The FibromiR miR-214-3p Is Upregulated in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Promotes Differentiation of Human Fibro-Adipogenic Muscle Progenitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Antibodies
2.2. Skeletal Muscle Samples and Progenitor Cell Amplification
2.3. Growth and Differentiation of FAPs and MPs
2.4. Transfection Assays
2.5. Immunofluorescence and Histological Staining
2.6. Second Harmonic Generation (SHG) Imaging
2.7. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.8. Small RNA Sequencing
2.9. Data Analysis
2.10. Luciferase Assay
2.11. Immunoblot Analysis
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
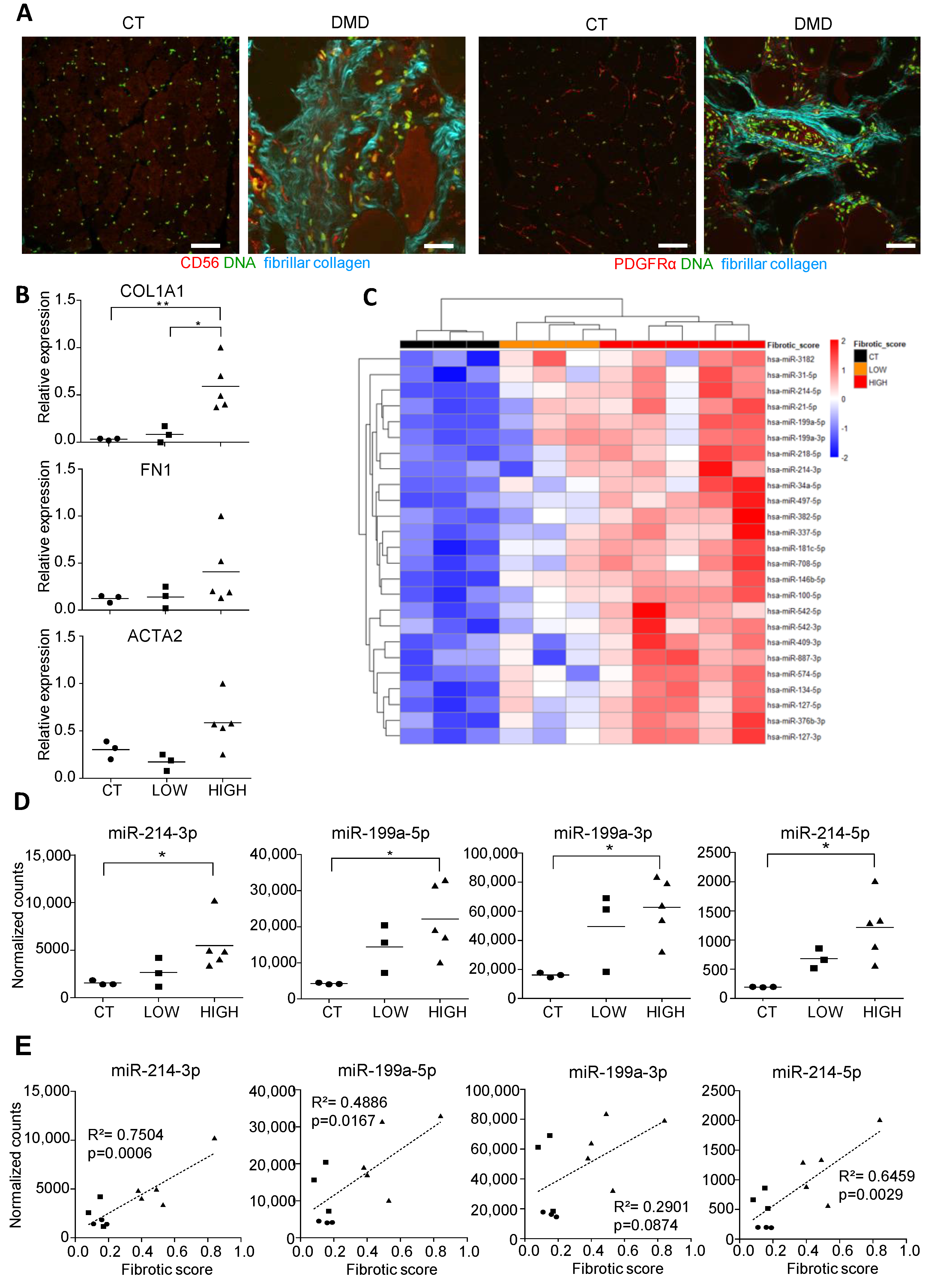
3.1. Small RNA Seq of DMD Muscle Biopsies Identifies an miRNA Signature Associated with Fibrotic Status
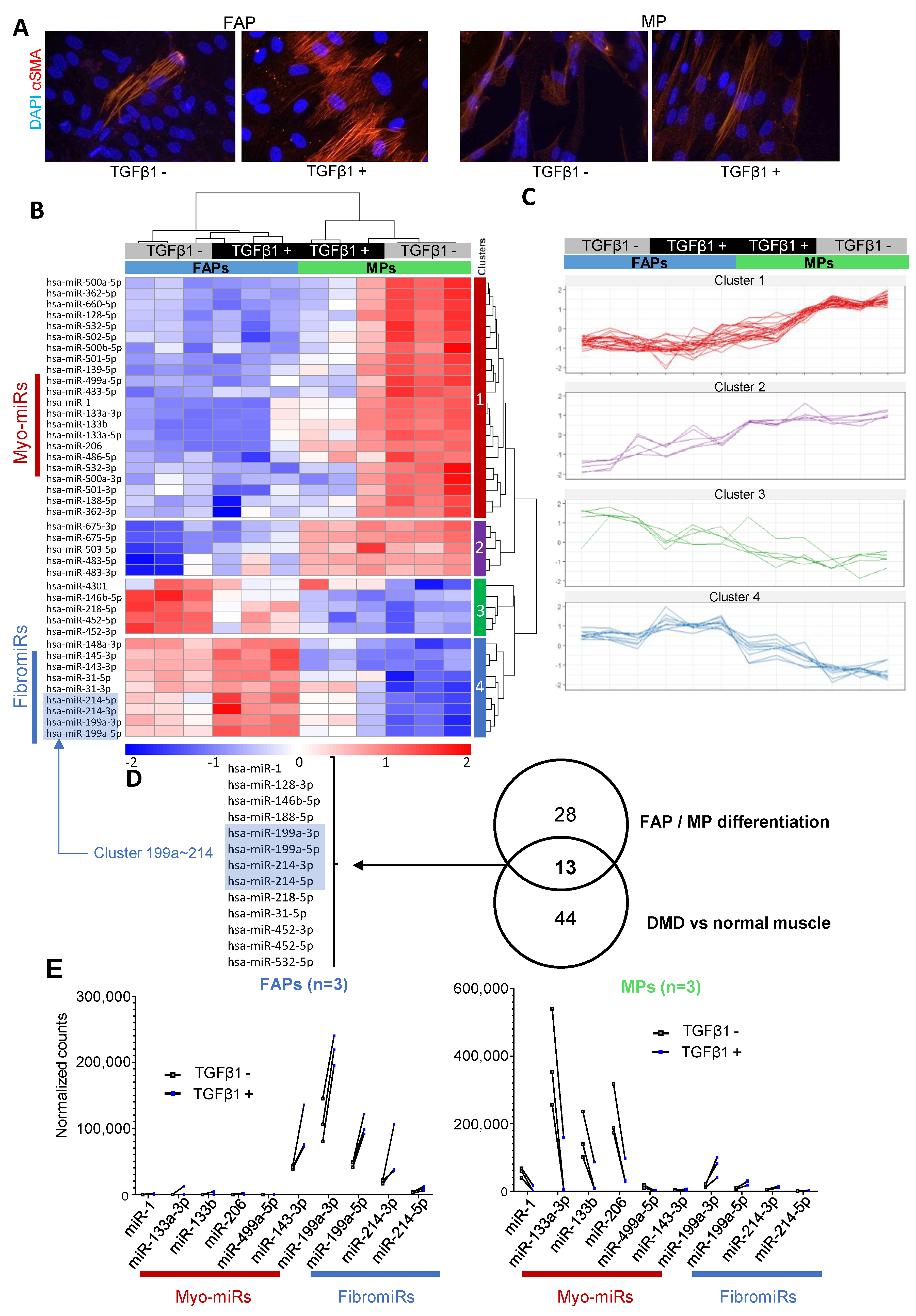
3.2. FAPs and MPs Display a Distinct miRNA Expression Profile That is Modulated in Response to TGFβ1
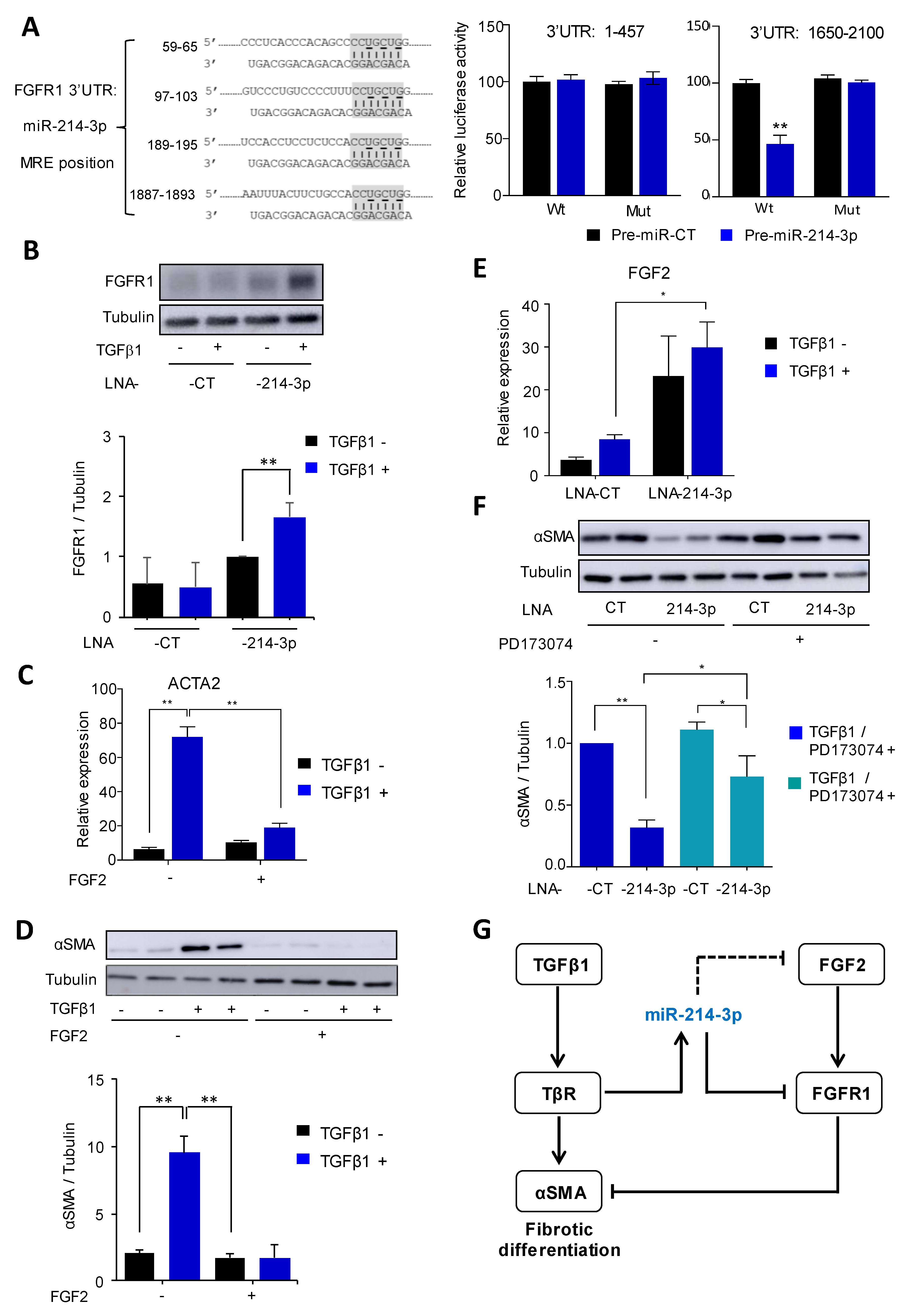
3.3. Knockdown of miR-214-3p Inhibits FAP Fibrogenesis
3.4. MiR-214-3p Mediates TGFβ1-Induced FAP Activation by Targeting the FGFR1 Pathway
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rockey, D.C.; Bell, P.D.; Hill, J.A. Fibrosis—A common pathway to organ injury and failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1138–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffield, J.S.; Lupher, M.; Thannickal, V.J.; Wynn, T.A. Host responses in tissue repair and fibrosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2013, 8, 241–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bochaton-Piallat, M.-L.; Gabbiani, G.; Hinz, B. The myofibroblast in wound healing and fibrosis: Answered and unanswered questions. F1000Research 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Desmoulière, A.; Geinoz, A.; Gabbiani, F.; Gabbiani, G. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 induces alpha-smooth muscle actin expression in granulation tissue myofibroblasts and in quiescent and growing cultured fibroblasts. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 122, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Serrano, A.L.; Mann, C.J.; Vidal, B.; Ardite, E.; Perdiguero, E.; Muñoz-Cánoves, P. Cellular and molecular mechanisms regulating fibrosis in skeletal muscle repair and disease. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2011, 96, 167–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uezumi, A.; Fukada, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Takeda, S.; Tsuchida, K. Mesenchymal progenitors distinct from satellite cells contribute to ectopic fat cell formation in skeletal muscle. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joe, A.W.B.; Yi, L.; Natarajan, A.; Le Grand, F.; So, L.; Wang, J.; Rudnicki, M.A.; Rossi, F.M.V. Muscle injury activates resident fibro/adipogenic progenitors that facilitate myogenesis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Natarajan, A.; Lemos, D.R.; Rossi, F.M.V. Fibro/adipogenic progenitors: A double-edged sword in skeletal muscle regeneration. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 2045–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uezumi, A.; Fukada, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Ikemoto-Uezumi, M.; Nakatani, M.; Morita, M.; Yamaguchi, A.; Yamada, H.; Nishino, I.; Hamada, Y.; et al. Identification and characterization of PDGFRα+ mesenchymal progenitors in human skeletal muscle. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uezumi, A.; Ikemoto-Uezumi, M.; Zhou, H.; Kurosawa, T.; Yoshimoto, Y.; Nakatani, M.; Hitachi, K.; Yamaguchi, H.; Wakatsuki, S.; Araki, T.; et al. Mesenchymal Bmp3b expression maintains skeletal muscle integrity and decreases in age-related sarcopenia. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, 139617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukjanenko, L.; Karaz, S.; Stuelsatz, P.; Gurriaran-Rodriguez, U.; Michaud, J.; Dammone, G.; Sizzano, F.; Mashinchian, O.; Ancel, S.; Migliavacca, E.; et al. Aging Disrupts Muscle Stem Cell Function by Impairing Matricellular WISP1 Secretion from Fibro-Adipogenic Progenitors. Cell Stem Cell 2019, 24, 433–446.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giuliani, G.; Rosina, M.; Reggio, A. Signaling pathways regulating the fate of fibro/adipogenic progenitors (FAPs) in skeletal muscle regeneration and disease. FEBS J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theret, M.; Rossi, F.M.V.; Contreras, O. Evolving Roles of Muscle-Resident Fibro-Adipogenic Progenitors in Health, Regeneration, Neuromuscular Disorders, and Aging. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 673404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Cánoves, P.; Serrano, A.L. Macrophages decide between regeneration and fibrosis in muscle. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 26, 449–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santini, M.P.; Malide, D.; Hoffman, G.; Pandey, G.; D’Escamard, V.; Nomura-Kitabayashi, A.; Rovira, I.; Kataoka, H.; Ochando, J.; Harvey, R.P.; et al. Tissue-Resident PDGFRα+ Progenitor Cells Contribute to Fibrosis versus Healing in a Context- and Spatiotemporally Dependent Manner. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 555–570.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.M.; Lawson, J.A.; Mathew, S.J.; Hutcheson, D.A.; Kardon, G. Satellite cells, connective tissue fibroblasts and their interactions are crucial for muscle regeneration. Development 2011, 138, 3625–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wosczyna, M.N.; Konishi, C.T.; Perez Carbajal, E.E.; Wang, T.T.; Walsh, R.A.; Gan, Q.; Wagner, M.W.; Rando, T.A. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Are Required for Regeneration and Homeostatic Maintenance of Skeletal Muscle. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 2029–2035.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arrighi, N.; Moratal, C.; Clément, N.; Giorgetti-Peraldi, S.; Peraldi, P.; Loubat, A.; Kurzenne, J.-Y.; Dani, C.; Chopard, A.; Dechesne, C.A. Characterization of adipocytes derived from fibro/adipogenic progenitors resident in human skeletal muscle. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moratal, C.; Arrighi, N.; Dechesne, C.A.; Dani, C. Control of Muscle Fibro-Adipogenic Progenitors by Myogenic Lineage is Altered in Aging and Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 53, 1029–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pisani, D.F.; Clement, N.; Loubat, A.; Plaisant, M.; Sacconi, S.; Kurzenne, J.-Y.; Desnuelle, C.; Dani, C.; Dechesne, C.A. Hierarchization of myogenic and adipogenic progenitors within human skeletal muscle. Stem Cells 2010, 28, 2182–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Chikenji, T.S.; Matsumura, T.; Nakano, M.; Fujimiya, M. Exercise enhances skeletal muscle regeneration by promoting senescence in fibro-adipogenic progenitors. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lino Cardenas, C.L.; Henaoui, I.S.; Courcot, E.; Roderburg, C.; Cauffiez, C.; Aubert, S.; Copin, M.-C.; Wallaert, B.; Glowacki, F.; Dewaeles, E.; et al. miR-199a-5p Is upregulated during fibrogenic response to tissue injury and mediates TGFbeta-induced lung fibroblast activation by targeting caveolin-1. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savary, G.; Dewaeles, E.; Diazzi, S.; Buscot, M.; Nottet, N.; Fassy, J.; Courcot, E.; Henaoui, I.-S.; Lemaire, J.; Martis, N.; et al. The Long Noncoding RNA DNM3OS Is a Reservoir of FibromiRs with Major Functions in Lung Fibroblast Response to TGF-β and Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgoulis, D.; Berenstein, P.; Cazacu, S.; Kazimirsky, G.; Dori, A.; Barnea, E.R.; Brodie, C. sPIF promotes myoblast differentiation and utrophin expression while inhibiting fibrosis in Duchenne muscular dystrophy via the H19/miR-675/let-7 and miR-21 pathways. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, M.S.; Kawahara, G.; Motohashi, N.; Casar, J.C.; Eisenberg, I.; Myers, J.A.; Gasperini, M.J.; Estrella, E.A.; Kho, A.T.; Mitsuhashi, S.; et al. MicroRNA-199a is induced in dystrophic muscle and affects WNT signaling, cell proliferation, and myogenic differentiation. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 1194–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Kuek, V.; Liu, Y.; Tickner, J.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, L.; Zeng, Z.; Shao, M.; He, W.; Xu, J. MiR-214 is an important regulator of the musculoskeletal metabolism and disease. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 234, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mueller, A.A.; van Velthoven, C.T.; Fukumoto, K.D.; Cheung, T.H.; Rando, T.A. Intronic polyadenylation of PDGFRα in resident stem cells attenuates muscle fibrosis. Nature 2016, 540, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güller, I.; Russell, A.P. MicroRNAs in skeletal muscle: Their role and regulation in development, disease and function. J. Physiol. 2010, 588, 4075–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dolivo, D.M.; Larson, S.A.; Dominko, T. Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 as an Antifibrotic: Antagonism of Myofibroblast Differentiation and Suppression of Pro-Fibrotic Gene Expression. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017, 38, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Bell, G.W.; Nam, J.-W.; Bartel, D.P. Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. eLife 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Froum, S.; Hamby, J.M.; Schroeder, M.C.; Panek, R.L.; Lu, G.H.; Eliseenkova, A.V.; Green, D.; Schlessinger, J.; Hubbard, S.R. Crystal structure of an angiogenesis inhibitor bound to the FGF receptor tyrosine kinase domain. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 5896–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mann, C.J.; Perdiguero, E.; Kharraz, Y.; Aguilar, S.; Pessina, P.; Serrano, A.L.; Muñoz-Cánoves, P. Aberrant repair and fibrosis development in skeletal muscle. Skelet. Muscle 2011, 1, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pottier, N.; Cauffiez, C.; Perrais, M.; Barbry, P.; Mari, B. FibromiRs: Translating molecular discoveries into new anti-fibrotic drugs. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, J.J. The MyomiR network in skeletal muscle plasticity. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2011, 39, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberg, I.; Eran, A.; Nishino, I.; Moggio, M.; Lamperti, C.; Amato, A.A.; Lidov, H.G.; Kang, P.B.; North, K.N.; Mitrani-Rosenbaum, S.; et al. Distinctive patterns of microRNA expression in primary muscular disorders. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 17016–17021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cacchiarelli, D.; Martone, J.; Girardi, E.; Cesana, M.; Incitti, T.; Morlando, M.; Nicoletti, C.; Santini, T.; Sthandier, O.; Barberi, L.; et al. MicroRNAs involved in molecular circuitries relevant for the Duchenne muscular dystrophy pathogenesis are controlled by the dystrophin/nNOS pathway. Cell Metab. 2010, 12, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moratal, C.; Raffort, J.; Arrighi, N.; Rekima, S.; Schaub, S.; Dechesne, C.A.; Chinetti, G.; Dani, C. IL-1β- and IL-4-polarized macrophages have opposite effects on adipogenesis of intramuscular fibro-adipogenic progenitors in humans. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchelson, K.R.; Qin, W.-Y. Roles of the canonical myomiRs miR-1, -133 and -206 in cell development and disease. World J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 6, 162–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Cui, X.; Crossman, D.K.; Hao, J.; Kazamel, M.; Kwon, Y.; King, P.H. Muscle microRNA signatures as biomarkers of disease progression in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 114, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Režen, T.; Kovanda, A.; Eiken, O.; Mekjavic, I.B.; Rogelj, B. Expression changes in human skeletal muscle miRNAs following 10 days of bed rest in young healthy males. Acta Physiol. 2014, 210, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.; Scheele, C.; Yfanti, C.; Akerström, T.; Nielsen, A.R.; Pedersen, B.K.; Laye, M.J.; Laye, M. Muscle specific microRNAs are regulated by endurance exercise in human skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. 2010, 588, 4029–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Ge, D.; Cao, X.; Ge, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H. MiR-214 Attenuates Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells via Targeting FGFR1. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 38, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yuan, H.; Ji, W.; Wang, K.; Lu, T.; Yu, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Li, F.; Xia, W.; et al. Reciprocal regulatory mechanism between miR-214-3p and FGFR1 in FGFR1-amplified lung cancer. Oncogenesis 2019, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ornitz, D.M.; Itoh, N. The Fibroblast Growth Factor signaling pathway. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2015, 4, 215–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pawlikowski, B.; Vogler, T.O.; Gadek, K.; Olwin, B.B. Regulation of skeletal muscle stem cells by fibroblast growth factors. Dev. Dyn. 2017, 246, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reggio, A.; Rosina, M.; Palma, A.; Cerquone Perpetuini, A.; Petrilli, L.L.; Gargioli, C.; Fuoco, C.; Micarelli, E.; Giuliani, G.; Cerretani, M.; et al. Adipogenesis of skeletal muscle fibro/adipogenic progenitors is affected by the WNT5a/GSK3/β-catenin axis. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 2921–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccone, V.; Consalvi, S.; Giordani, L.; Mozzetta, C.; Barozzi, I.; Sandoná, M.; Ryan, T.; Rojas-Muñoz, A.; Madaro, L.; Fasanaro, P.; et al. HDAC-regulated myomiRs control BAF60 variant exchange and direct the functional phenotype of fibro-adipogenic progenitors in dystrophic muscles. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 841–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crooke, S.T.; Witztum, J.L.; Bennett, C.F.; Baker, B.F. RNA-Targeted Therapeutics. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wurster, C.D.; Ludolph, A.C. Antisense oligonucleotides in neurological disorders. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Name | Gender | Age | Muscle Origin | Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMD donors | ||||
| A | M | 14 | paravertebral | Figure 1 |
| B | M | 12 | paravertebral | Figure 1 |
| C | M | 13 | paravertebral | Figure 1 |
| D | M | 15 | paravertebral | Figure 1 |
| E | M | 15 | paravertebral | Figure 1 |
| F | M | 14 | paravertebral | Figure 1 |
| G | M | 16 | paravertebral | Figure 1 |
| H | M | 15 | paravertebral | Figure 1 |
| Healthy Donors | ||||
| CT1 | M | 14 | intervertebral | Figure 1 |
| CT2 | M | <10 | Figure 1 | |
| CT3 | M | <10 | Figure 1 | |
| 1008 | F | 43 | Figure 2 | |
| 1019 | M | 30 | Figure 2 | |
| 1169 | F | 32 | Figure 2 | |
| D5 | M | 17 | gluteus maximus | Figure 3 |
| D9 | M | 57 | Figure 3 | |
| K12-2 | M | <10 | Figure 4 | |
| K14-1 | M | 3 | inguinal | Figure 4 |
| K13-6 | M | 4 | gluteus maximus | Figure 4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arrighi, N.; Moratal, C.; Savary, G.; Fassy, J.; Nottet, N.; Pons, N.; Clément, N.; Fellah, S.; Larrue, R.; Magnone, V.; et al. The FibromiR miR-214-3p Is Upregulated in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Promotes Differentiation of Human Fibro-Adipogenic Muscle Progenitors. Cells 2021, 10, 1832. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10071832
Arrighi N, Moratal C, Savary G, Fassy J, Nottet N, Pons N, Clément N, Fellah S, Larrue R, Magnone V, et al. The FibromiR miR-214-3p Is Upregulated in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Promotes Differentiation of Human Fibro-Adipogenic Muscle Progenitors. Cells. 2021; 10(7):1832. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10071832
Chicago/Turabian StyleArrighi, Nicole, Claudine Moratal, Grégoire Savary, Julien Fassy, Nicolas Nottet, Nicolas Pons, Noémie Clément, Sandy Fellah, Romain Larrue, Virginie Magnone, and et al. 2021. "The FibromiR miR-214-3p Is Upregulated in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Promotes Differentiation of Human Fibro-Adipogenic Muscle Progenitors" Cells 10, no. 7: 1832. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10071832
APA StyleArrighi, N., Moratal, C., Savary, G., Fassy, J., Nottet, N., Pons, N., Clément, N., Fellah, S., Larrue, R., Magnone, V., Lebrigand, K., Pottier, N., Dechesne, C., Vassaux, G., Dani, C., Peraldi, P., & Mari, B. (2021). The FibromiR miR-214-3p Is Upregulated in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Promotes Differentiation of Human Fibro-Adipogenic Muscle Progenitors. Cells, 10(7), 1832. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10071832







