Platelet Bone Morphogenetic Protein-4 Mediates Vascular Inflammation and Neointima Formation after Arterial Injury
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Tail Bleeding Assay
2.3. Complete Blood Count
2.4. Platelet Isolation from Mice
2.5. Intravital Microscopy of Mouse Mesenteric Venules
2.6. Mouse Model of Carotid Injury
2.7. Mouse Model of Re-Endothelialization
2.8. Morphometric and Immunofluorescence Analysis
2.9. ELISA
2.10. Flow Cytometry
2.11. Cell Culture
2.12. In Vitro Cell Proliferation Assay
2.13. Wound Healing Scratch Assay
2.14. Western Blot Analysis
2.15. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription
2.16. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.17. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Basic Characterization of Platelet BMP-4-Deficiency in Mice
3.2. Platelet BMP-4 Mediates Neointimal Formation in LDLr−/− Mice
3.3. Lack of Platelet BMP-4 Delays Re-Endothelialization by Inhibiting Endothelial Cell Proliferation and Migration
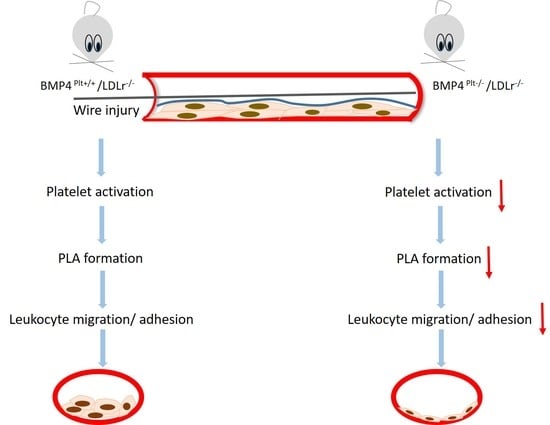
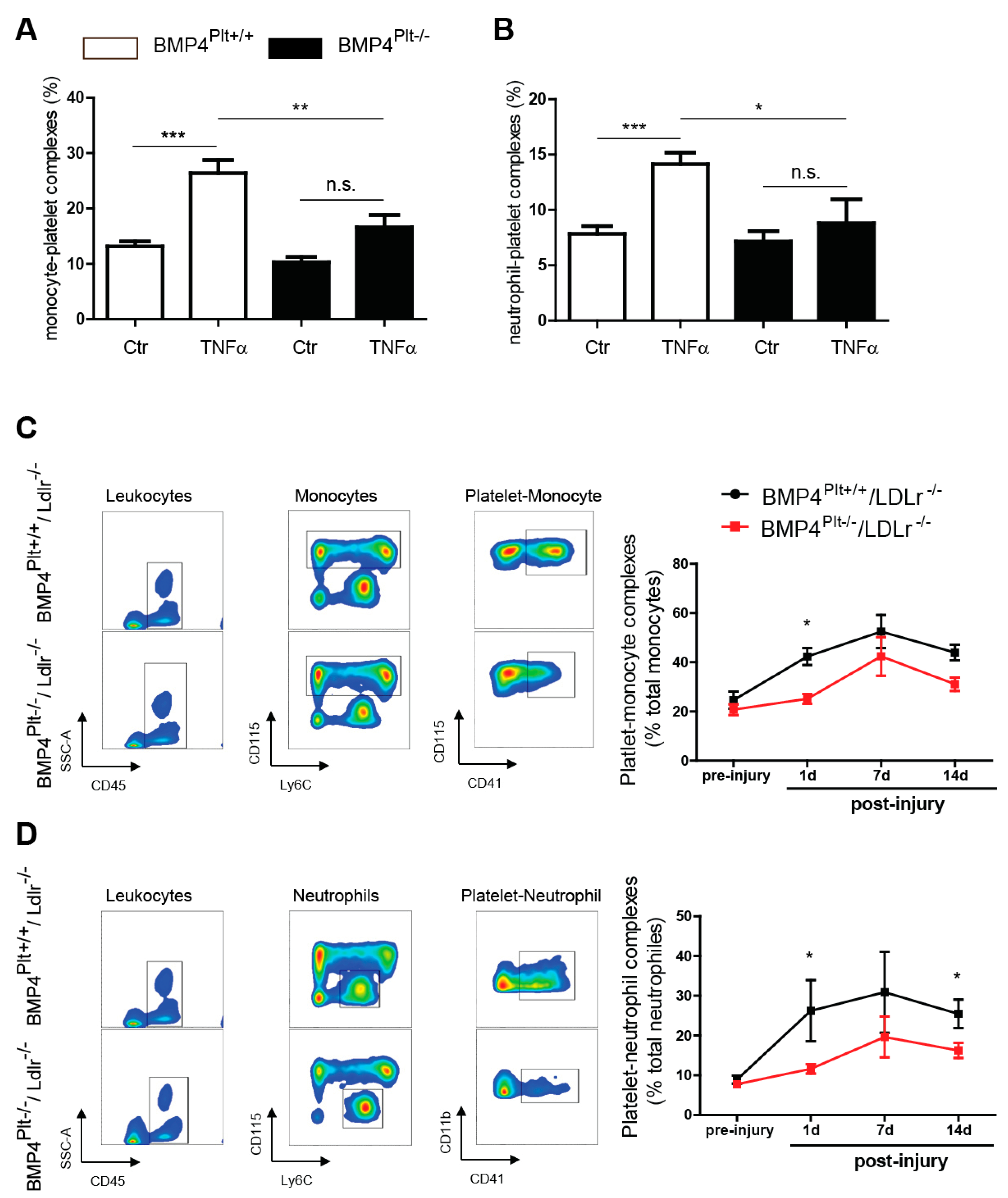
3.4. Platelet BMP-4 Mediates Leukocyte Rolling and Adhesion to the Vessel Wall
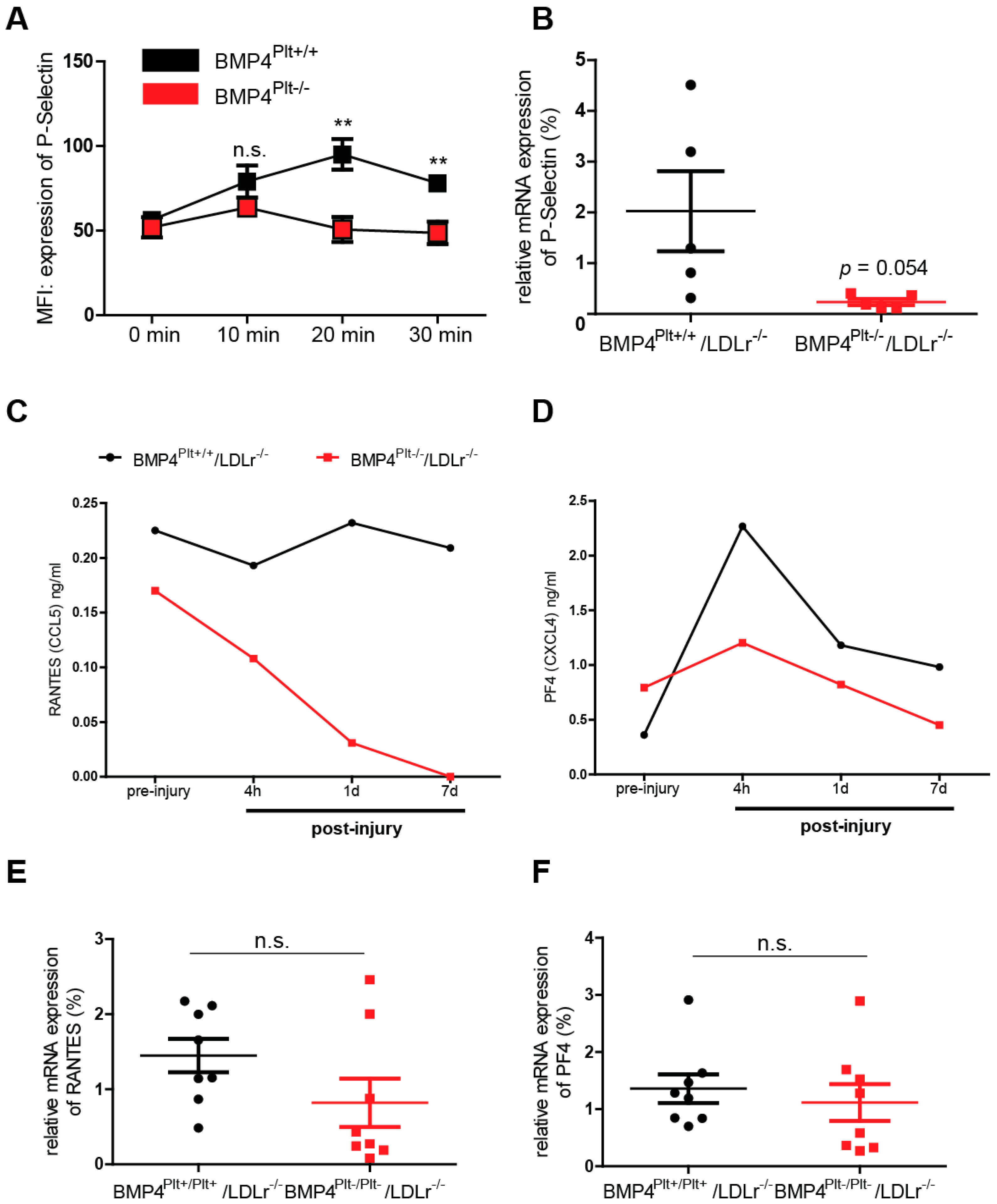
3.5. Platelet BMP-4 Is Indispensable for Platelet Activation, Secretion and Aggregation with Leukocytes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gimbrone, M.A., Jr.; Garcia-Cardena, G. Endothelial Cell Dysfunction and the Pathobiology of Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 620–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koupenova, M.; Clancy, L.; Corkrey, H.A.; Freedman, J.E. Circulating Platelets as Mediators of Immunity, Inflammation, and Thrombosis. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, D.D. New links between inflammation and thrombosis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 1321–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gear, A.R.; Camerini, D. Platelet chemokines and chemokine receptors: Linking hemostasis, inflammation, and host defense. Microcirculation 2003, 10, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slungaard, A. Platelet factor 4: A chemokine enigma. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2005, 37, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Hundelshausen, P.; Koenen, R.R.; Sack, M.; Mause, S.F.; Adriaens, W.; Proudfoot, A.E.; Hackeng, T.M.; Weber, C. Heterophilic interactions of platelet factor 4 and RANTES promote monocyte arrest on endothelium. Blood 2005, 105, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, R.N.; Green, J.; Wang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Qiao, M.; Peabody, M.; Zhang, Q.; Ye, J.; Yan, Z.; Denduluri, S.; et al. Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) signaling in development and human diseases. Genes. Dis. 2014, 1, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sieber, C.; Kopf, J.; Hiepen, C.; Knaus, P. Recent advances in BMP receptor signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009, 20, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goumans, M.J.; Zwijsen, A.; Ten Dijke, P.; Bailly, S. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins in Vascular Homeostasis and Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a031989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyer, L.A.; Pi, X.; Patterson, C. The role of BMPs in endothelial cell function and dysfunction. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 25, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sipe, J.B.; Zhang, J.; Waits, C.; Skikne, B.; Garimella, R.; Anderson, H.C. Localization of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs)-2, -4, and -6 within megakaryocytes and platelets. Bone 2004, 35, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiedt, R.; Schomber, T.; Hao-Shen, H.; Skoda, R.C. Pf4-Cre transgenic mice allow the generation of lineage-restricted gene knockouts for studying megakaryocyte and platelet function in vivo. Blood 2007, 109, 1503–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindner, V.; Fingerle, J.; Reidy, M.A. Mouse model of arterial injury. Circ. Res. 1993, 73, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leipner, J.; Dederichs, T.S.; von Ehr, A.; Rauterberg, S.; Ehlert, C.; Merz, J.; Dufner, B.; Hoppe, N.; Krebs, K.; Heidt, T.; et al. Myeloid cell-specific Irf5 deficiency stabilizes atherosclerotic plaques in Apoe-/- mice. Mol. Metab. 2021, 53, 101250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finsterbusch, M.; Schrottmaier, W.C.; Kral-Pointner, J.B.; Salzmann, M.; Assinger, A. Measuring and interpreting platelet-leukocyte aggregates. Platelets 2018, 29, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauler, M.; Herr, N.; Schoenichen, C.; Witsch, T.; Marchini, T.; Hardtner, C.; Koentges, C.; Kienle, K.; Ollivier, V.; Schell, M.; et al. Platelet Serotonin Aggravates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via Neutrophil Degranulation. Circulation 2019, 139, 918–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauler, M.; Seyfert, J.; Haenel, D.; Seeba, H.; Guenther, J.; Stallmann, D.; Schoenichen, C.; Hilgendorf, I.; Bode, C.; Ahrens, I.; et al. Platelet-neutrophil complex formation-a detailed in vitro analysis of murine and human blood samples. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 99, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisterfer, A.A.; Peach, M.J.; Owens, G.K. Angiotensin II induces hypertrophy, not hyperplasia, of cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Circ. Res. 1988, 62, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.W.; Liu, P.Y.; Oyama, N.; Rikitake, Y.; Kitamoto, S.; Gitlin, J.; Liao, J.K.; Boisvert, W.A. Deficiency of ROCK1 in bone marrow-derived cells protects against atherosclerosis in LDLR-/- mice. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 3561–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, C.C.; Park, A.Y.; Guan, J.L. In vitro scratch assay: A convenient and inexpensive method for analysis of cell migration in vitro. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, R.; Xiao, A.Y.; Song, Z.; Yu, S.; Li, J.; Cui, M.Z.; Li, G. Platelet CD40 Mediates Leukocyte Recruitment and Neointima Formation after Arterial Denudation Injury in Atherosclerosis-Prone Mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Konishi, H.; Katoh, Y.; Takaya, N.; Kashiwakura, Y.; Itoh, S.; Ra, C.; Daida, H. Platelets activated by collagen through immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif play pivotal role in initiation and generation of neointimal hyperplasia after vascular injury. Circulation 2002, 105, 912–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noels, H.; Zhou, B.; Tilstam, P.V.; Theelen, W.; Li, X.; Pawig, L.; Schmitz, C.; Akhtar, S.; Simsekyilmaz, S.; Shagdarsuren, E.; et al. Deficiency of endothelial CXCR4 reduces reendothelialization and enhances neointimal hyperplasia after vascular injury in atherosclerosis-prone mice. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 1209–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verma, S.K.; Garikipati, V.N.; Krishnamurthy, P.; Khan, M.; Thorne, T.; Qin, G.; Losordo, D.W.; Kishore, R. IL-10 Accelerates Re-Endothelialization and Inhibits Post-Injury Intimal Hyperplasia following Carotid Artery Denudation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furie, B.; Furie, B.C. Role of platelet P-selectin and microparticle PSGL-1 in thrombus formation. Trends Mol. Med. 2004, 10, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blann, A.D.; Nadar, S.K.; Lip, G.Y. The adhesion molecule P-selectin and cardiovascular disease. Eur. Heart J. 2003, 24, 2166–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Welt, F.G.; Rogers, C. Inflammation and restenosis in the stent era. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 1769–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stalker, T.J.; Welsh, J.D.; Brass, L.F. Shaping the platelet response to vascular injury. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2014, 21, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ni, C.W.; Qiu, H.; Rezvan, A.; Kwon, K.; Nam, D.; Son, D.J.; Visvader, J.E.; Jo, H. Discovery of novel mechanosensitive genes in vivo using mouse carotid artery endothelium exposed to disturbed flow. Blood 2010, 116, e66–e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corriere, M.A.; Rogers, C.M.; Eliason, J.L.; Faulk, J.; Kume, T.; Hogan, B.L.; Guzman, R.J. Endothelial Bmp4 is induced during arterial remodeling: Effects on smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation. J. Surg. Res. 2008, 145, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palabrica, T.; Lobb, R.; Furie, B.C.; Aronovitz, M.; Benjamin, C.; Hsu, Y.M.; Sajer, S.A.; Furie, B. Leukocyte accumulation promoting fibrin deposition is mediated in vivo by P-selectin on adherent platelets. Nature 1992, 359, 848–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijper, P.H.; Gallardo Torres, H.I.; van der Linden, J.A.; Lammers, J.W.; Sixma, J.J.; Koenderman, L.; Zwaginga, J.J. Platelet-dependent primary hemostasis promotes selectin- and integrin-mediated neutrophil adhesion to damaged endothelium under flow conditions. Blood 1996, 87, 3271–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, Z.; Mal, N.; Fan, L.; Zhang, M.; Lincoff, A.M.; Plow, E.F.; Topol, E.J.; Penn, M.S. Platelet, not endothelial, P-selectin is required for neointimal formation after vascular injury. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 1584–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zernecke, A.; Weber, C. Chemokines in the vascular inflammatory response of atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 86, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mause, S.F.; von Hundelshausen, P.; Zernecke, A.; Koenen, R.R.; Weber, C. Platelet microparticles: A transcellular delivery system for RANTES promoting monocyte recruitment on endothelium. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, G.; Field, D.J.; Long, X.; Mickelsen, D.; Ko, K.A.; Ture, S.; Korshunov, V.A.; Miano, J.M.; Morrell, C.N. Platelet factor 4 mediates vascular smooth muscle cell injury responses. Blood 2013, 121, 4417–4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Von Hundelshausen, P.; Schmitt, M.M. Platelets and their chemokines in atherosclerosis-clinical applications. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imhof, B.A.; Aurrand-Lions, M. Angiogenesis and inflammation face off. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 171–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naldini, A.; Carraro, F. Role of inflammatory mediators in angiogenesis. Curr. Drug Targets Inflamm. Allergy 2005, 4, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keeley, E.C.; Mehrad, B.; Strieter, R.M. Chemokines as mediators of neovascularization. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 1928–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suffee, N.; Hlawaty, H.; Meddahi-Pelle, A.; Maillard, L.; Louedec, L.; Haddad, O.; Martin, L.; Laguillier, C.; Richard, B.; Oudar, O.; et al. RANTES/CCL5-induced pro-angiogenic effects depend on CCR1, CCR5 and glycosaminoglycans. Angiogenesis 2012, 15, 727–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| HRP II | GCA CCA CGC CAA TGA CAT | GTG CGG CTG CTT CCA TAA |
| ICAM | AGG TGG TTC TTC TGA GCG GC | AAA CAG GAA CTT TCC CGC CA |
| VCAM | TCT TGG GAG CCT CAA CGG TA | CAA GTG AGG GCC ATG GAG TC |
| RANTES | GCA AGT GCT CCA ATC TTG CA | CTT GGC GGT TCC TTC GAG T |
| PF-4 | GAG GTG ATC AAG GCA GGA CG | TAT AGG GGT GCT TGC CGG TC |
| P-selectin | CCT GGC AAG TGG AAT GAT GA | AAG CTG CAG ACT GAC TGG TA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jank, M.; von Niessen, N.; Olivier, C.B.; Schmitt, H.; Anto-Michel, N.; Hilgendorf, I.; Bode, C.; Moser, M.; Esser, J.S.; Zhou, Q. Platelet Bone Morphogenetic Protein-4 Mediates Vascular Inflammation and Neointima Formation after Arterial Injury. Cells 2021, 10, 2027. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10082027
Jank M, von Niessen N, Olivier CB, Schmitt H, Anto-Michel N, Hilgendorf I, Bode C, Moser M, Esser JS, Zhou Q. Platelet Bone Morphogenetic Protein-4 Mediates Vascular Inflammation and Neointima Formation after Arterial Injury. Cells. 2021; 10(8):2027. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10082027
Chicago/Turabian StyleJank, Marietta, Nikolaus von Niessen, Christoph B. Olivier, Hannah Schmitt, Nathaly Anto-Michel, Ingo Hilgendorf, Christoph Bode, Martin Moser, Jennifer S. Esser, and Qian Zhou. 2021. "Platelet Bone Morphogenetic Protein-4 Mediates Vascular Inflammation and Neointima Formation after Arterial Injury" Cells 10, no. 8: 2027. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10082027
APA StyleJank, M., von Niessen, N., Olivier, C. B., Schmitt, H., Anto-Michel, N., Hilgendorf, I., Bode, C., Moser, M., Esser, J. S., & Zhou, Q. (2021). Platelet Bone Morphogenetic Protein-4 Mediates Vascular Inflammation and Neointima Formation after Arterial Injury. Cells, 10(8), 2027. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10082027