Neuronal and Astrocytic Extracellular Vesicle Biomarkers in Blood Reflect Brain Pathology in Mouse Models of Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
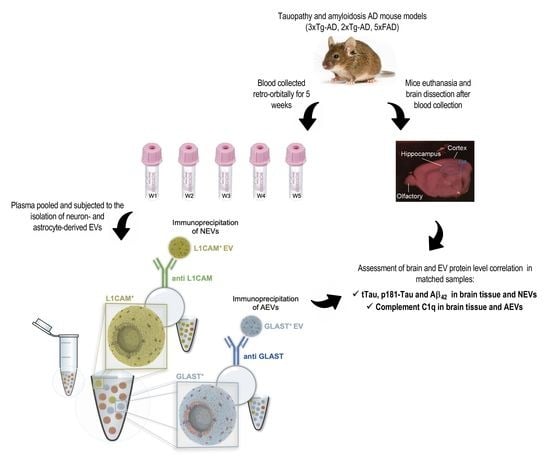
2.1. Mice
2.2. Plasma and Brain Sample Collection and Processing
2.3. Isolation of NEVs and AEVs
2.4. EV Characterization
2.5. Quantification of Analytes
2.6. tTau and p181-Tau Immunoblotting and Immunohistochemistry
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of EVs
3.2. Total Tau and p181-Tau Levels in NEVs from 3xTg-AD Mice Are Elevated and Correlated with Brain Levels
3.3. Aβ42 Levels in NEVs from 5xFAD Mice Are Elevated and Correlated with Brain Levels
3.4. C1q Levels Are Elevated in AEVs of 3xTg-AD Mice and Exhibit a Positive Correlation with Brain Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jellinger, K.A.; Bancher, C. Neuropathology of Alzheimer’s disease: A critical update. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 1998, 54, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, P.T.; Braak, H.; Markesbery, W.R. Neuropathology and cognitive impairment in Alzheimer disease: A complex but coherent relationship. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 68, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, K.; O’Bryant, S.E.; Hampel, H.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Montine, T.J.; Jeromin, A.; Blennow, K.; Lonneborg, A.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Soares, H.; et al. The future of blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2014, 10, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, A.F. Extracellular Vesicles and Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 9269–9273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieu, M.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Lavieu, G.; Thery, C. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegtel, D.M.; Gould, S.J. Exosomes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 487–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, D.J.; Mengel, D.; Mustapic, M.; Liu, W.; Selkoe, D.J.; Kapogiannis, D.; Galasko, D.; Rissman, R.A.; Bennett, D.A.; Walsh, D.M. miR-212 and miR-132 Are Downregulated in Neurally Derived Plasma Exosomes of Alzheimer’s Patients. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapic, M.; Eitan, E.; Werner, J.K., Jr.; Berkowitz, S.T.; Lazaropoulos, M.P.; Tran, J.; Goetzl, E.J.; Kapogiannis, D. Plasma Extracellular Vesicles Enriched for Neuronal Origin: A Potential Window into Brain Pathologic Processes. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulliam, L.; Sun, B.; Mustapic, M.; Chawla, S.; Kapogiannis, D. Plasma neuronal exosomes serve as biomarkers of cognitive impairment in HIV infection and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurovirol. 2019, 25, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Sheng, L.; Stewart, T.; Zabetian, C.P.; Zhang, J. New windows into the brain: Central nervous system-derived extracellular vesicles in blood. Prog. Neurobiol. 2019, 175, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiandaca, M.S.; Kapogiannis, D.; Mapstone, M.; Boxer, A.; Eitan, E.; Schwartz, J.B.; Abner, E.L.; Petersen, R.C.; Federoff, H.J.; Miller, B.L.; et al. Identification of preclinical Alzheimer’s disease by a profile of pathogenic proteins in neurally derived blood exosomes: A case-control study. Alzheimers Dement. 2015, 11, 600–607.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasca, C.; Dobbin, J.; Bigio, B.; Watson, K.; de Angelis, P.; Kautz, M.; Cochran, A.; Mathe, A.A.; Kocsis, J.H.; Lee, F.S.; et al. Insulin receptor substrate in brain-enriched exosomes in subjects with major depression: On the path of creation of biosignatures of central insulin resistance. Mol. Psychiatry 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Qiu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Chu, L.; Du, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, C.; Liang, F.; Shi, S.; Wang, S.; et al. Concordance between the assessment of Abeta42, T-tau, and P-T181-tau in peripheral blood neuronal-derived exosomes and cerebrospinal fluid. Alzheimers Dement. 2019, 15, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetzl, E.J.; Schwartz, J.B.; Abner, E.L.; Jicha, G.A.; Kapogiannis, D. High complement levels in astrocyte-derived exosomes of Alzheimer disease. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetzl, E.J.; Mustapic, M.; Kapogiannis, D.; Eitan, E.; Lobach, I.V.; Goetzl, L.; Schwartz, J.B.; Miller, B.L. Cargo proteins of plasma astrocyte-derived exosomes in Alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 3853–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapogiannis, D.; Mustapic, M.; Shardell, M.D.; Berkowitz, S.T.; Diehl, T.C.; Spangler, R.D.; Tran, J.; Lazaropoulos, M.P.; Chawla, S.; Gulyani, S.; et al. Association of Extracellular Vesicle Biomarkers With Alzheimer Disease in the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. JAMA Neurol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Borgmann, K.; Edara, V.V.; Stacy, S.; Ghorpade, A.; Ikezu, T. Activated human astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles modulate neuronal uptake, differentiation and firing. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1706801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, E.; Hunt, J.F.V.; Shardell, M.; Chawla, S.; Tran, J.; Gu, J.; Vogt, N.M.; Johnson, S.C.; Bendlin, B.B.; Kapogiannis, D. Extracellular vesicle biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease associated with sub-clinical cognitive decline in late middle age. Alzheimers Dement. 2020, 16, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaFerla, F.M.; Green, K.N. Animal models of Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaguri, H.; Nilsson, P.; Hashimoto, S.; Nagata, K.; Saito, T.; De Strooper, B.; Hardy, J.; Vassar, R.; Winblad, B.; Saido, T.C. APP mouse models for Alzheimer’s disease preclinical studies. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 2473–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullane, K.; Williams, M. Preclinical Models of Alzheimer’s Disease: Relevance and Translational Validity. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2019, 84, e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankowsky, J.L.; Slunt, H.H.; Ratovitski, T.; Jenkins, N.A.; Copeland, N.G.; Borchelt, D.R. Co-expression of multiple transgenes in mouse CNS: A comparison of strategies. Biomol. Eng. 2001, 17, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowsky, J.L.; Fadale, D.J.; Anderson, J.; Xu, G.M.; Gonzales, V.; Jenkins, N.A.; Copeland, N.G.; Lee, M.K.; Younkin, L.H.; Wagner, S.L.; et al. Mutant presenilins specifically elevate the levels of the 42 residue beta-amyloid peptide in vivo: Evidence for augmentation of a 42-specific gamma secretase. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oddo, S.; Caccamo, A.; Shepherd, J.D.; Murphy, M.P.; Golde, T.E.; Kayed, R.; Metherate, R.; Mattson, M.P.; Akbari, Y.; LaFerla, F.M. Triple-transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease with plaques and tangles: Intracellular Abeta and synaptic dysfunction. Neuron 2003, 39, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawhar, S.; Trawicka, A.; Jenneckens, C.; Bayer, T.A.; Wirths, O. Motor deficits, neuron loss, and reduced anxiety coinciding with axonal degeneration and intraneuronal Abeta aggregation in the 5XFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 196.e129–196.e140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, B.C.; Kurdakova, A.; Baches, S.; Bayer, T.A.; Weggen, S.; Wirths, O. Gene Dosage Dependent Aggravation of the Neurological Phenotype in the 5XFAD Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 45, 1223–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holcomb, L.; Gordon, M.N.; McGowan, E.; Yu, X.; Benkovic, S.; Jantzen, P.; Wright, K.; Saad, I.; Mueller, R.; Morgan, D.; et al. Accelerated Alzheimer-type phenotype in transgenic mice carrying both mutant amyloid precursor protein and presenilin 1 transgenes. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, H.; Cole, S.L.; Logan, S.; Maus, E.; Shao, P.; Craft, J.; Guillozet-Bongaarts, A.; Ohno, M.; Disterhoft, J.; Van Eldik, L.; et al. Intraneuronal beta-amyloid aggregates, neurodegeneration, and neuron loss in transgenic mice with five familial Alzheimer’s disease mutations: Potential factors in amyloid plaque formation. J Neurosci. 2006, 26, 10129–10140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Dejanovic, B.; Gandham, V.D.; Gogineni, A.; Edmonds, R.; Schauer, S.; Srinivasan, K.; Huntley, M.A.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.M.; et al. Complement C3 Is Activated in Human AD Brain and Is Required for Neurodegeneration in Mouse Models of Amyloidosis and Tauopathy. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 2111–2123.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witwer, K.W.; Buzas, E.I.; Bemis, L.T.; Bora, A.; Lasser, C.; Lotvall, J.; Nolte-’t Hoen, E.N.; Piper, M.G.; Sivaraman, S.; Skog, J.; et al. Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coumans, F.A.W.; Brisson, A.R.; Buzas, E.I.; Dignat-George, F.; Drees, E.E.E.; El-Andaloussi, S.; Emanueli, C.; Gasecka, A.; Hendrix, A.; Hill, A.F.; et al. Methodological Guidelines to Study Extracellular Vesicles. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 1632–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglis, H.; Norris, P.; Danesh, A. Techniques for the analysis of extracellular vesicles using flow cytometry. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrangelo, M.A.; Bowers, W.J. Detailed immunohistochemical characterization of temporal and spatial progression of Alzheimer’s disease-related pathologies in male triple-transgenic mice. BMC Neurosci. 2008, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Pitta, M.; Lee, J.H.; Ray, B.; Lahiri, D.K.; Furukawa, K.; Mughal, M.; Jiang, H.; Villarreal, J.; Cutler, R.G.; et al. The KATP channel activator diazoxide ameliorates amyloid-beta and tau pathologies and improves memory in the 3xTgAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 22, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Lu, H.; Stein, E.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, Y.; Mattson, M.P. Brain regional synchronous activity predicts tauopathy in 3xTgAD mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 70, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thery, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oddo, S.; Caccamo, A.; Cheng, D.; Jouleh, B.; Torp, R.; LaFerla, F.M. Genetically augmenting tau levels does not modulate the onset or progression of Abeta pathology in transgenic mice. J. Neurochem. 2007, 102, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, M.; Jakes, R.; Crowther, R.A.; Cohen, P.; Vanmechelen, E.; Vandermeeren, M.; Cras, P. Epitope mapping of monoclonal antibodies to the paired helical filaments of Alzheimer’s disease: Identification of phosphorylation sites in tau protein. Biochem. J. 1994, 301 Pt 3, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janelidze, S.; Mattsson, N.; Palmqvist, S.; Smith, R.; Beach, T.G.; Serrano, G.E.; Chai, X.; Proctor, N.K.; Eichenlaub, U.; Zetterberg, H.; et al. Plasma P-tau181 in Alzheimer’s disease: Relationship to other biomarkers, differential diagnosis, neuropathology and longitudinal progression to Alzheimer’s dementia. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanmechelen, E.; Vanderstichele, H.; Davidsson, P.; Van Kerschaver, E.; Van Der Perre, B.; Sjogren, M.; Andreasen, N.; Blennow, K. Quantification of tau phosphorylated at threonine 181 in human cerebrospinal fluid: A sandwich ELISA with a synthetic phosphopeptide for standardization. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 285, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonknecht, P.; Pantel, J.; Hunt, A.; Volkmann, M.; Buerger, K.; Hampel, H.; Schroder, J. Levels of total tau and tau protein phosphorylated at threonine 181 in patients with incipient and manifest Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 339, 172–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Andersson, E.; Janelidze, S.; Ossenkoppele, R.; Insel, P.; Strandberg, O.; Zetterberg, H.; Rosen, H.J.; Rabinovici, G.; Chai, X.; et al. Aβ deposition is associated with increases in soluble and phosphorylated tau that precede a positive Tau PET in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petry, F.R.; Pelletier, J.; Bretteville, A.; Morin, F.; Calon, F.; Hebert, S.S.; Whittington, R.A.; Planel, E. Specificity of anti-tau antibodies when analyzing mice models of Alzheimer’s disease: Problems and solutions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsuhashi, M.; Taub, D.D.; Kapogiannis, D.; Eitan, E.; Zukley, L.; Mattson, M.P.; Ferrucci, L.; Schwartz, J.B.; Goetzl, E.J. Aging enhances release of exosomal cytokine mRNAs by Abeta1-42-stimulated macrophages. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 5141–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Nie, S.; Cao, M.; Marshall, C.; Gao, J.; Xiao, N.; Hu, G.; Xiao, M. Characterization of AD-like phenotype in aged APPSwe/PS1dE9 mice. Age 2016, 38, 303–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.M.; Lee, S.; Yang, S.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, M.J.; Kim, H.V.; Kim, J.; Baek, S.; Yun, J.; Kim, D.; et al. Age-dependent inverse correlations in CSF and plasma amyloid-beta(1-42) concentrations prior to amyloid plaque deposition in the brain of 3xTg-AD mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eitan, E.; Hutchison, E.R.; Marosi, K.; Comotto, J.; Mustapic, M.; Nigam, S.M.; Suire, C.; Maharana, C.; Jicha, G.A.; Liu, D.; et al. Extracellular Vesicle-Associated Abeta Mediates Trans-Neuronal Bioenergetic and Ca(2+)-Handling Deficits in Alzheimer’s Disease Models. NPJ Aging Mech. Dis. 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polanco, J.C.; Scicluna, B.J.; Hill, A.F.; Gotz, J. Extracellular Vesicles Isolated from the Brains of rTg4510 Mice Seed Tau Protein Aggregation in a Threshold-dependent Manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 12445–12466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, S.; Polanco, J.C.; Gotz, J. Extracellular Vesicles Containing P301L Mutant Tau Accelerate Pathological Tau Phosphorylation and Oligomer Formation but Do Not Seed Mature Neurofibrillary Tangles in ALZ17 Mice. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2016, 54, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinkins, M.B.; Dasgupta, S.; Wang, G.; Zhu, G.; Bieberich, E. Exosome reduction in vivo is associated with lower amyloid plaque load in the 5XFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 1792–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardar Sinha, M.; Ansell-Schultz, A.; Civitelli, L.; Hildesjo, C.; Larsson, M.; Lannfelt, L.; Ingelsson, M.; Hallbeck, M. Alzheimer’s disease pathology propagation by exosomes containing toxic amyloid-beta oligomers. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 136, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.T.; Watts, K.D.; Tailor, P.; Nguyen, T.P.; Howell, J.C.; Lee, R.C.; Seyfried, N.T.; Gearing, M.; Hales, C.M.; Levey, A.I.; et al. CSF complement 3 and factor H are staging biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2016, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, B.P. Complement in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Semin. Immunopathol. 2018, 40, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueras-Ortiz, C.J.; Mahairaki, V.; Delgado-Peraza, F.; Das, D.; Avgerinos, K.; Eren, E.; Hentschel, M.; Goetzl, E.J.; Mattson, M.P.; Kapogiannis, D. Astrocyte- and Neuron-Derived Extracellular Vesicles from Alzheimer’s Disease Patients Effect Complement-Mediated Neurotoxicity. Cells 2020, 9, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Beja-Glasser, V.F.; Nfonoyim, B.M.; Frouin, A.; Li, S.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Merry, K.M.; Shi, Q.; Rosenthal, A.; Barres, B.A.; et al. Complement and microglia mediate early synapse loss in Alzheimer mouse models. Science 2016, 352, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, A.H.; Barres, B.A.; Stevens, B. The complement system: An unexpected role in synaptic pruning during development and disease. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 35, 369–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vella, L.J.; Scicluna, B.J.; Cheng, L.; Bawden, E.G.; Masters, C.L.; Ang, C.S.; Willamson, N.; McLean, C.; Barnham, K.J.; Hill, A.F. A rigorous method to enrich for exosomes from brain tissue. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2017, 6, 1348885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Z.; Pathak, D.; Venkatesan Kalavai, S.; Yoshii-Kitahara, A.; Muraoka, S.; Bhatt, N.; Takamatsu-Yukawa, K.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Hersh, S.; et al. Alzheimer’s disease brain-derived extracellular vesicles spread tau pathology in interneurons. Brain J. Neurol. 2021, 144, 288–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Goetzl, E.J.; Kapogiannis, D.; Lista, S.; Vergallo, A. Biomarker-Drug and Liquid Biopsy Co-development for Disease Staging and Targeted Therapy: Cornerstones for Alzheimer’s Precision Medicine and Pharmacology. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapic, M.; Tran, J.; Craft, S.; Kapogiannis, D. Extracellular Vesicle Biomarkers Track Cognitive Changes Following Intranasal Insulin in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 69, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Delgado-Peraza, F.; Nogueras-Ortiz, C.J.; Volpert, O.; Liu, D.; Goetzl, E.J.; Mattson, M.P.; Greig, N.H.; Eitan, E.; Kapogiannis, D. Neuronal and Astrocytic Extracellular Vesicle Biomarkers in Blood Reflect Brain Pathology in Mouse Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. Cells 2021, 10, 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10050993
Delgado-Peraza F, Nogueras-Ortiz CJ, Volpert O, Liu D, Goetzl EJ, Mattson MP, Greig NH, Eitan E, Kapogiannis D. Neuronal and Astrocytic Extracellular Vesicle Biomarkers in Blood Reflect Brain Pathology in Mouse Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. Cells. 2021; 10(5):993. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10050993
Chicago/Turabian StyleDelgado-Peraza, Francheska, Carlos J. Nogueras-Ortiz, Olga Volpert, Dong Liu, Edward J. Goetzl, Mark P. Mattson, Nigel H. Greig, Erez Eitan, and Dimitrios Kapogiannis. 2021. "Neuronal and Astrocytic Extracellular Vesicle Biomarkers in Blood Reflect Brain Pathology in Mouse Models of Alzheimer’s Disease" Cells 10, no. 5: 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10050993
APA StyleDelgado-Peraza, F., Nogueras-Ortiz, C. J., Volpert, O., Liu, D., Goetzl, E. J., Mattson, M. P., Greig, N. H., Eitan, E., & Kapogiannis, D. (2021). Neuronal and Astrocytic Extracellular Vesicle Biomarkers in Blood Reflect Brain Pathology in Mouse Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. Cells, 10(5), 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10050993