Increased Lipid Peroxidation and Lowered Antioxidant Defenses Predict Methamphetamine Induced Psychosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Clinical Assessments
2.3. Biomarkers Assays
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cluster and Factor Analysis
3.2. Sociodemographic Data and MA Features in the Study Groups
3.3. Psychotic Symptoms Scores among Study Groups
3.4. Serum Biomarkers Levels among the Study Groups
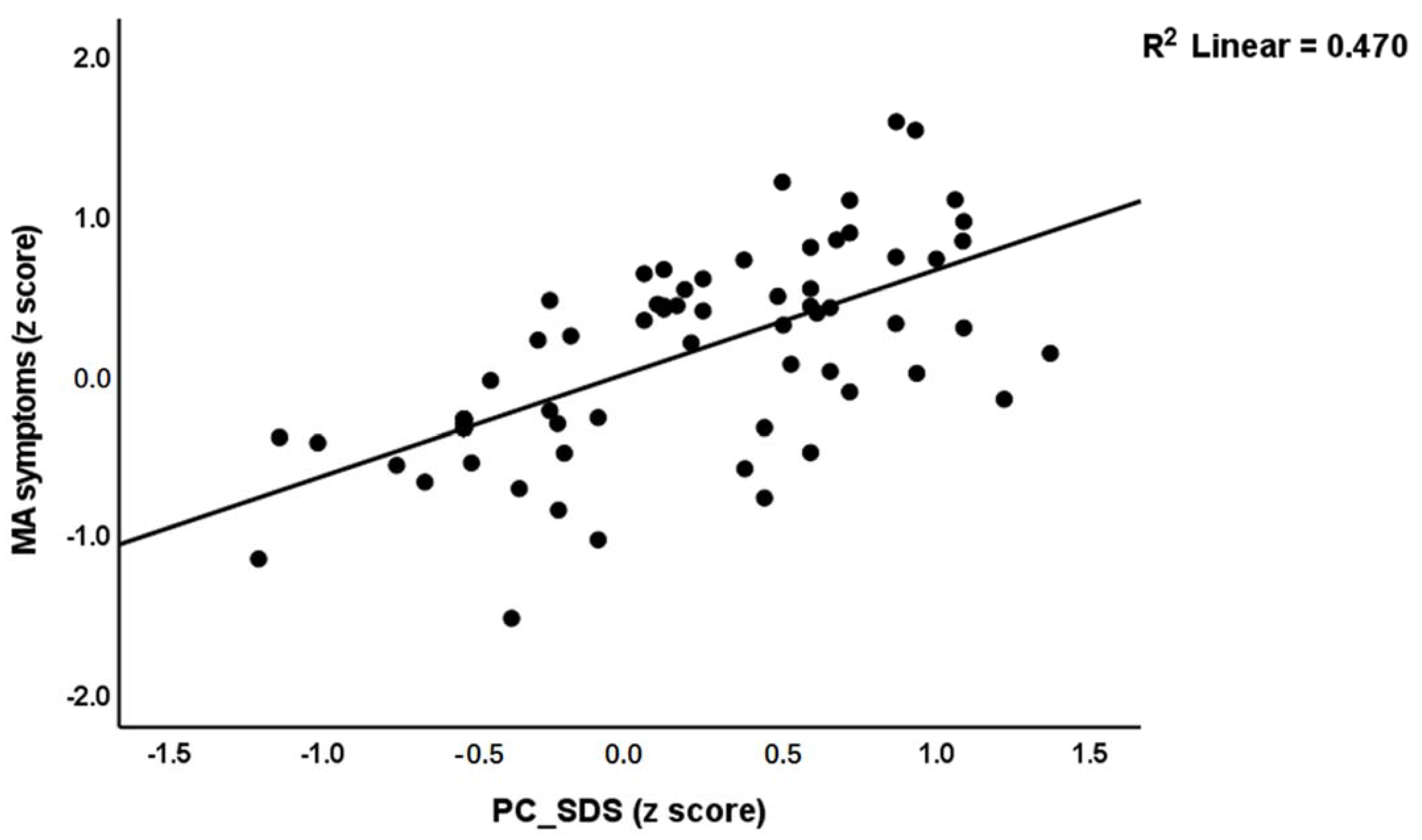
3.5. Intercorrelation between PC_SDS, PC_MA, Biomarkers, and Psychotic Symptoms
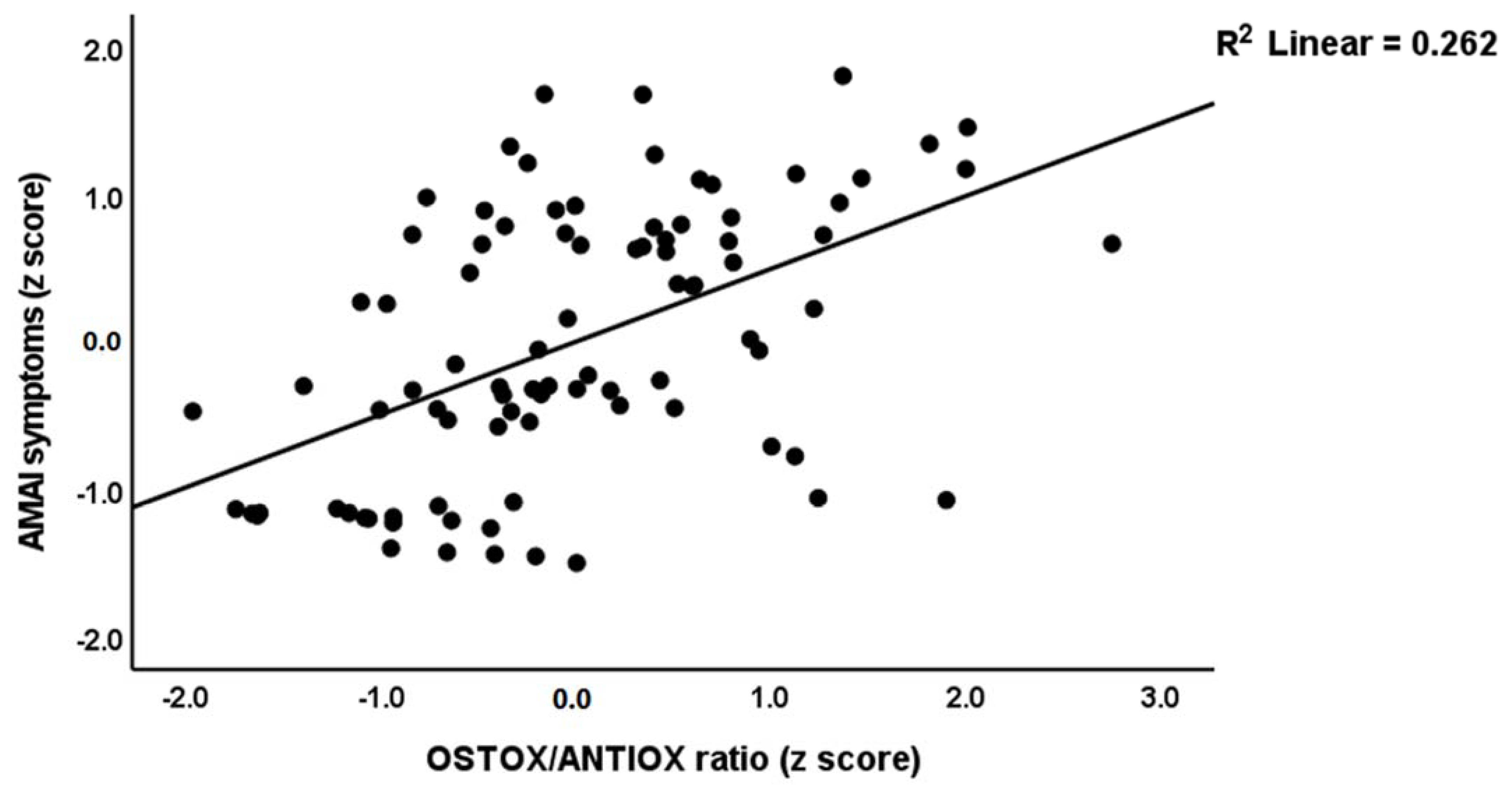
3.6. Prediction of MIP Symptoms and the OSTOX/ANTIOX Ratio
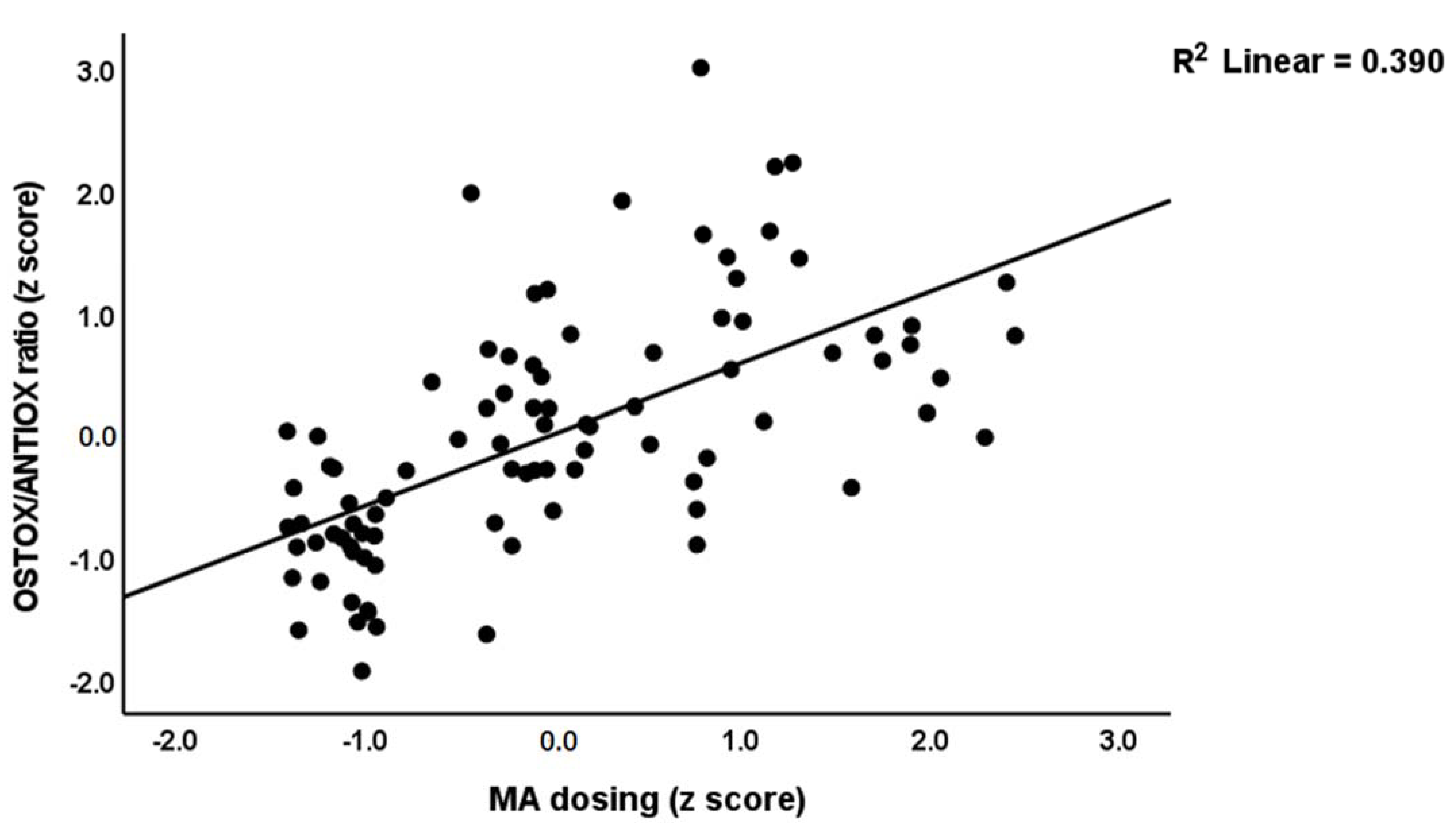
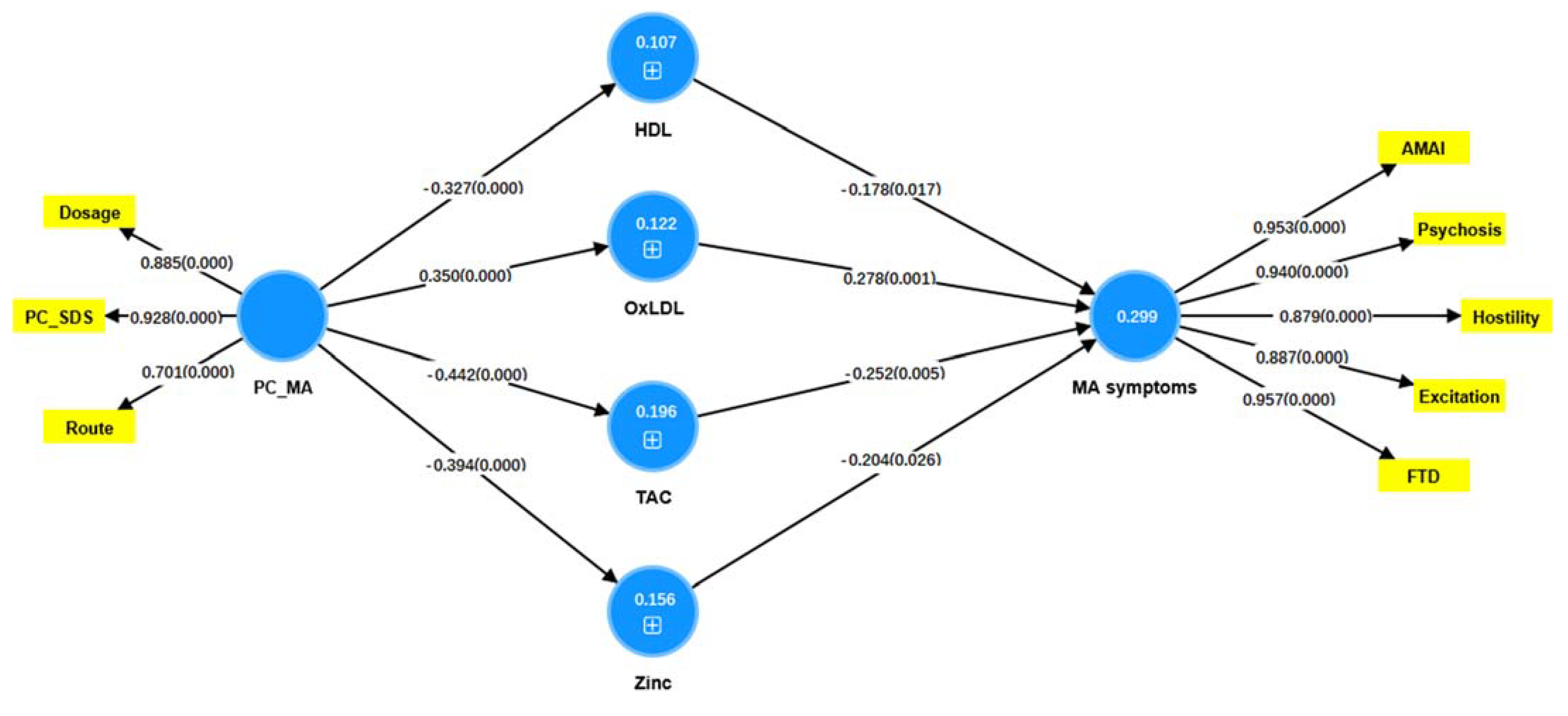
3.7. Results of PLS Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Aspects of MA Intoxication and MIP
4.2. MA Dependence, OSTOX and ANTIOX
4.3. MA Dependence, NOS Biomarkers and MIP
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Jones, C.M.; Houry, D.; Han, B.; Baldwin, G.; Vivolo-Kantor, A.; Compton, W.M. Methamphetamine use in the United States: Epidemiological update and implications for prevention, treatment, and harm reduction. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2022, 1508, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogarth, S.; Manning, E.; van den Buuse, M. Chronic Methamphetamine and Psychosis Pathways. In Handbook of Substance Misuse and Addictions: From Biology to Public Health; Patel, V.B., Preedy, V.R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Strickland, J.C.; Stoops, W.W.; Dunn, K.E.; Smith, K.E.; Havens, J.R. The continued rise of methamphetamine use among people who use heroin in the United States. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2021, 225, 108750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, K.; Dryden, D.M.; Liang, Y.; Friesen, C.; O’Gorman, K.; Durec, T.; Wild, T.C.; Klassen, T.P. Risk factors for methamphetamine use in youth: A systematic review. BMC Pediatr. 2008, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoptaw, S.; Li, M.J.; Javanbakht, M.; Ragsdale, A.; Goodman-Meza, D.; Gorbach, P.M. Frequency of reported methamphetamine use linked to prevalence of clinical conditions, sexual risk behaviors, and social adversity in diverse men who have sex with men in Los Angeles. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2022, 232, 109320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.K.; Larance, B.; Manning, V.; Hides, L.; Baker, A.L.; Deane, F.P.; Shakeshaft, A.; Raftery, D.; Kelly, P.J. Online SMART Recovery mutual support groups: Characteristics and experience of adults seeking treatment for methamphetamine compared to those seeking treatment for other addictive behaviours. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2022; Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIDA. What Are the Long-Term Effects of Methamphetamine Misuse? Available online: https://nida.nih.gov/publications/research-reports/methamphetamine/what-are-long-term-effects-methamphetamine-misuse (accessed on 19 September 2022).
- Meredith, C.W.; Jaffe, C.; Ang-Lee, K.; Saxon, A.J. Implications of chronic methamphetamine use: A literature review. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 2005, 13, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKetin, R.; Lubman, D.I.; Najman, J.M.; Dawe, S.; Butterworth, P.; Baker, A.L. Does methamphetamine use increase violent behaviour? Evidence from a prospective longitudinal study. Addiction 2014, 109, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harro, J. Neuropsychiatric Adverse Effects of Amphetamine and Methamphetamine. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2015, 120, 179–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wearne, T.A.; Cornish, J.L. A Comparison of Methamphetamine-Induced Psychosis and Schizophrenia: A Review of Positive, Negative, and Cognitive Symptomatology. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, A.C.; Aupperle, R.L.; Stewart, J.L. Dark Times: The Role of Negative Reinforcement in Methamphetamine Addiction. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasner-Edwards, S.; Mooney, L.J.; Marinelli-Casey, P.; Hillhouse, M.; Ang, A.; Rawson, R. Clinical course and outcomes of methamphetamine-dependent adults with psychosis. J. Subst. Abuse Treat. 2008, 35, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasner-Edwards, S.; Mooney, L.J.; Marinelli-Casey, P.; Hillhouse, M.; Ang, A.; Rawson, R.A. Psychopathology in methamphetamine-dependent adults 3 years after treatment. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2010, 29, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKetin, R. Methamphetamine psychosis: Insights from the past. Addiction 2018, 113, 1522–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zweben, J.E.; Cohen, J.B.; Christian, D.; Galloway, G.P.; Salinardi, M.; Parent, D.; Iguchi, M. Psychiatric symptoms in methamphetamine users. Am. J. Addict. 2004, 13, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKetin, R.; McLaren, J.; Lubman, D.I.; Hides, L. The prevalence of psychotic symptoms among methamphetamine users. Addiction 2006, 101, 1473–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salo, R.; Fassbender, C.; Iosif, A.-M.; Ursu, S.; Leamon, M.H.; Carter, C. Predictors of methamphetamine psychosis: History of ADHD-relevant childhood behaviors and drug exposure. Psychiatry Res. 2013, 210, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lecomte, T.; Dumais, A.; Dugre, J.R.; Potvin, S. The prevalence of substance-induced psychotic disorder in methamphetamine misusers: A meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 268, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batki, S.L.; Harris, D.S. Quantitative drug levels in stimulant psychosis: Relationship to symptom severity, catecholamines and hyperkinesia. Am. J. Addict. 2004, 13, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunogiri, S.; Foulds, J.A.; McKetin, R.; Lubman, D.I. A systematic review of risk factors for methamphetamine-associated psychosis. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2018, 52, 514–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, M.; Okahisa, Y.; Aleksic, B.; Won, M.; Kondo, N.; Naruse, N.; Aoyama-Uehara, K.; Sora, I.; Iyo, M.; Hashimoto, R. Evidence for shared genetic risk between methamphetamine-induced psychosis and schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 1864–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.; Song, Z.; Xu, P.; Su, H.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, M.; Liu, D. A comparison study of working memory deficits between patients with methamphetamine-associated psychosis and patients with schizophrenia. Shanghai Arch. Psychiatry 2018, 30, 168. [Google Scholar]
- Kalayasiri, R.; Kraijak, K.; Mutirangura, A.; Maes, M. Paranoid schizophrenia and methamphetamine-induced paranoia are both characterized by a similar LINE-1 partial methylation profile, which is more pronounced in paranoid schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2019, 208, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalayasiri, R.; Kraijak, K.; Maes, M.; Mutirangura, A. Methamphetamine (MA) Use Induces Specific Changes in LINE-1 Partial Methylation Patterns, Which Are Associated with MA-Induced Paranoia: A Multivariate and Neuronal Network Study. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 4258–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, M.; Sirivichayakul, S.; Matsumoto, A.K.; Maes, A.; Michelin, A.P.; de Oliveira Semeão, L.; de Lima Pedrão, J.V.; Moreira, E.G.; Barbosa, D.S.; Geffard, M.; et al. Increased Levels of Plasma Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Mediate Schizophrenia Symptom Dimensions and Neurocognitive Impairments and Are Inversely Associated with Natural IgM Directed to Malondialdehyde and Paraoxonase 1 Activity. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 2333–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, J.H.; Stein, D.J.; Howells, F.M. The neurobiology of methamphetamine induced psychosis. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermakov, E.A.; Dmitrieva, E.M.; Parshukova, D.A.; Kazantseva, D.V.; Vasilieva, A.R.; Smirnova, L.P. Oxidative Stress-Related Mechanisms in Schizophrenia Pathogenesis and New Treatment Perspectives. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 8881770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuenod, M.; Steullet, P.; Cabungcal, J.-H.; Dwir, D.; Khadimallah, I.; Klauser, P.; Conus, P.; Do, K.Q. Caught in vicious circles: A perspective on dynamic feed-forward loops driving oxidative stress in schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 1886–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limanaqi, F.; Gambardella, S.; Biagioni, F.; Busceti, C.L.; Fornai, F. Epigenetic effects induced by methamphetamine and methamphetamine-dependent oxidative stress. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 4982453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzali, S.; Fadaei, F.; Oftadeh, A.; Ranjbar, A. Salivary Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in Methamphetamine Users: A Case-Control Study. Nov. Clin. Med. 2022, 1, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Maes, M.; Sirivichayakul, S.; Matsumoto, A.K.; Michelin, A.P.; de Oliveira Semeão, L.; de Lima Pedrão, J.V.; Moreira, E.G.; Barbosa, D.S.; Carvalho, A.F.; Solmi, M.; et al. Lowered Antioxidant Defenses and Increased Oxidative Toxicity Are Hallmarks of Deficit Schizophrenia: A Nomothetic Network Psychiatry Approach. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 4578–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hakeim, H.K.; Almulla, A.F.; Maes, M. The Neuroimmune and Neurotoxic Fingerprint of Major Neurocognitive Psychosis or Deficit Schizophrenia: A Supervised Machine Learning Study. Neurotox. Res. 2020, 37, 753–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roomruangwong, C.; Noto, C.; Kanchanatawan, B.; Anderson, G.; Kubera, M.; Carvalho, A.F.; Maes, M. The Role of Aberrations in the Immune-Inflammatory Response System (IRS) and the Compensatory Immune-Regulatory Reflex System (CIRS) in Different Phenotypes of Schizophrenia: The IRS-CIRS Theory of Schizophrenia. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 778–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boll, K.M.; Noto, C.; Bonifácio, K.L.; Bortolasci, C.C.; Gadelha, A.; Bressan, R.A.; Barbosa, D.S.; Maes, M.; Moreira, E.G. Oxidative and nitrosative stress biomarkers in chronic schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2017, 253, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noto, C.; Maes, M.; Ota, V.K.; Teixeira, A.L.; Bressan, R.A.; Gadelha, A.; Brietzke, E. High predictive value of immune-inflammatory biomarkers for schizophrenia diagnosis and association with treatment resistance. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 16, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solberg, D.K.; Refsum, H.; Andreassen, O.A.; Bentsen, H. A five-year follow-up study of antioxidants, oxidative stress and polyunsaturated fatty acids in schizophrenia. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2019, 31, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidara, W.; Messedi, M.; Naifar, M.; Maalej, M.; Grayaa, S.; Omri, S.; Thabet, J.B.; Maalej, M.; Charfi, N.; Ayadi, F. Predictive value of oxidative stress biomarkers in drug-free patients with schizophrenia and schizo-affective disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 293, 113467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, M. Precision Nomothetic Medicine in Depression Research: A New Depression Model, and New Endophenotype Classes and Pathway Phenotypes, and A Digital Self. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association, A. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; American Psychiatric Association (APA): Arlington, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gossop, M.; Darke, S.; Griffiths, P.; Hando, J.; Powis, B.; Hall, W.; Strang, J. The Severity of Dependence Scale (SDS): Psychometric properties of the SDS in English and Australian samples of heroin, cocaine and amphetamine users. Addiction 1995, 90, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overall, J.E.; Gorham, D.R. The brief psychiatric rating scale. Psychol. Rep. 1962, 10, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, S.R.; Fiszbein, A.; Opler, L.A. The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 1987, 13, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almulla, A.F.; Al-Hakeim, H.K.; Maes, M. Schizophrenia phenomenology revisited: Positive and negative symptoms are strongly related reflective manifestations of an underlying single trait indicating overall severity of schizophrenia. CNS Spectr. 2021, 26, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dujaili, A.H.; Mousa, R.F.; Al-Hakeim, H.K.; Maes, M. High Mobility Group Protein 1 and Dickkopf-Related Protein 1 in Schizophrenia and Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia: Associations With Interleukin-6, Symptom Domains, and Neurocognitive Impairments. Schizophr. Bull. 2021, 47, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, M.; Vojdani, A.; Sirivichayakul, S.; Barbosa, D.S.; Kanchanatawan, B. Inflammatory and Oxidative Pathways Are New Drug Targets in Multiple Episode Schizophrenia and Leaky Gut, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and C1q Immune Complexes Are Additional Drug Targets in First Episode Schizophrenia. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 3319–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodological) 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalayasiri, R.; Mutirangura, A.; Verachai, V.; Gelernter, J.; Malison, R.T. Risk factors for methamphetamine-induced paranoia and latency of symptom onset in a Thai drug treatment cohort. Asian Biomed. 2009, 3, 635–643. [Google Scholar]
- Glasner-Edwards, S.; Mooney, L.J. Methamphetamine Psychosis: Epidemiology and Management. CNS Drugs 2014, 28, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalayasiri, R.; Verachai, V.; Gelernter, J.; Mutirangura, A.; Malison, R.T. Clinical features of methamphetamine-induced paranoia and preliminary genetic association with DBH-1021C→T in a Thai treatment cohort. Addiction 2014, 109, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKetin, R.; Lubman, D.I.; Baker, A.L.; Dawe, S.; Ali, R.L. Dose-related psychotic symptoms in chronic methamphetamine users: Evidence from a prospective longitudinal study. JAMA Psychiatry 2013, 70, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weich, L.; Pienaar, W. Occurrence of comorbid substance use disorders among acute psychiatric inpatients at Stikland Hospital in the Western Cape, South Africa. Afr. J. Psychiatry 2009, 12, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maes, M.; Plaimas, K.; Suratanee, A.; Noto, C.; Kanchanatawan, B. First Episode Psychosis and Schizophrenia Are Systemic Neuro-Immune Disorders Triggered by a Biotic Stimulus in Individuals with Reduced Immune Regulation and Neuroprotection. Cells 2021, 10, 2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hakeim, H.K.; Al-Musawi, A.F.; Al-Mulla, A.; Al-Dujaili, A.H.; Debnath, M.; Maes, M. The interleukin-6/interleukin-23/T helper 17-axis as a driver of neuro-immune toxicity in the major neurocognitive psychosis or deficit schizophrenia: A precision nomothetic psychiatry analysis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramness, J.G.; Gundersen, Ø.H.; Guterstam, J.; Rognli, E.B.; Konstenius, M.; Løberg, E.-M.; Medhus, S.; Tanum, L.; Franck, J. Amphetamine-induced psychosis—A separate diagnostic entity or primary psychosis triggered in the vulnerable? BMC Psychiatry 2012, 12, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.-C.; Lin, S.-K.; Chen, C.-H.; Pan, C.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Liu, H.-C. Oxidative stress status in recently abstinent methamphetamine abusers. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 67, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzmaurice, P.S.; Tong, J.; Yazdanpanah, M.; Liu, P.P.; Kalasinsky, K.S.; Kish, S.J. Levels of 4-hydroxynonenal and malondialdehyde are increased in brain of human chronic users of methamphetamine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 319, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suriyaprom, K.; Tanateerabunjong, R.; Tungtrongchitr, A.; Tungtrongchitr, R. Alterations in malondialdehyde levels and laboratory parameters among methamphetamine abusers. J. Med. Assoc. Thai. 2011, 94, 1533–1539. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moszczynska, A.; Fitzmaurice, P.; Ang, L.; Kalasinsky, K.S.; Peretti, F.J.; Aiken, S.S.; Wickham, D.J.; Sherwin, A.; Nobrega, J.N.; Forman, H.J.; et al. Brain antioxidant systems in human methamphetamine users. J. Neurochem. 2004, 89, 1396–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govitrapong, P.; Boontem, P.; Kooncumchoo, P.; Pinweha, S.; Namyen, J.; Sanvarinda, Y.; Vatanatunyakum, S. Increased blood oxidative stress in amphetamine users. Addict. Biol. 2010, 15, 100–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacimusalar, Y.; Karaaslan, O.; Bal, C.; Kocer, D.; Gok, G.; Yildiz, B. Methamphetamine’s effects on oxidative stress markers may continue after detoxification: A case–control study. Psychiatry Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 29, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potula, R.; Hawkins, B.J.; Cenna, J.M.; Fan, S.; Dykstra, H.; Ramirez, S.H.; Morsey, B.; Brodie, M.R.; Persidsky, Y. Methamphetamine causes mitrochondrial oxidative damage in human T lymphocytes leading to functional impairment. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 2867–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.W.; Ping, Y.H.; Yen, J.C.; Chang, C.Y.; Wang, S.F.; Yeh, C.L.; Chi, C.W.; Lee, H.C. Enhanced oxidative stress and aberrant mitochondrial biogenesis in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells during methamphetamine induced apoptosis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 220, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pubill, D.; Chipana, C.; Camins, A.; Pallàs, M.; Camarasa, J.; Escubedo, E. Free radical production induced by methamphetamine in rat striatal synaptosomes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 204, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell-Dowling, K.; Kelly, J.P. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Methamphetamine-induced Toxicity and Sources of Variation in the Design of Animal Studies. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeng, W.; Ramkissoon, A.; Parman, T.; Wells, P.G. Prostaglandin H synthase-catalyzed bioactivation of amphetamines to free radical intermediates that cause CNS regional DNA oxidation and nerve terminal degeneration. Faseb. J. 2006, 20, 638–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Ladenheim, B.; Jayanthi, S.; Cadet, J.L. Methamphetamine Administration Causes Death of Dopaminergic Neurons in the Mouse Olfactory Bulb. Biological. Psychiatry 2007, 61, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granado, N.; Ares-Santos, S.; Oliva, I.; O’Shea, E.; Martin, E.D.; Colado, M.I.; Moratalla, R. Dopamine D2-receptor knockout mice are protected against dopaminergic neurotoxicity induced by methamphetamine or MDMA. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 42, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayanthi, S.; Ladenheim, B.; Cadet, J.L. Methamphetamine-induced changes in antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxidation in copper/zinc-superoxide dismutase transgenic mice. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 844, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, P.G.; McCallum, G.P.; Chen, C.S.; Henderson, J.T.; Lee, C.J.J.; Perstin, J.; Preston, T.J.; Wiley, M.J.; Wong, A.W. Oxidative Stress in Developmental Origins of Disease: Teratogenesis, Neurodevelopmental Deficits, and Cancer. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 108, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moylan, S.; Berk, M.; Dean, O.M.; Samuni, Y.; Williams, L.J.; O’Neil, A.; Hayley, A.C.; Pasco, J.A.; Anderson, G.; Jacka, F.N.; et al. Oxidative & nitrosative stress in depression: Why so much stress? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 45, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIDA. Overview. 3 August 2021. Available online: https://nida.nih.gov/publications/research-reports/methamphetamine/overview (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Thompson, P.M.; Hayashi, K.M.; Simon, S.L.; Geaga, J.A.; Hong, M.S.; Sui, Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Toga, A.W.; Ling, W.; London, E.D. Structural Abnormalities in the Brains of Human Subjects Who Use Methamphetamine. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 6028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhu, L.; Shen, Q.; Bai, X.; Di, X. Recent advances in methamphetamine neurotoxicity mechanisms and its molecular pathophysiology. Behav Neurol 2015, 2015, 103969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, T.; Miyazaki, I.; Asanuma, M.; Takeshima, M.; Wagner, G.C. Chapter 3—Dopamine-Induced Behavioral Changes and Oxidative Stress in Methamphetamine-Induced Neurotoxicity. In International Review of Neurobiology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; Volume 88, pp. 43–64. [Google Scholar]
- Zare, A.; Ghanbari, A.; Hoseinpour, M.J.; Eskandarian Boroujeni, M.; Alimohammadi, A.; Abdollahifar, M.A.; Aliaghaei, A.; Mansouri, V.; Arani, H.Z. Methamphetamine-Triggered Neurotoxicity in Human Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex. Galen Med. J. 2021, 10, e2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, M.D.; Tangalakis, K.; Antonipillai, J.; Stojanovska, L.; Nurgali, K.; Apostolopoulos, V. Methamphetamine: Effects on the brain, gut and immune system. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 120, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskandarian Boroujeni, M.; Peirouvi, T.; Shaerzadeh, F.; Ahmadiani, A.; Abdollahifar, M.A.; Aliaghaei, A. Differential gene expression and stereological analyses of the cerebellum following methamphetamine exposure. Addict. Biol. 2020, 25, e12707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.; Ying, Z.; Gomez-Pinilla, F. The interplay between oxidative stress and brain-derived neurotrophic factor modulates the outcome of a saturated fat diet on synaptic plasticity and cognition. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 1699–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehterov, N.; Minchev, D.; Gevezova, M.; Sarafian, V.; Maes, M. Interactions among brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neuroimmune pathways are key components of the major psychiatric disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 4926–4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toborek, M.; Seelbach, M.J.; Rashid, C.S.; András, I.E.; Chen, L.; Park, M.; Esser, K.A. Voluntary exercise protects against methamphetamine-induced oxidative stress in brain microvasculature and disruption of the blood–brain barrier. Mol. Neurodegener. 2013, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevil, C.G.; Goeders, N.E.; Woolard, M.D.; Bhuiyan, M.S.; Dominic, P.; Kolluru, G.K.; Arnold, C.L.; Traylor, J.G.; Orr, A.W. Methamphetamine Use and Cardiovascular Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 1739–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzbach, V.; Lenk, K.; Laufs, U. Methamphetamine-related cardiovascular diseases. ESC Heart Fail. 2020, 7, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirillo, A.; Norata, G.D.; Catapano, A.L. LOX-1, OxLDL, and atherosclerosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 152786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, D.; Witztum, J.L. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein and atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 2311–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiva, E.; Wehinger, S.; Guzmán, L.; Orrego, R. Role of oxidized LDL in atherosclerosis. Hypercholesterolemia 2015, 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.; Ruckoanich, P.; Chang, Y.S.; Mahanonda, N.; Berk, M. Multiple aberrations in shared inflammatory and oxidative & nitrosative stress (IO&NS) pathways explain the co-association of depression and cardiovascular disorder (CVD), and the increased risk for CVD and due mortality in depressed patients. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, H.; Ueda, M.; Kojima, S.; Mashiba, S.; Michihata, T.; Takahashi, K.; Shishido, K.; Akizawa, T. Oxidized high-density lipoprotein as a risk factor for cardiovascular events in prevalent hemodialysis patients. Atherosclerosis 2012, 220, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, T.; Hara, A.; Komoda, T. Chapter 10—Oxidized High-Density Lipoprotein: Friend or Foe. In The HDL Handbook, 2nd ed.; Komoda, T., Ed.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 247–272. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, F.; Ito, T. High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Triglyceride and Oxidized HDL: New Lipid Biomarkers of Lipoprotein-Related Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.; Walder, K.; Carvalho, A.F.; Tye, S.J.; Lucas, K.; Berk, M.; Maes, M. The role of hypernitrosylation in the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of neuroprogressive diseases. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 84, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.; Berk, M.; Klein, H.; Walder, K.; Galecki, P.; Maes, M. Nitrosative stress, hypernitrosylation, and autoimmune responses to nitrosylated proteins: New pathways in neuroprogressive disorders including depression and chronic fatigue syndrome. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 4271–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almulla, A.F.; Vasupanrajit, A.; Tunvirachaisakul, C.; Al-Hakeim, H.K.; Solmi, M.; Verkerk, R.; Maes, M. The tryptophan catabolite or kynurenine pathway in schizophrenia: Meta-analysis reveals dissociations between central, serum, and plasma compartments. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uys, J.D.; Mulholland, P.J.; Townsend, D.M. Glutathione and redox signaling in substance abuse. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2014, 68, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | HCP (n = 30) A | MA-PSO (n = 30) B | MA+PSO (n = 30) C | F/X2 | df | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 27.3 (5.4) | 24.4 (6.6) C | 28.6 (5.4) B | 3.99 | 2/87 | 0.022 |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 25.33 (2.80) | 25.24 (4.05) | 24.94 (3.12) | 0.11 | 2/87 | 0.894 |
| Education (years) | 10.9 (3.7) | 7.8 (7.0) | 10.2 (6.8) | 2.16 | 2/87 | 0.121 |
| Marital state (Single/Married) | 8/22 | 13/17 | 8/22 | 2.54 | 2 | 0.280 |
| Employment (No/Yes) | 8/22 C | 10/20 C | 25/5 A,B | 23.07 | 2 | <0.0001 |
| Current MA use (No/Yes) | 0/30 | 30/0 | 30/0 | 90.0 | ||
| PC_SDS (z score) | −1.370 (0.0) B,C | 0.611 (0.297) A,C | 0.758 (0.237) A,B | KWT | <0.001 | |
| PC_MA dependence severity (z score) | −1.382 (0.0) B,C | 0.570 (0.166) A,C | 0.812 (0.219) A,B | KWT | <0.0001 | |
| MA Administration route (O/S/I) | - | 4/16/7 | 13/5/12 | FFHET | 0.001 | |
| Age at onset (years) | - | 23.4 (5.9) C | 25.8 (4.90) B | 3.02 | 1/58 | 0.088 |
| Duration of MA dependence (months) | - | 14.8 (14.1) C | 34.9 (17.2) B | 24.54 | 1/57 | <0.001 |
| MA dosing (gm) | - | 1.13 (0.47) C | 2.30 (0.79) B | 47.81 | 1/58 | <0.001 |
| Number of prior MIP episodes | - | 2.0 (2.4) | 2.2 (1.4) | 0.07 | 1/58 | 0.798 |
| Duration of the index MIP (days) | - | 2.4 (2.3) A | 2.8 (2.0) A | 0.43 | 1/58 | 0.513 |
| Days hospitalized due to MA intoxication | - | 1.3 (1.7) A | 1.8 (1.8) A | 1.19 | 1/58 | 0.280 |
| TUD (No/Yes) | 15/15 | 7/23 | 1/29 | 17.29 | 2 | <0.001 |
| Alcohol dependence (No/Yes) | 30/0 | 29/1 | 28/2 | FFHET | 0.770 | |
| Current drinker/past month (No/Yes) | 30/0 | 29/1 | 28/2 | FFHET | 0.770 | |
| Lifetime Cannabis use (No/Yes) | 30/0 | 29/1 | 28/2 | FFHET | 0.770 | |
| Any other substance, dependence | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - |
| Variables | HCP (n = 30) A | MA-PSO (n = 30) B | MA+PSO (n = 30) C | F | df | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAI symptoms (z score) | −1.052 (0.077) B,C | −0.114 (0.080) A,C | 1.165 (0.078) A,B | 208.77 | 2/85 | <0.0001 |
| Psychosis (z score) | −1.190 (0.090) B,C | 0.296 (0.094) A,C | 0.894 (0.091) A,B | 143.17 | 2/85 | <0.0001 |
| Hostility (z score) | −1.085 (0.112) B,C | 0.317 (0.117) A,C | 0.769 (0.114) A,B | 74.58 | 2/85 | <0.0001 |
| Excitement (z score) | −1.038 (0.115) B,C | 0.212 (0.120) A,C | 0.827 (0.116) A,B | 69.03 | 2/85 | <0.0001 |
| Mannerism (z score) | −0.562 (0.162) B,C | 0.122 (0.169) A | 0.440 (0.164) A | 10.06 | 2/85 | <0.001 |
| Formal though disorders (z score) | −1.143 (0.072) B,C | 0.036 (0.074) A,C | 1.107 (0.072) A,B | 250.22 | 2/85 | <0.0001 |
| Variables | HCP (n = 30) A | MA-PSO (n = 30) B | MA+PSO (n = 30) C | F | df | p | Partial Eta Squared |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalase (ng/mL) | 4.76 (0.30) C | 4.26 5(0.31) | 3.73 (0.31) A | 2.91 | 2/85 | 0.060 | 0.064 |
| GPx (U/mL) | 19.58 (1.39) C | 22.14 (1.43) C | 15.28 (1.42) A,B | 5.71 | 2/85 | 0.005 | 0.118 |
| Myeloperoxidase # (U/L) | 110.16 (5.74) | 115.70 (5.90) | 125.30 (5.84) | 2.64 | 2/85 | 0.077 | 0.058 |
| Malondialdehyde (nM) | 1213.2 (68.8) B,C | 1590.4 (70.6) A | 1494.9 (70.0) A | 8.03 | 2/85 | <0.001 | 0.159 |
| OxHDL (U/mL) | 136.1 (8.3) C | 152.4 (8.5) | 174.7 (8.5) A | 5.35 | 2/85 | 0.006 | 0.112 |
| OxLDL (ng/mL) | 50.1 (3.7) B,C | 67.3 (3.8) A | 65.8 (3.7) A | 6.77 | 2/85 | 0.002 | 0.137 |
| TAC (U/mL) | 4.36 (0.25) B,C | 3.42 (0.26) A,C | 2.53 (0.26) A,B | 13.36 | 2/85 | <0.001 | 0.239 |
| NO (uM) | 29.44 (1.44) C | 32.67 (1.48) C | 24.92 (1.47) A,B | 6.68 | 2/85 | 0.002 | 0.136 |
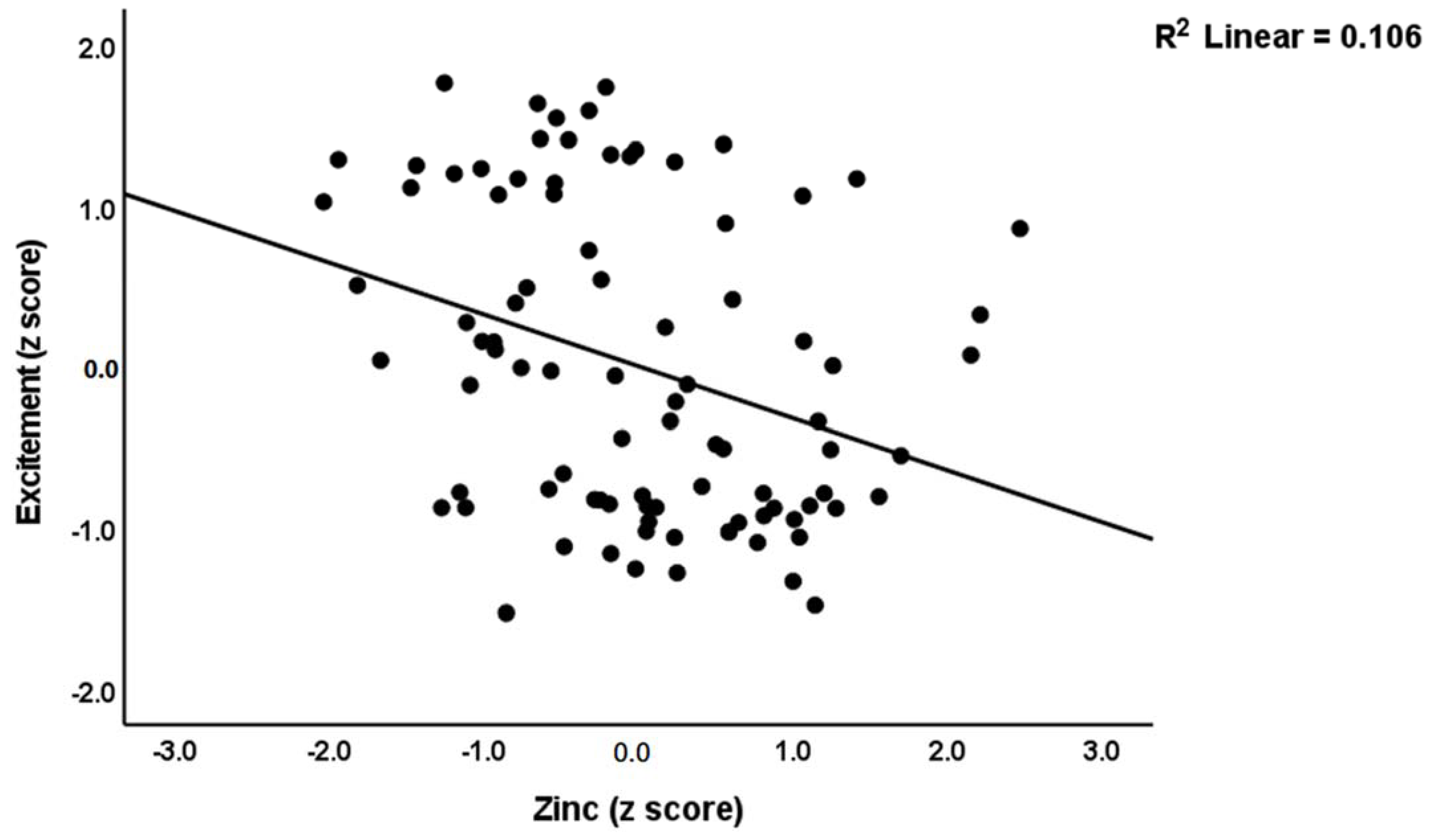
| Zinc (mg/l) | 0.761(0.025) C | 0.704 (0.026) C | 0.596 (0.026) A,B | 10.94 | 2/85 | <0.001 | 0.205 |
| HDL (mM) | 1.203 (0.023) B,C | 1.130 (0.024) A | 1.111 (0.024) A | 4.39 | 2/85 | 0.015 | 0.094 |
| OSTOX (z score) | −0.710(0.159) B,C | 0.225(0.163) A | 0.485(0.162) A | 15.64 | 2/85 | <0.001 | 0.269 |
| ANTIOX (z score) | 0.646(0.151) B,C | 0.120(0.155) A,C | −0.766(0.154) A,B | 21.93 | 2/85 | <0.001 | 0.340 |
| OSTOX/ANTIOX (z score) | −0.886(0.134) B,C | 0.069(0.138) A,C | 0.817(0.136) A,B | 40.39 | 2/85 | <0.001 | 0.487 |
| Variables | All Subjects Combined (n = 90) | MA Dependence (n = 60) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC_SDS | PC_MA | OSTOX | ANTIOX | OSTOX/ANTIOX | PC_SDS | PC_MA | |
| MAI symptoms | 0.783 ** | 0.799 ** | 0.434 ** | −0.415 ** | 0.555 ** | 0.330 * | 0.483 ** |
| Psychosis | 0.873 ** | 0.871 ** | 0.491 ** | −0.402 ** | 0.583 ** | 0.498 ** | 0.524 ** |
| Hostility | 0.790 ** | 0.793 ** | 0.360 ** | −0.285 * | 0.422 ** | 0.189 | 0.201 |
| Excitement | 0.782 ** | 0.779 ** | 0.336 ** | −0.269 * | 0.396 ** | 0.409 ** | 0.428 ** |
| Mannerism | 0.453 ** | 0.477 ** | 0.220 * | −0.109 | 0.215 * | 0.110 | 0.075 |
| Formal Thought Disorders | 0.839 ** | 0.850 ** | 0.451 ** | −0.426 ** | 0.573 ** | 0.382 ** | 0.500 ** |
| OSTOX | 0.520 ** | 0.520 ** | - | 0.164 | 0.168 | ||
| ANTIOX | −0.443 ** | −0.482 ** | 0.049 | −0.169 | |||
| OSTOX/ANTIOX ratio | 0.629 ** | 0.654 ** | 0.080 | 0.243 | |||
| Dependent Variables | Explanatory Variables | Parameter Estimates + Statistics | Model Statistics and Effect Size | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | t | p | R2 | F | df | p | ||
| #1. MAI symptoms | Model | 0.352 | 9.13 | 5/84 | <0.001 | |||
| TAC | −0.220 | −2.31 | 0.023 | |||||
| OxHDL | 0.276 | 3.04 | 0.003 | |||||
| HDL | −0.187 | −2.05 | 0.043 | |||||
| Zinc | −0.229 | −2.36 | 0.020 | |||||
| OxLDL | 0.191 | 2.09 | 0.040 | |||||
| #2. MAI symptoms | Model | 0.308 | 39.11 | 1/88 | <0.001 | |||
| OSTOX/ANTIOX | 0.555 | 6.25 | <0.001 | |||||
| #3 Psychosis | Model | 0.316 | 13.23 | 3/86 | <0.001 | |||
| TAC | −0.241 | −2.51 | 0.014 | |||||
| OxLDL | 0.345 | 3.82 | <0.001 | |||||
| Zinc | −0.273 | −2.88 | 0.005 | |||||
| #4. Hostility | Model | 0.147 | 7.49 | 2/87 | <0.001 | |||
| TAC | −0.264 | −2.63 | 0.010 | |||||
| OxLDL | 0.243 | 2.43 | 0.017 | |||||
| #5. Excitement | Model | 0.175 | 6.07 | 3/86 | <0.001 | |||
| Zinc | −0.322 | −3.19 | 0.002 | |||||
| OxLDL | 0.268 | 2.71 | 0.008 | |||||
| Age | 0.221 | 2.17 | 0.032 | |||||
| #6. Mannerism | Model | 0.141 | 7.12 | 2/87 | 0.001 | |||
| OxLDL | 0.309 | 3.11 | 0.003 | |||||
| Zinc | −0.219 | −2.21 | 0.030 | |||||
| #7. Formal thought disorders | Model | 0.355 | 9.25 | 5/84 | <0.001 | |||
| TAC | −0.265 | −2.78 | 0.007 | |||||
| OxHDL | 0.261 | 2.88 | 0.005 | |||||
| MPO | 0.190 | 2.12 | 0.037 | |||||
| Zinc | −0.242 | −2.56 | 0.012 | |||||
| OxLDL | 0.184 | 1.99 | 0.049 | |||||
| Dependent Variables | Explanatory Variables | Parameter Estimates + Statistics | Model Statistics and Effect Size | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | t | p | R2 | F | df | p | ||
| #1 MA symptoms | Model | 0.818 | 194.96 | 2/87 | <0.001 | |||
| PC_SDS | 0.630 | 8.79 | <0.001 | |||||
| MA dosing | 0.324 | 4.53 | <0.001 | |||||
| #2. OSTOX/ANTIOX ratio | Model | 0.447 | 35.18 | 2/87 | <0.001 | |||
| PC_SDS | 0.449 | 3.60 | <0.001 | |||||
| MA dosing | 0.258 | 2.07 | 0.041 | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Hakeim, H.K.; Altufaili, M.F.; Almulla, A.F.; Moustafa, S.R.; Maes, M. Increased Lipid Peroxidation and Lowered Antioxidant Defenses Predict Methamphetamine Induced Psychosis. Cells 2022, 11, 3694. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11223694
Al-Hakeim HK, Altufaili MF, Almulla AF, Moustafa SR, Maes M. Increased Lipid Peroxidation and Lowered Antioxidant Defenses Predict Methamphetamine Induced Psychosis. Cells. 2022; 11(22):3694. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11223694
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Hakeim, Hussein Kadhem, Mazin Fadhil Altufaili, Abbas F. Almulla, Shatha Rouf Moustafa, and Michael Maes. 2022. "Increased Lipid Peroxidation and Lowered Antioxidant Defenses Predict Methamphetamine Induced Psychosis" Cells 11, no. 22: 3694. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11223694
APA StyleAl-Hakeim, H. K., Altufaili, M. F., Almulla, A. F., Moustafa, S. R., & Maes, M. (2022). Increased Lipid Peroxidation and Lowered Antioxidant Defenses Predict Methamphetamine Induced Psychosis. Cells, 11(22), 3694. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11223694








