Mechanisms of Neurodegeneration in Various Forms of Parkinsonism—Similarities and Differences
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Location | Type of Pathology | Macroscopic Localisation | Microscopic Changes | Localisation | Spreading |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parkinson Disease | |||||
| CNS | LB and LN | SN, LC | Neuronal loss of neurons | Dopaminergic neurons of SN; neuronal loss of noradrenergic neurons in the LC, neuronal cell bodies—synapses, axons and astroglial cells [16,17,18] | Early: dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus and the anterior olfactory nucleus Medium: LC and SN Later: basal forebrain, amygdala, medial temporal lobe structures, and cortical areas |
| PNS | α-synuclein aggregates [19], phosphorylated α-synuclein inclusions [20] | Enteric, pelvic and cardiac ganglia [21,22,23,24,25,26,27] skin [28], pharyngeal motor and sensory branch of the vagus nerve, glossopharyngeal nerve, internal superior laryngeal nerve [29,30] | Axonal degeneration after traumatic nerve injury [31] small fibre neuropathy [32] | The spinous cell layer, pilosebaceous unit and eccrine glands [28], sympathetic ganglia and intermediolateral column of the medulla [27], distal cardiac sympathetic axons [25] gastrointestinal tract: 90% as neurites, 10% soma [33,34,35] | Peripheral-to-central spreading pattern of in sympathetic nervous system [36], rostro-caudal gradient in gastro-intestinal tract [37], spreading from vagal terminals of the gut to dorsal motor nucleus of vagus nerve [38,39] |
| Dementia with Lewy Bodies | |||||
| CNS | LB, LN, α-synuclein aggregates in oligodendrocytes [40,41] | Diffuse neocortical, limbic, brainstem, amygdala, olfactory bulb, SN [42] | Neuronal loss of neurons | Diffuse neocortical, limbic, brainstem, amygdala, olfactory bulb, SN [42] | Due to Braak stages |
| Progressive Supranuclear Palsy | |||||
| CNS | Accumulation of tau inclusions in neurons | Marked atrophy of the midbrain and superior cerebellar peduncle along with mild frontal cortical atrophy; STN smaller than normal | Inclusion bodies in astrocytes and in oligodendroglia | GP, STN, midbrain tectum, periaqueductal gray, LC, cerebellar dentate nucleus, corpus striatum, ventrolateral thalamus, red nucleus, pontine and medullary tegmentum, pontine base, inferior olivary nucleus | Due to Braak stages |
| Corticobasal Degeneration | |||||
| CNS | Deposition of tau in neurons and glia [10,11,12,13,43] | Disproportionately more in forebrain structures, than in hindbrain | Pretangles, NFT, neuropil threads, astrocytic plaques, oligodendroglial coiled bodies [10,43] | Forebrain structures > hindbrain | Due to Braak stages |
| Multiple System Atrophy | |||||
| CNS | α-synuclein inclusions [44] | Striatonigral degeneration and olivoponto-cerebellar atrophy | Accumulation of α-synuclein within GCIs, neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions [45,46] | Oligodendroglial cells, neurons [47,48] | |
| PNS | Filamentous α-synuclein aggregates [49] | Multidomain autonomic nervous system failure [50,51,52], reduction of sensory afferent and postganglionic sympathetic fibres [53] | Cholinergic, catecholaminergic, noradrenergic, serotonergic preganglionic, postganglionic neurons [54,55,56,57], postganglionic fibres [58] | Cholinergic neurons in dorsal motor nucleus and ventrolateral nucleus ambiguous of the vagus [55], catecholaminergic neurons of ventrolateral medulla [54], medullary arcuate nucleus [59], noradrenergic LC [56], medullary serotonergic groups, ventrolateral medulla [60,61], ventromedullary NK-1-receptor-immunoreactive neurons [62], A5 noradrenergic neurons [57], caudal raphe nucleus with sparing of rostral raphe neurons [63,64], Edinger-Westphal nucleus and posterior hypothalamus [65], suprachiasmatic nucleus [66], pontomedullary reticular formation [46,67] sympathetic preganglionic neurons in intermediolateral column of thoracolumbar spinal cord [56,68], postganglionic sudomotor nerves [69], cardiac postganglionic sympathetic fibres [58], Schwann cells’ cytoplasm [49] | |
2. Genetics of Parkinsonism
3. Protein Pathology in Various Forms of Parkinsonism
3.1. Synucleinopathies
Propagation of PD-Related Synucleinopathy
3.2. Mechanisms of α-Synuclein Toxicity in PD
3.2.1. Microglial Activation
3.2.2. Synaptic Dysfunction
3.2.3. Mitochondrial Dysfunction
3.2.4. DNA Repair Damage
3.2.5. Protein Clearance Pathology
3.2.6. Synucleinopathy in MSA and DLB
3.3. Tauopathies
4. Mitochondrial Dysfunction
5. Various Neurodegenerative Factors
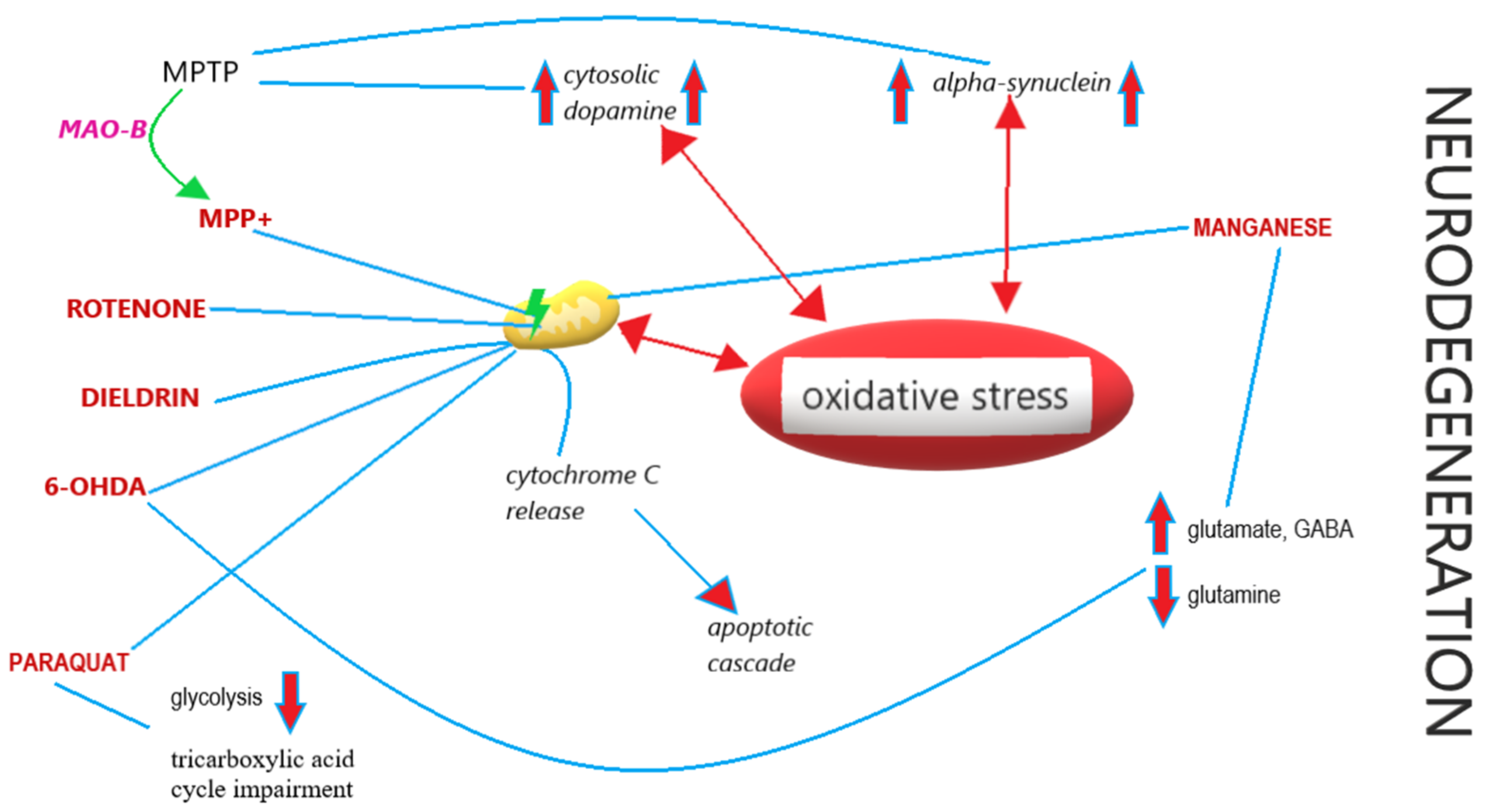
5.1. Oxidative Stress
5.2. Neuroinflammation as a Factor in the Neurodegeneration of Parkinsonisms
5.3. Toxic Neurodegeneration
5.4. Traumatic Brain Injury as a Neurodegenerative Factor
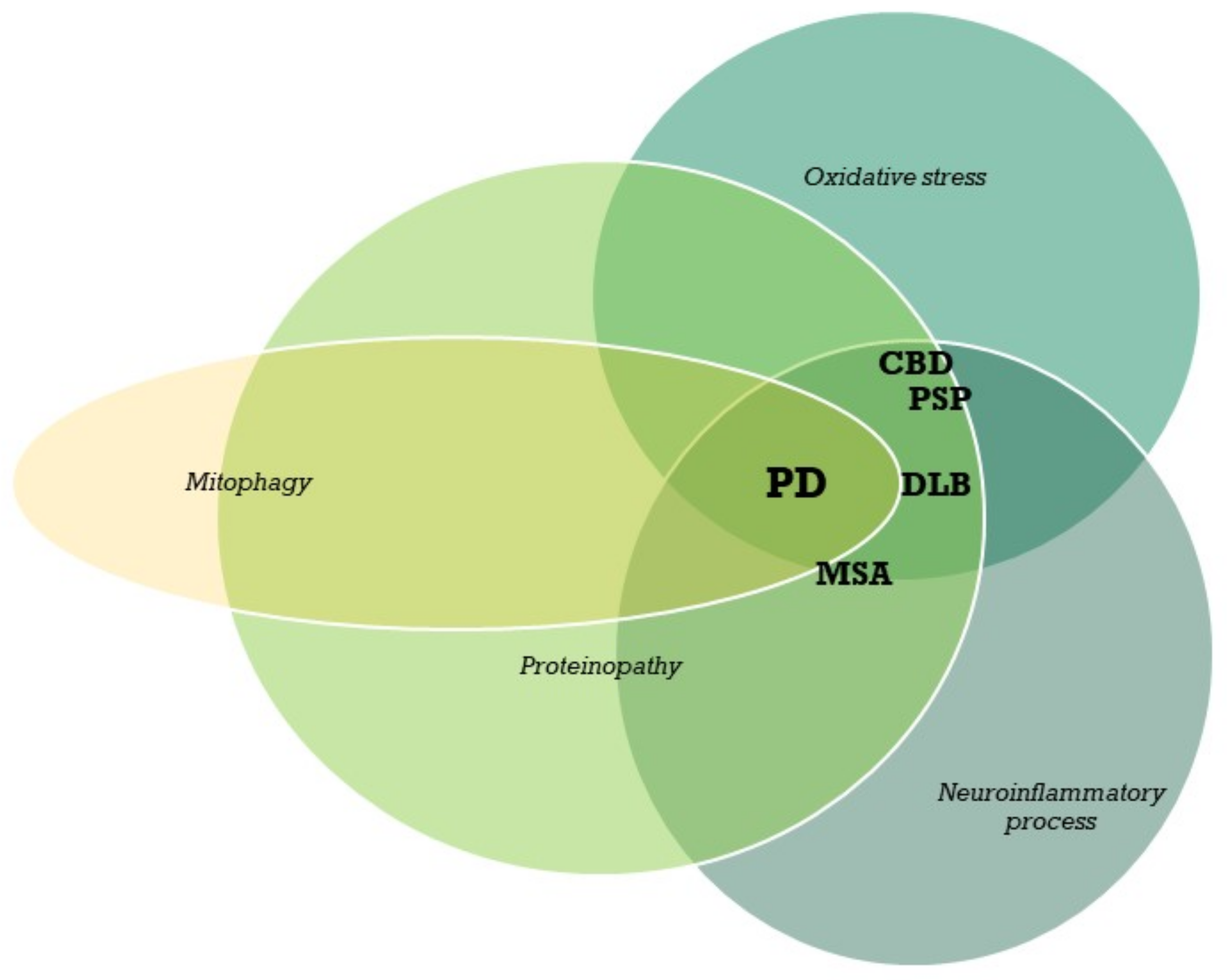
6. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.W.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilman, S.; Wenning, G.K.; A Low, P.; Brooks, D.J.; Mathias, C.J.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Wood, N.W.; Colosimo, C.; Durr, A.; Fowler, C.J.; et al. Second consensus statement on the diagnosis of multiple system atrophy. Neurology 2008, 71, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höglinger, G.U.; Respondek, G.; Stamelou, M.; Kurz, C.; Josephs, K.A.; Lang, A.E.; Mollenhauer, B.; Müller, U.; Nilsson, C.; Whitwell, J.L.; et al. Clinical diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy: The movement disorder society criteria. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; Bak, T.H.; Bhatia, K.P.; Borroni, B.; Boxer, A.L.; Dickson, D.W.; Grossman, M.; Hallett, M.; et al. Criteria for the diagnosis of corticobasal degeneration. Neurology 2013, 80, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Komatsu, J.; Nakamura, K.; Sakai, K.; Samuraki-Yokohama, M.; Nakajima, K.; Yoshita, M. Diagnostic Criteria for Dementia with Lewy Bodies: Updates and Future Directions. J. Mov. Disord. 2020, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussaud, S.; Jones, D.R.; Moussaud-Lamodière, E.L.; Delenclos, M.; A Ross, O.; McLean, P.J. Alpha-synuclein and tau: Teammates in neurodegeneration? Mol. Neurodegener. 2014, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, L.V.; E Lang, A. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2015, 386, 896–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomperts, S.N. Lewy body dementias: Dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson disease dementia. Continuum 2016, 22, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jellinger, K.A. Dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson’s disease-dementia: Current concepts and controversies. J. Neural Transm. 2018, 125, 615–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentino, R.R.; Koga, S.; Walton, R.L.; Soto-Beasley, A.I.; Kouri, N.; DeTure, M.A.; Murray, M.E.; Johnson, P.W.; Petersen, R.C.; Boeve, B.F.; et al. MAPT subhaplotypes in corticobasal degeneration: Assessing associations with disease risk, severity of tau pathology, and clinical features. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouri, N.; Whitwell, J.L.; Josephs, K.A.; Rademakers, R.; Dickson, D.W. Corticobasal degeneration: A pathologically distinct 4R tauopathy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 7, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alster, P.; Krzyżanowska, E.; Koziorowski, D.; Szlufik, S.; Różański, D.; Noskowska, J.; Mianowicz, J.; Michno, A.; Królicki, L.; Friedman, A. Difficulties in the diagnosis of four repeats (4R) tauopathic parkinsonian syndromes. Neurol. i Neurochir. Polska 2018, 52, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutschländer, A.B.; Ross, O.A.; Dickson, D.W.; Wszolek, Z.K. Atypical parkinsonian syndromes: A general neurologist’s perspective. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanciulli, A.; Wenning, G.K. Multiple-System Atrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickson, D.W. Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonism: Neuropathology. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a009258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Sastre, M.; Del Tredici, K. Development of α-synuclein immunoreactive astrocytes in the forebrain parallels stages of intraneuronal pathology in sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 114, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.J.C.; Halliday, G.M.; Holton, J.L.; Lashley, T.; O’Sullivan, S.S.; McCann, H.; Lees, A.J.; Ozawa, T.; Williams, D.R.; Lockhart, P.J.; et al. Degeneration in Different Parkinsonian Syndromes Relates to Astrocyte Type and Astrocyte Protein Expression. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 68, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Ang, L.-C.; Williams, B.; Furukawa, Y.; Fitzmaurice, P.; Guttman, M.; Boileau, I.; Hornykiewicz, O.; Kish, S.J. Low levels of astroglial markers in Parkinson’s disease: Relationship to α-synuclein accumulation. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 82, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Gibbons, C.H.; Lafo, J.; Freeman, R. α-Synuclein in cutaneous autonomic nerves. Neurology 2013, 81, 1604–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doppler, K.; Ebert, S.; Üçeyler, N.; Trenkwalder, C.; Ebentheuer, J.; Volkmann, J.; Sommer, C. Cutaneous neuropathy in Parkinson’s disease: A window into brain pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 128, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Ghebremedhin, E.; Rüb, U.; Bratzke, H.; Del Tredici, K. Stages in the development of Parkinson’s disease-related pathology. Cell Tissue Res. 2004, 318, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comi, C.; Magistrelli, L.; Oggioni, G.; Carecchio, M.; Fleetwood, T.; Cantello, R.; Mancini, F.; Antonini, A. Peripheral nervous system involvement in Parkinson’s disease: Evidence and controversies. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2014, 20, 1329–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Takahashi, H. Neuropathology of autonomic nervous system in Parkinson’s disease. Eur. Neurol. 1997, 38, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cersosimo, M.G.; Benarroch, E.E. Pathological correlates of gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Disease 2012, 46, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orimo, S.; Uchihara, T.; Nakamura, A.; Mori, F.; Kakita, A.; Wakabayashi, K.; Takahashi, H. Axonal α-synuclein aggregates herald centripetal degeneration of cardiac sympathetic nerve in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2008, 131, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tysnes, O.-B.; Muller, B.; Larsen, J.P. Are dysautonomic and sensory symptoms present in early Parkinson’s disease? Acta Neurol. Scand. 2010, 122, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, T.G.; Adler, C.H.; Sue, L.I.; Vedders, L.; Lue, L.; White, C.L., III; Akiyama, H.; Caviness, J.N.; Shill, H.A.; Sabbagh, M.N. Multi-organ distribution of phosphorylated α-synuclein histopathology in subjects with Lewy body disorders. Acta Neuro-Pathologica 2010, 119, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Leyva, I.; Calderón-Garcidueñas, A.L.; Jiménez-Capdeville, M.E.; Rentería-Palomo, A.A.; Hernandez-Rodriguez, H.G.; Valdés-Rodríguez, R.; Fuentes-Ahumada, C.; Torres-Álvarez, B.; Sepúlveda-Saavedra, J.; Soto-Domínguez, A. α-Synuclein inclusions in the skin of Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonism. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2014, 1, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, L.; Sobotka, S.; Chen, J.; Su, H.; Sanders, I.; Adler, C.H.; Shill, H.A.; Caviness, J.N.; Samanta, J.E.; Beach, T.G.; et al. Alpha-Synuclein Pathology and Axonal Degeneration of the Peripheral Motor Nerves Innervating Pharyngeal Muscles in Parkinson Disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 72, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Sobotka, S.; Chen, J.; Su, H.; Sanders, I.; Nyirenda, T.; Adler, C.H.; Shill, H.A.; Caviness, J.N.; Samanta, J.E.; et al. Parkinson Disease Affects Peripheral Sensory Nerves in the Pharynx. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 72, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebert, H.; Kahle, P.J.; Kramer, M.L.; Isik, T.; Schlüter, O.M.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J.; Brück, W. Over-expression of alpha-synuclein in the nervous system enhances axonal degeneration after peripheral nerve lesion in a transgenic mouse strain. J. Neurochem. 2010, 114, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donadio, V.; Incensi, A.; Leta, V.; Giannoccaro, M.P.; Scaglione, C.; Martinelli, P.; Capellari, S.; Avoni, P.; Baruzzi, A.; Liguori, R. Skin nerve α-synuclein deposits: A biomarker for idiopathic Parkinson disease. Neurology 2014, 82, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; de Vos, R.A.; Bohl, J.; Del Tredici, K. Gastric α-synuclein immunoreactive inclusions in Meissner’s and Auerbach’s plexuses in cases staged for Parkinson’s disease-related brain pathology. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 396, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, J.G. Causes and Consequences of Degeneration of the Dorsal Motor Nucleus of the Vagus Nerve in Parkinson’s Disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Takahashi, H.; Takeda, S.; Ohama, E.; Ikuta, F. Parkinson’s disease: The presence of Lewy bodies in Auerbach’s and Meissner’s plexuses. Acta Neuropathol. 1988, 76, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghammer, P.; Knudsen, K.; Brooks, D.J. Imaging Systemic Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2016, 16, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, D.A.; Bieger, D.; De Vente, J.; Steinbusch, H.W. Chapter 5 Vagal efferent projections: Viscerotopy, neurochemistry and effects of vagotomy. Prog. Brain Res. 1996, 107, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, C.H.; Shephard, B.C.; E Daniel, S. Olfactory dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1997, 62, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, E.; Horváth-Puhó, E.; Thomsen, R.W.; Djurhuus, J.C.; Pedersen, L.; Borghammer, P.; Sørensen, H.T. Vagotomy and subsequent risk of Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2015, 78, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, S.; Li, F.; Zhao, N.; Roemer, S.F.; Ferman, T.J.; Wernick, A.I.; Walton, R.L.; Faroqi, A.H.; Graff-Radford, N.R.; Cheshire, W.P.; et al. Clinicopathologic and genetic features of multiple system atrophy with Lewy body disease. Brain Pathol. 2020, 30, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Hayashi, S.; Yoshimoto, M.; Kudo, H.; Takahashi, H. NACP/α-synuclein-positive filamentous inclusions in astrocytes and oligodendrocytes of Parkinson’s disease brains. Acta Neuropathol. 2000, 99, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeith, I.G.; Boeve, B.F.; Dickson, D.W.; Halliday, G.; Taylor, J.-P.; Weintraub, D.; Aarsland, D.; Galvin, J.; Attems, J.; Ballard, C.G.; et al. Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: Fourth consensus report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology 2017, 89, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickson, D.W.; Bergeron, C.; Chin, S.S.; Duyckaerts, C.; Horoupian, D.; Ikeda, K.; Jellinger, K.; Lantos, P.L.; Lippa, C.F.; Mirra, S.S.; et al. Office of Rare Diseases Neuropathologic Criteria for Corticobasal Degeneration. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2002, 61, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cykowski, M.D.; Coon, E.A.; Powell, S.Z.; Jenkins, S.M.; Benarroch, E.E.; Low, P.A.; Schmeichel, A.M.; Parisi, J.E. Expanding the spectrum of neuronal pathology in multiple system atrophy. Brain 2015, 138, 2293–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jellinger, K.A. Neuropathology and pathophysiology of multiple system atrophy. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2012, 38, 379–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantos, P.L.; I Papp, M. Cellular pathology of multiple system atrophy: A review. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1994, 57, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overk, C.; Rockenstein, E.; Valera, E.; Stefanova, N.; Wenning, G.; Masliah, E. Multiple system atrophy: Experimental models and reality. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 135, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JellingerPeter, K.A.; Lantos, P.L. Papp-Lantos inclusions and the pathogenesis of multiple system atrophy: An update. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, F.; Inenaga, C.; Yoshimoto, M.; Umezu, H.; Takahashi, H.; Wakabayashi, K.; Tanaka, R. α-Synuclein immunoreactivity in normal and neoplastic Schwann cells. Acta Neuropathol. 2002, 103, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jellinger, K.A. Neuropathology of multiple system atrophy: New thoughts about pathogenesis. Mov. Disord. 2014, 29, 1720–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozawa, T. Morphological substrate of autonomic failure and neurohormonal dysfunction in multiple system atrophy: Impact on determining phenotype spectrum. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 114, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iodice, V.; Lipp, A.; Ahlskog, J.E.; Sandroni, P.; Fealey, R.D.; E Parisi, J.; Matsumoto, J.Y.; E Benarroch, E.; Kimpinski, K.; Singer, W.; et al. Autopsy confirmed multiple system atrophy cases: Mayo experience and role of autonomic function tests. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2012, 83, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, T.; Tsukagoshi, H.; Oda, M.; Miyamoto, K.; Tanabe, H. Changes of unmyelinated nerve fibers in sural nerve in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Acta Neuropathol. 1996, 91, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benarroch, E.E.; Smithson, I.L.; Low, P.A.; Parisi, J.E. Depletion of catecholaminergic neurons of the rostral ventrolateral medulla in multiple systems atrophy with autonomic failure. Ann. Neurol. 1998, 43, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benarroch, E.E.; Schmeichel, A.M.; Sandroni, P.; Low, P.A.; Parisi, J.E. Involvement of vagal autonomic nuclei in multiple system atrophy and Lewy body disease. Neurology 2006, 66, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenning, G.K.; Tison, F.; Ben Shlomo, Y.; Daniel, S.E.; Quinn, N.P. Multiple system atrophy: A review of 203 pathologically proven cases. Mov. Disord. 1997, 12, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benarroch, E.E.; Schmeichel, A.M.; Low, P.A.; Sandroni, P.; Parisi, J.E. Loss of A5 noradrenergic neurons in multiple system atrophy. Acta Neuropathol. 2008, 115, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orimo, S.; Kanazawa, T.; Nakamura, A.; Uchihara, T.; Mori, F.; Kakita, A.; Wakabayashi, K.; Takahashi, H. Degeneration of cardiac sympathetic nerve can occur in multiple system atrophy. Acta Neuropathol. 2006, 113, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nodaa, K.; Katayama, S.; Watanabe, C.; Yamamura, Y.; Nakamura, S. Decrease of neurons in the medullary arcuate nucleus of multiple system atrophy: Quantitative comparison with Parkinson’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 1997, 151, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, M.; Onodera, O.; Tada, M.; Ozawa, T.; Piao, Y.-S.; Kakita, A.; Takahashi, H.; Nishizawa, M. Early Development of Autonomic Dysfunction May Predict Poor Prognosis in Patients With Multiple System Atrophy. Arch. Neurol. 2007, 64, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benarroch, E.E.; Schmeichel, A.M.; Low, P.A.; Parisi, J.E. Involvement of medullary serotonergic groups in multiple system atrophy. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 55, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benarroch, E.E.; Schmeichel, A.M.; Parisi, J.E. Preservation of branchimotor neurons of the nucleus ambiguus in multiple system atrophy. Neurology 2003, 60, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benarroch, E.E.; Schmeichel, A.M.; Parisi, J.E. Depletion of mesopontine cholinergic and sparing of raphe neurons in multiple system atrophy. Neurology 2002, 59, 944–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benarroch, E.E.; Schmeichel, A.M.; Low, P.A.; Parisi, J.E. Depletion of putative chemosensitive respiratory neurons in the ventral medullary surface in multiple system atrophy. Brain 2007, 130, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shy, G.M. A Neurological Syndrome Associated with Orthostatic Hypotension. AMA Arch. Neurol. 1960, 2, 511–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benarroch, E.E.; Schmeichel, A.M.; Sandroni, P.; Low, P.A.; Parisi, J.E. Differential involvement of hypothalamic vasopressin neurons in multiple system atrophy. Brain 2006, 129, 2688–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wenning, G.K.; Tison, F.; Elliott, L.; Quinn, N.P.; Daniel, S.E. Olivopontocerebellar pathology in multiple system atrophy. Mov. Disord. 1996, 11, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, F.; Vincent, D.; Hauw, J.J. Quantitative study of lateral horn cells in 15 cases of multiple system atrophy. Acta Neuropathol. 1988, 75, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provitera, V.; Nolano, M.; Caporaso, G.; Stancanelli, A.; Manganelli, F.; Iodice, R.; Selim, M.M.; De Rosa, A.; Lanzillo, B.; Pellecchia, M.T.; et al. Postganglionic sudomotor denervation in patients with multiple system atrophy. Neurology 2014, 82, 2223–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balestrino, R.; Schapira, A.H. Parkinson disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polymeropoulos, M.H. Mutation in the -Synuclein Gene Identified in Families with Parkinson’s Disease. Science 1997, 276, 2045–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singleton, A.B. α-Synuclein Locus Triplication Causes Parkinson’s Disease. Science 2003, 302, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalls, M.A.; Blauwendraat, C.; Vallerga, C.L.; Heilbron, K.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; Chang, D.; Tan, M.X.; A Kia, D.; Noyce, A.J.; Xue, A.; et al. Identification of novel risk loci, causal insights, and heritable risk for Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 1091–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soreq, L.; Salomonis, N.; Bronstein, M.; Greenberg, D.S.; Israel, Z.; Bergman, H.; Soreq, H. Small RNA sequencing-microarray analyses in Parkinson leukocytes reveal deep brain stimulation-induced splicing changes that classify brain region tran-scriptomes. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2013, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, S.R.; Dionísio, P.A.; Guedes, L.C.; Gonçalves, N.; Coelho, M.; Rosa, M.M.; Amaral, J.D.; Ferreira, J.J.; Rodrigues, C.M.P. Circulating Inflammatory miRNAs Associated with Parkinson’s Disease Pathophysiology. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orme, T.; Guerreiro, R.; Bras, J. The Genetics of Dementia with Lewy Bodies: Current Understanding and Future Directions. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2018, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snowden, J.S.; Rollinson, S.; Lafon, C.; Harris, J.; Thompson, J.; Richardson, A.M.; Jones, M.; Gerhard, A.; Neary, D.; Mann, D.M.A.; et al. Psychosis, C9ORF72 and dementia with Lewy bodies: Table 1. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2012, 83, 1031–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, J.T.; Arthur, K.C.; Dawson, T.M.; Rosenthal, L.S.; Pantelyat, A.; Albert, M.; Hillis, A.E.; Crain, B.; Pletnikova, O.; Troncoso, J.C.; et al. C9orf72 Hexanucleotide Repeat Analysis in Cases with Pathologically Confirmed Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Neurodegener. Dis. 2016, 16, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kun-Rodrigues, C.; Ross, O.A.; Orme, T.; Shepherd, C.; Parkkinen, L.; Darwent, L.; Hernandez, D.; Ansorge, O.; Clark, L.N.; Honig, L.S.; et al. Analysis of C9orf72 repeat expansions in a large international cohort of dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 49, 214.e13–214.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keogh, M.J.; Wei, W.; Wilson, I.; Coxhead, J.; Ryan, S.; Rollinson, S.; Griffin, H.; Kurzawa-Akanbi, M.; Santibanez-Koref, M.; Talbot, K.; et al. Genetic compendium of 1511 human brains available through the UK Medical Research Council Brain Banks Network Resource. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walton, R.L.; Soto-Ortolaza, A.I.; Murray, M.E.; Lorenzo-Betancor, O.; Ogaki, K.; Heckman, M.G.; Rayaprolu, S.; Rademakers, R.; Ertekin-Taner, N.; Uitti, R.J.; et al. TREM2 p.R47H substitution is not associated with dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurol. Genet. 2016, 2, e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerreiro, R.; A Ross, O.; Kun-Rodrigues, C.; Hernandez, D.G.; Orme, T.; Eicher, J.D.; E Shepherd, C.; Parkkinen, L.; Darwent, L.; Heckman, M.G.; et al. Investigating the genetic architecture of dementia with Lewy bodies: A two-stage genome-wide association study. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilarino-Guell, C.; Soto-Ortolaza, A.I.; Rajput, A.; Mash, D.C.; Papapetropoulos, S.; Pahwa, R.; Lyons, K.E.; Uitti, R.J.; Wszolek, Z.K.; Dickson, D.W.; et al. MAPT H1 haplotype is a risk factor for essential tremor and multiple system atrophy. Neurology 2011, 76, 670–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, S.W.; Houlden, H.; Schulte, C.; Sharma, M.; Li, A.; Berg, D.; Melchers, A.; Paudel, R.; Bs, J.R.G.; Simon-Sanchez, J.; et al. SNCAvariants are associated with increased risk for multiple system atrophy. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 65, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Multiple-System Atrophy Research Collaboration Mutations in COQ2 in Familial and Sporadic Multiple-System Atrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 233–244. [CrossRef]
- Sailer, A.; Scholz, S.W.; Nalls, M.A.; Schulte, C.; Federoff, M.; Price, T.R.; Lees, A.; Ross, O.A.; Dickson, D.W.; Mok, K.; et al. A genome-wide association study in multiple system atrophy. Neurology 2016, 87, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shaikh, R.H.; Wernick, A.I.; Strongosky, A.J.; Soto-Beasley, A.I.; Van Gerpen, J.A.; Cheshire, W.P.; Uitti, R.J.; Ross, O.A.; Wszolek, Z.K. Spinocerebellar ataxia type 6 family with phenotypic overlap with Multiple System Atrophy. Neurol. Neurochir. Polska 2020, 54, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernick, A.I.; Walton, R.L.; Soto-Beasley, A.I.; Koga, S.; Heckman, M.G.; Valentino, R.R.; Milanowski, L.M.; Hoffman-Zacharska, D.; Koziorowski, D.; Hassan, A.; et al. Frequency of spinocerebellar ataxia mutations in patients with multiple system atrophy. Clin. Auton. Res. 2021, 31, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Jiao, B.; Shen, L. Genetics of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy: A Review. J. Park. Dis. 2021, 11, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.; Litvan, I.; Houlden, H.; Adamson, J.; Dickson, D.; Perez-Tur, J.; Hardy, J.; Lynch, T.; Bigio, E.; Hutton, M. Association of an Extended Haplotype in the Tau Gene with Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1999, 8, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höglinger, G.U.; PSP Genetics Study Group; Melhem, N.M.; Dickson, D.W.; Sleiman, P.M.A.; Wang, L.-S.; Klei, L.; Rademakers, R.; De Silva, R.; Litvan, I.; et al. Identification of common variants influencing risk of the tauopathy progressive supranuclear palsy. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouri, N.; Ross, O.A.; Dombroski, B.; Younkin, C.S.; Serie, D.J.; Soto-Ortolaza, A.; Baker, M.; Finch, N.C.A.; Yoon, H.; Kim, J.; et al. Genome-wide association study of corticobasal degeneration identifies risk variants shared with progressive supranuclear palsy. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, T.; Ross, O.A.; Teive, H.A.; Sławek, J.; Dickson, D.W.; Wszolek, Z.K. DCTN1 -related neurodegeneration: Perry syndrome and beyond. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2017, 41, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavich, L.; Jäkälä, P.; Tanila, H. Abnormal compartmentalization of norepinephrine in mouse dentate gyrus in α-synuclein knockout and A30P transgenic mice. J. Neurochem. 2006, 99, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavich, L.; Tanila, H.; Vepsäläinen, S.; Jäkälä, P. Role of α-synuclein in presynaptic dopamine recruitment. J. Neuro-Sci. 2004, 24, 11165–11170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J. The synaptic pathology of α-synuclein aggregation in dementia with Lewy bodies, Parkinson’s disease and Parkinson’s disease dementia. Acta Neurol. 2010, 120, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, L.V.; Kalia, S.K.; McLean, P.J.; Lozano, A.M.; Lang, A.E. α-Synuclein oligomers and clinical implications for Parkinson disease. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 73, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.-K.; Choi, M.-G.; Kim, J.-Y.; Yang, Y.; Lai, Y.; Kweon, D.-H.; Lee, N.K.; Shin, Y.-K. Large α-synuclein oligomers inhibit neuronal SNARE-mediated vesicle docking. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4087–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulds, P.; Mann, D.M.; Allsop, D. Phosphorylated α-synuclein as a potential biomarker for Parkinson’s disease and related disorders. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2012, 12, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K.; Rüb, U.; De Vos, R.A.; Steur, E.N.J.; Braak, E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Par-kinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, C.H.; Del Tredici, K.; Braak, H. Parkinson’s disease: A dual-hit hypothesis. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2007, 33, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanouilidou, E.; Minakaki, G.; Keramioti, M.V.; Xylaki, M.; Balafas, E.; Chrysanthou-Piterou, M.; Kloukina, I.; Vekrellis, K. GABA transmission via ATP-dependent K+channels regulates α-synuclein secretion in mouse striatum. Brain 2016, 139, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-J.; Cho, E.-D.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, J.-H.; Cho, S.-G.; Lee, S.-J. Autophagic failure promotes the exocytosis and intercellular transfer of α-synuclein. Exp. Mol. Med. 2013, 45, e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Erviti, L.; Seow, Y.; Schapira, A.H.; Gardiner, C.; Sargent, I.L.; Wood, M.J.; Cooper, J.M. Lysosomal dysfunction increases exosome-mediated alpha-synuclein release and transmission. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 42, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brundin, P.; Ma, J.; Kordower, J.H. How strong is the evidence that Parkinson’s disease is a prion disorder? Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2016, 29, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda-Suzukake, M.; Nonaka, T.; Hosokawa, M.; Oikawa, T.; Arai, T.; Akiyama, H.; Mann, D.M.A.; Hasegawa, M. Prion-like spreading of pathological α-synuclein in brain. Brain 2013, 136, 1128–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olanow, C.W.; Goetz, C.G.; Kordower, J.H.; Stoessl, A.J.; Sossi, V.; Brin, M.F.; Shannon, K.M.; Nauert, G.M.; Perl, D.P.; Godbold, J. A double-blind controlled trial of bilateral fetal nigral transplantation in Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 54, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Suk, J.-E.; Lee, K.-W.; Park, S.-H.; Blumbergs, P.C.; Gai, W.-P.; Lee, S.-J. Transmission of Synucleinopathies in the Enteric Nervous System of A53T Alpha-Synuclein Transgenic Mice. Exp. Neurobiol. 2011, 20, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Fang, F.; Pedersen, N.L.; Tillander, A.; Ludvigsson, J.F.; Ekbom, A.; Svenningsson, P.; Chen, H.; Wirdefeldt, K. Vagotomy and Parkinson disease. Neurology 2017, 88, 1996–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmeier, D.J.; Obeso, J.A.; Halliday, G.M. Parkinson’s disease is not simply a prion disorder. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 9799–9807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Tsujimura, A.; Tanaka, M. Expression of α-synuclein is regulated in a neuronal cell type-dependent manner. Anat. Sci. Int. 2018, 94, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamgüney, G.; Korczyn, A.D. A critical review of the prion hypothesis of human synucleinopathies. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 373, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, J.A.; Ivanova, M.I.; Sawaya, M.R.; Cascio, D.; Reyes, F.E.; Shi, D.; Sangwan, S.; Guenther, E.L.; Johnson, L.M.; Zhang, M.; et al. Structure of the toxic core of α-synuclein from invisible crystals. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 525, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, E.M.; De Miranda, B.; Sanders, L.H. Alpha-synuclein: Pathology, mitochondrial dysfunction and neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 109, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, I.; Zhang, Y.; Seegobin, S.P.; Pruvost, M.; Wang, Q.; Purtell, K.; Zhang, B.; Yue, Z. Microglia clear neuron-released α-synuclein via selective autophagy and prevent neurodegeneration. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; He, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, H.; Wang, D.; Li, L.; Hui, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, N. Alpha-synuclein induces microglial migration via PKM2-dependent glycolysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.-S.; Heng, Y.; Yuan, Y.-H.; Chen, N.-H. Pathological α-synuclein exacerbates the progression of Parkinson’s disease through microglial activation. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 265, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grozdanov, V.; Bousset, L.; Hoffmeister, M.; Bliederhaeuser, C.; Meier, C.; Madiona, K.; Pieri, L.; Kiechle, M.; McLean, P.J.; Kassubek, J.; et al. Increased Immune Activation by Pathologic α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 86, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Zhang, G.; Han, C.; Ma, K.; Guo, X.; Wan, F.; Kou, L.; Yin, S.; Liu, L.; Huang, J.; et al. Microglia as modulators of exosomal alpha-synuclein transmission. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burré, J.; Sharma, M.; Tsetsenis, T.; Buchman, V.; Etherton, M.R.; Südhof, T.C. α-Synuclein promotes SNARE-complex assembly in vivo and in vitro. Science 2010, 329, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridi, J.C.; Hirth, F. Mechanisms of α-Synuclein Induced Synaptopathy in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Reitböck, P.; Anichtchik, O.; Bellucci, A.; Iovino, M.; Ballini, C.; Fineberg, E.; Ghetti, B.; Della Corte, L.; Spano, P.; Tofaris, G.K.; et al. SNARE protein redistribution and synaptic failure in a transgenic mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2010, 133, 2032–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janezic, S.; Threlfell, S.; Dodson, P.D.; Dowie, M.J.; Taylor, T.N.; Potgieter, D.; Parkkinen, L.; Senior, S.L.; Anwar, S.; Ryan, B.; et al. Deficits in dopaminergic transmission precede neuron loss and dysfunction in a new Parkinson model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E4016–E4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludtmann, M.H.R.; Angelova, P.R.; Horrocks, M.H.; Choi, M.L.; Rodrigues, M.; Baev, A.Y.; Berezhnov, A.V.; Yao, Z.; Little, D.; Banushi, B.; et al. α-synuclein oligomers interact with ATP synthase and open the permeability transition pore in Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Maio, R.; Barrett, P.J.; Hoffman, E.K.; Barrett, C.W.; Zharikov, A.; Borah, A.; Hu, X.; McCoy, J.; Chu, C.T.; Burton, E.A.; et al. α-Synuclein binds to TOM20 and inhibits mitochondrial protein import in Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 342ra78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamp, F.; Exner, N.; Lutz, A.K.; Wender, N.; Hegermann, J.; Brunner, B.; Nuscher, B.; Bartels, T.; Giese, A.; Beyer, K.; et al. Inhibition of mitochondrial fusion by α-synuclein is rescued by PINK1, Parkin and DJ-1. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 3571–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, V.; Mitra, J.; Hegde, P.M.; Pandey, A.; Sengupta, S.; Mitra, S.; Rao, K.S.; Hegde, M.L. Chromatin-Bound Oxidized α-Synuclein Causes Strand Breaks in Neuronal Genomes in in vitro Models of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 60, S133–S150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Hunt, C.P.; Sanders, L.H. DNA damage and repair in Parkinson’s disease: Recent advances and new opportunities. J. Neurosci. Res. 2021, 99, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaser, A.J.; Osterberg, V.R.; Dent, S.E.; Stackhouse, T.L.; Wakeham, C.M.; Boutros, S.W.; Weston, L.J.; Owen, N.; Weissman, T.A.; Luna, E. Alpha-synuclein is a DNA binding protein that modulates DNA repair with implications for Lewy body dis-orders. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, V.; Mitra, J.; Wang, H.; Hegde, P.M.; Rao, K.; Hegde, M.L. A multi-faceted genotoxic network of alpha-synuclein in the nucleus and mitochondria of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease: Emerging concepts and challenges. Prog. Neurobiol. 2020, 185, 101729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xilouri, M.; Brekk, O.R.; Stefanis, L. Alpha-synuclein and Protein Degradation Systems: A Reciprocal Relationship. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 47, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, A.-C.; Minakaki, G.; Menges, S.; Salvi, R.; Savitskiy, S.; Kazman, A.; Miranda, H.V.; Mielenz, D.; Klucken, J.; Winkler, J.; et al. Extracellular aggregated alpha synuclein primarily triggers lysosomal dysfunction in neural cells prevented by trehalose. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.M.; Huang, Y.X.; Li, X.L.; Chen, C.; Shi, Q.; Wang, G.R.; Tian, C.; Wang, Z.Y.; Jing, Y.Y.; Gao, C.; et al. Molecular interaction of α-synuclein with tubulin influences on the polymerization of microtubule in vitro and structure of microtubule in cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2009, 37, 3183–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartelli, D.; Aliverti, A.; Barbiroli, A.; Santambrogio, C.; Ragg, E.M.; Casagrande, F.V.; Cantele, F.; Beltramone, S.; Marangon, J.; De Gregorio, C.; et al. α-Synuclein is a Novel Microtubule Dynamase. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, M.I.; Kahn, J.E.; Lantos, P.L. Glial cytoplasmic inclusions in the CNS of patients with multiple system atrophy (stria-tonigral degeneration, olivopontocerebellar atrophy and Shy-Drager syndrome). J. Neurol. Sci. 1989, 94, 79–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusiner, S.B.; Woerman, A.L.; Mordes, D.A.; Watts, J.C.; Rampersaud, R.; Berry, D.B.; Patel, S.; Oehler, A.; Lowe, J.K.; Kravitz, S.N.; et al. Evidence for α-synuclein prions causing multiple system atrophy in humans with parkinsonism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5308–E5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, J.C.; Giles, K.; Oehler, A.; Middleton, L.; Dexter, D.T.; Gentleman, S.M.; DeArmond, S.J.; Prusiner, S.B. Transmission of multiple system atrophy prions to transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 19555–19560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Gathagan, R.J.; Lee, V.M.-Y. Distinct α-Synuclein strains and implications for heterogeneity among α-Synucleinopathies. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 109, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asi, Y.T.; Simpson, J.E.; Heath, P.R.; Wharton, S.B.; Lees, A.J.; Revesz, T.; Houlden, H.; Holton, J.L. Alpha-synuclein mRNA expression in oligodendrocytes in MSA. Glia 2014, 62, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, C.M.G.; Elia, A.E.; Portaleone, S.M.; Cazzaniga, F.A.; Rossi, M.; Bistaffa, E.; De Cecco, E.; Narkiewicz, J.; Salzano, G.; Carletta, O. Efficient RT-QuIC seeding activity for α-synuclein in olfactory mucosa samples of patients with Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Transl. Neurodegener. 2019, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, W.; Schmeichel, A.M.; Shahnawaz, M.; Schmelzer, J.D.; Boeve, B.F.; Sletten, D.M.; Gehrking, T.L.; Gehrking, J.A.; Olson, A.D.; Savica, R.; et al. Alpha-Synuclein Oligomers and Neurofilament Light Chain in Spinal Fluid Differentiate Multiple System Atrophy from Lewy Body Synucleinopathies. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 88, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahnawaz, M.; Mukherjee, A.; Pritzkow, S.; Mendez, N.; Rabadia, P.; Liu, X.; Hu, B.; Schmeichel, A.; Singer, W.; Wu, G.; et al. Discriminating α-synuclein strains in Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 578, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, M.L.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J. Presynaptic -Synuclein Aggregates, Not Lewy Bodies, Cause Neurodegeneration in Dementia with Lewy Bodies. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuendl, A.; Kunadt, M.; Kruse, N.; Bartels, C.; Moebius, W.; Danzer, K.M.; Mollenhauer, B.; Schneider, A. Induction of α-synuclein aggregate formation by CSF exosomes from patients with Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Brain 2016, 139, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didonna, A. Tau at the interface between neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation. Genes Immun. 2020, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Iqbal, K.; Quinlan, M.; Tung, Y.C.; Zaidi, M.S.; Wisniewski, H.M. Microtubule-associated protein tau. A component of Alzheimer paired helical filaments. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 6084–6089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, V.M.-Y.; Goedert, M.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Neurodegenerative Tauopathies. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 1121–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, M.; Lendon, C.L.; Rizzu, P.; Baker, M.; Froelich, S.; Houlden, H.; Pickering-Brown, S.; Chakraverty, S.; Isaacs, A.; Grover, A.; et al. Association of missense and 5′-splice-site mutations in tau with the inherited dementia FTDP-17. Nat. Cell Biol. 1998, 393, 702–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, S.; Guo, J.L.; Changolkar, L.; Stieber, A.; McBride, J.D.; Silva, L.V.; He, Z.; Zhang, B.; Gathagan, R.J.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; et al. Pathological Tau Strains from Human Brains Recapitulate the Diversity of Tauopathies in Nontransgenic Mouse Brain. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 11406–11423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoeibi, A.; Olfati, N.; Litvan, I. Frontrunner in Translation: Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, T.; Ikeda, K.; Akiyama, H.; Nonaka, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Ishiguro, K.; Iritani, S.; Tsuchiya, K.; Iseki, E.; Yagishita, S.; et al. Identification of amino-terminally cleaved tau fragments that distinguish progressive supranuclear palsy from corticobasal degeneration. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 55, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boluda, S.; Iba, M.; Zhang, B.; Raible, K.M.; Lee, V.M.-Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Differential induction and spread of tau pathology in young PS19 tau transgenic mice following intracerebral injections of pathological tau from Alzheimer’s disease or corticobasal degeneration brains. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 129, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, S.; Sahara, N.; Saito, Y.; Murayama, S.; Ikai, A.; Takashima, A. Increased levels of granular tau oligomers: An early sign of brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 54, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerson, J.E.; Sengupta, U.; A Lasagna-Reeves, C.; Guerrero-Muñoz, M.J.; Troncoso, J.; Kayed, R. Characterization of tau oligomeric seeds in progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2014, 2, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerson, J.E.; Ekayed, R. Formation and Propagation of Tau Oligomeric Seeds. Front. Neurol. 2013, 4, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duka, T.; Duka, V.; Joyce, J.N.; Sidhu, A. α-Synuclein contributes to GSK-3β-catalyzed Tau phosphorylation in Parkinson’s disease models. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 2820–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.H.; Hager, H.; Nielsen, M.S.; Højrup, P.; Gliemann, J.; Jakes, R. α-Synuclein Binds to Tau and Stimulates the Protein Kinase A-catalyzed Tau Phosphorylation of Serine Residues 262 and 356. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 25481–25489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giasson, B.I.; Forman, M.S.; Higuchi, M.; Golbe, L.I.; Graves, C.L.; Kotzbauer, P.T.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M.-Y. Initiation and Synergistic Fibrillization of Tau and Alpha-Synuclein. Science 2003, 300, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagshal, D.; Sankaranarayanan, S.; Guss, V.; Hall, T.; Berisha, F.; Lobach, I.; Karydas, A.; Voltarelli, L.; Scherling, C.; Heuer, H. Divergent CSF τ alterations in two common tauopathies: Alzheimer’s disease and progressive supranuclear palsy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2015, 86, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, O.; Janelidze, S.; Hall, S.; Magdalinou, N.; Lees, A.J.; Andreasson, U.; Norgren, N.; Linder, J.; Forsgren, L.; Constantinescu, R.; et al. Blood-based NfL. Neurology 2017, 88, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, J.C.; Bang, J.; Lobach, I.V.; Tsai, R.M.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Miller, B.L.; Boxer, A.L. CSF neurofilament light chain and phosphorylated tau 181 predict disease progression in PSP. Neurology 2017, 90, e273–e281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.E.; Williams, M. Mitochondrial Function and Dysfunction: An Update. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 342, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, R.R.; Singer, T.P. Energy-dependent uptake of N-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium, the neurotoxic metabolite of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine, by mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 7585–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, D.; Nakamura, K. Understanding the susceptibility of dopamine neurons to mitochondrial stressors in Parkinson’s disease. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 3702–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.-X.; Yin, X.-M. Mitophagy: Mechanisms, pathophysiological roles, and analysis. Biol. Chem. 2012, 393, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exner, N.; Treske, B.; Paquet, D.; Holmström, K.; Schiesling, C.; Gispert, S.; Carballo-Carbajal, I.; Berg, D.; Hoepken, H.-H.; Gasser, T.; et al. Loss-of-Function of Human PINK1 Results in Mitochondrial Pathology and Can Be Rescued by Parkin. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 12413–12418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narendra, D.; Tanaka, A.; Suen, D.-F.; Youle, R.J. Parkin is recruited selectively to impaired mitochondria and promotes their autophagy. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 183, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole, A.C.; Thomas, R.E.; Yu, S.; Vincow, E.S.; Pallanck, L. The Mitochondrial Fusion-Promoting Factor Mitofusin Is a Substrate of the PINK1/Parkin Pathway. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, A.; Cleland, M.M.; Xu, S.; Narendra, D.P.; Suen, D.-F.; Karbowski, M.; Youle, R.J. Proteasome and p97 mediate mitophagy and degradation of mitofusins induced by Parkin. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 191, 1367–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Winter, D.; Ashrafi, G.; Schlehe, J.; Wong, Y.L.; Selkoe, D.; Rice, S.; Steen, J.; LaVoie, M.J.; Schwarz, T.L. PINK1 and Parkin Target Miro for Phosphorylation and Degradation to Arrest Mitochondrial Motility. Cell 2011, 147, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchell, V.S.; E Nelson, D.; Sanchez-Martinez, A.; Delgado-Camprubi, M.; Ivatt, R.M.; Pogson, J.H.; Randle, S.J.; Wray, S.; A Lewis, P.; Houlden, H.; et al. The Parkinson’s disease-linked proteins Fbxo7 and Parkin interact to mediate mitophagy. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irrcher, I.; Aleyasin, H.; Seifert, E.; Hewitt, S.; Chhabra, S.; Phillips, M.; Lutz, A.; Rousseaux, M.; Bevilacqua, L.; Jahani-Asl, A.; et al. Loss of the Parkinson’s disease-linked gene DJ-1 perturbs mitochondrial dynamics. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 3734–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compagnoni, G.M.; Kleiner, G.; Bordoni, A.; Fortunato, F.; Ronchi, D.; Salani, S.; Guida, M.; Corti, C.; Pichler, I.; Bergamini, C.; et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in fibroblasts of Multiple System Atrophy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 3588–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, A.; Nisbet, R.; Grimm, A.; Götz, J. March separate, strike together—Role of phosphorylated TAU in mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis of Dis. 2014, 1842, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, K.L.; Eckert, A.; Rhein, V.; Mai, S.; Haase, W.; Reichert, A.S.; Jendrach, M.; Müller, W.E.; Leuner, K. A New Link to Mitochondrial Impairment in Tauopathies. Mol. Neurobiol. 2012, 46, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Khondiker, M.; Hollerhage, M.; Muriel, M.-P.; Champy, P.; Bach, A.; Depienne, C.; Respondek, G.; Yamada, E.S.; Lannuzel, A.; Yagi, T.; et al. Annonacin, a Natural Mitochondrial Complex I Inhibitor, Causes Tau Pathology in Cultured Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 7827–7837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnham, K.J.; Masters, C.L.; Bush, A.I. Neurodegenerative diseases and oxidatives stress. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiteller, G. Peroxyl radicals: Inductors of neurodegenerative and other inflammatory diseases. Their origin and how they transform cholesterol, phospholipids, plasmalogens, polyunsaturated fatty acids, sugars, and proteins into deleterious products. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 41, 362–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Wen, X.; Jiang, H.; Wang, J.; Song, N.; Xie, J. Interactions between iron and α-synuclein pathology in Parkinson’s disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 141, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wypijewska, A.; Galazka-Friedman, J.; Bauminger, E.R.; Wszolek, Z.K.; Schweitzer, K.J.; Dickson, D.W.; Jaklewicz, A.; Elbaum, D.; Friedman, A. Iron and reactive oxygen species activity in parkinsonian substantia nigra. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2010, 16, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecca, L.; Zucca, F.A.; Albertini, A.; Rizzio, E.; Fariello, R.G. A proposed dual role of neuromelanin in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 2006, 67, S8–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zecca, L.; Stroppolo, A.; Gatti, A.; Tampellini, D.; Toscani, M.; Gallorini, M.; Giaveri, G.; Arosio, P.; Santambrogio, P.; Fariello, R.G.; et al. The role of iron and copper molecules in the neuronal vulnerability of locus coeruleus and substantia nigra during aging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9843–9848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faucheux, B.A.; Martin, M.-E.; Beaumont, C.; Hunot, S.; Hauw, J.-J.; Agid, Y.; Hirsch, E.C. Lack of up-regulation of ferritin is associated with sustained iron regulatory protein-1 binding activity in the substantia nigra of patients with Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2002, 83, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziorowski, D.; Friedman, A.; Arosio, P.; Santambrogio, P.; Dziewulska, D. ELISA reveals a difference in the structure of substantia nigra ferritin in Parkinson’s disease and incidental Lewy body compared to control. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2007, 13, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connor, J.R.; Snyder, B.S.; Arosio, P.; Loeffler, D.A.; LeWitt, P. A Quantitative Analysis of Isoferritins in Select Regions of Aged, Parkinsonian, and Alzheimer’s Diseased Brains. J. Neurochem. 2002, 65, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, J.R.; Boeshore, K.L.; Benkovic, S.A.; Menzies, S.L. Isoforms of ferritin have a specific cellular distribution in the brain. J. Neurosci. Res. 1994, 37, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, A.R.; Fey, C.; Morris, C.M.; Bindoff, L.A.; Ince, P.G.; Chinnery, P.F.; Coulthard, A.; Jackson, M.J.; Jackson, A.P.; McHale, D.P.; et al. Mutation in the gene encoding ferritin light polypeptide causes dominant adult-onset basal ganglia disease. Nat. Genet. 2001, 28, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukae, J.; Takanashi, M.; Kubo, S.-I.; Nishioka, K.-I.; Nakabeppu, Y.; Mori, H.; Mizuno, Y.; Hattori, N. Expression of 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase (OGG1) in Parkinson?s disease and related neurodegenerative disorders. Acta Neuropathol. 2004, 109, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Xie, J. Ferroportin 1 but not hephaestin contributes to iron accumulation in a cell model of Parkinson’s disease. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasvosve, I. Effect of ferroportin polymorphism on iron homeostasis and infection. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 416, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, S.; Liu, L.; Nemeth, E.; Gabayan, V.; Sörensen, O.E.; Ganz, T. Hepcidin excess induces the sequestration of iron and exacerbates tumor-associated anemia. Blood 2005, 105, 1797–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganz, T.; Nemeth, E. Hepcidin and Disorders of Iron Metabolism. Annu. Rev. Med. 2011, 62, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwiatek-Majkusiak, J.; Geremek, M.; Koziorowski, D.; Tomasiuk, R.; Szlufik, S.; Friedman, A. Serum levels of hepcidin and interleukin 6 in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2020, 80, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Song, N.; Xie, A.; Xie, J.; Jiang, H. High hepcidin level accounts for the nigral iron accumulation in acute peripheral iron intoxication rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 212, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, F.; Qian, C.; Qian, Z.M.; Wu, X.-M.; Xie, H.; Yung, W.-H.; Ke, Y. Hepcidin directly inhibits transferrin receptor 1 expression in astrocytes via a cyclic AMP-protein kinase a pathway. Glia 2011, 59, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visanji, N.P.; Collingwood, J.F.; Finnegan, M.E.; Tandon, A.; House, E.; Hazrati, L.-N. Iron Deficiency in Parkinsonism: Region-Specific Iron Dysregulation in Parkinson’s Disease and Multiple System Atrophy. J. Park. Dis. 2013, 3, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahim, A.S.; Kulathingal, J.; Murray, M.E.; Casey-Castanedes, M.; Dickson, D.W.; Yen, S.-H.; Sevlever, D. A proteomic study identifies different levels of light chain ferritin in corticobasal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 122, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bresgen, N.; Eckl, P.M. Oxidative Stress and the Homeodynamics of Iron Metabolism. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 808–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintana, C.; Cowley, J.; Marhic, C. Electron nanodiffraction and high-resolution electron microscopy studies of the structure and composition of physiological and pathological ferritin. J. Struct. Biol. 2004, 147, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałazka-Friedman, J.; Bauminger, E.; Szlachta, K.; Schweitzer, K.; Wszolek, Z.; Dickson, D.; Friedman, A. Mössbauer Studies of Pathological Brain Tissues Affected by PSP Disease. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2009, 115, 545–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuliński, R.; Bauminger, E.; Friedman, A.; Duda, P.; Gałązka-Friedman, J. Iron in typical and atypical parkinsonism-Mössbauer spectroscopy and MRI studies. Hyperfine Interact. 2016, 237, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gelders, G.; Baekelandt, V.; Van Der Perren, A. Linking Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunot, S.; Dugas, N.; Faucheux, B.; Hartmann, A.; Tardieu, M.; Debre, P.; Agid, Y.; Dugas, B.; Hirsch, E.C. FcεRII/CD23 Is Expressed in Parkinson’s Disease and Induces, In Vitro, Production of Nitric Oxide and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α in Glial Cells. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 3440–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, N.; Jiang, H.; Wang, J.; Xie, J. Pro-inflammatory cytokines modulate iron regulatory protein 1 expression and iron transportation through reactive oxygen/nitrogen species production in ventral mesencephalic neurons. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2013, 1832, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziorowski, D.; Tomasiuk, R.; Szlufik, S.; Friedman, A. Inflammatory cytokines and NT-proCNP in Parkinson’s disease patients. Cytokine 2012, 60, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogi, M.; Harada, M.; Riederer, P.; Narabayashi, H.; Fujita, K.; Nagatsu, T. Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) increases both in the brain and in the cerebrospinal fluid from parkinsonian patients. Neurosci. Lett. 1994, 165, 208–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boka, G.; Anglade, P.; Wallach, D.; Javoy-Agid, F.; Agid, Y.; Hirsch, E. Immunocytochemical analysis of tumor necrosis factor and its receptors in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 1994, 172, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbs, R.; Charlett, A.; Purkiss, A.; Dobbs, S.; Weller, C.; Peterson, D. Association of circulating TNF-α and IL-6 with ageing and parkinsonism. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1999, 100, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodacki, B.; Staszewski, J.; Toczyłowska, B.; Kozłowska, E.; Drela, N.; Chalimoniuk, M.; Stępien, A. Serum interleukin (IL-2, IL-10, IL-6, IL-4), TNFα, and INFγ concentrations are elevated in patients with atypical and idiopathic parkinsonism. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 441, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalzo, P.; Kümmer, A.; Cardoso, F.; Teixeira, A.L. Serum levels of interleukin-6 are elevated in patients with Parkinson’s disease and correlate with physical performance. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 468, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; O’Reilly, E.J.; Schwarzschild, M.A.; Ascherio, A. Peripheral inflammatory biomarkers and risk of Parkinson’s disease. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 167, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufek, M.; Hamanová, M.; Lokaj, J.; Goldemund, D.; Rektorová, I.; Michálková, Z.; Sheardová, K.; Rektor, I. Serum inflam-matory biomarkers in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2009, 15, 318–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rentzos, M.; Nikolaou, C.; Andreadou, E.; Paraskevas, G.; Rombos, A.; Zoga, M.; Tsoutsou, A.; Boufidou, F.; Kapaki, E.; Vassilopoulos, D. Circulating interleukin-10 and interleukin-12 in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2009, 119, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Jang, S.H.; Kim, H.; Yoon, J.H.; Chung, K.C. PINK1 stimulates interleukin-1β-mediated inflammatory signaling via the positive regulation of TRAF6 and TAK1. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 3301–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, T.H.; Zabetian, C.P.; Tenesa, A.; Laederach, A.; Montimurro, J.; Yearout, D.; Kay, D.M.; Doheny, K.F.; Paschall, J.; Pugh, E. Common genetic variation in the HLA region is associated with late-onset sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón-Sánchez, J.; Van Hilten, J.J.; Van De Warrenburg, B.C.; Post, B.; Berendse, H.W.; Arepalli, S.; Hernandez, D.G.; De Bie, R.M.A.; Velseboer, D.C.; Scheffer, H.; et al. Genome-wide association study confirms extant PD risk loci among the Dutch. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 19, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalls, M.A.; Plagnol, V.; Hernandez, D.G.; Sharma, M.; Sheerin, U.-M.; Saad, M.H.F.; Simonsanchez, J.; Schulte, C.; Lesage, S.; Sveinbjornsdottir, S.; et al. Imputation of sequence variants for identification of genetic risks for Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Lancet 2011, 377, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeer, P.L.; Itagaki, S.; Boyes, B.E.; McGeer, E. Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease brains. Neurology 1988, 38, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.S.; Koh, S.-H. Neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative disorders: The roles of microglia and astrocytes. Transl. Neurodegener. 2020, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passamonti, L.; Rodríguez, P.V.; Hong, Y.T.; Allinson, K.S.; Bevan-Jones, W.R.; Williamson, D.; Jones, P.S.; Arnold, R.; Borchert, R.J.; Surendranathan, A.; et al. [11C]PK11195 binding in Alzheimer disease and progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurology 2018, 90, e1989–e1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malpetti, M.; Passamonti, L.; Rittman, T.; Jones, P.S.; Rodríguez, P.V.; Bevan-Jones, W.R.; Hong, Y.T.; Fryer, T.D.; Aigbirhio, F.I.; Dm, J.T.O.; et al. Neuroinflammation and Tau Colocalize in vivo in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 88, 1194–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonninen, T.-M.; Hämäläinen, R.H.; Koskuvi, M.; Oksanen, M.; Shakirzyanova, A.; Wojciechowski, S.; Puttonen, K.; Naumenko, N.; Goldsteins, G.; Laham-Karam, N. Metabolic alterations in Parkinson’s disease astrocytes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Xie, J. Astroglial and microglial contributions to iron metabolism disturbance in Parkinson’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Zhong, Y. Interleukin-17A: The Key Cytokine in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 566922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.; Janelidze, S.; Surova, Y.; Widner, H.; Zetterberg, H.; Hansson, O. Cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of inflammatory markers in Parkinson’s disease and atypical parkinsonian disorders. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iba, M.; Kim, C.; Sallin, M.; Kwon, S.; Verma, A.; Overk, C.; Rissman, R.A.; Sen, R.; Sen, J.M.; Masliah, E. Neuroinflammation is associated with infiltration of T cells in Lewy body disease and α-synuclein transgenic models. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, A.S.; Kordower, J.H.; Sette, A.; Lindestam Arlehamn, C.S.; Sulzer, D.; Mach, R.H. Inflammation in Experimental Models of α-Synucleinopathies. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Soriano, A.; Segura, M.A.; Botta-Orfila, T.; Giraldo, D.; Fernández, M.; Compta, Y.; Fernández-Santiago, R.; Ezquerra, M.; Tartaglia, G.G.; Martí, M.J.; et al. Transcriptomic differences in MSA clinical variants. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishizawa, K.; Dickson, D.W. Microglial Activation parallels System Degeneration in progressive Supranuclear palsy and Corticobasal Degeneration. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2001, 60, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.P.; Marmion, D.J.; Schonhoff, A.M.; Jurkuvenaite, A.; Won, W.-J.; Standaert, D.G.; Kordower, J.H.; Harms, A.S. T cell infiltration in both human multiple system atrophy and a novel mouse model of the disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 139, 855–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heras-Garvin, A.; Refolo, V.; Reindl, M.; Wenning, G.K.; Stefanova, N. High-salt diet does not boost neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in a model of α-synucleinopathy. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagnoni, G.M.; Di Fonzo, A. Understanding the pathogenesis of multiple system atrophy: State of the art and future perspectives. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, Y.-M.; Kwon, Y.; Jo, M.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.-J. The Role of Glial Mitochondria in α-Synuclein Toxicity. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassil, F.; Guerin, P.A.; Dutheil, N.; Li, Q.; Klugmann, M.; Meissner, W.G.; Bezard, E.; Fernagut, P.O. Viral-mediated oli-godendroglial alpha-synuclein expression models multiple system atrophy. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 1230–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Botrán, R.; Ahmed, Z.; Crespo, F.A.; Gatenbee, C.; Gonzalez, J.; Dickson, D.W.; Litvan, I. Cytokine expression and microglial activation in progressive supranuclear palsy. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2011, 17, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, C.; Rossi, G.; Barbarulo, A.M.; Di Fede, G.; Foglia, C.; Piccoli, E.; Piscosquito, G.; Saracino, D.; Tagliavini, F.; Cotrufo, R. A progranulin mutation associated with cortico-basal syndrome in an Italian family expressing different phenotypes of fronto-temporal lobar degeneration. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 33, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markey, S.P.; Johannessen, J.N.; Chiueh, C.C.; Burns, R.S.; Herkenham, M.A. Intraneuronal generation of a pyridinium metabolite may cause drug-induced parkinsonism. Nat. Cell Biol. 1984, 311, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heikkila, R.E.; Manzino, L.; Cabbat, F.S.; Duvoisin, R.C. Protection against the dopaminergic neurotoxicity of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine by monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Nat. Cell Biol. 1984, 311, 467–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, R.-S.; Abell, C.; Gessner, W.; Brossi, A. Serotonergic conversion of MPTP and dopaminergic accumulation of MPP+. FEBS Lett. 1985, 189, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, R.; Kowal, A.T.; Johnson, M.K.; Salach, J.I.; Singer, T.P. The inhibition site of MPP+, the neurotoxic bioactivation product of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3, 6-tetrahydropyridine is near the Q-binding site of NADH dehydrogenase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1987, 259, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotharius, J.; Brundin, P. Pathogenesis of parkinson’s disease: Dopamine, vesicles and α-synuclein. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schapira, A.H.V.; Mann, V.M.; Cooper, J.M.; Dexter, D.; Daniel, S.E.; Jenner, P.; Clark, J.B.; Marsden, C.D. Anatomic and Disease Specificity of NADH CoQ1Reductase (Complex I) Deficiency in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurochem. 1990, 55, 2142–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purisai, M.G.; McCormack, A.L.; Langston, W.J.; Johnston, L.C.; Di Monte, D.A. α-Synuclein expression in the substantia nigra of MPTP-lesioned non-human primates. Neurobiol. Dis. 2005, 20, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terron, A.; Bal-Price, A.; Paini, A.; Monnet-Tschudi, F.; Bennekou, S.H.; Leist, M.; Schildknecht, S. An adverse outcome pathway for parkinsonian motor deficits associated with mitochondrial complex I inhibition. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 41–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Ohtaki, K.; Matsubara, K.; Aoyama, K.; Uezono, T.; Saito, O.; Suno, M.; Ogawa, K.; Hayase, N.; Kimura, K.; et al. Carrier-mediated processes in blood–brain barrier penetration and neural uptake of paraquat. Brain Res. 2001, 906, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, R.; Lei, S.; Anandhan, A.; Marshall, D.D.; Worley, B.; Cerny, R.L.; Dodds, E.D.; Huang, Y.; Panayiotidis, M.I.; Pappa, A.; et al. Metabolic Investigations of the Molecular Mechanisms Associated with Parkinson’s Disease. Metabolites 2017, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Stevenson, F.F.; Oo, M.L.; Andersen, J.K. Iron-enhanced paraquat-mediated dopaminergic cell death due to increased oxidative stress as a consequence of microglial activation. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgenson, J.L. Aldrin and dieldrin: A review of research on their production, environmental deposition and fate, bioaccumulation, toxicology, and epidemiology in the United States. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 113–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitazawa, M.; Anantharam, V.; Kanthasamy, A. Dieldrin induces apoptosis by promoting caspase-3-dependent proteolytic cleavage of protein kinase Cδ in dopaminergic cells: Relevance to oxidative stress and dopaminergic degeneration. Neuroscience 2003, 119, 945–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, N.; Shirai, Y. Protein Kinase C (PKC): Function of Neuron Specific Isotype. J. Biochem. 2002, 132, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinka, Y.Y.; Youdim, M.B. Inhibition of mitochondrial complexes I and IV by 6-hydroxydopamine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1995, 292, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, O. Role of Oxidative Stress in Parkinson’s Disease. Exp. Neurobiol. 2013, 22, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blesa, J.; Phani, S.; Jackson-Lewis, V.; Przedborski, S. Classic and New Animal Models of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Powers, R. NMR metabolomics analysis of Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Metab. 2013, 1, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couper, J. On the effects of black oxide of manganese when inhaled into the lungs. Br. Ann. Med. Pharm. 1837, 1, 41–42. [Google Scholar]
- Stepens, A.; Logina, I.; Liguts, V.; Aldiņš, P.; Ekšteina, I.; Platkājis, A.; Mārtiņsone, I.; Tērauds, E.; Rozentāle, B.; Donaghy, M. A Parkinsonian Syndrome in Methcathinone Users and the Role of Manganese. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilarte, T.R. Manganese and Parkinson’s disease: A critical review and new findings. Ciência & Saúde Coletiva 2011, 16, 4549–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavin, C.E.; Gunter, K.K.; Gunter, T.E. Mn2+ sequestration by mitochondria and inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1992, 115, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Finley, E.J.; Gavin, C.E.; Aschner, M.; Gunter, T.E. Manganese neurotoxicity and the role of reactive oxygen species. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 62, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidoryk-Wegrzynowicz, M.; Lee, E.; Mingwei, N.; Aschner, M. Disruption of astrocytic glutamine turnover by manganese is mediated by the protein kinase C pathway. Glia 2011, 59, 1732–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.E.; Ward, E.J.; Yeh, C.-L.; Snyder, S.; Long, Z.; Yavuz, F.G.; Zauber, S.E.; Dydak, U. Thalamic GABA levels and occupational manganese neurotoxicity: Association with exposure levels and brain MRI. NeuroToxicology 2018, 64, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikosaka, O. GABAergic output of the basal ganglia. Prog. Brain Res. 2007, 160, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Guo, Y.; Luo, W.; Lin, C.; Ding, M. Serum urate and the risk of Parkinson’s disease: Results from a meta-analysis. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 40, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asken, B.M.; Sullan, M.J.; DeKosky, S.T.; Jaffee, M.S.; Bauer, R.M. Research Gaps and Controversies in Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, E.E.; Sundman, M.H.; Chen, N.-K. Examining the Relationship between Head Trauma and Neurodegenerative Disease: A Review of Epidemiology, Pathology and Neuroimaging Techniques. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Park. 2014, 4, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, D.A.; Schneider, J.A.; Arvanitakis, Z.; Wilson, R.S. Overview and Findings from the Religious Orders Study. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2012, 9, 628–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, D.A.; Schneider, J.A.; Buchman, A.S.; Barnes, L.L.; Boyle, P.A.; Wilson, R.S. Overview and Findings from the Rush Memory and Aging Project. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2012, 9, 646–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crane, P.K.; Gibbons, L.E.; Dams-O’Connor, K.; Trittschuh, E.; Leverenz, J.B.; Keene, C.D.; Sonnen, J.; Montine, T.J.; Bennett, D.A.; Leurgans, S.; et al. Association of Traumatic Brain Injury With Late-Life Neurodegenerative Conditions and Neuropathologic Findings. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, R.C.; Byers, A.L.; Barnes, D.E.; Li, Y.; Boscardin, J.; Yaffe, K. Mild TBI and risk of Parkinson disease. Neurology 2018, 90, e1771–e1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delic, V.; Beck, K.D.; Pang, K.C.H.; Citron, B.A. Biological links between traumatic brain injury and Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, G.; Moreno-Gonzalez, I.; Soto, C. Amyloid-beta and tau pathology following repetitive mild traumatic brain injury. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 483, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, V.E.; Stewart, W.C.L.; Smith, D.H. Widespread Tau and Amyloid-Beta Pathology Many Years After a Single Traumatic Brain Injury in Humans. Brain Pathol. 2011, 22, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velazquez, A.; Ortega, M.; Rojas, S.; González-Oliván, F.J.; Rodriguez-Baeza, A. Widespread microglial activation in patients deceased from traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2015, 29, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saykally, J.N.; Ratliff, W.A.; Keeley, K.L.; Pick, C.G.; Mervis, R.F.; Citron, B.A. Repetitive Mild Closed Head Injury Alters Protein Expression and Dendritic Complexity in a Mouse Model. J. Neurotrauma 2018, 35, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prashar, A.; Schnettger, L.; Bernard, E.M.; Gutierrez, M.G. Rab GTPases in Immunity and Inflammation. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steger, M.; Tonelli, F.; Ito, G.; Davies, P.; Trost, M.; Vetter, M.; Wachter, S.; Lorentzen, E.; Duddy, G.; Wilson, S.; et al. Phosphoproteomics reveals that Parkinson’s disease kinase LRRK2 regulates a subset of Rab GTPases. eLife 2016, 5, e12813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Locus | Gene | Chromosomal Region | Inheritance | Role of the Encoded Protein |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PARK1/4 | SNCA | 4q22.1 | AD | -synaptic vesicles mobility |
| PARK2 | PRKN | 6q26 | AR | -mitophagy -ubiquitin-dependent protein degradation |
| PARK3 | --- | 2p13 | AD | -unknown |
| PARK5 | UCH-L1 | 4p13 | AD | -participate in generation of ubiquitin monomers |
| PARK6 | PINK1 | 1p36.12 | AR | -mitophagy |
| PARK7 | DJ1 | 1p36.23 | AR | -redox-sensitive chaperone (sensor for oxidative stress) |
| PARK8 | LRRK2 | 12p12 | AD | -chaperone mediated autophagy -participation in neuronal cell death -neuronal plasticity -vesicle trafficking |
| PARK9 | ATP13A2 | 1p36.13 | AR | -inorganic cations transport |
| PARK10 | --- | 1p32 | --- | -unknown |
| PARK11 | GIGYF2 | 2q37.1 | AD | -repressor of translation initiation |
| PARK12 | --- | Xq21-q25 | X-linked | -unknown |
| PARK13 | HTRA2 | 2p13.1 | AD | -caspase-dependent apoptosis |
| PARK14 | PLA2G6 | 22q13.1 | AR | -catalyse the release of fatty acids from phospholipids |
| PARK15 | FBXO7 | 22q12.3 | AR | -ubiquitination mediator |
| PARK16 | --- | 1q32 | --- | -unknown |
| PARK17 | VPS35 | 16q11.2 | AD | -retrograde transport of proteins from endosomes to the trans-Golgi network |
| PARK18 | EIF4G1 | 3q27.1 | AD | -mRNA binding in translation process |
| PARK19 | DNAJC6 | 1p31.3 | AR | -clarithin-mediated endocytosis |
| PARK20 | SYNJ1 | 21q22.11 | AR | -regulates levels of membrane phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate |
| PARK21 | DNAJC13/TMEM230 | 3q22.1 | AD | -co-chaperone of heat shock protein -stimulation of ATP hydrolysis |
| PARK22 | CHCHD2 | 7p11.2 | AD | -negative regulator of mitochondria-mediated apoptosis -reduction of oxidative stress |
| PARK23 | VPS13C | 15q22.2 | AR | -proper mitochondrial function (maintenance of mitochondrial transmembrane potential) |
| PD | PSP | MSA | CBD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aspects of neuro-inflammation in neurodegeneration | (1) Increased concentration of TNF-α in CSF as well as in serum blood (2) Increasedproinflammatory cytokine: IL-6 and IL-12, have been shown to be at increased concentrations in PD serum (3) Increased NT-proCNP (4) PINK1 upregulates IL-1β-mediated signalling (5) Changes in CRP, SAA, IL-8 and YKL-40 | (1) Abnormalities in the concentration of cytokines produced by activated microglia as TNF-α, interleukin 1Β and IL-6 (2) Deviations in the regulation of T and Natural Killer Cells related to IL-2 | (1) Abnormalities in gene sets of interferon, IL-1, IL-6, IL-8 (2) An increase of CD3+, CD4+ and CD8+ (3) iNOS elevated expression | Via oxidative stress |
| Neurodegeneration | Oxidative stress, iron metabolism, disturbances, glial mitochondrial dysfunction | Microglial activation affecting tau deposition | Inflammatory response induced by mitochondrial dysfunction | Not explored |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koziorowski, D.; Figura, M.; Milanowski, Ł.M.; Szlufik, S.; Alster, P.; Madetko, N.; Friedman, A. Mechanisms of Neurodegeneration in Various Forms of Parkinsonism—Similarities and Differences. Cells 2021, 10, 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10030656
Koziorowski D, Figura M, Milanowski ŁM, Szlufik S, Alster P, Madetko N, Friedman A. Mechanisms of Neurodegeneration in Various Forms of Parkinsonism—Similarities and Differences. Cells. 2021; 10(3):656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10030656
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoziorowski, Dariusz, Monika Figura, Łukasz M. Milanowski, Stanisław Szlufik, Piotr Alster, Natalia Madetko, and Andrzej Friedman. 2021. "Mechanisms of Neurodegeneration in Various Forms of Parkinsonism—Similarities and Differences" Cells 10, no. 3: 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10030656
APA StyleKoziorowski, D., Figura, M., Milanowski, Ł. M., Szlufik, S., Alster, P., Madetko, N., & Friedman, A. (2021). Mechanisms of Neurodegeneration in Various Forms of Parkinsonism—Similarities and Differences. Cells, 10(3), 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10030656







