Regulatory miRNA–mRNA Networks in Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Screening of Candidates Differentially Expressed Brain-Related miRNAs Based on a Systematic Review
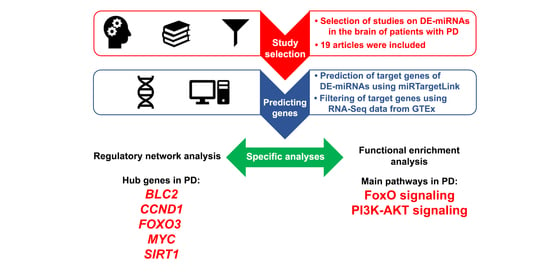
2.2. Study Selection and Data Extraction
2.3. Prediction of the Target Genes of the Differentially Expressed Brain-Related miRNAs
2.4. Regulatory Networks and Their Topology Analysis
2.5. Functional Enrichment Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Differentially Expressed Brain-Related miRNAs Based on the Systematic Review
3.2. Analysis of the Differentially Expressed Brain-Related miRNAs’ Target Genes
3.3. Regulatory Networks and Their Topology Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dorsey, E.R.; Bloem, B.R. The Parkinson Pandemic-A Call to Action. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2016 Parkinson’s Disease Collaborators Global, regional, and national burden of Parkinson’s disease, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 939–953.
- Poewe, W.; Seppi, K.; Tanner, C.M.; Halliday, G.M.; Brundin, P.; Volkmann, J.; Schrag, A.-E.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leggio, L.; Vivarelli, S.; L’Episcopo, F.; Tirolo, C.; Caniglia, S.; Testa, N.; Marchetti, B.; Iraci, N. microRNAs in Parkinson’s Disease: From Pathogenesis to Novel Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schulz, J.; Takousis, P.; Wohlers, I.; Itua, I.O.G.; Dobricic, V.; Rücker, G.; Binder, H.; Middleton, L.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Perneczky, R.; et al. Meta-analyses identify differentially expressed micrornas in Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 85, 835–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, O.; Nateghinia, S.; Estiar, M.A.; Taheri, M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. Assessment of the role of non-coding RNAs in the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 896, 173914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, A.; Ash, P.E.; Wolozin, B.; Emili, A. Protein Interaction Network Biology in Neuroscience. Proteomics 2020, 21, e1900311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gene Ontology Consortium Gene Ontology Consortium: Going forward. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D1049–D1056. [CrossRef]
- Titze-de-Almeida, S.S.; Soto-Sánchez, C.; Fernandez, E.; Koprich, J.B.; Brotchie, J.M.; Titze-de-Almeida, R. The Promise and Challenges of Developing miRNA-Based Therapeutics for Parkinson’s Disease. Cells 2020, 9, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamberg, M.; Backes, C.; Fehlmann, T.; Hart, M.; Meder, B.; Meese, E.; Keller, A. MiRTargetLink--miRNAs, Genes and Interaction Networks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, M.; Wiese, S.; Warscheid, B. Cytoscape: Software for Visualization and Analysis of Biological Networks. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 696, 291–303. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Pan, Y.; Wu, F.-X. CytoNCA: A Cytoscape Plugin for Centrality Analysis and Evaluation of Protein Interaction Networks. Biosystems 2015, 127, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Zhang, J. Why Do Hubs Tend to Be Essential in Protein Networks? PLoS Genet. 2006, 2, e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Franceschini, A.; Wyder, S.; Forslund, K.; Heller, D.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Roth, A.; Santos, A.; Tsafou, K.P.; et al. STRING v10: Protein-Protein Interaction Networks, Integrated over the Tree of Life. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D447–D452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Inoue, K.; Ishii, J.; Vanti, W.B.; Voronov, S.V.; Murchison, E.; Hannon, G.; Abeliovich, A. A MicroRNA Feedback Circuit in Midbrain Dopamine Neurons. Science 2007, 317, 1220–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sethi, P.; Lukiw, W.J. Micro-RNA Abundance and Stability in Human Brain: Specific Alterations in Alzheimer’s Disease Temporal Lobe Neocortex. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 459, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miñones-Moyano, E.; Porta, S.; Escaramís, G.; Rabionet, R.; Iraola, S.; Kagerbauer, B.; Espinosa-Parrilla, Y.; Ferrer, I.; Estivill, X.; Martí, E. MicroRNA Profiling of Parkinson’s Disease Brains Identifies Early Downregulation of miR-34b/c Which Modulate Mitochondrial Function. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 3067–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.J.; Liu, G.; Jin, S.M.; Parisiadou, L.; Xie, C.; Yu, J.; Sun, L.; Ma, B.; Ding, J.; Vancraenenbroeck, R.; et al. MicroRNA-205 Regulates the Expression of Parkinson’s Disease-Related Leucine-Rich Repeat Kinase 2 Protein. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alvarez-Erviti, L.; Seow, Y.; Schapira, A.H.V.; Rodriguez-Oroz, M.C.; Obeso, J.A.; Cooper, J.M. Influence of microRNA Deregulation on Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy and α-Synuclein Pathology in Parkinson’s Disease. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Lee, Y.; McKenna, N.D.; Yi, M.; Simunovic, F.; Wang, Y.; Kong, B.; Rooney, R.J.; Seo, H.; Stephens, R.M.; et al. miR-126 Contributes to Parkinson’s Disease by Dysregulating the Insulin-like Growth Factor/phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Signaling. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 1712–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schlaudraff, F.; Gründemann, J.; Fauler, M.; Dragicevic, E.; Hardy, J.; Liss, B. Orchestrated Increase of Dopamine and PARK mRNAs but Not miR-133b in Dopamine Neurons in Parkinson’s Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 2302–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villar-Menéndez, I.; Porta, S.; Buira, S.P.; Pereira-Veiga, T.; Díaz-Sánchez, S.; Albasanz, J.L.; Ferrer, I.; Martín, M.; Barrachina, M. Increased Striatal Adenosine A2A Receptor Levels Is an Early Event in Parkinson’s Disease-Related Pathology and It Is Potentially Regulated by miR-34b. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 69, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardo, L.F.; Coto, E.; Ribacoba, R.; Menéndez, M.; Moris, G.; Suárez, E.; Alvarez, V. MiRNA Profile in the Substantia Nigra of Parkinson’s Disease and Healthy Subjects. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 54, 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, C.E.; Wang, Y.; Kong, B.; Woo, T.-U.W.; Iyer, L.K.; Sonntag, K.C. Midbrain Dopamine Neurons in Parkinson’s Disease Exhibit a Dysregulated miRNA and Target-Gene Network. Brain Res. 2015, 1618, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pantano, L.; Friedländer, M.R.; Escaramís, G.; Lizano, E.; Pallarès-Albanell, J.; Ferrer, I.; Estivill, X.; Martí, E. Specific Small-RNA Signatures in the Amygdala at Premotor and Motor Stages of Parkinson’s Disease Revealed by Deep Sequencing Analysis. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wake, C.; Labadorf, A.; Dumitriu, A.; Hoss, A.G.; Bregu, J.; Albrecht, K.H.; DeStefano, A.L.; Myers, R.H. Novel microRNA Discovery Using Small RNA Sequencing in Post-Mortem Human Brain. BMC Genomics 2016, 17, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tatura, R.; Kraus, T.; Giese, A.; Arzberger, T.; Buchholz, M.; Höglinger, G.; Müller, U. Parkinson’s Disease: SNCA-, PARK2-, and LRRK2- Targeting microRNAs Elevated in Cingulate Gyrus. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2016, 33, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.D.; Ge, Y. Alterations of miRNAs Reveal a Dysregulated Molecular Regulatory Network in Parkinson’s Disease Striatum. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 629, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoss, A.G.; Labadorf, A.; Beach, T.G.; Latourelle, J.C.; Myers, R.H. microRNA Profiles in Parkinson’s Disease Prefrontal Cortex. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, P.; Roy, D. Comparative Analysis of RNA-Seq Data from Brain and Blood Samples of Parkinson’s Disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 484, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMillan, K.J.; Murray, T.K.; Bengoa-Vergniory, N.; Cordero-Llana, O.; Cooper, J.; Buckley, A.; Wade-Martins, R.; Uney, J.B.; O’Neill, M.J.; Wong, L.F.; et al. Loss of MicroRNA-7 Regulation Leads to α-Synuclein Accumulation and Dopaminergic Neuronal Loss In Vivo. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 2404–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, R.-X.; Li, L.-G.; Liu, X.-W.; Tian, B.-X.; Cheng, Y. Down Regulation of miR-218, miR-124, and miR-144 Relates to Parkinson’s Disease via Activating NF-κB Signaling. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2020, 36, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-B.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Wang, H.; Ren, R.-J.; Cui, H.-L.; Huang, W.-Y.; Cheng, Q.; Chen, H.-Z.; Wang, G. miR-425 Deficiency Promotes Necroptosis and Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s Disease. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Junn, E.; Lee, K.-W.; Jeong, B.S.; Chan, T.W.; Im, J.-Y.; Mouradian, M.M. Repression of Alpha-Synuclein Expression and Toxicity by microRNA-7. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13052–13057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kabaria, S.; Choi, D.C.; Chaudhuri, A.D.; Mouradian, M.M.; Junn, E. Inhibition of miR-34b and miR-34c Enhances α-Synuclein Expression in Parkinson’s Disease. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frankel, L.B.; Di Malta, C.; Wen, J.; Eskelinen, E.-L.; Ballabio, A.; Lund, A.H. A Non-Conserved miRNA Regulates Lysosomal Function and Impacts on a Human Lysosomal Storage Disorder. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Søndergaard, H.B.; Airas, L.; Christensen, J.R.; Nielsen, B.R.; Börnsen, L.; Oturai, A.; Sellebjerg, F. Pregnancy-Induced Changes in microRNA Expression in Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 552101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samadian, M.; Gholipour, M.; Hajiesmaeili, M.; Taheri, M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. The Eminent Role of microRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 641080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qie, S.; Diehl, J.A. Cyclin D1, Cancer Progression, and Opportunities in Cancer Treatment. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herrup, K.; Yang, Y. Cell Cycle Regulation in the Postmitotic Neuron: Oxymoron or New Biology? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höglinger, G.U.; Breunig, J.J.; Depboylu, C.; Rouaux, C.; Michel, P.P.; Alvarez-Fischer, D.; Boutillier, A.-L.; Degregori, J.; Oertel, W.H.; Rakic, P.; et al. The pRb/E2F Cell-Cycle Pathway Mediates Cell Death in Parkinson’s Disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3585–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, P.D.; Crocker, S.J.; Jackson-Lewis, V.; Jordan-Sciutto, K.L.; Hayley, S.; Mount, M.P.; O’Hare, M.J.; Callaghan, S.; Slack, R.S.; Przedborski, S.; et al. Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 5 Is a Mediator of Dopaminergic Neuron Loss in a Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13650–13655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Findeiss, E.; Schwarz, S.C.; Evsyukov, V.; Rösler, T.W.; Höllerhage, M.; Chakroun, T.; Nykänen, N.-P.; Shen, Y.; Wurst, W.; Kohl, M.; et al. Comprehensive miRNome-Wide Profiling in a Neuronal Cell Model of Synucleinopathy Implies Involvement of Cell Cycle Genes. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 561086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, E.; Amamoto, R.; Zheng, L.; Cacquevel, M.; Sarria, J.-C.; Knott, G.W.; Schneider, B.L. FOXO3 Determines the Accumulation of α-Synuclein and Controls the Fate of Dopaminergic Neurons in the Substantia Nigra. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 1435–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, P.; Hanson, P.S.; Morris, C.M. SIRT1 Ameliorates Oxidative Stress Induced Neural Cell Death and Is down-Regulated in Parkinson’s Disease. BMC Neurosci. 2017, 18, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X.-X.; Truong, D.; Wu, Y.-C. The Critical Role of SIRT1 in Parkinson’s Disease: Mechanism and Therapeutic Considerations. Aging Dis. 2020, 11, 1608–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-G.; Casadesus, G.; Nunomura, A.; Zhu, X.; Castellani, R.J.; Richardson, S.L.; Perry, G.; Felsher, D.W.; Petersen, R.B.; Smith, M.A. The Neuronal Expression of MYC Causes a Neurodegenerative Phenotype in a Novel Transgenic Mouse. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bekker, M.; Abrahams, S.; Loos, B.; Bardien, S. Can the Interplay between Autophagy and Apoptosis Be Targeted as a Novel Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease? Neurobiol. Aging 2021, 100, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo, E.E.; Paik, J. FOXO in Neural Cells and Diseases of the Nervous System. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2018, 127, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, G.G.; Lee, Y.H. Pathway Analysis of Genome-Wide Association Studies for Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 2599–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, T. Identification of Key Genes and Pathways in Parkinson’s Disease through Integrated Analysis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 3769–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, J.; Chen, X.-C.; Li, W.-J.; Han, Q.; Chen, C.; Lu, J.-M.; Zheng, J.-Y.; Xue, S.-R. Identification of Parkinson’s Disease-Related Pathways and Potential Risk Factors. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060520957197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Author, Year | Country | Brain Region | Sample Size | Age at Death | Disease Duration (years) | Postmortem Interval (hours) | PD Braak Staging | miRNAs | Upreg miRNAs | Downreg miRNAs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kim et al., 2007 [15] | USA | Midbrain, cerebellum, frontal and prefrontal cortex | 3 | 70 | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Sethi and Lukiw, 2009 [16] | USA | Temporal cortex | 4 | 69 | NA | 1.2 | NA | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Miñones-Moyano et al., 2011 [17] | Spain | SN, amygdala, cerebellum, frontal cortex | 14 | 72 | NA | 6.4 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Cho et al., 2013 [18] | USA | Frontal cortex | 15 | 80 | NA | 8.2 | 3.5 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Alvarez-Erviti et al., 2013 [19] | Spain | SN, amygdala | 6 | 76 | NA | 4.8 | NA | 6 | 6 | 0 |
| Kim et al., 2014 [20] | USA | SN | 8 | 78 | NA | 20.7 | NA | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Schlaudraff et al., 2014 [21] | Germany | SN | 5 | 78 | NA | 16 | NA | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Villar-Menéndez et al., 2014 [22] | Spain | Putamen | 6 | 76 | NA | 7.9 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Cardo et al., 2014 [23] | UK | SN | 8 | 77 | 4,25 | 45.8 | NA | 10 | 9 | 1 |
| Briggs et al., 2015 [24] | USA | SN | 8 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 17 | 15 | 2 |
| Pantano et al., 2015 [25] | Spain | Amygdala | 7 | 70 | NA | NA | NA | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Wake et al., 2016 [26] | USA | Prefrontal cortex | 29 | 77 | NA | 8 | NA | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Tatura et al., 2016 [27] | Germany | Anterior cingulate cortex | 22 | 73 | NA | 30.6 | NA | 5 | 5 | 0 |
| Nair and Ge, 2016 [28] | USA | Putamen | 12 | 75 | NA | 13.4 | NA | 13 | 6 | 7 |
| Hoss et al., 2016 [29] | USA | Prefrontal cortex | 29 | 77 | 10,5 | 11.1 | NA | 29 | 11 | 18 |
| Chatterjee and Roy, 2017 [30] | India | Prefrontal cortex | 29 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 11 | 9 | 2 |
| McMillan et al., 2017 [31] | UK | SN | 6 | 83 | 16,1 | NA | NA | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Xing et al., 2020 [32] | China | Prefrontal cortex | 15 | 70 | 5,5 | NA | NA | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| Hu et al., 2020 [33] | China | SN | 4 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Upregulated miRNAs | Downregulated miRNAs | SN DE-miRNAs | Putamen DE-miRNAs |
|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-let-7b | hsa-miR-10b-5p | hsa-miR-133b | hsa-miR-155-5p |
| hsa-let-7d-5p | hsa-miR-124 | hsa-miR-34b | hsa-miR-219-2-3p |
| hsa-let-7f-5p | hsa-miR-1294 | hsa-miR-34c | hsa-miR-3200-3p |
| hsa-miR-106a § | hsa-miR-129-5p | hsa-miR-425 | hsa-miR-34b |
| hsa-miR-106b-5p | hsa-miR-132-3p | hsa-miR-532-5p | hsa-miR-382-5p |
| hsa-miR-126 | hsa-miR-132-5p | hsa-miR-548d | hsa-miR-421 |
| hsa-miR-132 | hsa-miR-133b | hsa-miR-7 | hsa-miR-423-5p |
| hsa-miR-135a | hsa-miR-144 | hsa-miR-774 | hsa-miR-4421 |
| hsa-miR-135b | hsa-miR-145-5p | hsa-let-7b | hsa-miR-204-5p |
| hsa-miR-144 | hsa-miR-148b-3p | hsa-miR-106a § | hsa-miR-221-3p |
| hsa-miR-144-3p | hsa-miR-155-5p | hsa-miR-126 | hsa-miR-3195 |
| hsa-miR-144-5p | hsa-miR-205 | hsa-miR-132 | hsa-miR-425-5p |
| hsa-miR-145 | hsa-miR-212-5p | hsa-miR-135a | hsa-miR-485-3p |
| hsa-miR-148a | hsa-miR-217 | hsa-miR-135b | hsa-miR-95 |
| hsa-miR-151b | hsa-miR-218 | hsa-miR-145 | |
| hsa-miR-15b-5p | hsa-miR-219-2-3p | hsa-miR-148a | |
| hsa-miR-16-2-3p | hsa-miR-3200-3p | hsa-miR-184 | |
| hsa-miR-181a-5p | hsa-miR-320b | hsa-miR-198 | |
| hsa-miR-184 | hsa-miR-324-5p | hsa-miR-208b | |
| hsa-miR-198 | hsa-miR-338-5p | hsa-miR-21 * | |
| hsa-miR-199b | hsa-miR-34b § | hsa-miR-223 | |
| hsa-miR-204-5p | hsa-miR-34c | hsa-miR-224 | |
| hsa-miR-208b | hsa-miR-362-5p | hsa-miR-26a | |
| hsa-miR-21 * | hsa-miR-378c | hsa-miR-26b | |
| hsa-miR-216b-5p | hsa-miR-380-5p | hsa-miR-27a | |
| hsa-miR-221 | hsa-miR-382-5p | hsa-miR-28-5p | |
| hsa-miR-221-3p | hsa-miR-421 | hsa-miR-299-5p | |
| hsa-miR-223 | hsa-miR-423-5p | hsa-miR-301b | |
| hsa-miR-224 | hsa-miR-425 | hsa-miR-330-5p | |
| hsa-miR-26a | hsa-miR-4421 | hsa-miR-335 | |
| hsa-miR-26b | hsa-miR-490-5p | hsa-miR-337-5p | |
| hsa-miR-27a | hsa-miR-491-5p | hsa-miR-339-5p | |
| hsa-miR-28-5p | hsa-miR-532-5p | hsa-miR-373 * | |
| hsa-miR-299-5p | hsa-miR-548d | hsa-miR-374a | |
| hsa-miR-301b | hsa-miR-6511a-5p | hsa-miR-485-5p | |
| hsa-miR-3117-3p | hsa-miR-670-3p | hsa-miR-542-3p | |
| hsa-miR-3195 | hsa-miR-671-5p | hsa-miR-92a | |
| hsa-miR-330-5p | hsa-miR-7 | hsa-miR-95 | |
| hsa-miR-335 | hsa-miR-774 | ||
| hsa-miR-337-5p | |||
| hsa-miR-339-5p | |||
| hsa-miR-373 * | |||
| hsa-miR-374a | |||
| hsa-miR-376c-5p | |||
| hsa-miR-425-5p | |||
| hsa-miR-4443 | |||
| hsa-miR-454-3p | |||
| hsa-miR-485-3p | |||
| hsa-miR-485-5p | |||
| hsa-miR-488 | |||
| hsa-miR-5100 | |||
| hsa-miR-516b-5p | |||
| hsa-miR-542-3p | |||
| hsa-miR-544 | |||
| hsa-miR-5690 | |||
| hsa-miR-92a | |||
| hsa-miR-92a-3p | |||
| hsa-miR-92b-3p | |||
| hsa-miR-93-5p | |||
| hsa-miR-95 § |
| For Upreg miRNAs | For Downreg miRNAs | For SN DE-miRNAs | For Putamen DE-miRNAs |
|---|---|---|---|
| APC | ADD3 | BCL2 | APAF1 |
| APP | ANXA2 | CCND1 | BCL2 |
| ATG16L1 | APC | CDKN1A | CCND1 |
| ATM | ARID2 | CRK | ETS1 |
| BCL2 | ARL6IP5 | CXCR4 | FOXO3 |
| BCL2L11 | CAMTA1 | DNMT1 | ITPR1 |
| CCND1 | CBFB | EGFR | MAFB |
| CDKN1A | CCND1 | FBXW7 | MAP2K1 |
| CDKN1B | CDH2 | FGFR1 | MEIS1 |
| CDKN1C | CDK4 | FOXO1 | MYC |
| CRK | CDK6 | FOXO3 | PIK3R1 |
| DDIT4 | CDKN1A | IGF1R | PTEN |
| DICER1 | CEBPA | IRS1 | SIRT1 |
| DNMT1 | CHRAC1 | KRAS | SMAD4 |
| E2F1 | CPNE3 | MAPK1 | SNAI1 |
| E2F5 | CSRP1 | MYC | SSX2IP |
| EZR | CTGF | PTBP2 | TCF12 |
| FBXW7 | CTNNB1 | SIRT1 | THRB |
| FOS | DDX6 | SOX2 | |
| FOXO1 | DNAJB1 | SP1 | |
| FOXO3 | E2F3 | SP3 | |
| HIPK2 | EDN1 | VEGFA | |
| IRS1 | EGFR | ||
| ITGA5 | EIF4E | ||
| ITGB8 | ERG | ||
| KAT2B | ETS1 | ||
| KRAS | FLI1 | ||
| MAFB | FLOT2 | ||
| MAP2K1 | FOXO3 | ||
| MAP2K4 | FSCN1 | ||
| MAPK1 | FZD7 | ||
| MAPK9 | GNA13 | ||
| NFE2L2 | GNAI2 | ||
| NLK | GNAI3 | ||
| NOTCH1 | GOLGA7 | ||
| NTRK3 | HCN2 | ||
| PTEN | IGF1R | ||
| PURA | IL6R | ||
| RAP1B | JAG1 | ||
| RB1 | JUP | ||
| RECK | KLF4 | ||
| RGS5 | KRAS | ||
| SIRT1 | LIN7C | ||
| SMAD4 | LRP1 | ||
| SMAD7 | MECP2 | ||
| SOCS3 | MEF2A | ||
| SP1 | MYC | ||
| SP3 | NOTCH1 | ||
| STAT3 | NRAS | ||
| STAT5A | NT5E | ||
| TCEAL1 | PDLIM7 | ||
| TCF4 | PHC2 | ||
| TGFBR1 | PICALM | ||
| TGFBR2 | PIK3CA | ||
| THRB | PODXL | ||
| TMED7 | PSIP1 | ||
| VEGFA | PSMG1 | ||
| ZBTB4 | PTBP1 | ||
| PTBP2 | |||
| PTEN | |||
| RAB11FIP2 | |||
| RAC1 | |||
| RHOA | |||
| ROCK1 | |||
| SIRT1 | |||
| SMAD3 | |||
| SMAD4 | |||
| SOX2 | |||
| SOX9 | |||
| SP1 | |||
| SWAP70 | |||
| SYNE1 | |||
| TAGLN2 | |||
| TP53 | |||
| TPM1 | |||
| TPM3 | |||
| TWF1 | |||
| VEGFA | |||
| YWHAZ |
| Regulatory Network Targeted by Upregulated miRNAs | Regulatory Network Targeted by Downregulated miRNAs | ||||||||||
| Node | DC | Node | BC | Node | CC | Node | DC | Node | BC | Node | CC |
| CCND1 | 37 | CCND1 | 199.83435 | CCND1 | 0.7571428 | TP53 | 44 | EGFR | 648.0353 | TP53 | 0.6923077 |
| STAT3 | 36 | NOTCH1 | 188.92195 | NOTCH1 | 0.7571428 | EGFR | 43 | VEGFA | 606.03754 | EGFR | 0.6857143 |
| PTEN | 36 | STAT3 | 188.05045 | PTEN | 0.7571428 | MYC | 42 | TP53 | 524.7005 | MYC | 0.6792453 |
| NOTCH1 | 36 | KRAS | 162.67937 | KRAS | 0.7464788 | CTNNB1 | 41 | CTNNB1 | 334.24814 | VEGFA | 0.6666667 |
| KRAS | 36 | VEGFA | 162.09471 | STAT3 | 0.7464788 | VEGFA | 40 | RHOA | 282.5179 | PTEN | 0.6605505 |
| VEGFA | 34 | PTEN | 157.23015 | VEGFA | 0.7361111 | PTEN | 38 | MYC | 268.5208 | CTNNB1 | 0.6545454 |
| MAPK1 | 33 | MAPK1 | 153.92905 | MAPK1 | 0.7162162 | KRAS | 37 | ANXA2 | 264.8916 | KRAS | 0.6371681 |
| CDKN1A | 31 | CDKN1A | 126.64957 | CDKN1A | 0.6973684 | CCND1 | 36 | PTEN | 236.95053 | CCND1 | 0.6260869 |
| SMAD4 | 29 | E2F1 | 111.34685 | SMAD4 | 0.6794871 | NOTCH1 | 35 | NRAS | 180.74113 | NOTCH1 | 0.6206896 |
| FOS | 27 | SMAD4 | 90.59089 | FOS | 0.654321 | PIK3CA | 33 | PIK3CA | 167.35359 | PIK3CA | 0.6153846 |
| ATM | 26 | CRK | 57.47987 | SIRT1 | 0.654321 | SMAD4 | 32 | CDKN1A | 166.20766 | SMAD4 | 0.6 |
| SIRT1 | 26 | FOS | 57.051147 | ATM | 0.654321 | SIRT1 | 31 | TPM1 | 154.96588 | RHOA | 0.6 |
| FOXO1 | 24 | ATM | 52.87451 | FOXO1 | 0.6385542 | RHOA | 30 | TAGLN2 | 144.89015 | SIRT1 | 0.5901639 |
| FOXO3 | 24 | TGFBR1 | 52.30357 | CDKN1B | 0.6309523 | SMAD3 | 29 | PSIP1 | 142.28922 | CDKN1A | 0.5853658 |
| BCL2L11 | 23 | FOXO1 | 49.671513 | FOXO3 | 0.6309523 | CDKN2A | 28 | FLI1 | 142.0 | CDKN2A | 0.5806451 |
| Regulatory Network Targeted by DE-miRNAs in SN | Regulatory Network Targeted by DE-miRNAs in Putamen | ||||||||||
| Node | DC | Node | BC | Node | CC | Node | DC | Node | BC | Node | CC |
| EGFR | 18 | KRAS | 24.592207 | CCND1 | 0.9090909 | MYC | 13 | CCND1 | 69.53333 | CCND1 | 0.8421052 |
| MYC | 18 | CCND1 | 21.90339 | KRAS | 0.9090909 | CCND1 | 13 | MYC | 59.533333 | MYC | 0.8421052 |
| KRAS | 18 | MYC | 21.90339 | MYC | 0.9090909 | PTEN | 10 | BCL2 | 30.0 | FOXO3 | 0.6956522 |
| CCND1 | 18 | EGFR | 20.09127 | EGFR | 0.9090909 | FOXO3 | 10 | ETS1 | 14.333333 | PTEN | 0.6956522 |
| MAPK1 | 17 | MAPK1 | 19.217676 | MAPK1 | 0.8695652 | MAP2K1 | 9 | PIK3R1 | 6.3333335 | MAP2K1 | 0.6666667 |
| VEGFA | 16 | CDKN1A | 17.548702 | VEGFA | 0.8333333 | ETS1 | 8 | FOXO3 | 5.2 | ETS1 | 0.64 |
| CDKN1A | 14 | DNMT1 | 10.332828 | CDKN1A | 0.7692308 | SNAI1 | 7 | PTEN | 5.2 | PIK3R1 | 0.6153846 |
| SIRT1 | 13 | SP1 | 10.186725 | FOXO3 | 0.7407407 | SMAD4 | 7 | APAF1 | 2.6666667 | SIRT1 | 0.6153846 |
| IGF1R | 13 | VEGFA | 7.7579365 | IGF1R | 0.7407407 | SIRT1 | 7 | MAP2K1 | 2.2 | SMAD4 | 0.6153846 |
| FOXO3 | 13 | FGFR1 | 6.8968253 | SIRT1 | 0.7407407 | PIK3R1 | 7 | SIRT1 | 0.3333333 | SNAI1 | 0.6153846 |
| SOX2 | 12 | IGF1R | 5.0380955 | FOXO1 | 0.7142857 | APAF1 | 5 | SMAD4 | 0.3333333 | APAF1 | 0.5925926 |
| IRS1 | 12 | IRS1 | 3.0833333 | SOX2 | 0.7142857 | BCL2 | 4 | SNAI1 | 0.3333333 | BCL2 | 0.5714286 |
| FOXO1 | 12 | SOX2 | 3.0269842 | DNMT1 | 0.6896552 | THRB | 2 | ITPR1 | 0.0 | MEIS1 | 0.4848485 |
| FGFR1 | 11 | FOXO3 | 2.8960319 | FGFR1 | 0.6896552 | TCF12 | 2 | MAFB | 0.0 | TCF12 | 0.4848485 |
| DNMT1 | 11 | SIRT1 | 1.9690477 | IRS1 | 0.6896552 | MEIS1 | 2 | MEIS1 | 0.0 | THRB | 0.4848485 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos-Lobato, B.L.; Vidal, A.F.; Ribeiro-dos-Santos, Â. Regulatory miRNA–mRNA Networks in Parkinson’s Disease. Cells 2021, 10, 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061410
Santos-Lobato BL, Vidal AF, Ribeiro-dos-Santos Â. Regulatory miRNA–mRNA Networks in Parkinson’s Disease. Cells. 2021; 10(6):1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061410
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos-Lobato, Bruno Lopes, Amanda Ferreira Vidal, and Ândrea Ribeiro-dos-Santos. 2021. "Regulatory miRNA–mRNA Networks in Parkinson’s Disease" Cells 10, no. 6: 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061410
APA StyleSantos-Lobato, B. L., Vidal, A. F., & Ribeiro-dos-Santos, Â. (2021). Regulatory miRNA–mRNA Networks in Parkinson’s Disease. Cells, 10(6), 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061410