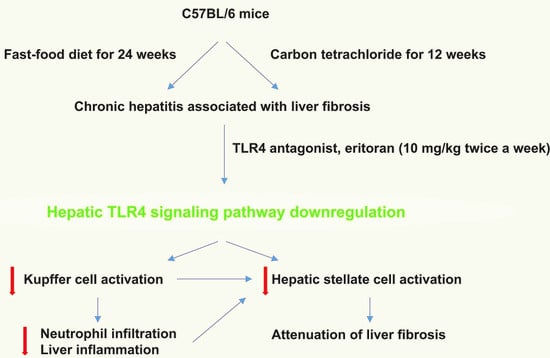
Eritoran Attenuates Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice with Chronic Liver Injury
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Study Design
2.3. LX-2 Cell Studies
2.4. Primary Cell Isolation and Culture
2.5. Measurement of Blood Biochemistry and Lipopolysaccharide
2.6. Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
2.7. Histological Studies
2.8. Western Blot Analysis
2.9. Sirius Red Staining
2.10. Measurement of Hepatic Hydroxyproline Levels
2.11. Measurement of Hepatic Steatosis
2.12. Glucose Tolerance and Insulin Tolerance Tests
2.13. Flow Cytometry
2.14. In Vitro Small Interfering RNA (siRNA) Transfection
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
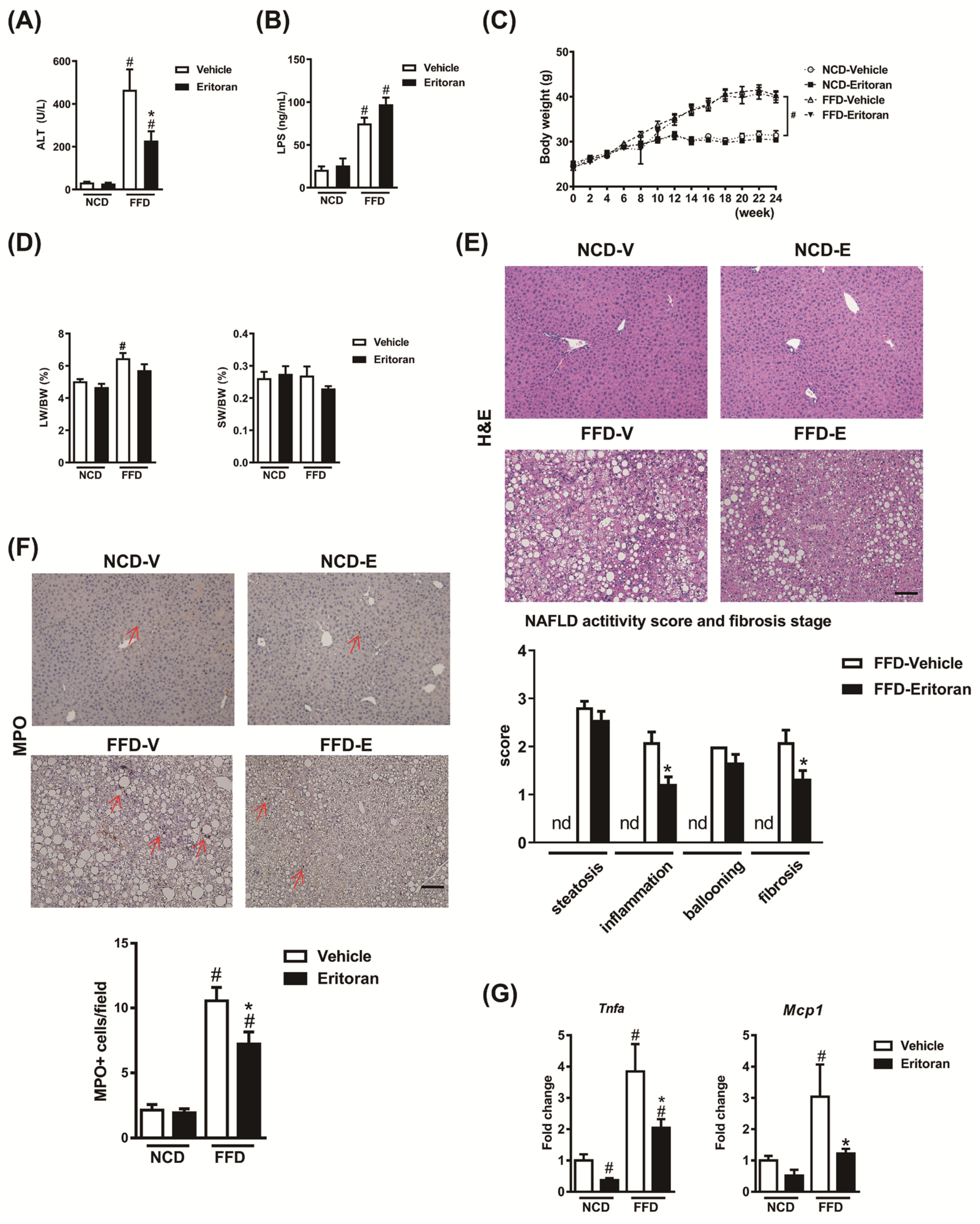
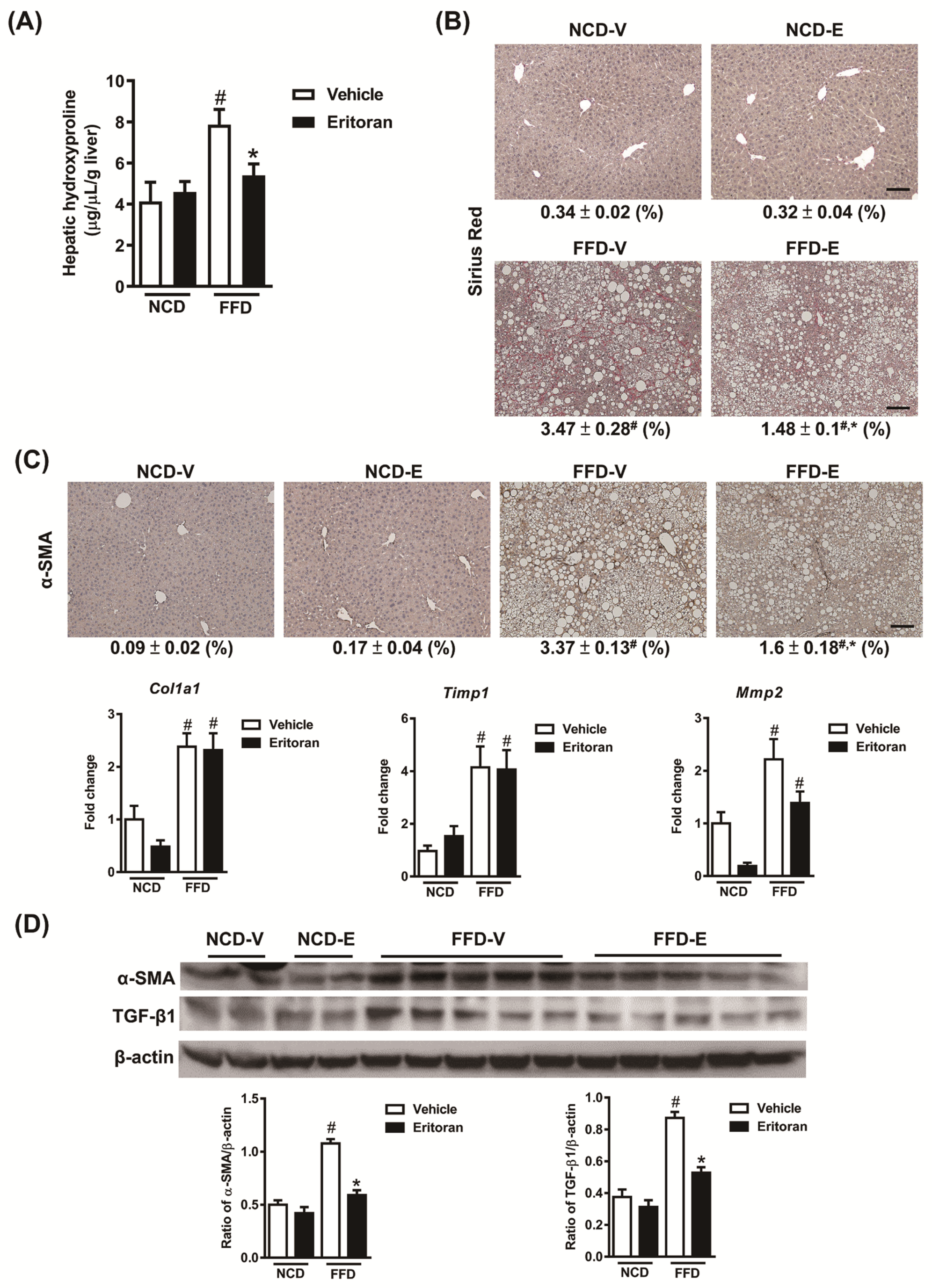
3.1. Eritoran-Attenuated Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrosis in the FFD-Fed Mice
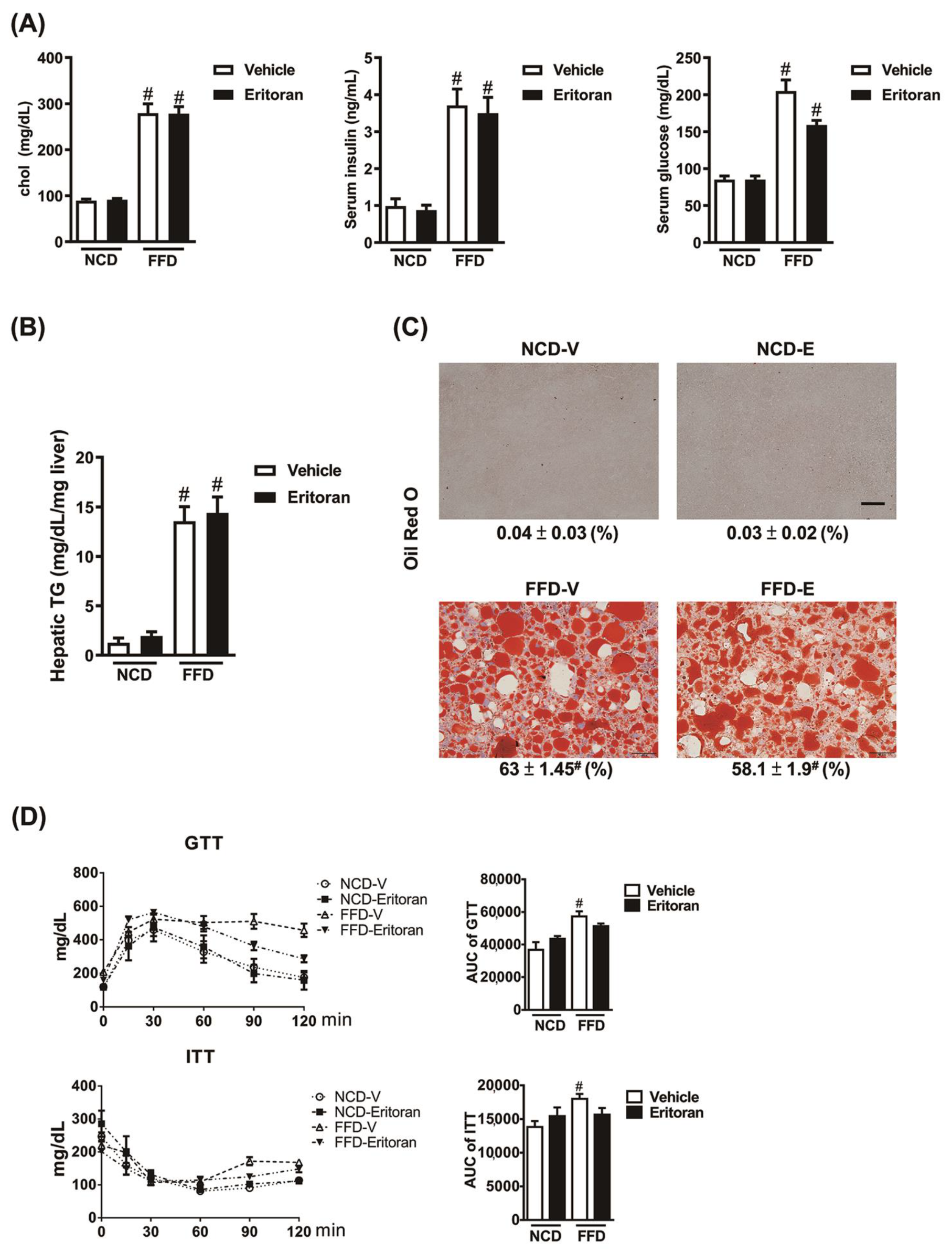
3.2. Eritoran Did Not Reduce Hepatic Steatosis or Systemic Insulin Resistance in the FFD-Fed Mice
3.3. Hepatic TLR4 Signaling Pathway in the FFD-Fed Mice Was Suppressed by Eritoran
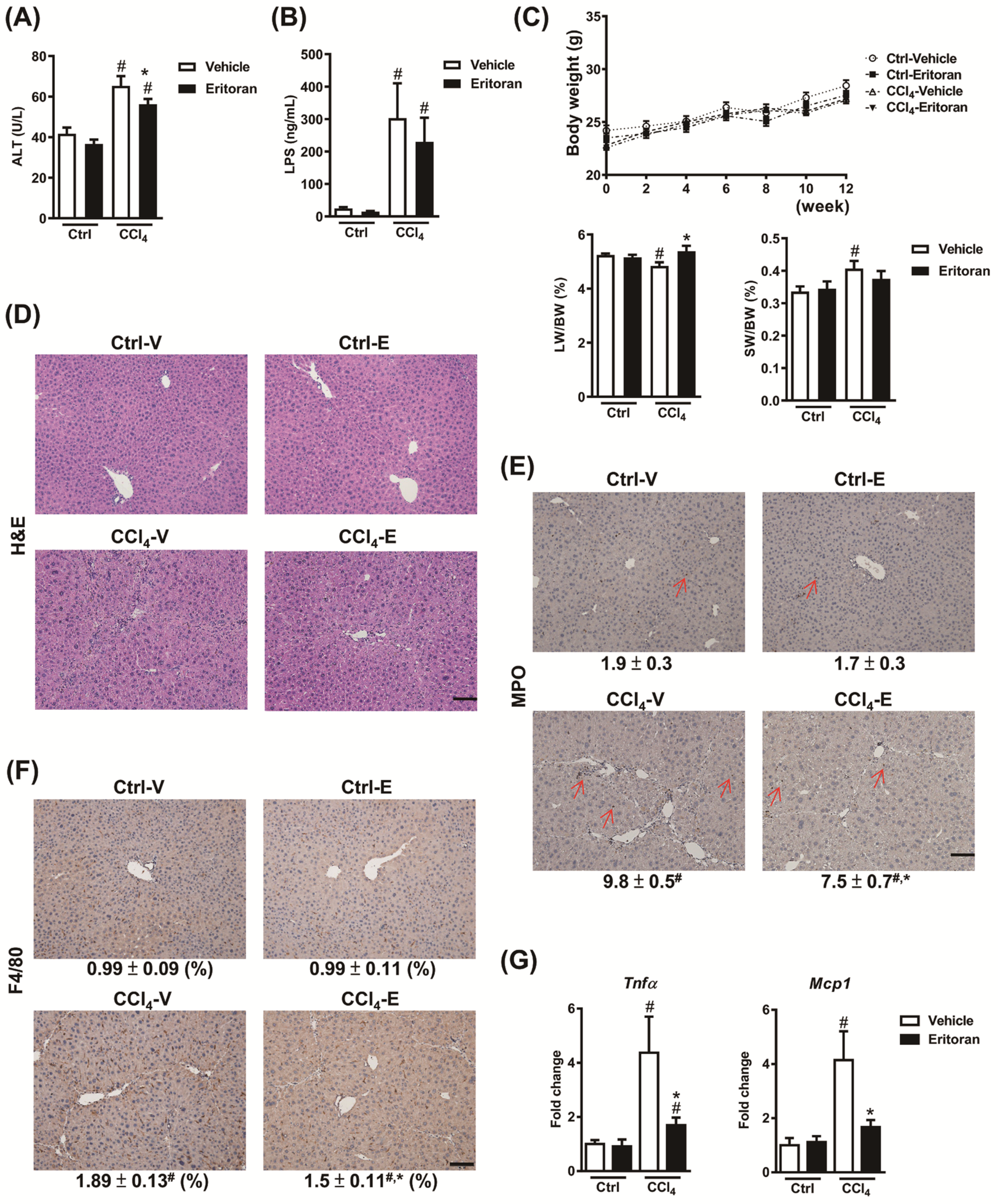
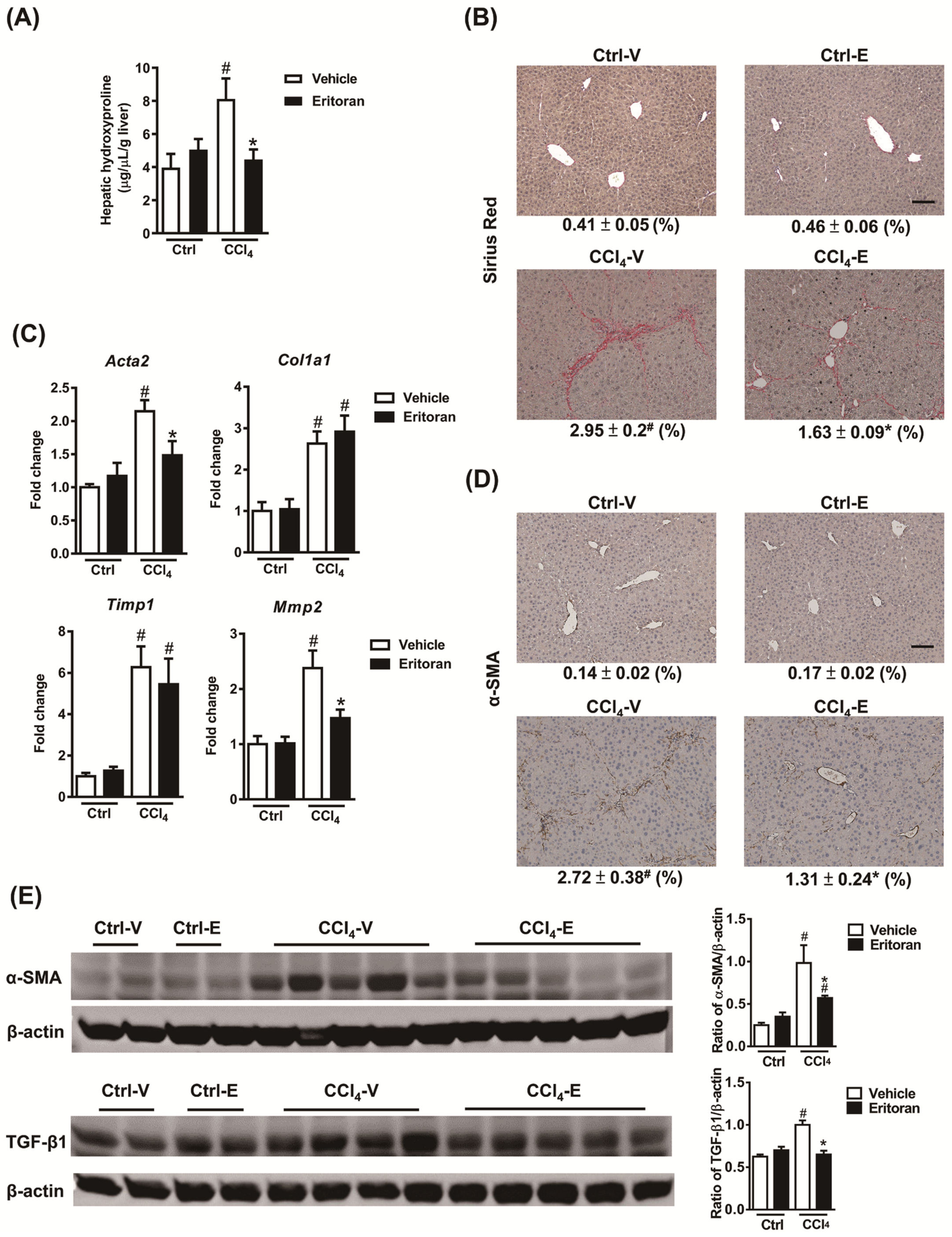
3.4. Eritoran Attenuated Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrosis in the CCl4-Treated Mice
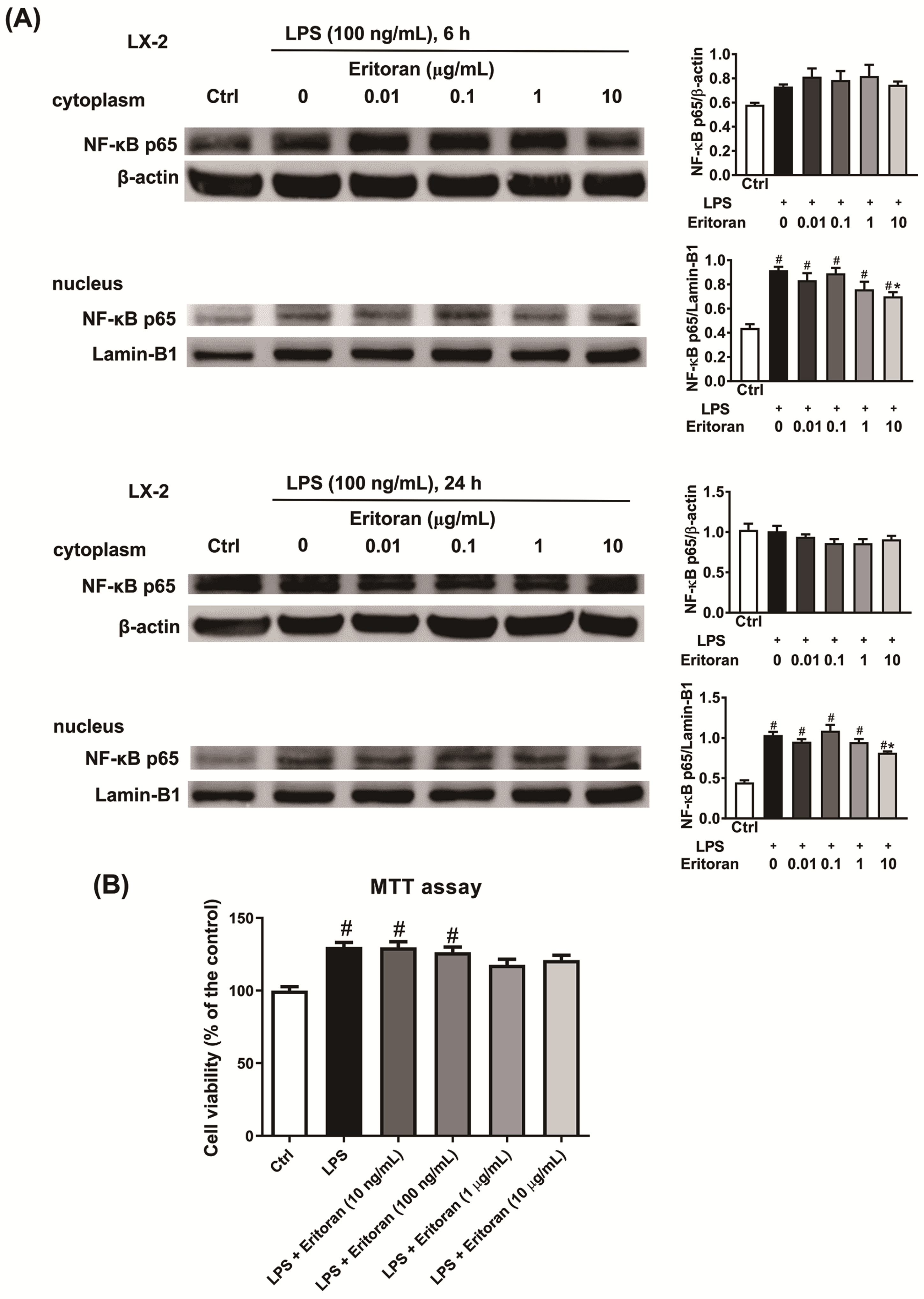
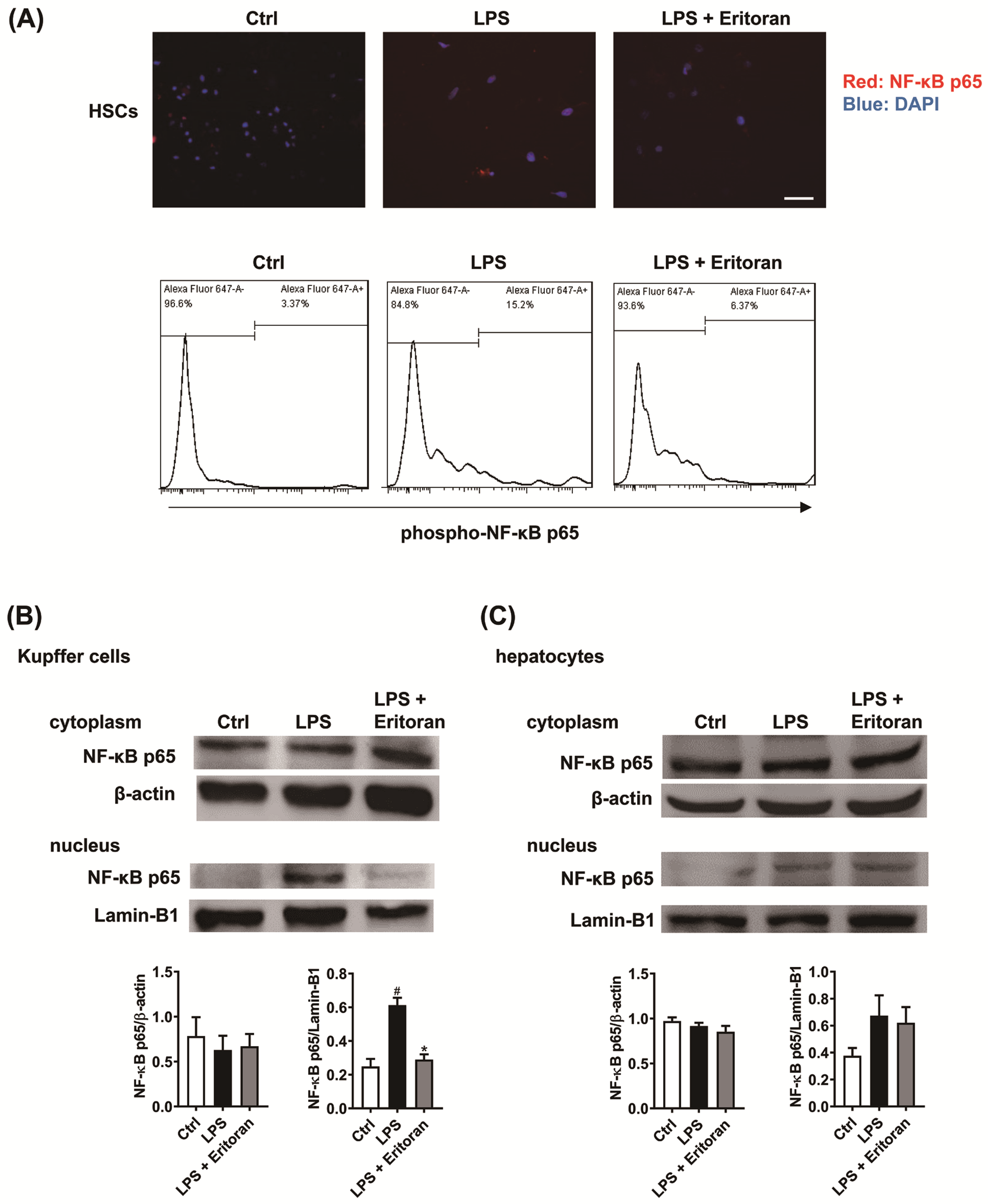
3.5. Eritoran Suppressed the NF-κB p65 Nuclear Translocation in HSCs and KCs
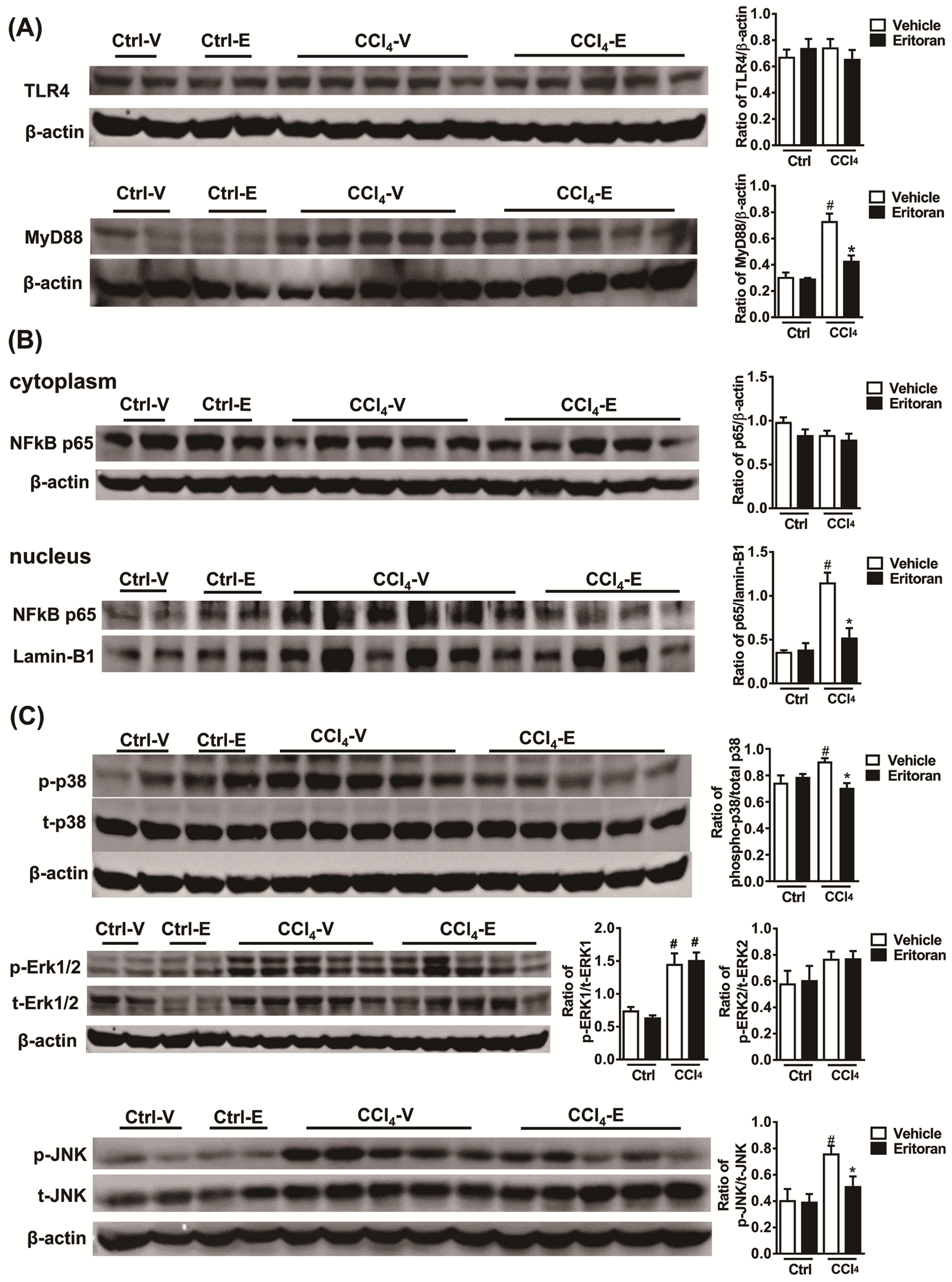
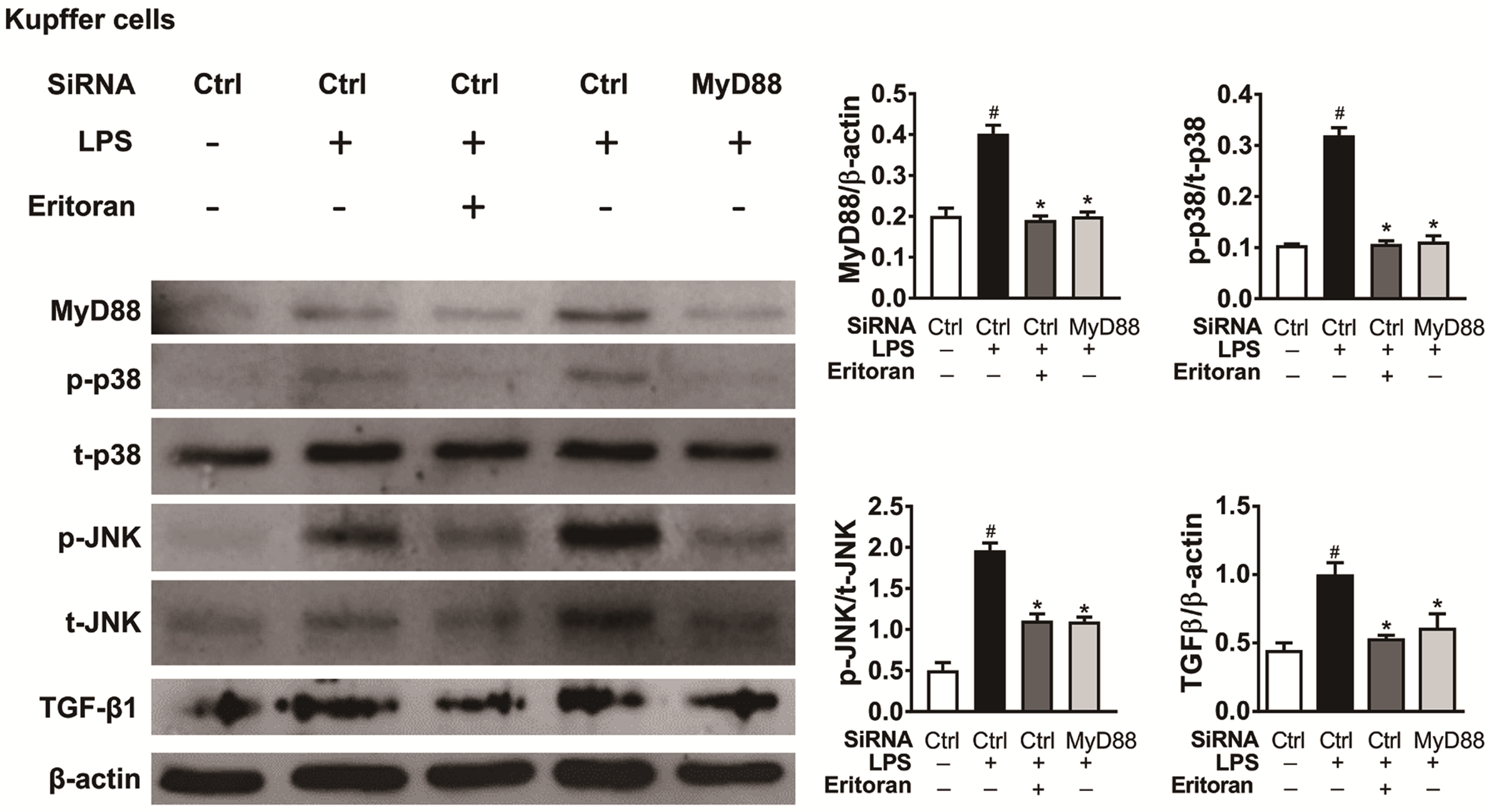
3.6. Eritoran Decreased MyD88-Mediated p38/JNK Phosphorylation in Kupffer Cells
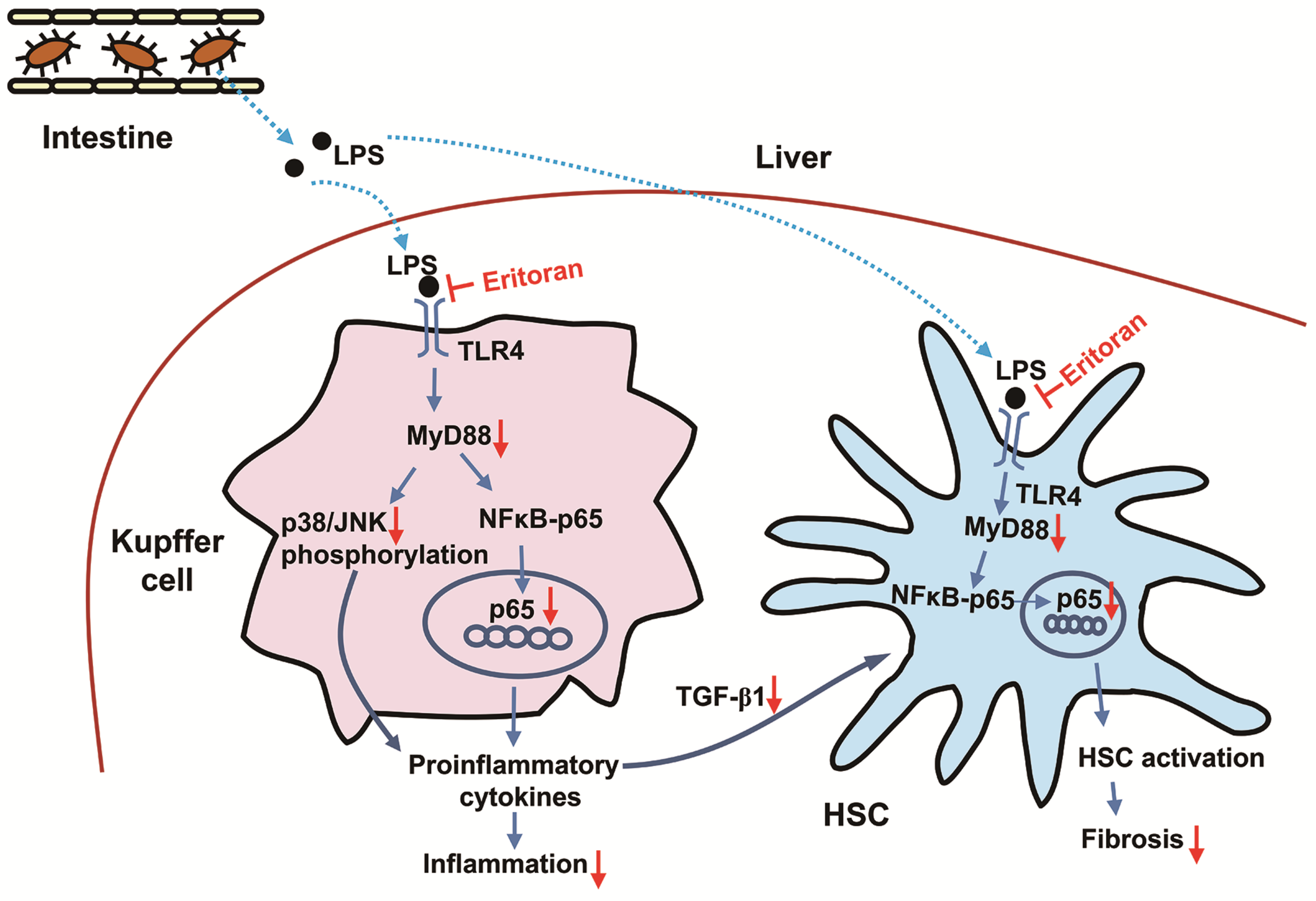
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friedman, S.L. Liver fibrosis—From bench to bedside. J. Hepatol. 2003, 38, S38–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoinne, S.; Friedman, S.L. New and emerging anti-fibrotic therapeutics entering or already in clinical trials in chronic liver diseases. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2019, 49, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.; Friedman, S.L. Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in liver injury and hepatic fibrogenesis. Fibrogenes. Tissue Repair 2010, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kesar, V.; Odin, J.A. Toll-like receptors and liver disease. Liver Int. 2014, 34, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, C.A.; Adegboyega, P.; van Rooijen, N.; Tagalicud, A.; Allman, M.; Wallace, M. Toll-like receptor-4 signaling and Kupffer cells play pivotal roles in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2007, 47, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miura, K.; Seki, E.; Ohnishi, H.; Brenner, D.A. Role of toll-like receptors and their downstream molecules in the development of nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2010, 2010, 362847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaure, C.; Liu, Y. A comparative review of toll-like receptor 4 expression and functionality in different animal species. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.C.; Yeh, W.C.; Ohashi, P.S. LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway. Cytokine 2008, 42, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Meng, Z.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, E.; Trippler, M.; Broering, R.; Bucchi, A.; Krux, F.; Dittmer, U.; Yang, D.; et al. Toll-like receptor-induced innate immune responses in non-parenchymal liver cells are cell type-specific. Immunology 2010, 129, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, E.; De Minicis, S.; Osterreicher, C.H.; Kluwe, J.; Osawa, Y.; Brenner, D.A.; Schwabe, R.F. TLR4 enhances TGF-beta signaling and hepatic fibrosis. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiziltas, S. Toll-like receptors in pathophysiology of liver diseases. World J. Hepatol. 2016, 8, 1354–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.M.; Park, B.S.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, S.E.; Lee, J.; Oh, S.C.; Enkhbayar, P.; Matsushima, N.; Lee, H.; Yoo, O.J.; et al. Crystal structure of the TLR4-MD-2 complex with bound endotoxin antagonist Eritoran. Cell 2007, 130, 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mullarkey, M.; Rose, J.R.; Bristol, J.; Kawata, T.; Kimura, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Przetak, M.; Chow, J.; Gusovsky, F.; Christ, W.J.; et al. Inhibition of endotoxin response by e5564, a novel Toll-like receptor 4-directed endotoxin antagonist. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 304, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Czeslick, E.; Struppert, A.; Simm, A.; Sablotzki, A. E5564 (Eritoran) inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine production in human blood monocytes. Inflamm. Res. 2006, 55, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrentraut, S.; Lohner, R.; Schwederski, M.; Ehrentraut, H.; Boehm, O.; Noga, S.; Langhoff, P.; Baumgarten, G.; Meyer, R.; Knuefermann, P. In vivo Toll-like receptor 4 antagonism restores cardiac function during endotoxemia. Shock 2011, 36, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, M.D.; Moore, J.N.; Vandenplas, M.L.; Sun, W.C.; Murray, T.F. Effects of the second-generation synthetic lipid A analogue E5564 on responses to endotoxin in [corrected] equine whole blood and monocytes. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2008, 69, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossignol, D.P.; Lynn, M. Antagonism of in vivo and ex vivo response to endotoxin by E5564, a synthetic lipid A analogue. J. Endotoxin Res. 2002, 8, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitazawa, T.; Tsujimoto, T.; Kawaratani, H.; Fukui, H. Salvage effect of E5564, Toll-like receptor 4 antagonist on d-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver failure in rats. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 25, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, K.A.; Huang, H.; Tohme, S.; Loughran, P.; Ferrero, K.; Billiar, T.; Tsung, A. Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) antagonist eritoran tetrasodium attenuates liver ischemia and reperfusion injury through inhibition of high-mobility group box protein B1 (HMGB1) signaling. Mol. Med. 2015, 20, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korff, S.; Loughran, P.; Cai, C.; Lee, Y.S.; Scott, M.; Billiar, T.R. Eritoran attenuates tissue damage and inflammation in hemorrhagic shock/trauma. J. Surg. Res. 2013, 184, e17–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlton, M.; Krishnan, A.; Viker, K.; Sanderson, S.; Cazanave, S.; McConico, A.; Masuoko, H.; Gores, G. Fast food diet mouse: Novel small animal model of NASH with ballooning, progressive fibrosis, and high physiological fidelity to the human condition. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 301, G825–G834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.C.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Chan, C.C.; Sun, H.J.; Huang, Y.H.; Hou, M.C.; Lin, H.C. Human relaxin-2 attenuates hepatic steatosis and fibrosis in mice with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Lab. Investig. 2019, 99, 1203–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwaisako, K.; Haimerl, M.; Paik, Y.H.; Taura, K.; Kodama, Y.; Sirlin, C.; Yu, E.; Yu, R.T.; Downes, M.; Evans, R.M.; et al. Protection from liver fibrosis by a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta agonist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E1369–E1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mederacke, I.; Dapito, D.H.; Affo, S.; Uchinami, H.; Schwabe, R.F. High-yield and high-purity isolation of hepatic stellate cells from normal and fibrotic mouse livers. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Severgnini, M.; Sherman, J.; Sehgal, A.; Jayaprakash, N.K.; Aubin, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, L.; Peng, C.G.; Yucius, K.; Butler, J.; et al. A rapid two-step method for isolation of functional primary mouse hepatocytes: Cell characterization and asialoglycoprotein receptor based assay development. Cytotechnology 2012, 64, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Jung, Y.S.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, D.K.; Na, S.Y.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, C.H.; Choi, H.S. Hepatocyte toll-like receptor 4 mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced hepcidin expression. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.C.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Yang, Y.Y.; Chan, C.C.; Huang, Y.H.; Lin, H.C. Aliskiren Reduces Hepatic steatosis and Epididymal Fat Mass and Increases Skeletal Muscle Insulin Sensitivity in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, G.N.; Zhang, P.; Gong, J.; Zhang, X.J.; Wang, P.X.; Yin, M.; Jiang, Z.; Shen, L.J.; Ji, Y.X.; Tong, J.; et al. Tmbim1 is a multivesicular body regulator that protects against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice and monkeys by targeting the lysosomal degradation of Tlr4. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 742–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukumo, D.M.; Carvalho-Filho, M.A.; Carvalheira, J.B.; Prada, P.O.; Hirabara, S.M.; Schenka, A.A.; Araujo, E.P.; Vassallo, J.; Curi, R.; Velloso, L.A.; et al. Loss-of-function mutation in Toll-like receptor 4 prevents diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1986–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vonghia, L.; Van Herck, M.A.; Weyler, J.; Francque, S. Targeting Myeloid-Derived Cells: New Frontiers in the Treatment of Non-alcoholic and Alcoholic Liver Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, M.; Liu, P.P.; Li, H. Innate Immune Signaling and Its Role in Metabolic and Cardiovascular Diseases. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 893–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Zhang, X.J.; Li, H. Role of Innate Immune Signaling in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, C.; Sheikh, M.; Sharma, S.; Kondo, T.; Loeffler-Wirth, H.; Zheng, Y.B.; Novelli, S.; Hall, A.; Kerbert, A.J.C.; Macnaughtan, J.; et al. Toll-like receptor 4 is a therapeutic target for prevention and treatment of liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opal, S.M.; Laterre, P.F.; Francois, B.; LaRosa, S.P.; Angus, D.C.; Mira, J.P.; Wittebole, X.; Dugernier, T.; Perrotin, D.; Tidswell, M.; et al. Effect of eritoran, an antagonist of MD2-TLR4, on mortality in patients with severe sepsis: The ACCESS randomized trial. JAMA 2013, 309, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angulo, P.; Kleiner, D.E.; Dam-Larsen, S.; Adams, L.A.; Bjornsson, E.S.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; Mills, P.R.; Keach, J.C.; Lafferty, H.D.; Stahler, A.; et al. Liver Fibrosis, but No Other Histologic Features, Is Associated with Long-term Outcomes of Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 389–397.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ekstedt, M.; Hagstrom, H.; Nasr, P.; Fredrikson, M.; Stal, P.; Kechagias, S.; Hultcrantz, R. Fibrosis stage is the strongest predictor for disease-specific mortality in NAFLD after up to 33 years of follow-up. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuppan, D.; Afdhal, N.H. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet 2008, 371, 838–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luedde, T.; Schwabe, R.F. NF-kB in the liver-linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paik, Y.H.; Schwabe, R.F.; Bataller, R.; Russo, M.P.; Jobin, C.; Brenner, D.A. Toll-like receptor 4 mediates inflammatory signaling by bacterial lipopolysaccharide in human hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 2003, 37, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Kokoeva, M.V.; Inouye, K.; Tzameli, I.; Yin, H.; Flier, J.S. TLR4 links innate immunity and fatty acid-induced insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 3015–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Vianna, C.R.; Fukuda, M.; Berglund, E.D.; Liu, C.; Tao, C.; Sun, K.; Liu, T.; Harper, M.J.; Lee, C.E.; et al. Hepatocyte Toll-like receptor 4 regulates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Csak, T.; Velayudham, A.; Hritz, I.; Petrasek, J.; Levin, I.; Lippai, D.; Catalano, D.; Mandrekar, P.; Dolganiuc, A.; Kurt-Jones, E.; et al. Deficiency in myeloid differentiation factor-2 and toll-like receptor 4 expression attenuates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 300, G433–G441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharifnia, T.; Antoun, J.; Verriere, T.G.; Suarez, G.; Wattacheril, J.; Wilson, K.T.; Peek, R.M., Jr.; Abumrad, N.N.; Flynn, C.R. Hepatic TLR4 signaling in obese NAFLD. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 309, G270–G278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fouts, D.E.; Torralba, M.; Nelson, K.E.; Brenner, D.A.; Schnabl, B. Bacterial translocation and changes in the intestinal microbiome in mouse models of liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bluemel, S.; Wang, L.; Martino, C.; Lee, S.; Wang, Y.; Williams, B.; Horvath, A.; Stadlbauer, V.; Zengler, K.; Schnabl, B. The Role of Intestinal C-type Regenerating Islet Derived-3 Lectins for Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatol. Commun. 2018, 2, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsieh, Y.-C.; Lee, K.-C.; Wu, P.-S.; Huo, T.-I.; Huang, Y.-H.; Hou, M.-C.; Lin, H.-C. Eritoran Attenuates Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice with Chronic Liver Injury. Cells 2021, 10, 1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061562
Hsieh Y-C, Lee K-C, Wu P-S, Huo T-I, Huang Y-H, Hou M-C, Lin H-C. Eritoran Attenuates Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice with Chronic Liver Injury. Cells. 2021; 10(6):1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061562
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsieh, Yun-Cheng, Kuei-Chuan Lee, Pei-Shan Wu, Teh-Ia Huo, Yi-Hsiang Huang, Ming-Chih Hou, and Han-Chieh Lin. 2021. "Eritoran Attenuates Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice with Chronic Liver Injury" Cells 10, no. 6: 1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061562
APA StyleHsieh, Y.-C., Lee, K.-C., Wu, P.-S., Huo, T.-I., Huang, Y.-H., Hou, M.-C., & Lin, H.-C. (2021). Eritoran Attenuates Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice with Chronic Liver Injury. Cells, 10(6), 1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061562