1,3,4-Thiadiazoles Effectively Inhibit Proliferation of Toxoplasma gondii
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
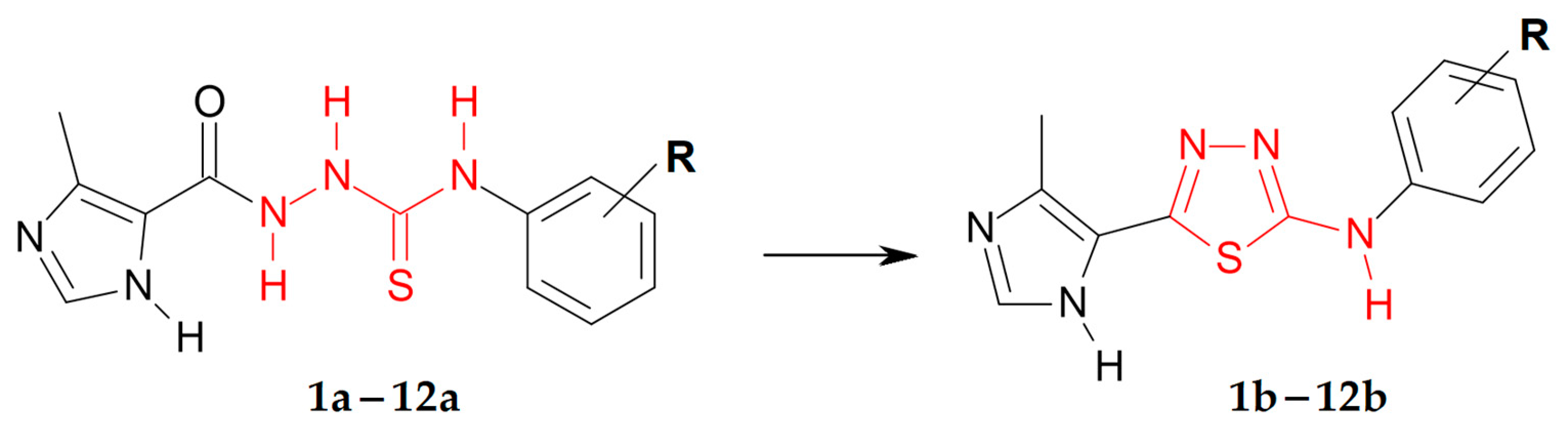
3.1. Synthetic Chemistry
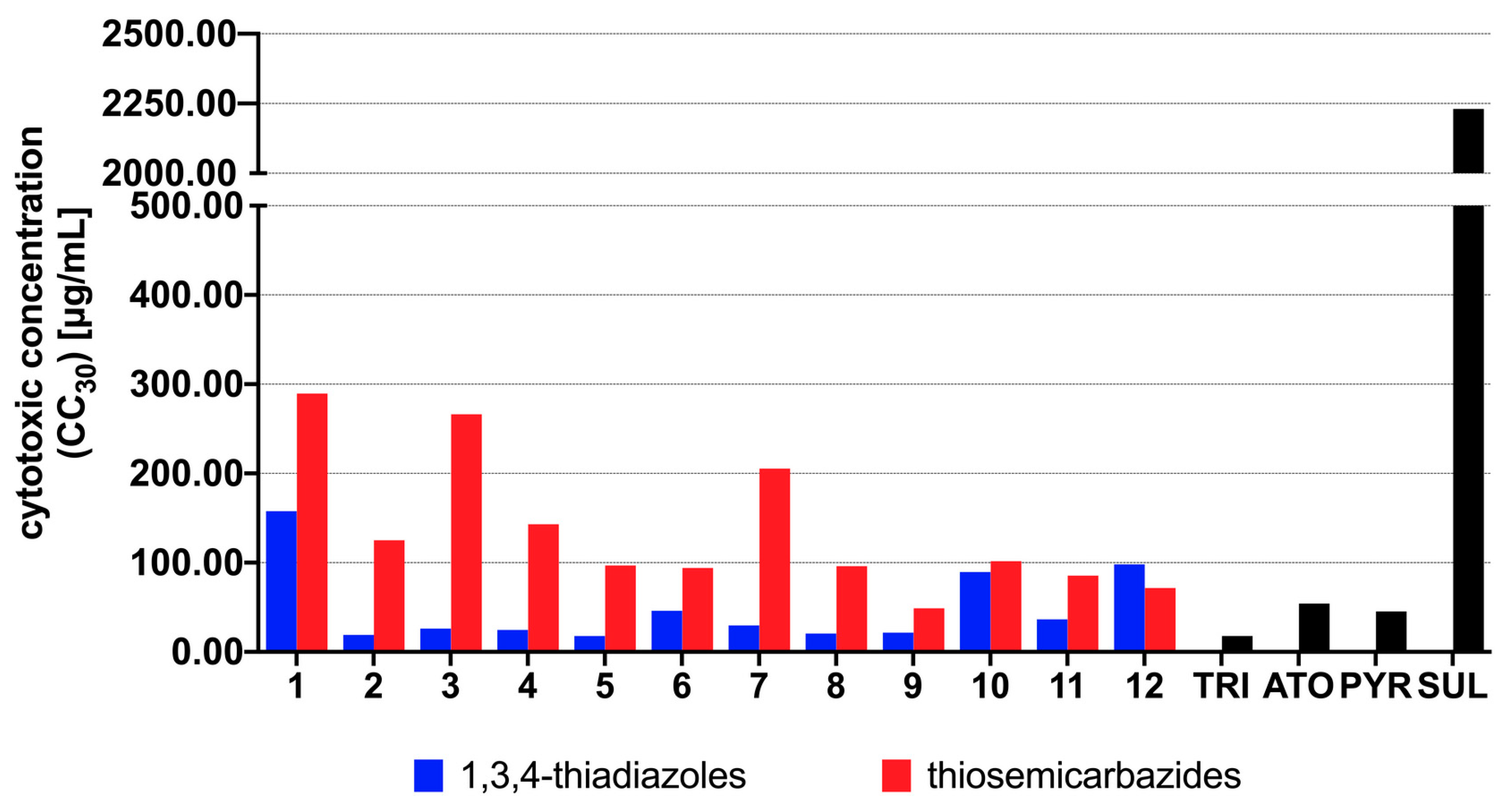
3.2. Antiparasitic Activity
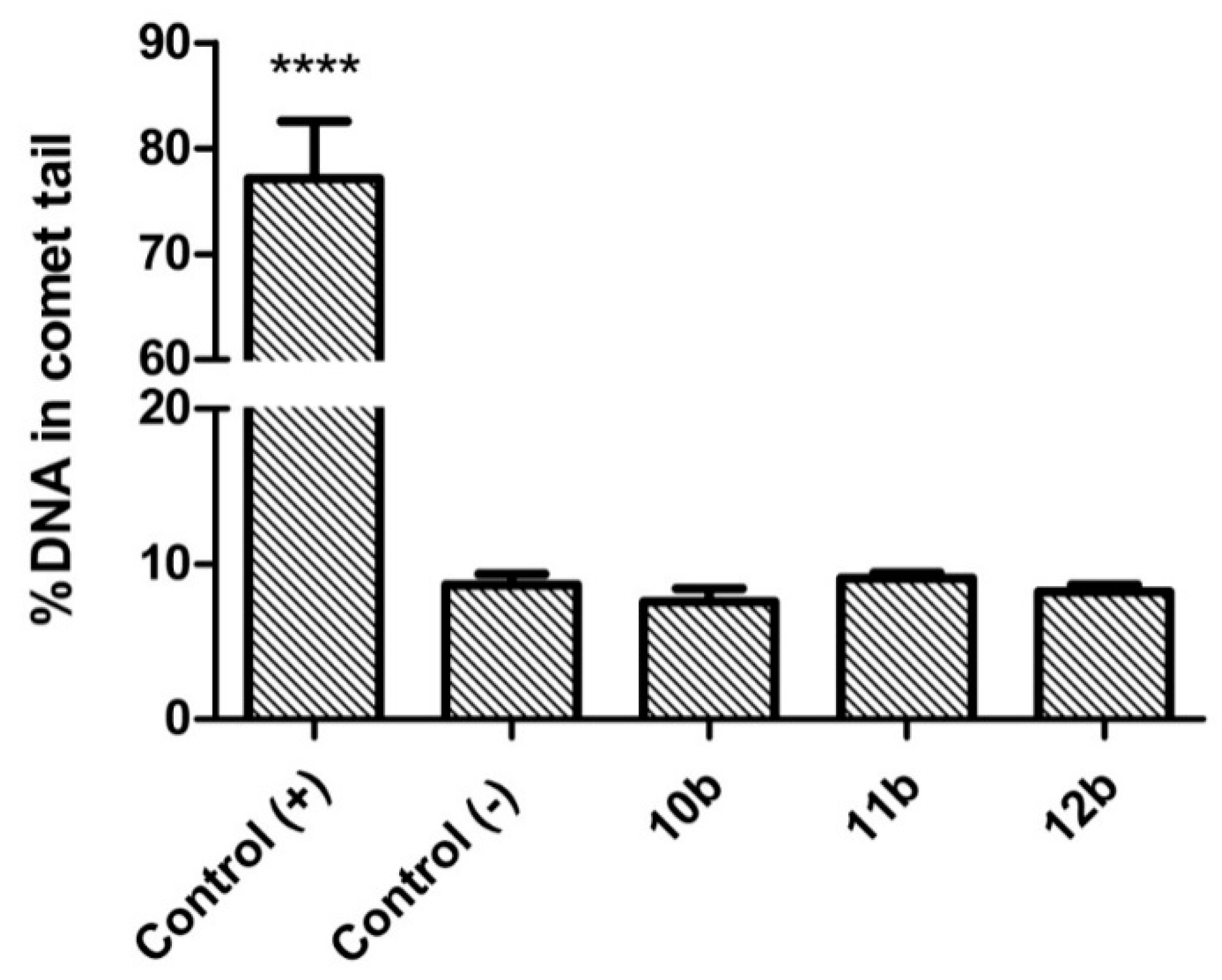
3.3. Genotoxicity
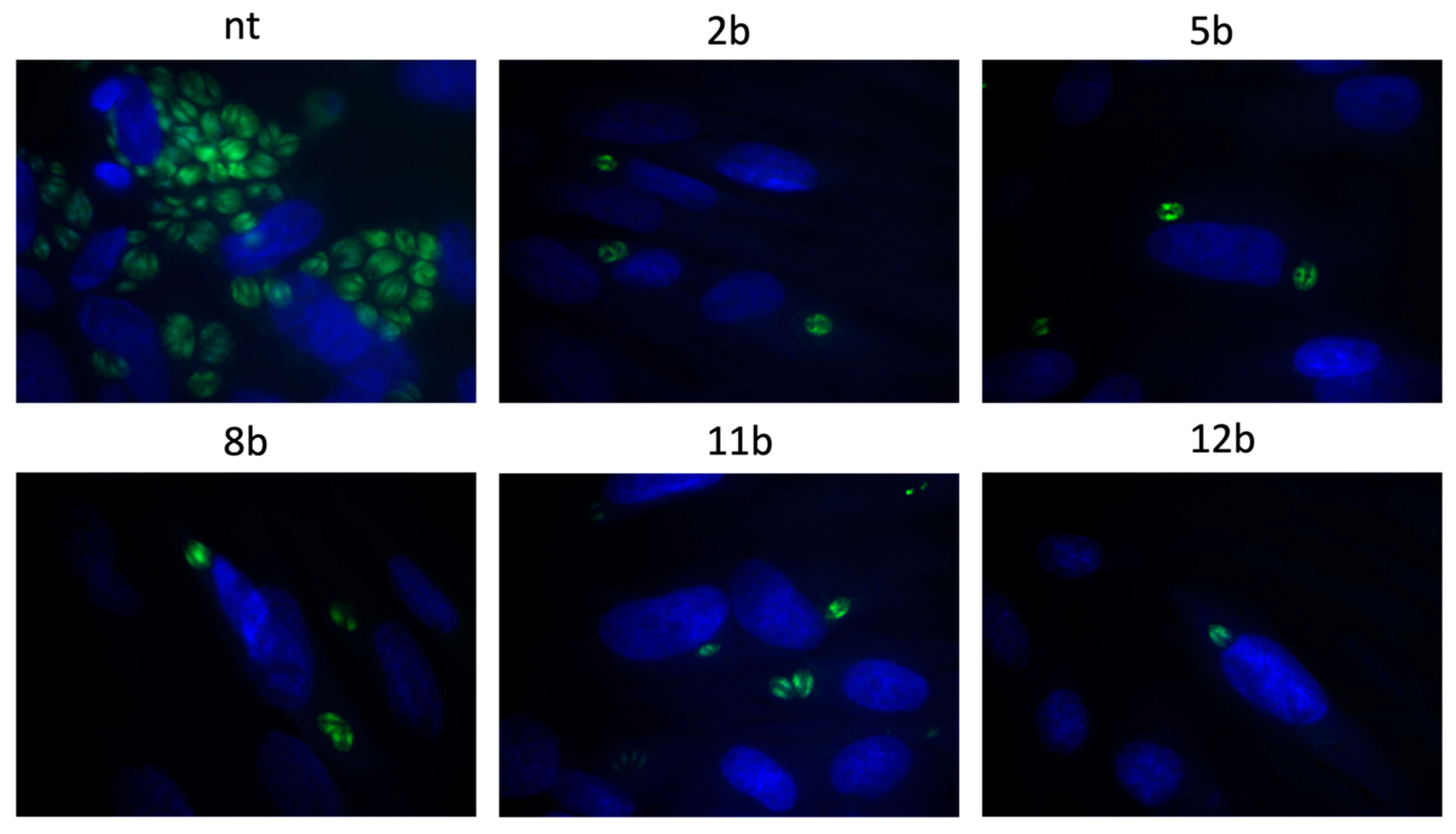
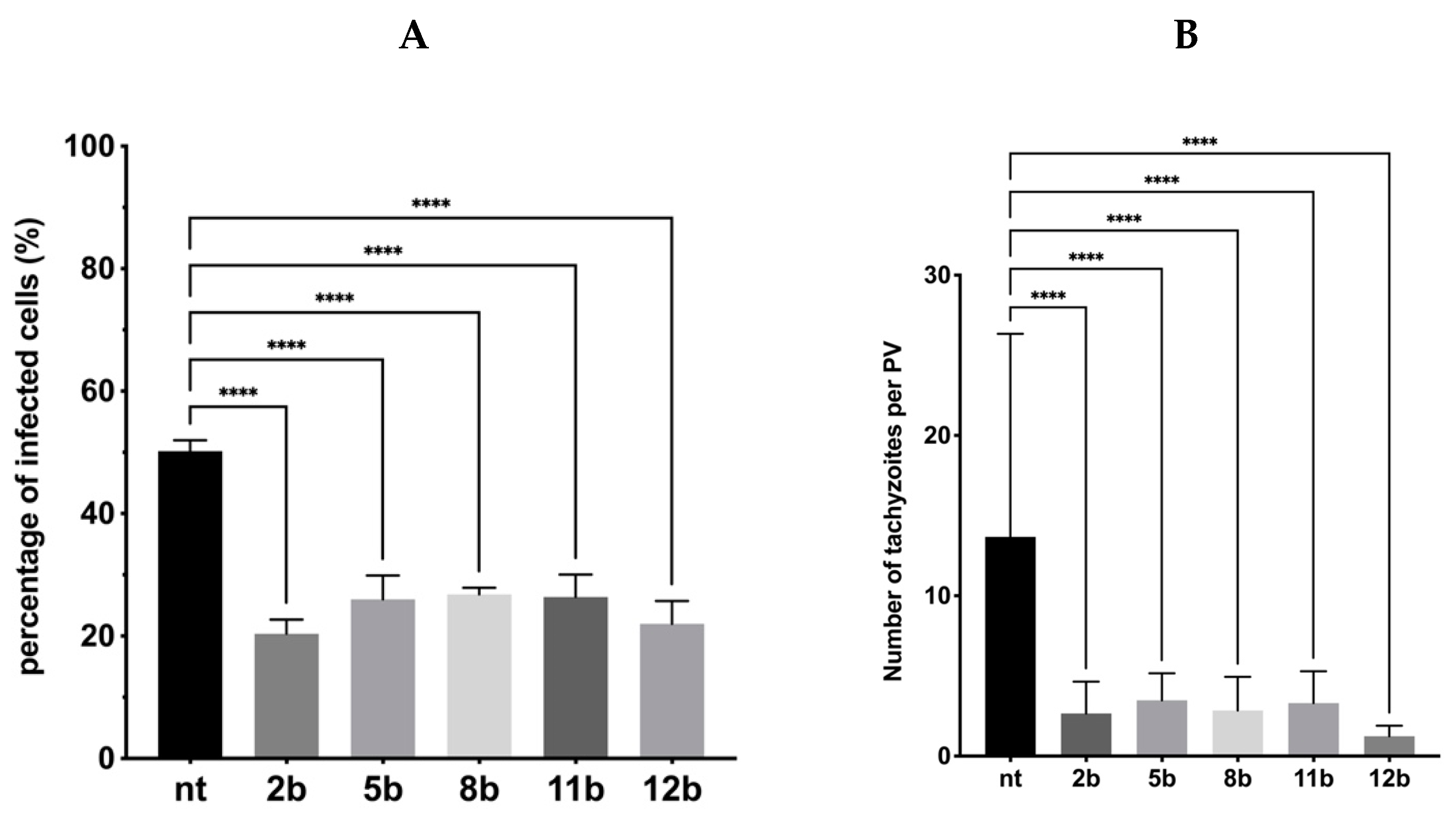
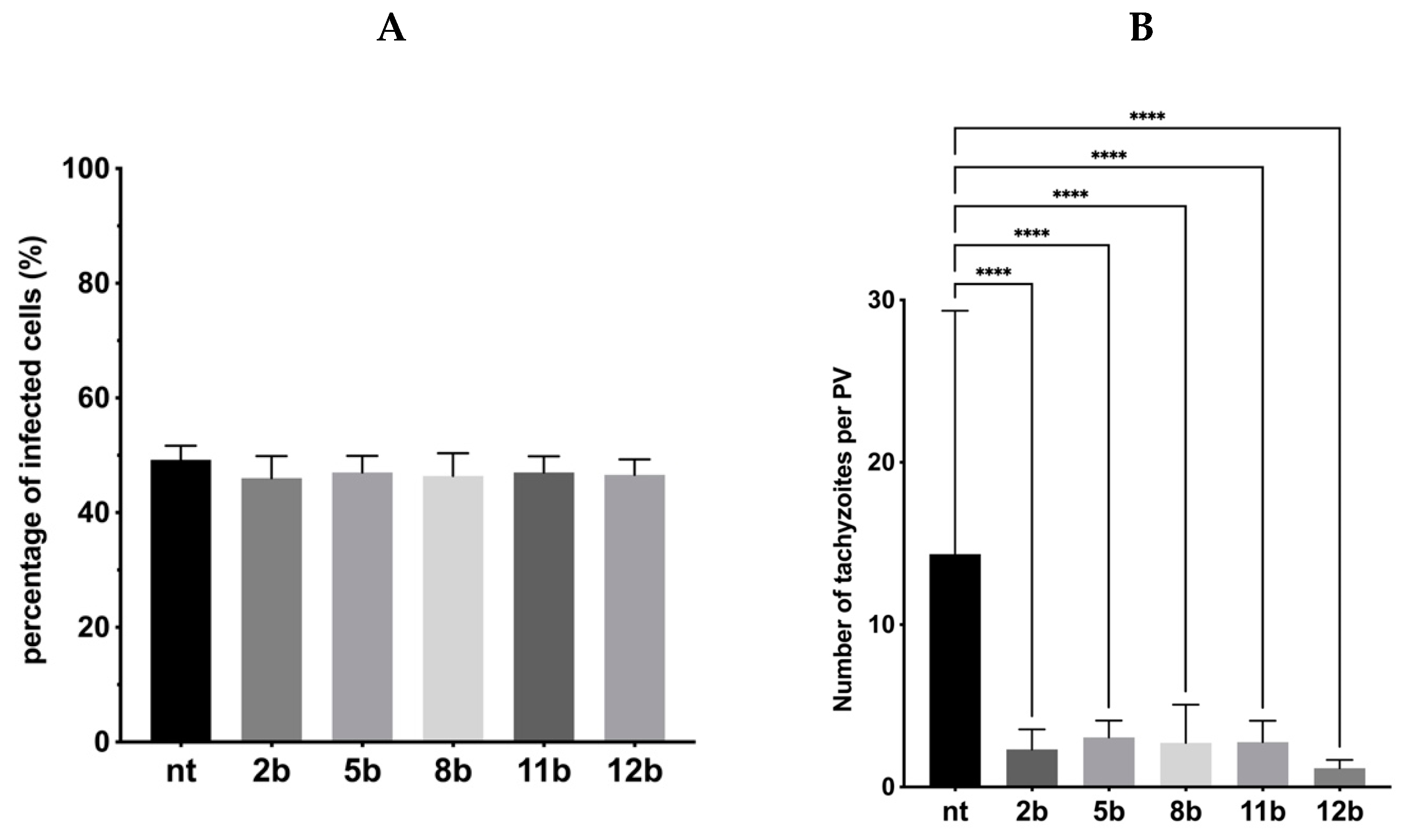
3.4. Influence of the Thiadiazoles during Toxoplasma Growth
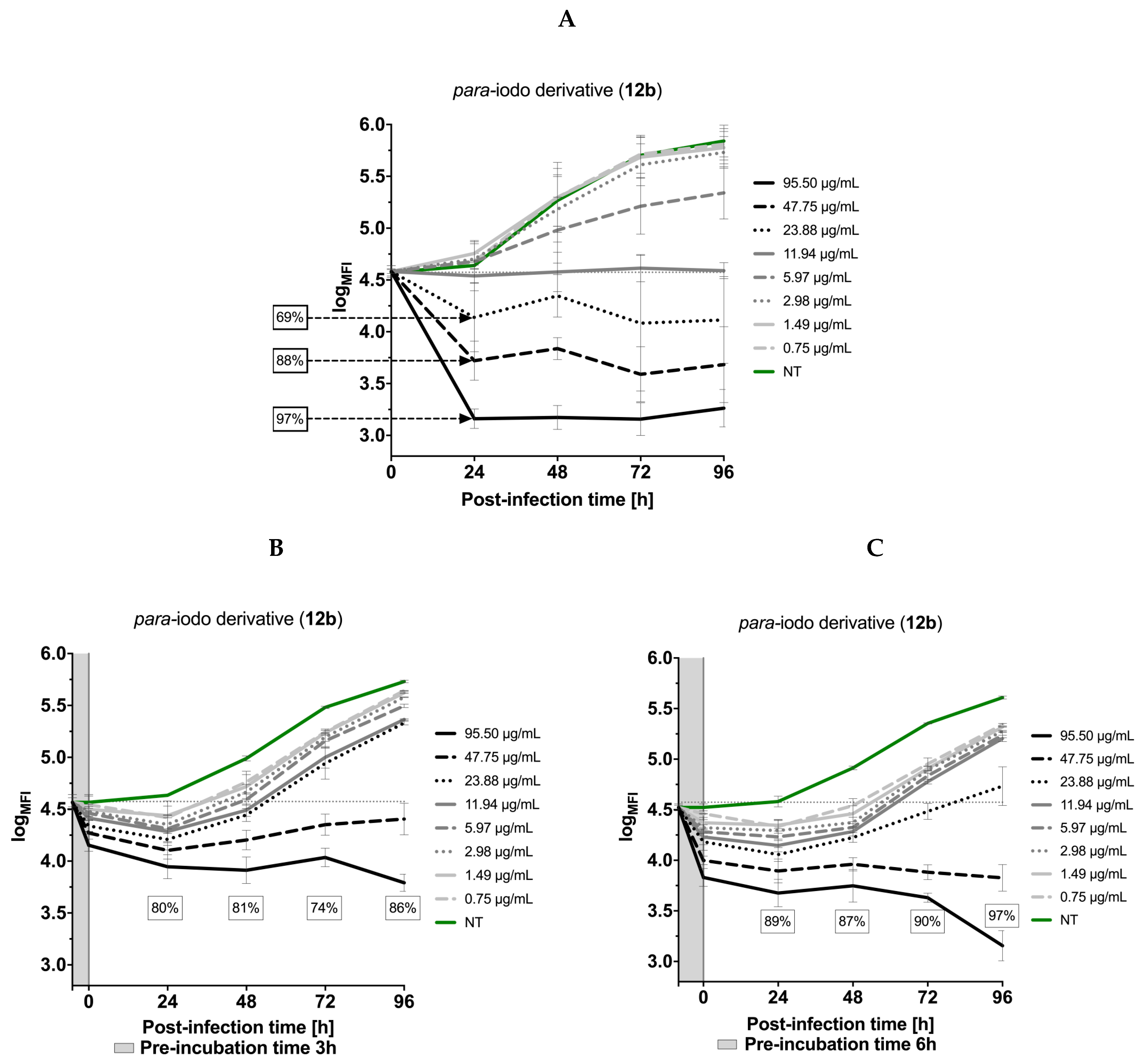
3.5. Effects of the Thiadiazoles on the Kinetics of Toxoplasma gondii Growth
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Webster, J.P.; Dubey, J. Toxoplasmosis of animals and humans. Parasit. Vectors 2010, 3, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hotez, P.J. Neglected parasitic infections and poverty in the United States. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe. The Burden of Foodborne Diseases in the WHO European Region. Available online: https://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0005/402989/50607-WHO-Food-Safety-publicationV4_Web.pdf (accessed on 18 February 2021).
- World Health Organization. WHO Estimates of the Global Burden of Foodborne Diseases. Available online: https://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0011/294599/Factsheet-Toxoplasmosis-en.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 18 February 2021).
- Koutsoumanis, K.; Allende, A.; Alvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Bolton, D.; Bover-Cid, S.; Chemaly, M.; Davies, R.; De Cesare, A.; Herman, L.; Hilbert, F.; et al. Public health risks associated with food-borne parasites. EFSA J. 2018, 16, 5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Yolken, R.H. Strain hypothesis of Toxoplasma gondii infection on the outcome of human diseases. Acta Physiol. 2015, 213, 828–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Opsteegh, M.; Kortbeek, T.M.; Havelaar, A.H.; van der Giessen, J.W. Intervention strategies to reduce human Toxoplasma gondii disease burden. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ballard, A.R. Toxoplasmosis. In Neonatal Infections; Cantey, J., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asproudis, I.; Koumpoulis, I.; Kalogeropoulos, C.; Sotiropoulos, G.; Papassava, M.; Aspiotis, M. Case report of a neonate with ocular toxoplasmosis due to congenital infection: Estimation of the percentage of ocular toxoplasmosis in Greece caused by congenital or acquired infection. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2013, 7, 2249–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eza, D.E.; Lucas, S.B. Fulminant toxoplasmosis causing fatal pneumonitis and myocarditis. HIV Med. 2006, 7, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, L.M.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis: A history of clinical observations. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilbert, R.E.; Stanford, M.R. Is ocular toxoplasmosis caused by prenatal or postnatal infection? Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2000, 84, 224–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yolken, R.; Dickerson, F.; Fuller Torrey, E. Toxoplasma and schizophrenia. Parasite Immunol. 2009, 31, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S. Psychosis may be associated with toxoplasmosis. Med. Hypotheses 2009, 73, 799–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunay, I.R.; Gajurel, K.; Dhakal, R.; Liesenfeld, O.; Montoya, J.G. Treatment of toxoplasmosis: Historical perspective, animal models, and current clinical practice. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00057-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neville, A.J.; Zach, S.J.; Wang, X.; Larson, J.J.; Judge, A.K.; Davis, L.A.; Vennerstrom, J.L.; Davis, P.H. Clinically available medicines demonstrating anti-Toxoplasma activity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 7161–7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Porter, S.B.; Sande, M.A. Toxoplasmosis of the central nervous system in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 327, 1643–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhai, S.Q.; Li, C.H. Recent progress on anti-Toxoplasma drugs discovery: Design, synthesis and screening. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 183, 111711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya, J.G.; Liesenfeld, O. Toxoplasmosis. Lancet 2004, 363, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Singla, L.D.; Zhou, H. Vaccines against Toxoplasma gondii: Status, challenges and future directions. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2012, 8, 1305–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.L.; Zhang, N.Z.; Li, T.T.; He, J.J.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Zhu, X.Q. Advances in the development of anti-Toxoplasma gondii vaccines: Challenges, opportunities, and perspectives. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Innes, E.A.; Bartley, P.M.; Maley, S.; Katzer, F.; Buxton, D. Veterinary vaccines against Toxoplasma gondii. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2009, 104, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montazeri, M.; Mikaeili Galeh, T.; Moosazadeh, M.; Sarvi, S.; Dodangeh, S.; Javidinia, J.; Sharif, M.; Daryani, A. The global serological prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in felids during the last five decades (1967–2017): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montazeri, M.; Mehrzadi, S.; Sharif, M.; Sarvi, S.; Tanzifi, A.; Aghayan, S.A.; Daryani, A. Drug resistance in Toxoplasma gondii. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paneth, A.; Weglinska, L.; Bekier, A.; Stefaniszyn, E.; Wujec, M.; Trotsko, N.; Hawrył, A.; Hawrył, M.; Dzitko, K. Discovery of potent and selective halogen-substituted imidazole-thiosemicarbazides for inhibition of Toxoplasma gondii growth in vitro via structure-based design. Molecules 2019, 24, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liesen, A.P.; de Aquino, T.M.; Carvalho, C.S.; Lima, V.T.; de Araújo, J.M.; de Lima, J.G.; de Faria, A.R.; de Melo, E.J.T.; Alves, A.J.; Alves, E.W.; et al. Synthesis and evaluation of anti-Toxoplasma gondii and antimicrobial activities of thiosemicarbazides, 4-thiazolidinones and 1,3,4-thiadiazoles. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 3685–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siwek, A.; Wujec, M.; Dobosz, M.; Wawrzycka-Gorczyca, I. Study of direction of cyclization of 1-azolil-4-aryl/alkyl-thiosemicarbazides. Heteroat. Chem. 2010, 21, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.E.; Dubey, J.P. 3-Update on Toxoplasma gondii as a parasite in food: Analysis and control. Adv. Microb. Food Saf. 2015, 2, 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mzabi, A.; Aubert, D.; Villena, I. Mechanisms of drug resistance in Toxoplasma gondii. In Antimicrobial Drug Resistance; Mayers, D.L., Sobel, J.D., Ouellette, M., Kaye, K.S., Marchaim, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 677–684. [Google Scholar]
- Molefe, N.I.; Yamasaki, S.; Macalanda, A.M.C.; Suganuma, K.; Watanabe, K.; Xuan, X.; Inoue, N. Oral administration of azithromycin ameliorates trypanosomosis in Trypanosoma congolense-infected mice. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 2407–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonhomme, A.; Bouchot, A.; Pezzella, N.; Gomez, J.; Le Moal, H.; Pinon, J.M. Signaling during the invasion of host cells by Toxoplasma gondii. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 23, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hencken, C.P.; Jones-Brando, L.; Bordón, C.; Stohler, R.; Mott, B.T.; Yolken, R.; Posner, G.H.; Woodard, L.E. Thiazole, oxadiazole, and carboxamide derivatives of artemisinin are highly selective and potent inhibitors of Toxoplasma gondii. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 3594–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Węglińska, L.; Bekier, A.; Dzitko, K.; Pacholczyk-Sienicka, B.; Albrecht, Ł.; Plech, T.; Paneth, P.; Paneth, A. 1,3,4-Thiadiazoles Effectively Inhibit Proliferation of Toxoplasma gondii. Cells 2021, 10, 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051053
Węglińska L, Bekier A, Dzitko K, Pacholczyk-Sienicka B, Albrecht Ł, Plech T, Paneth P, Paneth A. 1,3,4-Thiadiazoles Effectively Inhibit Proliferation of Toxoplasma gondii. Cells. 2021; 10(5):1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051053
Chicago/Turabian StyleWęglińska, Lidia, Adrian Bekier, Katarzyna Dzitko, Barbara Pacholczyk-Sienicka, Łukasz Albrecht, Tomasz Plech, Piotr Paneth, and Agata Paneth. 2021. "1,3,4-Thiadiazoles Effectively Inhibit Proliferation of Toxoplasma gondii" Cells 10, no. 5: 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051053
APA StyleWęglińska, L., Bekier, A., Dzitko, K., Pacholczyk-Sienicka, B., Albrecht, Ł., Plech, T., Paneth, P., & Paneth, A. (2021). 1,3,4-Thiadiazoles Effectively Inhibit Proliferation of Toxoplasma gondii. Cells, 10(5), 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051053






