Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α Attenuates Ischemic Brain Damage by Modulating Inflammatory Response and Glial Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Classification and Drug Administration
2.2. Induction of Focal Cerebral Ischemia by Endothelin-1
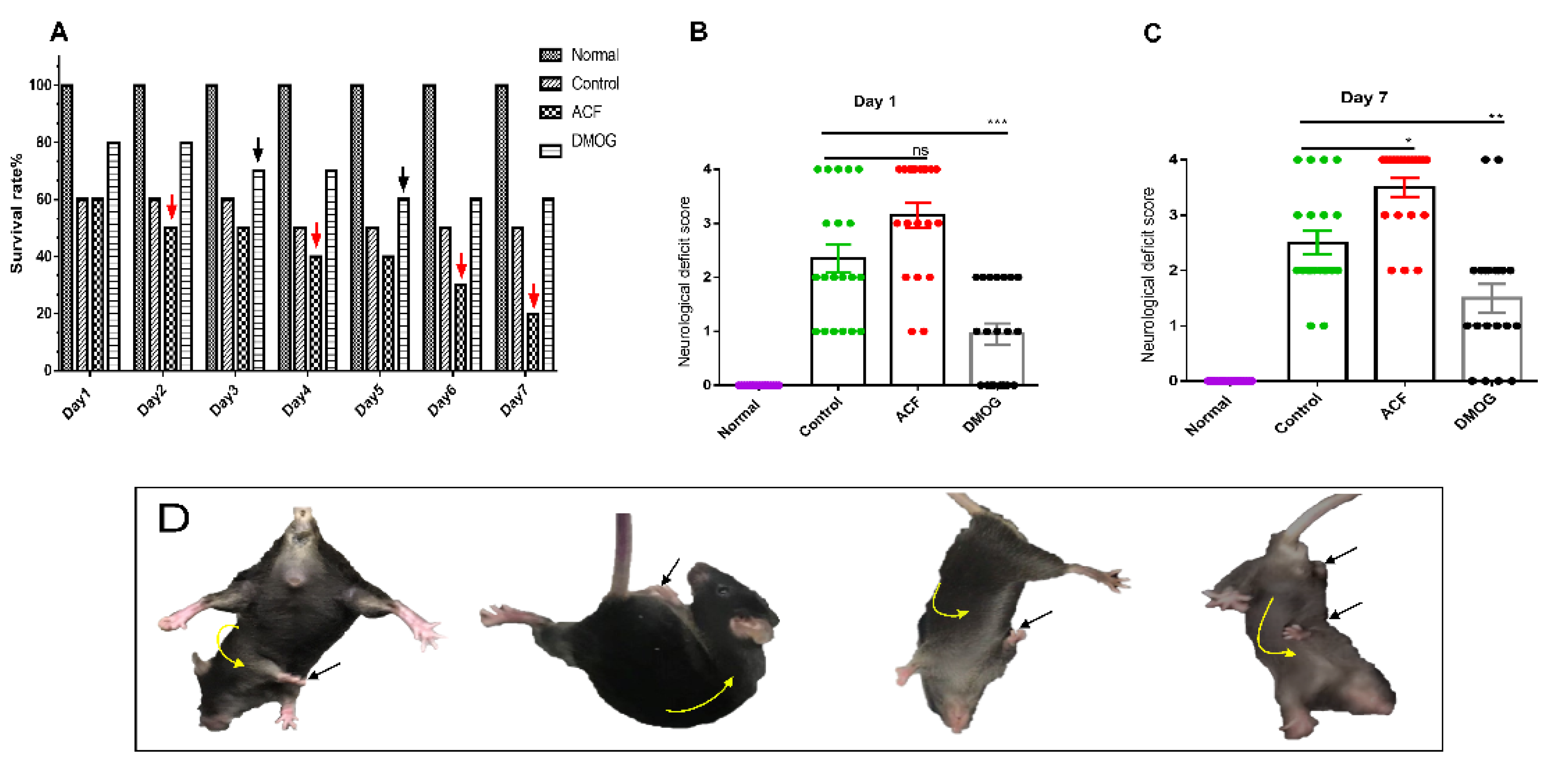
2.3. Neurological Deficit Score and Survival Rate
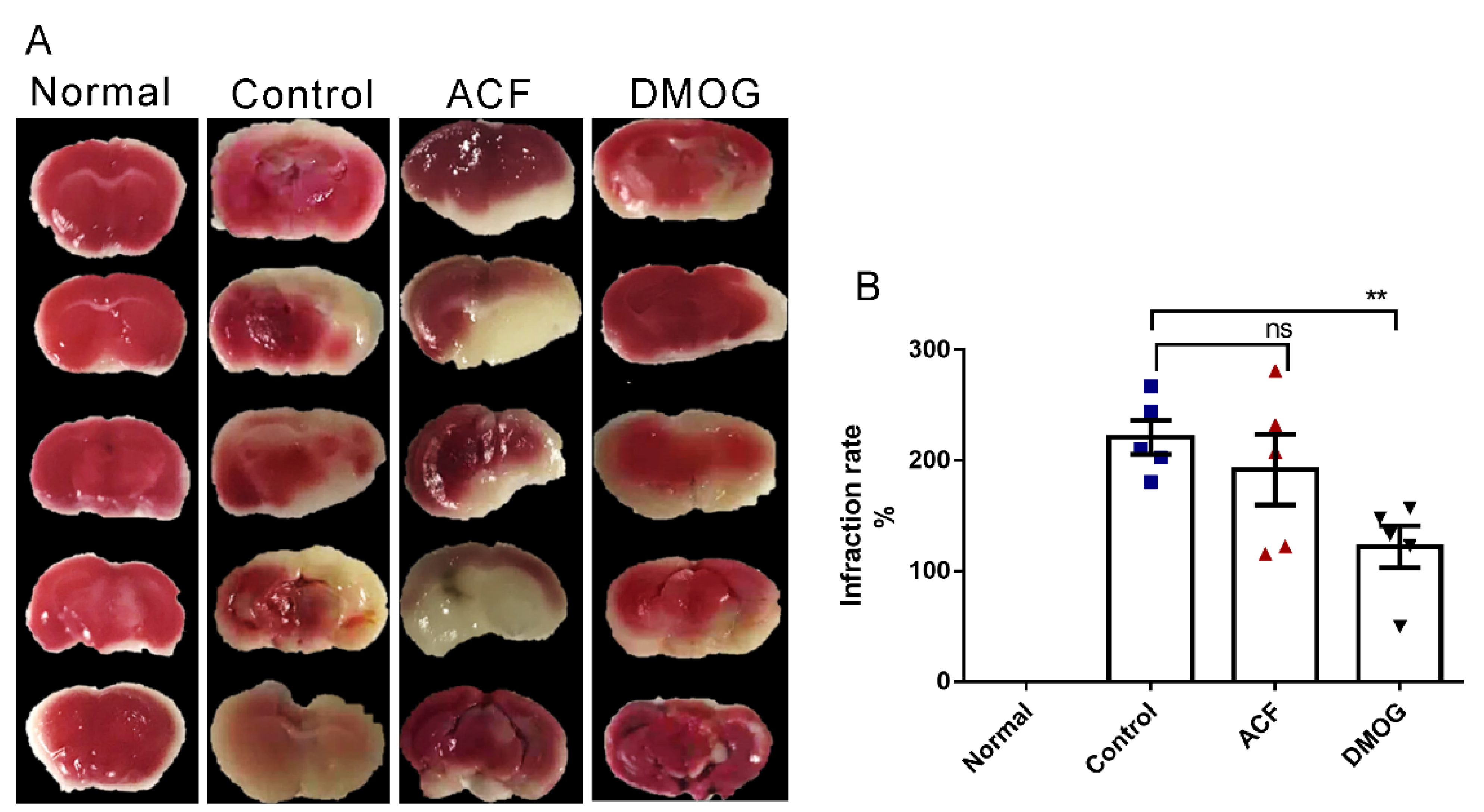
2.4. 2,3,5-. Triphenyl Tetrazolium Chloride [TTC] Staining
2.5. Hematoxylin-Eosin [HE]
2.6. Western Blotting
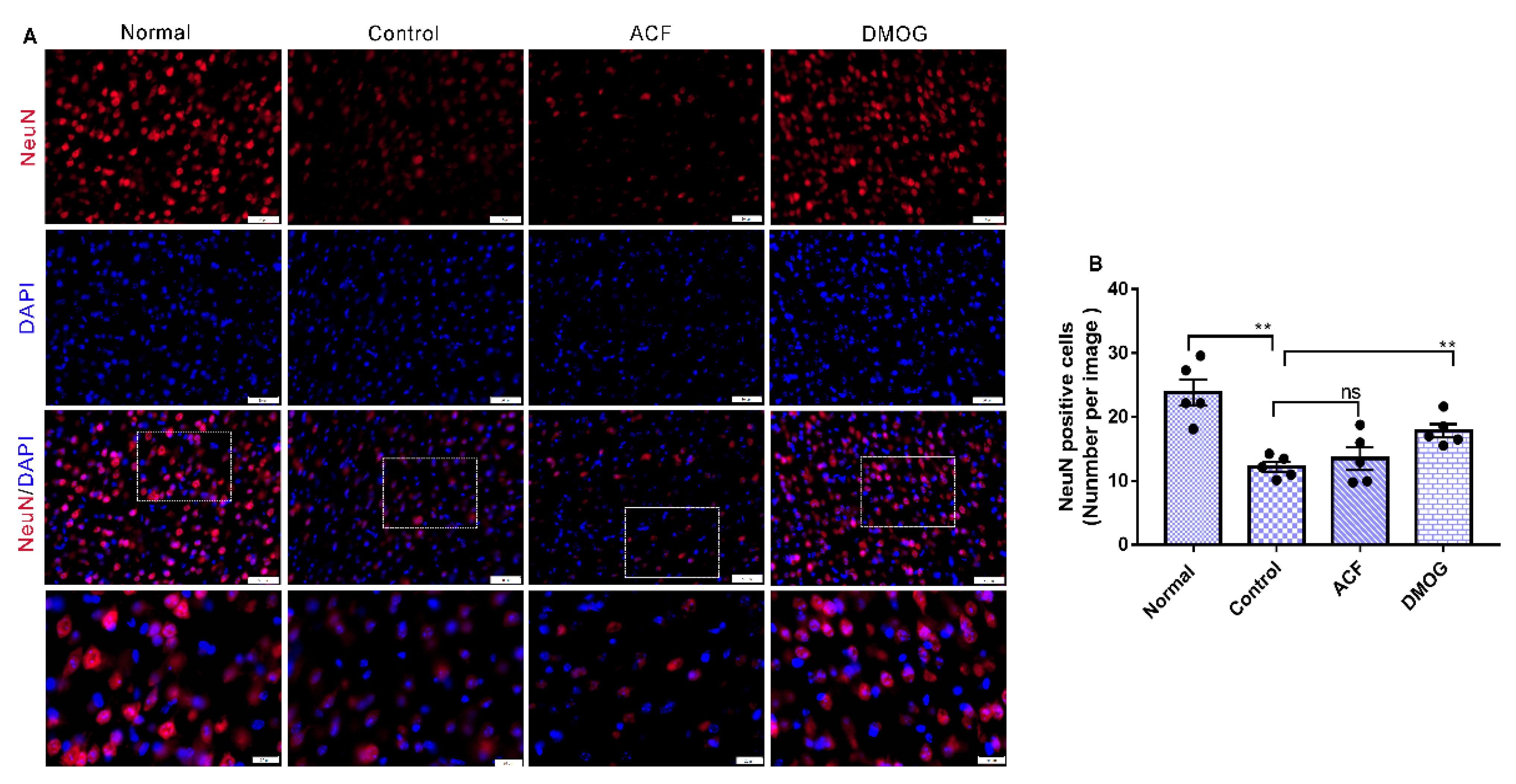
2.7. Immunofluorescence
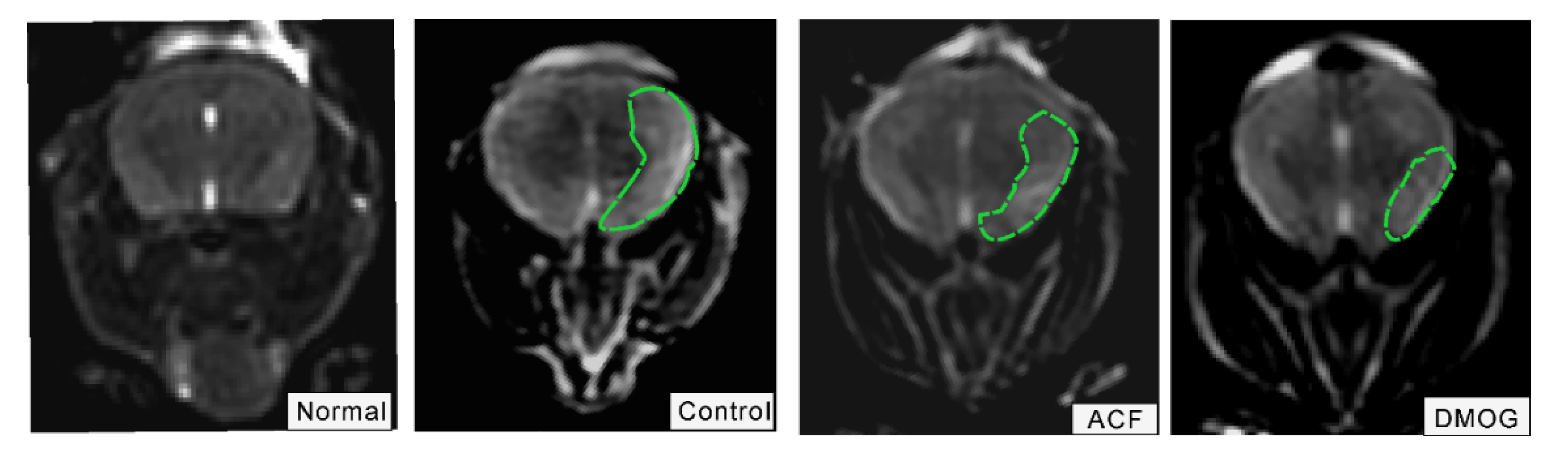
2.8. T2-Weighted MRI
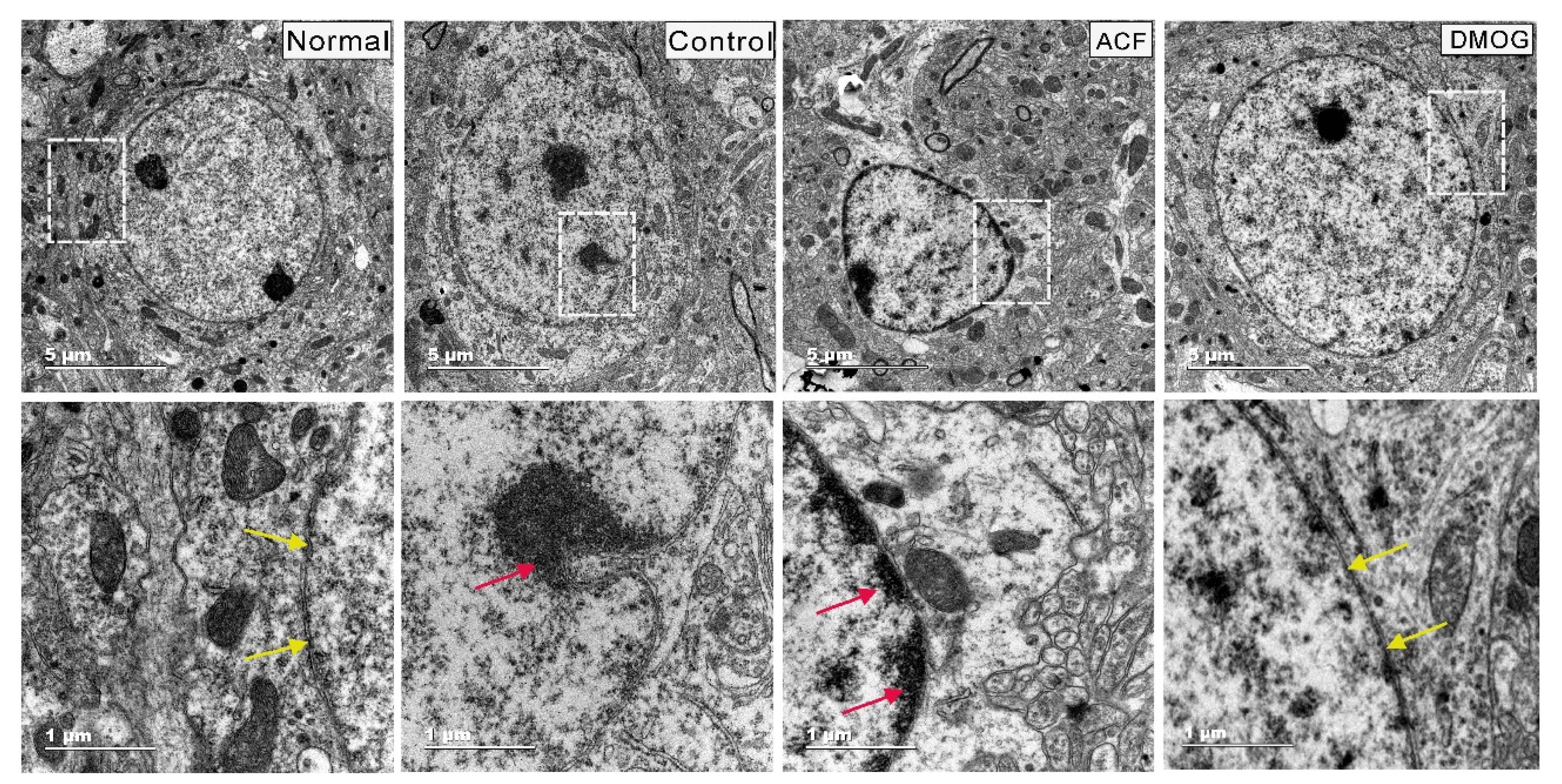
2.9. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.10. Real-Time PCR
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. HIF-1α Improved the Neurological Deficit Score
3.2. HIF-1 Reduces the Infarct Area Volume Resulting from ET-1 Injection
3.3. HIF-1α Activation Recovered the Brain Damage Following ET-1 Injection
3.4. HIF-1α Activation Possesses a Neuroprotective Effect Post-Stroke
3.5. HIF-1α Activation Can Modulate Brain Damage via Neuronal Soma Protection
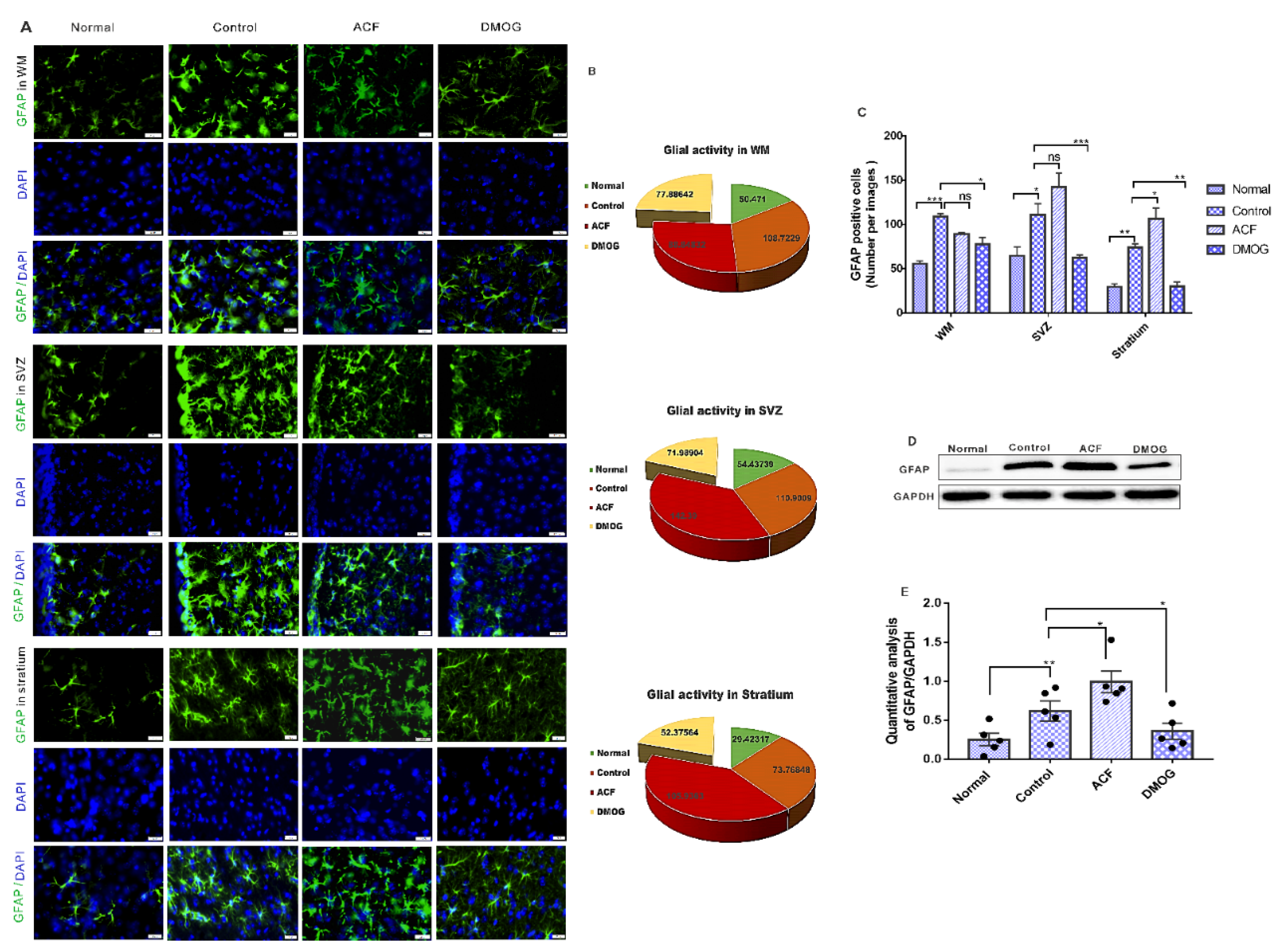
3.6. HIF-1α Reduces the Glial Activity Following ET-1 Injection
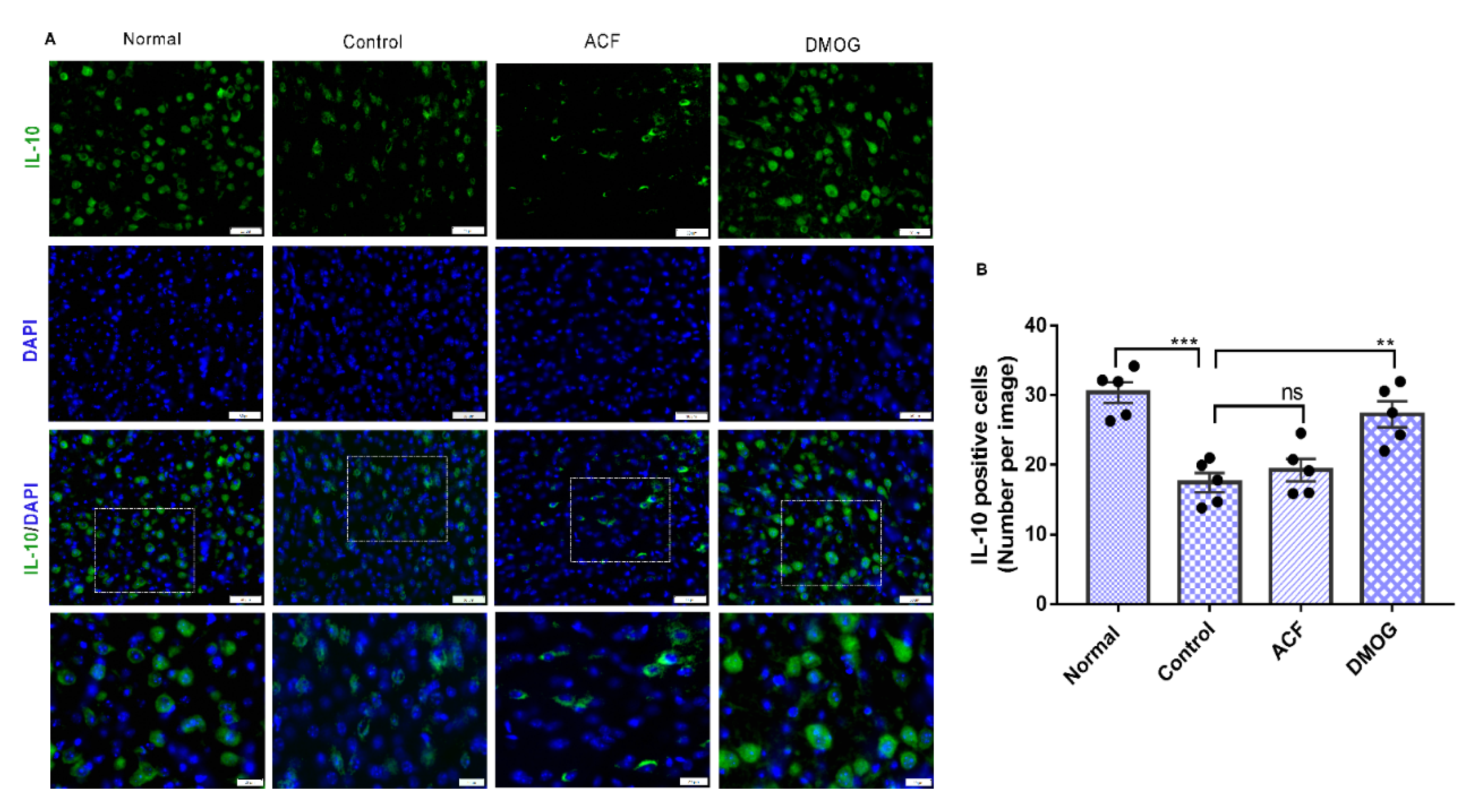
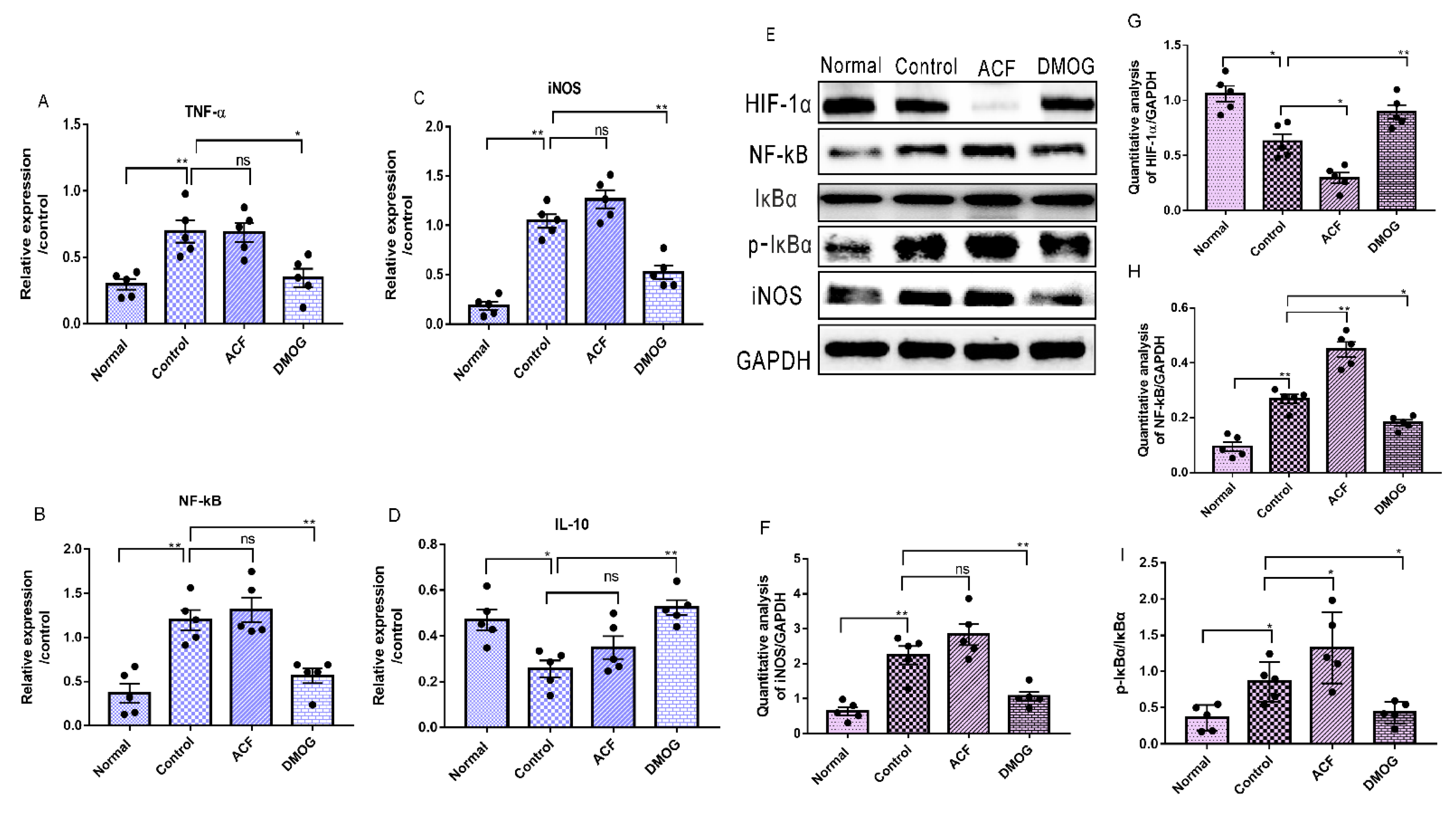
3.7. HIF-1α Activation Down-Regulates the Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines iNOS, NF-kB, and Upregulates the Anti-Inflammatory Marker IL-10
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panel; Mohr, J.P.; Albers, G.W.; Amarenco, P.; Babikian, V.L.; Biller, J.; Brey, R.L.; Coull, B.; Easton, J.D.; Gomez, C.R.; et al. Etiology of stroke. Stroke 1997, 28, 1501–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, H.J.; Bernaudin, M.; Bellail, A.; Schoch, H.; Euler, M.; Petit, E.; Risau, W. Hypoxia-Induced Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression Precedes Neovascularization after Cerebral Ischemia. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H. Hypoxia inducible factor 1 as a therapeutic target in ischemic stroke. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 4593–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernaudin, M.; Nedelec, A.S.; Divoux, D.; MacKenzie, E.T.; Petit, E.; Schumann-Bard, P. Normobaric hypoxia induces tolerance to focal permanent cerebral ischemia in association with an increased expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and its target genes, erythropoietin, and VEGF, in the adult mouse brain. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2002, 4, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N.M.; Bergeron, M. Hypoxic preconditioning induces changes in HIF-1A target genes in neonatal rat brain. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2001, 9, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, M.; Yu, A.Y.; Solway, K.E.; Semenza, G.L.; Sharp, F.R. Induction of hypoxia-inducible factor-1[HIF-1A] and its target genes following focal ischemia in rat brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1999, 12, 4159–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranova, O.; Miranda, L.F.; Pichiule, P.; Dragatsis, I.; Johnson, R.S.; Chavez, J.C. Neuron-specific inactivation of the hypoxia inducible factor 1α increases brain injury in a mouse model of transient focal cerebral ischemia. J. Neurosci. 2007, 23, 6320–6332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, F.R.; Bernaudin, M. HIF-I and oxygen sensing in the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 6, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichiule, P.; Agani, F.; Chavez, J.C.; Xu, K.; LaManna, J.C. HIF-1Aα and VEGF expression after transient global cerebral ischemia. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2003, 530, 611–617. [Google Scholar]
- Herx, L.M.; Yong, V.W. Interleukin-1 beta is required for the early evolution of reactive astrogliosis following CNS lesion. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2001, 60, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunello, A.G.; Weissenberger, J.; Kappeler, A.; Vallan, C.; Peters, M.; Rose, J.S.; Weis, J. Astrocytic alterations in interleukin-6/Soluble interleukin-6 receptor alpha double-transgenic mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarisbrick, I.A.; Radulovic, M.; Burda, J.E. Kallikrein 6 is a novel molecular trigger of reactive astrogliosis. Biol. Chem. 2012, 393, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, G.R.; Ding, S. Reactive astrocytes and therapeutic potential in focal ischemic stroke. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 85, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T.; Mori, T.; Shimoda, T.; Shinagawa, R.; Satoh, S.; Yada, N.; Katsumata, S.; Matsuda, S.; Kagamiishi, Y.; Tateishi, N. Arundic acid [ONO-2506] ameliorates delayed ischemic brain damage by preventing astrocytic overproduction of S100B. Curr. Drug Targets CNS Neurol. Disord. 2005, 4, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofroniew, M.V. Reactive astrocytes in neural repair and protection. Neuroscientist 2005, 11, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffo, A.; Rolando, C.; Ceruti, S. Astrocytes in the Damaged brain: Molecular and cellular insights into their reactive response and healing potential. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, G.; Jander, S.; Schroeter, M. Inflammation and glial responses in ischemic brain lesions. Prog. Neurobiol. 1998, 56, 149–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumari-Ramesh, S.; Alleyne, C.H.; Dhandapani, K.M. Astrocyte-specific expression of survivin after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice: A possible role in reactive gliosis? J. Neurotrauma 2012, 29, 2798–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezzi, P.; Domercq, M.; Brambilla, L.; Galli, R.; Schols, D.; De Clercq, E.; Vescovi, A.; Bagetta, G.; Kollias, G.; Meldolesi, J.; et al. CXCR4-activated astrocyte glutamate release via TNF_: Amplification by microglia triggers neurotoxicity. Nat. Neurosci. 2001, 4, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tang, X.N.; Yenari, M.A. The inflammatory response in stroke. J. Neuroimmunol. 2007, 184, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuxe, K.; Cintra, A.; Andbjer, B.; Anggard, E.; Goldstein, M.; Agnati, L.F. Centrally administered endothelin-1 produces lesions in the brain of the male rat. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1989, 137, 155–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnati, L.F.; Zoli, M.; Kurosawa, M.; Benfenati, F.; Biagini, G.; Zini, I.; Hallstròm, A.; Ungerstedt, U.; Toffano, G.; Fuxe, K. A new model of focal brain ischemia based on the intracerebral injection of endothelin 1. Ital. J. Neurol. Sci. 1991, 12, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, P.M.; Anthony, D.C.; Ruddin, M.; Botham, M.S.; Rankine, E.L.; Sablone, M.; Baumann, D.; Mir, A.K.; Perry, V.H. Focal lesions in the rat central nervous system induced by endothelin 1. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2003, 62, 1276–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delavaran, H.; Sjunnesson, H.; Arvidsson, A.; Lindvall, O.; Norrving, B.; van Westen, D.; Kokaia, Z.; Lindgren, A. Proximity of brain infarcts to regions of endogenous neurogenesis and involvement of striatum in ischemic stroke. Eur. J. Neurol. 2013, 20, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Memezawa, H.; Smith, M.-L.; Siej¨o, B.K. Hyperthermia complicates middle cerebral artery occlusion induced by an intraluminal filament. Brain Res. 1994, 649, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza-Rodrigues, R.D.; Costa, A.M.R.; Lima, R.R.; Dos, S.C.D.; Picanc, D.C.W.; Gomes-Leal, W. Inflammatory response and white matter damage after microinjections of endothelin-1 into the rat striatum. Brain Res. 2008, 1200, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, C.D.; Picanc, D.C.W.; Gomes-Leal, W. Differential patterns of inflammatory response, axonal damage and myelin impairment following excitotoxic or ischemic damage to the trigeminal spinal nucleus of adult rats. Brain Res. 2007, 1172, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, E.C.S.; Cardoso, M.M.; Gouveia, A.; Pereira, A.; Gomes-Leal, W. Modulation of microglial activation enhances neuroprotection and functional recovery derived from bone marrow mononuclear cell transplantation after cortical ischemia. Neurosci. Res. 2012, 73, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Y.; Cuiying, L.; Xiangnan, D.; Menglei, L.; Xunming, J.; Huishan, D.; Heng, Z. Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1a Plays a Key Role in Remote Ischemic Preconditioning Against Stroke by Modulating Inflammatory Responses in Rats. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e007589. [Google Scholar]
- Selvamani, A.; Sohrabji, F. Reproductive age modulates the impact of focal ischemia on the forebrain as well as the effects of estrogen treatment in female rats. Neurobiol. Aging 2010, 31, 1618–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkey, J.; Butcher, S.P. Characterization of an experimental model of stroke produced by intracerebral microinjection of endothelin-1 adjacent to the rat middle cerebral artery. J. Neurosci. Methods. 1995, 60, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoxue, D.; Feng, G.; Shijia, C.; Benson, O.A.B.; Nashwa, A.; Zhiying, H.; Marong, F. Combinational Pretreatment of Colony-Stimulating Factor 1 Receptor Inhibitor and Triptolide Upregulates BDNF-Akt and Autophagic Pathways to Improve Cerebral Ischemia. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 8796103. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Zhou, B.; Taheri, S.; Shi, H. Differential effects of HIF-1A inhibition by YC-1 on the overall outcome and blood-brain barrier damage in a rat model of ischemic stroke. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umschweif, G.; Alexandrovich, A.G.; Trembovler, V.; Horowitz, M.; Shohami, E. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is essential for spontaneous recovery from traumatic brain injury and is a key mediator of heat acclimation induced neuroprotection. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogle, M.E.; Gu, X.; Espinera, A.R.; Wei, L. Inhibition of prolyl hydroxylases by dimethyloxalylglycine after stroke reduces ischemic brain injury and requires hypoxia inducible factor-1a. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 45, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahra, G.M.; Mohsen, R.P.; Mohammad, H.M.; Kamran, M. Cancer cells change their glucose metabolism to overcome increased ROS: One step from cancer cell to cancer stem cell? Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108690. [Google Scholar]
- Marxsen, J.H.; Stengel, P.; Doege, K.; Heikkinen, P.; Jokilehto, T.; Wagner, T.; Jelkmann, W.; Jaakkola, P.; Metzen, E. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 [HIF-1A] promotes its degradation by induction of HIF-alpha-prolyl-4-hydroxylases. Biochem. J. 2004, 381, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zepeda, A.B.; Pessoa, A.; Castillo, R.L.; Figueroa, C.A.; Pulgar, V.M.; Farías, J.G. Cellular, and molecular mechanisms in the hypoxic tissue: Role of HIF-1A and ROS. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2013, 31, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alique, M.; Sánchez-López, E.; Bodega, G.; Giannarelli, C.; Carracedo, J.; Ramírez, R. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α: The Master Regulator of Endothelial Cell Senescence in Vascular Aging. Cells 2020, 9, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, I.G.; Park, C.V.; Kenneth, N.S. Translating the Hypoxic Response—The Role of HIF Protein Translation in the Cellular Response to Low Oxygen. Cells 2019, 8, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielockx, B.; Grinenko, T.; Mirtschink, P.; Chavakis, T. Hypoxia Pathway Proteins in Normal and Malignant Hematopoiesis. Cells 2019, 8, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, A.; Kaarniranta, K.; Kauppinen, A. Hypoxia-Inducible Histone Lysine Demethylases: Impact on the Aging Process and Age-Related Diseases. Aging Dis. 2016, 7, 180–200. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liao, Y.; Dong, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, F.; Wu, R.; Yuan, Z.; Cheng, J. Mib2 Deficiency Inhibits Microglial Activation and Alleviates Ischemia-Induced Brain Injury. Aging Dis. 2020, 11, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Li, J.; Zheng, J.; Qin, S. Reactive Astrocytes in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Aging Dis. 2019, 10, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | 5′-CTGTCCCTGTATGCCTCTG-3′. | 5′-ATGTCACGCACGATTTCC-3′. |
| IL-10 | 5′-CGGGAAGACAATAACTGCACCC-3′ | 5′-CGGTTAGCAGTATGTTGTCCAGC-3′ |
| NF-kB | 5′-GCTGCCAAAGAAGGACACGACA-3′ | 5′-GGCAGGCTATTGCTCATCACAG-3′ |
| iNOS | 5′-CACCTTGGAGTTCACCCAGT-3′ | 5′-ACCACTCGTACTTGGGATGC-3′ |
| TNF-ἀ | 5′-GGTGCCTATGTCTCAGCCTCTT-3′ | 5′-GCCATAGAACTGATGAGAGGGAG-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amin, N.; Chen, S.; Ren, Q.; Tan, X.; Botchway, B.O.A.; Hu, Z.; Chen, F.; Ye, S.; Du, X.; Chen, Z.; et al. Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α Attenuates Ischemic Brain Damage by Modulating Inflammatory Response and Glial Activity. Cells 2021, 10, 1359. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061359
Amin N, Chen S, Ren Q, Tan X, Botchway BOA, Hu Z, Chen F, Ye S, Du X, Chen Z, et al. Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α Attenuates Ischemic Brain Damage by Modulating Inflammatory Response and Glial Activity. Cells. 2021; 10(6):1359. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061359
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmin, Nashwa, Shijia Chen, Qiannan Ren, Xiaoning Tan, Benson O. A. Botchway, Zhiying Hu, Fengpei Chen, Shan Ye, Xiaoxue Du, Zuobing Chen, and et al. 2021. "Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α Attenuates Ischemic Brain Damage by Modulating Inflammatory Response and Glial Activity" Cells 10, no. 6: 1359. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061359
APA StyleAmin, N., Chen, S., Ren, Q., Tan, X., Botchway, B. O. A., Hu, Z., Chen, F., Ye, S., Du, X., Chen, Z., & Fang, M. (2021). Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α Attenuates Ischemic Brain Damage by Modulating Inflammatory Response and Glial Activity. Cells, 10(6), 1359. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061359






