The Interplay between the Immune and the Endocannabinoid Systems in Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
2.1. Receptors
Other Endocannabinoidome Receptors
2.2. Enzymes
3. Cannabinoids and Tumorigenesis
4. The Endocannabinoid System as Gate-Keeper of the Immune System
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2-AG | 2-arachidonoylglycerol |
| AEA or anandamide | N-arachidonoylethanolamide |
| ANGPT | angiopoietin |
| APC | antigen-presenting cell |
| B cell | B lymphocyte |
| BAD | BCL2 associated agonist of cell death |
| BMMC | bone-marrow-derived mast cell |
| cAMP | cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| CB | cannabinoid |
| CBD | cannabidiol |
| Cdk | cyclin-dependent kinase |
| CLL | chronic lymphocytic leukemia |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| COX | cyclooxygenase |
| CSC | cancer stem cells |
| CXCR4 | C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 |
| DC | dendritic cell |
| EC | endocannabinoid |
| ECS | endocannabinoid system |
| EGF | epidermal growth factor |
| EMT | epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| ERK | extracellular receptor kinase |
| FAAH | fatty acid amide hydrolase |
| GCS | glioblastoma stem-like cells |
| HGF | hepatocyte growth factor |
| HLM | human lung macrophage |
| IFN | interferon |
| IL | interleukin |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MAGL | monoacylglycerol lipase |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MCL | mantle cell lymphoma |
| MCs | mast cells |
| MDM | monocyte-derived macrophage |
| MMP | matrix metalloproteinase |
| NK cell | natural killer cell |
| OEA | oleoylethanolamide |
| pDC | plasmacytoid dendritic cell |
| PEA | palmitoylethanolamide |
| PI3K | phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| PKB | pro-tumorigenic protein kinase B |
| PIGF | placental growth factor |
| PMN | neutrophil |
| PPAR | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SCB | synthetic cannabinoid |
| T cell | T lymphocyte |
| Th cell | T helper cell |
| TIMP | tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases |
| TLR | toll-like receptor |
| TME | tumor microenvironment |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| TRB3 | Tribbles homolog 3 |
| TRP | transient receptor potential channels |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| Δ9-THC | Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. |
References
- Jiang, H.-E.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.-X.; Ferguson, D.K.; Hueber, F.; Bera, S.; Wang, Y.-F.; Zhao, L.-C.; Liu, C.-J.; Li, C.-S. A new insight into Cannabis sativa (Cannabaceae) utilization from 2500-year-old Yanghai Tombs, Xinjiang, China. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 108, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touw, M. The Religious and Medicinal Uses of Cannabis in China, India and Tibet. J. Psychoact. Drugs 1981, 13, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisanti, S.; Bifulco, M. MedicalCannabis: A plurimillennial history of an evergreen. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 8342–8351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, S.; Shekher, A.; Puneet; Narula, A.S.; Abrahamse, H.; Gupta, S.C. Cannabis and its constituents for cancer: History, biogenesis, chemistry and pharmacological activities. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 163, 105302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.M.; Adinoff, B. The Classification of Substance Use Disorders: Historical, Contextual, and Conceptual Considerations. Behav. Sci. 2016, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuardi, A.W. History of cannabis as a medicine: A review. Rev. Bras. Psiquiatr. 2006, 28, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pisanti, S.; Bifulco, M. Modern History of Medical Cannabis: From Widespread Use to Prohibitionism and Back. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bifulco, M.; Pisanti, S. Pisanti. Medicinal Use of Cannabis in Europe: The Fact That More Countries Legalize the Medicinal Use of Cannabis Should Not Become an Argument for Unfettered and Uncontrolled Use. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 130–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ko, G.D.; Bober, S.L.; Mindra, S.; Moreau, J.M. Medical cannabis – the Canadian perspective. J. Pain Res. 2016, 9, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuda, L.A.; Lolait, S.J.; Brownstein, M.J.; Young, A.C.; Bonner, T.I. Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nat. Cell Biol. 1990, 346, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, S.; Thomas, K.L.; Abu-Shaar, M. Molecular characterization of a peripheral receptor for cannabinoids. Nat. Cell Biol. 1993, 365, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devane, W.A.; Hanus, L.; Breuer, A.; Pertwee, R.G.; Stevenson, L.A.; Griffin, G.; Gibson, D.; Mandelbaum, A.; Etinger, A.; Mechoulam, R. Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor. Science 1992, 258, 1946–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechoulam, R.; Ben-Shabat, S.; Hanus, L.; Ligumsky, M.; Kaminski, N.E.; Schatz, A.R.; Gopher, A.; Almog, S.; Martin, B.R.; Compton, D.R.; et al. Identification of an Endogenous 2-Monoglyceride, Present in Canine Gut, That Binds to Canna-binoid Receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995, 50, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, T.; Kondo, S.; Sukagawa, A.; Nakane, S.; Shinoda, A.; Itoh, K.; Yamashita, A.; Waku, K. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol: A Possible Endogenous Cannabinoid Receptor Ligand in Brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 215, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marzo, V.; Fontana, A. Anandamide, an endogenous cannabinomimetic eicosanoid: ‘Killing two birds with one stone. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 1995, 53, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisogno, T.; Howell, F.; Williams, G.; Minassi, A.; Cascio, M.G.; Ligresti, A.; Matias, I.; Schiano-Moriello, A.; Paul, P.; Williams, E.-J.; et al. Cloning of the first sn1-DAG lipases points to the spatial and temporal regulation of endocannabinoid signaling in the brain. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 163, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cravatt, B.F.; Giang, D.K.; Mayfield, S.P.; Boger, D.L.; Lerner, R.A.; Gilula, N.B. Molecular characterization of an enzyme that degrades neuromodulatory fatty-acid amides. Nat. Cell Biol. 1996, 384, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristino, L.; Bisogno, T.; Di Marzo, V. Cannabinoids and the expanded endocannabinoid system in neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, C.M.; Hausman, J.-F.; Guerriero, G. Cannabis sativa: The Plant of the Thousand and One Molecules. Front. Plant. Sci. 2016, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mechoulam, R.; Hanuš, L. A historical overview of chemical research on cannabinoids. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2000, 108, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boychuk, D.G.; Goddard, G.; Mauro, G.; Orellana, M.F. The effectiveness of cannabinoids in the management of chronic nonmalignant neuropathic pain: A systematic review. J. Oral Facial Pain Headache 2015, 29, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pomorska, D.K.; Do-Rego, J.-C.; Do-Rego, J.-L.; Zubrzycka, M.; Janecka, A. Opioid and Cannabinoid System in Food Intake. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dujourdy, L.; Besacier, F. A study of cannabis potency in France over a 25 years period (1992–2016). Forensic Sci. Int. 2017, 272, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzo, A.A.; Borrelli, F.; Capasso, R.; Di Marzo, V.; Mechoulam, R. Non-psychotropic plant cannabinoids: New therapeutic opportunities from an ancient herb. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stinchcomb, A.L.; Valiveti, S.; Hammell, D.C.; Ramsey, D.R. Human Skin Permeation of Del-ta8-Tetrahydrocannabinol, Cannabidiol and Cannabinol. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2004, 56, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechoulam, R.; Peters, M.; Murillo-Rodriguez, E.; Hanus, L.O. Cannabidiol--Recent Advances. Chem. Biodivers. 2007, 4, 1678–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espejo-Porras, F.; Fernández-Ruiz, J.; Pertwee, R.G.; Mechoulam, R.; García, C. Motor effects of the non-psychotropic phytocannabinoid cannabidiol that are mediated by 5-HT1A receptors. Neuropharmacology 2013, 75, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumińska, A.; Dobrzyń, A. The endocannabinoid system and its role in regulation of metabolism in peripheral tissues. Postępy Biochemii 2012, 58, 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Staiano, R.I.; Loffredo, S.; Borriello, F.; Iannotti, F.A.; Piscitelli, F.; Orlando, P.; Secondo, A.; Granata, F.; Lepore, M.T.; Fiorelli, A.; et al. Human lung-resident macrophages express CB1 and CB2 receptors whose activation inhibits the release of angiogenic and lymphangiogenic factors. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 99, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.-Y.T.; Karoum, F.; Felder, C.; Badger, H.; Wang, T.-C.L.; Markey, S.P. GC/MS Analysis of Anandamide and Quantification of N-Arachidonoylphosphatidylethanolamides in Various Brain Regions, Spinal Cord, Testis, and Spleen of the Rat. J. Neurochem. 2008, 72, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beltramo, M.; Stella, N.; Calignano, A.; Lin, S.Y.; Makriyannis, A.; Piomelli, D. Functional Role of High-Affinity Anandamide Transport, as Revealed by Selective Inhibition. Science 1997, 277, 1094–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Marzo, V.; Fontana, A.; Cadas, H.; Schinelli, S.; Cimino, G.; Schwartz, J.-C.; Piomelli, D. Formation and inactivation of endogenous cannabinoid anandamide in central neurons. Nat. Cell Biol. 1994, 372, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.I.; Sobocinska, A.A.; Czarnecka, A.M.; Krol, M.; Botta, B.; Szczylik, C. The Therapeutic Aspects of the En-docannabinoid System (Ecs) for Cancer and Their Development: From Nature to Laboratory. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 1756–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galiegue, S.; Mary, S.; Marchand, J.; Dussossoy, D.; Carriere, D.; Carayon, P.; Bouaboula, M.; Shire, D.; le Fur, G.; Ca-sellas, P. Expression of Central and Peripheral Cannabinoid Receptors in Human Immune Tissues and Leukocyte Subpop-ulations. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 232, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, N.; Velmurugan, B.K. Therapeutic applications of cannabinoids. Chem. Interactions 2018, 293, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karwad, M.A.; Macpherson, T.; Wang, B.; Theophilidou, E.; Sarmad, S.; Barrett, D.A.; Larvin, M.; Wright, K.L.; Lund, J.N.; O’Sullivan, S.E. Oleoylethanolamine and Palmitoylethanolamine Modulate Intestinal Permeability in Vitro Via Trpv1 and Pparalpha. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calignano, A.; La Rana, G.; Giuffrida, A.; Piomelli, D. Control of pain initiation by endogenous cannabinoids. Nat. Cell Biol. 1998, 394, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Facci, L.; Toso, R.D.; Romanello, S.; Buriani, A.; Skaper, S.D.; Leon, A. Mast cells express a peripheral cannabinoid receptor with differential sensitivity to anandamide and palmitoylethanolamide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 3376–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiurchiù, V.; Battistini, L.; Maccarrone, M. Endocannabinoid signalling in innate and adaptive immunity. Immunology 2015, 144, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fezza, F.; Bari, M.; Florio, R.; Talamonti, E.; Feole, M.; Maccarrone, M. Endocannabinoids, Related Compounds and Their Metabolic Routes. Molecules 2014, 19, 17078–17106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneto, M.S.; Gorelick, D.A.; Desrosiers, N.A.; Hartman, R.L.; Pirard, S.; Huestis, M.A. Synthetic cannabinoids: Epidemiology, pharmacodynamics, and clinical implications. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014, 144, 12–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walsh, K.B.; Andersen, H.K. Molecular Pharmacology of Synthetic Cannabinoids: Delineating Cb1 Recep-tor-Mediated Cell Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debruyne, D.; Le Boisselier, R. Emerging drugs of abuse: Current perspectives on synthetic cannabinoids. Subst. Abus. Rehabil. 2015, 6, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lauritsen, K.J.; Rosenberg, H. Comparison of Outcome Expectancies for Synthetic Cannabinoids and Botanical Ma-rijuana. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abuse 2016, 42, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacher, P.; Steffens, S.; Haskó, G.; Schindler, T.H.; Kunos, G. Cardiovascular effects of marijuana and synthetic cannabinoids: The good, the bad, and the ugly. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braile, M.; Cristinziano, L.; Marcella, S.; Varricchi, G.; Marone, G.; Modestino, L.; Ferrara, A.L.; De Ciuceis, A.; Scala, S.; Galdiero, M.R.; et al. LPS-mediated neutrophil VEGF-A release is modulated by cannabinoid receptor activation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2021, 109, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, K.; Weinstein, A. The Effects of Cannabinoids on Executive Functions: Evidence from Cannabis and Synthetic Cannabinoids—A Systematic Review. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lossignol, D. Cannabinoids: A new approach for pain control? Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2019, 31, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javid, F.A.; Phillips, R.M.; Afshinjavid, S.; Verde, R.; Ligresti, A. Cannabinoid pharmacology in cancer research: A new hope for cancer patients? Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 775, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraguas-Sánchez, A.I.; Martín-Sabroso, C.; Torres-Suárez, A.I. Insights into the effects of the endocannabinoid system in cancer: A review. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 2566–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McHugh, D.; Tanner, C.; Mechoulam, R.; Pertwee, R.G.; Ross, R.A. Inhibition of Human Neutrophil Chemotaxis by Endogenous Cannabinoids and Phytocannabinoids: Evidence for a Site Distinct from CB1and CB2. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 73, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwood, B.K.; Mackie, K. CB2: A cannabinoid receptor with an identity crisis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pertwee, R.G. Pharmacological Actions of Cannabinoids. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2005, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozzi, A.; Mattei, V.; Martellucci, S.; Manganelli, V.; Saccomanni, G.; Garofalo, T.; Sorice, M.; Manera, C.; Misasi, R. Anti-Proliferative Properties and Proapoptotic Function of New CB2 Selective Cannabinoid Receptor Agonist in Jurkat Leukemia Cells. Int. J. Mol. Science 2018, 19, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carpi, S.; Fogli, S.; Polini, B.; Montagnani, V.; Podesta, A.; Breschi, M.C.; Romanini, A.; Stecca, B.; Nieri, P. Tu-mor-Promoting Effects of Cannabinoid Receptor Type 1 in Human Melanoma Cells. Toxicol. Vitro 2017, 40, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, P.; Jagerovic, N. Antitumor Cannabinoid Chemotypes: Structural Insights. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssif, B.G.M.; Mohamed, A.M.; Osman, E.E.A.; Abou-Ghadir, O.F.; Elnaggar, D.H.; Abdelrahman, M.H.; Treamblu, L.; Gomaa, H.A.M. 5-Chlorobenzofuran-2-Carboxamides: From Allosteric Cb1 Modulators to Potential Apoptotic An-titumor Agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 177, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauckner, J.E.; Jensen, J.B.; Chen, H.-Y.; Lu, H.-C.; Hille, B.; Mackie, K. GPR55 is a cannabinoid receptor that increases intracellular calcium and inhibits M current. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2699–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gangadharan, V.; Selvaraj, D.; Kurejova, M.; Njoo, C.; Gritsch, S.; Škoricová, D.; Horstmann, H.; Offermanns, S.; Brown, A.J.; Kuner, T.; et al. A novel biological role for the phospholipid lysophosphatidylinositol in nociceptive sensitization via activation of diverse G-protein signalling pathways in sensory nerves in vivo. Pain 2013, 154, 2801–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertwee, R.G. Emerging strategies for exploiting cannabinoid receptor agonists as medicines. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 156, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coke, C.J.; Scarlett, K.A.; Chetram, M.A.; Jones, K.J.; Sandifer, B.J.; Davis, A.S.; Marcus, A.I.; Hinton, C.V. Simul-taneous Activation of Induced Heterodimerization between Cxcr4 Chemokine Receptor and Cannabinoid Receptor 2 (Cb2) Reveals a Mechanism for Regulation of Tumor Progression. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 9991–10005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moreno, E.; Cavic, M.; Krivokuca, A.; Casadó, V.; Canela, E. The Endocannabinoid System as a Target in Cancer Diseases: Are We There Yet? Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Marzo, V.; Piscitelli, F. The Endocannabinoid System and its Modulation by Phytocannabinoids. Neurotherapeutics 2015, 12, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecera, L.; Gabrhelik, T.; Prasil, P.; Stourac, P. The role of cannabinoids in the treatment of cancer. Bratisl. Med. J. 2020, 121, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, P.; Reggio, P.H.; Jagerovic, N. An Overview on Medicinal Chemistry of Synthetic and Natural Derivatives of Cannabidiol. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Petrocellis, L.; Nabissi, M.; Santoni, G.; Ligresti, A. Actions and Regulation of Ionotropic Cannabinoid Receptors. Rapid Act. Antidepress. 2017, 80, 249–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambino, G.; Rizzo, V.; Giglia, G.; Ferraro, G.; Sardo, P. Cannabinoids, TRPV and nitric oxide: The three ring circus of neuronal excitability. Brain Struct. Funct. 2020, 225, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, B.; Ramer, R. Anti-tumour actions of cannabinoids. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 1384–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Yip, Y.; Lim, E.; Wahli, W.; Tan, N. PPARs and Tumor Microenvironment: The Emerging Roles of the Metabolic Master Regulators in Tumor Stromal–Epithelial Crosstalk and Carcinogenesis. Cancers 2021, 13, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelina, A.; Perez-Diego, M.; Lopez-Abente, J.; Palomares, O. The Role of Cannabinoids in Allergic Diseases: Colle-gium Internationale Allergologicum (Cia) Update 2020. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 181, 565–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiurchiù, V.; Leuti, A.; Maccarrone, M. Cannabinoid Signaling and Neuroinflammatory Diseases: A Melting pot for the Regulation of Brain Immune Responses. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2015, 10, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramer, R.; Schwarz, R.; Hinz, B. Modulation of the Endocannabinoid System as a Potential Anticancer Strategy. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cravatt, B.F.; Lichtman, A.H. The endogenous cannabinoid system and its role in nociceptive behavior. J. Neurobiol. 2004, 61, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maccarrone, M. Metabolism of the Endocannabinoid Anandamide: Open Questions after 25 Years. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murataeva, N.; Straiker, A.; Mackie, K. Parsing the players: 2-arachidonoylglycerol synthesis and degradation in the CNS. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schrot, R.J.; Hubbard, J.R. Cannabinoids: Medical implications. Ann. Med. 2016, 48, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurier, R.B.; Burstein, S.H. Cannabinoids, inflammation, and fibrosis. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 3682–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, R.; Mousawy, K.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P. Endocannabinoids and immune regulation. Pharmacol. Res. 2009, 60, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alhouayek, M.; Muccioli, G.G. COX-2-derived endocannabinoid metabolites as novel inflammatory mediators. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turcotte, C.; Zarini, S.; Jean, S.; Martin, C.; Murphy, R.C.; Marsolais, D.; LaViolette, M.; Blanchet, M.-R.; Flamand, N. The Endocannabinoid Metabolite Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)-Glycerol Inhibits Human Neutrophil Functions: Involvement of Its Hydrolysis into PGE2 and EP Receptors. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 3255–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, S.A.; Gupta, A.S.; Kumar, P. Emerging role of cannabinoids and synthetic cannabinoid receptor 1/cannabinoid receptor 2 receptor agonists in cancer treatment and chemotherapy-associated cancer management. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2021, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbasi, A.; Ribas, A. Tumour-intrinsic resistance to immune checkpoint blockade. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, S.; Fischer, O.M.; Ullrich, A. Cannabinoids Induce Cancer Cell Proliferation Via Tumor Necrosis Factor Al-pha-Converting Enzyme (Tace/Adam17)-Mediated Transactivation of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 1943–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malfitano, A.M.; Ciaglia, E.; Gangemi, G.; Gazzerro, P.; Laezza, C.; Bifulco, M. Update on the endocannabinoid system as an anticancer target. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2011, 15, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKallip, R.J.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S. Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol Enhances Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis by Suppression of the Antitumor Immune Response. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 3281–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sailler, S.; Schmitz, K.; Jäger, E.; Ferreiros, N.; Wicker, S.; Zschiebsch, K.; Pickert, G.; Geisslinger, G.; Walter, C.; Tegeder, I.; et al. Regulation of circulating endocannabinoids associated with cancer and metastases in mice and humans. Oncoscience 2014, 1, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, L.X.; Sharma, S.; Stolina, M.; Gardner, B.; Roth, M.D.; Tashkin, D.P.; Dubinett, S.M. Del-ta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol Inhibits Antitumor Immunity by a Cb2 Receptor-Mediated, Cytokine-Dependent Pathway. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demuth, D.G.; Molleman, A. Cannabinoid signalling. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munson, A.E.; Harris, L.S.; Friedman, M.A.; Dewey, W.L.; Carchman, R.A. Antineoplastic Activity of Cannabinoids2. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1975, 55, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, R.; Ramer, R.; Hinz, B. Targeting the endocannabinoid system as a potential anticancer approach. Drug Metab. Rev. 2018, 50, 26–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, G.; Sanchez, C.; Guzmán, M. Anticancer Mechanisms of Cannabinoids. Curr. Oncol. 2016, 23, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarfaraz, S.; Adhami, V.M.; Syed, D.N.; Afaq, F.; Mukhtar, H. Cannabinoids for Cancer Treatment: Progress and Promise: Figure 1. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pacher, P.; Bátkai, S.; Kunos, G. The Endocannabinoid System as an Emerging Target of Pharmacotherapy. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 389–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velasco, G.; Sanchez, C.; Guzmán, M. Towards the use of cannabinoids as antitumour agents. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.; De Ceballos, M.L.; Del Pulgar, T.G.; Rueda, D.; Corbacho, C.; Velasco, G.; Galve-Roperh, I.; Huffman, J.W.; Cajal, S.R.Y.; Guzmán, M. Inhibition of glioma growth in vivo by selective activation of the CB(2) cannabinoid receptor. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 5784–5789. [Google Scholar]
- Carracedo, A.; Lorente, M.; Egia, A.; Blazquez, C.; Garcia, S.; Giroux, V.; Malicet, C.; Villuendas, R.; Gironella, M.; Gonza-lez-Feria, L.; et al. The Stress-Regulated Protein P8 Mediates Canna-binoid-Induced Apoptosis of Tumor Cells. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vara, D.; Salazar, M.; Olea-Herrero, N.; Guzman, M.; Velasco, G.; Diaz-Laviada, I. Anti-Tumoral Action of Canna-binoids on Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Role of Ampk-Dependent Activation of Autophagy. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, W.; Hegde, V.L.; Singh, N.P.; Sisco, D.; Grant, S.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S. Del-ta9-Tetrahydrocannabinol-Induced Apoptosis in Jurkat Leukemia T Cells Is Regulated by Translocation of Bad to Mito-chondria. Mol. Cancer Res. 2006, 4, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greenhough, A.; Patsos, H.A.; Williams, A.C.; Paraskeva, C. The Cannabinoid Delta(9)-Tetrahydrocannabinol Inhibits Ras-Mapk and Pi3k-Akt Survival Signalling and Induces Bad-Mediated Apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 2172–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKallip, R.J.; Jia, W.; Schlomer, J.; Warren, J.W.; Nagarkatti, P.S.; Nagarkatti, M. Cannabidiol-Induced Apoptosis in Human Leukemia Cells: A Novel Role of Cannabidiol in the Regulation of p22phox and Nox4 Expression. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 70, 897–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dando, I.; Donadelli, M.; Costanzo, C.; Pozza, E.D.; D’Alessandro, A.; Zolla, L.; Palmieri, M. Cannabinoids inhibit energetic metabolism and induce AMPK-dependent autophagy in pancreatic cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donadelli, M.; Dando, I.; Zaniboni, T.; Costanzo, C.; Pozza, E.D.; Scupoli, M.T.; Scarpa, A.; Zappavigna, S.; Marra, M.; Abbruzzese, A.; et al. Gemcitabine/cannabinoid combination triggers autophagy in pancreatic cancer cells through a ROS-mediated mechanism. Cell Death Dis. 2011, 2, e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Hroudova, J.; Fisar, Z. Cannabinoid-Induced Changes in the Activity of Electron Transport Chain Com-plexes of Brain Mitochondria. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 56, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, L.; Valerio, A.; Dossena, M.; Cardile, A.; Ragni, M.; Pagano, C.; Pagotto, U.; Carruba, M.O.; Vettor, R.; Nisoli, E. Cannabinoid Receptor Stimulation Impairs Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Mouse White Adipose Tissue, Muscle, and Liver: The Role of eNOS, p38 MAPK, and AMPK Pathways. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2826–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.; Doyle, M.E.; Liu, Z.; Lao, Q.; Shin, Y.K.; Carlson, O.D.; Kim, H.S.; Thomas, S.; Napora, J.K.; Lee, E.K.; et al. Cannabinoids Inhibit Insulin Receptor Signaling in Pancreatic Beta-Cells. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1198–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, L.; Xiong, K.; Godlewski, G.; Mukhopadhyay, B.; Tam, J.; Yin, S.; Gao, P.; Shan, X.; Pickel, J.; et al. Hepatic Cannabinoid Receptor-1 Mediates Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance via Inhibition of Insulin Signaling and Clearance in Mice. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1218–1228.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nabissi, M.; Morelli, M.B.; Amantini, C.; Liberati, S.; Santoni, M.; Ricci-Vitiani, L.; Pallini, R.; Santoni, G. Cannabidiol Stimulates Aml-1a-Dependent Glial Differentiation and Inhibits Glioma Stem-Like Cells Proliferation by Inducing Au-tophagy in a Trpv2-Dependent Manner. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 1855–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caffarel, M.M.; Sarrio, D.; Palacios, J.; Guzman, M.; Sanchez, C. Delta9-Tetrahydrocannabinol Inhibits Cell Cycle Progression in Human Breast Cancer Cells through Cdc2 Regulation. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 6615–6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caffarel, M.M.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Cerutti, C.; Palacios, J.; Guzman, M.; Mechta-Grigoriou, F.; Sanchez, C. Jund Is Involved in the Antiproliferative Effect of Delta9-Tetrahydrocannabinol on Human Breast Cancer Cells. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5033–5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vara, D.; Morell, C.; Rodriguez-Henche, N.; Diaz-Laviada, I. Involvement of Ppargamma in the Antitumoral Action of Cannabinoids on Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elbaz, M.; Nasser, M.W.; Ravi, J.; Wani, N.A.; Ahirwar, D.K.; Zhao, H.; Oghumu, S.; Satoskar, A.R.; Shilo, K.; Carson, W.E., 3rd; et al. Modulation of the Tumor Microenvironment and Inhibition of Egf/Egfr Pathway: Novel Anti-Tumor Mechanisms of Cannabidiol in Breast Cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 906–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Wyckoff, J.; Condeelis, J. Cell migration in tumors. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2005, 17, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Shang, B.; Zhang, G.; Miele, L.; Sarkar, F.H.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Q. Tumor cell-mediated neovascularization and lymphangiogenesis contrive tumor progression and cancer metastasis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2013, 1836, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, A. The Cytoskeleton and Cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009, 28, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laezza, C.; Pisanti, S.; Malfitano, A.M.; Bifulco, M. The anandamide analog, Met-F-AEA, controls human breast cancer cell migration via the RHOA/RHO kinase signaling pathway. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2008, 15, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramer, R.; Bublitz, K.; Freimuth, N.; Merkord, J.; Rohde, H.; Haustein, M.; Borchert, P.; Schmuhl, E.; Linnebacher, M.; Hinz, B. Cannabidiol inhibits lung cancer cell invasion and metastasis via intercellular adhesion molecule-1. FASEB J. 2011, 26, 1535–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramer, R.; Hinz, B. Inhibition of Cancer Cell Invasion by Cannabinoids via Increased Expression of Tissue Inhibitor of Matrix Metalloproteinases-1. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2008, 100, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeda, S.; Okajima, S.; Miyoshi, H.; Yoshida, K.; Okamoto, Y.; Okada, T.; Amamoto, T.; Watanabe, K.; Omiecinski, C.J.; Aramaki, H. Cannabidiolic acid, a major cannabinoid in fiber-type cannabis, is an inhibitor of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell migration. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 214, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thapa, D.; Lee, J.S.; Heo, S.-W.; Lee, Y.R.; Kang, K.W.; Kwak, M.-K.; Choi, H.G.; Kim, J.-A. Novel hexahydrocannabinol analogs as potential anti-cancer agents inhibit cell proliferation and tumor angiogenesis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 650, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, C.; Morales, P.; Reggio, P.H. Cannabinoid Ligands Targeting TRP Channels. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 11, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, E.; Andradas, C.; Medrano, M.; Caffarel, M.M.; Pérez-Gómez, E.; Blasco-Benito, S.; Gómez-Cañas, M.; Pazos, M.R.; Irving, A.J.; Lluís, C.; et al. Targeting CB2-GPR55 Receptor Heteromers Modulates Cancer Cell Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 21960–21972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scarlett, K.A.; White, E.-S.Z.; Coke, C.J.; Carter, J.R.; Bryant, L.K.; Hinton, C.V. Agonist-induced CXCR4 and CB2 Heterodimerization Inhibits Gα13/RhoA-mediated Migration. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visciano, C.; Liotti, F.; Prevete, N.; Cali’, G.; Franco, R.; Collina, F.; De Paulis, A.; Marone, G.; Santoro, M.; Melillo, R.M. Mast cells induce epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stem cell features in human thyroid cancer cells through an IL-8–Akt–Slug pathway. Oncogene 2015, 34, 5175–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laezza, C.; D’Alessandro, A.; Paladino, S.; Malfitano, A.M.; Proto, M.C.; Gazzerro, P.; Pisanti, S.; Santoro, A.; Ciaglia, E.; Bifulco, M. Group Endocannabinoid Research Anandamide Inhibits the Wnt/Beta-Catenin Signalling Pathway in Human Breast Cancer Mda Mb 231 Cells. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 3112–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, D.; Ramesh, P.; Proto, M.C.; Piscopo, C.; Franceschelli, S.; Anzelmo, S.; Medema, J.P.; Bifulco, M.; Gazzerro, P. Rimonabant Kills Colon Cancer Stem Cells without Inducing Toxicity in Normal Colon Organoids. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 8, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Proto, M.C.; Fiore, D.; Piscopo, C.; Franceschelli, S.; Bizzarro, V.; Laezza, C.; Lauro, G.; Feoli, A.; Tosco, A.; Bifulco, G.; et al. Inhibition of Wnt/Beta-Catenin Pathway and Histone Acetyltransferase Activity by Rimonabant: A Therapeutic Target for Colon Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, S.B.; Wallenius, A.; Zackrisson, H.; Popova, D.; Forshell, L.P.; Jacobsson, S.O.P. Effects of cannabinoids and related fatty acids upon the viability of P19 embryonal carcinoma cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguado, T.; Carracedo, A.; Julien, B.; Velasco, G.; Milman, G.; Mechoulam, R.; Alvarez, L.; Guzmán, M.; Galve-Roperh, I. Cannabinoids Induce Glioma Stem-like Cell Differentiation and Inhibit Gliomagenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 6854–6862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Palma, M.; Biziato, D.; Petrova, T.V. Microenvironmental regulation of tumour angiogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varricchi, G.; Loffredo, S.; Borriello, F.; Pecoraro, A.; Rivellese, F.; Genovese, A.; Spadaro, G.; Marone, G. Superantigenic Activation of Human Cardiac Mast Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saharinen, P.; Leppänen, V.-M.; Alitalo, K. SnapShot: Angiopoietins and Their Functions. Cell 2017, 171, 724.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loffredo, S.; Staiano, R.I.; Granata, F.; Genovese, A.; Marone, G. Immune Cells as a Source and Target of Angiogenic and Lymphangiogenic Factors. Superantigens Superallerg. 2013, 99, 15–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varricchi, G.; De Paulis, A.; Marone, G.; Galli, S.J.; Paulis, D. Future Needs in Mast Cell Biology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, W.; Aspelund, A.; Alitalo, K. Lymphangiogenic factors, mechanisms, and applications. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solinas, M.; Massi, P.; Cantelmo, A.; Cattaneo, M.; Cammarota, R.; Bartolini, D.; Cinquina, V.; Valenti, M.; Vicentini, L.; Noonan, D.; et al. Cannabidiol inhibits angiogenesis by multiple mechanisms. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 1218–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pisanti, S.; Borselli, C.; Oliviero, O.; Laezza, C.; Gazzerro, P.; Bifulco, M. Antiangiogenic activity of the endocannabinoid anandamide: Correlation to its tumor-suppressor efficacy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 211, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portella, G.; Laezza, C.; Laccetti, P.; de Petrocellis, L.; di Marzo, V.; Bifulco, M. Inhibitory Effects of Cannabinoid Cb1 Receptor Stimulation on Tumor Growth and Metastatic Spreading: Actions on Signals Involved in Angiogenesis and Me-tastasis. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 1771–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blázquez, C.; González-Feria, L.; Álvarez, L.; Haro, A.; Casanova, M.L.; Guzmán, M. Cannabinoids Inhibit the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Pathway in Gliomas. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 5617–5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramer, R.; Hinz, B. Antitumorigenic targets of cannabinoids–current status and implications. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2016, 20, 1219–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramer, R.; Hinz, B. Cannabinoids as Anticancer Drugs. Rapid Act. Antidepress. 2017, 80, 397–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blázquez, C.; Casanova, M.L.; Planas, A.; Del Pulgar, T.G.; Villanueva, C.; Fernández-Aceñero, M.J.; Aragonés, J.; Huffman, J.W.; Jorcano, J.L.; Guzmán, M. Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis by cannabinoids. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramer, R.; Fischer, S.; Haustein, M.; Manda, K.; Hinz, B. Cannabinoids inhibit angiogenic capacities of endothelial cells via release of tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases-1 from lung cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 91, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sica, A.; Mantovani, A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization: In vivo veritas. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galdiero, M.R.; Varricchi, G.; Loffredo, S.; Bellevicine, C.; Lansione, T.; Ferrara, A.L.; Iannone, R.; Di Somma, S.; Borriello, F.; Clery, E.; et al. Potential involvement of neutrophils in human thyroid cancer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loffredo, S.; Borriello, F.; Iannone, R.; Ferrara, A.L.; Galdiero, M.R.; Gigantino, V.; Esposito, P.; Varricchi, G.; Lambeau, G.; Cassatella, M.A.; et al. Group V Secreted Phospholipase A2 Induces the Release of Proangiogenic and Antiangiogenic Factors by Human Neutrophils. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wallace, D.C. Mitochondria and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McAllister, S.D.; Christian, R.T.; Horowitz, M.P.; Garcia, A.; Desprez, P.-Y. Cannabidiol as a novel inhibitor of Id-1 gene expression in aggressive breast cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 2921–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McAllister, S.D.; Murase, R.; Christian, R.T.; Lau, D.; Zielinski, A.J.; Allison, J.; Almanza, C.; Pakdel, A.; Lee, J.; Limbad, C.; et al. Pathways mediating the effects of cannabidiol on the reduction of breast cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 129, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurley, S.N.; Abidi, A.H.; Allison, P.; Guan, P.; Duntsch, C.; Robertson, J.H.; Kosanke, S.D.; Keir, S.T.; Bigner, D.D.; Elberger, A.J.; et al. Mechanism of anti-glioma activity and in vivo efficacy of the cannabinoid ligand KM-233. J. Neuro Oncol. 2012, 110, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, D.A.; Al-Hammadi, S.; Balhaj, G.; Brown, O.M.; Penefsky, H.S.; Souid, A.-K. Cannabinoids Inhibit Cellular Respiration of Human Oral Cancer Cells. Pharmacology 2010, 85, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Mann, P.; Cohen, A.B.; Finley, T.N.; Ladman, A.J. Alveolar macrophages. Structural and functional differences between nonsmokers and smokers of marijuana and tobacco. Lab. Investig. 1971, 25, 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Chiurchiù, V. Endocannabinoids and Immunity. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2016, 1, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Anderson, H.D. Cannabinoid signaling in health and disease. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 95, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maccarrone, M.; Bab, I.; Bíró, T.; Cabral, G.A.; Dey, S.K.; Di Marzo, V.; Konje, J.C.; Kunos, G.; Mechoulam, R.; Pacher, P.; et al. Endocannabinoid signaling at the periphery: 50 years after THC. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oláh, A.; Bíró, T. Targeting Cutaneous Cannabinoid Signaling in Inflammation - A “High”-way to Heal? EBioMedicine 2017, 16, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Burkovskiy, I.; Yang, H.; Sardinha, J.; Lehmann, C. CB2 and GPR55 Receptors as Therapeutic Targets for Systemic Immune Dysregulation. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Sullivan, S.; Kendall, D. Cannabinoid activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: Potential for modulation of inflammatory disease. Immunobiology 2010, 215, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parenti, A.; De Logu, F.; Geppetti, P.; Benemei, S. What is the evidence for the role of TRP channels in inflammatory and immune cells? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 953–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoni, G.; Cardinali, C.; Morelli, M.B.; Santoni, M.; Nabissi, M.; Amantini, C. Danger- and pathogen-associated molecular patterns recognition by pattern-recognition receptors and ion channels of the transient receptor potential family triggers the inflammasome activation in immune cells and sensory neurons. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turcotte, C.; Chouinard, F.; Lefebvre, J.S.; Flamand, N. Regulation of Inflammation by Cannabinoids, the Endocan-nabinoids 2-Arachidonoyl-Glycerol and Arachidonoyl-Ethanolamide, and Their Metabolites. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 97, 1049–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noe, S.N.; Newton, C.; Widen, R.; Friedman, H.; Klein, T.W. Anti-CD40, anti-CD3, and IL-2 stimulation induce contrasting changes in CB1 mRNA expression in mouse splenocytes. J. Neuroimmunol. 2000, 110, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daaka, Y.; Friedman, H.; Klein, T.W. Cannabinoid receptor proteins are increased in Jurkat, human T-cell line after mitogen activation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1996, 276, 776–783. [Google Scholar]
- Cristinziano, L.; Modestino, L.; Loffredo, S.; Varricchi, G.; Braile, M.; Ferrara, A.L.; De Paulis, A.; Antonelli, A.; Marone, G.; Galdiero, M.R. Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cells Induce the Release of Mitochondrial Extracellular DNA Traps by Viable Neutrophils. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, S.M.; Fallahi, P.; Galdiero, M.R.; Ruffilli, I.; Elia, G.; Ragusa, F.; Paparo, S.R.; Patrizio, A.; Mazzi, V.; Varricchi, G.; et al. Immune and Inflammatory Cells in Thyroid Cancer Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sammarco, G.; Varricchi, G.; Ferraro, V.; Ammendola, M.; De Fazio, M.; Altomare, D.F.; Luposella, M.; Maltese, L.; Currò, G.; Marone, G.; et al. Mast Cells, Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis in Human Gastric Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Binabaj, M.M.; Bahrami, A.; ShahidSales, S.; Joodi, M.; Mashhad, M.J.; Hassanian, S.M.; Anvari, K.; Avan, A. The prognostic value of MGMT promoter methylation in glioblastoma: A meta-analysis of clinical trials. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajbakhsh, A.; Mokhtari-Zaer, A.; Rezaee, M.; Afzaljavan, F.; Rivandi, M.; Hassanian, S.M.; Ferns, G.A.; Pasdar, A.; Avan, A. Therapeutic Potentials of BDNF/TrkB in Breast Cancer; Current Status and Perspectives. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 2502–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, T.W.; Newton, C.A.; Friedman, H. Cannabinoids and the Immune System. Pain Res. Manag. 2001, 6, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śledziński, P.; Zeyland, J.; Słomski, R.; Nowak, A.N.-T. The current state and future perspectives of cannabinoids in cancer biology. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanasescu, R.; Constantinescu, C.S. Cannabinoids and the immune system: An overview. Immunobiology 2010, 215, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, M.L.; Blázquez, C.; Martínez-Palacio, J.; Villanueva, C.; Fernández-Aceñero, M.J.; Huffman, J.W.; Jorcano, J.L.; Guzmán, M. Inhibition of skin tumor growth and angiogenesis in vivo by activation of cannabinoid receptors. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharif, H.; Acharya, S.; Dhondalay, G.K.R.; Varricchi, G.; Krasner-Macleod, S.; Laisuan, W.; Switzer, A.; Lenormand, M.; Kashe, E.; Parkin, R.V.; et al. Altered chromatin landscape in circulating T follicular helper and regulatory cells following grass pollen subcutaneous and sublingual immunotherapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varricchi, G.; Pecoraro, A.; Marone, G.; Criscuolo, G.; Spadaro, G.; Genovese, A.; Marone, G. Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin Isoforms, Inflammatory Disorders, and Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garner, H.; de Visser, K.E. Immune Crosstalk in Cancer Progression and Metastatic Spread: A Complex Conversa-tion. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Börner, C.; Bedini, A.; Höllt, V.; Kraus, J. Analysis of Promoter Regions Regulating Basal and Interleukin-4-Inducible Expression of the Human CB1 Receptor Gene in T Lymphocytes. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 73, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Börner, C.; Höllt, V.; Kraus, J. Activation of Human T Cells Induces Upregulation of Cannabinoid Receptor Type 1 Transcription. Neuroimmunomodulation 2007, 14, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Börner, C.; Smida, M.; Höllt, V.; Schraven, B.; Kraus, J. Cannabinoid Receptor Type 1- and 2-mediated Increase in Cyclic AMP Inhibits T Cell Receptor-triggered Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 35450–35460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Derocq, J.M.; Bouaboula, M.; Marchand, J.; Rinaldi-Carmona, M.; Segui, M.; Casellas, P. The Endogenous Cannabinoid Anandamide Is a Lipid Messenger Activating Cell Growth Via a Cannabinoid Receptor-Independent Pathway in Hema-topoietic Cell Lines. FEBS Lett. 1998, 425, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lombard, C.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P. CB2 cannabinoid receptor agonist, JWH-015, triggers apoptosis in immune cells: Potential role for CB2-selective ligands as immunosuppressive agents. Clin. Immunol. 2007, 122, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, H.; Blanco, F.J.; Lotz, M. Anadamide, an endogenous cannabinoid receptor agonist inhibits lymphocyte proliferation and induces apoptosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 1994, 55, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Kiertscher, S.M.; Cheng, Q.; Zoumalan, R.; Tashkin, D.P.; Roth, M.D. Delta 9-Tetrahydrocannabinol Reg-ulates Th1/Th2 Cytokine Balance in Activated Human T Cells. J. Neuroimmunol. 2002, 133, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer-Stenger, K.; Updegrove, A.W.; Cabral, G.A. Delta 9-Tetrahydrocannabinol Decreases Cytotoxic T Lympho-cyte Activity to Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1-Infected Cells. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1992, 200, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockwell, C.E.; Raman, P.; Kaplan, B.; Kaminski, N.E. A COX-2 metabolite of the endogenous cannabinoid, 2-arachidonyl glycerol, mediates suppression of IL-2 secretion in activated Jurkat T cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matarese, G.; De Rosa, V.; La Cava, A. Regulatory CD4 T cells: Sensing the environment. Trends Immunol. 2008, 29, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colamatteo, A.; Carbone, F.; Bruzzaniti, S.; Galgani, M.; Fusco, C.; Maniscalco, G.T.; Di Rella, F.; De Candia, P.; De Rosa, V. Molecular Mechanisms Controlling Foxp3 Expression in Health and Autoimmunity: From Epigenetic to Post-translational Regulation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 10, 3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, V.L.; Hegde, S.; Cravatt, B.F.; Hofseth, L.J.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S. Attenuation of Experimental Autoimmune Hepatitis by Exogenous and Endogenous Cannabinoids: Involvement of Regulatory T Cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 74, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowthaman, U.; Chen, J.S.; Zhang, B.; Flynn, W.F.; Lu, Y.; Song, W.; Joseph, J.; Gertie, J.A.; Xu, L.; Collet, M.A.; et al. Identifi-cation of a T Follicular Helper Cell Subset That Drives Anaphylactic Ige. Science 2019, 365, eaaw6433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemmour, D.; Kiner, E.; Benoist, C. CD4+ teff cell heterogeneity: The perspective from single-cell transcriptomics. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2020, 63, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommen, D.S.; Koelzer, V.H.; Herzig, P.; Roller, A.; Trefny, M.; Dimeloe, S.; Kiialainen, A.; Hanhart, J.; Schill, C.; Hess, C.; et al. A transcriptionally and functionally distinct PD-1+ CD8+ T cell pool with predictive potential in non-small-cell lung cancer treated with PD-1 blockade. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Locati, M.; Curtale, G.; Mantovani, A. Diversity, Mechanisms, and Significance of Macrophage Plasticity. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2020, 15, 123–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bisogno, T.; Maurelli, S.; Melck, D.; de Petrocellis, L.; di Marzo, V. Biosynthesis, Uptake, and Degradation of Anan-damide and Palmitoylethanolamide in Leukocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 3315–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Marzo, V.; De Petrocellis, L.; Sepe, N.; Buono, A. Biosynthesis of anandamide and related acylethanolamides in mouse J774 macrophages and N18 neuroblastoma cells. Biochem. J. 1996, 316, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuwae, T.; Shiota, Y.; Schmid, P.C.; Krebsbach, R.; Schmid, H.H. Biosynthesis and turnover of anandamide and otherN-acylethanolamines in peritoneal macrophages. FEBS Lett. 1999, 459, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmid, P.C.; Kuwae, T.; Krebsbach, R.J.; Schmid, H.H. Anandamide and other N-acylethanolamines in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1997, 87, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.L.; Tsuboi, K.; Adibekian, A.; Pugh, H.; Masuda, K.; Cravatt, B.F. Daglbeta Inhibition Perturbs a Lipid Network Involved in Macrophage Inflammatory Responses. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 12, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacerdote, P.; Massi, P.; Panerai, A.E.; Parolaro, D. In vivo and in vitro treatment with the synthetic cannabinoid CP55,940 decreases the in vitro migration of macrophages in the rat: Involvement of both CB1 and CB2 receptors. J. Neuroimmunol. 2000, 109, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marzo, V.; Bisogno, T.; De Petrocellis, L.; Melck, D.; Orlando, P.; Wagner, J.A.; Kunos, G. Biosynthesis and inactivation of the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol in circulating and tumoral macrophages. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 1999, 264, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-H.; Lee, S.T.; Lin, W.-W. Effects of cannabinoids on LPS-stimulated inflammatory mediator release from macrophages: Involvement of eicosanoids. J. Cell. Biochem. 2001, 81, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, R.A.; Brockie, H.C.; Pertwee, R.G. Inhibition of Nitric Oxide Production in Raw264.7 Macrophages by Can-nabinoids and Palmitoylethanolamide. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 401, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdyshev, E.V.; Schmid, P.C.; Krebsbach, R.J.; Schmid, H.H.O. Activation of PAF receptors results in enhanced synthesis of 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) in immune cells. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 2171–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massi, P.; Vaccani, A.; Bianchessi, S.; Costa, B.; Macchi, P.; Parolaro, D. The non-psychoactive cannabidiol triggers caspase activation and oxidative stress in human glioma cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 2057–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raborn, E.S.; Marciano-Cabral, F.; Buckley, N.E.; Martin, B.R.; Cabral, G.A. The Cannabinoid Del-ta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol Mediates Inhibition of Macrophage Chemotaxis to Rantes/Ccl5: Linkage to the Cb2 Receptor. J. Neuroimmun. Pharmacol. 2008, 3, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokoh, M.; Kishimoto, S.; Oka, S.; Sugiura, T. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol Enhances the Phagocytosis of Opsonized Zy-mosan by Hl-60 Cells Differentiated into Macrophage-Like Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabral, G.A.; Toney, D.M.; Fischer-Stenger, K.; Harrison, M.P.; Marciano-Cabral, F. Anandamide Inhibits Macro-phage-Mediated Killing of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Sensitive Cells. Life Sci. 1995, 56, 2065–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokoh, M.; Kishimoto, S.; Oka, S.; Mori, M.; Waku, K.; Ishima, Y.; Sugiura, T. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol, an endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligand, induces rapid actin polymerization in HL-60 cells differentiated into macrophage-like cells. Biochem. J. 2005, 386, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiang, W.; Shi, R.; Kang, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, P.; Zhang, L.; Hou, A.; Wang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, K.; et al. Monoacylglycerol Lipase Regulates Can-nabinoid Receptor 2-Dependent Macrophage Activation and Cancer Progression. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ginhoux, F.; Guilliams, M. Tissue-Resident Macrophage Ontogeny and Homeostasis. Immunity 2016, 44, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S.; Plüddemann, A. Tissue macrophages: Heterogeneity and functions. BMC Biol. 2017, 15, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakarov, S.; Lim, H.Y.; Tan, L.; Lim, S.Y.; See, P.; Lum, J.; Zhang, X.-M.; Foo, S.; Nakamizo, S.; Duan, K.; et al. Two distinct interstitial macrophage populations coexist across tissues in specific subtissular niches. Science 2019, 363, eaau0964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdiero, M.R.; Bianchi, P.; Grizzi, F.; di Caro, G.; Basso, G.; Ponzetta, A.; Bonavita, E.; Barbagallo, M.; Tartari, S.; Polen-tarutti, N.; et al. Occurrence and Signif-icance of Tumor-Associated Neutrophils in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galdiero, M.R.; Varricchi, G.; Marone, G. The immune network in thyroid cancer. OncoImmunology 2016, 5, e1168556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurihara, R.; Tohyama, Y.; Matsusaka, S.; Naruse, H.; Kinoshita, E.; Tsujioka, T.; Katsumata, Y.; Yamamura, H. Effects of Peripheral Cannabinoid Receptor Ligands on Motility and Polarization in Neutrophil-Like Hl60 Cells and Human Neu-trophils. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 12908–12918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coffelt, S.B.; Wellenstein, M.D.; De Visser, K.E. Neutrophils in cancer: Neutral no more. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deusch, E.; Kraft, B.; Nahlik, G.; Weigl, L.; Hohenegger, M.; Kress, H.G. No evidence for direct modulatory effects of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J. Neuroimmunol. 2003, 141, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balenga, N.A.; Aflaki, E.; Kargl, J.; Platzer, W.; Schroder, R.; Blattermann, S.; Kostenis, E.; Brown, A.J.; Heinemann, A.; Waldhoer, M. Gpr55 Regulates Cannabinoid 2 Receptor-Mediated Responses in Human Neutrophils. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 1452–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jordà, M.A.; Löwenberg, B.; Delwel, R. The peripheral cannabinoid receptor Cb2, a novel oncoprotein, induces a reversible block in neutrophilic differentiation. Blood 2003, 101, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kargl, J.; Busch, S.E.; Yang, G.H.Y.; Kim, K.-H.; Hanke, M.L.; Metz, H.E.; Hubbard, J.J.; Lee, S.M.; Madtes, D.K.; McIntosh, M.W.; et al. Neutrophils dominate the immune cell composition in non-small cell lung cancer. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaul, M.E.; Fridlender, Z.G. Tumour-associated neutrophils in patients with cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borriello, F.; Granata, F.; Varricchi, G.; Genovese, A.; Triggiani, M.; Marone, G. Immunopharmacological modulation of mast cells. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2014, 17, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metcalfe, D.D.; Baram, D.; Mekori, Y.A. Mast cells. Physiol. Rev. 1997, 77, 1033–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, A.H.Y.; Chow, S.S.M. Effects of cannabinoid receptor agonists on immunologically induced histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 464, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, M.-T.; Small-Howard, A.; Shimoda, L.M.N.; Koblan-Huberson, M.; Stokes, A.J.; Turner, H. Differential Roles of CB1 and CB2 Cannabinoid Receptors in Mast Cells. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 4953–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siebenhaar, F.; Redegeld, F.A.; Bischoff, S.C.; Gibbs, B.F.; Maurer, M. Mast Cells as Drivers of Disease and Therapeutic Targets. Trends Immunol. 2018, 39, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varricchi, G.; Galdiero, M.R.; Loffredo, S.; Marone, G.; Iannone, R.; Marone, G.; Granata, F. Are Mast Cells MASTers in Cancer? Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vannacci, A.; Giannini, L.; Passani, M.B.; Di Felice, A.; Pierpaoli, S.; Zagli, G.; Fantappiè, O.; Mazzanti, R.; Masini, E.; Mannaioni, P.F. The Endocannabinoid 2-Arachidonylglycerol Decreases the Immunological Activation of Guinea Pig Mast Cells: Involvement of Nitric Oxide and Eicosanoids. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 311, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, K.; Bíró, T.; Tsuruta, D.; Tóth, B.I.; Kromminga, A.; Zákány, N.; Zimmer, A.; Funk, W.; Gibbs, B.F.; Zimmer, A.; et al. Endocannabinoids limit excessive mast cell maturation and activation in human skin. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 726–738.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Filippis, D.; Russo, A.; D’Amico, A.; Esposito, G.; Pietropaolo, C.; Cinelli, M.; Russo, G.; Iuvone, T. Cannabinoids Reduce Granuloma-Associated Angiogenesis in Rats by Controlling Transcription and Expression of Mast Cell Protease-5. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sugawara, K.; Zakany, N.; Hundt, T.; Emelianov, V.; Tsuruta, D.; Schafer, C.; Kloepper, J.E.; Biro, T.; Paus, R. Canna-binoid Receptor 1 Controls Human Mucosal-Type Mast Cell Degranulation and Maturation in Situ. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espinosa-Riquer, Z.P.; Ibarra-Sanchez, A.; Vibhushan, S.; Bratti, M.; Charles, N.; Blank, U.; Rodriguez-Manzo, G.; Gonzalez-Espinosa, C. Tlr4 Receptor Induces 2-Ag-Dependent Tolerance to Lipopolysaccharide and Trafficking of Cb2 Re-ceptor in Mast Cells. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 2360–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, S.L.; Sanchez-Miranda, E.; Castillo-Arellano, J.I.; Cervantes-Villagrana, R.D.; Ibarra-Sanchez, A.; Gonza-lez-Espinosa, C. Anandamide Inhibits Fcepsilonri-Dependent Degranulation and Cytokine Synthesis in Mast Cells through Cb2 and Gpr55 Receptor Activation. Possible Involvement of Cb2-Gpr55 Heteromers. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 64, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilliams, M.; Mildner, A.; Yona, S. Developmental and Functional Heterogeneity of Monocytes. Immunity 2018, 49, 595–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Canè, S.; Ugel, S.; Trovato, R.; Marigo, I.; De Sanctis, F.; Sartoris, S.; Bronte, V. The Endless Saga of Monocyte Diversity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, S.H.; Waldron, J.N.; Milosevic, M.; Shen, X.; Ringash, J.; Su, J.; Tong, L.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; Weinreb, I.; Bayley, A.J.; et al. Prognostic value of pretreatment circulating neutrophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes in oropharyngeal cancer stratified by human papillomavirus status. Cancer 2014, 121, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, R.N.; Cekic, C.; Sag, D.; Tacke, R.; Thomas, G.D.; Nowyhed, H.; Herrley, E.; Rasquinha, N.; McArdle, S.; Wu, R.; et al. Patrolling monocytes control tumor metastasis to the lung. Science 2015, 350, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kishimoto, S.; Gokoh, M.; Oka, S.; Muramatsu, M.; Kajiwara, T.; Waku, K.; Sugiura, T. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol Induces the Migration of HL-60 Cells Differentiated into Macrophage-like Cells and Human Peripheral Blood Monocytes through the Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor-dependent Mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 24469–24475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montecucco, F.; Burger, F.; Mach, F.; Steffens, S. CB2 cannabinoid receptor agonist JWH-015 modulates human monocyte migration through defined intracellular signaling pathways. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2008, 294, H1145–H1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, C.; Pamer, E.G. Monocyte recruitment during infection and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 762–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiurchiu, V.; Lanuti, M.; de Bardi, M.; Battistini, L.; Maccarrone, M. The Differential Characterization of Gpr55 Re-ceptor in Human Peripheral Blood Reveals a Distinctive Expression in Monocytes and Nk Cells and a Proinflammatory Role in These Innate Cells. Int. Immunol. 2015, 27, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mace, E.M.; Orange, J.S. Emerging insights into human health and NK cell biology from the study of NK cell deficiencies. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 287, 202–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiossone, L.; Dumas, P.-Y.; Vienne, M.; Vivier, E. Natural killer cells and other innate lymphoid cells in cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 671–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, T.W.; Newton, C.; Friedman, H. Inhibition of natural killer cell function by Marijuana components. J. Toxicol. Environ. Heal. Part. A 1987, 20, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.; Borysenko, M.; Kumar, M.; Millard, W. Effects of acute and subchronic Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol administration on the plasma catecholamine, beta-endorphin, and corticosterone levels and splenic natural killer cell activity in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1986, 17, 299–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specter, S.C.; Klein, T.W.; Newton, C.; Mondragon, M.; Widen, R.; Friedman, H. Marijuana effects on immunity: Suppression of human natural killer cell activity by delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 1986, 8, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massi, P.; Fuzio, D.; Viganò, D.; Sacerdote, P.; Parolaro, D. Relative involvement of cannabinoid CB(1) and CB(2) receptors in the Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol-induced inhibition of natural killer activity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 387, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, S.; Muramatsu, M.; Gokoh, M.; Oka, S.; Waku, K.; Sugiura, T. Endogenous Cannabinoid Receptor Ligand Induces the Migration of Human Natural Killer Cells. J. Biochem. 2005, 137, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrini, M.E.; Hong, S.; Stierle, A.; Stella, N.; Roberts, K.; Jaffar, Z. CB2 receptors regulate natural killer cells that limit allergic airway inflammation in a murine model of asthma. Allergy 2017, 72, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.L.; Kennedy, P.R.; Stacey, K.B.; Worboys, J.D.; Yarwood, A.; Seo, S.; Solloa, E.H.; Mistretta, B.; Chatterjee, S.S.; Gunaratne, P.; et al. Diversity of peripheral blood human NK cells identified by single-cell RNA sequencing. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 1388–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villar, J.; Segura, E. Decoding the Heterogeneity of Human Dendritic Cell Subsets. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wculek, S.K.; Cueto, F.J.; Mujal, A.M.; Melero, I.; Krummel, M.F.; Sancho, D. Dendritic cells in cancer immunology and immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, Y.; McKallip, R.J.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S. Activation through Cannabinoid Receptors 1 and 2 on Den-dritic Cells Triggers Nf-Kappab-Dependent Apoptosis: Novel Role for Endogenous and Exogenous Cannabinoids in Im-munoregulation. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 2373–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matias, I.; Pochard, P.; Orlando, P.; Salzet, M.; Pestel, J.; Di Marzo, V. Presence and regulation of the endocannabinoid system in human dendritic cells. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2002, 269, 3771–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maestroni, G.J.M. The endogenous cannabinoid 2-arachidonoyl glycerol as in vivo chemoattractant for dendritic cells and adjuvant for Th1 response to a soluble protein. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1914–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiurchiù, V.; Cencioni, M.T.; Bisicchia, E.; De Bardi, M.; Gasperini, C.; Borsellino, G.; Centonze, D.; Battistini, L.; Maccarrone, M. Distinct modulation of human myeloid and plasmacytoid dendritic cells by anandamide in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 73, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieu-Nosjean, M.-C.; Antoine, M.; Danel, C.; Heudes, D.; Wislez, M.; Poulot, V.; Rabbe, N.; Laurans, L.; Tartour, E.; De Chaisemartin, L.; et al. Long-Term Survival for Patients With Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer With Intratumoral Lymphoid Structures. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 4410–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goc, J.; Germain, C.; Vo-Bourgais, T.K.; Lupo, A.; Klein, C.; Knockaert, S.; de Chaisemartin, L.; Ouakrim, H.; Becht, E.; Alifano, M.; et al. Dendritic Cells in Tumor-Associated Tertiary Lymphoid Structures Signal a Th1 Cytotoxic Immune Con-texture and License the Positive Prognostic Value of Infiltrating Cd8+ T Cells. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ladányi, A.; Kiss, J.; Somlai, B.; Gilde, K.; Fejős, Z.; Mohos, A.; Gaudi, I.; Tímár, J. Density of DC-LAMP+ mature dendritic cells in combination with activated T lymphocytes infiltrating primary cutaneous melanoma is a strong independent prognostic factor. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2007, 56, 1459–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garris, C.S.; Luke, J.J. Dendritic Cells, the T-cell-inflamed Tumor Microenvironment, and Immunotherapy Treatment Response. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 3901–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharonov, G.V.; Serebrovskaya, E.O.; Yuzhakova, D.V.; Britanova, O.V.; Chudakov, D.M. B cells, plasma cells and antibody repertoires in the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, T.J.; Moore, J.M.; Griffith, T.S. Human B Cells Express Functional Trail/Apo-2 Ligand after Cpg-Containing Oligodeoxynucleotide Stimulation. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tao, H.; Lu, L.; Xia, Y.; Dai, F.; Wang, Y.; Bao, Y.; Lundy, S.K.; Ito, F.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, X.; et al. Antitumor effector B cells directly kill tumor cells via the Fas/FasL pathway and are regulated by IL-10. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.Y.; Gao, Q.; Wang, Z.C.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.Y.; Min, Z.H.; Shi, Y.H.; Shi, G.M.; Ding, Z.B.; Ke, A.W.; et al. Margin-Infiltrating Cd20(+) B Cells Display an Atypical Memory Phenotype and Correlate with Fa-vorable Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5994–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erdag, G.; Schaefer, J.T.; Smolkin, M.E.; Deacon, D.H.; Shea, S.M.; Dengel, L.T.; Patterson, J.W.; Slingluff, C.L. Immunotype and Immunohistologic Characteristics of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells Are Associated with Clinical Outcome in Metastatic Melanoma. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 1070–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolfson, M.; Muzzio, D.; Ehrhardt, J.; Franchi, A.; Zygmunt, M.; Jensen, F. Expression analysis of cannabinoid receptors 1 and 2 in B cells during pregnancy and their role on cytokine production. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2016, 116, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneda, J.T.; Harui, A.; Kiertscher, S.M.; Roth, J.D.; Roth, M.D. Differential Expression of Intracellular and Ex-tracellular Cb(2) Cannabinoid Receptor Protein by Human Peripheral Blood Leukocytes. J. Neuroimmun. Pharmacol. 2013, 8, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Ray, A.; Dittel, B.N. Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Is Critical for the Homing and Retention of Marginal Zone B Lineage Cells and for Efficient T-Independent Immune Responses. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 5720–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flygare, J.; Gustafsson, K.; Kimby, E.; Christensson, B.; Sander, B. Cannabinoid receptor ligands mediate growth inhibition and cell death in mantle cell lymphoma. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 6885–6889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wasik, A.M.; Christensson, B.; Sander, B. The role of cannabinoid receptors and the endocannabinoid system in mantle cell lymphoma and other non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2011, 21, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasik, A.M.; Almestrand, S.; Wang, X.; Hultenby, K.; Dackland, Å.-L.; Andersson, P.; Kimby, E.; Christensson, B.; Sander, B. WIN55,212-2 induces cytoplasmic vacuolation in apoptosis-resistant MCL cells. Cell Death Dis. 2011, 2, e225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gustafsson, K.; Christensson, B.; Sander, B.; Flygare, J. Cannabinoid Receptor-Mediated Apoptosis Induced byR(+)-Methanandamide and Win55,212-2 Is Associated with Ceramide Accumulation and p38 Activation in Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 70, 1612–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freund, P.; Porpaczy, E.A.; Le, T.; Gruber, M.; Pausz, C.; Staber, P.; Jäger, U.; Vanura, K. Cannabinoid Receptors Are Overexpressed in CLL but of Limited Potential for Therapeutic Exploitation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenberg, H.F.; Dyer, K.D.; Foster, P.S. Eosinophils: Changing perspectives in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 13, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnasco, D.; Ferrando, M.; Caminati, M.; Bragantini, A.; Puggioni, F.; Varricchi, G.; Passalacqua, G.; Canonica, G.W. Targeting Interleukin-5 or Interleukin-5ralpha: Safety Considerations. Drug Saf. 2017, 40, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mattei, F.; Andreone, S.; Marone, G.; Gambardella, A.R.; Loffredo, S.; Varricchi, G.; Schiavoni, G. Eosinophils in the Tumor Microenvironment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1273, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, T.W.; Newton, C.; Larsen, K.; Lu, L.; Perkins, I.; Nong, L.; Friedman, H. The cannabinoid system and immune modulation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2003, 74, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oka, S.; Yanagimoto, S.; Ikeda, S.; Gokoh, M.; Kishimoto, S.; Waku, K.; Ishima, Y.; Sugiura, T. Evidence for the In-volvement of the Cannabinoid Cb2 Receptor and Its Endogenous Ligand 2-Arachidonoylglycerol in 12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-Acetate-Induced Acute Inflammation in Mouse Ear. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 18488–18497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oka, S.; Ikeda, S.; Kishimoto, S.; Gokoh, M.; Yanagimoto, S.; Waku, K.; Sugiura, T. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol, an endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligand, induces the migration of EoL-1 human eosinophilic leukemia cells and human peripheral blood eosinophils. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 76, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frei, R.B.; Luschnig, P.; Parzmair, G.P.; Peinhaupt, M.; Schranz, S.; Fauland, A.; Wheelock, C.E.; Heinemann, A.; Sturm, E.M. Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Augments Eosinophil Responsiveness and Aggravates Allergen-Induced Pulmonary In-flammation in Mice. Allergy 2016, 71, 944–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisaru-Tal, S.; Itan, M.; Klion, A.D.; Munitz, A. A new dawn for eosinophils in the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 594–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varricchi, G.; Galdiero, M.R.; Loffredo, S.; Lucarini, V.; Marone, G.; Mattei, F.; Marone, G.; Schiavoni, G. Eosinophils: The unsung heroes in cancer? OncoImmunology 2018, 7, e1393134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Varricchi, G.; Rossi, F.W.; Galdiero, M.R.; Granata, F.; Criscuolo, G.; Spadaro, G.; De Paulis, A.; Marone, G. Physiological Roles of Mast Cells: Collegium Internationale Allergologicum Update 2019. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 179, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marone, G.; Borriello, F.; Varricchi, G.; Genovese, A.; Granata, F. Basophils: Historical Reflections and Perspectives. Chem. Immunol. Allergy 2014, 100, 172–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, J.T.; Chichester, K.L.; Bieneman, A.P. Human Basophils Secrete IL-3: Evidence of Autocrine Priming for Phenotypic and Functional Responses in Allergic Disease. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 2432–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patella, V.; Giuliano, A.; Bouvet, J.P.; Marone, G. Endogenous superallergen protein Fv induces IL-4 secretion from human Fc epsilon RI+ cells through interaction with the VH3 region of IgE. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 5647–5655. [Google Scholar]
- Genovese, A.; Borgia, G.; Bjorck, L.; Petraroli, A.; de Paulis, A.; Piazza, M.; Marone, G. Immunoglobulin Superantigen Protein L Induces Il-4 and Il-13 Secretion from Human Fc Epsilon Ri+ Cells through Interaction with the Kappa Light Chains of Ige. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 1854–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Paulis, A.; Prevete, N.; Fiorentino, I.; Rossi, F.W.; Staibano, S.; Montuori, N.; Ragno, P.; Longobardi, A.; Liccardo, B.; Genovese, A.; et al. Expression and Functions of the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors and Their Receptors in Human Basophils. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 7322–7331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marone, G.; Schroeder, J.T.; Mattei, F.; Loffredo, S.; Gambardella, A.R.; Poto, R.; De Paulis, A.; Schiavoni, G.; Varricchi, G. Is There a Role for Basophils in Cancer? Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Monte, L.; Reni, M.; Tassi, E.; Clavenna, D.; Papa, I.; Recalde, H.; Braga, M.; Di Carlo, V.; Doglioni, C.; Protti, M.P. Intratumor T helper type 2 cell infiltrate correlates with cancer-associated fibroblast thymic stromal lymphopoietin production and reduced survival in pancreatic cancer. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cencioni, M.T.; Chiurchiù, V.; Catanzaro, G.; Borsellino, G.; Bernardi, G.; Battistini, L.; Maccarrone, M. Anandamide Suppresses Proliferation and Cytokine Release from Primary Human T-Lymphocytes Mainly via CB2 Receptors. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, J.; Niggemann, B.; Zaenker, K.S.; Entschladen, F. Anandamide is an endogenous inhibitor for the migration of tumor cells and T lymphocytes. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2004, 53, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallily, R.; Breuer, A.; Mechoulam, R. 2-Arachidonylglycerol, an Endogenous Cannabinoid, Inhibits Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Production in Murine Macrophages, and in Mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 406, R5–R7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.H.; Lim, S.; Ryu, J.; Lee, C.-W.; Kim, Y.; Kang, J.-H.; Kang, S.-S.; Ahn, Y.K.; Park, C.-S.; Kim, J.J. CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors differentially regulate the production of reactive oxygen species by macrophages. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 84, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouinard, F.; Lefebvre, J.S.; Navarro, P.; Bouchard, L.; Ferland, C.; Lalancette-Hébert, M.; Marsolais, D.; LaViolette, M.; Flamand, N. The Endocannabinoid 2-Arachidonoyl-Glycerol Activates Human Neutrophils: Critical Role of Its Hydrolysis and De Novo Leukotriene B4 Biosynthesis. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 3188–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rayman, N.; Lam, K.H.; Laman, J.D.; Simons, P.J.; Löwenberg, B.; Sonneveld, P.; Delwel, R. Distinct Expression Profiles of the Peripheral Cannabinoid Receptor in Lymphoid Tissues Depending on Receptor Activation Status. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 2111–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jorda, M.A.; SVerbakel, E.; Valk, P.J.; Vankan-Berkhoudt, Y.V.; Maccarrone, M.; Finazzi-Agro, A.; Lowenberg, B.; Delwel, R. Hematopoietic Cells Expressing the Peripheral Cannabinoid Receptor Migrate in Response to the Endocanna-binoid 2-Arachidonoylglycerol. Blood 2002, 99, 2786–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanikawa, T.; Kurohane, K.; Imai, Y. Induction of Preferential Chemotaxis of Unstimulated B-Lymphocytes by 2-Arachidonoylglycerol in Immunized Mice. Microbiol. Immunol. 2007, 51, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guzmán, M. Cannabinoids: Potential anticancer agents. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laezza, C.; Pagano, C.; Navarra, G.; Pastorino, O.; Proto, M.C.; Fiore, D.; Piscopo, C.; Gazzerro, P.; Bifulco, M. The Endocannabinoid System: A Target for Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kienzl, M.; Kargl, J.; Schicho, R. The Immune Endocannabinoid System of the Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciaglia, E.; Torelli, G.; Pisanti, S.; Picardi, P.; D’Alessandro, A.; Laezza, C.; Malfitano, A.M.; Fiore, D.; Zottola, A.C.P.; Proto, M.C.; et al. Cannabinoid receptor CB1 regulates STAT3 activity and its expression dictates the responsiveness to SR141716 treatment in human glioma patients’ cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 15464–15481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utomo, W.K.; De Vries, M.; Braat, H.; Bruno, M.J.; Parikh, K.; Comalada, M.; Peppelenbosch, M.; Van Goor, H.; Fuhler, G.M. Modulation of Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell Signaling by Medicinal Cannabinoids. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavin, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Leader, A.; Amir, E.-A.D.; Elefant, N.; Bigenwald, C.; Remark, R.; Sweeney, R.; Becker, C.D.; Levine, J.H.; et al. Innate Immune Landscape in Early Lung Adenocarcinoma by Paired Single-Cell Analyses. Cell 2017, 169, 750–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braga, F.A.V.; Kar, G.; Berg, M.; Carpaij, O.A.; Polanski, K.; Simon, L.M.; Brouwer, S.; Gomes, T.; Hesse, L.; Jiang, J.; et al. A cellular census of human lungs identifies novel cell states in health and in asthma. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1153–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hua, T.; Li, X.; Wu, L.; Iliopoulos-Tsoutsouvas, C.; Wang, Y.; Wu, M.; Shen, L.; Brust, C.A.; Nikas, S.P.; Song, F.; et al. Activation and Signaling Mechanism Revealed by Cannabinoid Receptor-Gi Complex Structures. Cell 2020, 180, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Xu, T.-H.; Feng, Z.; Zhou, X.E.; Chen, M.; Wang, L.; Meng, X.; Xue, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Cryo-EM Structure of the Human Cannabinoid Receptor CB2-Gi Signaling Complex. Cell 2020, 180, 645–654.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
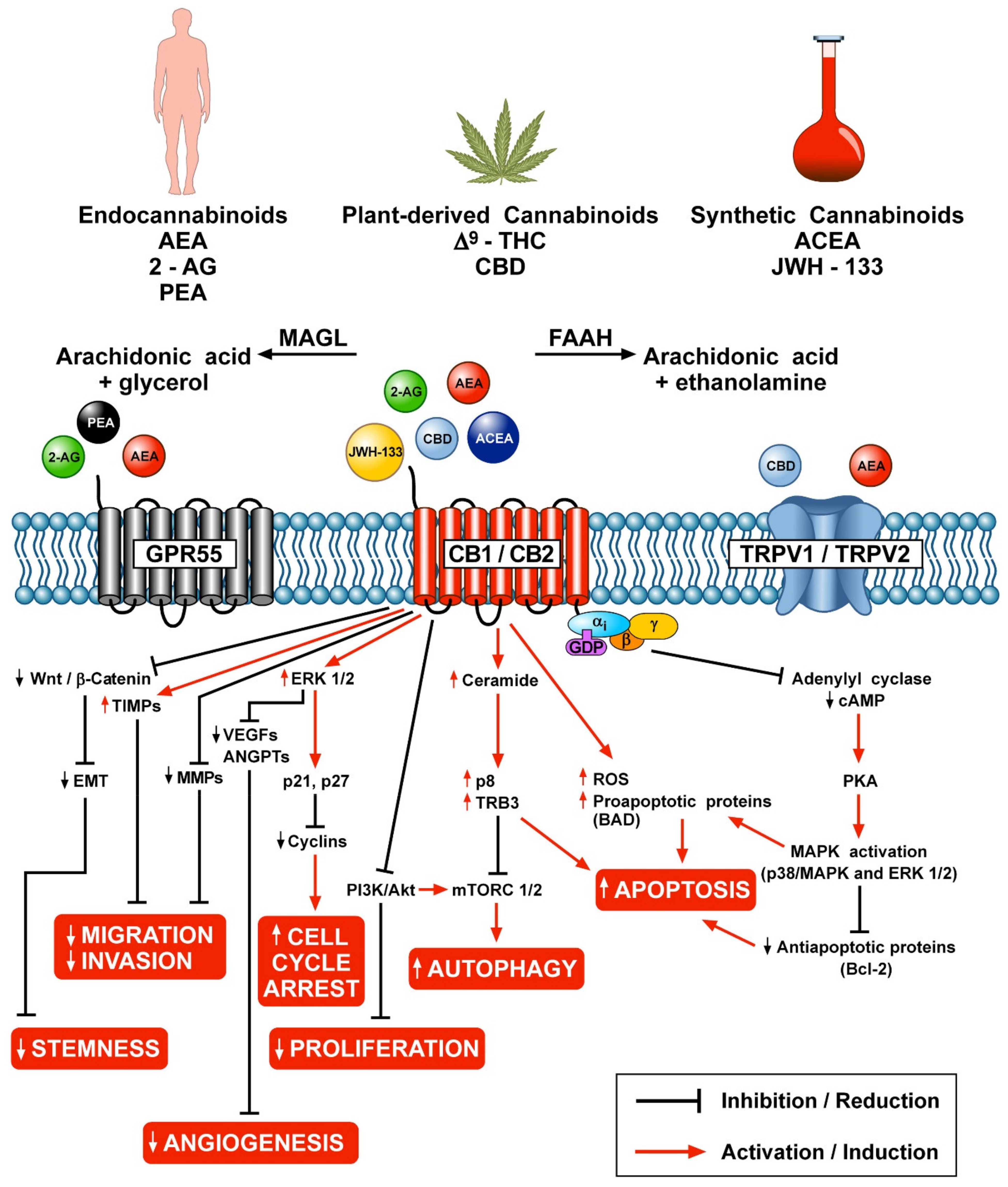

| Immune Cells | Effects of Cannabinoids and CB Receptor Ligands | Ligands | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| T Cells (human, mouse) | Inhibition of T cell proliferation | AEA | [180] |
| Inhibition of cytolytic activity | Δ9-THC | [182] | |
| Modulation of TH1/TH2 subsets | Δ9-THC | [181] | |
| Inhibition of IL-2 expression | AEA, 2-AG | [183] | |
| Inhibition of proliferation and cytokine release | JWH-015, AEA | [179,288] | |
| Up-regulation of CB receptors | Δ9-THC, JWH-015 | [177] | |
| Inhibition of T cell migration | AEA, JWH-133 | [289] | |
| Treg Cells | Up-regulation of Tregs | Δ9-THC | [186] |
| Macrophages (human, mouse, rat) | LPS and PAF induce the synthesis of 2-AG | [197,200] | |
| Inhibition of migration | CP55, 940 | [196] | |
| Inhibition of chemotaxis | O-2137 | [202] | |
| Modulation of phagocytosis | 2-AG | [203] | |
| Inhibition of macrophage cytotoxicity | AEA | [204] | |
| Inhibition of IL-6 release | Δ9-THC, 2-AG | [198] | |
| Inhibition of TNF-α | 2-AG | [290] | |
| Promotion of ROS production | ACEA | [291] | |
| Inhibition of angiogenic factor release | ACEA, JWH-133 | [29] | |
| Inhibition of lymphangiogenic factor release | ACEA, JWH-133 | [29] | |
| Neutrophils (human) | Inhibition of ROS production | 2-AG | [215] |
| Inhibition of chemotaxis | AEA | [51] | |
| Inhibition of motility | 2-AG, JWH-015 | [212] | |
| Inhibition of angiogenic factor release | ACEA, JWH-133 | [46] | |
| Promotion of myeloperoxidase release | 2-AG | [292] | |
| Promotion of LTB4 synthesis | 2-AG | [292] | |
| Mast Cells (human, guinea pig, mouse) | Inhibition of histamine release | 2-AG, AEA | [225,230] |
| Inhibition of activation of skin mast cells | AEA, ACEA | [226] | |
| Inhibition of TNF-α secretion | 2-AG | [229] | |
| Inhibition of cytokine release | AEA | [230] | |
| Modulation of angiogenesis | ACEA, JWH-015 | [227] | |
| Monocytes (human) | Promotion of migration | 2-AG | [235] |
| Inhibition of chemotaxis | JWH-015 | [236] | |
| Inhibition of ICAM-1 expression | JWH-015 | [236] | |
| Inhibition of cytokine release | AEA | [238] | |
| Modulation of ROS production | AEA, ACEA, WH-015 | [291] | |
| Natural Killer Cells (human, mouse) | Inhibition of cytolytic activity | Δ9-THC | [241,242,243,244] |
| Promotion of migration | 2-AG | [245] | |
| Modulation of lung NK cells | AM630 | [246] | |
| Dendritic Cells (human, mouse) | Induction of apoptosis | Δ9-THC | [250] |
| Promotion of chemotaxis | 2-AG | [252] | |
| Inhibition of cytokine release | AEA | [253] | |
| B cells (human) | B-cell differentiation | 2-AG | [265] |
| Accumulation of ceramide | Win55 | [269] | |
| Promotion of migration | 2-AG | [293,294,295] | |
| Eosinophils (human, mouse) | Promotion of chemotaxis | 2-AG, JWH-133 | [275,276,277] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Braile, M.; Marcella, S.; Marone, G.; Galdiero, M.R.; Varricchi, G.; Loffredo, S. The Interplay between the Immune and the Endocannabinoid Systems in Cancer. Cells 2021, 10, 1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061282
Braile M, Marcella S, Marone G, Galdiero MR, Varricchi G, Loffredo S. The Interplay between the Immune and the Endocannabinoid Systems in Cancer. Cells. 2021; 10(6):1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061282
Chicago/Turabian StyleBraile, Mariantonia, Simone Marcella, Gianni Marone, Maria Rosaria Galdiero, Gilda Varricchi, and Stefania Loffredo. 2021. "The Interplay between the Immune and the Endocannabinoid Systems in Cancer" Cells 10, no. 6: 1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061282
APA StyleBraile, M., Marcella, S., Marone, G., Galdiero, M. R., Varricchi, G., & Loffredo, S. (2021). The Interplay between the Immune and the Endocannabinoid Systems in Cancer. Cells, 10(6), 1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061282








