Açai Berry Mitigates Vascular Dementia-Induced Neuropathological Alterations Modulating Nrf-2/Beclin1 Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental Design and Groups
2.3. Behavioral Tests
2.3.1. Open Field Test (OFT)
2.3.2. Novel Object Recognition (NOR) Test
2.3.3. Social Interaction Test (SIT)
2.4. Histopathological Evaluation
2.5. Immunohistochemical Evaluation
2.6. Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Nick-End Labeling (TUNEL) Assay
2.7. Immunofluorescence Evaluation
2.8. RT-qPCR
2.9. Western Blot Analysis of Cytosolic and Nuclear Extracts
2.10. Materials
2.11. Statistical Evaluation
3. Results
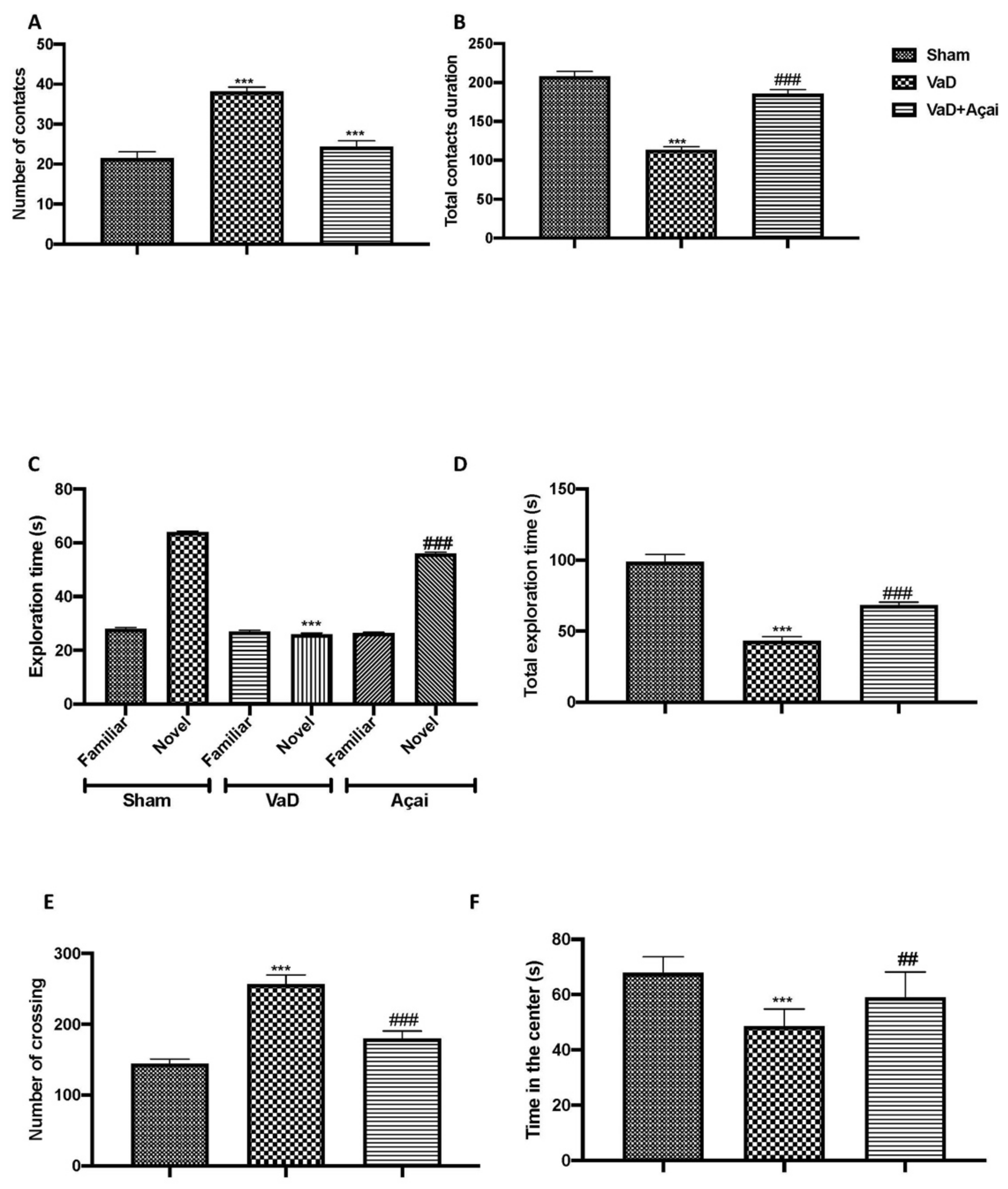
3.1. Açai Berry Improve Behavioral Changes Vascular Dementia-Induced
3.2. Açai Berry Limits Histological Changes Vascular Dementia-Induced
3.3. Açai Berry Limits Neuronal Death in the Hippocampus
3.4. Açai Berry Modulates Nrf-2 Pathways
3.5. Açai Berry Modulates Apoptotic and Autophagic Pathways
3.6. Açai Berry Mitigates Brain Structure Change VaD-Induced
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Orgogozo, J.M.; Abadie, E. Vascular dementia: European perspectives. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 1999, 13 (Suppl. 3), S192–S200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskys, A.; Hou, A.C. Vascular dementia: Pharmacological treatment approaches and perspectives. Clin. Interv. Aging 2007, 2, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago-Mujika, E.; Luthi-Carter, R.; Giorgini, F.; Kalaria, R.N.; Mukaetova-Ladinska, E.B. Tubulin and Tubulin Posttranslational Modifications in Alzheimer’s Disease and Vascular Dementia. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 730107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbatini, M.; Catalani, A.; Consoli, C.; Marletta, N.; Tomassoni, D.; Avola, R. The hippocampus in spontaneously hypertensive rats: An animal model of vascular dementia? Mech. Ageing Dev. 2002, 123, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulose, S.M.; Bielinski, D.F.; Carey, A.; Schauss, A.G.; Shukitt-Hale, B. Modulation of oxidative stress, inflammation, autophagy and expression of Nrf2 in hippocampus and frontal cortex of rats fed with acai-enriched diets. Nutr. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Harder, B.; Rojo de la Vega, M.; Wong, P.K.; Chapman, E.; Zhang, D.D. p62 links autophagy and Nrf2 signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jo, C.; Gundemir, S.; Pritchard, S.; Jin, Y.N.; Rahman, I.; Johnson, G.V. Nrf2 reduces levels of phosphorylated tau protein by inducing autophagy adaptor protein NDP52. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.Z.A.; Zhao, D.; Hussain, T.; Sabir, N.; Mangi, M.H.; Yang, L. p62-Keap1-NRF2-ARE Pathway: A Contentious Player for Selective Targeting of Autophagy, Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Prion Diseases. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Fan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Ding, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Fucoxanthin provides neuroprotection in models of traumatic brain injury via the Nrf2-ARE and Nrf2-autophagy pathways. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, X.T.; He, S.Q.; Wu, N.N.; Lin, X.C.; Zhao, J.; Tian, C. Green Tea Polyphenols Prevent Early Vascular Aging Induced by High-Fat Diet via Promoting Autophagy in Young Adult Rats. Curr. Med. Sci. 2022. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, C.; Salazar, L.A. Autophagy and Polyphenols in Osteoarthritis: A Focus on Epigenetic Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimson, J.M.; Prasanth, M.I.; Malar, D.S.; Thitilertdecha, P.; Kabra, A.; Tencomnao, T.; Prasansuklab, A. Plant Polyphenols for Aging Health: Implication from Their Autophagy Modulating Properties in Age-Associated Diseases. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Aguilar, A.; Palomino, O.; Benito, M.; Guillen, C. Dietary Polyphenols in Metabolic and Neurodegenerative Diseases: Molecular Targets in Autophagy and Biological Effects. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musial, C.; Siedlecka-Kroplewska, K.; Kmiec, Z.; Gorska-Ponikowska, M. Modulation of Autophagy in Cancer Cells by Dietary Polyphenols. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaszadeh, F.; Fakhri, S.; Khan, H. Targeting apoptosis and autophagy following spinal cord injury: Therapeutic approaches to polyphenols and candidate phytochemicals. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 160, 105069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Luo, Q.; Nie, R.; Yang, X.; Tang, Z.; Chen, H. Potential implications of polyphenols on aging considering oxidative stress, inflammation, autophagy, and gut microbiota. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 2175–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.; Huang, S.W.; Hu, P.F.; Tang, L.J. Regulation of autophagy by tea polyphenols in diabetic cardiomyopathy. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2018, 19, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabalala, S.; Muller, C.J.F.; Louw, J.; Johnson, R. Polyphenols, autophagy and doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Life Sci. 2017, 180, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.W.; Tian, C.; Xu, F.Y.; Chen, Z.; Burnside, R.; Yi, W.J.; Xiang, S.Y.; Xie, X.; Wu, N.N.; Yang, H.; et al. Green Tea Polyphenols Alleviate Autophagy Inhibition Induced by High Glucose in Endothelial Cells. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2016, 29, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallauf, K.; Rimbach, G. Autophagy, polyphenols and healthy ageing. Ageing Res. Rev. 2013, 12, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel-Silva, F.W.; Buller, L.S.; MBB Gonçalves, M.L.; Rostagno, M.A.; Forster-Carneiro, T. Sustainable development in the Legal Amazon: Energy recovery from açaí seeds. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2021, 15, 1174–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, P.S.; Massarioli, A.P.; Lazarini, J.G.; Soares, J.C.; Franchin, M.; Rosalen, P.L.; Alencar, S.M. Simulated gastrointestinal digestion of Brazilian acai seeds affects the content of flavan-3-ol derivatives, and their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, P.S.; Selani, M.M.; Gonçalves, R.H.; De Oliveira Paulino, J.; Massarioli, A.P.; De Alencar, S.M. Açaí seeds: An unexplored agro-industrial residue as a potential source of lipids, fibers, and antioxidant phenolic compounds. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 161, 113204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.B.; Lichtenthaler, R.; Zimmermann, B.F.; Papagiannopoulos, M.; Fabricius, H.; Marx, F.; Maia, J.G.; Almeida, O. Total oxidant scavenging capacity of Euterpe oleracea Mart. (acai) seeds and identification of their polyphenolic compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 4162–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Moura, R.S.; Pires, K.M.; Santos Ferreira, T.; Lopes, A.A.; Nesi, R.T.; Resende, A.C.; Sousa, P.J.; Da Silva, A.J.; Porto, L.C.; Valenca, S.S. Addition of acai (Euterpe oleracea) to cigarettes has a protective effect against emphysema in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kim, N.; Choi, Y.J.; Nam, R.H.; Lee, S.; Ham, M.H.; Suh, J.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, D.H. Anti-inflammatory and Anti-tumorigenic Effects of Acai Berry in Helicobacter felis-infected mice. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 21, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moura, R.S.; Ferreira, T.S.; Lopes, A.A.; Pires, K.M.; Nesi, R.T.; Resende, A.C.; Souza, P.J.; Silva, A.J.; Borges, R.M.; Porto, L.C.; et al. Effects of Euterpe oleracea Mart. (ACAI) extract in acute lung inflammation induced by cigarette smoke in the mouse. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poulose, S.M.; Fisher, D.R.; Larson, J.; Bielinski, D.F.; Rimando, A.M.; Carey, A.N.; Schauss, A.G.; Shukitt-Hale, B. Anthocyanin-rich acai (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) fruit pulp fractions attenuate inflammatory stress signaling in mouse brain BV-2 microglial cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.B.; De Bem, G.F.; Da Costa, C.A.; De Carvalho, L.; De Medeiros, A.F.; Silva, D.L.B.; Romao, M.H.; De Andrade Soares, R.; Ognibene, D.T.; De Moura, R.S.; et al. Acai seed extract prevents the renin-angiotensin system activation, oxidative stress and inflammation in white adipose tissue of high-fat diet-fed mice. Nutr. Res. 2020, 79, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ALNasser, M.N.; Mellor, I.R. Neuroprotective activities of acai berries (Euterpe sp.): A review. J. Herbmed Pharmacol. 2022, 11, 166–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Li, Z.; Wu, T.; Jensen, G.S.; Schauss, A.G.; Wu, X. Anti-oxidant capacities of flavonoid compounds isolated from acai pulp (Euterpe oleracea Mart.). Food Chem. 2010, 122, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moraes Arnoso, B.J.; Magliaccio, F.M.; De Araujo, C.A.; De Andrade Soares, R.; Santos, I.B.; De Bem, G.F.; Fernandes-Santos, C.; Ognibene, D.T.; De Moura, R.S.; Resende, A.C.; et al. Acai seed extract (ASE) rich in proanthocyanidins improves cardiovascular remodeling by increasing antioxidant response in obese high-fat diet-fed mice. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 351, 109721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellucci, E.R.B.; Dos Santos, J.M.; Carvalho, L.T.; Borgonovi, T.F.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Silva-Barretto, A.C.D. Acai extract powder as natural antioxidant on pork patties during the refrigerated storage. Meat Sci. 2022, 184, 108667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, T.V.N.; Torres, M.F.; Sampaio, L.A.; Hamoy, M.; Monserrat, J.M.; Barbas, L.A.L. Dietary Euterpe oleracea Mart. attenuates seizures and damage to lipids in the brain of Colossoma macropomum. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 47, 1851–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Kim, Y.; Jin, S.G.; Kim, J.Y. Acai berry extract as a regulator of intestinal inflammation pathways in a Caco-2 and RAW 264.7 co-culture model. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Costa, J.H.; Pacheco-Fill, T.; Ruiz, A.; Vidal, F.C.B.; Borges, K.R.A.; Guimaraes, S.J.A.; Azevedo-Santos, A.P.S.; Buglio, K.E.; Foglio, M.A.; et al. Acai (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) Seed Extract Induces ROS Production and Cell Death in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Line. Molecules 2021, 26, 3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, G.R.; Guedes, D.; Marques de Paula, U.L.; De Oliveira, M.; Lutterbach, M.T.S.; Reznik, L.Y.; Servulo, E.F.C.; Alviano, C.S.; Ribeiro da Silva, A.J.; Alviano, D.S. Acai (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) Seed Extracts from Different Varieties: A Source of Proanthocyanidins and Eco-Friendly Corrosion Inhibition Activity. Molecules 2021, 26, 3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bem, G.F.; Okinga, A.; Ognibene, D.T.; Da Costa, C.A.; Santos, I.B.; Soares, R.A.; Silva, D.L.B.; Da Rocha, A.P.M.; Isnardo Fernandes, J.; Fraga, M.C.; et al. Anxiolytic and antioxidant effects of Euterpe oleracea Mart. (acai) seed extract in adult rat offspring submitted to periodic maternal separation. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 45, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remigante, A.; Spinelli, S.; Straface, E.; Gambardella, L.; Caruso, D.; Falliti, G.; Dossena, S.; Marino, A.; Morabito, R. Acai (Euterpe oleracea) Extract Protects Human Erythrocytes from Age-Related Oxidative Stress. Cells 2022, 11, 2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordaro, M.; D′Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Genovese, T.; Interdonato, L.; Franco, G.; Arangia, A.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; et al. Discovering the Effects of Fisetin on NF-kappaB/NLRP-3/NRF-2 Molecular Pathways in a Mouse Model of Vascular Dementia Induced by Repeated Bilateral Carotid Occlusion. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusa, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Esposito, E.; Petrosino, S.; Cuzzocrea, S. Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effects of Co-UltraPEALut in a Mouse Model of Vascular Dementia. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, T.; D′Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Peritore, A.F.; Crupi, R.; Interdonato, L.; Gugliandolo, E.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Paola, R.D.; et al. Acai (Euterpe oleraceae Mart.) Seeds Regulate NF-kappaB and Nrf2/ARE Pathways Protecting Lung against Acute and Chronic Inflammation. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 56, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prut, L.; Belzung, C. The open field as a paradigm to measure the effects of drugs on anxiety-like behaviors: A review. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 463, 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crupi, R.; Cambiaghi, M.; Spatz, L.; Hen, R.; Thorn, M.; Friedman, E.; Vita, G.; Battaglia, F. Reduced adult neurogenesis and altered emotional behaviors in autoimmune-prone B-cell activating factor transgenic mice. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Cui, M.; Dai, G.; Yuan, T.; Li, Y.; Ji, T.; Pan, Y. Protective Effect of Anthocyanin on Neurovascular Unit in Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, D.; Iaria, C.; Capparucci, F.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Siracusa, R.; D′Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Aflatoxin B1 Toxicity in Zebrafish Larva (Danio rerio): Protective Role of Hericium erinaceus. Toxins 2021, 13, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, D.; Natale, S.; Gugliandolo, E.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Siracusa, R.; D′Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Assessment of 2-Pentadecyl-2-oxazoline Role on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation on Early Stage Development of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Life 2022, 12, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, D.; Capparucci, F.; Abbate, J.M.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Siracusa, R.; D′Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Genovese, T.; Impellizzeri, D.; et al. Environmental Risk Assessment of Oxaliplatin Exposure on Early Life Stages of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxics 2022, 10, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordaro, M.; Impellizzeri, D.; Gugliandolo, E.; Siracusa, R.; Crupi, R.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S. Adelmidrol, a Palmitoylethanolamide Analogue, as a New Pharmacological Treatment for the Management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 90, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fusco, R.; Siracusa, R.; D’Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Genovese, T.; Gugliandolo, E.; Peritore, A.F.; Crupi, R.; Di Paola, R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma Translocation 1 Inhibitor as a Novel Therapeutic Tool for Lung Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Siracusa, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Genovese, T.; D′Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Mandalari, G.; Impellizzeri, D.; et al. The Role of Cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.) Nuts on an Experimental Model of Painful Degenerative Joint Disease. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peritore, A.F.; Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; D′Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Genovese, T.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide and Paracetamol, a New Association to Relieve Hyperalgesia and Pain in a Sciatic Nerve Injury Model in Rat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; D′Amico, R.; Genovese, T.; Gugliandolo, E.; Peritore, A.F.; Crupi, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Biochemical Evaluation of the Antioxidant Effects of Hydroxytyrosol on Pancreatitis-Associated Gut Injury. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, S.; Gokulan, R.; Dongre, H.; Vaidya, M.; Chaukar, D.; Prabhash, K.; Ingle, A.; Joshi, S.; Dange, P.; Joshi, S.; et al. Prognostic role of Oct4, CD44 and c-Myc in radio-chemo-resistant oral cancer patients and their tumourigenic potential in immunodeficient mice. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2016, 20, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusa, R.; Paterniti, I.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Bruschetta, G.; Campolo, M.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Esposito, E. Neuroprotective Effects of Temsirolimus in Animal Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 2403–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliandolo, E.; D′Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Fusco, R.; Siracusa, R.; Crupi, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Di Paola, R. Effect of PEA-OXA on neuropathic pain and functional recovery after sciatic nerve crush. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Genovese, T.; Siracusa, R.; D′Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; Trovato Salinaro, A.; Raffone, E.; Impellizzeri, D.; et al. Regulation of Inflammatory and Proliferative Pathways by Fotemustine and Dexamethasone in Endometriosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peritore, A.F.; Crupi, R.; Scuto, M.; Gugliandolo, E.; Siracusa, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cordaro, M.; D′Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Di Paola, R.; et al. The Role of Annexin A1 and Formyl Peptide Receptor 2/3 Signaling in Chronic Corticosterone-Induced Depression-Like behaviors and Impairment in Hippocampal-Dependent Memory. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 19, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Genovese, T.; D′Amico, R.; Crupi, R.; Smeriglio, A.; Mandalari, G.; et al. Consumption of Anacardium occidentale L. (Cashew Nuts) Inhibits Oxidative Stress through Modulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-kB Pathways. Molecules 2020, 25, 4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Crupi, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Peritore, A.F.; D′Amico, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Di Paola, R.; Cuzzocrea, S. 2-Pentadecyl-2-Oxazoline Reduces Neuroinflammatory Environment in the MPTP Model of Parkinson Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 9251–9266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Impellizzeri, D.; Cordaro, M.; Bruschetta, G.; Crupi, R.; Pascali, J.; Alfonsi, D.; Marcolongo, G.; Cuzzocrea, S. 2-pentadecyl-2-oxazoline: Identification in coffee, synthesis and activity in a rat model of carrageenan-induced hindpaw inflammation. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 108, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; D′Amico, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Genovese, T.; Scuto, M.; Crupi, R.; Mandalari, G.; et al. Cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.) Nuts Counteract Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in an Acute Experimental Model of Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D′Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; Scuto, M.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Di Paola, R.; et al. Modulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome through Formyl Peptide Receptor 1 (Fpr-1) Pathway as a New Therapeutic Target in Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esposito, E.; Impellizzeri, D.; Bruschetta, G.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; Cuzzocrea, S. A new co-micronized composite containing palmitoylethanolamide and polydatin shows superior oral efficacy compared to their association in a rat paw model of carrageenan-induced inflammation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 782, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impellizzeri, D.; Siracusa, R.; Cordaro, M.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Mancuso, G.; Midiri, A.; Di Paola, R.; Cuzzocrea, S. Therapeutic potential of dinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (DNBS)-induced colitis in mice by targeting IL-1beta and IL-18. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 155, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, R.; Fusco, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cordaro, M.; Britti, D.; Morittu, V.M.; Evangelista, M.; Cuzzocrea, S. Adelmidrol, in combination with hyaluronic acid, displays increased anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects against monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis in rats. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fusco, R.; Cordaro, M.; Genovese, T.; Impellizzeri, D.; Siracusa, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Peritore, A.F.; D′Amico, R.; Crupi, R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Adelmidrol: A New Promising Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Therapeutic Tool in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Siracusa, R.; Scuto, M.; Cordaro, M.; D′Amico, R.; Evangelista, M.; Peli, A.; Peritore, A.F.; Impellizzeri, D.; et al. Formyl Peptide Receptor 1 Signaling in Acute Inflammation and Neural Differentiation Induced by Traumatic Brain Injury. Biology 2020, 9, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impellizzeri, D.; Siracusa, R.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; D′Amico, R.; Petrosino, S.; Evangelista, M.; Di Paola, R.; et al. N-Palmitoylethanolamine-oxazoline (PEA-OXA): A new therapeutic strategy to reduce neuroinflammation, oxidative stress associated to vascular dementia in an experimental model of repeated bilateral common carotid arteries occlusion. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 125, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordaro, M.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Crupi, R. An Update of Palmitoylethanolamide and Luteolin Effects in Preclinical and Clinical Studies of Neuroinflammatory Events. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, M.; Huang, L.; Zhong, X.; Huang, M. Dynamic Changes of Beclin-1 in the Hippocampus of Male Mice with Vascular Dementia at Different Time Points. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 70, 1611–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacruz, R.S.; Smith, C.E.; Smith, S.M.; Hu, P.; Bringas, P., Jr.; Sahin-Toth, M.; Moradian-Oldak, J.; Paine, M.L. Chymotrypsin C (caldecrin) is associated with enamel development. J. Dent. Res. 2011, 90, 1228–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paola, D.D.; Capparucci, F.; Natale, S.; Crupi, R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Spano, N.; Gugliandolo, E.; Peritore, A.F. Combined Effects of Potassium Perchlorate and a Neonicotinoid on Zebrafish Larvae (Danio rerio). Toxics 2022, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, D.; Capparucci, F.; Lanteri, G.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Siracusa, R.; D′Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Combined Toxicity of Xenobiotics Bisphenol A and Heavy Metals on Zebrafish Embryos (Danio rerio). Toxics 2021, 9, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, D.; Natale, S.; Iaria, C.; Crupi, R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Spano, N.; Gugliandolo, E.; Peritore, A.F. Environmental Co-Exposure to Potassium Perchlorate and Cd Caused Toxicity and Thyroid Endocrine Disruption in Zebrafish Embryos and Larvae (Danio rerio). Toxics 2022, 10, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, D.; Abbate, J.M.; Iaria, C.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Siracusa, R.; D′Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Environmental Risk Assessment of Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Tocilizumab Mixture in Zebrafish Early Life Stage (Danio rerio). Toxics 2022, 10, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, D.; Capparucci, F.; Lanteri, G.; Crupi, R.; Marino, Y.; Franco, G.A.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Spano, N.; Gugliandolo, E.; Peritore, A.F. Environmental Toxicity Assessment of Sodium Fluoride and Platinum-Derived Drugs Co-Exposure on Aquatic Organisms. Toxics 2022, 10, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, D.; Natale, S.; Iaria, C.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Siracusa, R.; D′Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Intestinal Disorder in Zebrafish Larvae (Danio rerio): The Protective Action of N-Palmitoylethanolamide-oxazoline. Life 2022, 12, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, T.; Impellizzeri, D.; D′Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Di Paola, D.; Interdonato, L.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; Di Paola, R.; et al. Role of Bevacizumab on Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Apolipoprotein E Deficient Mice after Traumatic Brain Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; D′Amico, R.; Genovese, T.; Franco, G.; Marino, Y.; Di Paola, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Impellizzeri, D.; Di Paola, R.; et al. Role of Etanercept and Infliximab on Nociceptive Changes Induced by the Experimental Model of Fibromyalgia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D′Amico, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Cordaro, M.; Fusco, R.; Genovese, T.; Peritore, A.F.; Crupi, R.; Interdonato, L.; Di Paola, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Toxic Effects of Endocrine Disruptor Exposure on Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D′Amico, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Siracusa, R.; Cordaro, M.; Genovese, T.; Peritore, A.F.; Crupi, R.; Interdonato, L.; Di Paola, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Toxic Exposure to Endocrine Disruptors Worsens Parkinson’s Disease Progression through NRF2/HO-1 Alteration. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; D′Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Gugliandolo, E.; Siracusa, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Crupi, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Di Paola, R. Absence of formyl peptide receptor 1 causes endometriotic lesion regression in a mouse model of surgically-induced endometriosis. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 31355–31366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Paola, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Fusco, R.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Crupi, R.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S. Ultramicronized palmitoylethanolamide (PEA-um((R))) in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Siracusa, R.; D′Amico, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Cordaro, M.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Di Paola, R. Melatonin Plus Folic Acid Treatment Ameliorates Reserpine-Induced Fibromyalgia: An Evaluation of Pain, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, H.B.; Kim, S.H.; Uhm, S.H.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, N.S.; Jeong, Y.G.; Sung, N.Y.; Kim, D.S.; Han, I.J.; Yoo, Y.C.; et al. Perilla frutescens Leaf Extract Attenuates Vascular Dementia-Associated Memory Deficits, Neuronal Damages, and Microglial Activation. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.M.; Kester, M.; Wang, H.G. Sphingolipids: Regulators of crosstalk between apoptosis and autophagy. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iadecola, C. The pathobiology of vascular dementia. Neuron 2013, 80, 844–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skoog, I. Status of risk factors for vascular dementia. Neuroepidemiology 1998, 17, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Zhang, B.; Xia, R.; Jia, Q.Y. Inflammation, apoptosis and autophagy as critical players in vascular dementia. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 9601–9614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barichella, M.; Cereda, E.; Pezzoli, G. Major nutritional issues in the management of Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 1881–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidl, S.E.; Santiago, J.A.; Bilyk, H.; Potashkin, J.A. The emerging role of nutrition in Parkinson’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.W.; Zhang, X.; Huang, W.J. Role of neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 3391–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Almeida Magalhaes, T.S.S.; De Oliveira Macedo, P.C.; Converti, A.; Neves de Lima, A.A. The Use of Euterpe oleracea Mart. As a New Perspective for Disease Treatment and Prevention. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denzer, I.; Munch, G.; Friedland, K. Modulation of mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases via activation of nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 by food-derived compounds. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 103, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, G.G. Molecular Pathological Classification of Neurodegenerative Diseases: Turning towards Precision Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewerenz, J.; Maher, P. Chronic Glutamate Toxicity in Neurodegenerative Diseases-What is the Evidence? Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, A.K.; Andreazza, A.C.; Da Silva, T.M.; Boligon, A.A.; Do Nascimento, V.; Scola, G.; Duong, A.; Cadona, F.C.; Ribeiro, E.E.; Da Cruz, I.B. Neuroprotective Effects of Acai (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) against Rotenone In Vitro Exposure. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 8940850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torma, P.D.; Brasil, A.V.; Carvalho, A.V.; Jablonski, A.; Rabelo, T.K.; Moreira, J.C.; Gelain, D.P.; Flores, S.H.; Augusti, P.R.; Rios, A.O. Hydroethanolic extracts from different genotypes of acai (Euterpe oleracea) presented antioxidant potential and protected human neuron-like cells (SH-SY5Y). Food Chem. 2017, 222, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Kang, J.; Li, Z.; Schauss, A.G.; Badger, T.M.; Nagarajan, S.; Wu, T.; Wu, X. The acai flavonoid velutin is a potent anti-inflammatory agent: Blockade of LPS-mediated TNF-alpha and IL-6 production through inhibiting NF-kappaB activation and MAPK pathway. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, S.; Ferris, S. Outcome measures for probable vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease with cerebrovascular disease. Int. J. Clin. Pract. Suppl. 2001, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Bathgate, D.; Snowden, J.S.; Varma, A.; Blackshaw, A.; Neary, D. Behaviour in frontotemporal dementia, Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2001, 103, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yan, J.; Li, Y.; Xin, Z.; Lin, Y.; Qu, Y. An overview of the molecular mechanisms and novel roles of Nrf2 in neurodegenerative disorders. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.D.; Yuan, X.; Chu, S.F.; Chen, C.; Ren, Q.; Luo, P.; Lin, M.Y.; Wang, S.S.; Zhu, T.B.; Ai, Q.D.; et al. CZ-7, a new derivative of Claulansine F, ameliorates 2VO-induced vascular dementia in rats through a Nrf2-mediated antioxidant responses. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xiao, Y.; Lv, P.; Teng, Z.; Dong, Y.; Qi, Q.; Liu, Z. Edaravone attenuates oxidative stress induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion injury: Role of ERK/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Neurol. Res. 2018, 40, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O′Brien, C.E.; Bonanno, L.; Zhang, H.; Wyss-Coray, T. Beclin 1 regulates neuronal transforming growth factor-beta signaling by mediating recycling of the type I receptor ALK5. Mol. Neurodegener. 2015, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diniz, L.P.; Matias, I.; Siqueira, M.; Stipursky, J.; Gomes, F.C.A. Astrocytes and the TGF-beta1 Pathway in the Healthy and Diseased Brain: A Double-Edged Sword. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 4653–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraci, F.; Gulisano, W.; Guida, C.A.; Impellizzeri, A.A.; Drago, F.; Puzzo, D.; Palmeri, A. A key role for TGF-beta1 in hippocampal synaptic plasticity and memory. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kandasamy, M.; Anusuyadevi, M.; Aigner, K.M.; Unger, M.S.; Kniewallner, K.M.; De Sousa, D.M.B.; Altendorfer, B.; Mrowetz, H.; Bogdahn, U.; Aigner, L. TGF-beta Signaling: A Therapeutic Target to Reinstate Regenerative Plasticity in Vascular Dementia? Aging Dis. 2020, 11, 828–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.X.; Zhang, J.J.; Zheng, P.; Zhang, Y. Altered expression of MAP-2, GAP-43, and synaptophysin in the hippocampus of rats with chronic cerebral hypoperfusion correlates with cognitive impairment. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2005, 139, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomazkov, O.; Lagunin, A. Vascular dementia: Molecular targets of neuroprotective therapy. Biol. Bull. Rev. 2017, 7, 528–536. [Google Scholar]
- Bertelli, S.; Remigante, A.; Zuccolini, P.; Barbieri, R.; Ferrera, L.; Picco, C.; Gavazzo, P.; Pusch, M. Mechanisms of Activation of LRRC8 Volume Regulated Anion Channels. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 55, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remigante, A.; Morabito, R.; Spinelli, S.; Trichilo, V.; Loddo, S.; Sarikas, A.; Dossena, S.; Marino, A. d-Galactose Decreases Anion Exchange Capability through Band 3 Protein in Human Erythrocytes. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Impellizzeri, D.; D’Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Genovese, T.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; Interdonato, L.; Di Paola, D.; Di Paola, R.; et al. Açai Berry Mitigates Vascular Dementia-Induced Neuropathological Alterations Modulating Nrf-2/Beclin1 Pathways. Cells 2022, 11, 2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11162616
Impellizzeri D, D’Amico R, Fusco R, Genovese T, Peritore AF, Gugliandolo E, Crupi R, Interdonato L, Di Paola D, Di Paola R, et al. Açai Berry Mitigates Vascular Dementia-Induced Neuropathological Alterations Modulating Nrf-2/Beclin1 Pathways. Cells. 2022; 11(16):2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11162616
Chicago/Turabian StyleImpellizzeri, Daniela, Ramona D’Amico, Roberta Fusco, Tiziana Genovese, Alessio Filippo Peritore, Enrico Gugliandolo, Rosalia Crupi, Livia Interdonato, Davide Di Paola, Rosanna Di Paola, and et al. 2022. "Açai Berry Mitigates Vascular Dementia-Induced Neuropathological Alterations Modulating Nrf-2/Beclin1 Pathways" Cells 11, no. 16: 2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11162616
APA StyleImpellizzeri, D., D’Amico, R., Fusco, R., Genovese, T., Peritore, A. F., Gugliandolo, E., Crupi, R., Interdonato, L., Di Paola, D., Di Paola, R., Cuzzocrea, S., Siracusa, R., & Cordaro, M. (2022). Açai Berry Mitigates Vascular Dementia-Induced Neuropathological Alterations Modulating Nrf-2/Beclin1 Pathways. Cells, 11(16), 2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11162616












