B Cells at the Cross-Roads of Autoimmune Diseases and Auto-Inflammatory Syndromes
Abstract
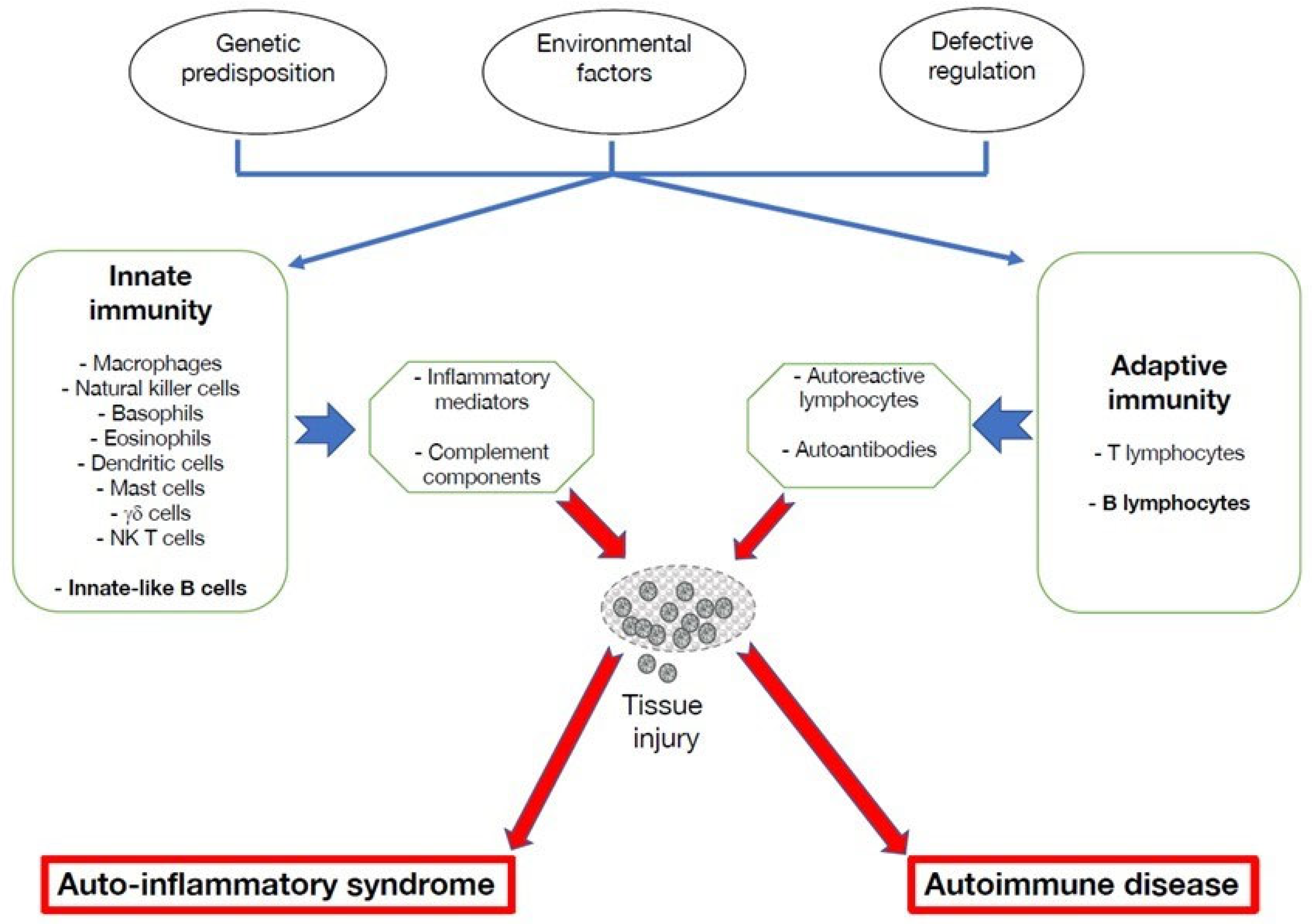
:1. Introduction
2. Altered Functions of B Lymphocytes in Autoinflammatory Disorders
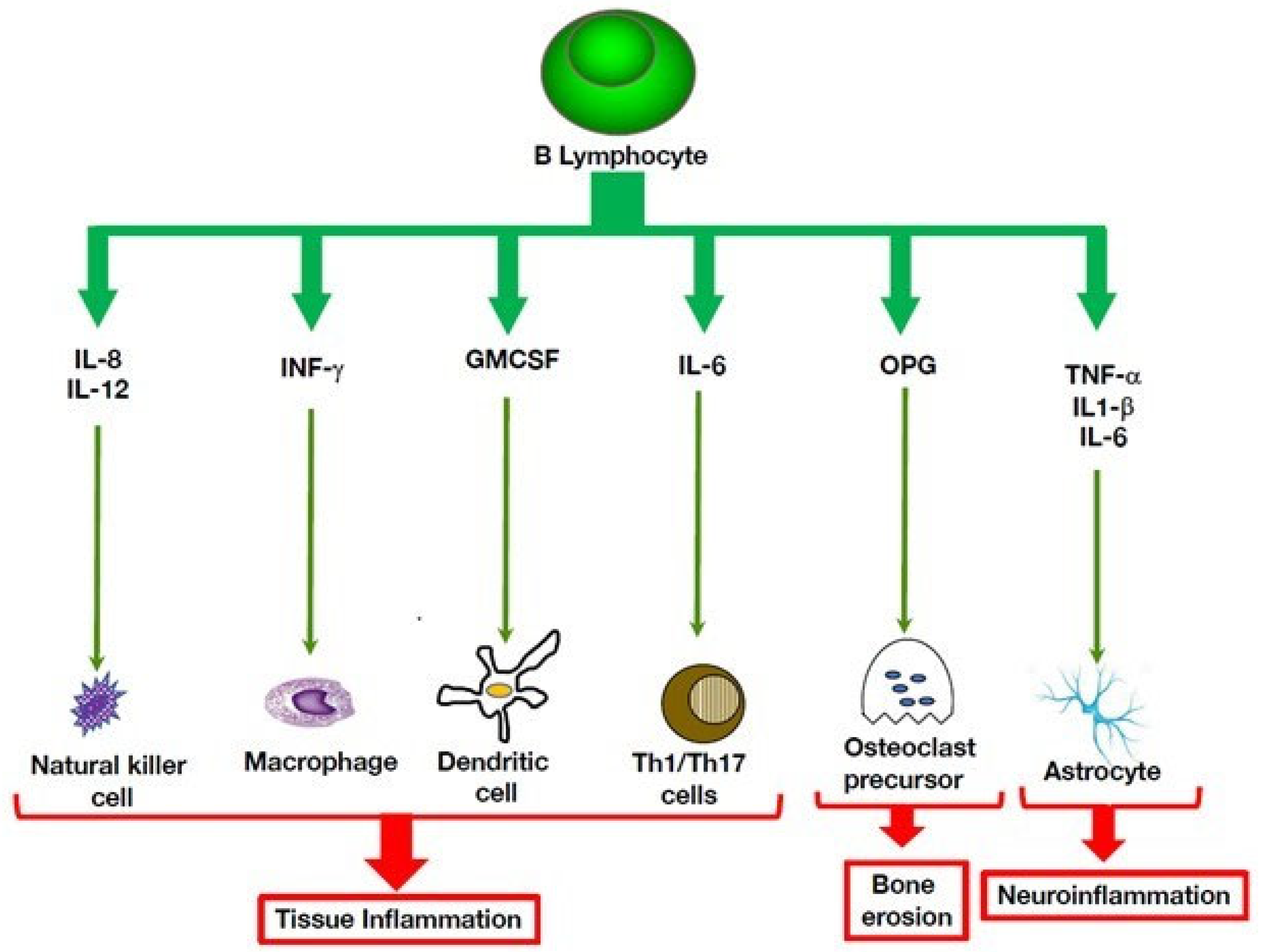
3. Multiple Roles of B Cells in Autoinflammatory Disorders
4. Potential Therapeutic Avenues for Autoinflammatory Disorders
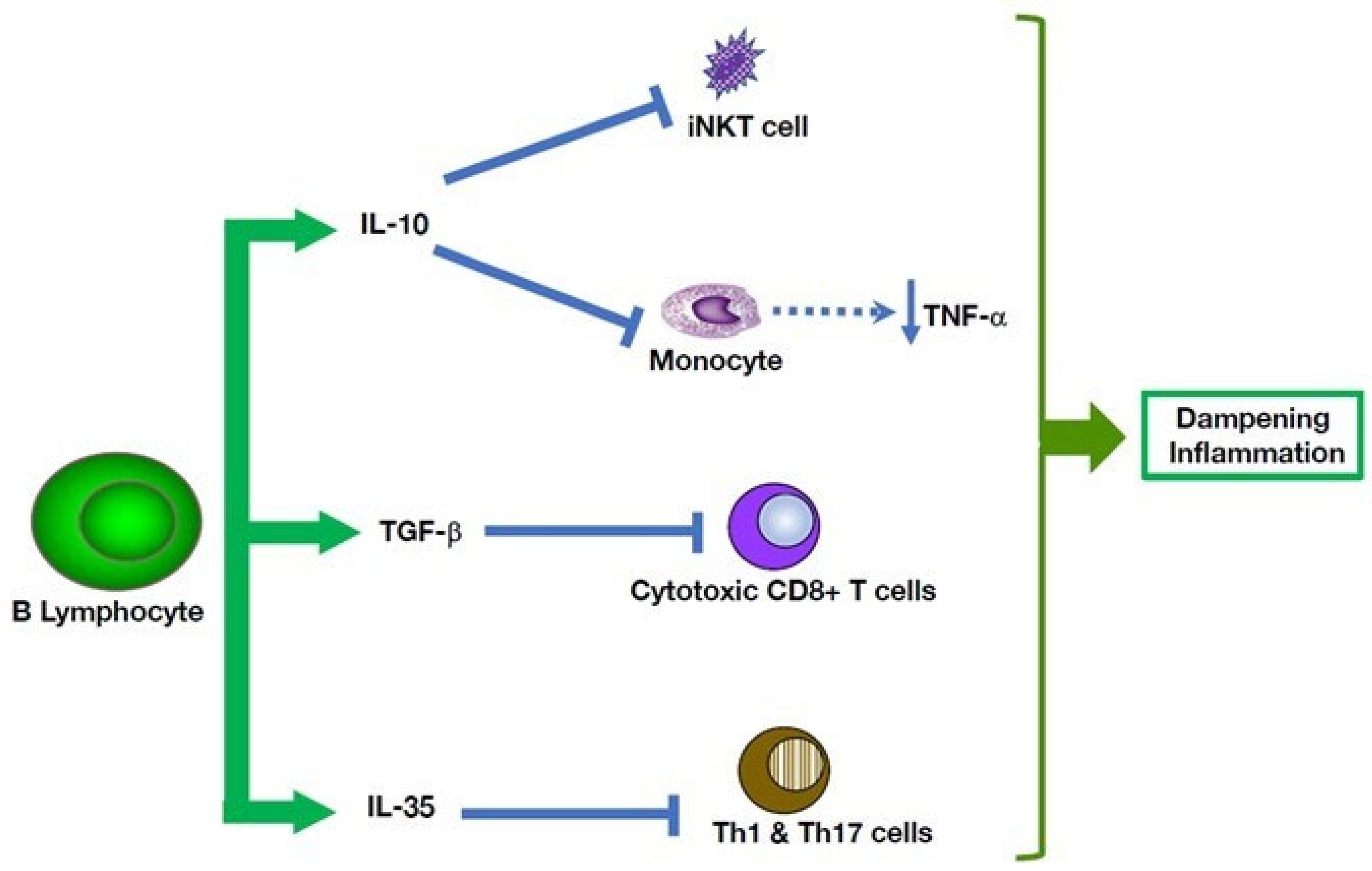
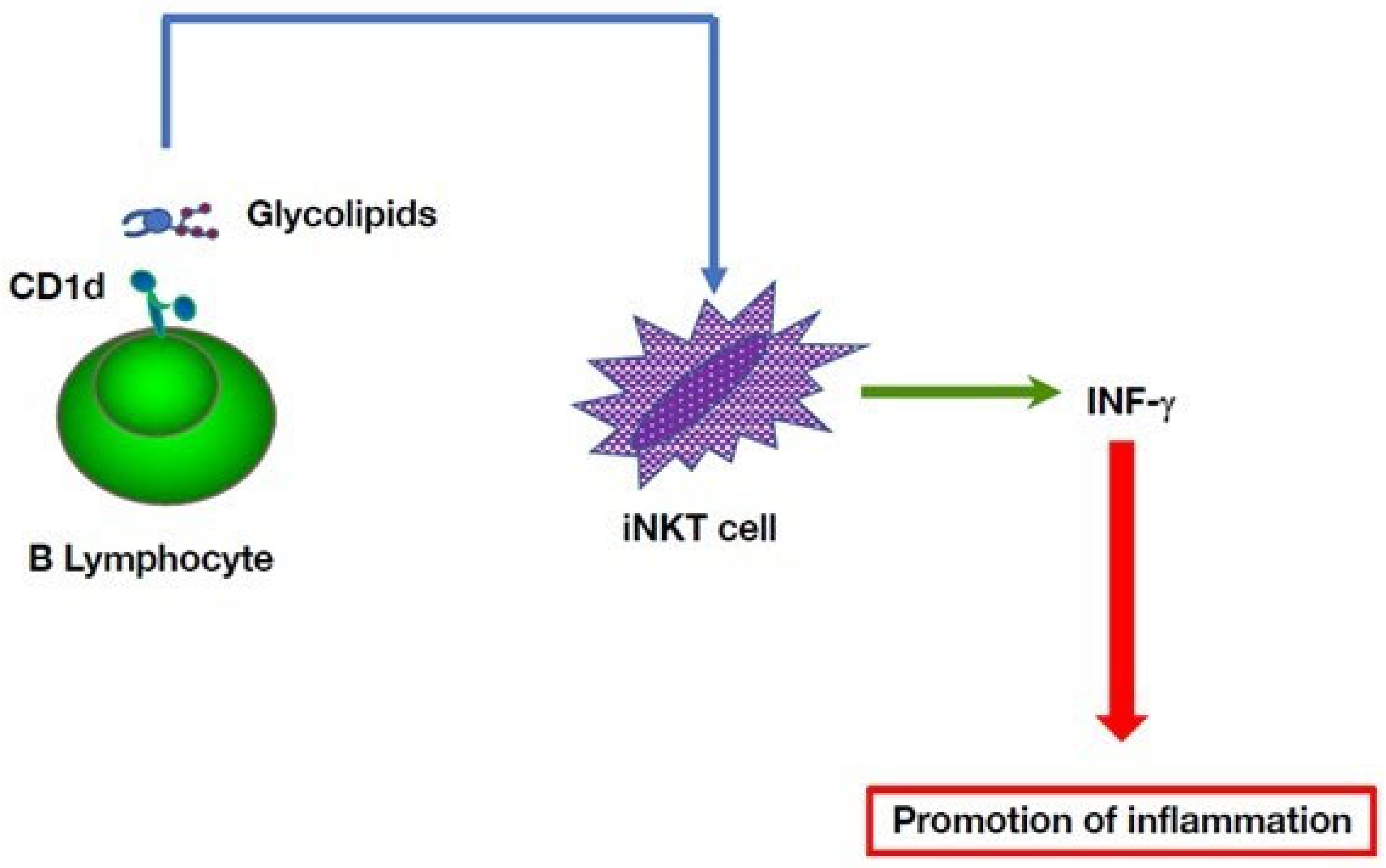
5. Multiple B Cell-Mediated Modulatory Effects in Autoinflammatory Disorders
6. Future Prospects
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McDermott, M.F.; Aksentijevich, I.; Galon, J.; McDermott, E.M.; Ogunkolade, B.W.; Centola, M.; Mansfield, E.; Gadina, M.; Karenko, L.; Pettersson, T.; et al. Germline mutations in the extracellular domains of the 55 kDa TNF receptor, TNFR1, define a family of dominantly inherited autoinflammatory syndromes. Cell 1999, 97, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betrains, A.; Staels, F.; Schrijvers, R.; Meyts, I.; Humblet-Baron, S.; De Langhe, E.; Wouters, C.; Blockmans, D.; Vanderschueren, S. Systemic autoinflammatory disease in adults. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szekanecz, Z.; McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G.; Szamosi, S.; Benko, S.; Szucs, G. Autoinflammation and autoimmunity across rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedrich, C.M. Shaping the spectrum—From autoinflammation to autoimmunity. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 165, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melek, M.; Gellert, M. RAG1/2-mediated resolution of transposition intermediates: Two pathways and possible consequences. Cell 2000, 101, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinon, F.; Petrilli, V.; Mayor, A.; Tardivel, A.; Tschopp, J. Gout-associated uric acid crystals activate the NALP3 inflammasome. Nature 2006, 440, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masters, S.L. Broadening the definition of autoinflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2015, 37, 311–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Houwen, T.B.; Dik, W.A.; Goeijenbier, M.; Hayat, M.; Nagtzaam, N.M.A.; van Hagen, M.; van Laar, J.A.M. Leukocyte toll-like receptor expression in pathergy positive and negative Behcet’s disease patients. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 3971–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovic, D.; Vucic, D.; Dikic, I. Ubiquitination in disease pathogenesis and treatment. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1242–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattah, M.G.; Malynn, B.A.; Ma, A. Ubiquitin-Modifying Enzymes and Regulation of the Inflammasome. J. Mol. Biol. 2017, 429, 3471–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, G.; Klafack, S.; Studencka-Turski, M.; Kruger, E.; Ebstein, F. The Ubiquitin-Proteasome System in Immune Cells. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetzke, C.C.; Ebstein, F.; Kallinich, T. Role of Proteasomes in Inflammation. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksentijevich, I.; Zhou, Q. NF-kappaB Pathway in Autoinflammatory Diseases: Dysregulation of Protein Modifications by Ubiquitin Defines a New Category of Autoinflammatory Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boisson, B.; Laplantine, E.; Prando, C.; Giliani, S.; Israelsson, E.; Xu, Z.; Abhyankar, A.; Israel, L.; Trevejo-Nunez, G.; Bogunovic, D.; et al. Immunodeficiency, autoinflammation and amylopectinosis in humans with inherited HOIL-1 and LUBAC deficiency. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saettini, F.; Herriot, R.; Prada, E.; Nizon, M.; Zama, D.; Marzollo, A.; Romaniouk, I.; Lougaris, V.; Cortesi, M.; Morreale, A.; et al. Prevalence of Immunological Defects in a Cohort of 97 Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome Patients. J. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 40, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perucha, E.; Melchiotti, R.; Bibby, J.A.; Wu, W.; Frederiksen, K.S.; Roberts, C.A.; Hall, Z.; LeFriec, G.; Robertson, K.A.; Lavender, P.; et al. The cholesterol biosynthesis pathway regulates IL-10 expression in human Th1 cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ter Haar, N.M.; Jeyaratnam, J.; Lachmann, H.J.; Simon, A.; Brogan, P.A.; Doglio, M.; Cattalini, M.; Anton, J.; Modesto, C.; Quartier, P.; et al. The Phenotype and Genotype of Mevalonate Kinase Deficiency: A Series of 114 Cases from the Eurofever Registry. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2795–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, P.; Roch, T.; Lampropoulou, V.; O’Connor, R.A.; Stervbo, U.; Hilgenberg, E.; Ries, S.; Dang, V.D.; Jaimes, Y.; Daridon, C.; et al. IL-35-producing B cells are critical regulators of immunity during autoimmune and infectious diseases. Nature 2014, 507, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bibby, J.A.; Purvis, H.A.; Hayday, T.; Chandra, A.; Okkenhaug, K.; Rosenzweig, S.; Aksentijevich, I.; Wood, M.; Lachmann, H.J.; Kemper, C.; et al. Cholesterol metabolism drives regulatory B cell IL-10 through provision of geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sornsakrin, M.; Wenner, K.; Ganschow, R. B cell cytopenia in two brothers with hyper-IgD and periodic fever syndrome. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2009, 168, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T. Kawasaki disease. Acta Paediatr. 1995, 84, 713–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindquist, M.E.; Hicar, M.D. B Cells and Antibodies in Kawasaki Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orenstein, J.M.; Rowley, A.H. An evaluation of the validity of the animal models of Kawasaki disease vasculopathy. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2014, 38, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schulte, D.J.; Yilmaz, A.; Shimada, K.; Fishbein, M.C.; Lowe, E.L.; Chen, S.; Wong, M.; Doherty, T.M.; Lehman, T.; Crother, T.R.; et al. Involvement of innate and adaptive immunity in a murine model of coronary arteritis mimicking Kawasaki disease. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 5311–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Onouchi, Y.; Ozaki, K.; Burns, J.C.; Shimizu, C.; Terai, M.; Hamada, H.; Honda, T.; Suzuki, H.; Suenaga, T.; Takeuchi, T.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies three new risk loci for Kawasaki disease. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.R.; Chang, T.Y.; Chiu, N.C.; Chi, H.; Yang, K.D.; Chang, L.; Huang, D.T.; Huang, F.Y.; Lien, Y.P.; Lin, W.S.; et al. Validation of genome-wide associated variants for Kawasaki disease in a Taiwanese case-control sample. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reth, M.; Wienands, J. Initiation and processing of signals from the B cell antigen receptor. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1997, 15, 453–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasler, P.; Zouali, M. B cell receptor signaling and autoimmunity. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 2085–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelson, E.M.; Laird, R.M.; Papillion, A.M.; Tatum, A.H.; Princiotta, M.F.; Hayes, S.M. Reduced B lymphoid kinase (Blk) expression enhances proinflammatory cytokine production and induces nephrosis in C57BL/6-lpr/lpr mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Kooten, C.; Banchereau, J. CD40-CD40 ligand. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2000, 67, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Oharaseki, T.; Naoe, S.; Wakayama, M.; Yokouchi, Y. Neutrophilic involvement in the damage to coronary arteries in acute stage of Kawasaki disease. Pediatr. Int. 2005, 47, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, T.; Fujiwara, H.; Nakano, H. Pathological features of coronary arteries in children with Kawasaki disease in which coronary arterial aneurysm was absent at autopsy. Quantitative analysis. Circulation 1988, 78, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zouali, M. B-cell superantigens: Implications for selection of the human antibody repertoire. Immunol. Today 1995, 16, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.H.; Park, I.H.; Shin, J.S.; Kim, D.S. Immunoglobulin V(H) chain gene analysis of peripheral blood IgM-producing B cells in patients with Kawasaki disease. Yonsei Med. J. 2009, 50, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rowley, A.H.; Shulman, S.T.; Mask, C.A.; Finn, L.S.; Terai, M.; Baker, S.C.; Galliani, C.A.; Takahashi, K.; Naoe, S.; Kalelkar, M.B.; et al. IgA plasma cell infiltration of proximal respiratory tract, pancreas, kidney, and coronary artery in acute Kawasaki disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 182, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shingadia, D.; O’Gorman, M.; Rowley, A.H.; Shulman, S.T. Surface and cytoplasmic immunoglobulin expression in circulating B-lymphocytes in acute Kawasaki disease. Pediatr. Res. 2001, 50, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, A.H.; Shulman, S.T.; Spike, B.T.; Mask, C.A.; Baker, S.C. Oligoclonal IgA response in the vascular wall in acute Kawasaki disease. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 1334–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rowley, A.H.; Shulman, S.T.; Garcia, F.L.; Guzman-Cottrill, J.A.; Miura, M.; Lee, H.L.; Baker, S.C. Cloning the arterial IgA antibody response during acute Kawasaki disease. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 8386–8391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swanson, K.V.; Deng, M.; Ting, J.P. The NLRP3 inflammasome: Molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, L.; Moreau, F.; MacDonald, J.A.; Chadee, K. NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition is disrupted in a group of auto-inflammatory disease CAPS mutations. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 1176–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.F.; Dasari, H.; Van Keulen, V.P.; Carmona, E.M. Canonical Stimulation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome by Fungal Antigens Links Innate and Adaptive B-Lymphocyte Responses by Modulating IL-1beta and IgM Production. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, M.; Zouali, M. Inflammasome is a central player in B cell development and homing. Life Sci. Alliance 2022, 6, e202201700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Koning, H.D. Schnitzler’s syndrome: Lessons from 281 cases. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2014, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pathak, S.; Rowczenio, D.; Lara-Reyna, S.; Kacar, M.; Owen, R.; Doody, G.; Krause, K.; Lachmann, H.; Doffinger, R.; Newton, D.; et al. Evidence of B Cell Clonality and Investigation Into Properties of the IgM in Patients with Schnitzler Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 569006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeway, C.A., Jr.; Medzhitov, R. Innate immune recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manilay, J.O.; Zouali, M. Tight relationships between B lymphocytes and the skeletal system. Trends. Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakane, T.; Takeno, M.; Suzuki, N.; Inaba, G. Behcet’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 1284–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Araji, A.; Kidd, D.P. Neuro-Behcet’s disease: Epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and management. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saruhan-Direskeneli, G.; Yentur, S.P.; Akman-Demir, G.; Isik, N.; Serdaroglu, P. Cytokines and chemokines in neuro-Behcet’s disease compared to multiple sclerosis and other neurological diseases. J. Neuroimmunol. 2003, 145, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzaoui, K.; Houman, H.; Hentati, F.; Hamzaoui, A. BAFF is up-regulated in central nervous system of neuro-Behcet’s disease. J. Neuroimmunol. 2008, 200, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghrebi, O.; Belghith, M.; Jeridi, C.; Rachdi, A.; Fatnassi, F.N.; Saied, Z.; Belal, S.; Ben Sassi, S.; Barbouche, M.R. B Cells Specific CpG Induces High IL-10 and IL-6 Expression In Vitro in Neuro-Behcet’s Disease. Cells 2022, 11, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davatchi, F.; Shams, H.; Rezaipoor, M.; Sadeghi-Abdollahi, B.; Shahram, F.; Nadji, A.; Chams-Davatchi, C.; Akhlaghi, M.; Faezi, T.; Naderi, N. Rituximab in intractable ocular lesions of Behcet’s disease; randomized single-blind control study (pilot study). Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 13, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Estrada, C.; Casallas-Vanegas, A.; Zabala-Angeles, I.; Gomez-Figueroa, E.; Rivas-Alonso, V.; Flores-Rivera, J. Rituximab as an effective therapeutic option in refractory Neuro-Behcet syndrome. J. Neuroimmunol. 2020, 346, 577308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Li, C.; Duan, F.J.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Du, Y.; Zhang, W. Case Report: Repeated Low-Dose Rituximab Treatment Is Effective in Relapsing Neuro Behcet’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 595984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingerchuk, D.M.; Lennon, V.A.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Pittock, S.J.; Weinshenker, B.G. The spectrum of neuromyelitis optica. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouali, M. Tweaking the B lymphocyte compartment in autoimmune diseases. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.L.; O’Connor, K.C.; Bar-Or, A.; Zamvil, S.S.; Hemmer, B.; Tedder, T.F.; von Budingen, H.C.; Stuve, O.; Yeaman, M.R.; Smith, T.J.; et al. B lymphocytes in neuromyelitis optica. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 2, e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, K.H.; Lee, C.Y. Treatment of Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavanescu, I.; Benoist, C.; Mathis, D. B cells are required for Aire-deficient mice to develop multi-organ autoinflammation: A therapeutic approach for APECED patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13009–13014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarlinton, D. B cells still front and centre in immunology. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, C.; Menon, M. Human regulatory B cells in health and disease: Therapeutic potential. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brennan, P.J.; Brigl, M.; Brenner, M.B. Invariant natural killer T cells: An innate activation scheme linked to diverse effector functions. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oleinika, K.; Rosser, E.C.; Matei, D.E.; Nistala, K.; Bosma, A.; Drozdov, I.; Mauri, C. CD1d-dependent immune suppression mediated by regulatory B cells through modulations of iNKT cells. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, A.R.; Hams, E.; Floudas, A.; Sparwasser, T.; Weaver, C.T.; Fallon, P.G. PD-L1hi B cells are critical regulators of humoral immunity. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okazaki, T.; Chikuma, S.; Iwai, Y.; Fagarasan, S.; Honjo, T. A rheostat for immune responses: The unique properties of PD-1 and their advantages for clinical application. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamphorst, A.O.; Ahmed, R. Manipulating the PD-1 pathway to improve immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viau, M.; Zouali, M. B-lymphocytes, innate immunity, and autoimmunity. Clin. Immunol. 2005, 114, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, T.A.; Brydges, S.D.; Hoffman, H.M. Autoinflammation: Translating mechanism to therapy. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 90, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsay, G.J.; Zouali, M. The Interplay Between Innate-Like B Cells and Other Cell Types in Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hikada, M.; Zouali, M. Multistoried roles for B lymphocytes in autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 1065–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zouali, M. B Cells at the Cross-Roads of Autoimmune Diseases and Auto-Inflammatory Syndromes. Cells 2022, 11, 4025. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11244025
Zouali M. B Cells at the Cross-Roads of Autoimmune Diseases and Auto-Inflammatory Syndromes. Cells. 2022; 11(24):4025. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11244025
Chicago/Turabian StyleZouali, Moncef. 2022. "B Cells at the Cross-Roads of Autoimmune Diseases and Auto-Inflammatory Syndromes" Cells 11, no. 24: 4025. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11244025
APA StyleZouali, M. (2022). B Cells at the Cross-Roads of Autoimmune Diseases and Auto-Inflammatory Syndromes. Cells, 11(24), 4025. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11244025





