An Epitope-Specific LGI1-Autoantibody Enhances Neuronal Excitability by Modulating Kv1.1 Channel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
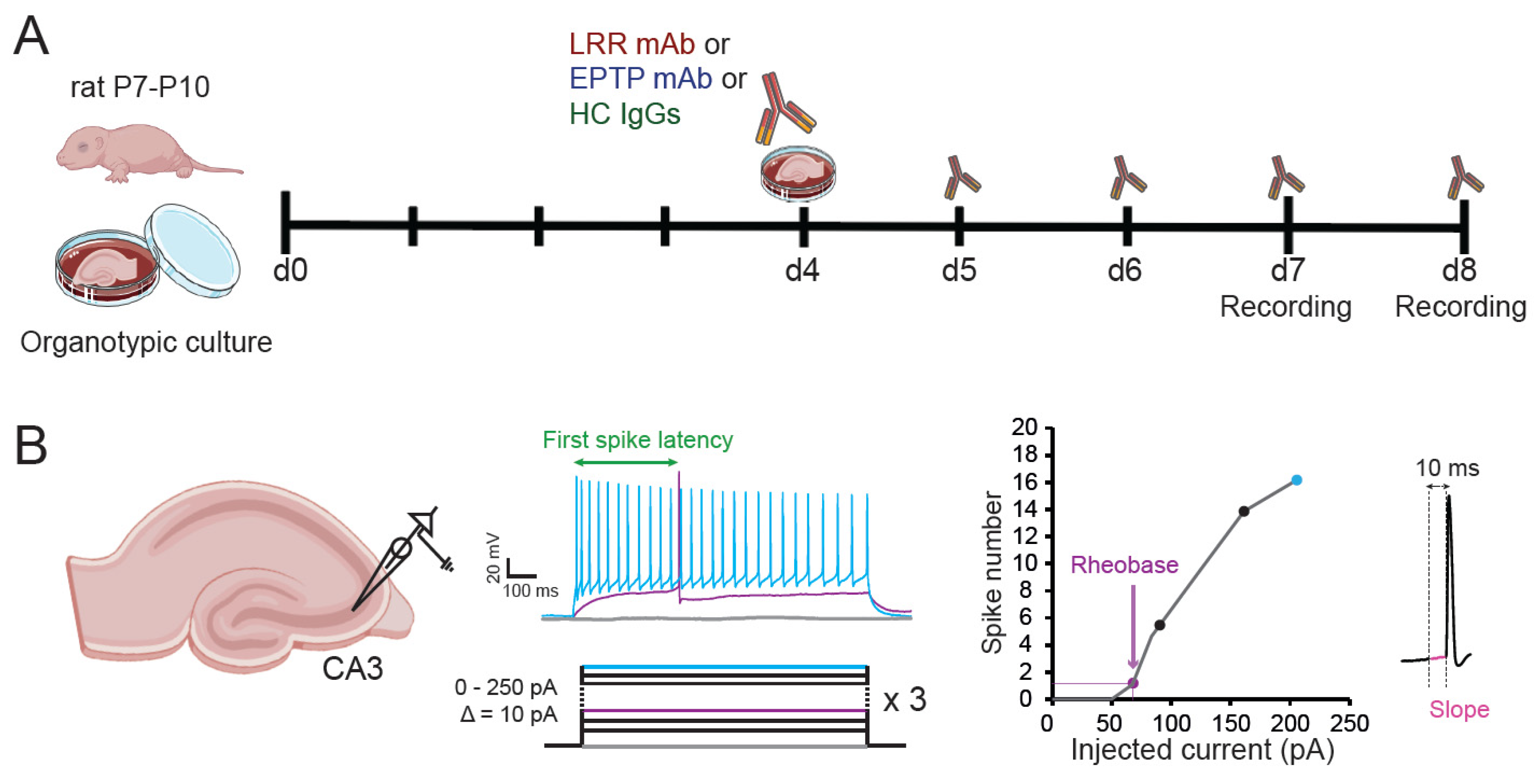
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
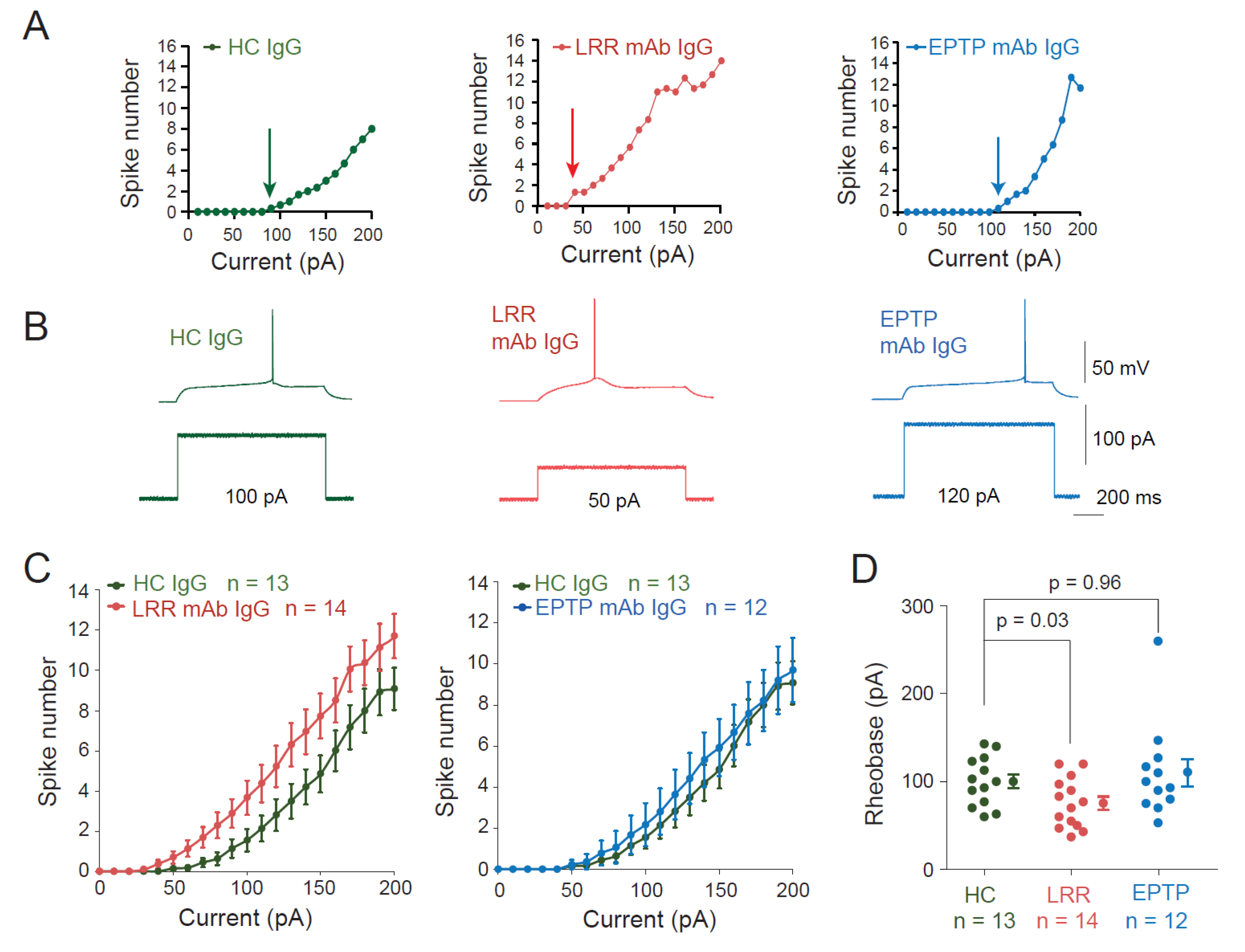
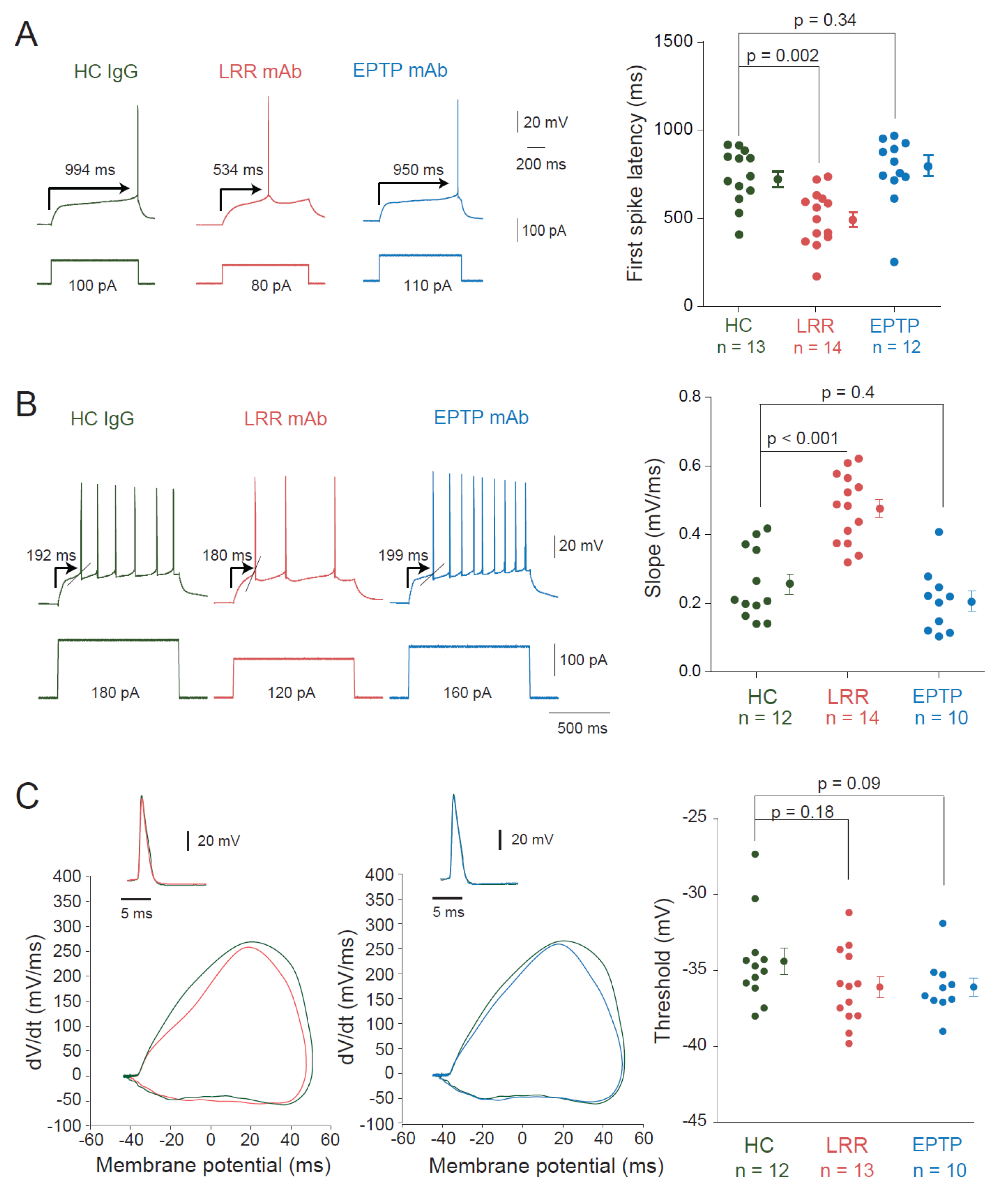
3.1. LRR-mAbs, but Not EPTP-mAbs, Increase Intrinsic Excitability in CA3 Pyramidal Neurons
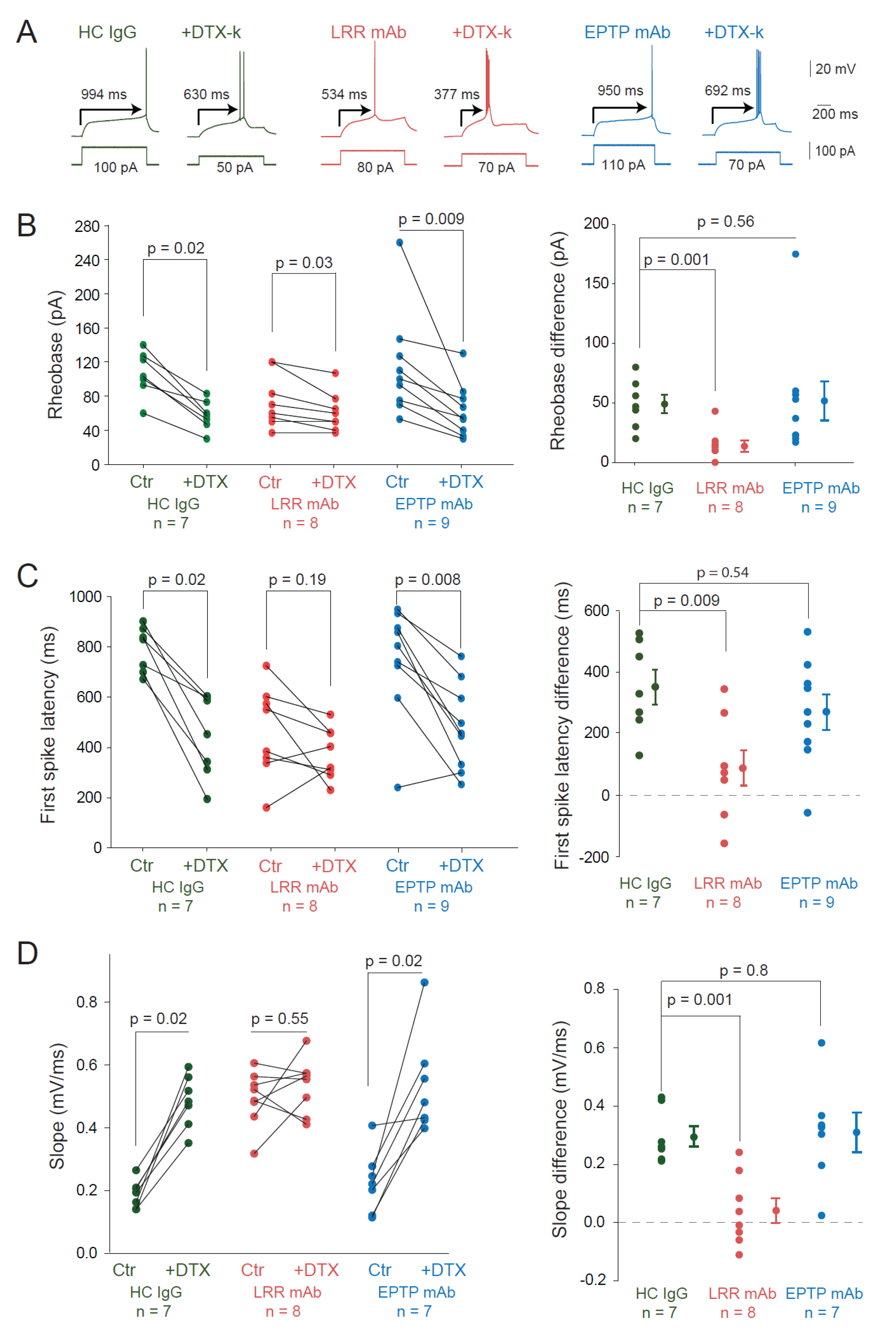
3.2. LRR-mAbs Increase Intrinsic Excitability through the Modulation of Kv1 Channels
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Irani, S.R.; Michell, A.W.; Lang, B.; Pettingill, P.; Waters, P.; Johnson, M.R.; Schott, J.M.; Armstrong, R.J.E.; Zagami, A.S.; Bleasel, A.; et al. Faciobrachial Dystonic Seizures Precede Lgi1 Antibody Limbic Encephalitis. Ann Neurol. 2011, 69, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurangzeb, S.; Symmonds, M.; Knight, R.; Kennett, R.; Wehner, T.; Irani, S. LGI1-Antibody Encephalitis Is Characterised by Frequent, Multifocal Clinical and Subclinical Seizures. Seizure 2017, 50, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.; Bi, M.; Murchison, A.G.; Makuch, M.; Bien, C.G.; Chu, K.; Farooque, P.; Gelfand, J.M.; Geschwind, M.D.; Hirsch, L.J.; et al. The Importance of Early Immunotherapy in Patients with Faciobrachial Dystonic Seizures. Brain 2018, 141, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalic, T.; Pettingill, P.; Vincent, A.; Capogna, M. Human Limbic Encephalitis Serum Enhances Hippocampal Mossy Fiber-CA3 Pyramidal Cell Synaptic Transmission: Limbic Encephalitis in the Hippocampus. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit-Pedrol, M.; Sell, J.; Planagumà, J.; Mannara, F.; Radosevic, M.; Haselmann, H.; Ceanga, M.; Sabater, L.; Spatola, M.; Soto, D.; et al. LGI1 Antibodies Alter Kv1.1 and AMPA Receptors Changing Synaptic Excitability, Plasticity and Memory. Brain 2018, 141, 3144–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagata, A.; Fukai, S. Insights into the Mechanisms of Epilepsy from Structural Biology of LGI1–ADAM22. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornau, H.-C.; Kreye, J.; Stumpf, A.; Fukata, Y.; Parthier, D.; Sammons, R.P.; Imbrosci, B.; Kurpjuweit, S.; Kowski, A.B.; Fukata, M.; et al. Human Cerebrospinal Fluid Monoclonal LGI1 Autoantibodies Increase Neuronal Excitability. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 87, 405–418. [Google Scholar]
- Ramberger, M.; Berretta, A.; Tan, J.M.M.; Sun, B.; Michael, S.; Yeo, T.; Theorell, J.; Bashford-Rogers, R.; Paneva, S.; O’Dowd, V.; et al. Distinctive Binding Properties of Human Monoclonal LGI1 Autoantibodies Determine Pathogenic Mechanisms. Brain 2020, 143, 1731–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, T.; Fukata, Y.; Yamasaki, M.; Miyazaki, T.; Yokoi, N.; Takashima, H.; Watanabe, M.; Watanabe, O.; Fukata, M. Autoantibodies to Epilepsy-Related LGI1 in Limbic Encephalitis Neutralize LGI1-ADAM22 Interaction and Reduce Synaptic AMPA Receptors. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 18161–18174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, U.; Thumfart, J.-O.; Klöcker, N.; Sailer, C.A.; Bildl, W.; Biniossek, M.; Dehn, D.; Deller, T.; Eble, S.; Abbass, K.; et al. The Epilepsy-Linked Lgi1 Protein Assembles into Presynaptic Kv1 Channels and Inhibits Inactivation by Kvβ1. Neuron 2006, 49, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rama, S.; Zbili, M.; Fékété, A.; Tapia, M.; Benitez, M.J.; Boumedine, N.; Garrido, J.J.; Debanne, D. The Role of Axonal Kv1 Channels in CA3 Pyramidal Cell Excitability. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Debanne, D.; Boudkkazi, S.; Campanac, E.; Cudmore, R.H.; Giraud, P.; Fronzaroli-Molinieres, L.; Carlier, E.; Caillard, O. Paired-Recordings from Synaptically Coupled Cortical and Hippocampal Neurons in Acute and Cultured Brain Slices. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1559–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudmore, R.H.; Fronzaroli-Molinieres, L.; Giraud, P.; Debanne, D. Spike-Time Precision and Network Synchrony Are Controlled by the Homeostatic Regulation of the D-Type Potassium Current. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 12885–12895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fékété, A.; Ankri, N.; Brette, R.; Debanne, D. Neural Excitability Increases with Axonal Resistance between Soma and Axon Initial Segment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2102217118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubb, M.S.; Burrone, J. Activity-Dependent Relocation of the Axon Initial Segment Fine-Tunes Neuronal Excitability. Nature 2010, 465, 1070–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seagar, M.; Russier, M.; Caillard, O.; Maulet, Y.; Fronzaroli-Molinieres, L.; De San Feliciano, M.; Boumedine-Guignon, N.; Rodriguez, L.; Zbili, M.; Usseglio, F.; et al. LGI1 Tunes Intrinsic Excitability by Regulating the Density of Axonal Kv1 Channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 7719–7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zbili, M.; Rama, S.; Benitez, M.-J.; Fronzaroli-Molinieres, L.; Bialowas, A.; Boumedine-Guignon, N.; Garrido, J.J.; Debanne, D. Homeostatic Regulation of Axonal Kv1.1 Channels Accounts for Both Synaptic and Intrinsic Modifications in the Hippocampal CA3 Circuit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2110601118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudin, P.; Whitmarsh, S.; Cousyn, L.; Roussel, D.; Lecas, S.; Lehongre, K.; Charpier, S.; Mahon, S.; Navarro, V. Kv1.1 Channels Inhibition in the Rat Motor Cortex Recapitulates Seizures Associated with Anti-LGI1 Encephalitis. Prog. Neurobiol. 2022, 213, 102262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debanne, D.; Thompson, S.M.; Gähwiler, B.H. A Brief Period of Epileptiform Activity Strengthens Excitatory Synapses in the Rat Hippocampus in Vitro. Epilepsia 2006, 47, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debanne, D.; El Far, O. Pre- and Postsynaptic Effects of LGI1 Autoantibodies in a Murine Model of Limbic Encephalitis. Brain 2018, 141, 3092–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Franco, J.; Debreux, K.; Extremet, J.; Maulet, Y.; Belghazi, M.; Villard, C.; Sangiardi, M.; Youssouf, F.; El Far, L.; Lévêque, C.; et al. Patient-Derived Antibodies Reveal the Subcellular Distribution and Heterogeneous Interactome of LGI1. Brain 2022, 145, awac218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Extrémet, J.; El Far, O.; Ankri, N.; Irani, S.R.; Debanne, D.; Russier, M. An Epitope-Specific LGI1-Autoantibody Enhances Neuronal Excitability by Modulating Kv1.1 Channel. Cells 2022, 11, 2713. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11172713
Extrémet J, El Far O, Ankri N, Irani SR, Debanne D, Russier M. An Epitope-Specific LGI1-Autoantibody Enhances Neuronal Excitability by Modulating Kv1.1 Channel. Cells. 2022; 11(17):2713. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11172713
Chicago/Turabian StyleExtrémet, Johanna, Oussama El Far, Norbert Ankri, Sarosh R. Irani, Dominique Debanne, and Michaël Russier. 2022. "An Epitope-Specific LGI1-Autoantibody Enhances Neuronal Excitability by Modulating Kv1.1 Channel" Cells 11, no. 17: 2713. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11172713
APA StyleExtrémet, J., El Far, O., Ankri, N., Irani, S. R., Debanne, D., & Russier, M. (2022). An Epitope-Specific LGI1-Autoantibody Enhances Neuronal Excitability by Modulating Kv1.1 Channel. Cells, 11(17), 2713. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11172713






