Schlafens: Emerging Proteins in Cancer Cell Biology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
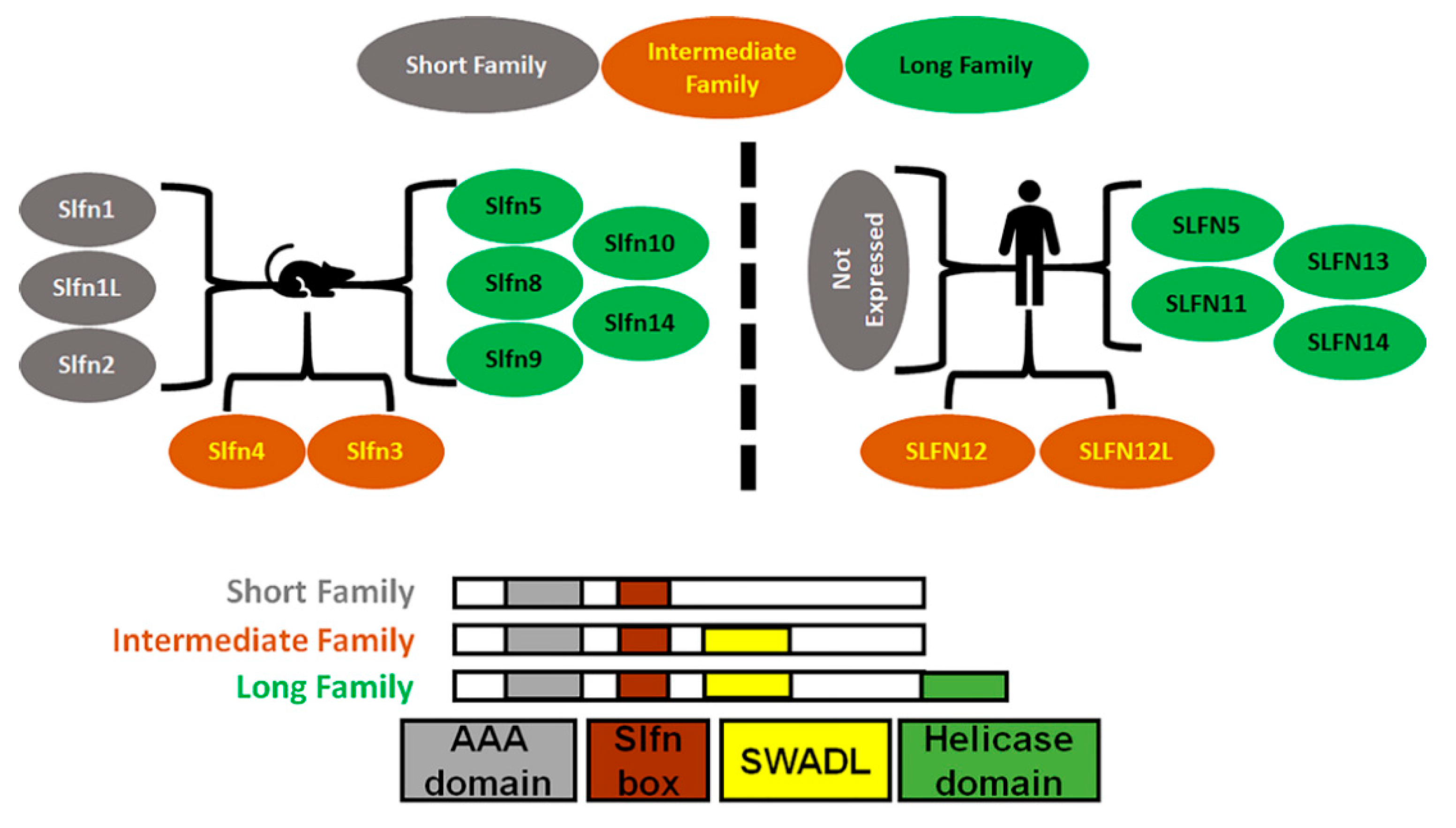
2. Schlafen Structure
3. Role of Schlafens in Non-Malignant Biology
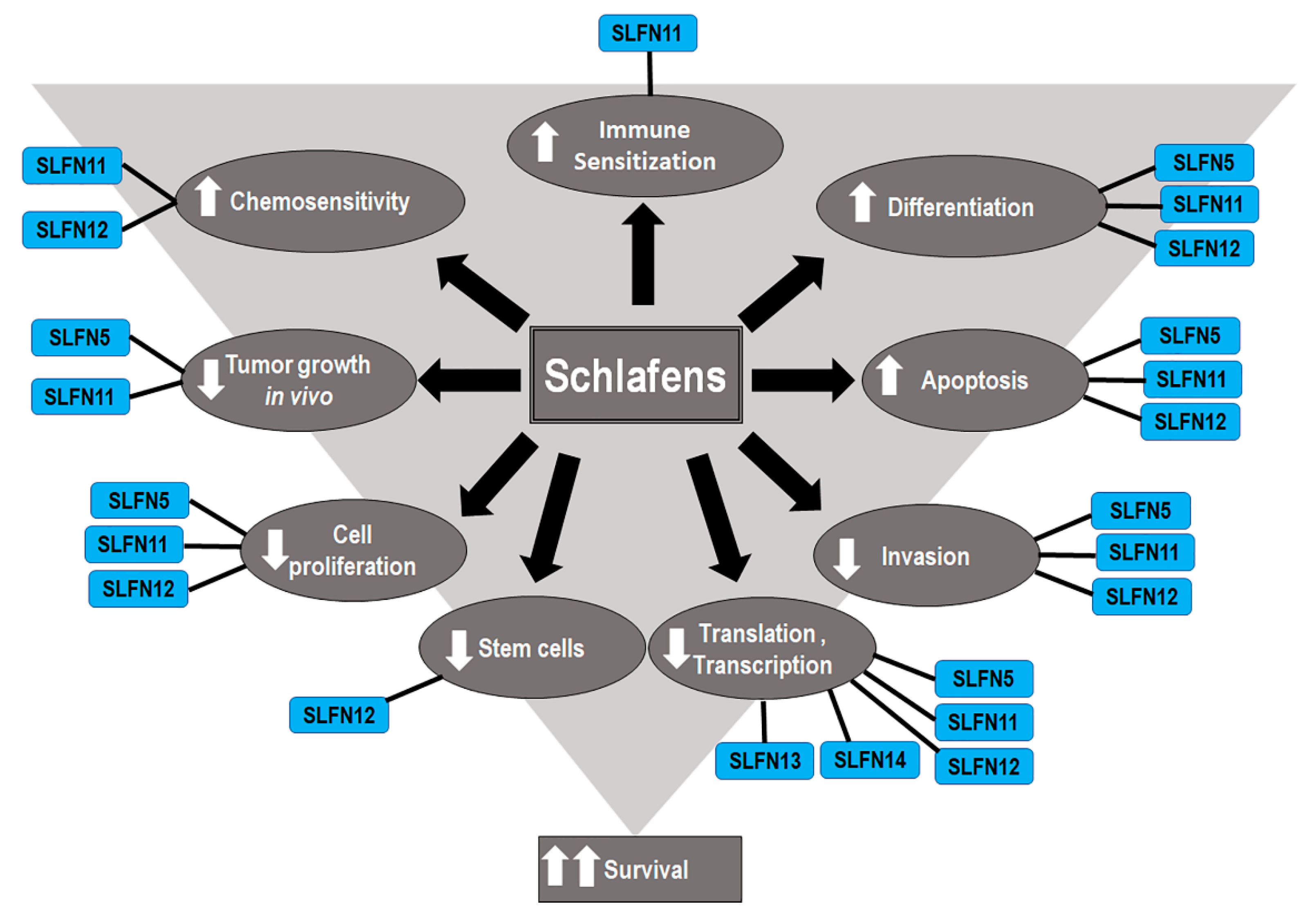
4. Schlafens in Cancer
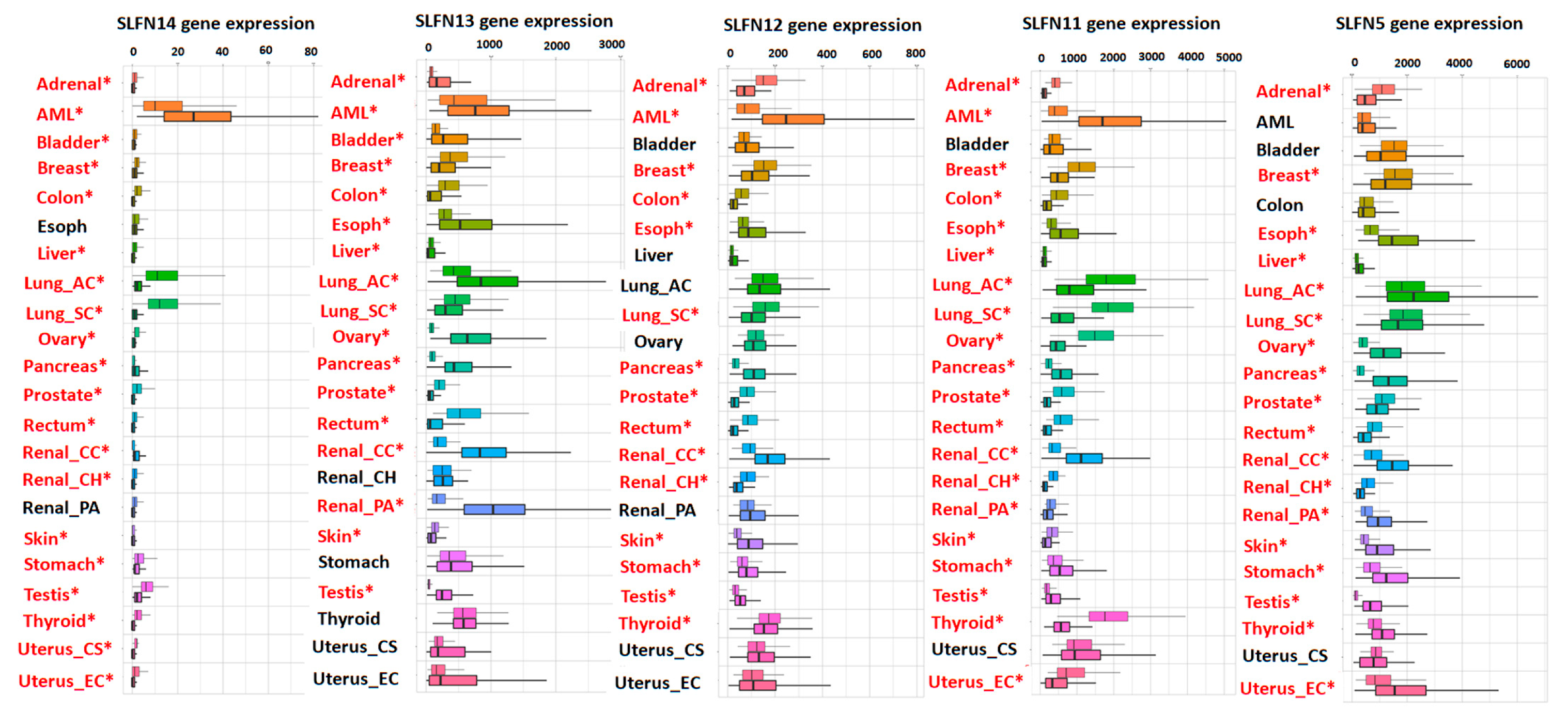
5. Expression of Schlafens in Cancer
6. Functions of Human Schlafens in Cancer
7. Schlafens in Gastric Carcinoma
8. Schlafens in Malignant Melanoma
9. Schlafens in Renal Carcinoma
10. Schlafens in Colorectal Carcinoma
11. Schlafens in Lung Cancer
12. Schlafens in Prostate Cancer
13. Schlafens in Liver Cancer
14. Schlafens in Esophageal Cancer
15. Schlafens in Breast Cancer
16. Schlafens in Central Nervous System Cancers
17. Schlafens in Hematological Malignancies
18. Role of Schlafens in the Antitumor Effects of Interferons
19. Role of Human Schlafens in Cancer Chemosensitivity
19.1. Role of Schlafen 11 in Chemosensitivity
19.2. Role of Schlafen 12 in Chemosensitivity
20. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schwarz, D.A.; Katayama, C.D.; Hedrick, S.M. Schlafen, a New Family of Growth Regulatory Genes that Affect Thymocyte Development. Immunity 1998, 9, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Kuhn, L.A. Deciphering the three-domain architecture in schlafens and the structures and roles of human schlafen12 and serpinB12 in transcriptional regulation. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2019, 90, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Tannoudji, M.; Vandormael-Pournin, S.; Le Bras, S.; Coumailleau, F.; Babinet, C.; Baldacci, P. A 2-Mb YAC/BAC-Based Physical Map of the Ovum Mutant (Om) Locus Region on Mouse Chromosome 11. Genomics 2000, 68, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geserick, P.; Kaiser, F.; Klemm, U.; Kaufmann, S.H.E.; Zerrahn, J. Modulation of T cell development and activation by novel members of the Schlafen (slfn) gene family harbouring an RNA helicase-like motif. Int. Immunol. 2004, 16, 1535–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bustos, O.; Naik, S.; Ayers, G.; Casola, C.; Perez-Lamigueiro, M.A.; Chippindale, P.T.; Pritham, E.J.; de la Casa-Esperón, E. Evolution of the Schlafen genes, a gene family associated with embryonic lethality, meiotic drive, immune processes and orthopoxvirus virulence. Gene 2009, 447, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Zhou, P.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Li, D. The Schlafen family: Complex roles in different cell types and virus replication. Cell Biol. Int. 2018, 42, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Casa-Esperón, E. From mammals to viruses: The Schlafen genes in developmental, proliferative and immune processes. Biomol. Concepts 2011, 2, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, G.; Boggan, L.; Bowie, A.; O’Neill, L. Schlafen-1 Causes a Cell Cycle Arrest by Inhibiting Induction of Cyclin D1. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 30723–30734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuang, C.-Y.; Yang, T.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Q. Schlafen 1 Inhibits the Proliferation and Tube Formation of Endothelial Progenitor Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basson, M.D.; Wang, Q.; Chaturvedi, L.S.; Vomhof-DeKrey, E. Schlafen 12 Promotes Human Intestinal Epithelial Differentiation via Serpin B12 Modulation of the Deubiquitylation of Transcription Factors Such as CDX2. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, S180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, P.-S.; Patel, V.B.; Sanders, M.A.; Kanwar, S.; Yu, Y.; Nautiyal, J.; Patel, B.B.; Majumdar, A.P.N. Schlafen-3 decreases cancer stem cell marker expression and autocrine/juxtacrine signaling in FOLFOX-resistant colon cancer cells. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2011, 301, G347–G355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Mohsen, M.; Raposo, R.A.S.; Deng, X.; Li, M.; Liegler, T.; Sinclair, E.; Salama, M.S.; Ghanem, A.H.E.-D.; Hoh, R.; Wong, J.K.; et al. Expression profile of host restriction factors in HIV-1 elite controllers. Retrovirology 2013, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Mohsen, M.; Wang, C.; Strain, M.C.; Lada, S.M.; Deng, X.; Cockerham, L.R.; Pilcher, C.D.; Hecht, F.; Liegler, T.; Richman, D.D.; et al. Select host restriction factors are associated with HIV persistence during antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 2015, 29, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Marsoummi, S.; Vomhof-DeKrey, E.; Basson, M.D. Schlafen12 Reduces the Aggressiveness of Triple Negative Breast Cancer through Post-Transcriptional Regulation of ZEB1 That Drives Stem Cell Differentiation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 53, 999–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Marsoummi, S.; Pacella, J.; Dockter, K.; Soderberg, M.; Singhal, S.K.; Vomhof-DeKrey, E.E.; Basson, M.D. Schlafen 12 Is Prognostically Favorable and Reduces C-Myc and Proliferation in Lung Adenocarcinoma but Not in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nápoles, O.C.; Tsao, A.C.; Sanz-Anquela, J.M.; Sala, N.; Bonet, C.; Pardo, M.L.; Ding, L.; Simo, O.; Saqui-Salces, M.; Blanco, V.P.; et al. SCHLAFEN 5 expression correlates with intestinal metaplasia that progresses to gastric cancer. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Isnaldi, E.; Ferraioli, D.; Ferrando, L.; Brohée, S.; Ferrando, F.; Fregatti, P.; Bedognetti, D.; Ballestrero, A.; Zoppoli, G. Schlafen-11 expression is associated with immune signatures and basal-like phenotype in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 177, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Song, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Hu, Y.; Xu, J. Schlafen-11 sensitizes colorectal carcinoma cells to irinotecan. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2014, 25, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoppoli, G.; Regairaz, M.; Leo, E.; Reinhold, W.C.; Varma, S.; Ballestrero, A.; Doroshow, J.H.; Pommier, Y. Putative DNA/RNA helicase Schlafen-11 (SLFN11) sensitizes cancer cells to DNA-damaging agents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 15030–15035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barretina, J.; Caponigro, G.; Stransky, N.; Venkatesan, K.; Margolin, A.A.; Kim, S.; Wilson, C.J.; Lehár, J.; Kryukov, G.; Sonkin, D.; et al. The Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia enables predictive modelling of anticancer drug sensitivity. Nature 2012, 483, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogales, V.; Reinhold, W.; Varma, S.; Cardus, A.M.; Moutinho, C.; Moran, S.; Heyn, H.; Sebio, A.; Barnadas, A.; Pommier, Y.; et al. Epigenetic inactivation of the putative DNA/RNA helicase SLFN11 in human cancer confers resistance to platinum drugs. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 3084–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, T.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, R.; Zheng, S.; Linghu, E.; Herman, J.G.; Guo, M. Methylation ofSLFN11is a marker of poor prognosis and cisplatin resistance in colorectal cancer. Epigenomics 2017, 9, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stewart, C.A.; Tong, P.; Cardnell, R.J.; Sen, T.; Li, L.; Gay, C.M.; Masrorpour, F.; Fan, Y.; Bara, R.O.; Feng, Y.; et al. Dynamic variations in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), ATM, and SLFN11 govern response to PARP inhibitors and cisplatin in small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 28575–28587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Protein BLAST: Search Protein Databases Using a Protein Query . Available online: https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?PROGRAM=blastp&PAGE_TYPE=BlastSearch&LINK_LOC=blasthome (accessed on 27 July 2021).
- Neumann, B.; Zhao, L.; Murphy, K.; Gonda, T.J. Subcellular localization of the Schlafen protein family. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 370, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrommatis, E.; Fish, E.N.; Platanias, L.C. The Schlafen Family of Proteins and Their Regulation by Interferons. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2013, 33, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.-Y.; Deng, X.-Y.; Li, Y.-S.; Ma, X.; Feng, J.-X.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Y.-L.; Wang, X.; Chen, M.-L.; et al. Structure of Schlafen13 reveals a new class of tRNA/rRNA- targeting RNase engaged in translational control. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaturvedi, L.; Sun, K.; Walsh, M.F.; Kuhn, L.A.; Basson, M.D. The P-loop region of Schlafen 3 acts within the cytosol to induce differentiation of human Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 2014, 1843, 3029–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Basson, M.D.; Wang, Q.; Chaturvedi, L.S.; More, S.; Vomhof-DeKrey, E.E.; Al-Marsoummi, S.; Sun, K.; Kuhn, L.A.; Kovalenko, P.; Kiupel, M. Schlafen 12 Interaction with Serpin B12 and Deubiquitylases Drives Human Enterocyte Differentiation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 1274–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Kao, E.; Gao, X.; Sandig, H.; Limmer, K.; Pavon-Eternod, M.; Jones, T.E.; Landry, S.; Pan, T.; Weitzman, M.D.; et al. Codon-usage-based inhibition of HIV protein synthesis by human schlafen 11. Nature 2012, 491, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valdez, F.; Salvador, J.; Palermo, P.M.; Mohl, J.; Hanley, K.; Watts, D.; Llano, M. Schlafen 11 Restricts Flavivirus Replication. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, N.K.; Choi, H.K.; Yoo, H.J.; Shin, J.; Lee, S.Y. RANKL-induced schlafen2 is a positive regulator of osteoclastogenesis. Cell. Signal. 2008, 20, 2302–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, I.; Guterman-Ram, G.; Rahat, D.; Tabach, Y.; Berger, M.; Levaot, N. Schlafen2 mutation in mice causes an osteopetrotic phenotype due to a decrease in the number of osteoclast progenitors. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kovalenko, P.L.; Yuan, L.; Sun, K.; Kunovska, L.; Seregin, S.; Amalfitano, A.; Basson, M.D. Regulation of Epithelial Differentiation in Rat Intestine by Intraluminal Delivery of an Adenoviral Vector or Silencing RNA Coding for Schlafen 3. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mavrommatis, E.; Arslan, A.D.; Sassano, A.; Hua, Y.; Kroczynska, B.; Platanias, L.C. Expression and Regulatory Effects of Murine Schlafen (Slfn) Genes in Malignant Melanoma and Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 33006–33015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lund, S.; Christensen, K.V.; Hedtjärn, M.; Mortensen, A.L.; Hagberg, H.; Falsig, J.; Hasseldam, H.; Schrattenholz, A.; Pörzgen, P.; Leist, M. The dynamics of the LPS triggered inflammatory response of murine microglia under different culture and in vivo conditions. J. Neuroimmunol. 2006, 180, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katsoulidis, E.; Carayol, N.; Woodard, J.; Konieczna, I.; Majchrzak-Kita, B.; Jordan, A.; Sassano, A.; Eklund, E.A.; Fish, E.N.; Platanias, L.C. Role of Schlafen 2 (SLFN2) in the Generation of Interferon α-induced Growth Inhibitory Responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 25051–25064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berger, M.; Krebs, P.; Crozat, K.; Li, X.; Croker, B.; Siggs, O.; Popkin, D.; Du, X.; Lawson, B.R.; Theofilopoulos, A.N.; et al. An Slfn2 mutation causes lymphoid and myeloid immunodeficiency due to loss of immune cell quiescence. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, I.; Lapenna, A.; Cohen-Daniel, L.; Tirosh, B.; Berger, M. Schlafen 2 mutation unravels a role for chronic ER stress in the loss of T cell quiescence. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 39396–39407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Omar, I.; Rom, O.; Aviram, M.; Cohen-Daniel, L.; Gebre, A.K.; Parks, J.S.; Berger, M. Slfn2 mutation-induced loss of T-cell quiescence leads to elevated de novo sterol synthesis. Immunology 2017, 152, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, W.-J.; Kim, D.; Lee, K.-W.; Kim, M.-S.; Kwon, S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, O.-S.; Kwon, H.-J. Novel transcriptional regulation of the schlafen-2 gene in macrophages in response to TLR-triggered stimulation. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 3273–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condamine, T.; LE Luduec, J.-B.; Chiffoleau, E.; Bériou, G.; Louvet, C.; Heslan, M.; Tilly, G.; Cuturi, M.-C. Characterization of Schlafen-3 expression in effector and regulatory T cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 87, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Yu, Y.; Sanders, M.A.; Majumdar, A.P.N.; Basson, M.D. Schlafen 3 induction by cyclic strain regulates intestinal epithelial differentiation. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2010, 298, G994–G1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walsh, M.F.; Hermann, R.; Lee, J.H.; Chaturvedi, L.; Basson, M.D. Schlafen 3 Mediates the Differentiating Effects of Cdx2 in Rat IEC-Cdx2L1 Enterocytes. J. Investig. Surg. 2015, 28, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, B.B.; Yu, Y.; Du, J.; Rishi, A.K.; Sarkar, F.H.; Tarca, A.L.; Wali, A.; Majumdar, A.P.N. Schlafen 3, a novel gene, regulates colonic mucosal growth during aging. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2009, 296, G955–G962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vomhof-DeKrey, E.E.; Lee, J.; Lansing, J.; Brown, C.; Darland, D.; Basson, M.D. Schlafen 3 knockout mice display gender-specific differences in weight gain, food efficiency, and expression of markers of intestinal epithelial differentiation, metabolism, and immune cell function. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Zuylen, W.J.; Garceau, V.; Idris, A.; Schroder, K.; Irvine, K.M.; Lattin, J.E.; Ovchinnikov, D.A.; Perkins, A.C.; Cook, A.D.; Hamilton, J.A.; et al. Macrophage Activation and Differentiation Signals Regulate Schlafen-4 Gene Expression: Evidence for Schlafen-4 as a Modulator of Myelopoiesis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e15723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zaatari, M.; Kao, J.Y.; Tessier, A.; Bai, L.; Hayes, M.M.; Fontaine, C.; Eaton, K.A.; Merchant, J.L. Gli1 Deletion Prevents Helicobacter-Induced Gastric Metaplasia and Expansion of Myeloid Cell Subsets. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, L.; Hayes, M.M.; Photenhauer, A.; Eaton, K.A.; Li, Q.; Ocadiz-Ruiz, J.R.; Merchant, J.L. Schlafen 4—Expressing myeloid-derived suppressor cells are induced during murine gastric metaplasia. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 2867–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Matsuki, T.; Zhao, L.; Kuniyoshi, K.; Tanaka, H.; Ebina, I.; Yoshida, K.J.; Nabeshima, H.; Fukushima, K.; Kanemaru, H.; et al. Schlafen-8 is essential for lymphatic endothelial cell activation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Int. Immunol. 2018, 30, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puck, A.; Aigner, R.; Modak, M.; Cejka, P.; Blaas, D.; Stöckl, J. Expression and regulation of Schlafen (SLFN) family members in primary human monocytes, monocyte-derived dendritic cells and T cells. Results Immunol. 2015, 5, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arslan, A.D.; Sassano, A.; Saleiro, D.; Lisowski, P.; Kosciuczuk, E.M.; Fischietti, M.; Eckerdt, F.; Fish, E.N.; Platanias, L.C. Human SLFN5 is a transcriptional co-repressor of STAT1-mediated interferon responses and promotes the malignant phenotype in glioblastoma. Oncogene 2017, 36, 6006–6019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yatim, A.; Benne, C.; Sobhian, B.; Laurent-Chabalier, S.; Deas, O.; Judde, J.-G.; Lelievre, J.-D.; Levy, Y.; Benkirane, M. NOTCH1 Nuclear Interactome Reveals Key Regulators of Its Transcriptional Activity and Oncogenic Function. Mol. Cell 2012, 48, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.-Z.; Sun, L.-K.; Zhu, D.-T.; Hu, Z.; Wang, X.-F.; Du, C.; Wang, Y.-H.; Wang, X.-J.; Zhou, J.-H. Equine schlafen 11 restricts the production of equine infectious anemia virus via a codon usage-dependent mechanism. Virology 2016, 495, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moribe, F.; Nishikori, M.; Takashima, T.; Taniyama, D.; Onishi, N.; Arima, H.; Sasanuma, H.; Akagawa, R.; Elloumi, F.; Takeda, S.; et al. Epigenetic suppression of SLFN11 in germinal center B-cells during B-cell development. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0237554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puck, A.; Hopf, S.; Modak, M.; Majdic, O.; Cejka, P.; Blüml, S.; Schmetterer, K.; Arnold-Schrauf, C.; Gerwien, J.G.; Frederiksen, K.S.; et al. The soluble cytoplasmic tail of CD45 (ct-CD45) in human plasma contributes to keep T cells in a quiescent state. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, R.-K.; Seo, S.-W.; Kim, J.-A.; Fletcher, S.J.; Morgan, N.; Kumar, M.; Choi, Y.-K.; Shin, O.S. Schlafen 14 (SLFN14) is a novel antiviral factor involved in the control of viral replication. Immunobiology 2017, 222, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marconi, C.; Di Buduo, C.A.; Barozzi, S.; Palombo, F.; Pardini, S.; Zaninetti, C.; Pippucci, T.; Noris, P.; Balduini, A.; Seri, M.; et al. SLFN14-related thrombocytopenia: Identification within a large series of patients with inherited thrombocytopenia. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 115, 1076–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisareva, V.P.; Muslimov, I.A.; Tcherepanov, A.; Pisarev, A.V. Characterization of Novel Ribosome-Associated Endoribonuclease SLFN14 from Rabbit Reticulocytes. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 3286–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fletcher, S.J.; Johnson, B.; Lowe, G.C.; Bem, D.; Drake, S.; Lordkipanidze, M.; Guiú, I.S.; Dawood, B.; Rivera, J.; Simpson, M.A.; et al. SLFN14 mutations underlie thrombocytopenia with excessive bleeding and platelet secretion defects. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3600–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gubse, C.; Goodbody, R.; Ecker, A.; Brady, G.; O’Neill, L.; Jacobs, N.; Smith, G.L. Camelpox virus encodes a schlafen-like protein that affects orthopoxvirus virulence. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoulidis, E.; Mavrommatis, E.; Woodard, J.; Shields, M.A.; Sassano, A.; Carayol, N.; Sawicki, K.T.; Munshi, H.G.; Platanias, L.C. Role of interferon α (IFNα)-inducible Schlafen-5 in regulation of anchorage-independent growth and invasion of malignant melanoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 40333–40341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sassano, A.; Mavrommatis, E.; Arslan, A.D.; Kroczynska, B.; Beauchamp, E.M.; Khuon, S.; Chew, T.-L.; Green, K.J.; Munshi, H.G.; Verma, A.K.; et al. Human Schlafen 5 (SLFN5) Is a Regulator of Motility and Invasiveness of Renal Cell Carcinoma Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 35, 2684–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takashima, T.; Sakamoto, N.; Murai, J.; Taniyama, D.; Honma, R.; Ukai, S.; Maruyama, R.; Kuraoka, K.; Rajapakse, V.N.; Pommier, Y.; et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of SLFN11 expression uncovers potential non-responders to DNA-damaging agents overlooked by tissue RNA-seq. Virchows Arch. 2021, 478, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takashima, T.; Taniyama, D.; Sakamoto, N.; Yasumoto, M.; Asai, R.; Hattori, T.; Honma, R.; Thang, P.Q.; Ukai, S.; Maruyama, R.; et al. Schlafen 11 predicts response to platinum-based chemotherapy in gastric cancers. Br. J. Cancer 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Peng, R.; Peng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Long, G.; Wu, G.; Liang, Z. The association between SLFN5 expression and the prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2019, 12, 682–689. [Google Scholar]
- Shee, K.; Wells, J.D.; Jiang, A.; Miller, T.W. Integrated pan-cancer gene expression and drug sensitivity analysis reveals SLFN11 mRNA as a solid tumor biomarker predictive of sensitivity to DNA-damaging chemotherapy. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0224267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, R.S.; Salji, M.J.; Rushworth, L.; Ntala, C.; Rodriguez Blanco, G.; Hedley, A.; Clark, W.; Peixoto, P.; Hervouet, E.; Renaude, E.; et al. SLFN5 regulates LAT1-mediated mTOR activation in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conteduca, V.; Ku, S.-Y.; Puca, L.; Slade, M.; Fernandez, L.; Hess, J.; Bareja, R.; Vlachostergios, P.J.; Sigouros, M.; Mosquera, J.M.; et al. SLFN11 Expression in Advanced Prostate Cancer and Response to Platinum-based Chemotherapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, H.; Yang, M.; Xu, X.M.; She, S.; Ran, X.P.; Li, S.Y.; Hu, H.D.; Ren, H.; Hu, P. Decreased expression of schlafen5 (SLFN5) correlates with unfavorable survival in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2016, 9, 7014–7096. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Liu, C.; Liu, W.; Chen, W.; Yin, Y.; Li, C.-W.; Hsu, J.L.; Sun, J.; Zhou, Q.; Li, H.; et al. SLFN11 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis and metastasis by targeting RPS4X via mTOR pathway. Theranostics 2020, 10, 4627–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagami, T.; Yamade, M.; Suzuki, T.; Uotani, T.; Tani, S.; Hamaya, Y.; Iwaizumi, M.; Osawa, S.; Sugimoto, K.; Miyajima, H.; et al. The first evidence for SLFN11 expression as an independent prognostic factor for patients with esophageal cancer after chemoradiotherapy. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.; Zhu, J.; Gu, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, H.; Huang, G.; Lu, C. Human Schlafen 5 regulates reversible epithelial and mesenchymal transitions in breast cancer by suppression of ZEB1 transcription. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 123, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Wan, G.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, L. SLFN5 influences proliferation and apoptosis by upregulating PTEN transcription via ZEB1 and inhibits the purine metabolic pathway in breast cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 2832–2850. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bartha, Á.; Győrffy, B. TNMplot.com: A Web Tool for the Comparison of Gene Expression in Normal, Tumor and Metastatic Tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Liu, Z.; Tang, X. Overexpression of SLFN5 induced the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human lung cancer cell line A549 through β-catenin/Snail/E-cadherin pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 862, 172630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Guo, L.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Gu, X.; Deng, L.-L.; Lu, C. SLFN5 suppresses cancer cell migration and invasion by inhibiting MT1-MMP expression via AKT/GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway. Cell. Signal. 2019, 59, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Lou, J.; Srivastava, M.; Zhao, B.; Feng, X.; Liu, T.; Chen, J.; Huang, J. SLFN11 inhibits checkpoint maintenance and homologous recombination repair. EMBO Rep. 2016, 17, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Kao, E.; Malone, D.; Gao, X.; Wang, J.Y.J.; David, M. DNA damage-induced cell death relies on SLFN11-dependent cleavage of distinct type II tRNAs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, U.; Murai, Y.; Chakka, S.; Chen, L.; Cheng, K.; Murai, J.; Saha, L.K.; Miller Jenkins, L.M.; Pommier, Y. SLFN11 promotes CDT1 degradation by CUL4 in response to replicative DNA damage, while its absence leads to synthetic lethality with ATR/CHK1 inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2015654118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, J.; Zhang, H.; Pongor, L.; Tang, S.W.; Jo, U.; Moribe, F.; Ma, Y.; Tomita, M.; Pommier, Y. Chromatin Remodeling and Immediate Early Gene Activation by SLFN11 in Response to Replication Stress. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 4137–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murai, J.; Tang, S.W.; Leo, E.; Baechler, S.A.; Redon, C.E.; Zhang, H.; Al Abo, M.; Rajapakse, V.N.; Nakamura, E.; Jenkins, L.M.M.; et al. SLFN11 Blocks Stressed Replication Forks Independently of ATR. Mol. Cell 2018, 69, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Chen, J.; Ai, Y.; Gu, X.; Li, L.; Che, D.; Jiang, Z.; Li, L.; Chen, S.; Huang, H.; et al. Estrogen-Related Hormones Induce Apoptosis by Stabilizing Schlafen-12 Protein Turnover. Mol. Cell 2019, 75, 1103–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvie, C.W.; Wu, X.; Papanastasiou, M.; Lee, S.; Fuller, J.; Schnitzler, G.R.; Horner, S.W.; Baker, A.; Zhang, T.; Mullahoo, J.P.; et al. Structure of PDE3A-SLFN12 complex reveals requirements for activation of SLFN12 RNase. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merchant, J.L.; Ding, L. Hedgehog Signaling Links Chronic Inflammation to Gastric Cancer Precursor Lesions. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 3, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaur, S.; Schwartz, A.L.; Jordan, D.G.; Soto-Pantoja, D.R.; Kuo, B.; Elkahloun, A.G.; Mathews Griner, L.; Thomas, C.J.; Ferrer, M.; Thomas, A.; et al. Identification of Schlafen-11 as a Target of CD47 Signaling That Regulates Sensitivity to Ionizing Radiation and Topoisomerase Inhibitors. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van der Voort van Zijp, J.; Hoekstra, H.J.; Basson, M.D. Evolving management of colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 3956–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bali, M.; Bakkach, J.; Bennani Mechita, M. Colorectal Cancer: From Genetic Landscape to Targeted Therapy. J. Oncol. 2021, 2021, 9918116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vomhof-DeKrey, E.E.; Umthun, J.; Basson, M.D. Loss of Schlafen3 influences the expression levels of Schlafen family members in ileum, thymus, and spleen tissue. PeerJ 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, T.S.; Iglesias-Gato, D.; Souza, L.D.O.; Stenvang, J.; Lima, D.S.; Røder, M.A.; Brasso, K.; Moreira, J.M.A. Molecular Profiling of Docetaxel-Resistant Prostate Cancer Cells Identifies Multiple Mechanisms of Therapeutic Resistance. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 13, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavridou, M.; Strati, A.; Bournakis, E.; Smilkou, S.; Tserpeli, V.; Lianidou, E. Prognostic Significance of Gene Expression and DNA Methylation Markers in Circulating Tumor Cells and Paired Plasma Derived Exosomes in Metastatic Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 13, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalenko, P.L.; Basson, M.D. Schlafen 12 expression modulates prostate cancer cell differentiation. J. Surg. Res. 2014, 190, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yersal, S.B.O. Biological subtypes of breast cancer: Prognostic and therapeutic implications. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 5, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, C.; Armenia, J.; Jones, G.N.; Tobalina, L.; Sale, M.J.; Petreus, T.; Baird, T.; Serra, V.; Wang, A.T.; Lau, A.; et al. SLFN11 informs on standard of care and novel treatments in a wide range of cancer models. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Cui, Y. Dysregulation of DNA methylation patterns may identify patients with breast cancer resistant to endocrine therapy: A predictive classifier based on differentially methylated regions. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 1287–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goldshtein, A.; Zerbib, S.M.; Omar, I.; Cohen-Daniel, L.; Popkin, D.; Berger, M. Loss of T-cell quiescence by targeting Slfn2 prevents the development and progression of T-ALL. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 46835–46847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersson, E.; Eldfors, S.; Edgren, H.; Ellonen, P.; Väkevä, L.; Ranki, A.; Mustjoki, S. Novel TBL1XR1, EPHA7 and SLFN12 mutations in a Sezary syndrome patient discovered by whole exome sequencing. Exp. Dermatol. 2014, 23, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mezzadra, R.; de Bruijn, M.; Jae, L.; Gomez-Eerland, R.; Duursma, A.; Scheeren, F.A.; Brummelkamp, T.R.; Schumacher, T.N. SLFN11 can sensitize tumor cells towards IFN-γ-mediated T cell killing. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aricò, E.; Castiello, L.; Capone, I.; Gabriele, L.; Belardelli, F. Type I Interferons and Cancer: An Evolving Story Demanding Novel Clinical Applications. Cancers 2019, 11, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ningrum, R.A. Human Interferon Alpha-2b: A Therapeutic Protein for Cancer Treatment. Scientifica 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murai, J.; Feng, Y.; Yu, G.K.; Ru, Y.; Tang, S.-W.; Shen, Y.; Pommier, Y. Resistance to PARP inhibitors by SLFN11 inactivation can be overcome by ATR inhibition. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 76534–76550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rathkey, D.; Khanal, M.; Murai, J.; Zhang, J.; Sengupta, M.; Jiang, Q.; Morrow, B.; Evans, C.N.; Chari, R.; Fetsch, P.; et al. Sensitivity of Mesothelioma Cells to PARP Inhibitors Is Not Dependent on BAP1 but Is Enhanced by Temozolomide in Cells with High-Schlafen 11 and Low-O6-methylguanine-DNA Methyltransferase Expression. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 843–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lok, B.; Gardner, E.; Schneeberger, V.E.; Ni, A.; Desmeules, P.; Rekhtman, N.; De Stanchina, E.; Teicher, B.A.; Riaz, N.; Powell, S.N.; et al. PARP Inhibitor Activity Correlates with SLFN11 Expression and Demonstrates Synergy with Temozolomide in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inno, A.; Stagno, A.; Gori, S. Schlafen-11 (SLFN11): A step forward towards personalized medicine in small-cell lung cancer? Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2018, 7, S341–S345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serzan, M.T.; Farid, S.; Liu, S.V. Drugs in development for small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 6298–6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Erp, A.E.M.; van Houdt, L.; Hillebrandt-Roeffen, M.H.S.; van Bree, N.F.H.N.; Flucke, U.E.; Mentzel, T.; Shipley, J.; Desar, I.M.E.; Fleuren, E.D.G.; Versleijen-Jonkers, Y.M.H.; et al. Olaparib and temozolomide in desmoplastic small round cell tumors: A promising combination in vitro and in vivo. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 146, 1659–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tlemsani, C.; Pongor, L.; Elloumi, F.; Girard, L.; Huffman, K.E.; Roper, N.; Varma, S.; Luna, A.; Rajapakse, V.N.; Sebastian, R.; et al. SCLC-CellMiner: A Resource for Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Line Genomics and Pharmacology Based on Genomic Signatures. Cell Rep. 2020, 33, 108296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.-W.; Thomas, A.; Murai, J.; Trepel, J.B.; Bates, S.E.; Rajapakse, V.N.; Pommier, Y. Overcoming Resistance to DNA-Targeted Agents by Epigenetic Activation of Schlafen 11 (SLFN11) Expression with Class I Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1944–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iwasaki, J.; Komori, T.; Nakagawa, F.; Nagase, H.; Uchida, J.; Matsuo, K.; Uto, Y. Schlafen11 Expression Is Associated with the Antitumor Activity of Trabectedin in Human Sarcoma Cell Lines. Anticancer. Res. 2019, 39, 3553–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coussy, F.; El-Botty, R.; Château-Joubert, S.; Dahmani, A.; Montaudon, E.; Leboucher, S.; Morisset, L.; Painsec, P.; Sourd, L.; Huguet, L.; et al. BRCAness, SLFN11, and RB1 loss predict response to topoisomerase I inhibitors in triple-negative breast cancers. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaax2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marzi, L.; Szabova, L.; Gordon, M.; Ohler, Z.W.; Sharan, S.K.; Beshiri, M.; Etemadi, M.; Murai, J.; Kelly, K.; Pommier, Y. The Indenoisoquinoline TOP1 Inhibitors Selectively Target Homologous Recombination-Deficient and Schlafen 11-Positive Cancer Cells and Synergize with Olaparib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6206–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, S.; Chaerkady, R.; Yu, W.; D’Angelo, G.; Garcia, A.; Chen, H.; Barrett, A.M.; Phipps, S.; Fleming, R.; Hess, S.; et al. Resistance to Pyrrolobenzodiazepine Dimers Is Associated with SLFN11 Downregulation and Can Be Reversed through Inhibition of ATR. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, T.A.; De Waal, L.; Wu, X.; Ellerman, M.; Kopitz, C.; Wengner, A.; Eis, K.; Lange, M.; Tersteegen, A.; Lienau, P.; et al. Abstract 5880: Small-molecule modulators of PDE3/SLFN12 to kill cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 5880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Waal, L.; Lewis, T.; Rees, M.G.; Tsherniak, A.; Wu, X.; Choi, P.; Gechijian, L.; Hartigan, C.; Faloon, P.W.; Hickey, M.J.; et al. Identification of cancer-cytotoxic modulators of PDE3A by predictive chemogenomics. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, T.A.; De Waal, L.; Wu, X.; Youngsaye, W.; Wengner, A.; Kopitz, C.; Lange, M.; Gradl, S.; Ellermann, M.; Lienau, P.; et al. Optimization of PDE3A Modulators for SLFN12-Dependent Cancer Cell Killing. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 1537–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazir, M.; Senkowski, W.; Nyberg, F.; Blom, K.; Edqvist, P.-H.; Jarvius, M.; Andersson, C.; Gustafsson, M.G.; Nygren, P.; Larsson, R.; et al. Targeting tumor cells based on Phosphodiesterase 3A expression. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 361, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; He, H.; Chen, P.; Yan, B.; Zhang, W.; Ding, Z.; Li, D.; Chen, J.; Ma, Y.; Cao, Y.; et al. An alkaloid initiates phosphodiesterase 3A–schlafen 12 dependent apoptosis without affecting the phosphodiesterase activity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Schnitzler, G.R.; Gao, G.F.; Diamond, B.; Baker, A.R.; Kaplan, B.; Williamson, K.; Westlake, L.; Lorrey, S.; Lewis, T.A.; et al. Mechanistic insights into cancer cell killing through interaction of phosphodiesterase 3A and schlafen family member 12. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 3431–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cancer | Schlafen | Expression Level | Survival Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Malignant Melanoma | SLFN5 | Downregulated [62]. | Positive [62]. |
| SLFN11 | No significant change. | Negative. | |
| SLFN12 | No significant change. | Negative. | |
| SLFN14 | No significant change. | Positive. | |
| Renal Carcinoma | SLFN5 | Downregulated. | Positive [63]. |
| SLFN11 | Downregulated [64]. | Positive [64]. | |
| SLFN12 | Downregulated. | Negative. | |
| SLFN14 | Downregulated. | Negative. | |
| Gastric Carcinoma | SLFN5 | Upregulated [16]. | Negative [16]. |
| SLFN11 | Downregulated [65]. | Positive [65]. | |
| SLFN12 | Upregulated. | Not prognostic. | |
| SLFN14 | Downregulated. | Not prognostic. | |
| Colorectal Carcinoma | SLFN5 | No significant change. | Negative. |
| SLFN11 | Downregulated [22,64]. | Positive [22]. | |
| SLFN12 | Downregulated. | Positive. | |
| SLFN14 | Downregulated. | Not prognostic. | |
| Lung Carcinoma | SLFN5 | Downregulated [64,66]. | Positive [66]. |
| SLFN11 | Downregulated [22]. | Positive [67]. | |
| SLFN12 | Downregulated [15]. | Positive [15]. | |
| SLFN14 | Downregulated. | Positive in lung adenocarcinoma. | |
| Prostate Carcinoma | SLFN5 | Upregulated [68]. | Negative [68]. |
| SLFN11 | Upregulated in metastatic prostate cancer [69]. | No correlation to O.S., but positive correlation to rPFS [69]. | |
| SLFN12 | Downregulated. | Not prognostic. | |
| SLFN14 | Downregulated. | Not prognostic. | |
| Liver Cancer | SLFN5 | Downregulated [70]. | Positive [70]. |
| SLFN11 | Downregulated [71]. | Positive [71]. | |
| SLFN12 | Not Significant. | Negative. | |
| SLFN14 | Downregulated. | Not prognostic. | |
| Esophageal Cancer | SLFN5 | Upregulated. | No data available. |
| SLFN11 | Downregulated with age [72]. | Positive [72]. | |
| SLFN12 | Upregulated | No data available. | |
| SLFN14 | No significant change. | No data available. | |
| Breast Cancer | SLFN5 | Downregulated [73,74]. | Positive [73,74]. |
| SLFN11 | Downregulated. | Positive/negative after hormone therapy [17]. | |
| SLFN12 | Downregulated [14]. | Positive in triple negative breast cancer [14]. | |
| SLFN14 | Downregulated. | Positive. | |
| CNS Tumors | SLFN5 | Upregulated [52]. | Negative [52]. |
| SLFN11 | Upregulated [52]. | Negative [52]. | |
| SLFN12 | Upregulated [52]. | Negative [52]. | |
| SLFN13 | Upregulated [52]. | Negative [52]. | |
| Leukemia | SLFN5 | No significant change. | No data available. |
| SLFN11 | Upregulated. | No data available. | |
| SLFN12 | Upregulated. | No data available. | |
| SLFN14 | Upregulated. | No data available. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Marsoummi, S.; Vomhof-DeKrey, E.E.; Basson, M.D. Schlafens: Emerging Proteins in Cancer Cell Biology. Cells 2021, 10, 2238. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10092238
Al-Marsoummi S, Vomhof-DeKrey EE, Basson MD. Schlafens: Emerging Proteins in Cancer Cell Biology. Cells. 2021; 10(9):2238. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10092238
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Marsoummi, Sarmad, Emilie E. Vomhof-DeKrey, and Marc D. Basson. 2021. "Schlafens: Emerging Proteins in Cancer Cell Biology" Cells 10, no. 9: 2238. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10092238
APA StyleAl-Marsoummi, S., Vomhof-DeKrey, E. E., & Basson, M. D. (2021). Schlafens: Emerging Proteins in Cancer Cell Biology. Cells, 10(9), 2238. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10092238







