Sleep Alterations in a Mouse Model of Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 3
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Motor Function Evaluation
2.3. Electrophysiology
2.4. Sleep and EEG Analysis
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. SCA3 Mice Show Similar Motor Impairment in the Lights-on Phase to Previous Findings
3.2. SCA3 Mice Show a Trend for Circadian Differences
3.3. SCA3 Mice Display Increased REM Duration and Sleep/Wake Fragmentation Compared to Wild-Type Mice
3.4. SCA3 Mice Display Altered Neural Oscillations during REM and NREM Sleep
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruano, L.; Melo, C.; Silva, M.C.; Coutinho, P. The global epidemiology of hereditary ataxia and spastic paraplegia: A systematic review of prevalence studies. Neuroepidemiology 2014, 42, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klockgether, T.; Mariotti, C.; Paulson, H.L. Spinocerebellar ataxia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettencourt, C.; Santos, C.; Montiel, R.; Do Carmo Costa, M.; Cruz-Morales, P.; Santos, L.R.; Simões, N.; Kay, T.; Vasconcelos, J.; Maciel, P.; et al. Increased transcript diversity: Novel splicing variants of Machado-Joseph Disease gene (ATXN3). Neurogenetics 2010, 11, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATXN3 Ataxin 3 [Homo Sapiens (human)]—Gene—NCBI. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/4287 (accessed on 16 February 2022).
- Rüb, U.; Schöls, L.; Paulson, H.; Auburger, G.; Kermer, P.; Jen, J.C.; Seidel, K.; Korf, H.W.; Deller, T. Clinical features, neurogenetics and neuropathology of the polyglutamine spinocerebellar ataxias type 1, 2, 3, 6 and 7. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013, 104, 38–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, K.; Siswanto, S.; Brunt, E.R.P.; Den Dunnen, W.; Korf, H.W.; Rüb, U. Brain pathology of spinocerebellar ataxias. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 124, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLoughlin, H.S.; Moore, L.R.; Paulson, H.L. Pathogenesis of SCA3 and implications for other polyglutamine diseases. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 134, 104635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.d.C.; Paulson, H.L. Toward understanding Machado-Joseph Disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2012, 97, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paulson, H.; Shakkottai, V. Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 3. In GeneReviews® 10 October 1998 [Updated 4 June 2020]; Adam, M.P., Everman, D.B., Mirzaa, G.M., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2020; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih (accessed on 9 May 2022).
- Pedroso, J.L.; Braga-Neto, P.; Martinez, A.R.M.; Martins, C.R.; Filho, F.M.R.; Sobreira-Neto, M.A.; Prado, L.B.F.; do Prado, G.F.; Franca, M.C.; Barsottini, O.G.P. Sleep disorders in Machado-Joseph disease. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2016, 29, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Abreu, A.; Friedman, J.; Coskun, J. Non-movement disorder heralds symptoms of Macho-Joseph disease year before ataxia. Mov. Disord. 2005, 20, 739–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukutake, T.; Shinotoh, H.; Nishino, H.; Ichikawa, Y.; Goto, J.; Kanazawa, I.; Hattori, T. Homozygous Machado-Joseph disease presenting as REM sleep behaviour disorder and prominent psychiatric symptoms. Eur. J. Neurol. 2002, 9, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Abreu, A.; França, M.; Conz, L.; Friedman, J.H.; Nucci, A.M.; Cendes, F.; Lopes-Cendes, I. Sleep symptoms and their clinical correlates in Machado-Joseph disease. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2009, 119, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takei, A.; Fukazawa, T.; Hamada, T.; Sohma, H.; Yabe, I.; Sasaki, H.; Tashiro, K. Effects of Tandospirone on “5-HT1A Receptor-Associated Symptoms” in Patients with Machado-Josephe Disease An Open-Label Study. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2004, 27, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushida, C.A.; Clerk, A.A.; Kirsch, C.M.; Hotson, J.R.; Guilleminault, C. Prolonged confusion with nocturnal wandering arising from NREM and REM sleep: A case report. Sleep 1995, 18, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.H.; Fernandez, H.H.; Sudarsky, L.R. REM behavior disorder and excessive daytime somnolence in Machado-Joseph disease (SCA-3). Mov. Disord. 2003, 18, 1520–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroso, J.L.; Braga-Neto, P.; Felício, A.C.; Dutra, L.A.; Santos, W.A.C.; Do Prado, G.F.; Barsottini, O.G.P. Sleep disorders in Machado-Joseph disease: Frequency, discriminative thresholds, predictive values, and correlation with ataxia-related motor and non-motor features. Cerebellum 2011, 10, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folha Santos, F.A.; de Carvalho, L.B.C.; do Prado, L.F.; do Prado, G.F.; Barsottini, O.G.; Pedroso, J.L. Sleep apnea in Machado-Joseph disease: A clinical and polysomnographic evaluation. Sleep Med. 2018, 48, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.R.M.; Nunes, M.B.; Faber, I.; D’Abreu, A.; Lopes-Cendes, Í.; França, M.C. Fatigue and Its Associated Factors in Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 3/Machado-Joseph Disease. Cerebellum 2017, 16, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.S.; Xu, H.L.; Chen, P.P.; Sikandar, A.; Qian, M.Z.; Lin, H.X.; Lin, M.T.; Chen, W.J.; Wang, N.; Wu, H.; et al. Ataxic Severity Is Positively Correlated With Fatigue in Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 3 Patients. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abele, M.; Bürk, K.; Laccone, F.; Dichgans, J.; Klockgether, T. Restless legs syndrome in spinocerebellar ataxia types 1, 2, and 3. J. Neurol. 2001, 248, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitaí, L.L.G.; Éckeli, A.L.; Sobreira-Neto, M.A.; Diniz, P.R.B.; Santos, A.C.; Júnior, W.M.; Fernandes, R.M.F. Which Factors in Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 3 Patients Are Associated with Restless Legs Syndrome/Willis-Ekbom Disease? Cerebellum 2021, 20, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroso, J.L.; Braga-Neto, P.; Felício, A.C.; Minett, T.; Yamaguchi, E.; do Prado, L.B.F.; Carvalho, L.B.C.; Dutra, L.A.; Hoexter, M.Q.; Da Rocha, A.J.; et al. Sleep disorders in Machado-Joseph disease: A dopamine transporter imaging study. J. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 324, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimold, M.; Globas, C.; Gleichmann, M.; Schulze, M.; Gerloff, C.; Bares, R.; Machulla, H.J.; Bürk, K. Spinocerebellar ataxia type 1,2, and 3 and restless legs syndrome: Striatal dopamine D2 receptor status investigated by [11C] Raclopride positron emission tomography. Mov. Disord. 2006, 21, 1667–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schöls, L.; Haan, J.; Riess, O.; Amoiridis, G.; Przuntek, H. Sleep disturbance in spinocerebellar ataxias: Is the SCA3 mutation a cause of restless legs syndrome? Neurology 1998, 51, 1603–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroso, J.L.; Bezerra, M.L.E.; Braga-Neto, P.; Pinheiro, D.S.; Minett, T.; Do Prado, G.F.; Manzano, G.M.; Barsottini, O.G.P. Is Neuropathy Involved with Restless Legs Syndrome in Machado-Joseph Disease? Eur. Neurol. 2011, 66, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedroso, J.L.; Bor-Seng-Shu, E.; Braga-Neto, P.; Ribeiro, R.S.; Bezerra, M.L.E.; Do Prado, L.B.F.; Batista, I.R.; Alessi, H.; Teixeira, M.J.; Manzano, G.M.; et al. Neurophysiological studies and non-motor symptoms prior to ataxia in a patient with Machado-Joseph disease: Trying to understand the natural history of brain degeneration. Cerebellum 2014, 13, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, G.M.F.; Pedroso, J.L.; Dos Santos, D.F.; Braga-Neto, P.; Do Prado, L.B.F.; De Carvalho, L.B.C.; Barsottini, O.G.P.; Do Prado, G.F. NREM-related parasomnias in Machado-Joseph disease: Clinical and polysomnographic evaluation. J. Sleep Res. 2016, 25, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chi, N.F.; Shiao, G.M.; Ku, H.L.; Soong, B.W. Sleep disruption in spinocerebellar ataxia type 3: A genetic and polysomnographic study. J. Chinese Med. Assoc. 2013, 76, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iranzo, A.; Muñoz, E.; Santamaria, J.; Vilaseca, I.; Milà, M.; Tolosa, E. REM sleep behavior disorder and vocal cord paralysis in Machado-Joseph disease. Mov. Disord. 2003, 18, 1179–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Presumed rapid eye movement behavior disorder in Machado-Joseph disease (Spinocerebellar ataxia type 3). Mov. Disord. 2002, 17, 1350–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, B.H.; Rye, D.B.; Singh, G. REM sleep behavior disorder and SCA-3 (Machado-Joseph disease). Neurology 2003, 60, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshagiri, D.V.; Botta, R.; Sasidharan, A.; Kumar Pal, P.; Jain, S.; Yadav, R.; Kutty, B.M. Assessment of Sleep Spindle Density among Genetically Positive Spinocerebellar Ataxias Types 1, 2, and 3 Patients. Ann. Neurosci. 2018, 25, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cemal, C.K.; Carroll, C.J.; Lawrence, L.; Lowrie, M.B.; Ruddle, P.; Al-Mahdawi, S.; King, R.H.M.; Pook, M.A.; Huxley, C.; Chamberlain, S. YAC transgenic mice carrying pathological alleles of the MJD1 locus exhibit a mild and slowly progressive cerebellar deficit. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2002, 11, 1075–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do Carmo Costa, M.; Luna-Cancalon, K.; Fischer, S.; Ashraf, N.S.; Ouyang, M.; Dharia, R.M.; Martin-Fishman, L.; Yang, Y.; Shakkottai, V.G.; Davidson, B.L.; et al. Toward RNAi therapy for the polyglutamine disease Machado-Joseph disease. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 1898–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; He, X.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, W.; Pan, D.; Shi, L.; Xu, L.; Shi, L.; Gu, R.; Wei, J. Nonlinear analysis of local field potentials and motor cortex EEG in spinocerebellar ataxia 3. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 59, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, B.O.; Levenstein, D.; Greene, J.P.; Gelinas, J.N.; Buzsáki, G. Network Homeostasis and State Dynamics of Neocortical Sleep. Neuron 2016, 90, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huebra, L.; Coelho, F.M.; Filho, F.M.R.; Barsottini, O.G.; Pedroso, J.L. Sleep Disorders in Hereditary Ataxias. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2019, 19, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St Louis, E.K.; Boeve, A.R.; Boeve, B.F. REM Sleep Behavior Disorder in Parkinson’s Disease and Other Synucleinopathies. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, G.A.; Hubbard, E.K.; Fasano, A.; Tijssen, M.A.J.; Lynch, T.; Anderson, K.N.; Peall, K.J. Sleep disturbance in movement disorders: Insights, treatments and challenges. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2021, 92, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, D.F.; Pedroso, J.L.; Braga-Neto, P.; Silva, G.M.F.; de Carvalho, L.B.C.; Prado, L.B.F.; Barsottini, O.G.P.; do Prado, G.F. Excessive fragmentary myoclonus in Machado-Joseph disease. Sleep Med. 2014, 15, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tononi, G.; Cirelli, C. Sleep function and synaptic homeostasis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2006, 10, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, M.G.; Heller, H.C. The Function(s) of Sleep. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2019, 253, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minakawa, E.N.; Miyazaki, K.; Maruo, K.; Yagihara, H.; Fujita, H.; Wada, K.; Nagai, Y. Chronic sleep fragmentation exacerbates amyloid β deposition in Alzheimer’s disease model mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 653, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, G.E.; Luo, S.; Chen, L.N.; Lu, J.P.; Huang, Y.J.; Ye, Q.Y. Sleep fragmentation as an important clinical characteristic of sleep disorders in Parkinson’s disease: A preliminary study. Chin. Med. J. 2019, 132, 1788–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.S.P.; Fleischman, D.A.; Dawe, R.J.; Yu, L.; Arfanakis, K.; Buchman, A.S.; Bennett, D.A. Regional Neocortical Gray Matter Structure and Sleep Fragmentation in Older Adults. Sleep 2016, 39, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wennberg, A.M.V.; Wu, M.N.; Rosenberg, P.B.; Spira, A.P. Sleep Disturbance, Cognitive Decline, and Dementia: A Review. Semin. Neurol. 2017, 37, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Ba, L.; Wang, M.; Deng, S.Y.; Chen, S.M.; Huang, L.F.; Zhang, M.; Wang, W.; Ding, F.F. Chronic sleep fragmentation shares similar pathogenesis with neurodegenerative diseases: Endosome-autophagosome-lysosome pathway dysfunction and microglia-mediated neuroinflammation. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2020, 26, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Owen, J.E.; Veasey, S.C. Impact of sleep disturbances on neurodegeneration: Insight from studies in animal models. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 139, 104820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufort-Gervais, J.; Mongrain, V.; Brouillette, J. Bidirectional relationships between sleep and amyloid-beta in the hippocampus. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2019, 160, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.; Chiaravalloti, A.; Manfredi, N.; Placidi, F.; Nuccetelli, M.; Izzi, F.; Camedda, R.; Bernardini, S.; Schillaci, O.; Mercuri, N.B.; et al. Nocturnal Hypoxia and Sleep Fragmentation May Drive Neurodegenerative Processes: The Compared Effects of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome and Periodic Limb Movement Disorder on Alzheimer’s Disease Biomarkers. J. Alzheimers. Dis. 2022, 88, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, S.M.; Videnovic, A. Chronic sleep disturbance and neural injury: Links to neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2016, 8, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunchillos, J.D.; De Andrés, I. Participation of the cerebellum in the regulation of the sleep-wakefulness cycle. Results in cerebellectomized cats. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1982, 53, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DelRosso, L.M.; Hoque, R. The cerebellum and sleep. Neurol. Clin. 2014, 32, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canto, C.B.; Onuki, Y.; Bruinsma, B.; van der Werf, Y.D.; De Zeeuw, C.I. The Sleeping Cerebellum. Trends Neurosci. 2017, 40, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luppi, P.H.; Clement, O.; Sapin, E.; Peyron, C.; Gervasoni, D.; Léger, L.; Fort, P. Brainstem mechanisms of paradoxical (REM) sleep generation. Pflugers Arch. 2012, 463, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraigne, J.J.; Torontali, Z.A.; Snow, M.B.; Peever, J.H. REM Sleep at its Core—Circuits, Neurotransmitters, and Pathophysiology. Front. Neurol. 2015, 6, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paxinos, G.; Franklin, K.B.J. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; ISBN 9780123742445. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Ding, S.L.; Li, Y.; Royall, J.; Feng, D.; Lesnar, P.; Graddis, N.; Naeemi, M.; Facer, B.; Ho, A.; et al. The Allen Mouse Brain Common Coordinate Framework: A 3D Reference Atlas. Cell 2020, 181, 936–953.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizrahi-Kliger, A.D.; Kaplan, A.; Israel, Z.; Deffains, M.; Bergman, H. Basal ganglia beta oscillations during sleep underlie Parkinsonian insomnia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 17359–17368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urrestarazu, E.; Iriarte, J.; Alegre, M.; Clavero, P.; Rodríguez-Oroz, M.C.; Guridi, J.; Obeso, J.A.; Artieda, J. Beta activity in the subthalamic nucleus during sleep in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, A.J.; Kushida, C.A.; Summers, M.O.; Kern, D.S.; Abosch, A.; Thompson, J.A. Basal Ganglia Local Field Potentials as a Potential Biomarker for Sleep Disturbance in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 765203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackius, M.; Werth, E.; Sürücü, O.; Baumann, C.R.; Imbach, L.L. Electrophysiological evidence for alternative motor networks in REM sleep behavior disorder. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 11795–11800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Sanabria, D.E.; Wang, J.; Hendrix, C.M.; Zhang, J.; Nebeck, S.D.; Amundson, A.M.; Busby, Z.B.; Bauer, D.L.; Johnson, M.D.; et al. Parkinsonism Alters Beta Burst Dynamics across the Basal Ganglia-Motor Cortical Network. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 2274–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, R.; Wegscheider, M.; Mühlberg, C.; Gast, R.; Fricke, C.; Rumpf, J.J.; Nikulin, V.V.; Knösche, T.R.; Classen, J. Spatiotemporal features of β-γ phase-amplitude coupling in Parkinson’s disease derived from scalp EEG. Brain 2021, 144, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghilardi, M.F.; Tatti, E.; Quartarone, A. Beta power and movement-related beta modulation as hallmarks of energy for plasticity induction: Implications for Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2021, 88, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisinger, R.S.; Cagle, J.N.; Opri, E.; Alcantara, J.; Cernera, S.; Foote, K.D.; Okun, M.S.; Gunduz, A. Parkinsonian Beta Dynamics during Rest and Movement in the Dorsal Pallidum and Subthalamic Nucleus. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devergnas, A.; Pittard, D.; Bliwise, D.; Wichmann, T. Relationship between oscillatory activity in the cortico-basal ganglia network and parkinsonism in MPTP-treated monkeys. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 68, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morton, A.J. Circadian and sleep disorder in Huntington’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 243, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, S.P.; Black, S.W.; Schwartz, M.D.; Wilk, A.J.; Chen, T.M.; Lincoln, W.U.; Liu, H.W.; Kilduff, T.S.; Morairty, S.R. Longitudinal analysis of the electroencephalogram and sleep phenotype in the R6/2 mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Brain 2013, 136, 2159–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piano, C.; Imperatori, C.; Losurdo, A.; Bentivoglio, A.R.; Cortelli, P.; Della Marca, G. Sleep-related modifications of EEG connectivity in the sensory-motor networks in Huntington Disease: An eLORETA study and review of the literature. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, 1354–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piano, C.; Mazzucchi, E.; Bentivoglio, A.R.; Losurdo, A.; Calandra Buonaura, G.; Imperatori, C.; Cortelli, P.; Della Marca, G. Wake and Sleep EEG in Patients With Huntington Disease: An eLORETA Study and Review of the Literature. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2017, 48, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piano, C.; Della Marca, G.; Losurdo, A.; Imperatori, C.; Solito, M.; Calandra-Buonaura, G.; Provini, F.; Cortelli, P.; Bentivoglio, A.R. Subjective Assessment of Sleep in Huntington Disease: Reliability of Sleep Questionnaires Compared to Polysomnography. Neurodegener. Dis. 2017, 17, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ren, R.; Yang, L.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Shi, J.; Lu, L.; Sanford, L.D.; Tang, X. Sleep in Huntington’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of polysomongraphic findings. Sleep 2019, 42, zsz15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smarr, B.; Cutler, T.; Loh, D.H.; Kudo, T.; Kuljis, D.; Kriegsfeld, L.; Ghiani, C.A.; Colwell, C.S. Circadian dysfunction in the Q175 model of Huntington’s disease: Network analysis. J. Neurosci. Res. 2019, 97, 1606–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herzog-Krzywoszanska, R.; Krzywoszanski, L. Sleep disorders in Huntington’s disease. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kantor, S.; Szabo, L.; Varga, J.; Cuesta, M.; Morton, A.J. Progressive sleep and electroencephalogram changes in mice carrying the Huntington’s disease mutation. Brain 2013, 136, 2147–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeantet, Y.; Cayzac, S.; Cho, Y.H. β oscillation during slow wave sleep and rapid eye movement sleep in the electroencephalogram of a transgenic mouse model of Huntington’s disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neutel, D.; Tchikviladzé, M.; Charles, P.; Leu-Semenescu, S.; Roze, E.; Durr, A.; Arnulf, I. Nocturnal agitation in Huntington disease is caused by arousal-related abnormal movements rather than by rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder. Sleep Med. 2015, 16, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piano, C.; Losurdo, A.; Della Marca, G.; Solito, M.; Calandra-Buonaura, G.; Provini, F.; Bentivoglio, A.R.; Cortelli, P. Polysomnographic findings and clinical correlates in Huntington disease: A cross-sectional cohort study. Sleep 2015, 38, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lazar, A.S.; Panin, F.; Goodman, A.O.G.; Lazic, S.E.; Lazar, Z.I.; Mason, S.L.; Rogers, L.; Murgatroyd, P.R.; Watson, L.P.E.; Singh, P.; et al. Sleep deficits but no metabolic deficits in premanifest Huntington’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2015, 78, 630–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lebreton, F.; Cayzac, S.; Pietropaolo, S.; Jeantet, Y.; Cho, Y.H. Sleep physiology alterations precede plethoric phenotypic changes in R6/1 Huntington’s disease mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kantor, S.; Varga, J.; Morton, A.J. A single dose of hypnotic corrects sleep and EEG abnormalities in symptomatic Huntington’s disease mice. Neuropharmacology 2016, 105, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, S.P.; Schwartz, M.D.; Wurts-Black, S.; Thomas, A.M.; Chen, T.M.; Miller, M.A.; Palmerston, J.B.; Kilduff, T.S.; Morairty, S.R. Quantitative electroencephalographic analysis provides an early-stage indicator of disease onset and progression in the zQ175 knock-in mouse model of huntington’s disease. Sleep 2016, 39, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stylianou, M.; Zaaimi, B.; Thomas, A.; Taylor, J.P.; LeBeau, F.E.N. Early Disruption of Cortical Sleep-Related Oscillations in a Mouse Model of Dementia With Lewy Bodies (DLB) Expressing Human Mutant (A30P) Alpha-Synuclein. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 579867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, M.; Sanchez, P.E.; Verret, L.; Beagle, A.J.; Guo, W.; Dubal, D.; Ranasinghe, K.G.; Koyama, A.; Ho, K.; Yu, G.Q.; et al. Network dysfunction in α-synuclein transgenic mice and human Lewy body dementia. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2015, 2, 1012–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegelhalder, K.; Regen, W.; Feige, B.; Holz, J.; Piosczyk, H.; Baglioni, C.; Riemann, D.; Nissen, C. Increased EEG sigma and beta power during NREM sleep in primary insomnia. Biol. Psychol. 2012, 91, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figorilli, M.; Lanza, G.; Congiu, P.; Lecca, R.; Casaglia, E.; Mogavero, M.P.; Puligheddu, M.; Ferri, R. Neurophysiological Aspects of REM Sleep Behavior Disorder (RBD): A Narrative Review. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valomon, A.; Riedner, B.A.; Jones, S.G.; Nakamura, K.P.; Tononi, G.; Plante, D.T.; Benca, R.M.; Boly, M. A high-density electroencephalography study reveals abnormal sleep homeostasis in patients with rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferri, R.; Rundo, F.; Silvani, A.; Zucconi, M.; Bruni, O.; Ferini-Strambi, L.; Plazzi, G.; Manconi, M. REM Sleep EEG Instability in REM Sleep Behavior Disorder and Clonazepam Effects. Sleep 2017, 40, zsx080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deffains, M.; Bergman, H. Parkinsonism-related β oscillations in the primate basal ganglia networks—Recent advances and clinical implications. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2019, 59, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, D.; Gagnon, J.F.; Fantini, M.L.; Ferini-Strambi, L.; Montplaisir, J. Sleep and quantitative EEG in neurodegenerative disorders. J. Psychosom. Res. 2004, 56, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Niu, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Yu, H.; Le, W. Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Behavior Disorder and Neurodegenerative Diseases: An Update. Aging Dis. 2020, 11, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, A.; Moscovich, M.; Farah, M.; Camargo, C.H.F.; Teive, H.A.G.; Munhoz, R.P. Nonmotor symptoms in spinocerebellar ataxias (SCAs). Cerebellum Ataxias 2019, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aoh, Y.; Hsiao, H.J.; Lu, M.K.; Macerollo, A.; Huang, H.C.; Hamada, M.; Tsai, C.H.; Chen, J.C. Event-Related Desynchronization/Synchronization in Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 3. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
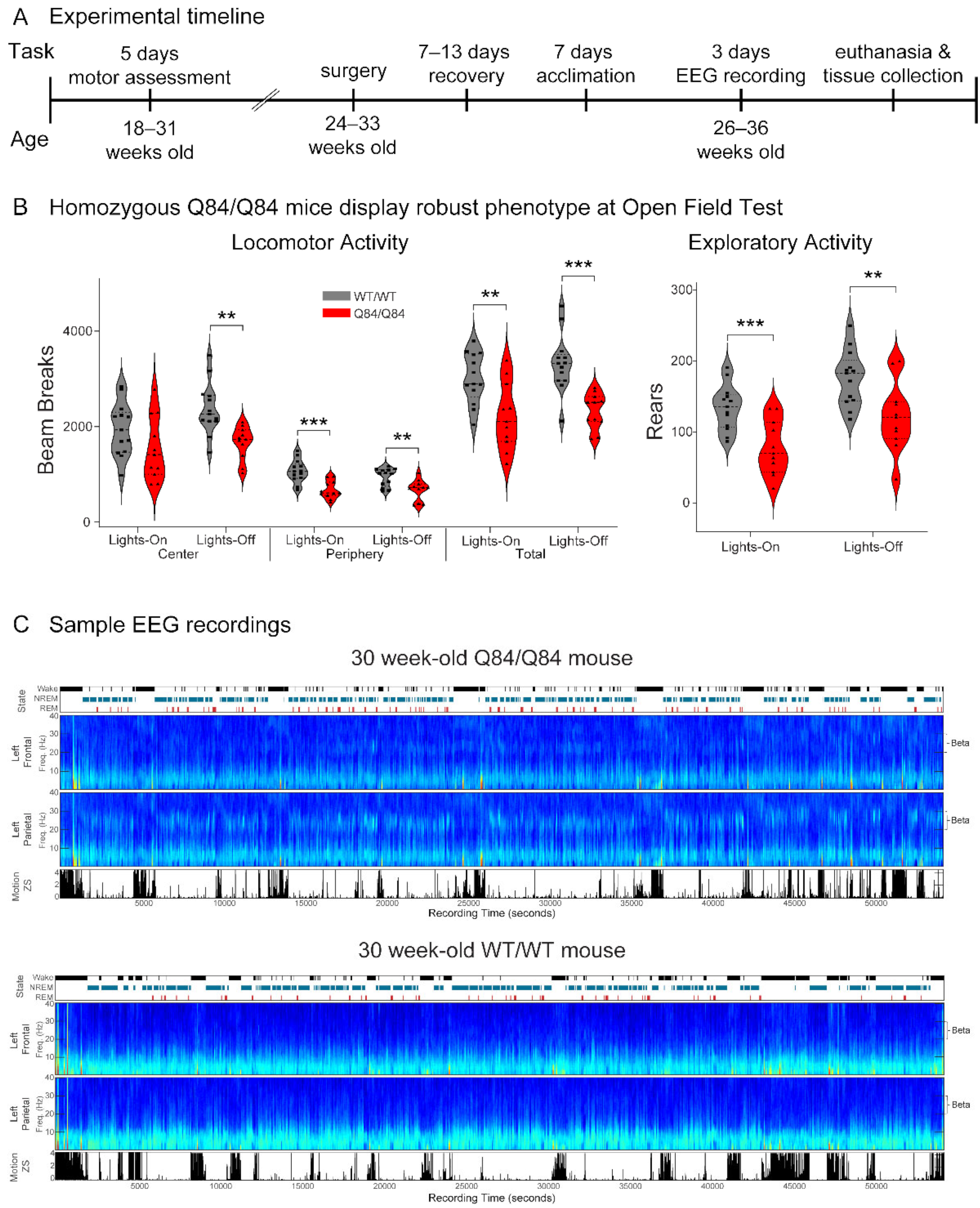


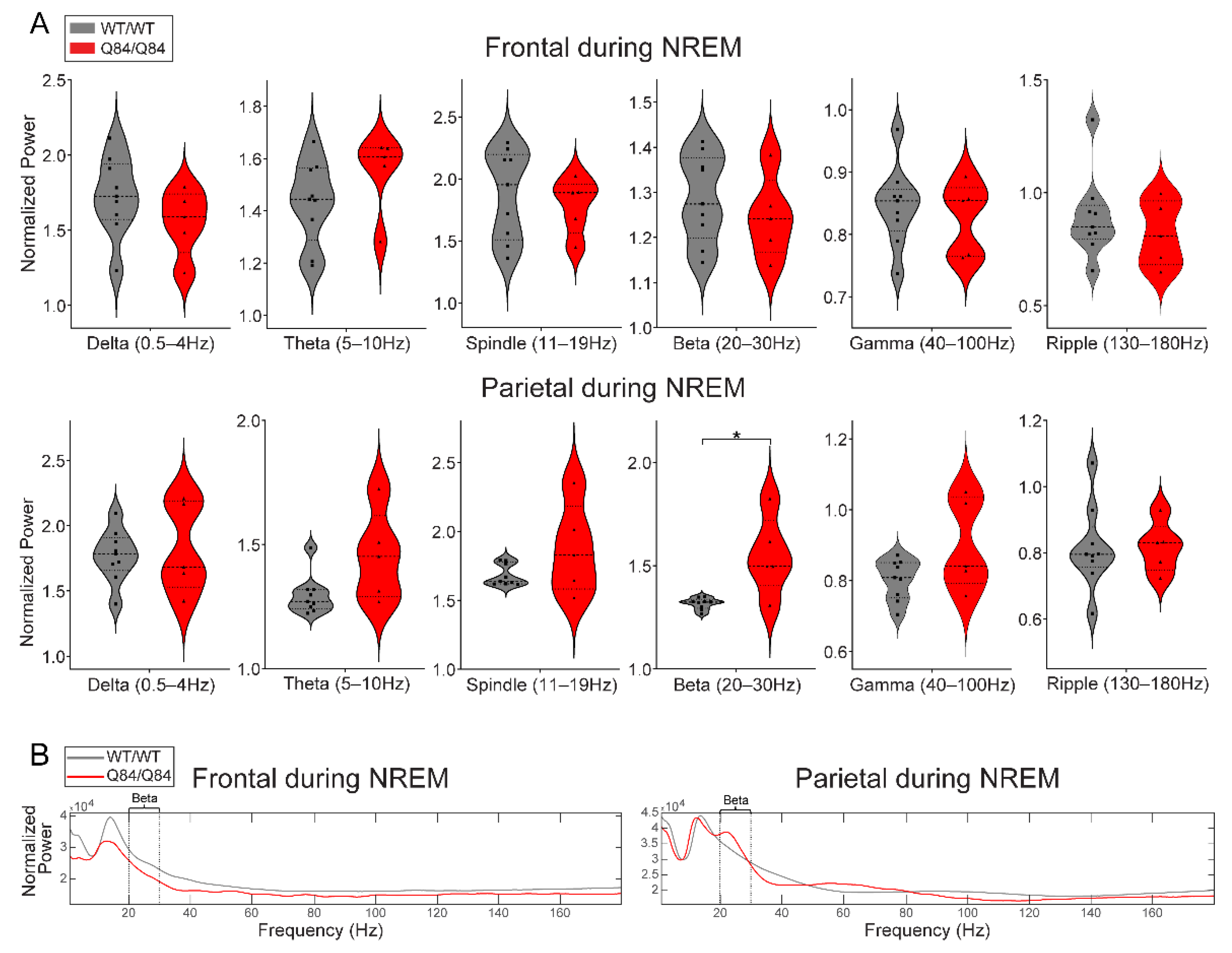
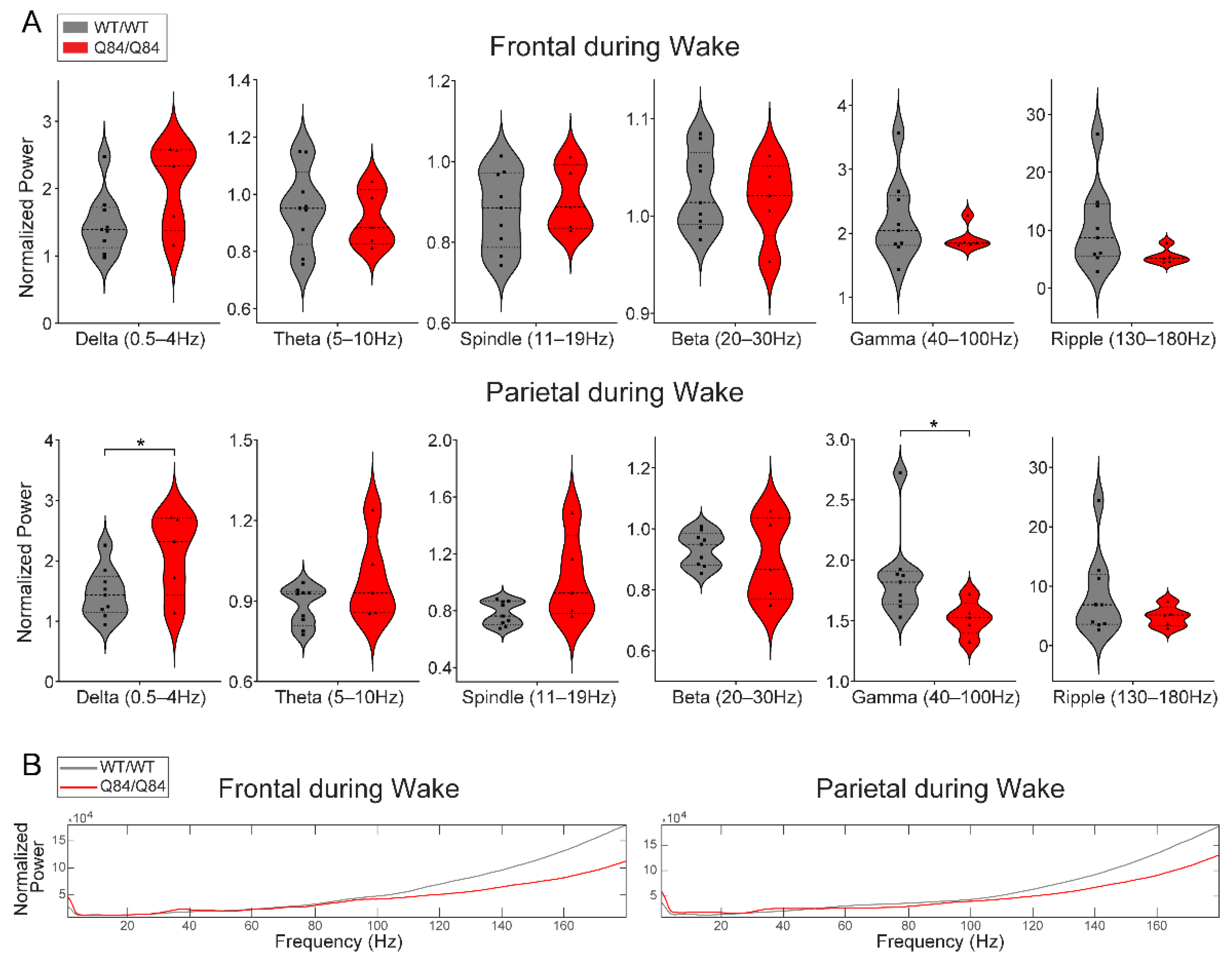
| Assessment Type | Genotype | Females (N) | Males (N) | Sex Differences | Min Age (Weeks) | Max Age (Weeks) | Mean Age (Weeks) | Age Differences |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motor Phenotype | Q84/Q84 | 5 | 6 | Q84/Q84 vs. WT/WT: p > 0.05 | 17.71 | 31.14 | 24.55 | Q84/Q84 vs. WT/WT: p > 0.05 |
| WT/WT | 5 | 7 | 19.86 | 31.14 | 24.36 | |||
| EEG Recordings | Q84/Q84 | 3 | 2 | Q84/Q84 vs. WT/WT: p > 0.05 | 30.14 | 35.86 | 31.80 | Q84/Q84 vs. WT/WT: p > 0.05 |
| WT/WT | 5 | 4 | 26.43 | 36.14 | 31.67 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsimpanouli, M.-E.; Ghimire, A.; Barget, A.J.; Weston, R.; Paulson, H.L.; Costa, M.d.C.; Watson, B.O. Sleep Alterations in a Mouse Model of Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 3. Cells 2022, 11, 3132. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11193132
Tsimpanouli M-E, Ghimire A, Barget AJ, Weston R, Paulson HL, Costa MdC, Watson BO. Sleep Alterations in a Mouse Model of Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 3. Cells. 2022; 11(19):3132. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11193132
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsimpanouli, Maria-Efstratia, Anjesh Ghimire, Anna J. Barget, Ridge Weston, Henry L. Paulson, Maria do Carmo Costa, and Brendon O. Watson. 2022. "Sleep Alterations in a Mouse Model of Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 3" Cells 11, no. 19: 3132. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11193132
APA StyleTsimpanouli, M.-E., Ghimire, A., Barget, A. J., Weston, R., Paulson, H. L., Costa, M. d. C., & Watson, B. O. (2022). Sleep Alterations in a Mouse Model of Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 3. Cells, 11(19), 3132. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11193132







