Blocking Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Subtype 7 via the Venus Flytrap Domain Promotes a Chronic Stress-Resilient Phenotype in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
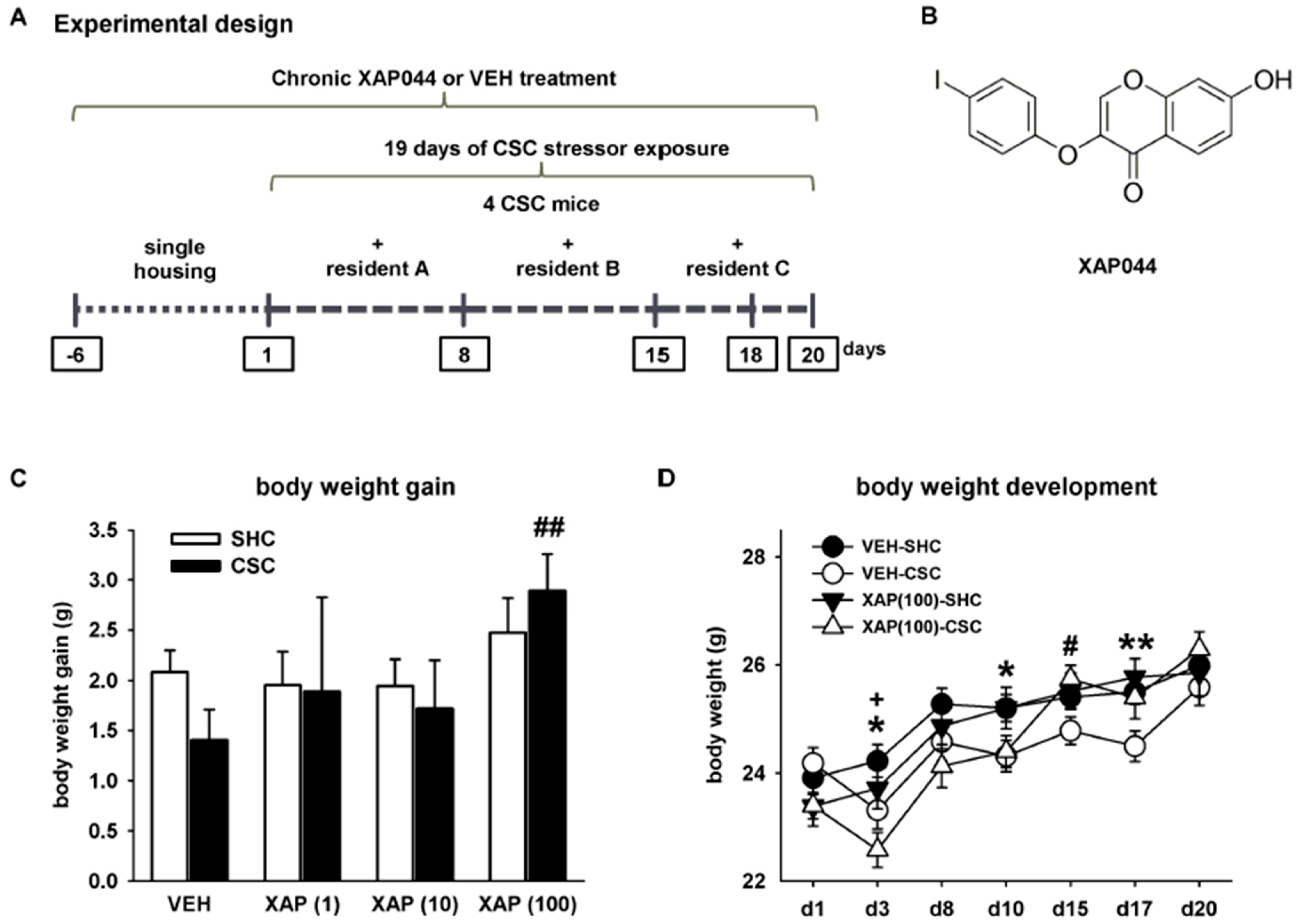
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Chronic Subordinate Colony Housing (CSC) Paradigm
2.4. Drug Treatment/Surgical Procedure
2.5. Light-Dark Box (LDB) Test
2.6. Stress-Induced Hyperthermia (SIH) Test
2.7. Determination of Body Weight and Organ Weight
2.8. Trunk Blood Sampling
2.9. ACTH Stimulation of Adrenal Explants In Vitro
2.10. ELISA for CORT
2.11. Cannula Placement and Remaining Volume in the Micro-Osmotic Pumps
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
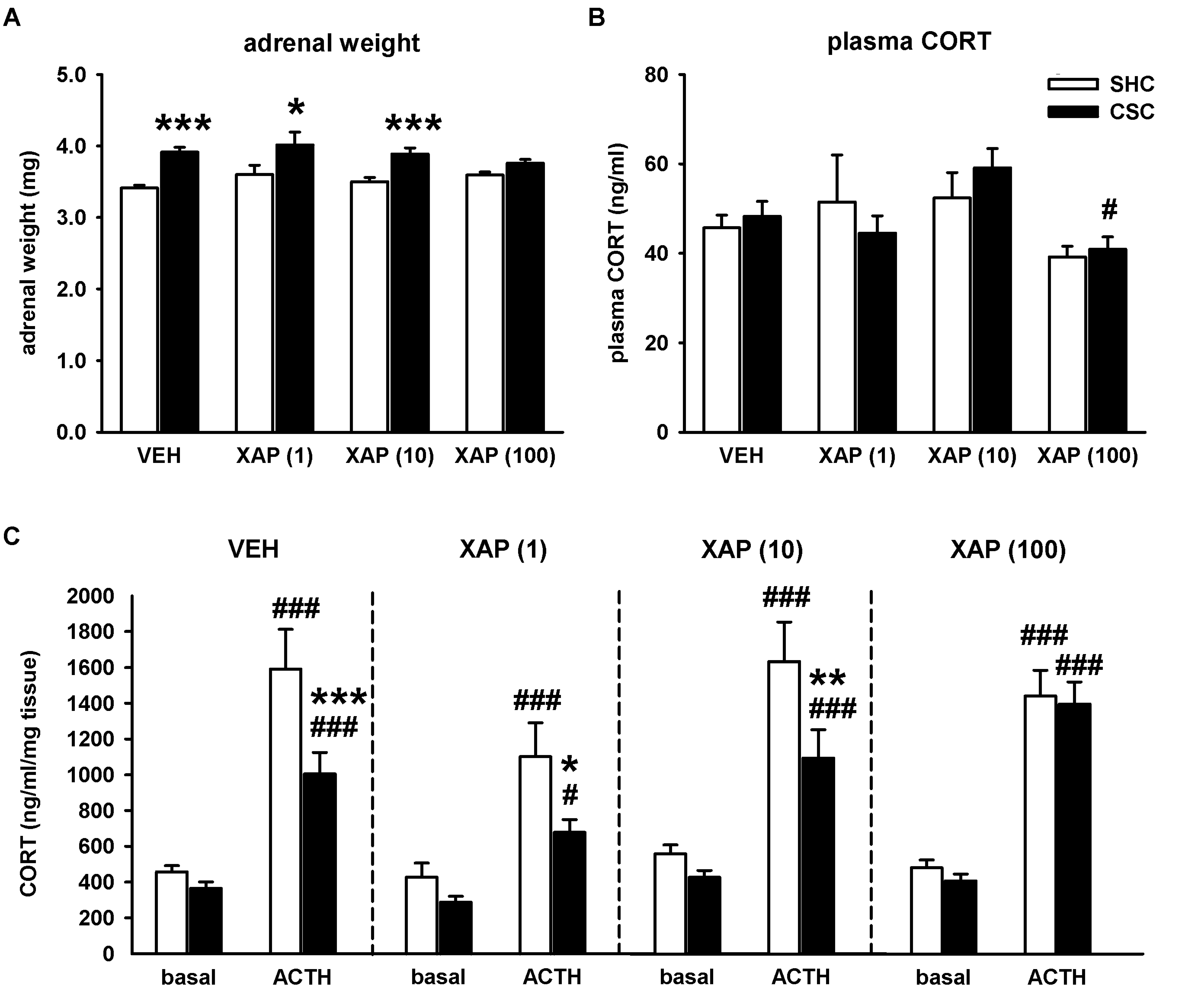
3.1. Chronic Pharmacological mGlu7 Blockade Interferes with Multiple CSC-Induced Physiological Alterations and Weight Changes in Lymphatic Organs in a Dose-Dependent Manner
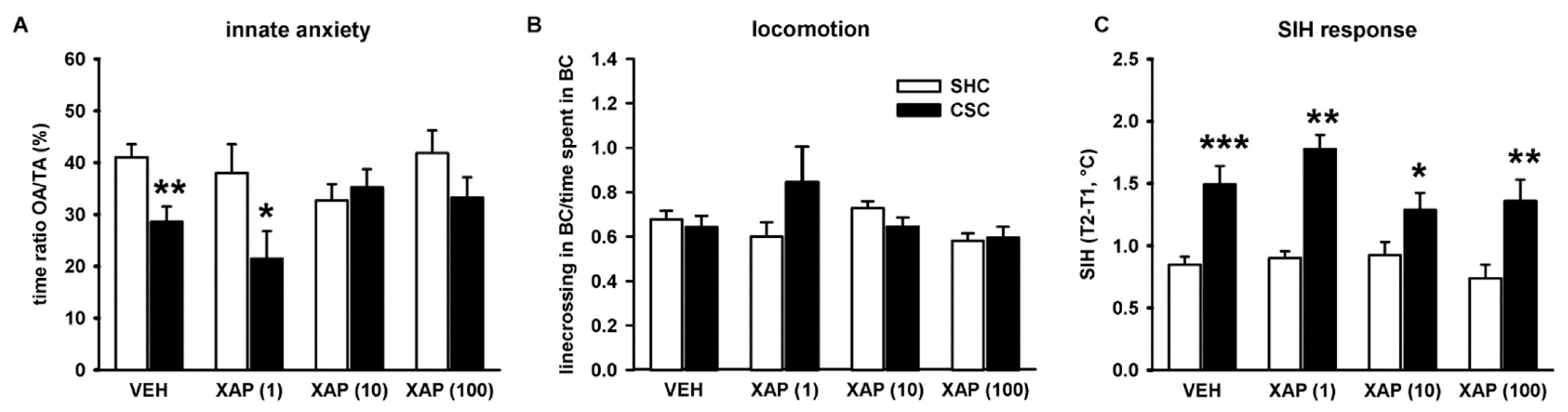
3.2. Chronic Pharmacological mGlu7 Blockade Dose-Dependently Reverses CSC-Induced Innate but Not Physiological Anxiety
4. Discussion
4.1. Chronic Pharmacological mGlu7 Blockade Reverses Multiple CSC-Induced Physiological Alterations and Weight Changes of Lymphatic Organs
4.2. Chronic Pharmacological mGlu7 Blockade Reverses CSC-Induced Innate but Not Physiological Anxiety
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chrousos, G.P. Stress and disorders of the stress system. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2009, 5, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupien, S.J.; McEwen, B.S.; Gunnar, M.R.; Heim, C. Effects of stress throughout the lifespan on the brain, behaviour and cognition. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langgartner, D.; Füchsl, A.M.; Uschold-Schmidt, N.; Slattery, D.A.; Reber, S.O. Chronic subordinate colony housing paradigm: A mouse model to characterize the consequences of insufficient glucocorticoid signaling. Front. Psychiatry 2015, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peterlik, D.; Flor, P.J.; Uschold-Schmidt, N. The Emerging Role of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors in the Pathophysiology of Chronic Stress-Related Disorders. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 514–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pin, J.P.; Galvez, T.; Prézeau, L. Evolution, structure, and activation mechanism of family 3/C G-protein-coupled receptors. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 98, 325–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niswender, C.M.; Conn, P.J. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: Physiology, pharmacology, and disease. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 50, 295–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kinoshita, A.; Shigemoto, R.; Ohishi, H.; van der Putten, H.; Mizuno, N. Immunohistochemical localization of metabotropic glutamate receptors, mGluR7a and mGluR7b, in the central nervous system of the adult rat and mouse: A light and electron microscopic study. J. Comp. Neurol. 1998, 393, 332–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosinski, C.M.; Bradley, S.R.; Conn, P.J.; Levey, A.I.; Landwehrmeyer, G.B.; Penney, J.B.; Young, A.B.; Standaert, D.G. Localization of metabotropic glutamate receptor 7 mRNA and mGluR7a protein in the rat basal ganglia. J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 415, 266–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngomba, R.T.; Santolini, I.; Salt, T.E.; Ferraguti, F.; Battaglia, G.; Nicoletti, F.; van Luijtelaar, G. Metabotropic glutamate receptors in the thalamocortical network: Strategic targets for the treatment of absence epilepsy. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 1211–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julio-Pieper, M.; Flor, P.J.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Exciting times beyond the brain: Metabotropic glutamate receptors in peripheral and non-neural tissues. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 35–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, M.; Kurihara, H.; Suzuki, G.; Mitsuya, M.; Ohkubo, M.; Ohta, H. Isoxazolopyridone derivatives as allosteric metabotropic glutamate receptor 7 antagonists. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 726–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaccianoce, S.; Matrisciano, F.; Del Bianco, P.; Caricasole, A.; Di Giorgi Gerevini, V.; Cappuccio, I.; Melchiorri, D.; Battaglia, G.; Nicoletti, F. Endogenous activation of group-II metabotropic glutamate receptors inhibits the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis. Neuropharmacology 2003, 44, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaerts-Vegh, Z.; Beckers, T.; Ball, S.M.; Baeyens, F.; Callaerts, P.F.; Cryan, J.F.; Molnar, E.; D’Hooge, R. Concomitant Deficits in Working Memory and Fear Extinction Are Functionally Dissociated from Reduced Anxiety in Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 7-Deficient Mice. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 6573–6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cryan, J.F.; Kelly, P.H.; Neijt, H.C.; Sansig, G.; Flor, P.J.; van der Putten, H. Antidepressant and anxiolytic-like effects in mice lacking the group III metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR7. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 17, 2409–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gee, C.E.; Peterlik, D.; Neuhäuser, C.; Bouhelal, R.; Kaupmann, K.; Laue, G.; Uschold-Schmidt, N.; Feuerbach, D.; Zimmermann, K.; Ofner, S.; et al. Blocking metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 7 (mGlu7) via the venus flytrap domain (VFTD) inhibits amygdala plasticity, stress, and anxiety-related behavior. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 10975–10987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalinichev, M.; Rouillier, M.; Girard, F.; Royer-Urios, I.; Bournique, B.; Finn, T.; Charvin, D.; Campo, B.; Le Poul, E.; Mutel, V.; et al. ADX71743, a Potent and Selective Negative Allosteric Modulator of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 7: In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 344, 624–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, C.W.; Yohn, S.E.; Washecheck, J.P.; Roenfanz, H.F.; Quitalig, M.C.; Luscombe, V.B.; Jenkins, M.T.; Rodriguez, A.L.; Engers, D.W.; Blobaum, A.L.; et al. Discovery of an Orally Bioavailable and Central Nervous System (CNS) Penetrant mGlu 7 Negative Allosteric Modulator (NAM) in Vivo Tool Compound: N-(2-(1 H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-5-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)-4-(cyclopropylmethoxy)-3-methoxybenzamide (VU6012962). J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 1690–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendt, M.; Schmid, S.; Thakker, D.R.; Jacobson, L.H.; Yamamoto, R.; Mitsukawa, K.; Maier, R.; Natt, F.; Hüsken, D.; Kelly, P.H.; et al. mGluR7 facilitates extinction of aversive memories and controls amygdala plasticity. Mol. Psychiatry 2008, 13, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Connor, R.M.; Thakker, D.R.; Schmutz, M.; van der Putten, H.; Hoyer, D.; Flor, P.J.; Cryan, J.F. Adult siRNA-induced knockdown of mGlu7 receptors reduces anxiety in the mouse. Neuropharmacology 2013, 72, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reber, S.O.; Birkeneder, L.; Veenema, A.H.; Obermeier, F.; Falk, W.; Straub, R.H.; Neumann, I.D. Adrenal insufficiency and colonic inflammation after a novel chronic psycho-social stress paradigm in mice: Implications and mechanisms. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 670–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uschold-Schmidt, N.; Nyuyki, K.D.; Füchsl, A.M.; Neumann, I.D.; Reber, S.O. Chronic psychosocial stress results in sensitization of the HPA axis to acute heterotypic stressors despite a reduction of adrenal in vitro ACTH responsiveness. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2012, 37, 1676–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterlik, D.; Stangl, C.; Bludau, A.; Grabski, D.; Strasser, R.; Schmidt, D.; Flor, P.J.; Uschold-Schmidt, N. Relief from detrimental consequences of chronic psychosocial stress in mice deficient for the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 7. Neuropharmacology 2017, 115, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterlik, D.; Stangl, C.; Bauer, A.; Bludau, A.; Keller, J.; Grabski, D.; Killian, T.; Schmidt, D.; Zajicek, F.; Jaeschke, G.; et al. Blocking metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 relieves maladaptive chronic stress consequences. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 59, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singewald, G.M.; Nguyen, N.K.; Neumann, I.D.; Singewald, N.; Reber, S.O. Effect of chronic psychosocial stress-induced by subordinate colony (CSC) housing on brain neuronal activity patterns in mice. Stress 2009, 12, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolomucci, A.; Palanza, P.; Sacerdote, P.; Ceresini, G.; Chirieleison, A.; Panerai, A.E.; Parmigiani, S. Individual housing induces altered immuno-endocrine responses to psychological stress in male mice. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2003, 28, 540–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourbaji, S.; Zacher, C.; Sanchis-Segura, C.; Spanagel, R.; Gass, P. Social and structural housing conditions influence the development of a depressive-like phenotype in the learned helplessness paradigm in male mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2005, 164, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparotto, O.C.; Lopes, D.M.; Carobrez, S.G. Pair housing affects anxiety-like behaviors induced by a social but not by a physiological stressor in male Swiss mice. Physiol. Behav. 2005, 85, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uschold-Schmidt, N.; Peterlik, D.; Füchsl, A.M.; Reber, S.O. HPA axis changes during the initial phase of psychosocial stressor exposure in male mice. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 218, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foertsch, S.; Füchsl, A.M.; Faller, S.D.; Hölzer, H.; Langgartner, D.; Messmann, J.; Strauß, G.; Reber, S.O. Splenic glucocorticoid resistance following psychosocial stress requires physical injury. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langgartner, D.; Marks, J.; Nguyen, T.C.; Reber, S.O. Changes in adrenal functioning induced by chronic psychosocial stress in male mice: A time course study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2020, 122, 104880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery, D.A.; Uschold, N.; Magoni, M.; Bär, J.; Popoli, M.; Neumann, I.D.; Reber, S.O. Behavioural consequences of two chronic psychosocial stress paradigms: Anxiety without depression. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2012, 37, 702–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryksa, K.; Mittmann, L.; Bauer, A.; Peterlik, D.; Flor, P.J.; Uschold-Schmidt, N.; Bosch, O.J. Metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 7 controls maternal care, maternal motivation and maternal aggression in mice. Genes Brain Behav. 2020, 19, e12627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempter, E.; Amoroso, M.; Duffner, H.L.; Werner, A.M.; Langgartner, D.; Kupfer, S.; Reber, S.O. Changes in Functional Glucocorticoid Sensitivity of Isolated Splenocytes Induced by Chronic Psychosocial Stress—A Time Course Study. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 753822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langgartner, D.; Füchsl, A.M.; Kaiser, L.M.; Meier, T.; Foertsch, S.; Buske, C.; Reber, S.O.; Mulaw, M.A. Biomarkers for classification and class prediction of stress in a murine model of chronic subordination stress. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reber, S.O.; Neumann, I.D. Defensive behavioral strategies and enhanced state anxiety during chronic subordinate colony housing are accompanied by reduced hypothalamic vasopressin, but not oxytocin, expression. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1148, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, N.M.; Seto, M.; Lindsley, C.W.; Niswender, C.M. Metabotropic glutamate receptor 7: A new therapeutic target in neurodevelopmental disorders. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okamoto, N.; Hori, S.; Akazawa, C.; Hayashi, Y.; Shigemoto, R.; Mizuno, N.; Nakanishi, S. Molecular characterization of a new metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR7 coupled to inhibitory cyclic AMP signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraguti, F.; Shigemoto, R. Metabotropic glutamate receptors. Cell Tissue Res. 2006, 326, 483–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinzie, J.M.; Saugstad, J.A.; Westbrook, G.L.; Segerson, T.P. Distribution of metabotropic glutamate receptor 7 messenger RNA in the developing and adult rat brain. Neuroscience 1995, 69, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartmell, J.; Schoepp, D.D. Regulation of neurotransmitter release by metabotropic glutamate receptors. J. Neurochem. 2000, 75, 889–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koolhaas, J.M.; de Boer, S.F.; Coppens, C.M.; Buwalda, B. Neuroendocrinology of coping styles: Towards understanding the biology of individual variation. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2010, 31, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, E.D.; Hale, M.W.; Lukkes, J.L.; Valentine, M.J.; Sarchet, D.M.; Lowry, C.A. Repeated social defeat increases reactive emotional coping behavior and alters functional responses in serotonergic neurons in the rat dorsal raphe nucleus. Physiol. Behav. 2011, 104, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wood, S.K.; Walker, H.E.; Valentino, R.J.; Bhatnagar, S. Individual differences in reactivity to social stress predict susceptibility and resilience to a depressive phenotype: Role of corticotropin-releasing factor. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 1795–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bryant, R.A.; Marosszeky, J.E.; Crooks, J.; Baguley, I.; Gurka, J. Coping style and post-traumatic stress disorder following severe traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2000, 14, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reber, S.O.; Siebler, P.H.; Donner, N.C.; Morton, J.T.; Smith, D.G.; Kopelman, J.M.; Lowe, K.R.; Wheeler, K.J.; Fox, J.H.; Hassell, J.E.; et al. Immunization with a heat-killed preparation of the environmental bacterium Mycobacterium vaccae promotes stress resilience in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E3130–E3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Estrela, K.A.R.; Senninger, L.; Arndt, J.; Kabas, M.; Schmid, F.; Dillmann, L.; Auer, S.; Stepfer, T.; Flor, P.J.; Uschold-Schmidt, N. Blocking Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Subtype 7 via the Venus Flytrap Domain Promotes a Chronic Stress-Resilient Phenotype in Mice. Cells 2022, 11, 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11111817
Estrela KAR, Senninger L, Arndt J, Kabas M, Schmid F, Dillmann L, Auer S, Stepfer T, Flor PJ, Uschold-Schmidt N. Blocking Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Subtype 7 via the Venus Flytrap Domain Promotes a Chronic Stress-Resilient Phenotype in Mice. Cells. 2022; 11(11):1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11111817
Chicago/Turabian StyleEstrela, Karolyne A. R., Lisa Senninger, Josephine Arndt, Melanie Kabas, Ferdinand Schmid, Larissa Dillmann, Sophia Auer, Thomas Stepfer, Peter J. Flor, and Nicole Uschold-Schmidt. 2022. "Blocking Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Subtype 7 via the Venus Flytrap Domain Promotes a Chronic Stress-Resilient Phenotype in Mice" Cells 11, no. 11: 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11111817
APA StyleEstrela, K. A. R., Senninger, L., Arndt, J., Kabas, M., Schmid, F., Dillmann, L., Auer, S., Stepfer, T., Flor, P. J., & Uschold-Schmidt, N. (2022). Blocking Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Subtype 7 via the Venus Flytrap Domain Promotes a Chronic Stress-Resilient Phenotype in Mice. Cells, 11(11), 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11111817





