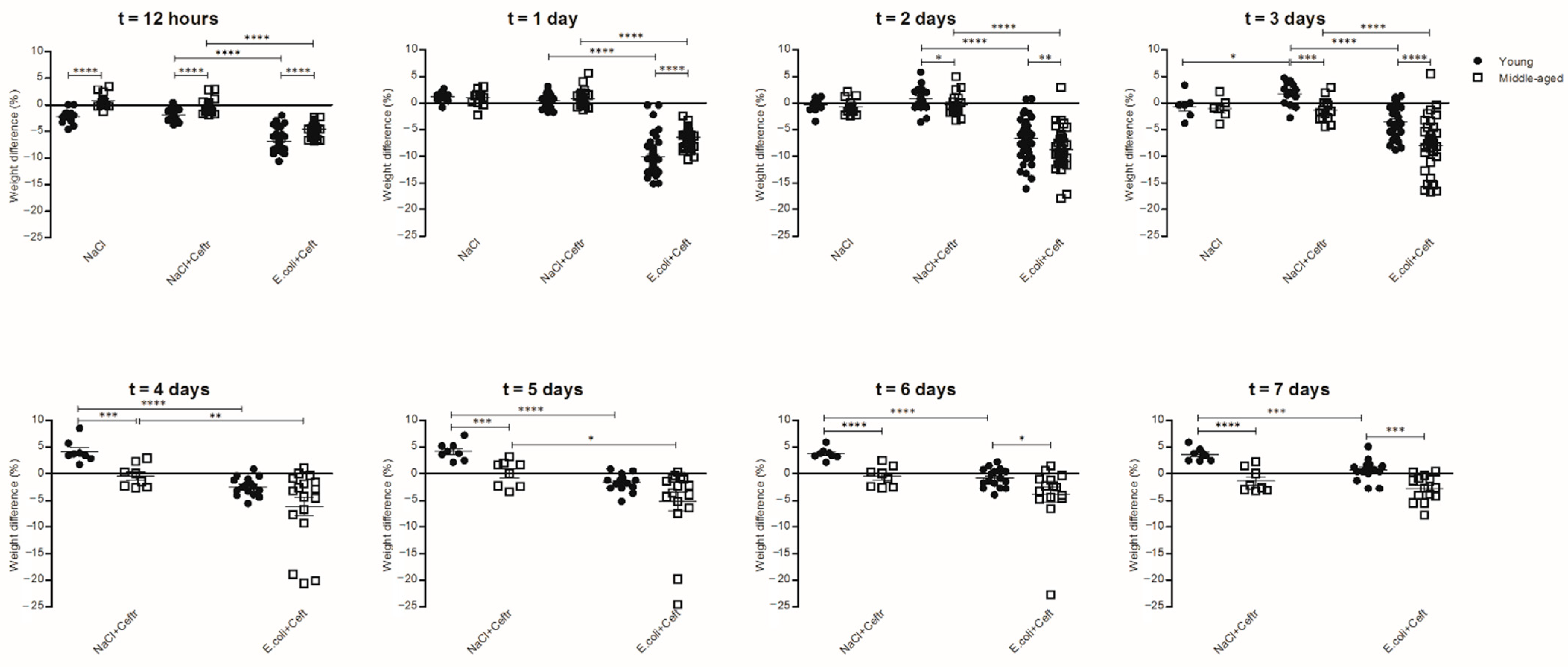
3.1. Description of Mouse Models
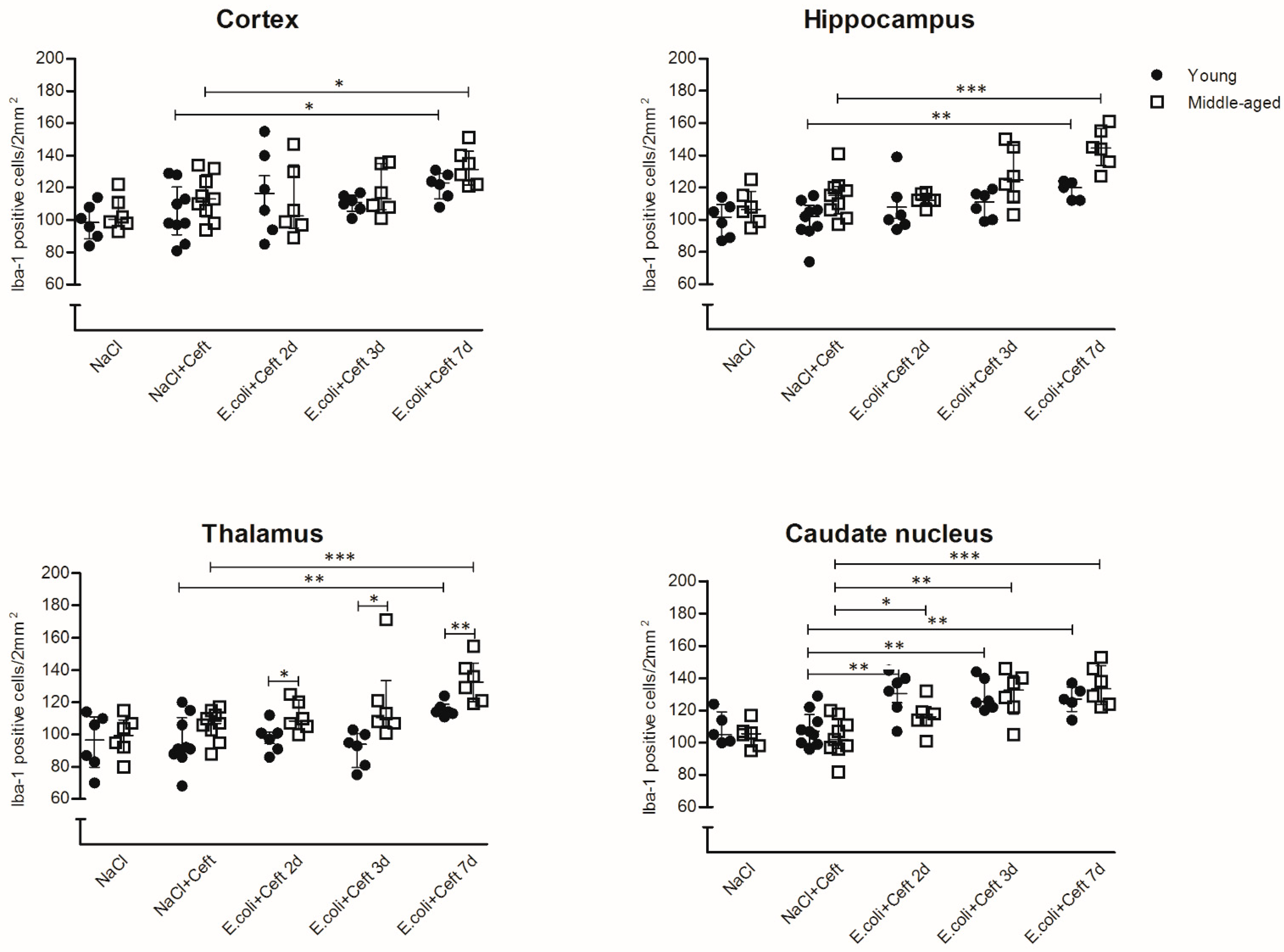
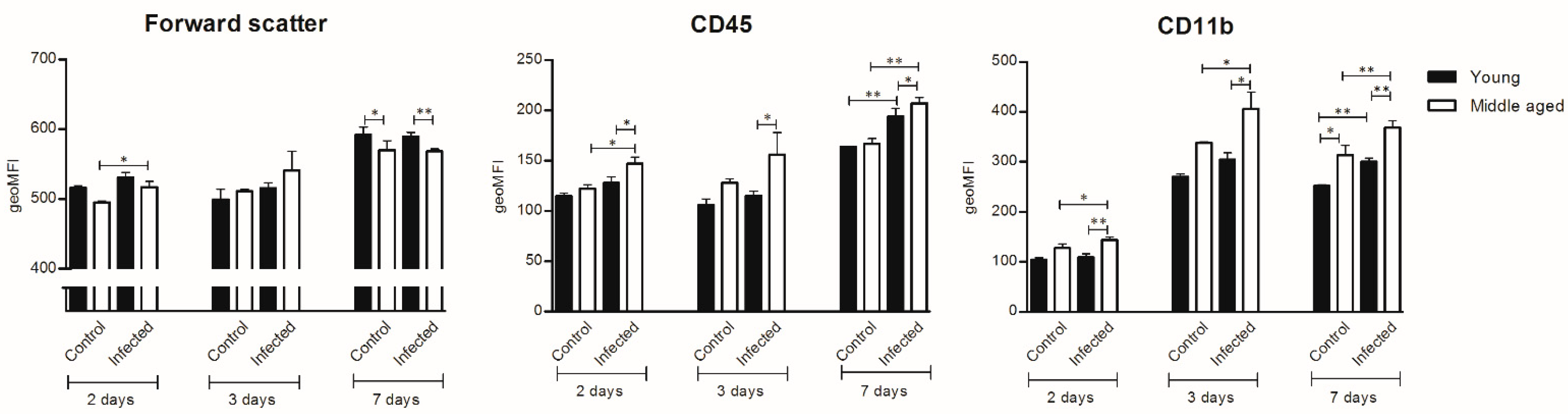
3.2. Microglial Cell Response
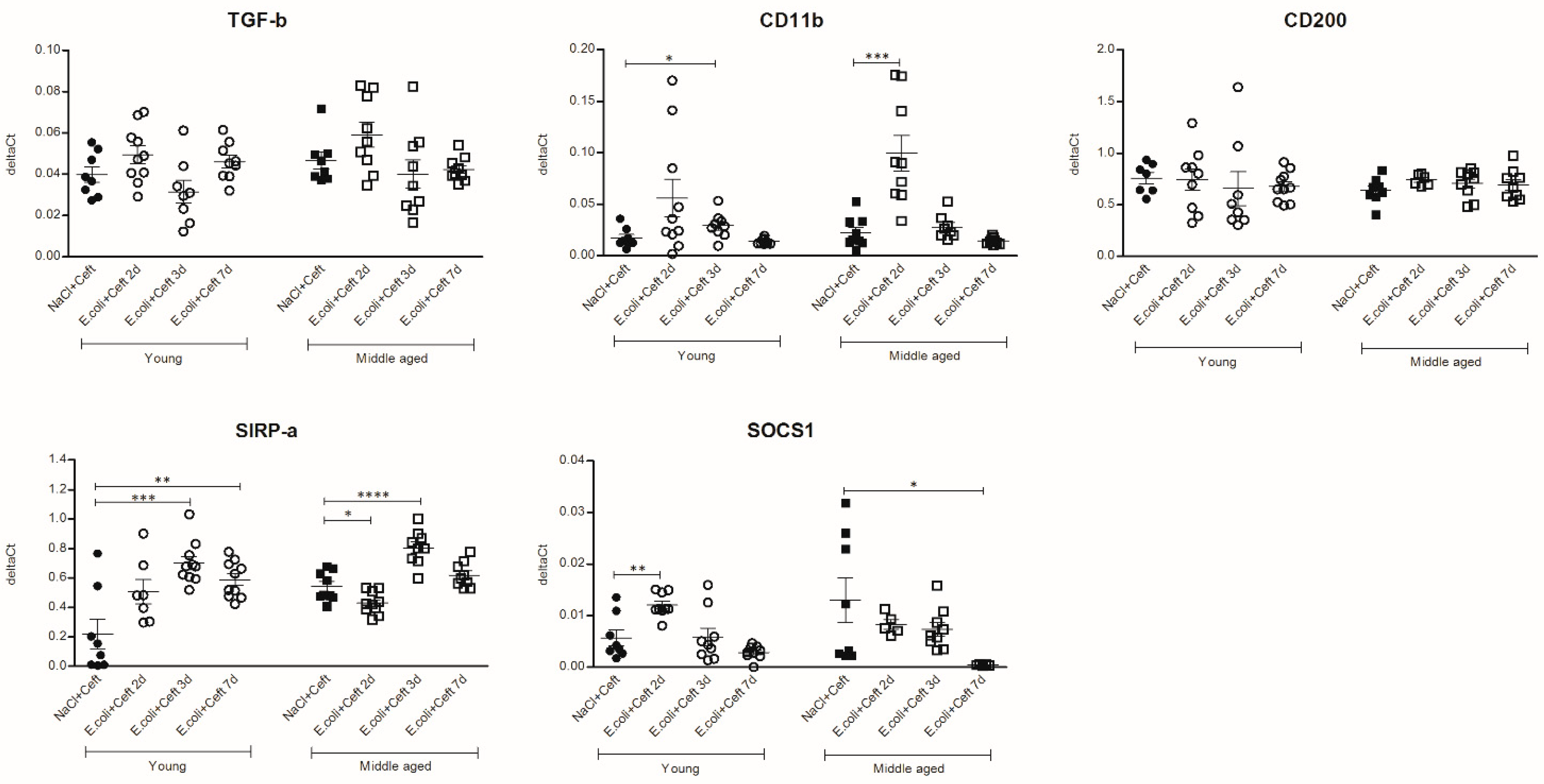
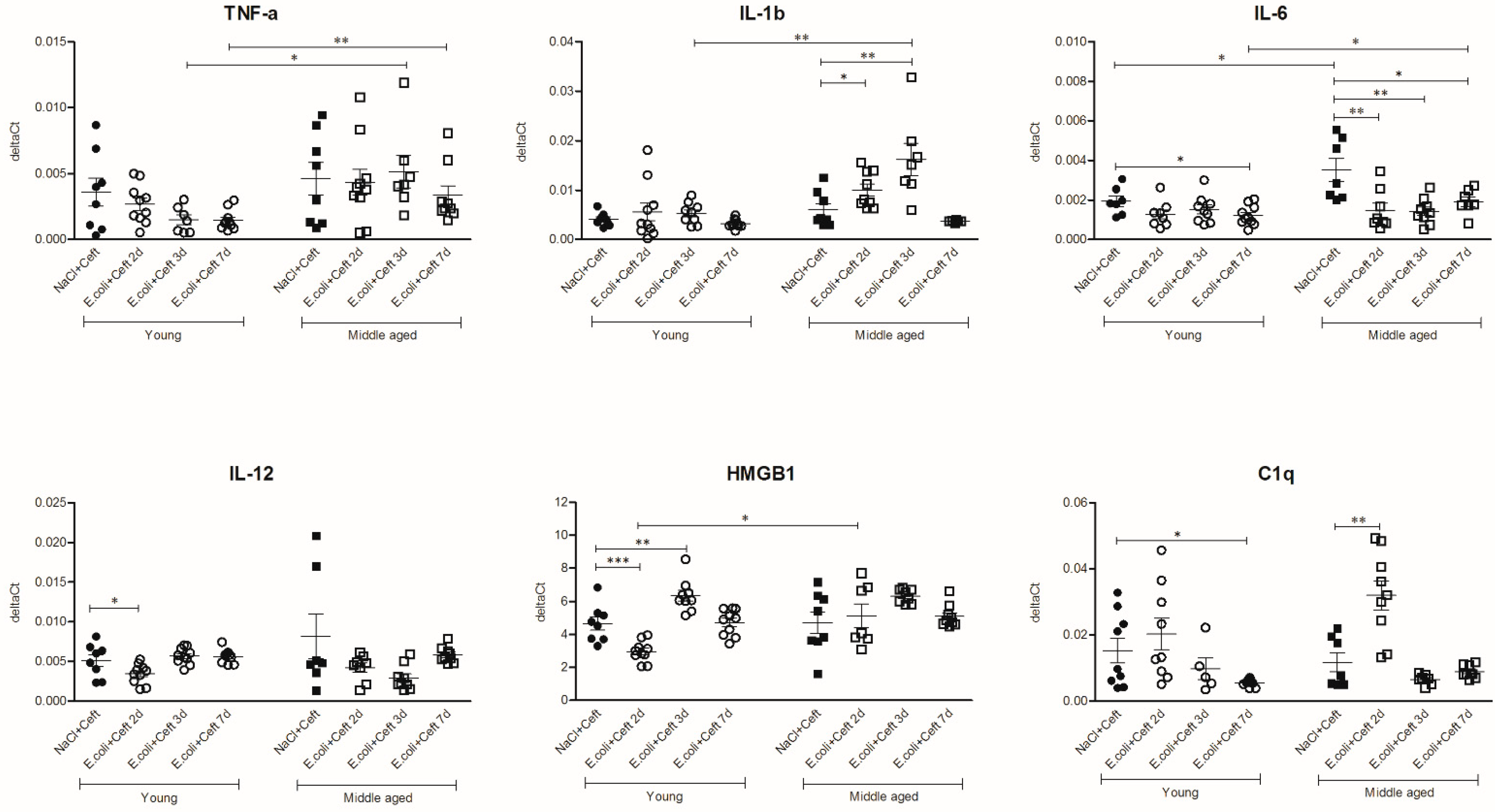
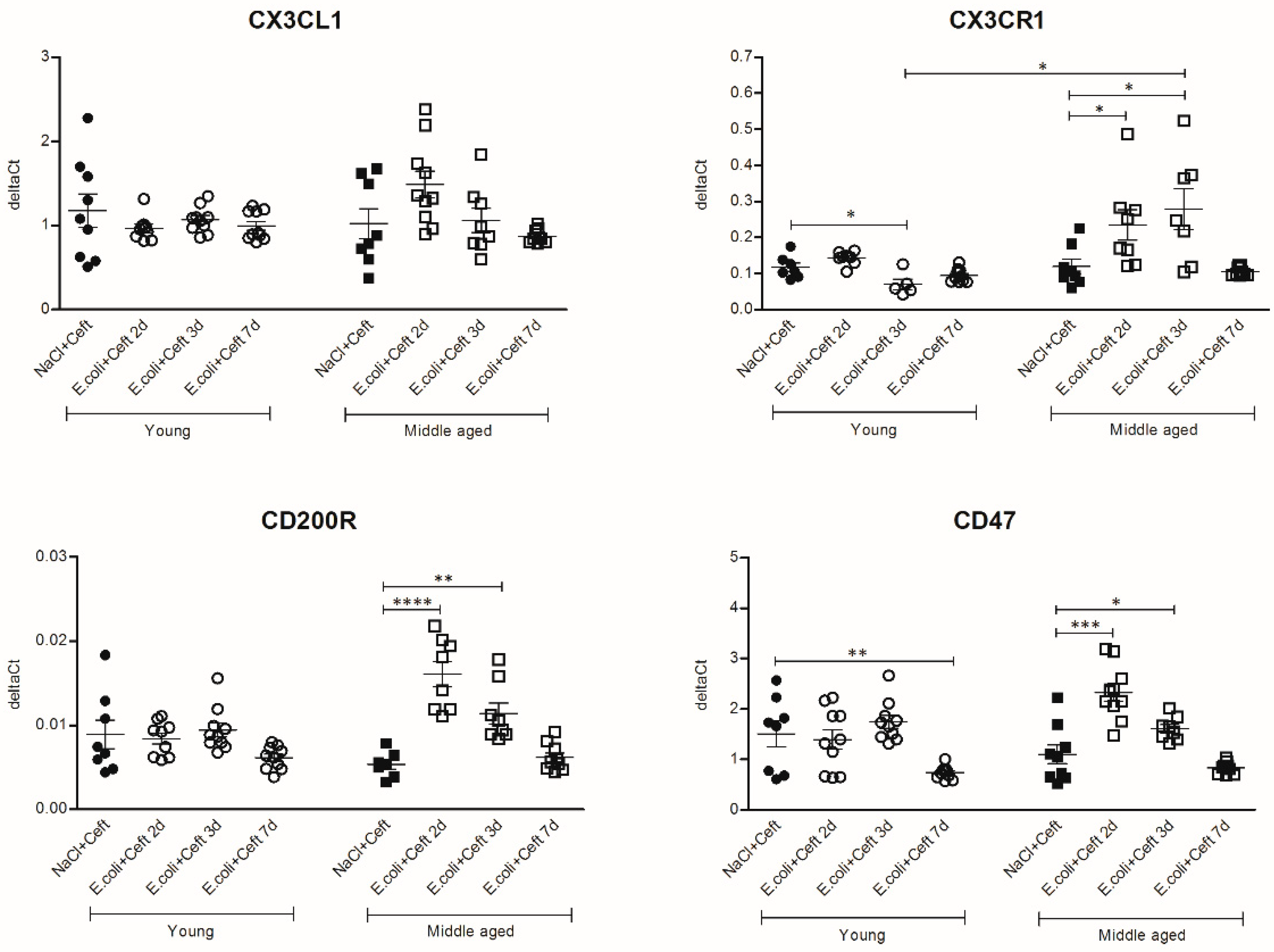
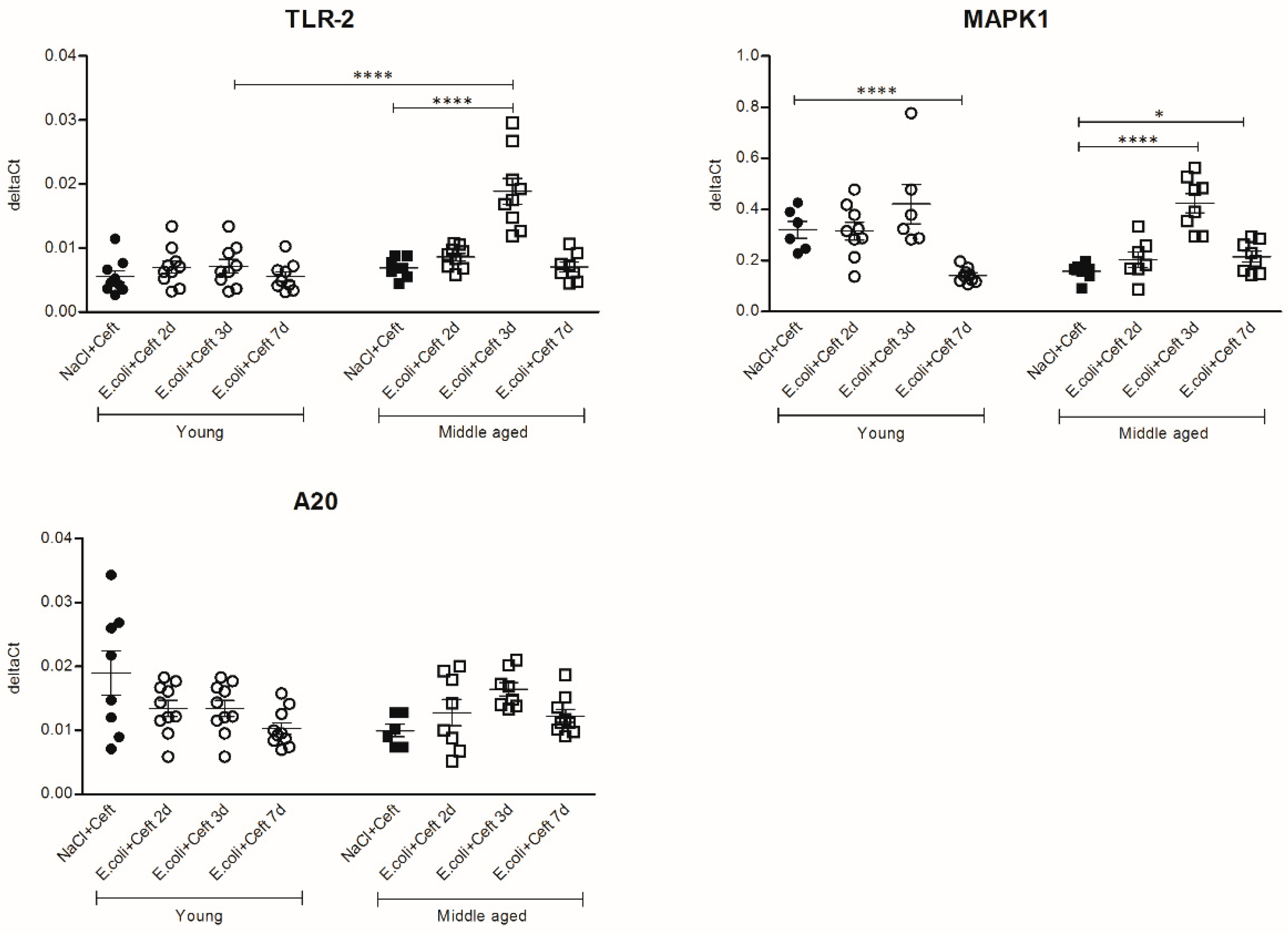
3.3. Inflammatory Mediators in Brain
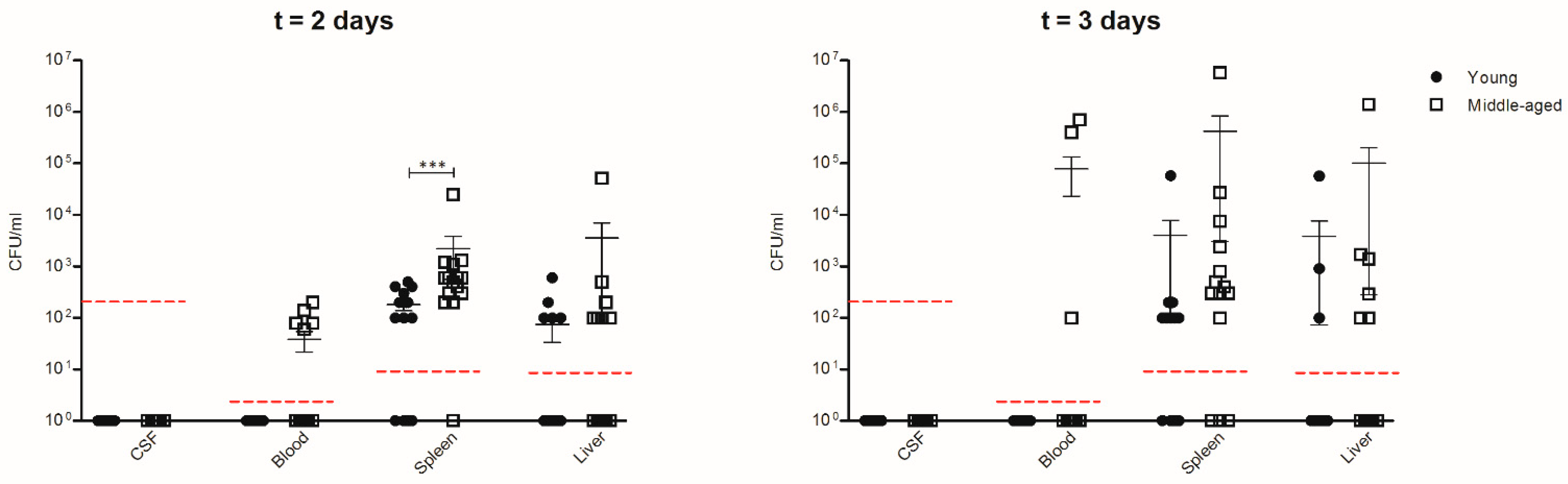
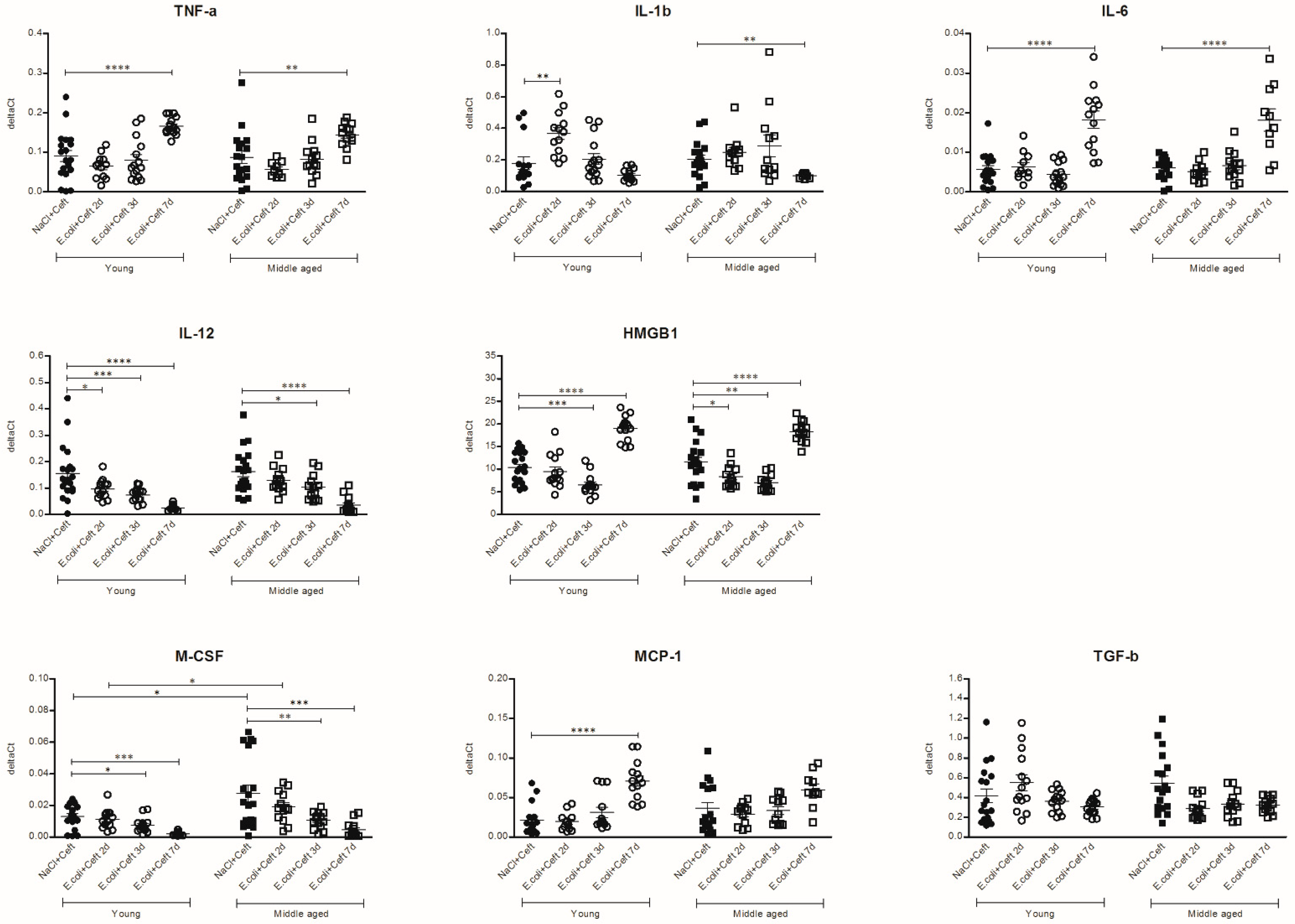
3.4. Inflammatory Mediators in Spleen
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Number of Mice Per Experimental Group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Round | Time Point | NaCl (Young/Middle-Aged) | NaCl + Ceft (Young/Middle-Aged) | E. coli + Ceft (Young/Middle-Aged) |
| 1 | t = 2 days | 6 (3/3) | 6 (3/3) | 10 (5/5) |
| t = 3 days | 6 (3/3) | 6 (3/3) | 10 (5/5) | |
| 2 | t = 2 days | 6 (3/3) | 6 (3/3) | 20 (10/10) |
| t = 3 days | 6 (3/3) | 6 (3/3) | 20 (10/10) | |
| 3 | t = 7 days | 16 (8/8) | 35 (16/19) | |
| Gene | Direction | PCR Primer 5′ → 3′ | Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NoNo | Forward | TGCTCCTGTGCCACCTGGTACTC | 170 |
| Reverse | CCGGAGCTGGACGGTTGAATGC | ||
| TNF-α | Forward | ACGGCATGGATCTCAAAGAC | 138 |
| Reverse | AGATAGCAAATCGGCTGACG | ||
| IL-1β | Forward | GGGCCTCAAAGGAAAGAATC | 183 |
| Reverse | TACCAGTTGGGGAACTCTGC | ||
| IL-6 | Forward | AGTTGCCTTCTTGGGACTGA | 191 |
| Reverse | CAGAATTGCCATTGCACAAC | ||
| HMGB1 | Forward | CCATTGGTGATGTTGCAAAG | 158 |
| Reverse | CTTTTTCGCTGCATCAGGTT | ||
| M-CSF | Forward | CCTGTGTCCGAACTTTCCAT | 181 |
| Reverse | TACAGGCAGTTGCAATCAGG | ||
| MCP-1 | Forward | AGCACCAGCCAACTCTCACT | 185 |
| Reverse | TCATTGGGATCATCTTGCTG | ||
| TGF-β | Forward | TTGCTTCAGCTCCACAGAGA | 183 |
| Reverse | TGGTTGTAGAGGGCAAGGAC | ||
| IL-12 | Forward | CATCGATGAGCTGATGCAGT | 163 |
| Reverse | CAGATAGCCCATCACCCTGT | ||
| Iba-1 | Forward | AGCTTTTGGACTGCTGAAGG | 197 |
| Reverse | GTTTCTCCAGCATTCGCTTC | ||
| CD11b | Forward | CATCAATAGCCAGCCTCAG | 197 |
| Reverse | GGTTGCCTCCAGTCTCAG | ||
| CX3CL1 | Forward | GGAAAGAAACGTGGTCCAGA | 165 |
| Reverse | GCCCTCAGAATCACAGGGTA | ||
| CX3CR1 | Forward | GAGTATGACGATTCTGCTGAGG | 102 |
| Reverse | CAGACCGAACGTGAAGACGAG | ||
| CD200 | Forward | AACGTCACCGAAATCAGGAG | 194 |
| Reverse | ACAGGCTCGTGTCTGGTCTT | ||
| CD200R | Forward | TCAGTGGCTTCAGAAAATGC | 187 |
| Reverse | GCCGACAAAGTAAGGCAGTC | ||
| CD47 | Forward | GCTACGTCCTTGCTTTGGTC | 189 |
| Reverse | CCGTCACTTCCCTTCACCTA | ||
| SIRP-α | Forward | CAACATCTTCCACACGGTTG | 203 |
| Reverse | ATCCTCTGGCCTAGGCACTT | ||
| C1q | Forward | CTTCTGGCCCTACCACTCAG | 171 |
| Reverse | CTTCTGACCCTTGGGTCCTC | ||
| TLR-2 | Forward | GCGGACTGTTTCCTTCTGAC | 165 |
| Reverse | CCAAAGAGCTCGTAGCATCC | ||
| MAPK1 | Forward | ACAAGAGCATCCCTGTGGAG | 161 |
| Reverse | GAGGTAAGCAAGGCAGATGG | ||
| SOCS1 | Forward | TTAACCCGGTACTCCGTGAC | 209 |
| Reverse | GAGGTCTCCAGCCAGAAGTG | ||
| A20 | Forward | TTCATCGAAGCTCAGAACCA | 183 |
| Reverse | GTGCTGGCACTCCATACAGA |
References
- Witlox, J.; Eurelings, L.S.; de Jonghe, J.F.; Kalisvaart, K.J.; Eikelenboom, P.; van Gool, W.A. Delirium in elderly patients and the risk of postdischarge mortality, institutionalization, and dementia: A meta-analysis. JAMA 2010, 304, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inouye, S.K. Delirium in older persons. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, C. Microglia and neurodegeneration: The role of systemic inflammation. Glia 2013, 61, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemstra, A.W.; Hoozemans, J.J.; van Haastert, E.S.; Rozemuller, A.J.; Eikelenboom, P.; van Gool, W.A. Microglia activation in sepsis: A case-control study. J. Neuroinflamm. 2007, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Semmler, A.; Frisch, C.; Debeir, T.; Ramanathan, M.; Okulla, T.; Klockgether, T.; Heneka, M.T. Long-term cognitive impairment, neuronal loss and reduced cortical cholinergic innervation after recovery from sepsis in a rodent model. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 204, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmler, A.; Okulla, T.; Sastre, M.; Dumitrescu-Ozimek, L.; Heneka, M.T. Systemic inflammation induces apoptosis with variable vulnerability of different brain regions. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2005, 30, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwashyna, T.J.; Ely, E.W.; Smith, D.M.; Langa, K.M. Long-term cognitive impairment and functional disability among survivors of severe sepsis. JAMA 2010, 304, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmann, C.N.; Heneka, M.T. Long-term cerebral consequences of sepsis. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiersinga, W.J.; Rhodes, A.; Cheng, A.C.; Peacock, S.J.; Prescott, H.C. Pathophysiology, Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review. JAMA 2020, 324, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niraula, A.; Sheridan, J.F.; Godbout, J.P. Microglia Priming with Aging and Stress. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 318–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norden, D.M.; Godbout, J.P. Review: Microglia of the aged brain: Primed to be activated and resistant to regulation. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2013, 39, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, V.H.; Holmes, C. Microglial priming in neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLullich, A.M.; Beaglehole, A.; Hall, R.J.; Meagher, D.J. Delirium and long-term cognitive impairment. Int. Rev. Psychiatry 2009, 21, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gool, W.A.; van de Beek, D.; Eikelenboom, P. Systemic infection and delirium: When cytokines and acetylcholine collide. Lancet 2010, 375, 773–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, A.E.; Pioro, E.P.; Sasse, M.E.; Kostenko, V.; Cardona, S.M.; Dijkstra, I.M.; Huang, D.; Kidd, G.; Dombrowski, S.; Dutta, R.; et al. Control of microglial neurotoxicity by the fractalkine receptor. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, R.M.; Ruuls, S.R.; Murphy, C.A.; Wright, G.J.; Goddard, R.; Zurawski, S.M.; Blom, B.; Homola, M.E.; Streit, W.J.; Brown, M.H.; et al. Down-regulation of the macrophage lineage through interaction with OX2 (CD200). Science 2000, 290, 1768–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenborg, P.A.; Gresham, H.D.; Lindberg, F.P. CD47-signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPalpha) regulates Fcgamma and complement receptor-mediated phagocytosis. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 193, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamerman, J.A.; Pottle, J.; Ni, M.; He, Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Buckner, J.H. Negative regulation of TLR signaling in myeloid cells-implications for autoimmune diseases. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 269, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laflamme, N.; Rivest, S. Toll-like receptor 4: The missing link of the cerebral innate immune response triggered by circulating gram-negative bacterial cell wall components. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laflamme, N.; Soucy, G.; Rivest, S. Circulating cell wall components derived from gram-negative, not gram-positive, bacteria cause a profound induction of the gene-encoding Toll-like receptor 2 in the CNS. J. Neurochem. 2001, 79, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoogland, I.C.; Houbolt, C.; van Westerloo, D.J.; van Gool, W.A.; van de Beek, D. Systemic inflammation and microglial activation: Systematic review of animal experiments. J Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogland, I.C.M.; Westhoff, D.; Engelen-Lee, J.Y.; Melief, J.; Valls Seron, M.; Houben-Weerts, J.; Huitinga, I.; van Westerloo, D.J.; van der Poll, T.; van Gool, W.A.; et al. Microglial Activation After Systemic Stimulation With Lipopolysaccharide and Escherichia coli. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wu, Z.; Hayashi, Y.; Nakanishi, H. Age-dependent neuroinflammatory responses and deficits in long-term potentiation in the hippocampus during systemic inflammation. Neuroscience 2012, 216, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, H.; Jeon, J.; Seo, H. Systemic injection of LPS induces region-specific neuroinflammation and mitochondrial dysfunction in normal mouse brain. Neurochem. Int. 2014, 69, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, A.Y.; Dhami, K.S.; Dibal, C.D.; Todd, K.G. Neonatal rat microglia derived from different brain regions have distinct activation responses. Neuron Glia Biol. 2011, 7, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, A.D.; Wyttenbach, A.; Perry, V.H.; Teeling, J.L. Age related changes in microglial phenotype vary between CNS regions: Grey versus white matter differences. Brain Behav. Immun. 2012, 26, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.W.; Yoo, K.Y.; Hwang, I.K.; Kim, D.W.; Chung, J.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Choi, J.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Youn, H.Y.; Lee, I.S.; et al. Systemic administration of lipopolysaccharide induces cyclooxygenase-2 immunoreactivity in endothelium and increases microglia in the mouse hippocampus. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2010, 30, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, C.J.; Huang, Y.; Wynne, A.; Hanke, M.; Himler, J.; Bailey, M.T.; Sheridan, J.F.; Godbout, J.P. Minocycline attenuates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced neuroinflammation, sickness behavior, and anhedonia. J. Neuroinflamm. 2008, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, C.J.; Huang, Y.; Wynne, A.M.; Godbout, J.P. Peripheral lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge promotes microglial hyperactivity in aged mice that is associated with exaggerated induction of both pro-inflammatory IL-1beta and anti-inflammatory IL-10 cytokines. Brain Behav. Immun. 2009, 23, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavendra, V.; Tanga, F.Y.; DeLeo, J.A. Complete Freunds adjuvant-induced peripheral inflammation evokes glial activation and proinflammatory cytokine expression in the CNS. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 20, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godbout, J.P.; Chen, J.; Abraham, J.; Richwine, A.F.; Berg, B.M.; Kelley, K.W.; Johnson, R.W. Exaggerated neuroinflammation and sickness behavior in aged mice following activation of the peripheral innate immune system. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1329–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.C.; Panda, A.; Joshi, S.R.; Qian, F.; Allore, H.G.; Montgomery, R.R. Dysregulation of human Toll-like receptor function in aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2011, 10, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehmer, E.D.; Goral, J.; Faunce, D.E.; Kovacs, E.J. Age-dependent decrease in Toll-like receptor 4-mediated proinflammatory cytokine production and mitogen-activated protein kinase expression. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 75, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renshaw, M.; Rockwell, J.; Engleman, C.; Gewirtz, A.; Katz, J.; Sambhara, S. Cutting edge: Impaired Toll-like receptor expression and function in aging. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 4697–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letiembre, M.; Hao, W.; Liu, Y.; Walter, S.; Mihaljevic, I.; Rivest, S.; Hartmann, T.; Fassbender, K. Innate immune receptor expression in normal brain aging. Neuroscience 2007, 146, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonken, L.K.; Frank, M.G.; Kitt, M.M.; D’Angelo, H.M.; Norden, D.M.; Weber, M.D.; Barrientos, R.M.; Godbout, J.P.; Watkins, L.R.; Maier, S.F. The Alarmin HMGB1 Mediates Age-Induced Neuroinflammatory Priming. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 7946–7956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Wu, X.; Block, M.L.; Liu, Y.; Breese, G.R.; Hong, J.S.; Knapp, D.J.; Crews, F.T. Systemic LPS causes chronic neuroinflammation and progressive neurodegeneration. Glia 2007, 55, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurink, B.; Roos, E.; Radonic, T.; Barbe, E.; Bouman, C.S.C.; de Boer, H.H.; de Bree, G.J.; Bulle, E.B.; Aronica, E.M.; Florquin, S.; et al. Viral presence and immunopathology in patients with lethal COVID-19: A prospective autopsy cohort study. Lancet Microbe 2020, 1, e290–e299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puelles, V.G.; Lutgehetmann, M.; Lindenmeyer, M.T.; Sperhake, J.P.; Wong, M.N.; Allweiss, L.; Chilla, S.; Heinemann, A.; Wanner, N.; Liu, S.; et al. Multiorgan and Renal Tropism of SARS-CoV-2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, I.H.; Normandin, E.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Mukerji, S.S.; Keller, K.; Ali, A.S.; Adams, G.; Hornick, J.L.; Padera, R.F., Jr.; Sabeti, P. Neuropathological Features of Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 989–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carfi, A.; Bernabei, R.; Landi, F. Persistent Symptoms in Patients After Acute COVID-19. JAMA 2020, 324, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, J.P.; Chesney, E.; Oliver, D.; Pollak, T.A.; McGuire, P.; Fusar-Poli, P.; Zandi, M.S.; Lewis, G.; David, A.S. Psychiatric and neuropsychiatric presentations associated with severe coronavirus infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis with comparison to the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Sanchez, C.M.; Diaz-Maroto, I.; Fernandez-Diaz, E.; Sanchez-Larsen, A.; Layos-Romero, A.; Garcia-Garcia, J.; Gonzalez, E.; Redondo-Penas, I.; Perona-Moratalla, A.B.; Del Valle-Perez, J.A.; et al. Neurologic manifestations in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: The ALBACOVID registry. Neurology 2020, 95, e1060–e1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; Golenbock, D.; Latz, E.; Morgan, D.; Brown, R. Immediate and long-term consequences of COVID-19 infections for the development of neurological disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2020, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ising, C.; Venegas, C.; Zhang, S.; Scheiblich, H.; Schmidt, S.V.; Vieira-Saecker, A.; Schwartz, S.; Albasset, S.; McManus, R.M.; Tejera, D.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation drives tau pathology. Nature 2019, 575, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pocock, J.M.; Kettenmann, H. Neurotransmitter receptors on microglia. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guneykaya, D.; Ivanov, A.; Hernandez, D.P.; Haage, V.; Wojtas, B.; Meyer, N.; Maricos, M.; Jordan, P.; Buonfiglioli, A.; Gielniewski, B.; et al. Transcriptional and Translational Differences of Microglia from Male and Female Brains. Cell Rep. 2018, 24, 2773–2783.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoogland, I.C.M.; Westhoff, D.; Engelen-Lee, J.-Y.; Valls Seron, M.; Houben-Weerts, J.H.M.P.; van Westerloo, D.J.; van der Poll, T.; van Gool, W.A.; van de Beek, D. Aging and Microglial Response following Systemic Stimulation with Escherichia coli in Mice. Cells 2021, 10, 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020279
Hoogland ICM, Westhoff D, Engelen-Lee J-Y, Valls Seron M, Houben-Weerts JHMP, van Westerloo DJ, van der Poll T, van Gool WA, van de Beek D. Aging and Microglial Response following Systemic Stimulation with Escherichia coli in Mice. Cells. 2021; 10(2):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020279
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoogland, Inge C.M., Dunja Westhoff, Joo-Yeon Engelen-Lee, Mercedes Valls Seron, Judith H.M.P. Houben-Weerts, David J. van Westerloo, Tom van der Poll, Willem A. van Gool, and Diederik van de Beek. 2021. "Aging and Microglial Response following Systemic Stimulation with Escherichia coli in Mice" Cells 10, no. 2: 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020279
APA StyleHoogland, I. C. M., Westhoff, D., Engelen-Lee, J.-Y., Valls Seron, M., Houben-Weerts, J. H. M. P., van Westerloo, D. J., van der Poll, T., van Gool, W. A., & van de Beek, D. (2021). Aging and Microglial Response following Systemic Stimulation with Escherichia coli in Mice. Cells, 10(2), 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020279






