Neurodegeneration Induced by Anti-IgLON5 Antibodies Studied in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Human Neurons
Abstract
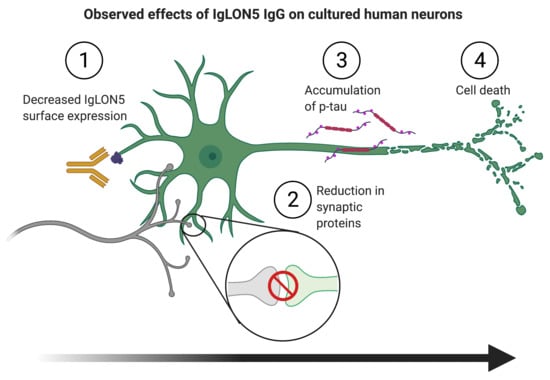
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation of Anti-IgLON5 IgG Fractions
2.2. Human Stem Cell-Derived Neurons (hNSCs and hiPSCs)
2.3. IgLON5 Live Staining
2.4. Immunocytochemistry
2.5. Image Acquisition and Analysis
2.6. Neuronal Spike Rate
2.7. Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Short-Term Autoantibody Exposure of hNSC-Derived Neural Cultures
3.2. Long-Term Autoantibody Exposure of hiPSC-Derived Neural Cultures
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Anti-IgLON5 IgG Short-Term Exposure on hNSC-Derived Cultures
4.2. Effects of Anti-IgLON5 IgG Long-Term Exposure on hiPSC-Derived Cultures
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sabater, L.; Gaig, C.; Gelpi, E.; Bataller, L.; Lewerenz, J.; Torres-Vega, E.; Contreras, A.; Giometto, B.; Compta, Y.; Embid, C.; et al. A novel non-rapid-eye movement and rapid-eye-movement parasomnia with sleep breathing disorder associated with antibodies to IgLON5: A case series, characterisation of the antigen, and post-mortem study. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelpi, E.; Höftberger, R.; Graus, F.; Ling, H.; Holton, J.L.; Dawson, T.; Popovic, M.; Pretnar-Oblak, J.; Högl, B.; Schmutzhard, E.; et al. Neuropathological criteria of anti-IgLON5-related tauopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 132, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaig, C.; Graus, F.; Compta, Y.; Högl, B.; Bataller, L.; Brüggemann, N.; Giordana, C.; Heidbreder, A.; Kotschet, K.; Lewerenz, J.; et al. Clinical manifestations of the anti-IgLON5 disease. Neurology 2017, 88, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, M.S.; Blaabjerg, M. Anti-IgLON5 Disease: A Case With 11-Year Clinical Course and Review of the Literature. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezudo-García, P.; Mena-Vázquez, N.; Torrús, G.E.; Serrano-Castro, P. Response to immunotherapy in anti-IgLON5 disease: A systematic review. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2019, 141, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991, 82, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Jellinger, K.; Braak, E.; Bohl, J. Allocortical neurofibrillary changes in progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol. 1992, 84, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaig, C.; Ercilla, G.; Daura, X.; Ezquerra, M.; Fernández-Santiago, R.; Palou, E.; Sabater, L.; Höftberger, R.; Heidbreder, A.; Högl, B.; et al. HLA and microtubule-associated protein tau H1 haplotype associations in anti-IgLON5 disease. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 6, e605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaig, C.; Compta, Y. Neurological profiles beyond the sleep disorder in patients with anti-IgLON5 disease. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2019, 32, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaig, C.; Iranzo, A.; Santamaria, J.; Graus, F. The Sleep Disorder in Anti-lgLON5 Disease. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. 2018, 18, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranaivoson, F.M.; Turk, L.S.; Ozgul, S.; Kakehi, S.; von Daake, S.; Lopez, N.; Trobiani, L.; De Jaco, A.; Denissova, N.; Demeler, B.; et al. A Proteomic Screen of Neuronal Cell-Surface Molecules Reveals IgLONs as Structurally Conserved Interaction Modules at the Synapse. Structure 2019, 27, 893–906.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, T.; Maekawa, S.; Miyata, S. IgLON cell adhesion molecules regulate synaptogenesis in hippocampal neurons. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2009, 27, 496–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabater, L.; Planaguma, J.; Dalmau, J.; Graus, F. Cellular investigations with human antibodies associated with the anti-IgLON5 syndrome. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landa, J.; Gaig, C.; Planagumà, J.; Saiz, A.; Antonell, A.; Sanchez-Valle, R.; Dalmau, J.; Graus, F.; Sabater, L. Effects of IgLON5 Antibodies on Neuronal Cytoskeleton: A Link between Autoimmunity and Neurodegeneration. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 88, 1023–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, A.; Snyder, E.Y.; Vescovi, A.; Martínez-Serrano, A. Establishment and Properties of a Growth Factor-Dependent, Perpetual Neural Stem Cell Line from the Human CNS. Exp. Neurol. 2000, 161, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okarmus, J.; Bogetofte, H.; Schmidt, S.I.; Ryding, M.; García-López, S.; Ryan, B.J.; Martínez-Serrano, A.; Hyttel, P.; Meyer, M. Lysosomal perturbations in human dopaminergic neurons derived from induced pluripotent stem cells with PARK2 mutation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loehfelm, A.; Elder, M.K.; Boucsein, A.; Jones, P.P.; Williams, J.M.; Tups, A. Docosahexaenoic acid prevents palmitate-induced insulin-dependent impairments of neuronal health. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 4635–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravarty, D.; Saadi, F.; Kundu, S.; Bose, A.; Khan, R.; Dine, K.; Kenyon, L.C.; Shindler, K.S.; Das Sarma, J. CD4 Deficiency Causes Poliomyelitis and Axonal Blebbing in Murine Coronavirus-Induced Neuroinflammation. J. Virol. 2020, 94, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Sen, N. Tauopathy: A common mechanism for neurodegeneration and brain aging. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2019, 178, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalmau, J.; Gleichman, A.J.; Hughes, E.G.; E Rossi, J.; Peng, X.; Lai, M.; Dessain, S.K.; Rosenfeld, M.R.; Balice-Gordon, R.; Lynch, D.R. Anti-NMDA-receptor encephalitis: Case series and analysis of the effects of antibodies. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Hughes, E.G.; Moscato, E.H.; Parsons, T.D.; Dalmau, J.; Balice-Gordon, R.J. Cellular plasticity induced by anti–α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptor encephalitis antibodies. Ann. Neurol. 2015, 77, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit-Pedrol, M.; Sell, J.; Planagumà, J.; Mannara, F.; Radosevic, M.; Haselmann, H.; Ceanga, M.; Sabater, L.; Spatola, M.; Soto, D.; et al. LGI1 antibodies alter Kv1.1 and AMPA receptors changing synaptic excitability, plasticity and memory. Brain 2018, 141, 3144–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryding, M.; Gamre, M.; Nissen, M.S.; Nilsson, A.C.; Okarmus, J.; Poulsen, A.A.E.; Meyer, M.; Blaabjerg, M. Neurodegeneration Induced by Anti-IgLON5 Antibodies Studied in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Human Neurons. Cells 2021, 10, 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040837
Ryding M, Gamre M, Nissen MS, Nilsson AC, Okarmus J, Poulsen AAE, Meyer M, Blaabjerg M. Neurodegeneration Induced by Anti-IgLON5 Antibodies Studied in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Human Neurons. Cells. 2021; 10(4):837. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040837
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyding, Matias, Mattias Gamre, Mette S. Nissen, Anna C. Nilsson, Justyna Okarmus, Anne A. E. Poulsen, Morten Meyer, and Morten Blaabjerg. 2021. "Neurodegeneration Induced by Anti-IgLON5 Antibodies Studied in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Human Neurons" Cells 10, no. 4: 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040837
APA StyleRyding, M., Gamre, M., Nissen, M. S., Nilsson, A. C., Okarmus, J., Poulsen, A. A. E., Meyer, M., & Blaabjerg, M. (2021). Neurodegeneration Induced by Anti-IgLON5 Antibodies Studied in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Human Neurons. Cells, 10(4), 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040837