Adipokines as Regulators of Autophagy in Obesity-Linked Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
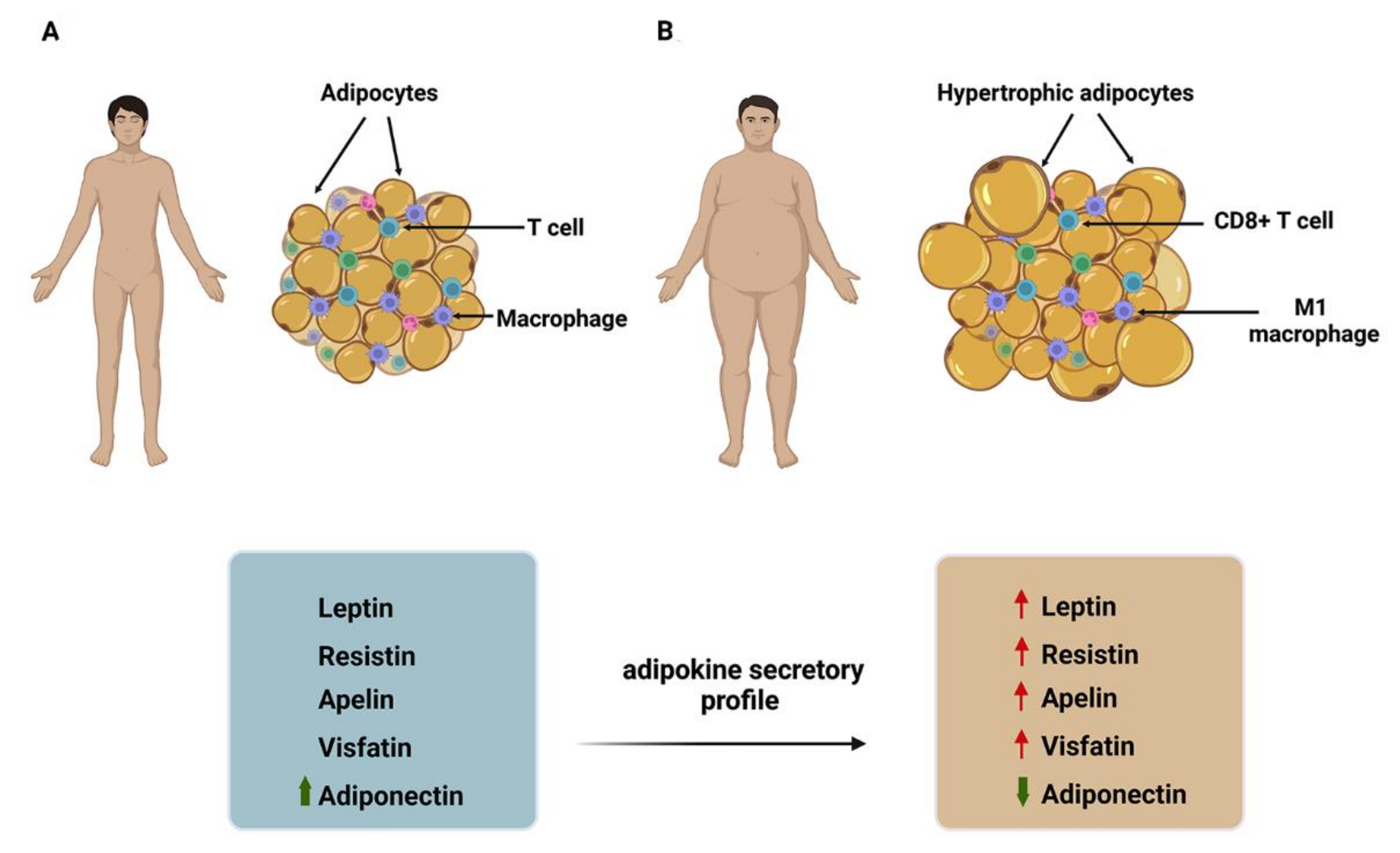
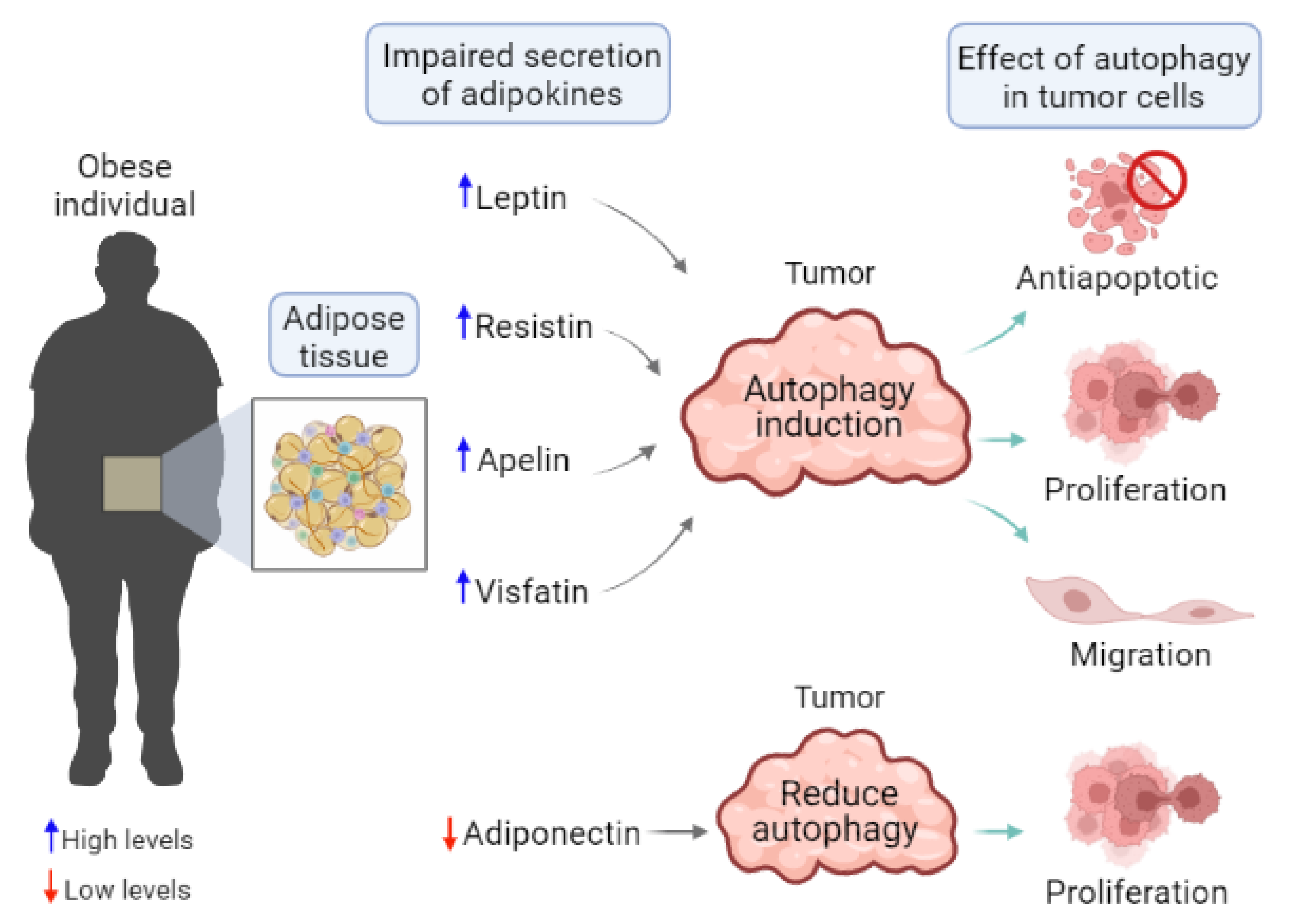
2. Obesity, Adipose Tissue, and Adipokines in Cancer
2.1. Leptin
2.2. Resistin
2.3. Visfatin
2.4. Apelin
2.5. Adiponectin
3. Autophagy in Cancer
4. Drugs for Targeting Autophagy
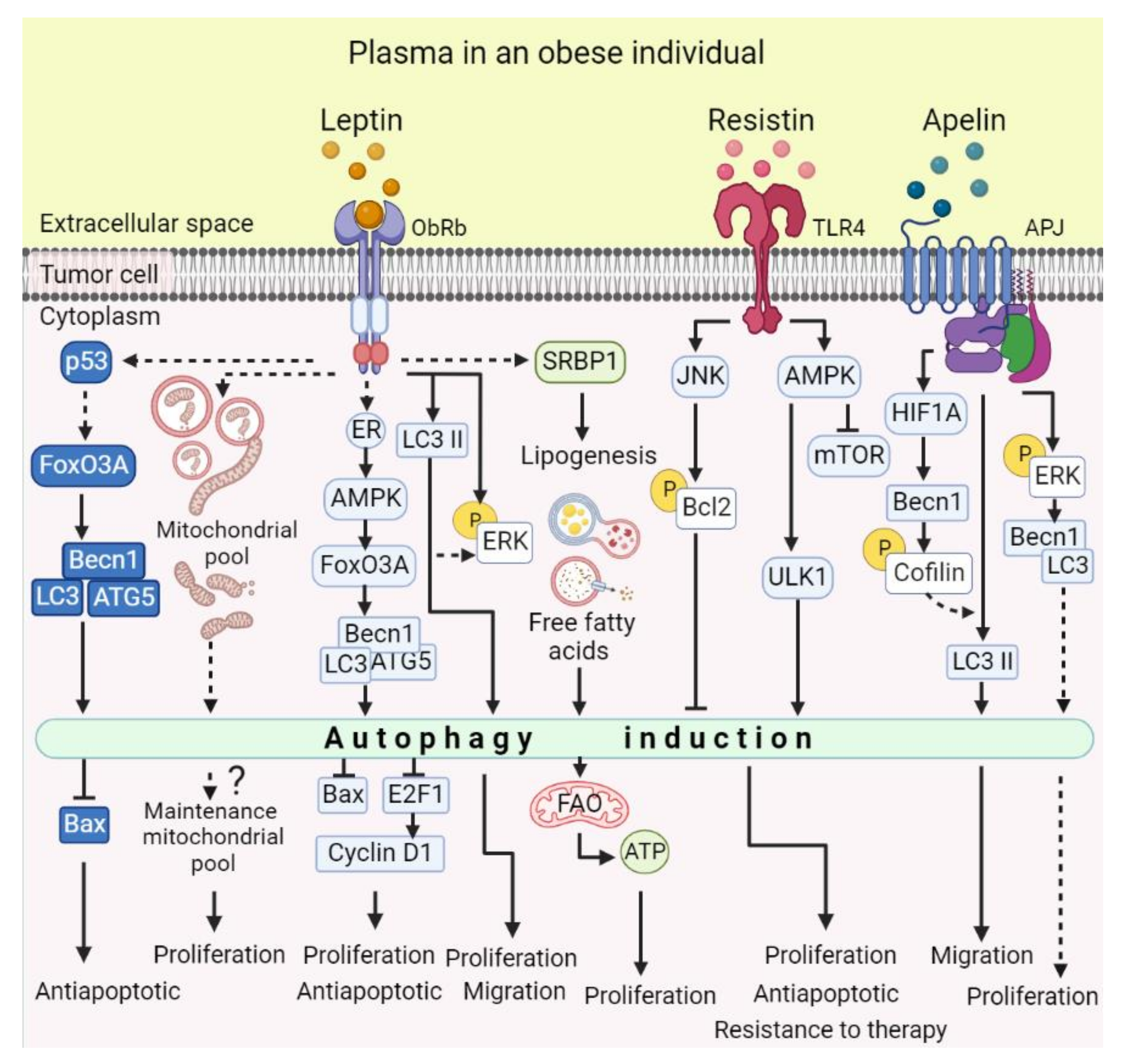
5. Autophagy Regulation by Adipokines in Cancer
| Adipokines | Effect on Autophagy | Effect of Autophagy in Cancer | Experimental Model | Cancer Type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leptin | Inductor | - | HeLa | Cervical | [143] |
| HCT116 | Colorectal | ||||
| U2OS | Osteosarcoma | ||||
| Leptin and adipsin | Inductor | Protects against apoptosis | U266 | Multiple Myeloma | [144] |
| ARP-1 | |||||
| Tumor xenograft | |||||
| Leptin | Inductor | Maintains proliferation and prevents apoptosis | MCF-7 | Breast | [145] |
| HepG2 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | ||||
| Tumor Xenograft | |||||
| Leptin | Inductor | Promotes tumor growth and proliferation | MCF-7 | Breast | [146] |
| Tumor xenograft | |||||
| Leptin | Inductor | Promotes proliferation, migration, and morphological change | MCF-7 | Breast | [147] |
| Resistin | Inductor | Inhibits doxorubicin-induced apoptosis | MCF-7 | Breast | [149] |
| Apelin | Inductor | Promote proliferation and cell migration | A549 | Human lung adenocarcinoma | [90] |
| Adiponectin | Inductor | Increased proliferation in glucose-deprivedmedium | DLD-1 | Human Colorectal | [150] |
| HT-29 | Mouse Colorectal | ||||
| Adiponectin | Inductor | Adiponectin deficiency fails to induce autophagy, avoiding LDLR turnover and increasing tumor growth. Adiponectin treatment induces autophagy and rescues adiponectin deficiency effects. | Adiponectin deficient MMTV-PyMT mice and MDA-MB-231 | Breast | [151] |
| Adiponectin | Inductor | Inhibits adiponectin- induced apoptosis | MCF-7 | Breast | [152] |
| HepG2 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | ||||
| Adiponectin | Inductor | Cytotoxic, contributes to cancer cell death and decreases tumor growth | MCF-7 | Breast | [153] |
| MDA-MB-231 | |||||
| Tumor xenograft |
6. Perspectives and Limitations of Targeting Adipokine-Induced Autophagy for Cancer Treatment
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global Epidemiology and Pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Avgerinos, K.I.; Spyrou, N.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Dalamaga, M. Obesity and Cancer Risk: Emerging Biological Mechanisms and Perspectives. Metabolism 2019, 92, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, J.B.; Rosendahl, A.H.; Borgquist, S. Local Biomarkers Involved in the Interplay between Obesity and Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-S.; Scherer, P.E. Obesity, Diabetes, and Increased Cancer Progression. Diabetes Metab. J. 2021, 45, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.-J.; Zheng, W.; Xiao, L.; Tan, L.-M.; Song, J.; Li, X.-P.; Xiao, D.; Cui, J.-J.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.-H.; et al. Circulating Resistin Levels and Obesity-Related Cancer Risk: A Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 57694–57704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.; Pan, Q.; Chen, X.; Xu, S.; Luo, X.; Chen, L. The Association between Obesity Related Adipokines and Risk of Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 75389–75399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Mianabadi, F.; Mehrad-Majd, H. Circulating Visfatin Levels and Cancers Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 5011–5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Woo, Y.C.; Wang, Y.; Yeung, C.Y.; Xu, A.; Lam, K.S.L. Obesity, Adipokines and Cancer: An Update. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2015, 83, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Pietrocola, F.; Bravo-San Pedro, J.M.; Amaravadi, R.K.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Cecconi, F.; Codogno, P.; Debnath, J.; Gewirtz, D.A.; Karantza, V.; et al. Autophagy in Malignant Transformation and Cancer Progression. Embo J. 2015, 34, 856–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, A.; Magnuson, A.; Fouts, J.; Foster, M. Adipose Tissue, Obesity and Adipokines: Role in Cancer Promotion. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2015, 21, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renehan, A.G.; Zwahlen, M.; Egger, M. Adiposity and Cancer Risk: New Mechanistic Insights from Epidemiology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantuzzi, G. Adipose Tissue, Adipokines, and Inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Lyon, C.J.; Bergin, S.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Hsueh, W.A. Obesity, Inflammation, and Cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2016, 11, 421–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romacho, T.; Elsen, M.; Röhrborn, D.; Eckel, J. Adipose Tissue and Its Role in Organ Crosstalk. Acta Physiol. Oxf. Engl. 2014, 210, 733–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J. Leptin at 20: An Overview. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 223, T1-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Considine, R.V.; Sinha, M.K.; Heiman, M.L.; Kriauciunas, A.; Stephens, T.W.; Nyce, M.R.; Ohannesian, J.P.; Marco, C.C.; McKee, L.J.; Bauer, T.L.; et al. Serum Immunoreactive-Leptin Concentrations in Normal-Weight and Obese Humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidori, A.M.; Strollo, F.; Morè, M.; Caprio, M.; Aversa, A.; Moretti, C.; Frajese, G.; Riondino, G.; Fabbri, A. Leptin and Aging: Correlation with Endocrine Changes in Male and Female Healthy Adult Populations of Different Body Weights. J. Clin. Endocrinol. 2000, 85, 1954–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostlund, E.; Yang, W. Relation between Plasma Leptin Concentration and Body Fat, Gender, Diet, Age, and Metabolic Covariates. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 81, 3909–3913. [Google Scholar]
- Liuzzi, A.; Savia, G.; Tagliaferri, M.; Lucantoni, R.; Berselli, M.; Petroni, M.; De Medici, C.; Viberti, G. Serum Leptin Concentration in Moderate and Severe Obesity: Relationship with Clinical, Anthropometric and Metabolic Factors. Int. J. Obes. 1999, 23, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münzberg, H.; Morrison, C.D. Structure, Production and Signaling of Leptin. Metab.—Clin. Exp. 2015, 64, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, N.; Hirako, S.; Takenoya, F.; Kageyama, H.; Okabe, M.; Shioda, S. Leptin and Its Receptors. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2014, 61–62, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Heiman, M.; Dimarchi, R. Leptin: Structure, Function and Biology. Vitam. Horm. 2005, 71, 345–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühbeck, G. Intracellular Signalling Pathways Activated by Leptin. Biochem. J. 2005, 393, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leshan, R.L.; Björnholm, M.; Münzberg, H.; Myers, M.G. Leptin Receptor Signaling and Action in the Central Nervous System. Obesity 2006, 14, 208S–212S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-P.; Zou, J.; Xu, Z.-Q.; Ruan, J.; Yang, S.-D.; Yin, Y.; Mu, H.-J. Association of Leptin, Visfatin, Apelin, Resistin and Adiponectin with Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pan, H.; Deng, L.-L.; Cui, J.-Q.; Shi, L.; Yang, Y.-C.; Luo, J.-H.; Qin, D.; Wang, L. Association between Serum Leptin Levels and Breast Cancer Risk: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e11345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Jiménez, F.; Pérez-Pérez, A.; de la Cruz-Merino, L.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Obesity and Breast Cancer: Role of Leptin. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, M.; Gonzalez-Perez, R.R. Leptin-Induced JAK/STAT Signaling and Cancer Growth. Vaccines 2016, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olea-Flores, M.; Juárez-Cruz, J.C.; Mendoza-Catalán, M.A.; Padilla-Benavides, T.; Navarro-Tito, N. Signaling Pathways Induced by Leptin during Epithelial—Mesenchymal Transition in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva-Duque, A.; Zuniga-Eulogio, M.D.; Dena-Beltran, J.; Castaneda-Saucedo, E.; Calixto-Galvez, M.; Mendoza-Catalán, M.A.; Ortuno-Pineda, C.; Navarro-Tito, N. Leptin Induces Partial Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in a FAK-ERK Dependent Pathway in MCF10A Mammary Non-Tumorigenic Cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2017, 10, 10334–10342. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemi, A.; Saeidi, J.; Azimi-Nejad, M.; Hashemy, S.I. Leptin-Induced Signaling Pathways in Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion. Cell. Oncol. Dordr. 2019, 42, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Fahrmann, J.F.; Lee, H.; Li, Y.-J.; Tripathi, S.C.; Yue, C.; Zhang, C.; Lifshitz, V.; Song, J.; Yuan, Y.; et al. JAK/STAT3-Regulated Fatty Acid β-Oxidation Is Critical for Breast Cancer Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Chemoresistance. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 136–150.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiagarajan, P.S.; Zheng, Q.; Bhagrath, M.; Mulkearns-Hubert, E.E.; Myers, M.G.; Lathia, J.D.; Reizes, O. STAT3 Activation by Leptin Receptor Is Essential for TNBC Stem Cell Maintenance. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2017, 24, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Tan, M.; Tian, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, W.; Sheng, H. Leptin Receptor Mediates the Proliferation and Glucose Metabolism of Pancreatic Cancer Cells via AKT Pathway Activation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Li, K.; Pang, X.; Guo, B.; Su, M.; Huang, Y.; Wang, N.; Ji, F.; Zhong, C.; Yang, J.; et al. Leptin Promotes Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Breast Cancer via the Upregulation of Pyruvate Kinase M2. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Fei, Z.; Yang, Z.; Duan, K.; Zi, J.; Cui, Q.; Yu, M.; Xiong, W. Leptin Promotes Fatty Acid Oxidation and OXPHOS via the C-Myc/PGC-1 Pathway in Cancer Cells. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2019, 51, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanquer-Rosselló, M.M.; Santandreu, F.M.; Oliver, J.; Roca, P.; Valle, A. Leptin Modulates Mitochondrial Function, Dynamics and Biogenesis in MCF-7 Cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 2039–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Mar Blanquer-Rosselló, M.; Oliver, J.; Sastre-Serra, J.; Valle, A.; Roca, P. Leptin Regulates Energy Metabolism in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 72, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquarone, E.; Monacelli, F.; Borghi, R.; Nencioni, A.; Odetti, P. Resistin: A Reappraisal. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2019, 178, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McTernan, P.G.; Kusminski, C.M.; Kumar, S. Resistin. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2006, 17, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorena, K.; Jachimowicz-Duda, O.; Ślęzak, D.; Robakowska, M.; Mrugacz, M. Adipokines and Obesity. Potential Link to Metabolic Disorders and Chronic Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.K.; Kwak, M.K.; Kim, H.J.; Ahima, R.S. Linking Resistin, Inflammation, and Cardiometabolic Diseases. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2017, 32, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiray, G.; Değirmencioğlu, S.; Uğurlu, E.; Yaren, A. Effects of Serum Leptin and Resistin Levels on Cancer Cachexia in Patients With Advanced-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol. 2017, 11, 1179554917690144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallio, J.; Hämäläinen, M.; Luukkaala, T.; Moilanen, E.; Tammela, T.L.; Kellokumpu-Lehtinen, P.-L. Resistin and Interleukin 6 as Predictive Factors for Recurrence and Long-Term Prognosis in Renal Cell Cancer. In Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 35, pp. 544.e25–544.e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, J.O.; Kim, N.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, Y.W.; Kim, S.J.; Park, S.H.; Kim, H.S. Resistin, a Fat-Derived Secretory Factor, Promotes Metastasis of MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells through ERM Activation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Fan, W.; Luo, B.; Xu, Z.; Wang, P.; Tang, S.; Xu, P.; Yu, M. Circulating Resistin Levels and Risk of Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Biomed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 7367485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adipocytokines, Energy Balance, and Cancer; Reizes, O., Berger, N.A., Eds.; Energy Balance and Cancer; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 12, ISBN 978-3-319-41675-5. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, S. Resistin Promotes the Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Ovary Carcinoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 9751–9766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.-Y.; Shen, C.-H.; Huang, W.-S.; Chin, C.-C.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Hsieh, M.C.; Yu, H.-R.; Chang, T.-S.; Lin, T.-H.; Chiu, Y.-W.; et al. Resistin-Induced Stromal Cell-Derived Factor-1 Expression through Toll-like Receptor 4 and Activation of P38 MAPK/NFκB Signaling Pathway in Gastric Cancer Cells. J. Biomed. Sci. 2014, 21, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.-C.; Cheng, S.-P.; Han, C.-K.; Huang, Y.-L.; Wang, S.-W.; Lee, J.-J.; Lai, C.-T.; Fong, Y.-C.; Tang, C.-H. Resistin Enhances Angiogenesis in Osteosarcoma via the MAPK Signaling Pathway. Aging 2019, 11, 9767–9777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-H.; Tsai, H.-C.; Huang, H.-N.; Hung, C.-H.; Hsu, C.-J.; Fong, Y.-C.; Hsu, H.-C.; Huang, Y.-L.; Tang, C.-H. Resistin Promotes Tumor Metastasis by Down-Regulation of MiR-519d through the AMPK/P38 Signaling Pathway in Human Chondrosarcoma Cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, G.-F.; Yu, L.; Wang, H.-Y.; Jia, X.-J.; Wang, T.-J. Novel Oncogenic and Chemoresistance-Inducing Functions of Resistin in Ovarian Cancer Cells Require MiRNAs-Mediated Induction of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.-J.; Liu, J.-Y.; Yin, J.-Y.; Cui, J.-J.; Xiao, D.; Zhuo, W.; Luo, C.; Liu, R.-J.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; et al. Resistin Facilitates Metastasis of Lung Adenocarcinoma through the TLR4/Src/EGFR/PI3K/NF-ΚB Pathway. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 2391–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeghate, E. Visfatin: Structure, Function and Relation to Diabetes Mellitus and Other Dysfunctions. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 1851–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-C. The Role of Visfatin in Cancer Proliferation, Angiogenesis, Metastasis, Drug Resistance and Clinical Prognosis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 3481–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-C.; Chang, T.-J.; Lee, W.-J.; Chuang, L.-M. The Relationship of Visfatin/Pre-B-Cell Colony-Enhancing Factor/Nicotinamide Phosphoribosyltransferase in Adipose Tissue with Inflammation, Insulin Resistance, and Plasma Lipids. Metabolism 2010, 59, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahorska-Markiewicz, B.; Olszanecka-Glinianowicz, M.; Janowska, J.; Kocełak, P.; Semik-Grabarczyk, E.; Holecki, M.; Dąbrowski, P.; Skorupa, A. Serum Concentration of Visfatin in Obese Women. Metabolism 2007, 56, 1131–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petelin, A.; Jurdana, M.; Jenko Pražnikar, Z.; Žiberna, L. Serum Bilirubin Correlates with Serum Adipokines in Normal Weight and Overweight Asymptomatic Adults. Acta Clin. Croat. 2020, 59, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuhara, A.; Matsuda, M.; Nishizawa, M.; Segawa, K.; Tanaka, M.; Kishimoto, K.; Matsuki, Y.; Murakami, M.; Ichisaka, T.; Murakami, H.; et al. Visfatin: A Protein Secreted by Visceral Fat That Mimics the Effects of Insulin. Science 2005, 307, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stastny, J.; Bienertova-Vasku, J.; Vasku, A. Visfatin and Its Role in Obesity Development. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2012, 6, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralisch, S.; Klein, J.; Lossner, U.; Bluher, M.; Paschke, R.; Stumvoll, M.; Fasshauer, M. Hormonal Regulation of the Novel Adipocytokine Visfatin in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 185, R1-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segawa, K.; Fukuhara, A.; Hosogai, N.; Morita, K.; Okuno, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Nakagawa, Y.; Kihara, S.; Funahashi, T.; Komuro, R.; et al. Visfatin in Adipocytes Is Upregulated by Hypoxia through HIF1alpha-Dependent Mechanism. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 349, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrouzfar, K.; Alaee, M.; Nourbakhsh, M.; Gholinejad, Z.; Golestani, A. Extracellular NAMPT/Visfatin Causes P53 Deacetylation via NAD Production and SIRT1 Activation in Breast Cancer Cells. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2017, 35, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholinejad, Z.; Kheiripour, N.; Nourbakhsh, M.; Ilbeigi, D.; Behroozfar, K.; Hesari, Z.; Golestani, A.; Shabani, M.; Einollahi, N. Extracellular NAMPT/Visfatin Induces Proliferation through ERK1/2 and AKT and Inhibits Apoptosis in Breast Cancer Cells. Peptides 2017, 92, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, A.C.; Lo, S.; Hou, M.-F.; Lee, Y.-C.; Tsai, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Liu, W.; Su, Y.-H.; Lo, Y.-H.; Wang, C.-H.; et al. Extracellular Visfatin-Promoted Malignant Behavior in Breast Cancer Is Mediated Through c-Abl and STAT3 Activation. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4478–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, A.C.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Lee, K.-T.; Chiang, H.-H.; Chen, Y.-K.; Du, J.-K.; Chen, C.-M.; Chen, M.Y.; Chen, K.-J.; Hu, S.C.-S.; et al. Reduced Tissue and Serum Resistin Expression as a Clinical Marker for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.G.; Kim, E.O.; Jeong, B.R.; Min, Y.J.; Park, J.W.; Kim, E.S.; Namgoong, I.S.; Kim, Y.I.; Lee, B.J. Visfatin Stimulates Proliferation of MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Cells 2010, 30, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miethe, C.; Torres, L.; Beristain, J.; Zamora, M.; Price, R.S. The Role of Visfatin and Resistin in an in Vitro Model of Obesity-Induced Invasive Liver Cancer. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021, 99, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, J.-Y.; Zhang, J.; Long, Y.-X.; Li, Y.-J.; Guo, X.-D.; Wei, M.-N.; Liu, W.-J. Role of Visfatin in Promoting Proliferation and Invasion of Colorectal Cancer Cells by Downregulating SDF-1/CXCR4-Mediated MiR-140-3p Expression. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 5367–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Chu, L.; Xu, Z.; Gong, J.; Deng, R.; Wang, B.; Zhou, S. Visfatin Facilitates Gastric Cancer Malignancy by Targeting Snai1 via the NF-ΚB Signaling. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2021, 40, 1646–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miethe, C.; Torres, L.; Zamora, M.; Price, R.S. Inhibition of PI3K/Akt and ERK Signaling Decreases Visfatin-Induced Invasion in Liver Cancer Cells. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2021, 42, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatemoto, K.; Hosoya, M.; Habata, Y.; Fujii, R.; Kakegawa, T.; Zou, M.X.; Kawamata, Y.; Fukusumi, S.; Hinuma, S.; Kitada, C.; et al. Isolation and Characterization of a Novel Endogenous Peptide Ligand for the Human APJ Receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 251, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinz, M.J.; Davenport, A.P. Emerging Roles of Apelin in Biology and Medicine. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 107, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castan-Laurell, I.; Dray, C.; Attané, C.; Duparc, T.; Knauf, C.; Valet, P. Apelin, Diabetes, and Obesity. Endocrine 2011, 40, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunduzova, O.; Alet, N.; Delesque-Touchard, N.; Millet, L.; Castan-Laurell, I.; Muller, C.; Dray, C.; Schaeffer, P.; Herault, J.P.; Savi, P.; et al. Apelin/APJ Signaling System: A Potential Link between Adipose Tissue and Endothelial Angiogenic Processes. Faseb J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2008, 22, 4146–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, K.; Muendlein, A.; Stark, N.; Saely, C.H.; Wabitsch, M.; Fraunberger, P.; Drexel, H. Hypoxia Induces Apelin Expression in Human Adipocytes. Horm. Metab. Res. Horm. Stoffwechs. Horm. Metab. 2011, 43, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Hou, X.; Tatemoto, K. Regulation of Apelin MRNA Expression by Insulin and Glucocorticoids in Mouse 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Regul. Pept. 2005, 132, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorli, S.C.; Le Gonidec, S.; Knibiehler, B.; Audigier, Y. Apelin Is a Potent Activator of Tumour Neoangiogenesis. Oncogene 2007, 26, 7692–7699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berta, J.; Kenessey, I.; Dobos, J.; Tovari, J.; Klepetko, W.; Ankersmit, H.J.; Hegedus, B.; Renyi-Vamos, F.; Varga, J.; Lorincz, Z.; et al. Apelin Expression in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Role in Angiogenesis and Prognosis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakowska, D.; Markocka-Mączka, K.; Szelachowski, P.; Grabowski, K. Serum Levels of Resistin, Adiponectin, and Apelin in Gastroesophageal Cancer Patients. Dis. Markers 2014, 2014, 619649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picault, F.-X.; Chaves-Almagro, C.; Projetti, F.; Prats, H.; Masri, B.; Audigier, Y. Tumour Co-Expression of Apelin and Its Receptor Is the Basis of an Autocrine Loop Involved in the Growth of Colon Adenocarcinomas. Eur. J. Cancer Oxf. Engl. 1990 2014, 50, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Greeley, G.H.; Qiu, S. Immunohistochemical Localization of Apelin in Human Normal Breast and Breast Carcinoma. J. Mol. Histol. 2008, 39, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altinkaya, S.O.; Nergiz, S.; Küçük, M.; Yüksel, H. Apelin Levels Are Higher in Obese Patients with Endometrial Cancer. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2015, 41, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farid, R.M.; Abu-Zeid, R.M.; El-Tawil, A. Emerging Role of Adipokine Apelin in Hepatic Remodelling and Initiation of Carcinogensis in Chronic Hepatitis C Patients. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 2707–2717. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berta, J.; Hoda, M.A.; Laszlo, V.; Rozsas, A.; Garay, T.; Torok, S.; Grusch, M.; Berger, W.; Paku, S.; Renyi-Vamos, F.; et al. Apelin Promotes Lymphangiogenesis and Lymph Node Metastasis. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 4426–4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, K.; Kim, Y.H.; Sung, H.J.; Li, H.Y.; Yoo, C.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, U.L.; Nam, B.H.; Kim, E.O.; et al. Hypoxia-Induced up-Regulation of Apelin Is Associated with a Poor Prognosis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, D.; Li, L.; Lu, Q.; Li, Y.; Xie, F.; Li, H.; Cao, J.; Liu, M.; Wu, D.; He, L.; et al. PAK1-Cofilin Phosphorylation Mediates Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells Migration Induced by Apelin-13. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2016, 43, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Li, F.; Wang, P.; Jia, S.; Sun, L.; Huo, H. Apelin-13 Induces MCF-7 Cell Proliferation and Invasion via Phosphorylation of ERK1/2. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 36, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Su, T.; Lv, D.; Xie, F.; Liu, W.; Cao, J.; Sheikh, I.A.; Qin, X.; Li, L.; Chen, L. ERK1/2 Mediates Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Proliferation and Autophagy Induced by Apelin-13. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2014, 46, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, P.E.; Williams, S.; Fogliano, M.; Baldini, G.; Lodish, H.F. A Novel Serum Protein Similar to C1q, Produced Exclusively in Adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 26746–26749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, E.; Liang, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. AdipoQ Is a Novel Adipose-Specific Gene Dysregulated in Obesity. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 10697–10703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Okubo, K.; Shimomura, I.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Matsubara, K. CDNA Cloning and Expression of a Novel Adipose Specific Collagen-like Factor, ApM1 (AdiPose Most Abundant Gene Transcript 1). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 221, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trayhurn, P.; Beattie, J.H. Physiological Role of Adipose Tissue: White Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine and Secretory Organ. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2001, 60, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Park, C.W. Mechanisms of Adiponectin Action: Implication of Adiponectin Receptor Agonism in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalamaga, M.; Diakopoulos, K.N.; Mantzoros, C.S. The Role of Adiponectin in Cancer: A Review of Current Evidence. Endocr. Rev. 2012, 33, 547–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Judd, R.L. Adiponectin Regulation and Function. In Comprehensive Physiology; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2018; pp. 1031–1063. ISBN 978-0-470-65071-4. [Google Scholar]
- Di Zazzo, E.; Polito, R.; Bartollino, S.; Nigro, E.; Porcile, C.; Bianco, A.; Daniele, A.; Moncharmont, B. Adiponectin as Link Factor between Adipose Tissue and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadowaki, T.; Yamauchi, T.; Kubota, N.; Hara, K.; Ueki, K.; Tobe, K. Adiponectin and Adiponectin Receptors in Insulin Resistance, Diabetes, and the Metabolic Syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1784–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Iwabu, M.; Okada-Iwabu, M.; Kadowaki, T. Adiponectin Receptors: A Review of Their Structure, Function and How They Work. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 28, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, J.; Wankell, M.; Subramaniam, V.N.; Hebbard, L.W.; Sternberg, J.; Wankell, M.; Subramaniam, V.N.; Hebbard, L.W. The Functional Roles of T-Cadherin in Mammalian Biology. Aims Mol. Sci. 2017, 4, 62–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, L.; Pellegrino, M.; De Amicis, F.; Ricchio, E.; Giordano, F.; Rizza, P.; Catalano, S.; Bonofiglio, D.; Sisci, D.; Panno, M.L.; et al. Evidences That Estrogen Receptor α Interferes with Adiponectin Effects on Breast Cancer Cell Growth. Cell Cycle Georget. Tex. 2014, 13, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illiano, M.; Nigro, E.; Sapio, L.; Caiafa, I.; Spina, A.; Scudiero, O.; Bianco, A.; Esposito, S.; Mazzeo, F.; Pedone, P.V.; et al. Adiponectin Down-Regulates CREB and Inhibits Proliferation of A549 Lung Cancer Cells. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, E.; Scudiero, O.; Sarnataro, D.; Mazzarella, G.; Sofia, M.; Bianco, A.; Daniele, A. Adiponectin Affects Lung Epithelial A549 Cell Viability Counteracting TNFα and IL-1ß Toxicity through AdipoR1. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Klionsky, D.J. At a Glance: A History of Autophagy and Cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 66, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, M.-S. Autophagy—A Key Player in Cellular and Body Metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowitz, J.D.; White, E. Autophagy and Metabolism. Science 2010, 330, 1344–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holczer, M.; Hajdú, B.; Lőrincz, T.; Szarka, A.; Bánhegyi, G.; Kapuy, O. Fine-Tuning of AMPK–ULK1–MTORC1 Regulatory Triangle Is Crucial for Autophagy Oscillation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parzych, K.R.; Klionsky, D.J. An Overview of Autophagy: Morphology, Mechanism, and Regulation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushima, N.; Komatsu, M. Autophagy: Renovation of Cells and Tissues. Cell 2011, 147, 728–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E. The Role for Autophagy in Cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Yu, J.; Bhagat, G.; Furuya, N.; Hibshoosh, H.; Troxel, A.; Rosen, J.; Eskelinen, E.-L.; Mizushima, N.; Ohsumi, Y.; et al. Promotion of Tumorigenesis by Heterozygous Disruption of the Beclin 1 Autophagy Gene. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1809–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.; Jin, S.; Yang, C.; Levine, A.J.; Heintz, N. Beclin 1, an Autophagy Gene Essential for Early Embryonic Development, Is a Haploinsufficient Tumor Suppressor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15077–15082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiuri, M.C.; Tasdemir, E.; Criollo, A.; Morselli, E.; Vicencio, J.M.; Carnuccio, R.; Kroemer, G. Control of Autophagy by Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.Y.; Chen, H.-Y.; Mathew, R.; Fan, J.; Strohecker, A.M.; Karsli-Uzunbas, G.; Kamphorst, J.J.; Chen, G.; Lemons, J.M.S.; Karantza, V.; et al. Activated Ras Requires Autophagy to Maintain Oxidative Metabolism and Tumorigenesis. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strohecker, A.M.; Guo, J.Y.; Karsli-Uzunbas, G.; Price, S.M.; Chen, G.J.; Mathew, R.; McMahon, M.; White, E. Autophagy Sustains Mitochondrial Glutamine Metabolism and Growth of BrafV600E-Driven Lung Tumors. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 1272–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, C.; Lee, S. The Roles of Autophagy in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giatromanolaki, A.; Sivridis, E.; Mendrinos, S.; Koutsopoulos, A.V.; Koukourakis, M.I. Autophagy Proteins in Prostate Cancer: Relation with Anaerobic Metabolism and Gleason Score. In Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 32, pp. 39.e11–39.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazova, R.; Camp, R.L.; Klump, V.; Siddiqui, S.F.; Amaravadi, R.K.; Pawelek, J.M. Punctate LC3B Expression Is a Common Feature of Solid Tumors and Associated with Proliferation, Metastasis and Poor Outcome. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yang, M.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q. High Expression of LC3B Is Associated with Progression and Poor Outcome in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Med. Oncol. Northwood Lond. Engl. 2013, 30, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugnoni, M.; Sancisi, V.; Manzotti, G.; Gandolfi, G.; Ciarrocchi, A. Autophagy and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition: An Intricate Interplay in Cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowers, E.E.; Sharifi, M.N.; Macleod, K.F. Autophagy in Cancer Metastasis. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Guo, L.; Wu, X.; He, C.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hao, D. Combining Radiation with Autophagy Inhibition Enhances Suppression of Tumor Growth and Angiogenesis in Esophageal Cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.-P.; Zheng, H. Inhibiting Autophagy Increases Epirubicin’s Cytotoxicity in Breast Cancer Cells. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 1610–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Chen, R.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Kong, N.; Zhang, M.; Han, W.; Lou, F.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Autophagy and Chemotherapy Resistance: A Promising Therapeutic Target for Cancer Treatment. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onorati, A.V.; Dyczynski, M.; Ojha, R.; Amaravadi, R.K. Targeting Autophagy in Cancer. Cancer 2018, 124, 3307–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, P.M.P.; de Sousa, R.W.R.; de Oliveira Ferreira, J.R.; Militão, G.C.G.; Bezerra, D.P. Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine in Antitumor Therapies Based on Autophagy-Related Mechanisms. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 168, 105582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, H.; Kuchnio, A.; Peric, A.; Moens, S.; Nys, K.; De Bock, K.; Quaegebeur, A.; Schoors, S.; Georgiadou, M.; Wouters, J.; et al. Tumor Vessel Normalization by Chloroquine Independent of Autophagy. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 190–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, T.; Kenific, C.M.; Suresh, D.; Gonzalez, H.; Shamir, E.R.; Mei, W.; Tankka, A.; Leidal, A.M.; Kalavacherla, S.; Woo, K.; et al. Autophagic Degradation of NBR1 Restricts Metastatic Outgrowth during Mammary Tumor Progression. Dev. Cell 2020, 52, 591–604.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotzomi-Ortega, I.; Rosas-Cruz, A.; Ramírez-Ramírez, D.; Reyes-Leyva, J.; Rodriguez-Sosa, M.; Aguilar-Alonso, P.; Maycotte, P. Autophagy Inhibition Induces the Secretion of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) with Autocrine and Paracrine Effects on the Promotion of Malignancy in Breast Cancer. Biology 2020, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towers, C.G.; Fitzwalter, B.E.; Regan, D.; Goodspeed, A.; Morgan, M.J.; Liu, C.-W.; Gustafson, D.L.; Thorburn, A. Cancer Cells Upregulate NRF2 Signaling to Adapt to Autophagy Inhibition. Dev. Cell 2019, 50, 690–703.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Yang, F.; Fu, R.; Li, X.; French, R.; Mose, E.; Pu, X.; Trinh, B.; Kumar, A.; Liu, J.; et al. Cancer Cells Escape Autophagy Inhibition via NRF2-Induced Macropinocytosis. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 678–693.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, P.-H. Autophagy Induction: A Critical Event for the Modulation of Cell Death/Survival and Inflammatory Responses by Adipokines. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2018, 41, 1062–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakol, S.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Deng, S.; Azarian, M.; Abdoli, A.; Motavaf, M.; Poormoghadam, D.; Khanbabaei, H.; Ghasemipour Afshar, E.; Mandegary, A.; et al. Autophagy Modulators: Mechanistic Aspects and Drug Delivery Systems. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stacchiotti, A.; Corsetti, G. Natural Compounds and Autophagy: Allies against Neurodegeneration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 555409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.-Y.; Su, J.-H.; Chiu, C.-F.; Lin, W.-Y.; Hu, J.-L.; Feng, C.-H.; Shu, C.-W.; Weng, J.-R. Antitumor Effects of a Sesquiterpene Derivative from Marine Sponge in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Hu, Y.-L.; Wang, H. Ursolic Acid Inhibits Breast Cancer Growth by Inhibiting Proliferation, Inducing Autophagy and Apoptosis, and Suppressing Inflammatory Responses via the PI3K/AKT and NF-ΚB Signaling Pathways in Vitro. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 3623–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Sun, D.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, K.; Wang, L.; Huang, J.; Chen, L. Growth Inhibitory Effect of Paratocarpin E, a Prenylated Chalcone Isolated from Euphorbia Humifusa Wild., by Induction of Autophagy and Apoptosis in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Bioorganic Chem. 2016, 69, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji-Kawata, S.; Sumpter, R.; Leveno, M.; Campbell, G.R.; Zou, Z.; Kinch, L.; Wilkins, A.D.; Sun, Q.; Pallauf, K.; MacDuff, D.; et al. Identification of a Candidate Therapeutic Autophagy-Inducing Peptide. Nature 2013, 494, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bari, M.A.A.; Ito, Y.; Ahmed, S.; Radwan, N.; Ahmed, H.S.; Eid, N. Targeting Autophagy with Natural Products as a Potential Therapeutic Approach for Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulcahy Levy, J.M.; Thorburn, A. Autophagy in Cancer: Moving from Understanding Mechanism to Improving Therapy Responses in Patients. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 843–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, M.; Cheng, F.; Chen, S.; Zheng, Q.; Sun, Y.; Chen, L. The Marine Natural Product, Dicitrinone B, Induces Apoptosis through Autophagy Blockade in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 50, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.A.; Mariño, G.; BenYounès, A.; Shen, S.; Harper, F.; Maiuri, M.C.; Kroemer, G. Neuroendocrine Regulation of Autophagy by Leptin. Cell Cycle Georget. Tex. 2011, 10, 2917–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; He, J.; Liu, H.; Lin, P.; Wan, X.; Navone, N.M.; Tong, Q.; Kwak, L.W.; Orlowski, R.Z.; et al. Mature Adipocytes in Bone Marrow Protect Myeloma Cells against Chemotherapy through Autophagy Activation. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 34329–34341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, S.; Kim, M.J.; Hong, J.T.; Kim, S.H.; Sohn, D.-H.; Lee, S.H.; Song, K.; Choi, D.Y.; Lee, E.S.; Park, P.-H. Autophagy Induction by Leptin Contributes to Suppression of Apoptosis in Cancer Cells and Xenograft Model: Involvement of P53/FoxO3A Axis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 7166–7181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, P.K.; Choi, D.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Hong, J.T.; Kwon, T.K.; Jeong, J.H.; Park, P.-H. Estrogen Receptor Signaling Mediates Leptin-Induced Growth of Breast Cancer Cells via Autophagy Induction. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 109417–109435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Miranda, A.; Solano-Alcalá, K.A.; Montes-Alvarado, J.B.; Rosas-Cruz, A.; Reyes-Leyva, J.; Navarro-Tito, N.; Maycotte, P.; Castañeda-Saucedo, E. Autophagy Mediates Leptin-Induced Migration and ERK Activation in Breast Cancer Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 644851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.; Tilija Pun, N.; Park, P. Autophagy Activation and SREBP-1 Induction Contribute to Fatty Acid Metabolic Reprogramming by Leptin in Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 657–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shi, A.; Song, D.; Han, B.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, L.; Liu, D.; Fan, Z. Resistin Confers Resistance to Doxorubicin-Induced Apoptosis in Human Breast Cancer Cells through Autophagy Induction. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 574–583. [Google Scholar]
- Habeeb, B.S.; Kitayama, J.; Nagawa, H. Adiponectin Supports Cell Survival in Glucose Deprivation through Enhancement of Autophagic Response in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, A.; Lam, K.S.-L.; Wong, N.-S.; Chen, J.; Shepherd, P.R.; Wang, Y. Cholesterol-Induced Mammary Tumorigenesis Is Enhanced by Adiponectin Deficiency: Role of LDL Receptor Upregulation. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 1804–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, S.; Park, P.-H. Regulatory Role of Autophagy in Globular Adiponectin-Induced Apoptosis in Cancer Cells. Biomol. Ther. 2014, 22, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chung, S.J.; Nagaraju, G.P.; Nagalingam, A.; Muniraj, N.; Kuppusamy, P.; Walker, A.; Woo, J.; Győrffy, B.; Gabrielson, E.; Saxena, N.K.; et al. ADIPOQ/Adiponectin Induces Cytotoxic Autophagy in Breast Cancer Cells through STK11/LKB1-Mediated Activation of the AMPK-ULK1 Axis. Autophagy 2017, 13, 1386–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lv, S.-Y.; Ye, W.; Zhang, L. Apelin/APJ System and Cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 457, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Luo, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Huang, S.; Tang, M.; Yang, L.; Lu, L.; et al. Apelin/APJ Signaling Activates Autophagy to Promote Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Migration. Life Sci. 2021, 281, 119763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cea, M.; Cagnetta, A.; Fulciniti, M.; Tai, Y.-T.; Hideshima, T.; Chauhan, D.; Roccaro, A.; Sacco, A.; Calimeri, T.; Cottini, F.; et al. Targeting NAD+ Salvage Pathway Induces Autophagy in Multiple Myeloma Cells via MTORC1 and Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase (ERK1/2) Inhibition. Blood 2012, 120, 3519–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, T.; Ahn, D.-G.; Liu, R.-Z.; Pringle, E.; Martell, E.; Dai, C.; Nunokawa, A.; Kwak, M.; Clements, D.; Murphy, J.P.; et al. The NAD+ Salvage Pathway Modulates Cancer Cell Viability via P73. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Kirtane, A.R.; Kiyokawa, J.; Nagashima, H.; Lopes, A.; Tirmizi, Z.A.; Lee, C.K.; Traverso, G.; Cahill, D.P.; Wakimoto, H. Local Targeting of NAD+ Salvage Pathway Alters the Immune Tumor Microenvironment and Enhances Checkpoint Immunotherapy in Glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 5024–5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Q.-J.; Lu, Y.-B.; Wu, M.; Wei, E.-Q.; Zhang, W.-P. Nicotinamide Phosphoribosyltransferase Inhibitor APO866 Induces C6 Glioblastoma Cell Death via Autophagy. Die Pharmazie 2015, 70, 650–655. [Google Scholar]
- Dower, C.M.; Wills, C.A.; Frisch, S.M.; Wang, H.-G. Mechanisms and Context Underlying the Role of Autophagy in Cancer Metastasis. Autophagy 2018, 14, 1110–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Sanchez, G.; Cotzomi-Ortega, I.; Pazos-Salazar, N.G.; Reyes-Leyva, J.; Maycotte, P. Autophagy and Its Relationship to Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition: When Autophagy Inhibition for Cancer Therapy Turns Counterproductive. Biology 2019, 8, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez-Cruz, J.C.; Okoniewski, M.; Ramírez, M.; Ortuño-Pineda, C.; Navarro-Tito, N.; Castañeda-Saucedo, E. Chronic Leptin Treatment Induces Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in MCF10A Mammary Epithelial Cells. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2022, 27, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.-H.; Lee, M. Autophagy Inhibition in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes Breaks the Crosstalk with Tumor Cells by Suppression of Adipokine Production. Anim. Cells Syst. 2019, 24, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez, C.E.; Rodrigues, V.S.; Gomes, F.S.; de Moura, R.F.; Victorio, S.C.; Bombassaro, B.; Chaim, E.A.; Pareja, J.C.; Geloneze, B.; Velloso, L.A.; et al. Defective Regulation of Adipose Tissue Autophagy in Obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo-San Pedro, J.M.; Sica, V.; Martins, I.; Pol, J.; Loos, F.; Maiuri, M.C.; Durand, S.; Bossut, N.; Aprahamian, F.; Anagnostopoulos, G.; et al. Acyl-CoA-Binding Protein Is a Lipogenic Factor That Triggers Food Intake and Obesity. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 754–767.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedro, J.M.B.-S.; Sica, V.; Madeo, F.; Kroemer, G. Acyl-CoA-Binding Protein (ACBP): The Elusive ‘hunger Factor’ Linking Autophagy to Food Intake. Cell Stress 2019, 3, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denton, D.; Kumar, S. Autophagy-Dependent Cell Death. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Autophagy Inducer/ Inhibitor | Target | Drug(s) | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinically available inducers | mTOR inhibitors | Rapamycin | [134] |
| Everolimus | |||
| Temsirolimus | |||
| PI3K/mTOR inhibitors | Dactolisib | ||
| AMPK activators | Metformin | ||
| Simvastatin | |||
| Lipid metabolism | Carbamazepine | ||
| Inducers with potential clinical relevance | Sirtuins | Polyphenols | [135] |
| (resveratrol) | |||
| Unknown | Phenolic oleosides | [135,136,137,138] | |
| Caffeine | |||
| Alkaloids | |||
| Terpenes and terpenoids | |||
| Ilimaquinone | |||
| Paratocarpin E | |||
| Beclin 1/Vps34 | Tat-beclin-1 | [139] | |
| TFEB | Trehalose | [135,140] | |
| Curcumin | |||
| AMPK activators | Polyphenols | [140] | |
| Epigallocatechin gallate | |||
| Kaempferol | |||
| Quercetin | |||
| Clinically availableinhibitors | Lysosomotropic agents (antimalarials) | Chloroquine | [134] |
| Hydroxychloroquine | |||
| Inhibitors with potential clinical relevance | Lysosomotropic agents | Lys05 | [141] |
| Vps34 inhibitors | 3-MA | [134] | |
| Wortmannin | |||
| ULK1/2 inhibitor | SBI-0206965 | ||
| MRT67307 | |||
| MRT68921 | |||
| USP13 and USP10 inhibitor | Spautin-1 | ||
| ATG4B inhibitor | NSC185058 | ||
| Microtubules | Vinca alkaloids | [140] | |
| Colchicine | |||
| Autophagosomal acidification | Azithromycin | ||
| Clarithromycin | |||
| Matrine | |||
| Unknown | Lucanthone | [140,142] | |
| Coibamide A | |||
| Dicitrinone B | |||
| ATP synthase inhibitor | Bafilomycin A | [141] | |
| P62 | Verteporfin | [134] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Miranda, A.; Garcia-Hernandez, A.; Castañeda-Saucedo, E.; Navarro-Tito, N.; Maycotte, P. Adipokines as Regulators of Autophagy in Obesity-Linked Cancer. Cells 2022, 11, 3230. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11203230
García-Miranda A, Garcia-Hernandez A, Castañeda-Saucedo E, Navarro-Tito N, Maycotte P. Adipokines as Regulators of Autophagy in Obesity-Linked Cancer. Cells. 2022; 11(20):3230. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11203230
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Miranda, Alin, Alejandra Garcia-Hernandez, Eduardo Castañeda-Saucedo, Napoleon Navarro-Tito, and Paola Maycotte. 2022. "Adipokines as Regulators of Autophagy in Obesity-Linked Cancer" Cells 11, no. 20: 3230. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11203230
APA StyleGarcía-Miranda, A., Garcia-Hernandez, A., Castañeda-Saucedo, E., Navarro-Tito, N., & Maycotte, P. (2022). Adipokines as Regulators of Autophagy in Obesity-Linked Cancer. Cells, 11(20), 3230. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11203230








