Challenges with Methods for Detecting and Studying the Transcription Factor Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-?B) in the Central Nervous System
Abstract
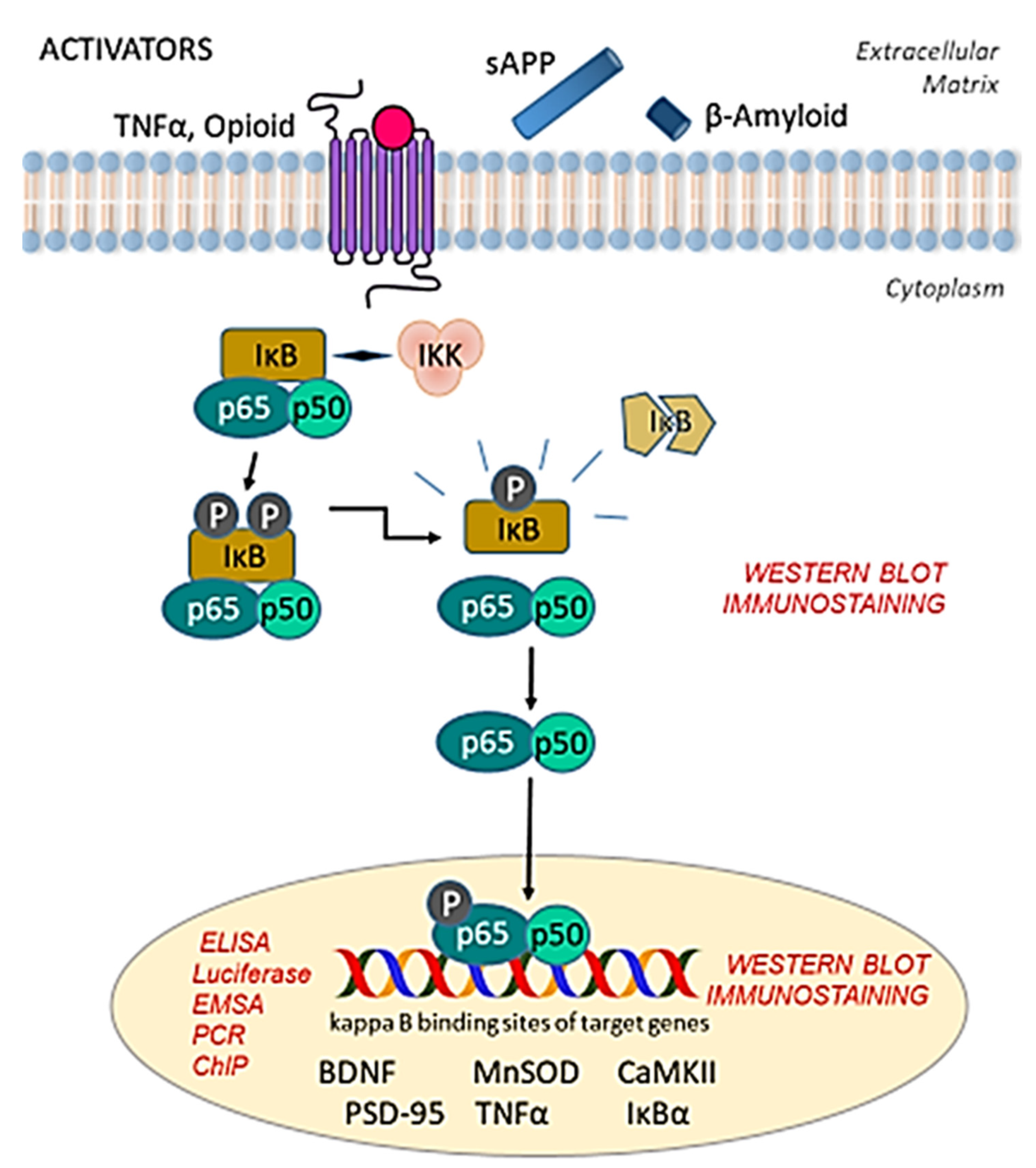
:1. Introduction
2. Identification of NF-κB in the CNS
2.1. Gel Electrophoresis Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) for NF-κB
2.2. Oligonucleotide-Based Chemiluminescent Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.3. Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.4. Immunostaining
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
2.7. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
2.8. High-Throughput Microscopic Imaging System for NF-κB Detection
2.9. Sample Consideration for NF-κB Detection
3. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sen, R.; Baltimore, D. Multiple Nuclear Factors Interact with the Immunoglobulin Enhancer Sequences. Cell 1986, 46, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, P.; Amita, A. NF-κB Transcription Factor: A Key Player in the Generation of Immune Response. Curr. Sci. 2006, 90, 519–531. [Google Scholar]
- Bonizzi, G.; Bebien, M.; Otero, D.C.; Johnson-Vroom, K.E.; Cao, Y.; Vu, D.; Jegga, A.G.; Aronow, B.J.; Ghosh, G.; Rickert, R.C.; et al. Activation of IKKalpha Target Genes Depends on Recognition of Specific kappaB Binding Sites by RelB:p52 Dimers. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 4202–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zabel, U.; Schreck, R.; Baeuerle, P.A. DNA Binding of Purified Transcription Factor NF-kappa B. Affinity, Specificity, Zn2+ Dependence, and Differential Half-site Recognition. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.S.; Sanker, G. NF-κB, the First Quarter-century: Remarkable Progress and Outstanding Questions. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 203–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Napetschnig, J.; Wu, H. Molecular Basis of NF-κB Signaling. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2013, 42, 443–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espinosa, L.; Bigas, A.; Mulero, M.C. Alternative Nuclear Functions for NF-κB Family Members. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2011, 1, 446–459. [Google Scholar]
- Basak, S.; Shih, V.F.; Hoffmann, A. Generation and Activation of Multiple Dimeric Transcription Factors within the NF-kappaB Signaling System. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 28, 3139–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savinova, O.V.; Hoffmann, A.; Ghosh, G. The Nfkb1 and Nfkb2 Proteins p105 and p100 Function as the Core of High-molecular-weight Heterogeneous Complexes. Mol. Cell 2009, 34, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biswas, R.; Bagchi, A. NF-kB pathway and inhibition: An Overview. Comput. Mol. Biol. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, T.D. Introduction to NF-kappaB: Players, Pathways, Perspectives. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6680–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.E.; Huang, D.-B.; Chen, Y.-Q.; Ghosh, G. Crystal Structure of p50/p65 Heterodimer of Transcription Factor NF-kappaB bound to DNA. Nature 1998, 391, 410–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lenardo, M.J.; Baltimore, D. 30 Years of NF-κB: A Blossoming of Relevance to Human Pathobiology. Cell 2017, 168, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perkins, N.D. Post-translational Modifications Regulating the Activity and Function of the Nuclear Factor kappa B Pathway. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6717–6730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsui, R.; Kearns, J.D.; Lynch, C.; Vu, D.; Ngo, K.; Basak, S.; Ghosh, G.; Hoffmann, A. IkappaBbeta Enhances the Generation of the Low-affinity NFkappaB/RelA Homodimer. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, A.; Baltimore, D. Circuitry of Nuclear Factor kappaB Signaling. Immunol. Rev. 2006, 210, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreiro, D.U.; Komives, E.A. Molecular Mechanisms of System Control of NF-kappaB Signaling by IkappaBalpha. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 1560–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Finco, T.S.; Baldwin, A.S. Mechanistic Aspects of NF-κB Regulation: The Emerging Role of Phosphorylation and Proteolysis. Immunity 1995, 3, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giridharan, S.; Srinivasan, M. Mechanisms of NF-κB p65 and Strategies for Therapeutic Manipulation. J. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 11, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Ghosh, S. The NF-kappaB Family of Transcription Factors and Its Regulation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a000034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Transcription Factor NF-kappaB: A Sensor for Smoke and Stress Signals. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1056, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snow, W.M.; Albensi, B.C. Neuronal Gene Targets of NF-κB and Their Dysregulation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haack, K.K.; Mitra, A.K.; Zucker, I.H. NF-kappaB and CREB are Required for Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Upregulation in Neurons. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, S.C. The Non-canonical NF-kappaB Pathway in Immunity and Inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, B.R.B.; Silva, R.C.M.C.; Ferreira, G.M.; Abdelhay, E. NF-kappaB: Two Sides of the Same Coin. Genes 2018, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaltschmidt, B.; Uherek, M.; Volk, B.; Baeuerle, P.A.; Kaltschmidt, C. Transcription Factor NF-kappaB is Activated in Primary Neurons by Amyloid Beta Peptides and in Neurons Surrounding Early Plaques from Patients with Alzheimer Disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 2642–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gessi, S.; Borea, P.A.; Bencivenni, S.; Fazzi, D.; Varani, K.; Merighi, S. The Activation of μ-opioid Receptor Potentiates LPS-Induced NF-kB Promoting an Inflammatory Phenotype in Microglia. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 2813–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandt, J.A.; Churchill, L.; Rehman, A.; Ellis, G.; Mémet, S.; Israël, A.; Krueger, J.M. Sleep Deprivation Increases the Activation of Nuclear Factor kappa B in Lateral Hypothalamic Cells. Brain Res. 2004, 1004, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meffert, M.K.; Chang, J.M.; Wiltgen, B.J.; Fanselow, M.S.; Baltimore, D. NF-kappa B Functions in Synaptic Signaling and Behavior. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberini, C.M. Transcription Factors in Long-term Memory and Synaptic Plasticity. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 121–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P.; Camandola, S. NF-kappaB in Neuronal Plasticity and Neurodegenerative Disorders. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahn, H.J.; Hernandez, C.M.; Levenson, J.M.; Lubin, F.D.; Liou, H.-C.; Sweatt, J.D. c-Rel, an NF-kappaB Family Transcription Factor, is Required for Hippocampal Long-term Synaptic Plasticity and Memory Formation. Learn. Mem. 2008, 15, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albensi, B.C.; Mattson, M.P. Evidence for the Involvement of TNF and NF-kappaB in Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity. Synapse 2000, 35, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.W.; Russo, S.J.; Ferguson, D.; Nestler, E.J.; Duman, R.S. Nuclear Factor-kappaB is a Critical Mediator of Stress-impaired Neurogenesis and Depressive Behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2669–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rolls, A.; Shechter, R.; London, A.; Ziv, Y.; Ronen, A.; Levy, R.; Schwartz, M. Toll-like Receptors Modulate Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltschmidt, C.; Kaltschmidt, B.; Baeuerle, P.A. Brain Synapses Contain Inducible Forms of the Transcription Factor NF-kappa B. Mech. Dev. 1993, 43, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Listwak, S.J.; Rathore, P.; Herkenham, M. Minimal NF-κB Activity in Neurons. Neuroscience 2013, 250, 282–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, A.S.; Waters, M.R.; Biswas, D.D.; Brown, L.N.; Surace, M.J.; Floros, C.; Siebenlist, U.; Kordula, T. RelB Controls Adaptive Responses of Astrocytes during Sterile Inflammation. Glia 2019, 67, 1449–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, L.J.; Surles-Zeigler, M.C.; Li, Y.; Ford, G.D.; Newman, G.D.; Ford, B.D. Regulation of Inflammatory Responses by Neuregulin-1 in Brain Ischemia and Microglial Cells In Vitro Involves the NF-kappa B Pathway. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Purkayastha, S.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yin, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, G.; Cai, D. Hypothalamic Programming of Systemic Aeing Involving IKK-β, NF-κB and GnRH. Nature 2013, 497, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzillotta, A.; Porrini, V.; Bellucci, A.; Benarese, M.; Branca, C.; Parrella, E.; Spano, P.F.; Pizzi, M. NF-κB in Innate Neuroprotection and Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Neurol. 2015, 6, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jones, S.V.; Kounatidis, I. Nuclear Factor-Kappa B and Alzheimer Disease, Unifying Genetic and Environmental Risk Factors from Cell to Humans. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, C.; Kivipelto, M.; von Strauss, E. Epidemiology of Alzheimer’s Disease: Occurrence, Determinants, and Strategies toward Intervention. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2009, 11, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jha, N.K.; Jha, S.K.; Kar, R.; Nand, P.; Swati, K.; Goswami, V.K. Nuclear Factor-kappa β as a Therapeutic Target for Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurochem. 2019, 150, 113–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mattson, M.P.; Meffert, M.K. Roles for NF-kappaB in Nerve Cell Survival, Plasticity, and Disease. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, R.X.; Zhou, P.K. DNA Damage Response Signaling Pathways and Targets for Radiotherapy Sensitization in Cancer. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2020, 5, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, K.E.; Morshed, R.A.; Yamini, B. Nuclear Factor-kappaB in Glioblastoma: Insights into Regulators and Targeted Therapy. Neuro. Oncol. 2016, 18, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Mani, A.M.; Wu, Z.H. DNA Damage-induced Nuclear Factor-kappa B Activation and Its Roles in Cancer Progression. J. Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2017, 3, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, S.; Tschopp, J. Signals from within: The DNA-damage-induced NF-kappaB Response. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puliyappadamba, V.T.; Hatanpaa, K.J.; Chakraborty, S.; Habib, A.A. The Role of NF-kappaB in the Pathogenesis of Glioma. Mol. Cell Oncol. 2014, 1, e963478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tilstra, J.S.; Clauson, C.L.; Niedernhofer, L.J.; Robbins, P.D. NF-κB in Aging and Disease. Aging Dis. 2011, 2, 449–465. [Google Scholar]
- Albensi, B.C. What Is Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-κB) Doing in and to the Mitochondrion? Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltschmidt, B.; Kaltschmidt, C. NF-kappaB in the Nervous System. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a001271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaltschmidt, C.; Kaltschmidt, B.; Neumann, H.; Wekerle, H.; Baeuerle, P.A. Constitutive NF-kappa B Activity in Neurons. Mol. Cell Biol. 1994, 14, 3981–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snow, W.M.; Pahlavan, P.S.; Djordjevic, J.; McAllister, D.; Platt, E.E.; Alashmali, S.; Bernstein, M.J.; Suh, M.; Albensi, B.C. Morris Water Maze Training in Mice Elevates Hippocampal Levels of Transcription Factors Nuclear Factor (Erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 and Nuclear Factor Kappa B p65. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Djordjevic, J.; Thomson, E.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Snow, W.M.; Perez, C.; Wong, T.P.; Fernyhough, P.; Albensi, B.C. Brain Region- and Sex-specific Alterations in Mitochondrial Function and NF-kappaB Signaling in the TgCRND8 Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuroscience 2017, 361, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, O.; O’Loughlin, K.; Minderman, H. Simultaneous Assessment of NF-κB/p65 Phosphorylation and Nuclear Localization Using Imaging Flow Cytometry. J. Immunol. Methods 2015, 423, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, S.; Ge, J.; Yu, J.Y. Icariin Prevents Cytokine-induced β-cell Death by Inhibiting NF-κB Signaling. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 2756–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sadhukhan, R.; Leung, J.W.C.; Garg, S.; Krager, K.J.; Savenka, A.V.; Basnakian, A.G.; Pathak, R. Fractionated Radiation Suppresses Kruppel-like Factor 2 Pathway to a Greater Extent than by Single Exposure to the same Total Dose. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.-J.; Choi, G.-E.; Ryu, S.; Kwon, S.J.; Kim, S.C.; Booth, C.; Nichols, K.E.; Kim, H.S. Stepwise Phosphorylation of p65 Promotes NF-κB Activation and NK Cell Responses during TargetCell Recognition. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, J.M.; Clingman, C.C.; Ryder, S.P. Quantitative Approaches to Monitor Protein-nucleic Acid Interactions Using Fluorescent Probes. RNA 2011, 17, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrmann, O.; Baumann, B.; de Lorenzi, R.; Muhammad, S.; Zhang, W.; Kleesiek, J.; Malfertheiner, M.; Köhrmann, M.; Potrovita, I.; Maegele, I.; et al. IKK Mediates Ischemia-induced Neuronal Death. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 1322–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maqbool, A.; Lattke, M.; Wirth, T.; Baumann, B. Sustained, Neuron-specific IKK/NF-κB Activation Generates a Selective Neuroinflammatory Response Promoting Local Neurodegeneration with Aging. Mol. Neurodegener. 2013, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birbach, A.; Gold, P.; Binder, B.R.; Hofer, E.; de Martin, R.; Schmid, J.A. Signaling Molecules of the NF-kappa B Pathway Shuttle Constitutively between Cytoplasm and Nucleus. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 10842–10851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phelps, C.B.; Sengchanthalangsy, L.L.; Huxford, T.; Ghosh, G. Mechanism of I kappa B Alpha Binding to NF-kappa B Dimers. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 29840–29846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karin, M.; Ben-Neriah, Y. Phosphorylation Meets Ubiquitination: The Control of NF-[kappa]B activity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000, 18, 621–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israël, A. The IKK Complex, a Central Regulator of NF-kappaB Activation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a000158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guan, H.; Hou, S.; Ricciardi, R.P. DNA Binding of Repressor Nuclear Factor-kappaB p50/p50 Depends on Phosphorylation of Ser337 by the Protein Kinase A Catalytic Subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 9957–9962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Chen, L.F. Methods to Detect NF-κB Acetylation and Methylation. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1280, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shrum, C.K.; Defrancisco, D.; Meffert, M.K. Stimulated Nuclear Translocation of NF-kappaB and Shuttling Differentially Depend on Dynein and the Dynactin Complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2647–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blondeau, N.; Widmann, C.; Lazdunski, M.; Heurteaux, C. Activation of the Nuclear Factor-kappaB is a Key Event in Brain Tolerance. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 4668–4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fillebeen, C.; Wilkinson, N.; Pantopoulos, K. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) for the Study of RNA-protein Interactions: The IRE/IRP Example. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 52230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holden, N.S.; Tacon, C.E. Principles and Problems of the Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2011, 63, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, H.J.; O’Connor, J.J. A Role for COX-2 and p38 Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase in Long-term Depression in the Rat Dentate Gyrus In Vitro. Neuropharmacology 2003, 44, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Hara, T.; Ishido, Y.; Yoshihara, A.; Oda, K.; Makino, M.; Ishii, N.; Hiroi, N.; Suzuki, K. Rapid Preparation of High-purity nuclear Proteins from a Small Number of Cultured Cells for Use in Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assays. BMC Immunol. 2014, 15, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marwarha, G.; Raza, S.; Prasanthi, J.R.P.; Ghribi, O. Gadd153 and NF-κB Crosstalk Regulates 27-hydroxycholesterol-induced Increase in BACE1 and β-amyloid Production in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70773. [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga, S.; Stegeman, J.J. Elimination of Nonspecific Bands in Non-radioactive Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assays Using the Digoxigenin System. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 465, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jullien, N.; Herman, J.P. LUEGO: A Cost and Time Saving Gel Shift Procedure. Biotechniques 2011, 51, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellman, L.M.; Fried, M.G. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) for Detecting Protein-nucleic Acid Interactions. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1849–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, P.; Ernest, I.; Houbion, A.; Art, M.; Le Calvez, H.; Raes, M.; Remacle, J. Development of a Sensitive Multi-well Colorimetric Assay for Active NFkappaB. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, E21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challis, B.; Heyman, J.A.; Baer, S.; Wasden, C. Simplified Quantitation of Activated Transcription Factors. Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Lu, D.; Ye, S.; Ye, H.; Zhu, L.; Feng, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, D.; Hu, Q. A Simplified Probe Preparation for ELISA-based NF-kappaB Activity Assay. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2005, 65, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, N.; Sarno, A.; Idler, I.S.; Führer, M.; Zenz, T.; Döhner, H.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Mertens, D. High.-throughput Detection of Nuclear Factor-kappaB Activity Using a Sensitive oligo-based Chemiluminescent Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porrini, V.; Sarnico, I.; Benarese, M.; Branca, C.; Mota, M.; Lanzillotta, A.; Bellucci, A.; Parrella, E.; Faggi, L.; Spano, P.; et al. Neuroprotective and Anti-Apoptotic Effects of CSP-1103 in Primary Cortical Neurons Exposed to Oxygen and Glucose Deprivation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shim, D.J.; Yang, L.; Reed, J.G.; Noebels, J.L.; Chiao, P.J.; Zheng, H. Disruption of the NF-κB/IκBα Autoinhibitory Loop Improves Cognitive Performance and Promotes Hyperexcitability of Hippocampal Neurons. Mol. Neurodegener. 2011, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheppard, P.W.; Sun, X.; Emery, J.F.; Giffard, R.G.; Khammash, M. Quantitative Characterization and Analysis of the Dynamic NF-κB Response in Microglia. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osorio, F.G.; de la Rosa, J.; Freije, J.M. Luminescence-based In Vivo Monitoring of NF-κB Activity through a Gene Delivery Approach. Cell Commun. Signal. 2013, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Branchini, B.R.; Southworth, T.L.; Fontaine, D.M.; Kohrt, D.; Florentine, C.M.; Grossel, M.J. A Firefly Luciferase Dual Color. Bioluminescence Reporter Assay Using Two Substrates To Simultaneously Monitor Two Gene Expression Events. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsen, H.; Moskaug, J.; Fromm, S.H.; Blomhoff, R. In Vivo Imaging of NF-kappa B Activity. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Viviani, V.R. The Origin, Diversity, and Structure Function Relationships of Insect Luciferases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2002, 59, 1833–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matta, H.; Gopalakrishnan, R.; Choi, S.; Prakash, R.; Natarajan, V.; Prins, R.; Gong, S.; Chitnis, S.D.; Kahn, M.; Han, X.; et al. Development and Characterization of a Novel Luciferase based Cytotoxicity Assay. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sherf, B.; Navarro, S.L.; Hannah, R.R.; Wood, K.V. Dual-Luciferase TM Reporter Assay: An. Advanced Co-Reporter Technology Integrating Firefly and Renilla Luciferase Assays. Promega Notes 1996, 57, 2–8. [Google Scholar]
- Auld, D.S.; Lovell, S.; Thorne, N.; Lea, W.A.; Maloney, D.J.; Shen, M.; Rai, G.; Battaile, K.P.; Thomas, C.J.; Simeonov, A.; et al. Molecular Basis for the High-affinity Binding and Stabilization of Firefly Luciferase by PTC124. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4878–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andruska, N.; Mao, C.; Cherian, M.; Zhang, C.; Shapiro, D.J. Evaluation of a Luciferase-based Reporter Assay as a Screen for Inhibitors of Estrogen-ERalpha-induced Proliferation of Breast Cancer Cells. J. Biomol. Screen. 2012, 17, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buckley, S.M.; Delhove, J.M.K.M.; Perocheau, D.P.; Karda, R.; Rahim, A.A.; Howe, S.J.; Ward, N.J.; Birrell, M.A.; Belvisi, M.G.; Arbuthnot, P.; et al. In Vivo Bioimaging with Tissue-specific Transcription Factor Activated Luciferase Reporters. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Badr, C.E.; Niers, J.M.; Tjon-Kon-Fat, L.-A.; Noske, D.P.; Wurdinger, T.; Tannous, B.A. Real-time Monitoring of Nuclear Factor kappaB Activity in Cultured Cells and in Animal Models. Mol. Imaging 2009, 8, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.W.; Roh, J.; Park, C.S. Immunohistochemistry for Pathologists: Protocols, Pitfalls, and Tips. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2016, 50, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Matos, L.L.; Trufelli, D.C.; de Matos, M.G.L.; da Silva Pinhal, M.A. Immunohistochemistry as an Important Tool in Biomarkers Detection and Clinical Practice. Biomark Insights 2010, 5, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandtzaeg, P. The Increasing Power of Immunohistochemistry and Immunocytochemistry. J. Immunol. Methods 1998, 216, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlimoghaddam, A.; Albensi, B.C. The Nuclear Factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) Signaling Pathway is Involved in Ammonia-induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Mitochondrion 2021, 57, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koedel, U.; Bayerlein, I.; Paul, R.; Sporer, B.; Pfister, H.W. Pharmacologic Interference with NF-κB Activation Attenuates Central Nervous System Complications in Experimental Pneumococcal Meningitis. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 182, 1437–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mettang, M.; Reichel, S.N.; Lattke, M.; Palmer, A.; Abaei, A.; Rasche, V.; Huber-Lang, M.; Baumann, B.; Wirth, T. IKK2/NF-kappaB Signaling Protects Neurons after Traumatic Brain Injury. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 1916–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stack, E.C.; Wang, C.; Roman, K.A.; Hoyt, C.C. Multiplexed Immunohistochemistry, Imaging, and Quantitation: A Review, with an Assessment of Tyramide Signal Amplification, Multispectral Imaging and Multiplex Analysis. Methods 2014, 70, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlimoghaddam, A.; Odero, G.G.; Glazner, G.; Turner, R.S.; Albensi, B.C. Nilotinib Improves Bioenergetic Profiling in Brain Astroglia in the 3xTg Mouse Model. of Alzheimer’s Disease. Aging Dis. 2021, 12, 441–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, J.J.; Wilkinson, D.J.; Rankin, D.; Phillips, B.E.; Szewczyk, N.J.; Smith, K.; Atherton, P.J. An Overview of Technical Considerations for Western Blotting Applications to Physiological Research. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2017, 27, 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, T.; Yang, P.C. Western Blot: Technique, Theory, and Trouble Shooting. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 4, 429–434. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, E.C. The Basics of Western Blotting. Anat. Rec. 2012, 295, 369–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maguire, O.; Collins, C.; O’Loughlin, K.; Miecznikowski, J.; Minderman, H. Quantifying Nuclear p65 as a Parameter for NF-kappaB Activation: Correlation between ImageStream Cytometry, Microscopy, and Western Blot. Cytom. Part A 2011, 79, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Christian, F.; Smith, E.L.; Carmody, R.J. The Regulation of NF-kappaB Subunits by Phosphorylation. Cells 2016, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, S.C. Non-canonical NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, B.; Yang, X.-D.; Lamb, A.; Chen, L.-F. Posttranslational Modifications of NF-kappaB: Another Layer of Regulation for NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway. Cell Signal. 2010, 22, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slotta, C.; Müller, J.; Tran, L.; Hauser, S.; Widera, D.; Kaltschmidt, B.; Kaltschmidt, C. An Investigation of the Specificity of Research Antibodies against NF-κB-subunit p65. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2014, 62, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, R.; Gilda, J.E.; Gomes, A.V. The Necessity of and Strategies for Improving Confidence in the Accuracy of Western Blots. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2014, 11, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bottero, V.; Imbert, V.; Freiin, C.; Formento, J.-L.; Peyron, J.-F. Monitoring NF-kappa B Transactivation Potential via Real-time PCR Quantification of I kappa B-alpha Gene Expression. Mol. Diagn. 2003, 7, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deepak, S.; Kottapalli, K.R.; Rakwal, R.; Oros, G.; Rangappa, K.S.; Iwahashi, H.; Masuo, Y.; Agrawal, G.K. Real-Time PCR: Revolutionizing Detection and Expression Analysis of Genes. Curr. Genom. 2007, 8, 234–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulson, D.T.; Brockbank, S.; Quinn, J.G.; Murphy, S.; Ravid, R.; Irvine, G.B.; Johnston, J.A. Identification of Valid Reference Genes for the Normalization of RT qPCR Gene Expression Data in Human Brain Tissue. BMC Mol. Biol. 2008, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Penna, I.; Vella, S.; Gigoni, A.; Russo, C.; Cancedda, R.; Pagano, A. Selection of Candidate Housekeeping Genes for Normalization in Human Postmortem Brain Samples. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5461–5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rydbirk, R.; Folke, J.; Winge, K.; Aznar, S.; Pakkenberg, B.; Brudek, T. Assessment of Brain Reference Genes for RT-qPCR Studies in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nazari, M.; Khodadadi, H.; Fathalizadeh, J.; Hassanshahi, G.; Bidaki, R.; Ayoobi, F.; Hajebrahimi, B.; Bagheri, F.; Arababadi, M.K. Defective NF-kB Transcription Factor as the Mediator of Inflammatory Responses: A Study on Depressed Iranian Medical Students. Clin. Lab. 2013, 59, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, W.C.; Wang, C.-X.; Pan, Y.-X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.-M.; Zhang, X.-S.; Shi, J.-X.; Zhou, M.-L. Activation of Nuclear Factor-κB in the Brain after Experimental Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Its Potential Role in Delayed Brain Injury. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, D. Quantification Using Real-time PCR Technology: Applications and Limitations. Trends Mol. Med. 2002, 8, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valasek, M.A.; Repa, J.J. The Power of Real-time PCR. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2005, 29, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gade, P.; Kalvakolanu, D.V. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assay as a Tool for Analyzing Transcription Factor Activity. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 809, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assays Analyzing Transcription Factor.pdf. Available online: https://www.future-science.com/doi/pdf/10.2144/04376RV01 (accessed on 1 December 2004).
- Riedlinger, T.; Liefke, R.; Meier-Soelch, J.; Jurida, L.; Nist, A.; Stiewe, T.; Kracht, M.; Lienhard Schmitz, M. NF-kappaB p65 Dimerization and DNA-binding is Important for Inflammatory Gene Expression. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 4188–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, P.M.; Ramachandran, K.; VanWert, J.; Singal, R. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assay. Biotechniques 2004, 37, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njikan, S.; Manning, A.J.; Ovechkina, Y.; Awasthi, D.; Parish, T. High Content, High-throughput Screening for Small Molecule Inducers of NF-kappaB Translocation. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199966. [Google Scholar]
- Noursadeghi, M.; Tsang, J.; Haustein, T.; Miller, R.F.; Chain, B.M.; Katz, D.R. Quantitative Imaging Assay for NF-kappaB Nuclear Translocation in Primary Human Macrophages. J. Immunol. Methods 2008, 329, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di, Z.; Herpers, B.; Fredriksson, L.; Yan, K.; van de Water, B.; Verbeek, F.J.; Meerman, J.H.N. Automated Analysis of NF-kappaB Nuclear Translocation Kinetics in High-throughput Screening. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, S.; Bianchi, M.E.; Agresti, A. High-throughput Analysis of NF-κB Dynamics in Single Cells Reveals Basal Nuclear Localization of NF-κB and Spontaneous Activation of Oscillations. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafarge, S.; Hamzeh-Cognasse, H.; Chavarin, P.; Genin, C.; Garraud, O.; Cognasse, F. A Flow Cytometry Technique to Study Intracellular Signals NF-kappaB and STAT3 in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. BMC Mol. Biol. 2007, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- George, T.C.; Fanning, S.L.; Fitzgeral-Bocarsly, P.; Medeiros, R.B.; Highfill, S.; Shimizu, Y.; Hall, B.E.; Frost, K.; Basiji, D.; Ortyn, W.E.; et al. Quantitative Measurement of Nuclear Translocation Events Using Similarity Analysis of Multispectral Cellular Images Obtained in Flow. J. Immunol. Methods 2006, 311, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Bose, P.; Leong-Quong, R.Y.Y.; Fujita, D.J.; Riabowol, K. REAP: A Two Minute Cell Fractionation Method. BMC Res. Notes 2010, 3, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salles, A.; Boccia, M.; Blake, M.; Corbi, N.; Passananti, C.; Baratti, C.M.; Romano, A.; Freudenthal, R. Hippocampal Dynamics of Synaptic NF-kappa B during Inhibitory Avoidance Long-term Memory Consolidation in Mice. Neuroscience 2015, 291, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meffert, M.K.; Baltimore, D. Physiological Functions for Brain NF-kappaB. Trends Neurosci. 2005, 28, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghirova, S.; Hughes, B.G.; Hendzel, M.J.; Schulz, R. Sequential Fractionation and Isolation of Subcellular Proteins from Tissue or Cultured Cells. MethodsX 2015, 2, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pryor, P.R. The Quarterly Review of Biology. In Subcellular Fractionation: A Laboratory Manual; Paul, R., Ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 91, p. 95. ISBN 978-1-62182-038-3/978–1-62182–042-0. [Google Scholar]
- Shehadul Islam, M.; Aryasomayajula, A.; Selvaganapathy, P.R. A Review on Macroscale and Microscale Cell Lysis Methods. Micromachines 2017, 8, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolotto, V.; Cuccurazzu, B.; Canonico, P.L.; Grilli, M. NF-kappaB Mediated Regulation of Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis: Relevance to Mood Disorders and Antidepressant Activity. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 612798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, A.S.; Ruzov, A.S.; Budanov, A.V.; Prokhortchouk, A.V.; Ivanov, A.V.; Prokhortchouk, E.B. High Constitutive Level of NF-kappaB is Crucial for Viability of Adenocarcinoma Cells. Cell Death Differ. 2001, 8, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Berger, E.A. Characterization of Site-Specific Phosphorylation of NF-kappaB p65 in Retinal Cells in Response to High. Glucose and Cytokine Polarization. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 3020675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, H.; May, M.J.; Jimi, E.; Ghosh, S. The Phosphorylation Status of Nuclear NF-κB Determines Its Association with CBP/p300 or HDAC-1. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiernan, R.; Brès, V.; Ng, R.W.M.; Coudart, M.-P.; El Messaoudi, S.; Sardet, C.; Jin, D.-Y.; Emiliani, S.; Benkirane, M. Post-activation turn-off of NF-kappa B-dependent Transcription is Regulated by Acetylation of p65. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 2758–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ernst, O.; Vayttaden, S.J.; Fraser, I.D.C. Measurement of NF-kappaB Activation in TLR-Activated Macrophages. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1714, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- The IκB-NF-κB Signaling Module: Temporal Control and Selective Gene Activation.pdf. Available online: https://science.sciencemag.org/content/298/5596/1241/tab-figures-data (accessed on 28 August 2002).



| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) | High specificity and sensitivity because of antigen-antibody reaction High efficiency | High possibility of false-negative and false-positive results Expensive to prepare antibody Labor intensive Antibody stability |
| Luciferase Reporter Assay | Highly sensitive quantification Widely used for cell-based gene expression assays Large dynamic range of bioluminescence affords | Time consuming |
| Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction | Rapid and sensitive Applicable for primary cells and frozen samples | High possibility of false-negative or false-positive results |
| Western Blotting | High sensitivity and specificity due to antigen-antibody reaction Has the ability to detect picogram level of proteins in a sample | High false or subjective results High cost High technical demand Requirement of a specific antibody to detect the protein of interest |
| Gel Electrophoresis Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) | Simple, sensitive, and robust | Does not provide information regarding the location of nucleic acid sequences, molecular weight and identities of the protein in a protein-nucleic acid complex |
| Immunohistochemistry (Immunostaining) | High specificity due to antigen-antibody reaction High resolution Good signal amplification | Reaction bias Interruption bias Possibility of having a high background Species cross-reactivity |
| Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) | Rapid and effective Determines interactions between DNA binding proteins, target genes and unknown DNA sequences | Not a quantitative approach Variability in crosslinking between DNA and target protein among samples Variability in crosslinking with antibody immunoprecipitation |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mostafizar, M.; Cortes-Pérez, C.; Snow, W.; Djordjevic, J.; Adlimoghaddam, A.; Albensi, B.C. Challenges with Methods for Detecting and Studying the Transcription Factor Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-?B) in the Central Nervous System. Cells 2021, 10, 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061335
Mostafizar M, Cortes-Pérez C, Snow W, Djordjevic J, Adlimoghaddam A, Albensi BC. Challenges with Methods for Detecting and Studying the Transcription Factor Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-?B) in the Central Nervous System. Cells. 2021; 10(6):1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061335
Chicago/Turabian StyleMostafizar, Marina, Claudia Cortes-Pérez, Wanda Snow, Jelena Djordjevic, Aida Adlimoghaddam, and Benedict C. Albensi. 2021. "Challenges with Methods for Detecting and Studying the Transcription Factor Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-?B) in the Central Nervous System" Cells 10, no. 6: 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061335
APA StyleMostafizar, M., Cortes-Pérez, C., Snow, W., Djordjevic, J., Adlimoghaddam, A., & Albensi, B. C. (2021). Challenges with Methods for Detecting and Studying the Transcription Factor Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-?B) in the Central Nervous System. Cells, 10(6), 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061335







