Differential Levels of Tryptophan–Kynurenine Pathway Metabolites in the Hippocampus, Anterior Temporal Lobe, and Neocortex in an Animal Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Epilepsy Model Development
2.2. Tissue Preparation for Histology
2.3. Estimation of Metabolites
2.4. In Vitro Electrophysiology
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Histopathological Features of Pilocarpine (TLE) Treated Rats
3.2. The Levels of Tryptophan–Kynurenine Pathway Metabolites and Enzyme Activities Were Altered in Acute Model of TLE
3.3. Spontaneous Glutamatergic Activity Was Higher in the Hippocampus and ATL but Not in Frontal Neocortex in Acute Model of TLE
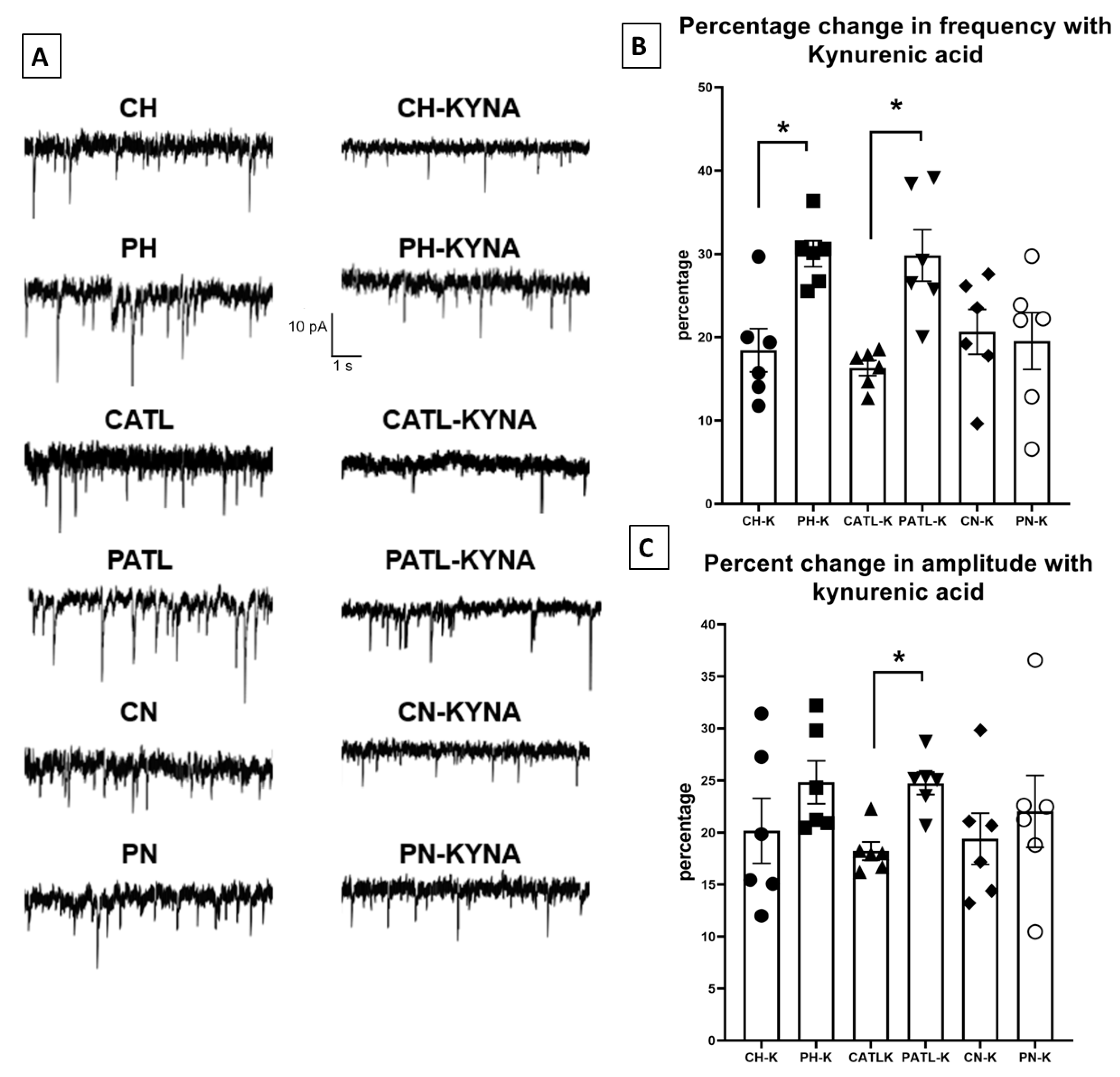
3.4. Exogenously Applied Kynurenic Acid Suppressed the Spontaneous Glutamatergic Activity in Acute Model of TLE
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perkins, M.; Stone, T. Actions of excitatory amino acids and kynurenic acid in the primate hippocampus: A preliminary study. Neurosci. Lett. 1984, 52, 335–340. [Google Scholar]
- Kessler, M.; Terramani, T.; Lynch, G.; Baudry, M. A glycine site associated with NMDA receptors: Characterisation and identification of a new class of antagonist. J. Neurochem. 1989, 52, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarcz, R.; Bruno, J.; Muchowski, P.; Wu, H. Kynurenines in the mammalian brain: When physiology meets pathology. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vécsei, L.; Szalardy, L.; Fülöp, F.; Toldi, J. Kynurenines in the CNS: Recent advances and new questions. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 64–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cull-Candy, S.; Brickley, S.; Farrant, M. NMDA receptor subunits: Diversity, development and disease. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2001, 11, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenedo, R.; Pittaluga, A.; Cozzi, A.; Attucci, S.; Galli, A.; Raiteriet, M.; Moroni, F. Presynaptic kynurenate-sensitive receptors inhibit glutamate release. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2001, 13, 2141–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, R.M.; Zielinski, E.; Dekundy, A.; van Luijtelaar, G.; Turski, W. Deficit of endogenous kynurenic acid in the frontal cortex of rats with a genetic form of absence epilepsy. Pol. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 55, 741–746. [Google Scholar]
- Szyndler, J.; Maciejak, P.; Turzynska, D.; Sobolewska, A.; Walkowiak, J.; Płaznik, A. The effects of electrical hippocampal kindling of seizures on amino acids and kynurenic acid concentrations in brain structures. J. Neural Transm. 2012, 119, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maciejak, P.; Szyndler, J.; Turzynska, D.; Sobolewska, A.; Taracha, E.; Skorzewska, A.; Lehner, M.; Bidzinski, A.; Płaznik, A. Time course of changes in the concentration of kynurenic acid in the brain of pentylenetetrazol-kindled rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2008, 78, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curia, G.; Lucchi, C.; Vinet, J.; Gualtieri, F.; Marinelli, C.; Torsello, A.; Costantino, L.; Biagini, G. Pathophysiogenesis of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: Is prevention of damage antiepileptogenic? Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 663–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldi, M.; Avoli, M.; de Villers-Sidani, E. Resting state networks in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 2048–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, J.; Banerjee Dixit, A.; Tripathi, M.; Sarkar, C.; Gupta, Y.K.; Chandra, P.S. Enhanced endogenous activation of NMDA receptors in pyramidal neurons of hippocampal tissues from patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: A mechanism of hyper excitation. Epilepsy Res. 2015, 117, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, J.; Banerjee Dixit, A.; Srivastava, A.; Ramanujam, B.; Kakkar, A.; Sarkar, C.; Tripathi, M.; Chandra, P.S. Altered glutamatergic tone reveals two distinct resting state networks at the cellular level in hippocampal sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, V.; Dey, S.; Dixit, A.B.; Tripathi, M.; Chandra, P.S.; Banerjee, J. Differential glutamate receptor expression and function in the hippocampus, anterior temporal lobe and neocortex in a pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Exp. Neurol. 2022, 347, 113916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, S.; Banerjee Dixit, A.; Tripathi, M.; Doddamani, R.S.; Sharma, M.C.; Lalwani, S.; Chandra, P.S.; Banerjee, J. Altered hippocampal kynurenine pathway metabolism contributes to hyperexcitability in human mesial temporal lobe epilepsy–hippocampal sclerosis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 3959–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- L’evesque, M.; Avoli, M.; Bernard, C. Animal models of temporal lobe epilepsy following systemic chemoconvulsant administration. J. Neurosci. Methods 2016, 260, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turski, W.A.; Cavalheiro, E.A.; Bortolotto, Z.A.; Mello, L.M.; Schwarz, M.; Turski, L. Seizures produced by pilocarpine in mice: A behavioral, electroencephalographic and morphological analysis. Brain Res. 1984, 321, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racine, R.J. Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1972, 32, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, Y.; Fujii, T.; Suzuki, T.; Yamahatsu, K.; Kawahara, K.; Teduka, K.; Kawamoto, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Ishiwata, T.; Naito, Z. Comparison of fixation methods for preservation of morphology, RNAs, and proteins from paraffin- embedded human cancer cell-implanted mouse models. J. Histochem. Cytochem. Off. J. Histochem. Soc. 2011, 59, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabo, R.; Kozik, K.; Milanowski, M.; Hernes, S.; Slettan, A.; Haugen, M.; Ye, S.; Blomhoff, R.; Mansoor, M.A. A simple high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method for the measurement of pyridoxal-5-phosphate and 4-pyridoxic acid in human plasma. Clin. Chim. Acta 2014, 433, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.D.; Luo, X.B.; Pi, L.G.; Tang, A.G. Simultaneous determination of kynurenine and kynurenic acid concentrations in human serum by HPLC with dual wavelengths fluorescence detection. Clin. Chim. Acta 2008, 395, 178–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, N.; Hu, J.; Hong, Y.; Ding, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, Z.; Xie, W. Indoleamine-2,3-Dioxygenase 1 Deficiency Suppresses Seizures in Epilepsy. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 638854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, J.; Dey, S.; Dixit, A.B.; Tripathi, M.; Doddamani, R.; Sharma, M.C.; Chandra, P.S. α7 nicotinic receptors contributes to glutamatergic activity in the hippocampus of patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis (MTLE-HS). J. Neural Transm. 2020, 127, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.; Soares, F.; de Mello, N.; Nunes, J.; Cajado, A.; de Brito, D.; de Cordova, F.; da Cunha, R.; Walz, R.; Leal, R. Time-dependent modulation of AMPA receptor phosphorylation and mRNA expression of NMDA receptors and glial glutamate transporters in the rat hippocampus and cerebral cortex in a pilocarpine model of epilepsy. Exp. Brain Res. 2013, 226, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Moura, J.; Tirapelli, D.P.; Neder, L.; Saggioro, F.P.; Sakamoto, A.C.; Velasco, T.R.; Panepucci, R.A.; Leite, J.P.; Assirati, J.A., Jr.; Colli, B.O.; et al. Amygdala gene expression of NMDA and GABA(A) receptors in patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Hippocampus 2012, 22, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meurs, A.; Clinckers, R.; Ebinger, G.; Michotte, Y.; Smolders, I. Seizure activity and changes in hippocampal extracellular glutamate, GABA, dopamine and serotonin. Epilepsy Res. 2008, 78, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | Control Hippocampus (10) | Control Hippocampus-KYNA (10) |
| Frequency (Hz) | 0.68 ± 0.04 | 0.55 ± 0.07 a |
| Amplitude (pA) | 12.05 ± 0.16 | 10.02 ± 0.38 a |
| Rise time (ms) | 1.9 ± 0.7 | 2.0 ± 0.6 |
| Decay time constant (τd, ms) | 10.6 ± 1.2 | 9.9 ± 1.7 |
| Pilocarpine Hippocampus (10) | Pilocarpine Hippocampus-KYNA (10) | |
| Frequency (Hz) | 0.98 ± 0.04 a | 0.68 ± 0.05 b |
| Amplitude (pA) | 14.70 ± 0.92 a | 11.06 ± 1.13 b |
| Rise time (ms) | 2.0 ± 0.9 | 2.8 ± 0.5 |
| Decay time constant (τd, ms) | 11.4 ± 2.2 | 10.9 ± 0.8 |
| Control ATL (10) | Control ATL-KYNA (10) | |
| Frequency (Hz) | 0.67 ± 0.04 | 0.56 ± 0.03 c |
| Amplitude (pA) | 12.51 ± 0.6 | 10.23 ± 0.62 c |
| Rise time (ms) | 3.1 ± 0.3 | 2.9 ± 0.5 |
| Decay time constant (τd, ms) | 12.3 ± 3.2 | 11.5 ± 2.8 |
| Pilocarpine ATL (10) | Pilocarpine ATL-KYNA (10) | |
| Frequency (Hz) | 1.10 ± 0.09 c | 0.77 ± 0.05 d |
| Amplitude (pA) | 16.16 ± 1.04 c | 12.17 ± 0.99 d |
| Rise time (ms) | 2.7 ± 0.3 | 2.3 ± 0.9 |
| Decay time constant (τd, ms) | 13.5 ± 2.6 | 12.9 ± 3.1 |
| Control Neocortex (10) | Control Neocortex-KYNA (10) | |
| Frequency (Hz) | 0.70 ± 0.16 | 0.54 ± 0.02 e |
| Amplitude (pA) | 12.53 ± 1.15 | 10.13 ± 1.5 e |
| Rise time (ms) | 2.9 ± 0.7 | 2.7 ± 0.4 |
| Decay time constant (τd, ms) | 11.7 ± 3.4 | 11.5 ± 2.0 |
| Pilocarpine Neocortex (10) | Pilocarpine Neocortex KYNA (10) | |
| Frequency (Hz) | 0.74 ± 0.12 | 0.52 ± 0.06 f |
| Amplitude (pA) | 12.17 ± 0.41 | 9.5 ± 1.17 f |
| Rise time (ms) | 2.7 ± 0.6 | 2.3 ± 0.9 |
| Decay time constant (τd, ms) | 12.6 ± 0.8 | 11.4 ± 0.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dey, S.; Dubey, V.; Dixit, A.B.; Tripathi, M.; Chandra, P.S.; Banerjee, J. Differential Levels of Tryptophan–Kynurenine Pathway Metabolites in the Hippocampus, Anterior Temporal Lobe, and Neocortex in an Animal Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Cells 2022, 11, 3560. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11223560
Dey S, Dubey V, Dixit AB, Tripathi M, Chandra PS, Banerjee J. Differential Levels of Tryptophan–Kynurenine Pathway Metabolites in the Hippocampus, Anterior Temporal Lobe, and Neocortex in an Animal Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Cells. 2022; 11(22):3560. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11223560
Chicago/Turabian StyleDey, Soumil, Vivek Dubey, Aparna Banerjee Dixit, Manjari Tripathi, Poodipedi Sarat Chandra, and Jyotirmoy Banerjee. 2022. "Differential Levels of Tryptophan–Kynurenine Pathway Metabolites in the Hippocampus, Anterior Temporal Lobe, and Neocortex in an Animal Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy" Cells 11, no. 22: 3560. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11223560
APA StyleDey, S., Dubey, V., Dixit, A. B., Tripathi, M., Chandra, P. S., & Banerjee, J. (2022). Differential Levels of Tryptophan–Kynurenine Pathway Metabolites in the Hippocampus, Anterior Temporal Lobe, and Neocortex in an Animal Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Cells, 11(22), 3560. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11223560






