Aspirin Inhibition of Group VI Phospholipase A2 Induces Synthetic Lethality in AAM Pathway Down-Regulated Gingivobuccal Squamous Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Reagents
2.2. Cell Viability Assay
2.3. Colony Formation Assay
2.4. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.5. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.6. Annexin V and Propidium Iodide Staining
2.7. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.8. Scratch Assay
2.9. siRNA Transfection
2.10. RT-PCR and qRT-PCR
2.11. Immunoblotting
2.12. RNA Sequencing
2.13. Mouse Xenograft and Positron Emission Tomography Imaging
2.14. Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Higher Inhibitory Effect of Aspirin on Cell Viability and Colony Formation in AAM Pathway Down-Regulated Cell Line
3.2. Cell Cycle Arrest, Apoptosis and Migration Affected with Aspirin Treatment
3.3. Inhibition of PLA2G6/COX/LOX and PLA2G6/NF-ĸB Pathway
3.4. Transcriptome Analysis Revealed Deregulation of AAM Pathway in ITOC-04 Cells
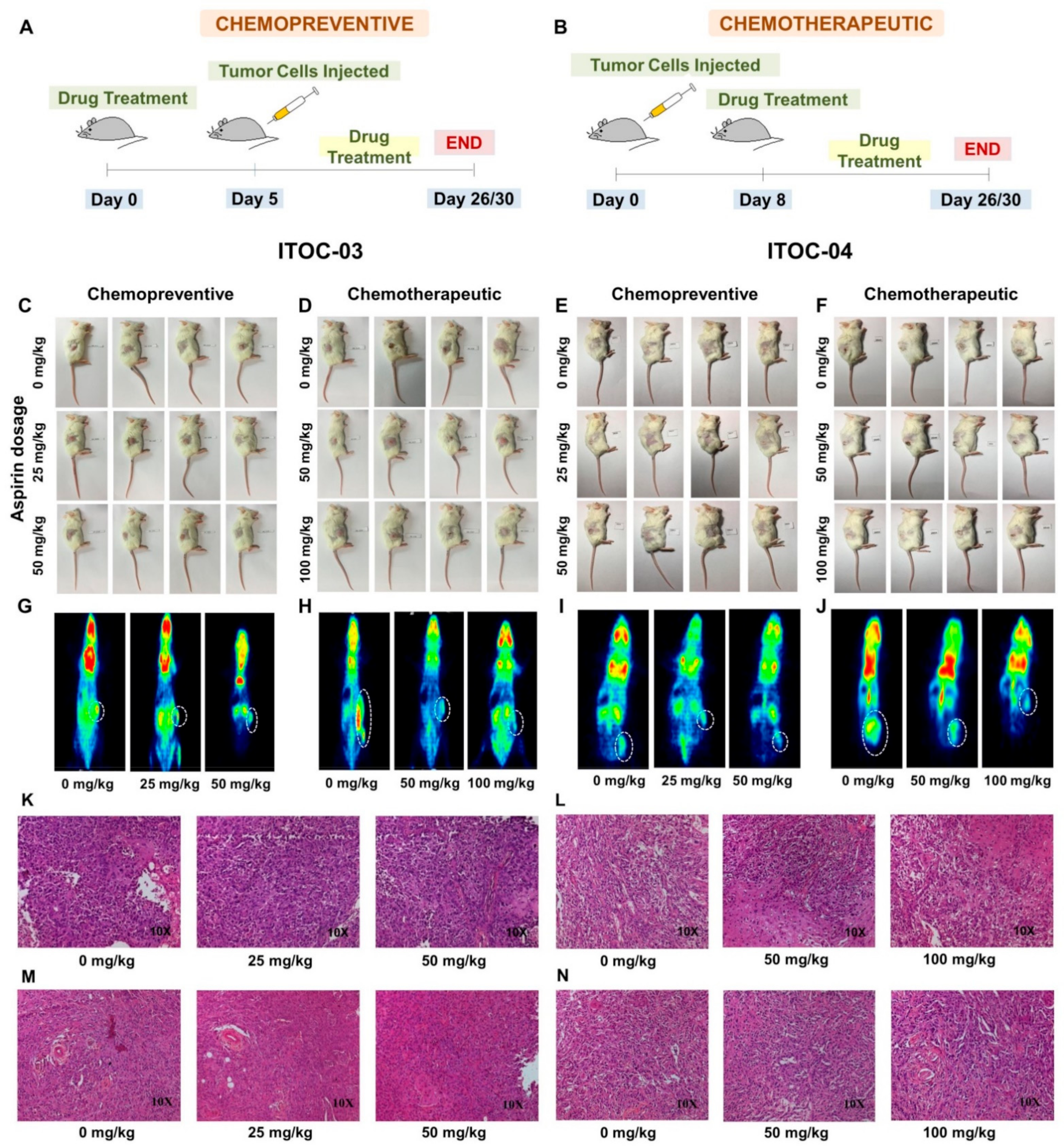
3.5. Aspirin-Induced In Vivo Inhibition of PLA2G6 Leads to Synthetic Lethality in AAM Pathway Down-Regulated Xenografts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Gupta, R.; Sinha, D.N.; Mehrotra, R. Relationship between type of smokeless tobacco & risk of cancer: A systematic review. Indian J. Med. Res. 2018, 148, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- India Project Team of the International Cancer Genome Consortium. Mutational landscape of gingivo-buccal oral squamous cell carcinoma reveals new recurrently-mutated genes and molecular subgroups. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujan, O.; Sloan, P. Dilemmas of oral cancer screening: An update. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 3369–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, J.B.; Lee, C.S.; Jang, J.H.; Ghim, J.; Kim, Y.J.; You, S.; Hwang, D.; Suh, P.G.; Ryu, S.H. Phospholipase signalling networks in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, C.A.; Missailidis, S. Inhibition of arachidonic acid metabolism and its implication on cell proliferation and tumour-angiogenesis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2009, 9, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Dubois, R.N. Prostaglandins and cancer. Gut 2006, 55, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crusz, S.M.; Balkwill, F.R. Inflammation and cancer: Advances and new agents. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayburn, E.R.; Ezell, S.J.; Zhang, R. Anti-Inflammatory Agents for Cancer Therapy. Mol. Cell Pharmacol. 2009, 1, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C.; Albers, R.; Antoine, J.M.; Blum, S.; Bourdet-Sicard, R.; Ferns, G.A.; Folkerts, G.; Friedmann, P.S.; Frost, G.S.; Guarner, F.; et al. Inflammatory disease processes and interactions with nutrition. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 101 (Suppl. 1), 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, K.F.; Sajinovic, M.; Hein, J.; Nixdorf, S.; Galettis, P.; Liauw, W.; de Souza, P.; Dong, Q.; Graham, G.G.; Russell, P.J. Emerging roles for phospholipase A2 enzymes in cancer. Biochimie 2010, 92, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso, L.; Ai, G.; Spitale, R.C.; Bhat, G.J. Molecular targets of aspirin and cancer prevention. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, A.T.; Ogino, S.; Fuchs, C.S. Aspirin use and survival after diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Jama 2009, 302, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.D.; Chen, W.Y.; Li, L.; Hertzmark, E.; Spiegelman, D.; Hankinson, S.E. Aspirin intake and survival after breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1467–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burn, J.; Gerdes, A.M.; Macrae, F.; Mecklin, J.P.; Moeslein, G.; Olschwang, S.; Eccles, D.; Evans, D.G.; Maher, E.R.; Bertario, L.; et al. Long-term effect of aspirin on cancer risk in carriers of hereditary colorectal cancer: An analysis from the CAPP2 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2011, 378, 2081–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thun, M.J.; Jacobs, E.J.; Patrono, C. The role of aspirin in cancer prevention. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 9, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaprakash, V.; Rigual, N.R.; Moysich, K.B.; Loree, T.R.; Nasca, M.A.; Menezes, R.J.; Reid, M.E. Chemoprevention of head and neck cancer with aspirin: A case-control study. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2006, 132, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.S.; Yeh, C.C.; Huang, S.F.; Chou, Y.S.; Kuo, L.T.; Sung, F.C.; Muo, C.H.; Su, C.T.; Su, F.H. Aspirin associated with risk reduction of secondary primary cancer for patients with head and neck cancer: A population-based analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, E.; Ghosh, S. Inhibition of NF-kappa B by sodium salicylate and aspirin. Science 1994, 265, 956–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.J.; Yamamoto, Y.; Gaynor, R.B. The anti-inflammatory agents aspirin and salicylate inhibit the activity of I(kappa)B kinase-beta. Nature 1998, 396, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, D.; Zhong, L.; Duan, T.; Zhang, R.-H.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Hu, K.; Lv, X.; Kang, T. Aspirin suppresses the growth and metastasis of osteosarcoma through the NF-κB pathway. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 5349–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goel, A.; Chang, D.K.; Ricciardiello, L.; Gasche, C.; Boland, C.R. A novel mechanism for aspirin-mediated growth inhibition of human colon cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dikshit, P.; Chatterjee, M.; Goswami, A.; Mishra, A.; Jana, N.R. Aspirin induces apoptosis through the inhibition of proteasome function. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 29228–29235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, Q.; Wang, J.D.; Xia, H.H.; Lin, M.C.; He, H.; Zou, B.; Tu, S.P.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.G.; Lam, S.K.; et al. Activation of the caspase-8/Bid and Bax pathways in aspirin-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurpinar, E.; Grizzle, W.E.; Piazza, G.A. COX-Independent Mechanisms of Cancer Chemoprevention by Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Front. Oncol. 2013, 3, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Fu, X.; Jin, T.; Zhang, L.; Liu, B.; Wu, Y.; Xu, F.; Wang, X.; Ye, K.; Zhang, W. Aspirin targets P4HA2 through inhibiting NF-κB and LMCD1-AS1/let-7g to inhibit tumour growth and collagen deposition in hepatocellular carcinoma. EBioMedicine 2019, 45, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biswas, N.K.; Das, S.; Maitra, A.; Sarin, R.; Majumder, P.P. Somatic mutations in arachidonic acid metabolism pathway genes enhance oral cancer post-treatment disease-free survival. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pansare, K.; Gardi, N.; Kamat, S.; Dange, P.; Previn, R.; Gera, P.; Kowtal, P.; Amin, K.; Sarin, R. Establishment and genomic characterization of gingivobuccal carcinoma cell lines with smokeless tobacco associated genetic alterations and oncogenic PIK3CA mutation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, K.; Karin, M. NF-κB, inflammation, immunity and cancer: Coming of age. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buttar, N.S.; Wang, K.K.; Anderson, M.A.; Dierkhising, R.A.; Pacifico, R.J.; Krishnadath, K.K.; Lutzke, L.S. The effect of selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition in Barrett’s esophagus epithelium: An in vitro study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurihara, Y.; Hatori, M.; Ando, Y.; Ito, D.; Toyoshima, T.; Tanaka, M.; Shintani, S. Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 suppresses the invasiveness of oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines via down-regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 production and activation. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2009, 26, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henry, W.S.; Laszewski, T.; Tsang, T.; Beca, F.; Beck, A.H.; McAllister, S.S.; Toker, A. Aspirin Suppresses Growth in PI3K-Mutant Breast Cancer by Activating AMPK and Inhibiting mTORC1 Signaling. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 790–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, Z.; Chang, Y.; Fan, J.; Ji, W.; Su, C. Phospholipase A2 superfamily in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2020, 497, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHowat, J.; Gullickson, G.; Hoover, R.G.; Sharma, J.; Turk, J.; Kornbluth, J. Platelet-activating factor and metastasis: Calcium-independent phospholipase A2β deficiency protects against breast cancer metastasis to the lung. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2011, 300, C825–C832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wei, G.; Yan, L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, H.; Sandusky, G.E.; Turk, J.; Xu, Y. Group VIA phospholipase A2 in both host and tumor cells is involved in ovarian cancer development. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 4103–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, M.; Strohecker, A.; Chen, F.; Kwan, T.; Bosman, J.; Jordan, V.C.; Cryns, V.L. Aspirin sensitizes cancer cells to TRAIL–induced apoptosis by reducing survivin levels. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 3168–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, P.; Manna, A.; Saha, S.; Mohanty, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Mazumdar, M.; Guha, D.; Das, T. Aspirin inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and migration of oncogenic K-ras-expressing non-small cell lung carcinoma cells by down-regulating E-cadherin repressor Slug. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.K.; Ethayathulla, A.; Jabeen, T.; Sharma, S.; Kaur, P.; Singh, T.P. Aspirin induces its anti-inflammatory effects through its specific binding to phospholipase a2: Crystal structure of the complex formed between phospholipase a2 and aspirin at 1.9 å resolution. J. Drug Target. 2005, 13, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.P.; Tan, Z.R.; Huang, S.L.; Huang, Z.; Ou-Yang, D.S.; Zhou, H.H. Isozyme-specific induction of low-dose aspirin on cytochrome P450 in healthy subjects. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 73, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mufti, N.A.; Shuler, M.L. Possible role of arachidonic acid in stress-induced cytochrome P450IA1 activity. Biotechnol. Prog. 1996, 12, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seree, E.; Villard, P.H.; Pascussi, J.M.; Pineau, T.; Maurel, P.; Nguyen, Q.B.; Fallone, F.; Martin, P.M.; Champion, S.; Lacarelle, B.; et al. Evidence for a new human CYP1A1 regulation pathway involving PPAR-alpha and 2 PPRE sites. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 1436–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Li, C.; Liu, W.X.; Liu, C.; Cui, J.; Li, Q.; Ni, H.; Yang, Y.; Wu, C.; Chen, C.; et al. Dysfunction of PLA2G6 and CYP2C44-associated network signals imminent carcinogenesis from chronic inflammation to hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 9, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, G.; De, A.; Das, A.; Banerjee, S.; Sarkar, S.; Banerjee, S.K. Aspirin blocks growth of breast tumor cells and tumor-initiating cells and induces reprogramming factors of mesenchymal to epithelial transition. Lab. Investig. 2015, 95, 702–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kodela, R.; Chattopadhyay, M.; Velázquez-Martínez, C.A.; Kashfi, K. NOSH-aspirin (NBS-1120), a novel nitric oxide-and hydrogen sulfide-releasing hybrid has enhanced chemo-preventive properties compared to aspirin, is gastrointestinal safe with all the classic therapeutic indications. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 98, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pommergaard, H.C.; Burcharth, J.; Rosenberg, J.; Raskov, H. Chemoprevention with acetylsalicylic acid, vitamin D and calcium reduces risk of carcinogen-induced lung tumors. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 4767–4770. [Google Scholar]
- Duperron, C.; Castonguay, A. Chemopreventive efficacies of aspirin and sulindac against lung tumorigenesis in A/J mice. Carcinogenesis 1997, 18, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ricciotti, E.; FitzGerald, G.A. Prostaglandins and inflammation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 986–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.H. Renal effects of prostaglandins and cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Electrolyte Blood Press. 2008, 6, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burn, J.; Bishop, D.T.; Mecklin, J.P.; Macrae, F.; Moslein, G.; Olschwang, S.; Bisgaard, M.L.; Ramesar, R.; Eccles, D.; Maher, E.R.; et al. Effect of aspirin or resistant starch on colorectal neoplasia in the Lynch syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2567–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burn, J.; Bishop, D.T.; Chapman, P.D.; Elliott, F.; Bertario, L.; Dunlop, M.G.; Eccles, D.; Ellis, A.; Evans, D.G.; Fodde, R. A randomized placebo-controlled prevention trial of aspirin and/or resistant starch in young people with familial adenomatous polyposis. Cancer Prev. Res. 2011, 4, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giovannucci, E.; Egan, K.M.; Hunter, D.J.; Stampfer, M.J.; Colditz, G.A.; Willett, W.C.; Speizer, F.E. Aspirin and the risk of colorectal cancer in women. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flossmann, E.; Rothwell, P.M. Effect of aspirin on long-term risk of colorectal cancer: Consistent evidence from randomised and observational studies. Lancet 2007, 369, 1603–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, C.; Cafferty, F.H.; Rowley, S.; MacKenzie, M.; Berkman, L.; Gupta, S.; Pramesh, C.S.; Gilbert, D.; Kynaston, H.; Cameron, D.; et al. ADD-ASPIRIN: A phase III, double-blind, placebo controlled, randomised trial assessing the effects of aspirin on disease recurrence and survival after primary therapy in common non-metastatic solid tumours. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2016, 51, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joharatnam-Hogan, N.; Cafferty, F.; Hubner, R.; Swinson, D.; Sothi, S.; Gupta, K.; Falk, S.; Patel, K.; Warner, N.; Kunene, V. Aspirin as an adjuvant treatment for cancer: Feasibility results from the Add-Aspirin randomised trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Topatana, W.; Juengpanich, S.; Li, S.; Cao, J.; Hu, J.; Lee, J.; Suliyanto, K.; Ma, D.; Zhang, B.; Chen, M.; et al. Advances in synthetic lethality for cancer therapy: Cellular mechanism and clinical translation. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pansare, K.; Mohanty, B.; Dhotre, R.; Pettiwala, A.M.; Parab, S.; Gupta, N.; Gera, P.; Gardi, N.; Dugge, R.; Sahu, P.; et al. Aspirin Inhibition of Group VI Phospholipase A2 Induces Synthetic Lethality in AAM Pathway Down-Regulated Gingivobuccal Squamous Carcinoma. Cells 2022, 11, 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11010123
Pansare K, Mohanty B, Dhotre R, Pettiwala AM, Parab S, Gupta N, Gera P, Gardi N, Dugge R, Sahu P, et al. Aspirin Inhibition of Group VI Phospholipase A2 Induces Synthetic Lethality in AAM Pathway Down-Regulated Gingivobuccal Squamous Carcinoma. Cells. 2022; 11(1):123. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11010123
Chicago/Turabian StylePansare, Kshama, Bhabani Mohanty, Ranjeeta Dhotre, Aafrin M. Pettiwala, Saili Parab, Neha Gupta, Poonam Gera, Nilesh Gardi, Rucha Dugge, Priyanka Sahu, and et al. 2022. "Aspirin Inhibition of Group VI Phospholipase A2 Induces Synthetic Lethality in AAM Pathway Down-Regulated Gingivobuccal Squamous Carcinoma" Cells 11, no. 1: 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11010123
APA StylePansare, K., Mohanty, B., Dhotre, R., Pettiwala, A. M., Parab, S., Gupta, N., Gera, P., Gardi, N., Dugge, R., Sahu, P., Alhans, R., Kowtal, P., Chaudhari, P., & Sarin, R. (2022). Aspirin Inhibition of Group VI Phospholipase A2 Induces Synthetic Lethality in AAM Pathway Down-Regulated Gingivobuccal Squamous Carcinoma. Cells, 11(1), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11010123





