Apoptosis of Hepatocytes: Relevance for HIV-Infected Patients under Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. HIV: Infection and Therapy
1.2. HIV Pathogenesis and the Liver
1.3. Apoptosis and the Liver
2. HIV, HIV-Encoded Proteins, and Apoptosis
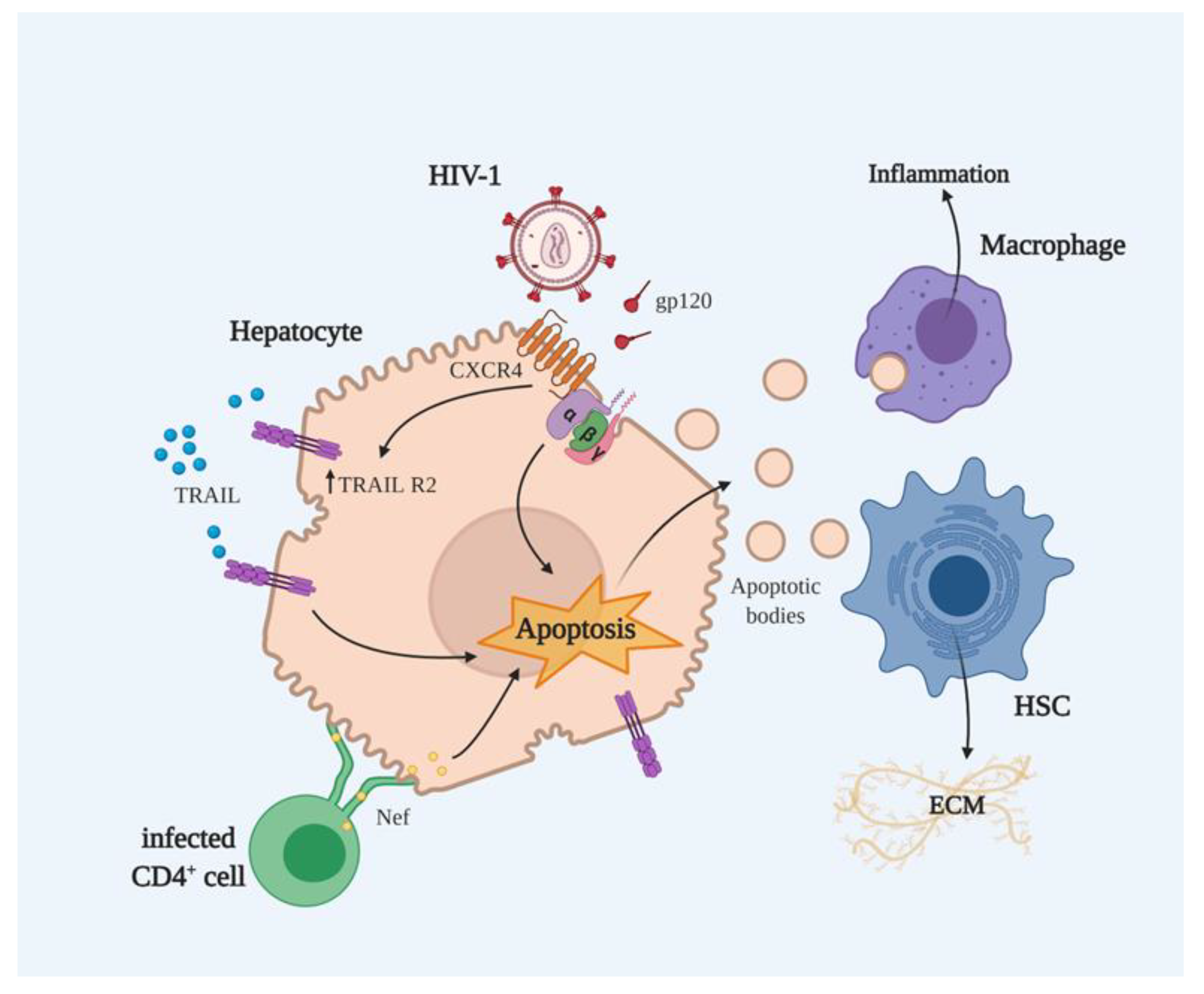
2.1. HIV as an Inducer of Hepatocyte Apoptosis
2.2. HIV Proteins and Apoptosis
2.2.1. gp120-Mediated Apoptosis
2.2.2. Nef-Mediated Apoptosis
3. cART-Related Apoptosis in Hepatocytes
3.1. NRTIs
3.2. NNRTIs
3.3. PIs
3.4. INSTIs
3.5. Entry and Fusion Inhibitors
3.6. Attachment and Post-Attachment Inhibitors
4. Metabolic Alterations and Hepatic Cell Death
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deeks, S.G.; Overbaugh, J.; Phillips, A.; Buchbinder, S. HIV infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015, 1, 15035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervo, A.; Shengir, M.; Patel, K.; Sebastiani, G. NASH in HIV. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2020, 17, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNAIDS. UNAIDS Data 2020. Available online: https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/2020_aids-data-book_en.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2020).
- Pierson, T.C.; Zhou, Y.; Kieffer, T.L.; Ruff, C.T.; Buck, C.; Siliciano, R.F. Molecular Characterization of Preintegration Latency in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Infection. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 8518–8531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maartens, G.; Celum, C.; Lewin, S.R. HIV infection: epidemiology, pathogenesis, treatment, and prevention. Lancet 2014, 384, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.C.; Kim, P.S. HIV Entry and Its Inhibition. Cell 1998, 93, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Kim, B.O.; Gattone, V.H.; Li, J.; Nath, A.; Blum, J.; He, J.J. CD4-Independent Infection of Astrocytes by Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1: Requirement for the Human Mannose Receptor. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 4120–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, P.; Chen, B.K.; Mosoian, A.; Hays, T.; Ross, M.J.; Klotman, P.E.; Klotman, M.E. Virological Synapses Allow HIV-1 Uptake and Gene Expression in Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clinical Info HIV gov. What to Start: Initial Combination Regimens for the Antiretroviral-Naive Patient. Available online: https://clinicalinfo.hiv.gov/en/guidelines/adult-and-adolescent-arv/what-start-initial-combination-regimens-antiretroviral-naive?view=brief (accessed on 19 October 2020).
- De Clercq, E. Anti-HIV drugs: 25 compounds approved within 25 years after the discovery of HIV. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 33, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalapila, A.G.; Marrazzo, J. Antiretroviral Therapy for Prevention of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection. Med Clin. North Am. 2016, 100, 927–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, K.E. HIV and Liver Disease; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-1-4419-1712-6. [Google Scholar]
- Núñez, M. Clinical syndromes and consequences of antiretroviral-related hepatotoxicity. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.; Núñez, M. Liver Toxicity of Antiretroviral Drugs. Semin. Liver Dis. 2012, 32, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallapiazza, M.; Amorosa, V.K.; Localio, R.; Kostman, J.R.; Re, V.L. Prevalence and risk factors for significant liver fibrosis among HIV-monoinfected patients. BMC Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blackard, J.T.; Welge, J.A.; Taylor, L.E.; Mayer, K.H.; Klein, R.S.; Celentano, D.D.; Jamieson, D.J.; Gardner, L.; Sherman, K.E. HIV Mono-infection Is Associated With FIB-4 - A Noninvasive Index of Liver Fibrosis - in Women. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Division of AIDS (DAIDS) Table for Grading the Severity of Adult and Pediatric Adverse Events. Available online: https://rsc.niaid.nih.gov/sites/default/files/daidsgradingcorrectedv21.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2020).
- Sulkowski, M.S.; Thomas, D.L.; Mehta, S.H.; Chaisson, R.E.; Moore, R.D. Hepatotoxicity associated with nevirapine or efavirenz-containing antiretroviral therapy: Role of hepatitis C and B infections. Hepatology 2002, 35, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, L.V.; Gilson, I.; Jacobson, J.; Affi, A.; Puetz, T.R.; Dindzans, V.J. Antiretroviral hepatotoxicity in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 15, 1627–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Osikowicz, M.; Sebastiani, G. Clinical significance of elevated liver transaminases in HIV-infected patients. AIDS 2019, 33, 1267–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mata-Marín, J.A.; Gaytán-Martínez, J.; Grados-Chavarría, B.H.; Fuentes-Allen, J.L.; Arroyo-Anduiza, C.I.; Alfaro-Mejía, A. Correlation between HIV viral load and aminotransferases as liver damage markers in HIV infected naive patients: A concordance cross-sectional study. Virol. J. 2009, 6, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sterling, R.K.; Chiu, S.; Snider, K.; Nixon, D. The Prevalence and Risk Factors for Abnormal Liver Enzymes in HIV-Positive Patients without Hepatitis B or C Coinfections. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2008, 53, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovari, H.; Weber, R. Influence of antiretroviral therapy on liver disease. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2011, 6, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.C.; Ryom, L.; Weber, R.; Morlat, P.P.; Pradier, C.; Reiss, P.; Kowalska, J.J.; De Wit, S.; Law, M.M.; Sadr, W.W.; et al. Trends in underlying causes of death in people with HIV from 1999 to 2011 (D:A:D): A multicohort collaboration. Lancet 2014, 384, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Böttcher, J.P.; Knolle, P.A.; Stabenow, D. Mechanisms Balancing Tolerance and Immunity in the Liver. Dig. Dis. 2011, 29, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Housset, C.; Lamas, E.; Courgnaud, V.; Boucher, O.; Girard, P.-M.; Marche, C.; Brechot, C. Presence of HIV-1 in human parenchymal and non-parenchymal liver cells in vivo. J. Hepatol. 1993, 19, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Dieterich, D.; Thomas, P.A.; Huang, Y.; Mirabile, M.; Ho, D.D. Identification and quantitation of HIV-1 in the liver of patients with AIDS. AIDS 1992, 6, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, M.; Dagur, R.S.; Makarov, E.; Poluektova, L.I.; Kidambi, S.; Osna, N.A. Matrix stiffness regulate apoptotic cell death in HIV-HCV co-infected hepatocytes: Importance for liver fibrosis progression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 500, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, M.; New-Aaron, M.; Dagur, R.S.; Makarov, E.; Wang, W.; Kharbanda, K.K.; Kidambi, S.; Poluektova, L.Y.; Osna, N.A. Alcohol Metabolism Potentiates HIV-Induced Hepatotoxicity: Contribution to End-Stage Liver Disease. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fromentin, R.; Tardif, M.R.; Tremblay, M.J. Inefficient fusion due to a lack of attachment receptor/co-receptor restricts productive human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in human hepatoma Huh7.5 cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 92, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Usami, O.; Suzuki, Y.; Ling, H.; Shimizu, N.; Hoshino, H.; Zhuang, M.; Ashino, Y.; Gu, H.; Hattori, T. Characterization of a CD4-independent clinical HIV-1 that can efficiently infect human hepatocytes through chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4. AIDS 2008, 22, 1749–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.Z.; E Friedman-Kien, A.; Huang, Y.X.; Li, X.L.; Mirabile, M.; Moudgil, T.; Zucker-Franklin, D.; Ho, D.D. CD4-independent, productive human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of hepatoma cell lines in vitro. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 2553–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sherman, K.E.; Peters, M.G.; Thomas, D.L. HIV and the Liver. Top Antivir. Med. 2019, 27, 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Balagopal, A.; Ray, S.C.; De Oca, R.M.; Sutcliffe, C.G.; Vivekanandan, P.; Higgins, Y.; Mehta, S.H.; Moore, R.D.; Sulkowski, M.S.; Thomas, D.L.; et al. Kupffer cells are depleted with HIV immunodeficiency and partially recovered with antiretroviral immune reconstitution. AIDS 2009, 23, 2397–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuyama, A.C.; Hong, F.; Saiman, Y.; Wang, C.; Ozkok, D.; Mosoian, A.; Chen, P.; Chen, B.K.; Klotman, M.E.; Bansal, M.B. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1 infects human hepatic stellate cells and promotes collagen I and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression: Implications for the pathogenesis of HIV/hepatitis C virus-induced liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2010, 52, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Budihardjo, I.; Oliver, H.; Lutter, M.; Luo, X.; Wang, X. Biochemical Pathways of Caspase Activation During Apoptosis. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1999, 15, 269–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evan, G. A Matter of Life and Cell Death. Science 1998, 281, 1317–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A Review of Programmed Cell Death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alimonti, J.B.; Ball, T.B.; Fowke, K.R. Mechanisms of CD4+ T lymphocyte cell death in human immunodeficiency virus infection and AIDS. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 1649–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vīksna, L.; Ekšteina, I.; Madelāne, M.; Zeltiņa, I.; Krūmiņa, A.; Koļesovs, A.; Simanis, R. Markers of liver fibrosis and apoptosis in patients with HIV mono-infection and HIV/HCV co-infection. HIV AIDS Rev. 2019, 18, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías, J.; Japón, M.A.; Sáez, C.; Palacios, R.B.; Mira, J.A.; García-García, J.A.; Merchante, N.; Vergara, S.; Lozano, F.; Gómez-Mateos, J.; et al. Increased Hepatocyte Fas Expression and Apoptosis in HIV and Hepatitis C Virus Coinfection. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 192, 1566–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iser, D.M.; Avihingsanon, A.; Wisedopas, N.; Thompson, A.J.; Boyd, A.; Matthews, G.V.; A Locarnini, S.; Slavin, J.; Desmond, P.V.; Lewin, S.R. Increased intrahepatic apoptosis but reduced immune activation in HIV-HBV co-infected patients with advanced immunosuppression. AIDS 2011, 25, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagur, R.S.; Wang, W.; Cheng, Y.; Makarov, E.; Ganesan, M.; Suemizu, H.; Gebhart, C.L.; Gorantla, S.; Osna, N.; Poluektova, L.Y. Human hepatocyte depletion in the presence of HIV-1 infection in dual reconstituted humanized mice. Biol. Open 2018, 7, bio029785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehta, S.H.; Astemborski, J.; Sterling, T.R.; Thomas, D.L.; Vlahov, D. Serum Albumin as a Prognostic Indicator for HIV Disease Progression. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2006, 22, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, P.K.; Gendelman, H.E.; Roy, U.; Balkundi, S.; Alnouti, Y.; Mosley, R.L.; Gelbard, H.A.; McMillan, J.; Gorantla, S.; Poluektova, L.Y. Long-acting nanoformulated antiretroviral therapy elicits potent antiretroviral and neuroprotective responses in HIV-1-infected humanized mice. AIDS 2012, 26, 2135–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selliah, N.; Finkel, T.H. Biochemical mechanisms of HIV induced T cell apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2001, 8, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahr, B.; Robert-Hebmann, V.; Devaux, C.; Biard-Piechaczyk, M. Apoptosis of uninfected cells induced by HIV envelope glycoproteins. Retrovirology 2004, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hellerstein, M.K.; Hanley, M.B.; Cesar, D.V.; Siler, S.Q.; A Papageorgopoulos, C.; Wieder, E.D.; E Schmidt, D.; Hoh, R.; A Neese, R.; MacAllan, D.C.; et al. Directly measured kinetics of circulating T lymphocytes in normal and HIV-1-infected humans. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badley, A.D.; Pilon, A.A.; Landay, A.; Lynch, D.H. Mechanisms of HIV-associated lymphocyte apoptosis. Blood 2000, 96, 2951–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumlová, M.; Křížová, I.; Keprová, A.; Hadravová, R.; Doležal, M.; Strohalmová, K.; Pichová, I.; Hájek, M.; Ruml, T. HIV-1 protease-induced apoptosis. Retrovirology 2014, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyaizu, N.; McCloskey, T.W.; Than, S.; Hu, R.; Kalyanaraman, V.S.; Pahwa, S. Cross-linking of CD4 molecules upregulates Fas antigen expression in lymphocytes by inducing interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha secretion. Blood 1994, 84, 2622–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hashimoto, F.; Oyaizu, N.; Kalyanaraman, V.S.; Pahwa, S. Modulation of Bcl-2 protein by CD4 cross-linking: A possible mechanism for lymphocyte apoptosis in human immunodeficiency virus infection and for rescue of apoptosis by interleu-kin-2. Blood 1997, 90, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicala, C.; Arthos, J.; Rubbert, A.; Selig, S.; Wildt, K.; Cohen, O.J.; Fauci, A.S. HIV-1 envelope induces activation of caspase-3 and cleavage of focal adhesion kinase in primary human CD4+ T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 1178–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Somma, F.; Tuosto, L.; Montani, M.S.G.; Di Somma, M.M.; Cundari, E.; Piccolella, E. Engagement of CD4 Before TCR Triggering Regulates Both Bax- and Fas (CD95)-Mediated Apoptosis. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 5078–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfettini, J.-L.; Castedo, M.; Roumier, T.; Andreau, K.; Nardacci, R.; Piacentini, M.; Kroemer, G. Mechanisms of apoptosis induction by the HIV-1 envelope. Cell Death Differ. 2005, 12, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vlahakis, S.R.; Villasis-Keever, A.; Gomez, T.S.; Bren, G.D.; Paya, C.V. Human Immunodeficiency Virus–Induced Apoptosis of Human Hepatocytes via CXCR4. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 188, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, C.K.; Suwansrinon, K.; Bren, G.D.; Badley, A.D.; Rizza, S.A. HIV Induces TRAIL Sensitivity in Hepatocytes. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jang, J.Y.; Shao, R.-X.; Lin, W.; Weinberg, E.; Chung, W.J.; Tsai, W.L.; Zhao, H.; Goto, K.; Zhang, L.; Mendez-Navarro, J.; et al. HIV infection increases HCV-induced hepatocyte apoptosis. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osna, N.A.; New-Aaron, M.; Ganesan, M.; Dagur, R.S.; Poluektova, L.Y. HIV-infected apoptotic hepatocytes program mac-rophages for inflammasome development: role of alcohol. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 248.12. [Google Scholar]
- Zauli, G.; Gibellini, D.; Secchiero, P.; Dutartre; Olive, D.; Capitani, S.; Collette, Y. Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Nef Protein Sensitizes CD4+ T Lymphoid Cells to Apoptosis via Functional Upregulation of the CD95/CD95 Ligand Pathway. J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 1999, 93, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Santini, P.A.; Sullivan, J.S.; He, B.; Shan, M.; Ball, S.C.; Dyer, W.B.; Ketas, T.J.; Chadburn, A.; Cohen-Gould, L.; et al. HIV-1 evades virus-specific IgG2 and IgA responses by targeting systemic and intestinal B cells via long-range intercellular conduits. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 1008–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nobile, C.; Rudnicka, D.; Hasan, M.; Aulner, N.; Porrot, F.; Machu, C.; Renaud, O.; PrévostM, -C.; Hivroz, C.; Schwartz, O.; et al. HIV-1 Nef Inhibits Ruffles, Induces Filopodia, and Modulates Migration of Infected Lymphocytes. J. Virol. 2009, 84, 2282–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, I.-W.; Fan, Y.; Luo, X.; Ryou, M.-G.; Liu, J.; Green, L.; He, J.J. HIV-1 Nef Is Transferred from Expressing T Cells to Hepatocytic Cells through Conduits and Enhances HCV Replication. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.A.; Abbas, W.; Varin, A.; Kumar, A.; Di Martino, V.; Dichamp, I.; Herbein, G. HIV-1 Nef Interacts with HCV Core, Recruits TRAF2, TRAF5 and TRAF6, and Stimulates HIV-1 Replication in Macrophages. J. Innate Immun. 2013, 5, 639–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillaye, J.N.; Marakalala, M.J.; Khumalo, N.; Spearman, W.; Ndlovu, H. Mechanistic insights into antiretroviral drug-induced liver injury. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2020, 8, e00598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, W.; Dalakas, M.C. Mitochondrial toxicity of antiviral drugs. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maagaard, A.; Kvale, D. Long term adverse effects related to nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors: Clinical impact of mitochondrial toxicity. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 41, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.-L.; Beland, F.A. Long-Term Exposure to Zidovudine Delays Cell Cycle Progression, Induces Apoptosis, and Decreases Telomerase Activity in Human Hepatocytes. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 111, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Q.; Beland, F.A.; Chang, C.-W.; Fang, J.-L. XPC is essential for nucleotide excision repair of zidovudine-induced DNA damage in human hepatoma cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 251, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Walker, U.; Setzer, B.; Venhoff, N. Increased long-term mitochondrial toxicity in combinations of nucleoside analogue reverse-transcriptase inhibitors. AIDS 2002, 16, 2165–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stankov, M.V.; Panayotova-Dimitrova, D.; Leverkus, M.; Vondran, F.W.; Bauerfeind, R.; Binz, A.; Behrens, G.M. Autophagy inhibition due to thymidine analogues as novel mechanism leading to hepatocyte dysfunction and lipid accumulation. AIDS 2012, 26, 1995–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinsztein, D.C.; Mariño, G.; Kroemer, G. Autophagy and Aging. Cell 2011, 146, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adebiyi, O.O.; Adebiyi, O.A.; Owira, P.M.O. Naringin Reverses Hepatocyte Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress Associated with HIV-1 Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors-Induced Metabolic Complications. Nutrients 2015, 7, 10352–10368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desai, V.G.; Lee, T.; Moland, C.L.; Branham, W.S.; Mittelstaedt, R.A.; Lewis, S.M.; Leakey, J.E.A.; Fuscoe, J.C. Evaluation of Hepatic Mitochondria and Hematological Parameters in Zidovudine-TreatedB6C3F1Mice. AIDS Res. Treat. 2012, 2012, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venhoff, N.; Setzer, B.; Melkaoui, K.; A Walker, U. Mitochondrial toxicity of tenofovir, emtricitabine and abacavir alone and in combination with additional nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Antivir. Ther. 2007, 12, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Namasivayam, V.; Vanangamudi, M.; Kramer, V.G.; Kurup, S.; Zhan, P.; Liu, X.; Kongsted, J.; Byrareddy, S.N. The Journey of HIV-1 Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTIs) from Lab to Clinic. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 4851–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.-L.; Beland, F.A. Differential responses of human hepatocytes to the non-nucleoside HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitor nevirapine. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 38, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- A Erickson, D.; Mather, G.; Trager, W.F.; Levy, R.H.; Keirns, J.J. Characterization of the in vitro biotransformation of the HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitor nevirapine by human hepatic cytochromes P-450. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1999, 27, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.M.; Li, Y.; Novalen, M.; Hayes, M.A.; Uetrecht, J. Bioactivation of Nevirapine to a Reactive Quinone Methide: Implications for Liver Injury. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 1708–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, C.J.S.; Seneviratne, H.K.; Bumpus, N.N. Twelfth-Position Deuteration of Nevirapine Reduces 12-Hydroxy-Nevirapine Formation and Nevirapine-Induced Hepatocyte Death. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 6561–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terelius, Y.; Figler, R.A.; Marukian, S.; Collado, M.S.; Lawson, M.J.; Mackey, A.J.; Manka, D.; Qualls, C.W.; Blackman, B.R.; Wamhoff, B.R.; et al. Transcriptional profiling suggests that Nevirapine and Ritonavir cause drug induced liver injury through distinct mechanisms in primary human hepatocytes. Chem. Interactions 2016, 255, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Apostolova, N.; Blas-Garcia, A.; Galindo, M.J.; Esplugues, J.V. Efavirenz: What is known about the cellular mechanisms responsible for its adverse effects. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 812, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolova, N.; Sucerquia, L.J.G.; Moran, A.; Alvarez, A.; García, A.B.; Esplugues, J.V. Enhanced oxidative stress and increased mitochondrial mass during Efavirenz-induced apoptosis in human hepatic cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 2069–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Apostolova, N.; Gomez-Sucerquia, L.J.; Gortat, A.; Blas-Garcia, A.; Esplugues, J.V. Compromising mitochondrial function with the antiretroviral drug efavirenz induces cell survival-promoting autophagy. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blas-García, A.; Apostolova, N.; Ballesteros, D.; Monleon, D.; Morales, J.M.; Rocha, M.; Víctor, V.M.; Esplugues, J.V. Inhibition of mitochondrial function by efavirenz increases lipid content in hepatic cells. Hepatology 2010, 52, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolova, N.; Gomez-Sucerquia, L.J.; Alegre, F.; Funes, H.A.; Víctor, V.M.; Barrachina, M.D.; Blas-García, A.; Esplugues, J.V. ER stress in human hepatic cells treated with Efavirenz: Mitochondria again. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhi, H.; Kaufman, R.J. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 795–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bumpus, N.N. Efavirenz and 8-hydroxyefavirenz induce cell death via a JNK- and BimEL-dependent mechanism in primary human hepatocytes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 257, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heck, C.J.S.; Hamlin, A.N.; Bumpus, N.N. Efavirenz and Efavirenz-like Compounds Activate Human, Murine, and Macaque Hepatic IRE1α-XBP1. Mol. Pharmacol. 2019, 95, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Imaizumi, N.; Lee, K.K.; Zhang, C.; Boelsterli, U.A. Mechanisms of cell death pathway activation following drug-induced inhibition of mitochondrial complex I. Redox Biol. 2015, 4, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blas-García, A.; Polo, M.; Alegre, F.; Funes, H.A.; Martinez, E.; Apostolova, N.; Esplugues, J.V. Lack of mitochondrial toxicity of darunavir, raltegravir and rilpivirine in neurons and hepatocytes: A comparison with efavirenz. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 2995–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruno, R.; Sacchi, P.; Maiocchi, L.; Patruno, S.; Filice, G. Hepatotoxicity and antiretroviral therapy with protease inhibitors: A review. Dig. Liver Dis. 2006, 38, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dara, L.; Ji, C.; Kaplowitz, N. The contribution of endoplasmic reticulum stress to liver diseases. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1752–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaplowitz, N.; Than, T.A.; Shinohara, M.; Ji, C. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Liver Injury. Semin. Liver Dis. 2007, 27, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taura, M.; Kariya, R.; Kudo, E.; Goto, H.; Iwawaki, T.; Amano, M.; Suico, M.A.; Kai, H.; Mitsuya, H.; Okada, S. Comparative analysis of ER stress response into HIV protease inhibitors: Lopinavir but not darunavir induces potent ER stress response via ROS/JNK pathway. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, X.; Gurley, E.C.; Kennedy, E.; Hylemon, P.B.; Pandak, W.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Zhou, H. The role of CCAAT enhancer-binding protein homologous protein in human immunodeficiency virus protease-inhibitor-induced hepatic lipotoxicity in mice. Hepatology 2012, 57, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuang, C.-C.; Wang, Y.; Hu, P.-C.; Gao, F.-F.; Bu, L.; Wen, X.-M.; Xiang, Q.-M.; Song, H.; Li, Q.; Wei, L.; et al. Ritonavir-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Ultrastructural Changes of Hepatocytes. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2014, 38, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganta, K.K.; Chaubey, B. Endoplasmic reticulum stress leads to mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in cells treated with anti-HIV protease inhibitor ritonavir. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2019, 35, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alauddin; Chaturvedi, S.; Malik, M.Y.; Azmi, L.; Shukla, I.; Naseem, Z.; Rao, C.; Agarwal, N.K. Formononetin and biochanin A protects against ritonavir induced hepatotoxicity via modulation of NfκB/pAkt signaling molecules. Life Sci. 2018, 213, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Niu, L.; Zhu, X.; Hao, J.; Wang, P.; Wang, H. Antitumour effects of a protease inhibitor, nelfinavir, in hepatocellular carcinoma cancer cells. J. Chemother. 2012, 24, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, U.; Lau, B.; Lazo, M.; McCaul, M.E.; Hutton, H.E.; Sulkowski, M.S.; Moore, R.D.; Chander, G. Interaction Between Alcohol Consumption Patterns, Antiretroviral Therapy Type, and Liver Fibrosis in Persons Living with HIV. AIDS Patient Care STDs 2016, 30, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahler, C.W.; Liu, T.; Cioe, P.A.; Bryant, V.; Pinkston, M.M.; Kojic, E.M.; Onen, N.; Baker, J.V.; Hammer, J.; Brooks, J.T.; et al. Direct and Indirect Effects of Heavy Alcohol Use on Clinical Outcomes in a Longitudinal Study of HIV Patients on ART. AIDS Behav. 2016, 21, 1825–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.; Shinohara, M.; Feng, M.; Lau, M.Y.; Ji, C. Human immunodeficiency virus protease inhibitors modulate Ca2+ homeostasis and potentiate alcoholic stress and injury in mice and primary mouse and human hepatocytes. Hepatology 2012, 56, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Han, H.; Lau, M.Y.; Lee, H.; MacVeigh-Aloni, M.; Ji, C. Effects of combined alcohol and anti-HIV drugs on cellular stress responses in primary hepatocytes and hepatic stellate and kupffer cells. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2015, 39, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Gurley, E.C.; Jarujaron, S.; Ding, H.; Fang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Pandak, W.M.; Hylemon, P.B. HIV protease inhibitors activate the unfolded protein response and disrupt lipid metabolism in primary hepatocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2006, 291, G1071–G1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, J.G.; Tarze, A.; Moffat, T.C.; Lebras, M.; Deniaud, A.; Brenner, C.; Bren, G.D.; Morin, M.Y.; Phenix, B.N.; Dong, L.; et al. Inhibition of adenine nucleotide translocator pore function and protection against apoptosis in vivo by an HIV protease inhibitor. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1828–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, R.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gurley, E.C.; Studer, E.J.; Wang, X.; Hylemon, P.B.; Pandak, W.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Zhang, L.; et al. Prevention of HIV Protease Inhibitor-Induced Dysregulation of Hepatic Lipid Metabolism by Raltegravir via Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Signaling Pathways. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 334, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matthews, T.J.; Salgo, M.; E Greenberg, M.; Chung, J.; Demasi, R.; Bolognesi, D.P. Enfuvirtide: the first therapy to inhibit the entry of HIV-1 into host CD4 lymphocytes. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzarin, A.; Clotet, B.; A Cooper, D.; Reynes, J.; Arastéh, K.; Nelson, M.; Katlama, C.; Stellbrink, H.-J.; Delfraissy, J.-F.; A Lange, J.M.; et al. Efficacy of Enfuvirtide in Patients Infected with Drug-Resistant HIV-1 in Europe and Australia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2186–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsamis, F.; Gavrilov, S.; Kajumo, F.; Seibert, C.; Kuhmann, S.; Ketas, T.; Trkola, A.; Palani, A.; Clader, J.W.; Tagat, J.R.; et al. Analysis of the Mechanism by Which the Small-Molecule CCR5 Antagonists SCH-351125 and SCH-350581 Inhibit Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Entry. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 5201–5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghebremedhin, B. Maraviroc in Antiretroviral-Naïve HIV-1 Patients. Infect. Dis. Res. Treat. 2012, 5, IDRT.S7597–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ochoa-Callejero, L.; Pérez-Martínez, L.; Rubio-Mediavilla, S.; Oteo, J.A.; Martínez, A.; Blanco, J.R. Maraviroc, a CCR5 Antagonist, Prevents Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in a Mouse Model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seval, N.; Frank, C.; Kozal, M. Fostemsavir for the treatment of HIV. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2021, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacob, S.A.; Iacob, D.G. Ibalizumab Targeting CD4 Receptors, An Emerging Molecule in HIV Therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine, M.; Serfaty, L.; Capeau, J. From nonalcoholic fatty liver to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and cirrhosis in HIV-infected patients. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 25, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, A.D.; Balasubramanyam, A. Dysregulation of glucose metabolism in HIV patients: epidemiology, mechanisms, and management. Endocrine 2012, 41, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frühbeck, G.; Méndez-Giménez, L.; Fernández-Formoso, J.-A.; Fernández, S.; Rodríguez, A. Regulation of adipocyte lipolysis. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2014, 27, 63–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, B.; Cai, G.H.; Yang, H.; Wang, S.P.; Mitchell, G.A.; Wu, J.W. Adipose tissue deficiency of hormone-sensitive lipase causes fatty liver in mice. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1007110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willig, A.L.; Overton, E.T. Metabolic Complications and Glucose Metabolism in HIV Infection: A Review of the Evidence. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2016, 13, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miserez, A.R.; Muller, P.Y.; Spaniol, V. Indinavir inhibits sterol-regulatory element-binding protein-1c-dependent lipoprotein lipase and fatty acid synthase gene activations. AIDS 2002, 16, 1587–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hresko, R.C.; Hruz, P.W. HIV Protease Inhibitors Act as Competitive Inhibitors of the Cytoplasmic Glucose Binding Site of GLUTs with Differing Affinities for GLUT1 and GLUT4. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gardner, K.; Hall, P.A.; Chinnery, P.F.; Payne, B.A.I. HIV Treatment and Associated Mitochondrial Pathology. Toxicol. Pathol. 2014, 42, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Drug Class | Mechanism of Action | Drugs |
|---|---|---|
| Fusion Inhibitors | Interfere with the entry of HIV into cells by inhibiting fusion of viral and cellular membranes | Enfuvirtide |
| Entry Inhibitors | CCR5 antagonist, prevents the interaction with HIV gp120 and prevents the virus from entering the cell | Maraviroc |
| Attachment Inhibitors | Bind to the gp120 protein on the outer surface of HIV, preventing HIV from entering CD4 cells | Fostemsavir |
| Post-Attachment Inhibitors | Inhibit the conformational changes in the CD4/gp120 complex that allow binding to CXCR4, thus inhibiting HIV fusion and entry | Ibalizumab |
| Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors Nucleoside analogues (NRTIs) Nonnucleoside analogues (NNRTIs) | Inhibit the HIV replication by binding directly to the reverse transcriptase (RT) enzyme | Zidovudine Lamivudine Emtricitabine Abacavir Tenofovir Nevirapine Efavirenz Doravirine Etravirine Rilpivirine |
| Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitors (INSTIs) | Block the strand transfer step of viral DNA integration into the host genome | Raltegravir Elvitegravir Dolutegravir Bictegravir |
| Protease Inhibitors (PIs) | Inhibit HIV protease, thereby preventing cleavage of viral proteins and the subsequent generation of individual viral proteins | Ritonavir Saquinavir Lopinavir Atazanavir Fosamprenavir Tipranavir Darunavir |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gruevska, A.; Moragrega, Á.B.; Cossarizza, A.; Esplugues, J.V.; Blas-García, A.; Apostolova, N. Apoptosis of Hepatocytes: Relevance for HIV-Infected Patients under Treatment. Cells 2021, 10, 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020410
Gruevska A, Moragrega ÁB, Cossarizza A, Esplugues JV, Blas-García A, Apostolova N. Apoptosis of Hepatocytes: Relevance for HIV-Infected Patients under Treatment. Cells. 2021; 10(2):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020410
Chicago/Turabian StyleGruevska, Aleksandra, Ángela B. Moragrega, Andrea Cossarizza, Juan V. Esplugues, Ana Blas-García, and Nadezda Apostolova. 2021. "Apoptosis of Hepatocytes: Relevance for HIV-Infected Patients under Treatment" Cells 10, no. 2: 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020410
APA StyleGruevska, A., Moragrega, Á. B., Cossarizza, A., Esplugues, J. V., Blas-García, A., & Apostolova, N. (2021). Apoptosis of Hepatocytes: Relevance for HIV-Infected Patients under Treatment. Cells, 10(2), 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020410







