Tissue–Resident Memory T Cells in Chronic Inflammation—Local Cells with Systemic Effects?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. TRM: Drivers of Chronic Inflammation
1.2. TRM Phenotype
1.3. TRM Development
2. TRM Are Enriched at Sites of Chronic Inflammation at Barrier and Non-Barrier Tissues
2.1. Skin
2.2. Gut
2.3. Joints
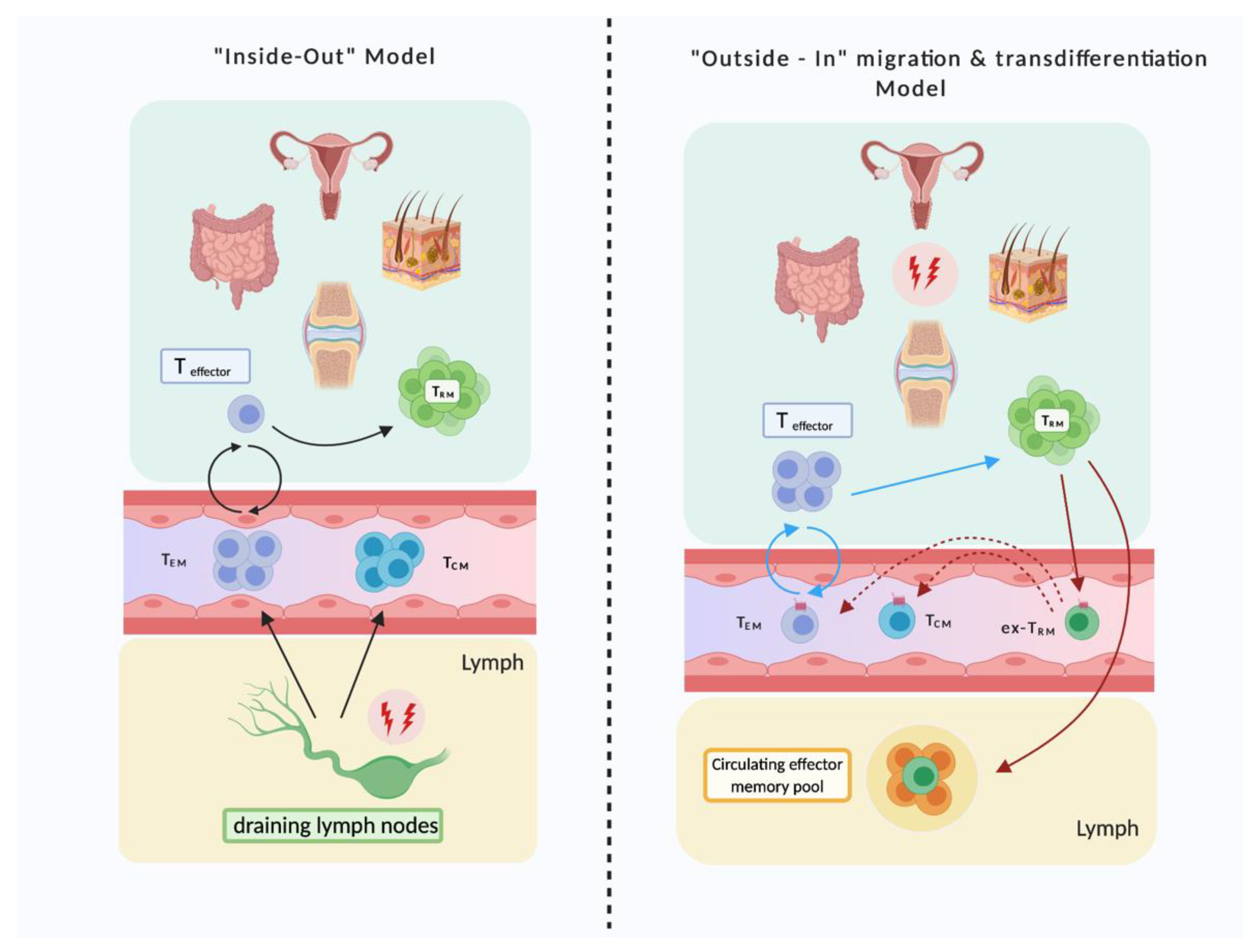
3. Recirculation of Tissue–Resident Memory T Cells
3.1. TRM Migrate Out of Non-Lymphoid Tissue into Circulation
3.2. Ex-TRM, Present in the Circulation, Share Characteristics with TRM in Tissue, But Also Display Molecules Characteristic of Circulating T Cells
3.3. Indications for Recirculation of TRM in Chronic Inflammatory Disease
4. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schenkel, J.M.; Masopust, D. Tissue-Resident Memory T Cells. Immunity 2014, 41, 886–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richmond, J.M.; Strassner, J.P.; Rashighi, M.; Agarwal, P.; Garg, M.; Essien, K.I.; Pell, L.S.; Harris, J.E. Resident Memory and Recirculating Memory T Cells Cooperate to Maintain Disease in a Mouse Model of Vitiligo. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, B.; Ma, W.; Miron, M.; Granot, T.; Guyer, R.; Carpenter, D.; Senda, T.; Sun, X.; Ho, S.; Lerner, H.; et al. Human Tissue-Resident Memory T Cells Are Defined by Core Transcriptional and Functional Signatures in Lymphoid and Mucosal Sites. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 2921–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mueller, S.N.; Mackay, L.K. Tissue-resident memory T cells: Local specialists in immune defence. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, P.A.; Miron, M.; Farber, D.L. Location, location, location: Tissue resident memory T cells in mice and humans. Sci. Immunol. 2019, 4, eaas9673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thome, J.J.; Yudanin, N.; Ohmura, Y.; Kubota, M.; Grinshpun, B.; Sathaliyawala, T.; Kato, T.; Lerner, H.; Shen, Y.; Farber, D.L. Spatial Map of Human T Cell Compartmentalization and Maintenance over Decades of Life. Cell 2014, 159, 814–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schenkel, J.M.; Fraser, K.A.; Masopust, D. Cutting Edge: Resident Memory CD8 T Cells Occupy Frontline Niches in Secondary Lymphoid Organs. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 2961–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, M.; Kumar, B.V.; Meng, W.; Granot, T.; Carpenter, D.J.; Senda, T.; Chen, D.; Rosenfeld, A.M.; Zhang, B.; Lerner, H.; et al. Human Lymph Nodes Maintain TCF-1hi Memory T Cells with High Functional Potential and Clonal Diversity throughout Life. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 2132–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mackay, L.; Rahimpour, A.; Ma, J.; Collins, N.; Stock, A.; Hafon, M.; Vega-Ramos, J.; Lauzurica, P.; Mueller, S.; Stefanovic, T.; et al. The developmental pathway for CD103+CD8+ tissue-resident memory T cells of skin. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusa, F.; Durek, P.; McGrath, M.; Sercan-Alp, Ö.; Rao, A.; Du, W.; Cendón, C.; Chang, H.; Heinz, G.; Mashreghi, M.; et al. CD69 + memory T lymphocytes of the bone marrow and spleen express the signature transcripts of tissue-resident memory T lymphocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 2019, 49, 966–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mackay, L.K.; Wynne-Jones, E.; Freestone, D.; Pellicci, D.G.; Mielke, L.A.; Newman, D.M.; Braun, A.; Masson, F.; Kallies, A.; Belz, G.T.; et al. T-box Transcription Factors Combine with the Cytokines TGF-β and IL-15 to Control Tissue-Resident Memory T Cell Fate. Immunity 2015, 43, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mackay, L.; Minnich, M.; Kragten, N.; Liao, Y.; Nota, B.; Seillet, C.; Zaid, A.; Man, K.; Preston, S.; Freestone, D.; et al. Hobit and Blimp1 instruct a universal transcriptional pro-gram of tissue residency in lymphocytes. Science 2016, 352, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milner, J.J.; Toma, C.; Yu, B.; Zhang, K.; Omilusik, K.; Phan, A.T.; Wang, D.; Getzler, A.J.; Nguyen, T.; Crotty, S.; et al. Runx3 programs CD8+ T cell residency in non-lymphoid tissues and tumours. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 552, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, J.J.; Toma, C.; He, Z.; Kurd, N.S.; Nguyen, Q.P.; McDonald, B.; Quezada, L.; Widjaja, C.E.; Witherden, D.A.; Crowl, J.T.; et al. Heterogenous Populations of Tissue-Resident CD8+ T Cells Are Generated in Response to Infection and Malignancy. Immunity 2020, 52, 808–824.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thome, J.J.; Bickham, K.L.; Ohmura, Y.; Kubota, M.; Matsuoka, N.; Gordon, C.; Granot, T.; Griesemer, A.; Lerner, H.; Kato, T.; et al. Early-life compartmentalization of human T cell differentiation and regulatory function in mucosal and lymphoid tissues. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallusto, F.; Geginat, J.; Lanzavecchia, A. Central Memory and Effector Memory T Cell Subsets: Function, Generation, and Maintenance. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 22, 745–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masopust, D.; Soerens, A.G. Tissue-Resident T Cells and Other Resident Leukocytes. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 37, 521–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, R.; Beura, L.; Quarnstrom, C.; Ghoneim, H.; Fan, Y.; Zebley, C.; Scott, M.; Fares-Frederickson, N.; Wijeyesinghe, S.; Thompson, E.; et al. Developmental plasticity allows out-side-in immune responses by resident memory T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Künzli, M.; King, C.G. Resident Memory T Cells Escape ‘Home Quarantine’. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 454–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, R.; Gehad, A.; Yang, C.; Scott, L.L.; Teague, J.E.; Schlapbach, C.; Elco, C.P.; Huang, V.; Matos, T.R.; Kupper, T.S.; et al. Human skin is protected by four functionally and phenotypically discrete populations of resident and recirculating memory T cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 279ra39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.L.; Zaid, A.; Hor, J.L.; Christo, S.N.; Prier, J.E.; Davies, B.; Alexandre, Y.O.; Gregory, J.L.; Russell, T.A.; Gebhardt, T.; et al. Local proliferation maintains a stable pool of tissue-resident memory T cells after antiviral recall responses. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beura, L.K.; Mitchell, J.S.; Thompson, E.A.; Schenkel, J.M.; Mohammed, J.; Wijeyesinghe, S.; Fonseca, R.; Burbach, B.J.; Hickman, H.D.; Vezys, V.; et al. Intravital mucosal imaging of CD8+ resident memory T cells shows tissue-autonomous recall responses that amplify secondary memory. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, L.K.; Kallies, A. Transcriptional Regulation of Tissue-Resident Lymphocytes. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zundler, S.; Becker, E.; Spocinska, M.; Slawik, M.; Parga-Vidal, L.; Stark, R.; Wiendl, M.; Atreya, R.; Rath, T.; Leppkes, M.; et al. Author Correction: Hobit- and Blimp-1-driven CD4+ tissue-resident memory T cells control chronic intestinal inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oja, A.E.; Piet, B.; Helbig, C.; Stark, R.; Van Der Zwan, D.; Blaauwgeers, H.; Remmerswaal, E.B.M.; Amsen, D.; Jonkers, R.E.; Moerland, P.D.; et al. Trigger-happy resident memory CD4+ T cells inhabit the human lungs. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 654–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, M.E.; Finlayson, M.O.; Connors, T.J.; Dogra, P.; Senda, T.; Bush, E.; Carpenter, D.; Marboe, C.; Benvenuto, L.; Shah, L.; et al. Generation and persistence of human tissue-resident memory T cells in lung transplantation. Sci. Immunol. 2019, 4, eaav5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, F.A.V.; Hertoghs, K.M.L.; Kragten, N.A.M.; Doody, G.M.; Barnes, N.A.; Remmerswaal, E.B.M.; Hsiao, C.-C.; Moerland, P.D.; Wouters, D.; Derks, I.A.M.; et al. Blimp-1 homolog Hobit identifies effector-type lymphocytes in humans. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 2945–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Zander, R.; Khatun, A.; Schauder, D.M.; Cui, W. Transcriptional and Epigenetic Regulation of Effector and Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Shen, Z. Tissue-resident memory T cells and their biological characteristics in the recurrence of inflam-matory skin disorders. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuric, E.; Seiron, P.; Krogvold, L.; Edwin, B.; Buanes, T.; Hanssen, K.; Skog, O.; Dahl-Jørgensen, K.; Korsgren, O. Demonstration of Tissue Resident Memory CD8 T Cells in Insulitic Lesions in Adult Patients with Recent-Onset Type 1 Di-abetes. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, C.; Yao, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, S.; Chu, H.; Tsuneyama, K.; Li, X.; Gershwin, M.; Lian, Z. Tissue-Resident Memory CD 8+ T Cells Acting as Mediators of Salivary Gland Damage in a Murine Model of Sjögren’s Syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, M.; Guo, C.; Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, N. JAK/STAT signaling controls the fate of CD8+CD103+ tissue-resident memory T cell in lupus nephritis. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 109, 102424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fransen, N.L.; Hsiao, C.-C.; Van Der Poel, M.; Engelenburg, H.J.; Verdaasdonk, K.; Vincenten, M.C.J.; Remmerswaal, E.B.M.; Kuhlmann, T.; Mason, M.R.J.; Hamann, J.; et al. Tissue-resident memory T cells invade the brain parenchyma in multiple sclerosis white matter lesions. Brain 2020, 143, 1714–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado-Santos, J.; Saji, E.; Tröscher, A.R.; Paunovic, M.; Liblau, R.; Gabriely, G.; Bien, C.G.; Bauer, J.; Lassmann, H. The compartmentalized inflammatory response in the multiple sclerosis brain is composed of tissue-resident CD8+ T lymphocytes and B cells. Brain 2018, 141, 2066–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrelli, A.; Mijnheer, G.; Van Konijnenburg, D.P.H.; Van Der Wal, M.M.; Giovannone, B.; Mocholi, E.; Vazirpanah, N.; Broen, J.C.; Hijnen, D.; Oldenburg, B.; et al. PD-1+CD8+ T cells are clonally expanding effectors in human chronic inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4669–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maschmeyer, P.; Heinz, G.; Skopnik, C.; Lutter, L.; Mazzoni, A.; Heinrich, F.; Stuckrad, S.; Wirth, L.; Tran, C.; Riedel, R.; et al. Antigen-driven PD-1 + TOX + BHLHE40 + and PD-1 + TOX + EOMES + T lymphocytes regulate juvenile idiopathic arthritis in situ. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, K.J.A.; Srenathan, U.; Ridley, M.; Durham, L.E.; Wu, S.; Ryan, S.E.; Hughes, C.D.; Chan, E.; Kirkham, B.W.; Taams, L.S. Polyfunctional, Proinflammatory, Tissue-Resident Memory Phenotype and Function of Synovial Interleukin-17A+ CD 8+ T Cells in Psoriatic Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 72, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qaiyum, Z.; Gracey, E.; Yao, Y.; Inman, R.D. Integrin and transcriptomic profiles identify a distinctive synovial CD8+ T cell subpopulation in spondyloarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1566–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, Y.; Lee, C.; Yoo, B.; Shin, E.; Hong, S. Synovial fluid CD69 + CD8 + T cells with tissue-resident phenotype mediate perforin-dependent citrullination in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2020, 9, e1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheuk, S.; Wikén, M.; Blomqvist, L.; Nylén, S.; Talme, T.; Ståhle, M.; Eidsmo, L. Epidermal Th22 and Tc17 Cells Form a Localized Disease Memory in Clinically Healed Psoriasis. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 3111–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vo, S.; Watanabe, R.; Koguchi-Yoshioka, H.; Matsumura, Y.; Ishitsuka, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Okiyama, N.; Fujisawa, Y.; Fujimoto, M. CD 8 resident memory T cells with interleukin 17A-producing potential are accumulated in disease-naïve nonlesional sites of psoriasis possibly in correlation with disease duration. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 181, 410–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boniface, K.; Jacquemin, C.; Darrigade, A.-S.; Dessarthe, B.; Martins, C.; Boukhedouni, N.; Vernisse, C.; Grasseau, A.; Thiolat, D.; Rambert, J.; et al. Vitiligo Skin Is Imprinted with Resident Memory CD8 T Cells Expressing CXCR3. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richmond, J.M.; Strassner, J.P.; Zapata, L.; Garg, M.; Riding, R.L.; Refat, M.A.; Fan, X.; Azzolino, V.; Tovar-Garza, A.; Tsurushita, N.; et al. Antibody blockade of IL-15 signaling has the potential to durably reverse vitiligo. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaam7710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, H.; Suryawanshi, H.; Morozov, P.; Gay-Mimbrera, J.; Del Duca, E.; Kim, H.J.; Kameyama, N.; Estrada, Y.; Der, E.; Krueger, J.G.; et al. Single-cell transcriptome analysis of human skin identifies novel fibroblast subpopulation and enrichment of immune subsets in atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 1615–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; van Vliet, C.; Rufaut, N.; Jones, L.; Sinclair, R.; Carbone, F. Laser Capture Microdissection Reveals Transcriptional Abnormalities in Alopecia Areata before, during, and after Active Hair Loss. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Duca, E.; Ruano Ruiz, J.; Pavel, A.; Sanyal, R.; Song, T.; Gay-Mimbrera, J.; Zhang, N.; Estrada, Y.; Peng, X.; Renert-Yuval, Y.; et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia shows robust T helper 1 and Janus kinase 3 skewing. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishu, S.; El Zaatari, M.; Hayashi, A.; Hou, G.; Bowers, N.; Kinnucan, J.; Manoogian, B.; Muza-Moons, M.; Zhang, M.; Grasberger, H.; et al. CD4+ Tissue-resident Memory T Cells Expand and Are a Major Source of Mucosal Tumour Necrosis Factor α in Active Crohn’s Disease. J. Crohn’s Coliti 2019, 13, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, D.A.; Gurish, M.F.; Marshall, J.L.; Slowikowski, K.; Fonseka, K.S.C.Y.; Liu, Y.; Donlin, L.T.; Henderson, L.A.; Wei, K.; Mizoguchi, F.; et al. Pathologically expanded peripheral T helper cell subset drives B cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 542, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, R. Protective and pathogenic roles of resident memory T cells in human skin disorders. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2019, 95, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strazzulla, L.; Wang, E.; Avila, L.; Lo Sicco, K.; Brinster, N.; Christiano, A.; Shapiro, J. Alopecia areata: Disease characteristics, clinical evaluation, and new perspectives on pathogenesis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 78, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheuk, S.; Schlums, H.; Sérézal, I.G.; Martini, E.; Chiang, S.C.; Marquardt, N.; Gibbs, A.; Detlofsson, E.; Introini, A.; Forkel, M.; et al. CD49a Expression Defines Tissue-Resident CD8 + T Cells Poised for Cytotoxic Function in Human Skin. Immunity 2017, 46, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gallais Sérézal, I.; Classon, C.; Cheuk, S.; Barrientos-Somarribas, M.; Wadman, E.; Martini, E.; Chang, D.; Xu Landén, N.; Ehrström, M.; Nylén, S.; et al. Resident T Cells in Resolved Psoriasis Steer Tissue Responses that Stratify Clinical Outcome. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 1754–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matos, T.; O’Malley, J.; Lowry, E.; Hamm, D.; Kirsch, I.; Robins, H.; Kupper, T.; Krueger, J.; Clark, R. Clinically resolved psoriatic lesions contain psoriasis-specific IL-17–producing αβ T cell clones. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 4031–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sérézal, I.G.; Hoffer, E.; Ignatov, B.; Martini, E.; Zitti, B.; Ehrström, M.; Eidsmo, L. A skewed pool of resident T cells triggers psoriasis-associated tissue responses in never-lesional skin from patients with psoriasis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1444–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hegazy, A.; West, N.; Stubbington, M.; Wendt, E.; Suijker, K.; Datsi, A.; This, S.; Danne, C.; Campion, S.; Duncan, S.; et al. Circulating and Tissue-Resident CD4 + T Cells With Reactivity to Intestinal Microbiota Are Abundant in Healthy Individuals and Function Is Altered During Inflammation. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 1320–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleinschek, M.A.; Boniface, K.; Sadekova, S.; Grein, J.; Murphy, E.E.; Turner, S.P.; Raskin, L.; Desai, B.; Faubion, W.A.; Malefyt, R.D.W.; et al. Circulating and gut-resident human Th17 cells express CD161 and promote intestinal inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolomé-Casado, R.; Landsverk, O.J.; Chauhan, S.K.; Richter, L.; Phung, D.; Greiff, V.; Risnes, L.F.; Yao, Y.; Neumann, R.S.; Yaqub, S.; et al. Resident memory CD8 T cells persist for years in human small intestine. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 2412–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, A.; Durant, L.; Hoyles, L.; McCartney, A.L.; Man, R.; Segal, J.; Costello, S.P.; Hendy, P.; Reddi, D.; Bouri, S.; et al. Deficient Resident Memory T Cell and CD8 T Cell Response to Commensals in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohn’s Coliti 2019, 14, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.; Aletaha, D.; McInnes, I. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijnheer, G.; van Wijk, F. T-Cell Compartmentalization and Functional Adaptation in Autoimmune Inflammation: Lessons from Pediatric Rheumatic Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrens, E.J.; Prakken, B.J.; Van Wijk, F. T cells out of control—Impaired immune regulation in the inflamed joint. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 9, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beura, L.K.; Wijeyesinghe, S.; Thompson, E.A.; Macchietto, M.G.; Rosato, P.C.; Pierson, M.J.; Schenkel, J.M.; Mitchell, J.S.; Vezys, V.; Fife, B.T.; et al. T Cells in Nonlymphoid Tissues Give Rise to Lymph-Node-Resident Memory T Cells. Immunity 2018, 48, 327–338.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beura, L.K.; Fares-Frederickson, N.J.; Steinert, E.M.; Scott, M.C.; Thompson, E.A.; Fraser, K.A.; Schenkel, J.M.; Vezys, V.; Masopust, D. CD4+ resident memory T cells dominate immunosurveillance and orchestrate local recall responses. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 1214–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klicznik, M.M.; Morawski, P.A.; Höllbacher, B.; Varkhande, S.R.; Motley, S.J.; Kuri-Cervantes, L.; Goodwin, E.; Rosenblum, M.D.; Long, S.A.; Brachtl, G.; et al. Human CD4+CD103+ cutaneous resident memory T cells are found in the circulation of healthy individuals. Sci. Immunol. 2019, 4, eaav8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallusto, F.; Lenig, D.; Förster, R.; Lipp, M.; Lanzavecchia, A. Two subsets of memory T lymphocytes with distinct homing potentials and effector functions. Nat. Cell Biol. 1999, 401, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratz, I.K.; Campbell, D.J. Resident memory T cells show that it is never too late to change your ways. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 359–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spreafico, R.; Rossetti, M.; Van Loosdregt, J.; A Wallace, C.; Massa, M.; Magni-Manzoni, S.; Gattorno, M.; Martini, A.; Lovell, D.J.; Albani, S. A circulating reservoir of pathogenic-like CD4+T cells shares a genetic and phenotypic signature with the inflamed synovial micro-environment. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 75, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakaguchi, S.; Mikami, N.; Wing, J.B.; Tanaka, A.; Ichiyama, K.; Ohkura, N. Regulatory T Cells and Human Disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 38, 541–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mijnheer, G.; Lutter, L.; Mokry, M.; van der Wal, M.; Fleskens, V.; Scholman, R.; Pandit, A.; Tao, W.; Wekking, M.; Vervoort, S.; et al. Conserved human effector Treg signature is reflected in transcriptomic and epigenetic landscape. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, P.A.; Levitin, H.M.; Miron, M.; Snyder, M.E.; Senda, T.; Yuan, J.; Cheng, Y.L.; Bush, E.C.; Dogra, P.; Thapa, P.; et al. Single-cell transcriptomics of human T cells reveals tissue and activation signatures in health and disease. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wienke, J.; Brouwers, L.; Van Der Burg, L.M.; Mokry, M.; Scholman, R.C.; Nikkels, P.G.; Van Rijn, B.B.; Van Wijk, F. Human Tregs at the materno-fetal interface show site-specific adaptation reminiscent of tumor Tregs. JCI Insight 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossetti, M.; Spreafico, R.; Consolaro, A.; Leong, J.Y.; Chua, C.; Massa, M.; Saidin, S.; Magni-Manzoni, S.; Arkachaisri, T.; Wallace, C.A.; et al. TCR repertoire sequencing identifies synovial Treg cell clonotypes in the bloodstream during active inflammation in human arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 76, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, M.M.; Farber, D.L. The Whole Body as the System in Systems Immunology. iScience 2020, 23, 101509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggino, G.; Rizzo, A.; Mauro, D.; Macaluso, F.; Ciccia, F. Gut-derived CD8+ tissue-resident memory T cells are expanded in the peripheral blood and synovia of SpA patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, –2019–216456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vastert, S.J.; Bhat, P.; Goldstein, D.A. Pathophysiology of JIA-associated Uveitis. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2014, 22, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argollo, M.; Fiorino, G.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Danese, S. Vedolizumab for the treatment of Crohn’s disease. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeire, S.; Loftus, E.V.; Colombel, J.-F.; Feagan, B.G.; Sandborn, W.J.; Sands, B.E.; Danese, S.; D’Haens, G.R.; Kaser, A.; Panaccione, R.; et al. Long-term Efficacy of Vedolizumab for Crohn’s Disease. J. Crohn’s Coliti 2016, 11, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalla Costa, G.; Martinelli, V.; Moiola, L.; Sangalli, F.; Colombo, B.; Finardi, A.; Cinque, P.; Kolb, E.; Haghikia, A.; Gold, R.; et al. Serum neurofilaments increase at progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy onset in natalizumab-treated multiple sclerosis patients. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 85, 606–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
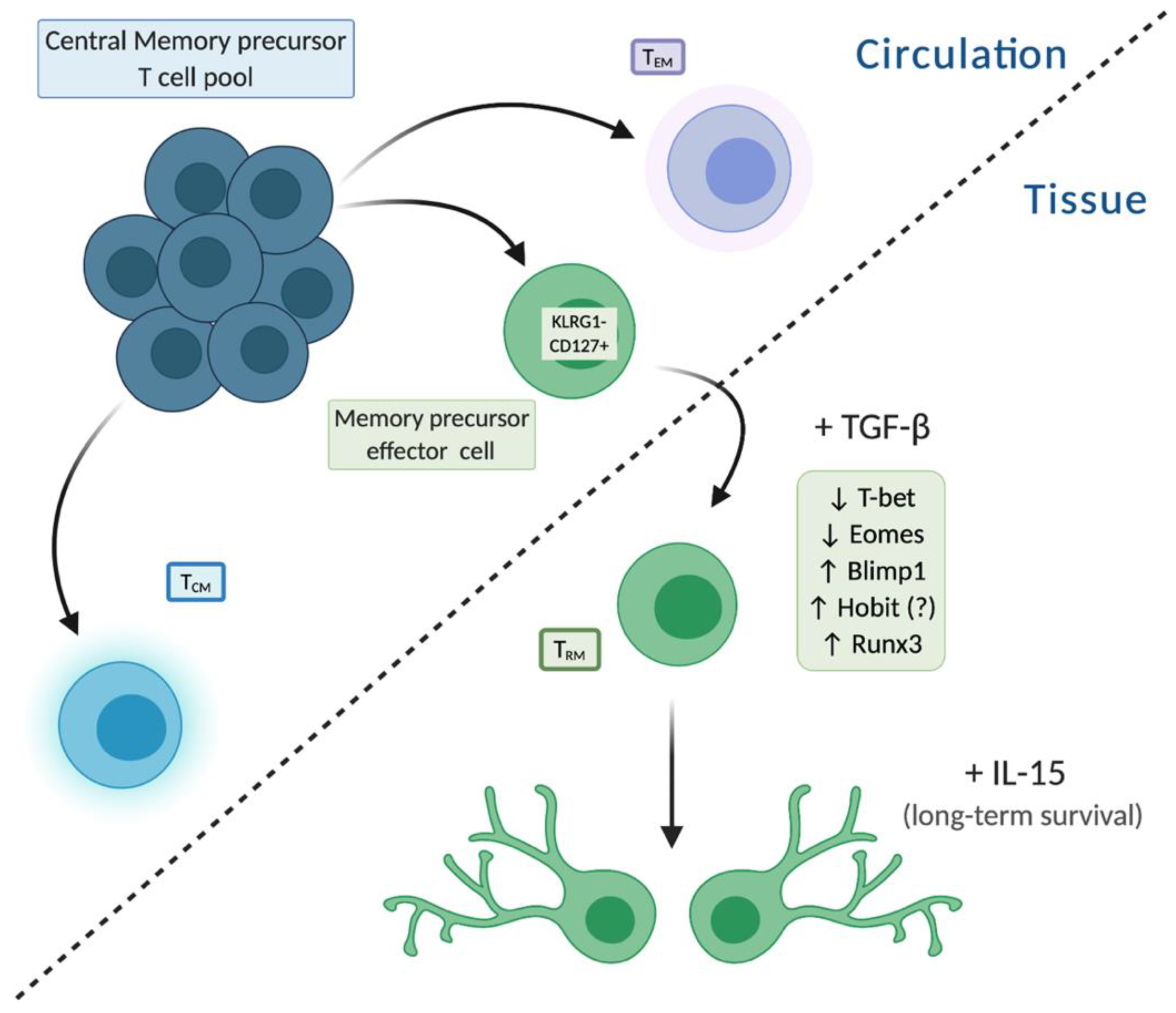

| Transcript | Gene | Up- (↑) or Down (↓) Regulated | Expression-Human vs. Mouse | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface markers | ||||
| CD69 | Cd69 | ↑ | Both | [3,9,10] |
| CD103 | Itgae | ↑ | Both | [3,9,10] |
| CD49a | Itga1 | ↑ | Both | [3,9,10] |
| CD101 | Cd101 | ↑ | Both | [3] |
| CD62L | Sell | ↓ | Human | [3,9,10] |
| CXCR6 | Cxcr6 | ↑ | Both | [3,10] |
| CX3CR1 | Cx3cr1 | ↑ | Human | [3] |
| CCR7 | Ccr7 | ↓ | Human | [3,9] |
| PD-1 | Pdcd1 | ↑ | Human | [3,10] |
| S1PR1 | S1pr1 | ↓ | Both | [3,9,10] |
| Intracellular proteins | ||||
| DUSP6 | Dusp6 | ↑ | Both | [3,10] |
| KLF2 | Klf2 | ↓ | Both | [3,10] |
| KLF3 | Kl3 | ↓ | Human | [3,10] |
| Eomes | Eomes | ↓ | Human | [9,11] |
| T-bet | Tbx21 | ↓ * | Human | [11] |
| Blimp1 | Prdm1 | ↑ | Mouse | [12] |
| Hobit | Zfp683 | ↑ | Mouse | [12] |
| Runx3 | Runx3 | ↑ | Mouse & Human TIL ** | [13] |
| Id3 | Id3 | ↑ | Mouse | [14] |
| Nr4a1 | Nr4a1 | ↑ | Human | [9] |
| Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. | Tissue Enrichment | Specific Markers/Factors/Genes Associated | Characteristics of Enriched TRM Population | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Psoriasis | Skin | IL-17 | CD49a+ CD103+ CD8+ | [40] |
| CD103+ CD8+ | [41] | |||
| Vitiligo | Skin | IFN-γ, CXCR3 | CCR7− CD69+ CD103+ CD8+ | [42] |
| CD69+ CD103+ CD8+ | [43] | |||
| Atopic dermatitis | Skin | CCL1, IL13, IL26, ANXA1, ANXA2 | CD69+ CD103+ CD8+ | [44] |
| Alopecia areata | Skin | ITGAE | CD103+ CD8+ | [45] |
| CD69+ or CD103+ (CD4 or CD8 not specified) | [46] | |||
| Inflammatory bowel disease | Gut | CD161, β7 | CCR7− CD69+ CD4+ | [47] |
| CXCR6, CD101, KLF2lo | CD69+ CD103+ (CD4 or CD8 not specified) | [24] | ||
| Type 1 diabetes | Pancreas | IFN-γ, IL-18, IL-22 | CD69+ CD103+ CD8+ | [30] |
| Sjögren’s syndrome | Nerve/Connective tissue | IFN-γ | CD69+ CD103+ CD8+ | [31] |
| Lupus nephritis | Connective tissue | JAK/STAT, TNF-α, IFN-γ | CD103+ CD8+ | [32] |
| Multiple sclerosis | Central nervous system | CD69− | CD103+ CD8+ | [34] |
| CXCR6, Ki67 | PD-1+ CD44+ CD49a+ CD69+ CD103+/– CD8+ | [33] | ||
| Juvenile idiopathic arthritis | Joint | ITGAE, ITGA, CXCR6 | PD-1+ CD69+ CD8+ | [35] |
| DUSP6, ITGAE, CXCR6, PD-1 | PD-1+ CD8+, PD-1+ CD39+/CD161+ CD4+ and PD-1+ CD39−/CD161− CD4+ | [36] | ||
| Psoriatic arthritis | Joint/Skin | PD-1, ITGAE, ZNF683, CXCR6, β7, CLA, CD49a | IL-17A+ CD69+ and/or CD103+ CD8+ | [37] |
| Ankylosing spondylitis | Connective tissue/Joint | β7, CD29, IL-10, CXCR6 | CD49a+ CD103+ CD8+ T cells | [38] |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Connective tissue/Joint | PD-1, Blimp, 1, CD44 | PD-1+ CXCR5− CD69+ CD4+ | [48] |
| CXCR6, CD49a, CD101, PD-1, Ki-67 | CD69+ CD103+/− CD8+ | [39] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samat, A.A.K.; van der Geest, J.; Vastert, S.J.; van Loosdregt, J.; van Wijk, F. Tissue–Resident Memory T Cells in Chronic Inflammation—Local Cells with Systemic Effects? Cells 2021, 10, 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020409
Samat AAK, van der Geest J, Vastert SJ, van Loosdregt J, van Wijk F. Tissue–Resident Memory T Cells in Chronic Inflammation—Local Cells with Systemic Effects? Cells. 2021; 10(2):409. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020409
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamat, Anoushka Ashok Kumar, Jolijn van der Geest, Sebastiaan J. Vastert, Jorg van Loosdregt, and Femke van Wijk. 2021. "Tissue–Resident Memory T Cells in Chronic Inflammation—Local Cells with Systemic Effects?" Cells 10, no. 2: 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020409
APA StyleSamat, A. A. K., van der Geest, J., Vastert, S. J., van Loosdregt, J., & van Wijk, F. (2021). Tissue–Resident Memory T Cells in Chronic Inflammation—Local Cells with Systemic Effects? Cells, 10(2), 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020409





