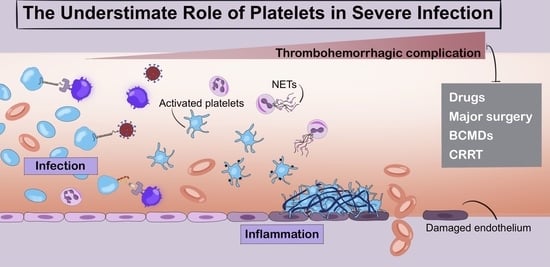
The Underestimated Role of Platelets in Severe Infection a Narrative Review
Abstract
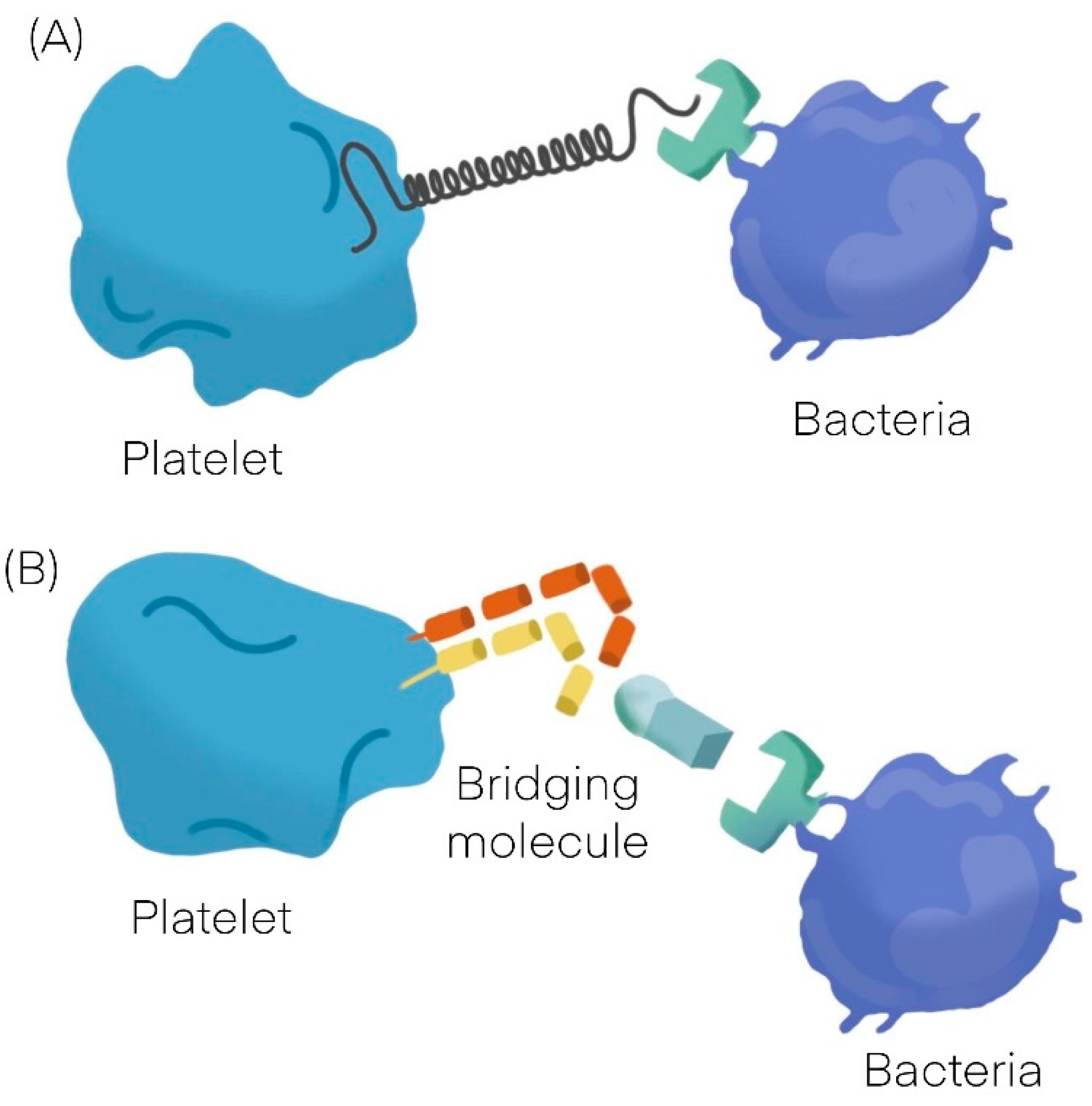
:1. Platelets Interactions with Bacteria
| Platelet-Bacteria Interactions | ||
|---|---|---|
| Direct adhesion | Indirect adhesion | |
| Short lag | Bridging protein | |
| S. sanguinis [11] | S. aureus [12,13,14] | Fibrinogen |
| S. aureus [12,13,14] | H. pylori [19] | Fibronectin |
| VWF | ||
| Direct adhesion | ||
| Long lag | ||
| S. gordonii [20] | ||
| S. sanguinis [11] | ||
| Non aggregating | ||
| S. gordonii [20] | H. pylori [19] |
2. Platelets Interactions with Viruses
3. Cellular Changes in Platelet Structure and Function during Infection
4. Main Techniques to Monitor Platelet Function
5. Platelet Response to Pharmacological and Non-Pharmacological Agents or Devices
6. Clinical Consequences of Platelets Dysregulation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clemetson, K.J.; Clemetson, J.M.; Proudfoot, A.E.; Power, C.A.; Baggiolini, M.; Wells, T.N. Functional expression of CCR1, CCR3, CCR4, and CXCR4 chemokine receptors on human platelets. Blood 2000, 96, 4046–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssefian, T.; Drouin, A.; Massé, J.-M.; Guichard, J.; Cramer, E.M. Host defense role of platelets: Engulfment of HIV andStaphylococcus aureus occurs in a specific subcellular compartment and is enhanced by platelet activation. Blood 2002, 99, 4021–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antczak, A.J.; Singh, N.; Gay, S.R.; Worth, R.G. IgG-complex stimulated platelets: A source of sCD40L and RANTES in initiation of inflammatory cascade. Cell Immunol. 2010, 263, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleissner, C.A.; von Hundelshausen, P.; Ley, K. Platelet Chemokines in Vascular Disease. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 1920–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeaman, M.R. Bacterial–platelet interactions: Virulence meets host defense. Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 471–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, K.; Massberg, S. Interplay between inflammation and thrombosis in cardiovascular pathology. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 666–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolai, L.; Schiefelbein, K.; Lipsky, S.; Leunig, A.; Hoffknecht, M.; Pekayvaz, K.; Raude, B.; Marx, C.; Ehrlich, A.; Pircher, J.; et al. Vascular surveillance by haptotactic blood platelets in inflammation and in-fection. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschoor, A.; Neuenhahn, M.; Navarini, A.A.; Graef, P.; Plaumann, A.; Seidlmeier, A.; Nieswandt, B.; Massberg, S.; Zinkernagel, R.M.; Hengartner, H.; et al. A platelet-mediated system for shuttling blood-borne bacteria to CD8α+ dendritic cells depends on glycoprotein GPIb and complement C3. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 1194–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourbakos, A.; Yuan, Y.P.; Jenkins, A.L.; Travis, J.; Andrade-Gordon, P.; Santulli, R.; Potempa, J.; Pike, R.N. Activation of prote-ase-activated receptors by gingipains from Porphyromonas gingivalis leads to platelet aggregation: A new trait in mi-crobial pathogenicity. Blood 2001, 97, 3790–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ståhl, A.L.; Svensson, M.; Mörgelin, M.; Svanborg, C.; Tarr, P.I.; Mooney, J.C.; Watkins, S.L.; Johnson, R.; Karpman, D. Lipopolysac-charide from enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli binds to platelets through TLR4 and CD62 and is detected on circulating platelets in patients with hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood 2006, 108, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerrigan, S.W.; Douglas, I.; Wray, A.; Heath, J.; Byrne, M.F.; Fitzgerald, D.; Cox, D. A role for glycoprotein Ib in Streptococcus sanguis–induced platelet aggregation. Blood 2002, 100, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miajlovic, H.; Zapotoczna, M.; Geoghegan, J.A.; Kerrigan, S.W.; Speziale, P.; Foster, T.J. Direct interaction of iron-regulated surface determinant IsdB of Staphylococcus aureus with the GPIIb/IIIa receptor on platelets. Microbiology 2010, 156, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loughman, A.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; Brennan, M.P.; Higgins, J.; Downer, R.; Cox, D.; Foster, T.J. Roles for fibrinogen, immunoglobulin and complement in platelet activation promoted by Staphylococcus aureus clumping factor A. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 57, 804–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, J.R.; Loughman, A.; Keane, F.; Brennan, M.; Knobel, M.; Higgins, J.; Visai, L.; Speziale, P.; Cox, D.; Foster, T.J. Fibron-ectin-binding proteins of Staphylococcus aureus mediate activation of human platelets via fibrinogen and fibronectin bridges to integrin GPIIb/IIIa and IgG binding to the FcgammaRIIa receptor. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 212–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dornieden, C.; Beyrich, C.; Schinke, B.; Schubert-Unkmeir, A.; Abele-Horn, M.; Speer, C.P.; Siauw, C.; Kobsar, A.; Eigenthaler, M. Group B streptococcus isolates from septic patients and healthy carriers differentially activate platelet signaling cascades. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 95, 836–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerrigan, S.W. The expanding field of platelet–bacterial interconnections. Platelets 2015, 26, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerrigan, S.W.; Cox, D. Platelet-bacterial interactions. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, D.; Kerrigan, S.W.; Watson, S.P. Platelets and the innate immune system: Mechanisms of bacterial-induced platelet ac-tivation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, M.F.; Kerrigan, S.W.; Corcoran, P.A.; Atherton, J.C.; Murray, F.E.; Fitzgerald, D.J.; Cox, D.M. Helicobacter pylori binds von Willebrand factor and interacts with GPIb to induce platelet aggregation. Gastroenterology 2003, 124, 1846–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerrigan, S.W.; Jakubovics, N.; Keane, C.; Maguire, P.; Wynne, K.; Jenkinson, H.; Cox, D. Role of Streptococcus gordonii Surface Proteins SspA/SspB and Hsa in Platelet Function. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 5740–5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beynon, R.P.; Bahl, V.K.; Prendergast, B.D. Infective endocarditis. BMJ 2006, 333, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claessens, Y.-E.; Dhainaut, J.-F. Diagnosis and treatment of severe sepsis. Crit. Care 2007, 11, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yaguchi, A.; Lobo, F.L.M.; Vincent, J.-L.; Pradier, O. Platelet function in sepsis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 2, 2096–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alt, E.; Amann-Vesti, B.R.; Madl, C.; Funk, G.; Koppensteiner, R. Platelet aggregation and blood rheology in severe sepsis/septic shock: Relation to the Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2004, 30, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.; Sharma, M.; Majumder, M.; Steier, W.; Sangal, A.; Kalawar, M. Thrombocytopenia in septic shock patients—A pro-spective observational study of incidence, risk factors and correlation with clinical outcome. Anaesth. Intensive Care 2007, 35, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coppinger, J.A.; Cagney, G.; Toomey, S.; Kislinger, T.; Belton, O.; McRedmond, J.P.; Cahill, D.J.; Emili, A.; Fitzgerald, D.J.; Maguire, P.B. Characterization of the proteins released from activated platelets leads to localization of novel platelet proteins in human atherosclerotic lesions. Blood 2004, 103, 2096–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McRedmond, J.P.; Park, S.D.; Reilly, D.F.; Coppinger, J.A.; Maguire, P.B.; Shields, D.C.; Fitzgerald, D.J. Integration of proteomics and genomics in platelets: A profile of platelet proteins and platelet-specific genes. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2004, 3, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gawaz, M.; Stellos, K.; Langer, H.F. Platelets modulate atherogenesis and progression of atherosclerotic plaques via interaction with progenitor and dendritic cells. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, H.; Nishizawa, Y. Platelet in progression of atherosclerosis: A potential target in diabetic patients. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2005, 1, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, H.F.; Gawaz, M. Platelet-vessel wall interactions in atherosclerotic disease. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 99, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, A.E.; Seizer, P.; Gawaz, M. Platelets: Inflammatory Firebugs of Vascular Walls. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuckleburg, C.J.; Tiwari, R.; Czuprynski, C.J. Endothelial cell apoptosis induced by bacteria-activated platelets requires caspase-8 and -9 and generation of reactive oxygen species. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 99, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campo, G.; Contoli, M.; Fogagnolo, A.; Sega, F.V.D.; Zucchetti, O.; Ronzoni, L.; Verri, M.; Fortini, F.; Pavasini, R.; Morandi, L.; et al. Over time relationship between platelet reactivity, myocardial injury and mortality in patients with SARS-CoV-2-associated respiratory failure. Platelets 2020, 32, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira-De-Abreu, A.; Campbell, R.A.; Weyrich, A.S.; Zimmerman, G.A. Platelets: Versatile effector cells in hemostasis, inflammation, and the immune continuum. Semin. Immunopathol. 2011, 34, 5–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Middleton, E.A.; Weyrich, A.; Zimmerman, G.A. Platelets in Pulmonary Immune Responses and Inflammatory Lung Diseases. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1211–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assinger, A. Platelets and infection—an emerging role of platelets in viral infection. Front. Immunol. 2014, 18, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Kuhn, R.J.; Rossmann, M.G. A structural perspective of the flavivirus life cycle. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blijleven, J.S.; Boonstra, S.; Onck, P.; van der Giessen, E.; van Oijen, A.M. Mechanisms of influenza viral membrane fusion. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 60, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dutartre, H.; Clavière, M.; Journo, C.; Mahieux, R. Cell-Free versus Cell-to-Cell Infection by Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 and Human T-Lymphotropic Virus Type 1: Exploring the Link among Viral Source, Viral Trafficking, and Viral Replication. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 7607–7617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, L.; Feng, K.; Wang, Y.C.; Mei, J.J.; Ning, R.T.; Zheng, H.W.; Wang, J.J.; Worthen, G.S.; Wang, X.; Song, J.; et al. Critical role of CXCL4 in the lung pathogenesis of influenza (H1N1) respiratory infection. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 1529–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenne, C.N.; Wong, C.; Zemp, F.J.; McDonald, B.; Rahman, M.M.; Forsyth, P.A.; McFadden, G.; Kubes, P. Neutrophils Recruited to Sites of Infection Protect from Virus Challenge by Releasing Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 13, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loria, G.D.; Romagnoli, P.; Moseley, N.B.; Rucavado, A.; Altman, J.D. Platelets support a protective immune response to LCMV by preventing splenic necrosis. Blood 2013, 121, 940–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shashkin, P.N.; Brown, G.T.; Ghosh, A.; Marathe, G.; McIntyre, T.M. Lipopolysaccharide Is a Direct Agonist for Platelet RNA Splicing. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 3495–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Metcalf Pate, K.A.; Lyons, C.E.; Dorsey, J.L.; Queen, S.E.; Adams, R.J.; Morrell, C.N.; Mankowski, J.L. TGFβ-Mediated Downregulation of Thrombopoietin Is Associated With Platelet Decline in Asymptomatic SIV Infection. J. Acquir. Immune. Defic Syndr. 2014, 65, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Isomura, H.; Yoshida, M.; Oda, M.; Seino, Y.; Ohuchi, R.; Uno, F.; Yamada, M.; Namba, H.; Fujiwara, N. Suppressive effects of human herpesvirus-6 on thrombopoietin-inducible megakaryocytic colony formation in vitro. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonelli, A.; Mirandola, P.; Grill, V.; Secchiero, P.; Zauli, G. Human herpesvirus 7 infection impairs the survival/differentiation of megakaryocytic cells. Haematologica 2002, 87, 1223–1225. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Afdhal, N.; McHutchison, J.; Brown, R.; Jacobson, I.; Manns, M.; Poordad, F.; Weksler, B.; Esteban, R. Thrombocytopenia associated with chronic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chelucci, C.; Federico, M.; Guerriero, R.; Mattia, G.; Casella, I.; Pelosi, E.; Testa, U.; Mariani, G.; Hassan, H.J.; Peschle, C. Productive human immunodeficiency virus-1 infection of purified megakaryocytic progenitors/precursors and maturing megakar-yocytes. Blood 1998, 91, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jeffers, L.J.; Garon, C.; Fischer, E.R.; Scheffel, J.; Moore, B.; Reddy, K.R.; Demedina, M.; Schiff, E.R. Persistence of hepatitis C virus in a human megakaryoblastic leukaemia cell line. J. Viral Hepat. 1999, 6, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crapnell, K.; Zanjani, E.D.; Chaudhuri, A.; Ascensao, J.L.; Jeor, S.S.; Maciejewski, J.P. In vitro infection of megakaryocytes and their precursors by human cytomegalovirus. Blood 2000, 95, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaujac, C.; Boukour, S.; Cramer-Bordé, E. Platelets and viruses: An ambivalent relationship. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 67, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assinger, A.; Kral, J.B.; Yaiw, K.-C.; Schrottmaier, W.C.; Kurzejamska, E.; Wang, Y.; Mohammad, A.-A.; Religa, P.; Rahbar, A.; Schabbauer, G.; et al. Human Cytomegalovirus–Platelet Interaction Triggers Toll-Like Receptor 2–Dependent Proinflammatory and Proangiogenic Responses. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coulson, B.; Londrigan, S.; Lee, D.J. Rotavirus contains integrin ligand sequences and a disintegrin-like domain that are implicated in virus entry into cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 5389–5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mackow, E.R.; Gavrilovskaya, I.N. Cellular Receptors and Hantavirus Pathogenesis. In Hantaviruses. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology; Schmaljohn, C.S., Nichol, S.T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 91–115. [Google Scholar]
- Nunez, D.; Charriaut-Marlangue, C.; Barel, M.; Benveniste, J.; Frade, R. Activation of human platelets through gp140, the C3d/EBV receptor (CR2). Eur. J. Immunol. 1987, 17, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaipan, C.; Soilleux, E.J.; Simpson, P.; Hofmann, H.; Gramberg, T.; Marzi, A.; Geier, M.; Stewart, E.A.; Eisemann, J.; Steinkasserer, A.; et al. DC-SIGN and CLEC-2 Mediate Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Capture by Platelets. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 8951–8960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maugeri, N.; Cattaneo, M.; Rovere-Querini, P.; Manfredi, A.A. Platelet clearance by circulating leukocytes: A rare event or a de-terminant of the “immune continuum”? Platelets 2014, 25, 224–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grozovsky, R.; Hoffmeister, K.M.; Falet, H. Novel clearance mechanisms of platelets. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2010, 17, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeaman, M.R. Platelets in defense against bacterial pathogens. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 67, 525–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goeijenbier, M.; van Wissen, M.; van de Weg, C.; Jong, E.; Gerdes, V.; Meijers, J.; Brandjes, D.; van Gorp, E. Review: Viral infections and mechanisms of thrombosis and bleeding. J. Med. Virol. 2012, 84, 1680–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, L.; Briggs, C.; McFadden, S.; Zini, G.; Burthem, J.; Rozenberg, G.; Proytcheva, M.; Machin, S.J. ICSH recommendations for the standardization of nomenclature and grading of peripheral blood cell morphological features. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2015, 37, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogagnolo, A.; Taccone, F.S.; Campo, G.; Montanari, G.; Capatti, B.; Ferraro, G.; Erriquez, A.; Ragazzi, R.; Creteur, J.; Volta, C.A.; et al. Impaired platelet reactivity in patients with septic shock: A proof-of-concept study. Platelets 2019, 31, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drews, R.E.; Weinberger, S.E. Thrombocytopenic Disorders in Critically Ill Patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagroop, I.A.; Clatworthy, I.; Lewin, J.; Mikhailidis, D.P. Shape change in human platelets: Measurement with a channelyzer and visualisation by electron microscopy. Platelets 2000, 11, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zampieri, F.G.; Ranzani, O.T.; Sabatoski, V.; De Souza, H.P.; Barbeiro, H.; Da Neto, L.M.C.; Park, M.; Da Silva, F.P. An increase in mean platelet volume after admission is associated with higher mortality in critically ill patients. Ann. Intensive Care 2014, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajarernmuang, P.; Phrommintikul, A.; Limsukon, A.; Pothirat, C.; Chittawatanarat, K. The Role of Mean Platelet Volume as a Predictor of Mortality in Critically Ill Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Crit. Care Res. Pr. 2016, 2016, 4370834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fogagnolo, A.; Taccone, F.S.; Benetto, G.; Franchi, F.; Scolletta, S.; Cotoia, A.; Kozhevnikova, I.; Volta, C.A.; Spadaro, S. Platelet mor-phological indices on Intensive Care Unit admission predict mortality in septic but not in non-septic patients. Minerva Anestesiol. 2021, 87, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, Z.; Eralp, O.; Ilcol, Y.O. Evaluation of platelet count and its association with plateletcrit, mean platelet volume, and platelet size distribution width in a canine model of endotoxemia. Veter. Clin. Pathol. 2008, 37, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotoia, A.; Franchi, F.; De Fazio, C.; Vincent, J.-L.; Creteur, J.; Taccone, F.S. Platelet indices and outcome after cardiac arrest. BMC Emerg. Med. 2018, 18, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furie, B.; Furie, B.C. Role of platelet P-selectin and microparticle PSGL-1 in thrombus formation. Trends Mol. Med. 2004, 10, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xu, E.; Shao, K.; Shen, W.; Gu, Y.; Li, M.; Shen, W. Circulating platelet-neutrophil aggregates as risk factor for deep venous thrombosis. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2018, 57, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrijver, I.T.; Kemperman, H.; Roest, M.; Kesecioglu, J.; De Lange, D. Soluble P-selectin as a Biomarker for Infection and Survival in Patients With a Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome on the Intensive Care Unit. Biomark. Insights 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spadaro, S.; Fogagnolo, A.; Campo, G.; Zucchetti, O.; Verri, M.; Ottaviani, I.; Tunstall, T.; Grasso, S.; Scaramuzzo, V.; Murgolo, F.; et al. Markers of endothelial and epithelial pulmonary injury in mechanically ventilated COVID-19 ICU patients. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Stoppelaar, S.F.; Van’t Veer, C.; Roelofs, J.J.; Claushuis, T.A.; de Boer, O.J.; Tanck, M.W.; Hoogendijk, A.J.; van der Poll, T. Platelet and endothelial cell P-selectin are required for host defense against Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced pneumosepsis. J. Thromb Haemost. 2015, 13, 1128–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Femia, E.A.; Scavone, M.; Lecchi, A.; Cattaneo, M. Effect of platelet count on platelet aggregation measured with impedance aggregometry (Multiplate™ analyzer) and with light transmission aggregometry. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 2193–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Blanc, J.; Lordkipanidzé, M. Platelet Function in Aging. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 6, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, M.; Cerletti, C.; Harrison, P.; Hayward, C.; Kenny, D.; Nugent, D.; Nurden, P.; Rao, A.K.; Schmaier, A.H.; Watson, S.; et al. Recommendations for the standardization of light transmission aggregometry: A consensus of the working party from the platelet physiology subcommittee of SSC/ISTH. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfert, U.T.; Haubelt, H.; Vogt, A.; Hellstern, P. Variables influencing Multiplate(TM) whole blood impedance platelet ag-gregometry and turbidimetric platelet aggregation in healthy individuals. Platelets 2007, 18, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurgeon, B.E.; Naseem, K.M. Platelet Flow Cytometry: Instrument Setup, Controls, and Panel Performance. Cytom. Part. B: Clin. Cytom. 2019, 98, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurgeon, B.E.J.; Michelson, A.D.; Iii, A.L.F. Platelet mass cytometry: Optimization of sample, reagent, and analysis parameters. Cytom. A 2021, 99, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharf, R.E. Drugs that Affect Platelet Function. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2012, 38, 865–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burroughs, S.F.; Johnson, G.J. Beta-lactamantibiotic-induced platelet dysfunction: Evidence for irreversible inhibition of platelet activation in vitro and in vivo after prolonged exposure to penicillin. Blood 1990, 75, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shattil, S.J.; Bennett, J.S.; McDonough, M.; Turnbull, J. Carbenicillin and penicillin G inhibit platelet function in vitro by im-pairing the interaction of agonists with the platelet surface. J. Clin. Investig. 1980, 65, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiliaki, S. Piperacillin–Tazobactam-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia: A Case Report. J. Pharm. Pr. 2021, 08971900211048140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, T.D.; Nylander, S.; Whatling, C. Anti-platelet therapy: Cyclo-oxygenase inhibition and the use of aspirin with par-ticular regard to dual anti-platelet therapy. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 72, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schafer, A.I. Effects of Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs on Platelet Function and Systemic Hemostasis. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1995, 35, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Boylan, B.; Fang, J.; Wilcox, D.A.; Newman, D.K.; Newman, P.J. Heparin promotes platelet responsiveness by potentiating αIIbβ3-mediated outside-in signaling. Blood 2011, 117, 4946–4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arepally, G.M. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood 2017, 129, 2864–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuker, A.; Arepally, G.M.; Chong, B.H.; Cines, D.B.; Greinacher, A.; Gruel, Y.; Linkins, L.A.; Rodner, S.B.; Selleng, S.; Warkentin, T.E.; et al. American Society of Hematology 2018 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 3360–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greinacher, A.; Eichler, P.; Lubenow, N.; Kwasny, H.; Luz, M. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia with thromboembolic complications: Meta-analysis of 2 prospective trials to assess the value of parenteral treatment with lepirudin and its therapeutic aPTT range. Blood 2000, 96, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozek-Langenecker, S.A.; Afshari, A.; Albaladejo, P.; Santullano, C.A.; De Robertis, E.; Filipescu, D.C.; Fries, D.; Görlinger, K.; Haas, T.; Imberger, G.; et al. Management of severe perioperative bleeding: Guidelines from the European Society of Anaesthesiology. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2013, 30, 270–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fogagnolo, A.; Taccone, F.S.; Vincent, J.L.; Benetto, G.; Cavalcante, E.; Marangoni, E.; Ragazzi, R.; Creteur, J.; Volta, C.A.; Spadaro, S. Using arterial-venous oxygen difference to guide red blood cell transfusion strategy. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mossberg, K.E.; Pournaras, D.J.; Welbourn, R.; le Roux, C.W.; Brogren, H. Differential response of plasma plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 after weight loss surgery in patients with or without type 2 diabetes. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2016, 13, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, K.; Nishino, N.; Baba, S.; Urano, T.; Takada, A. Postoperative changes in plasma tissue-type plasminogen activator and type I plasminogen activator inhibitor. Surg. Today 1994, 24, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, D.; Zheng, D. Coagulation is more affected by quick than slow bleeding in patients with massive blood loss. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2017, 28, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Losos, M.; Yang, S.; Li, J.; Wu, H.; Cataland, S. Increased complement activation during platelet storage. Transfusion 2017, 57, 2182–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
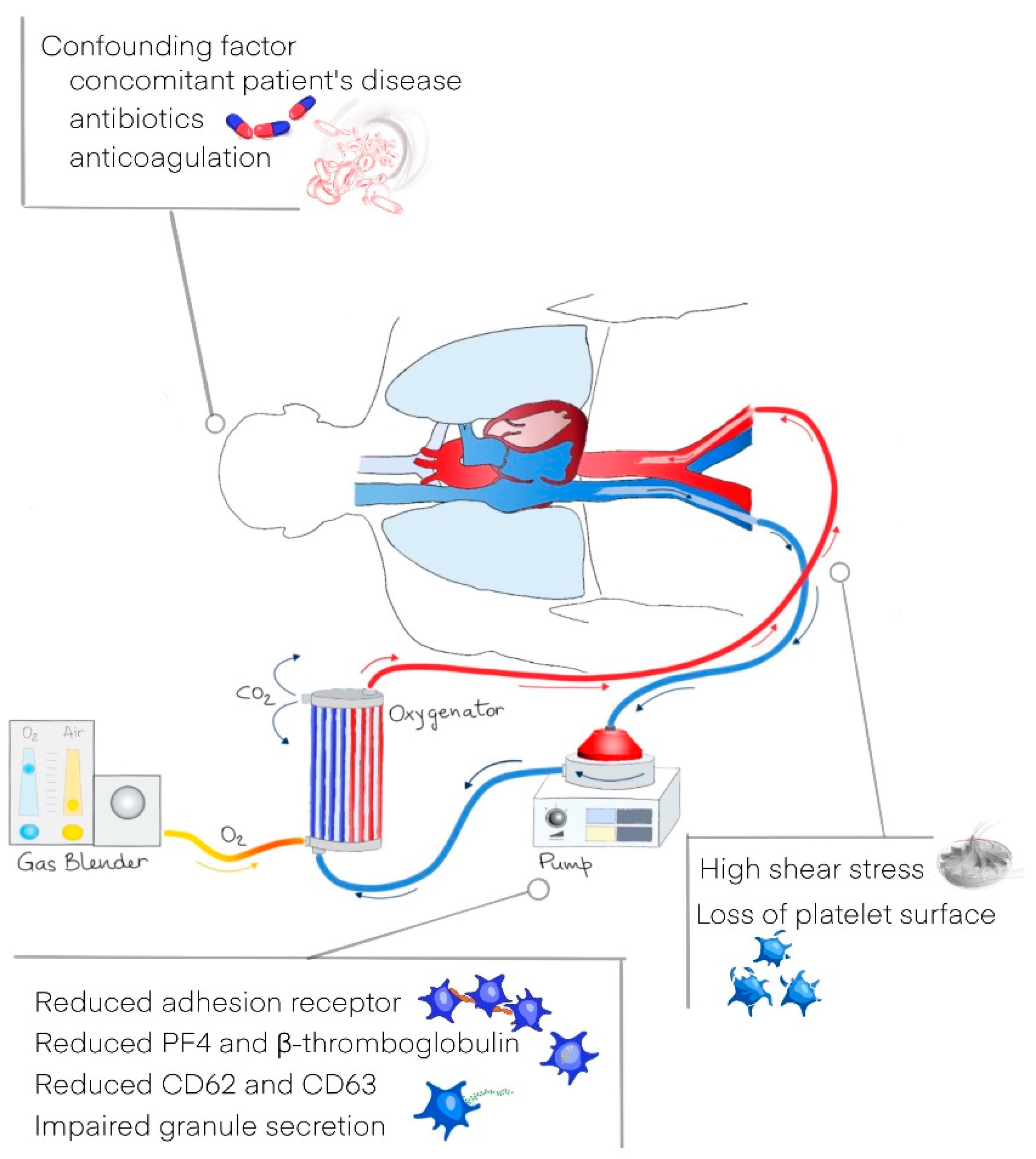
- Jiritano, F.; Serraino, G.F.; Cate, H.T.; Fina, D.; Matteucci, M.; Mastroroberto, P.; Lorusso, R. Platelets and extra-corporeal membrane oxygenation in adult patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensiv. Care Med. 2020, 46, 1154–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balle, C.M.; Jeppesen, A.N.; Christensen, S.; Hvas, A.-M. Platelet Function During Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Adult Patients: A Systematic Review. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 5, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquer, S.; De Haro, C.; Peruga, P.; Oliva, J.C.; Artigas, A. Systematic review and meta-analysis of complications and mortality of veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for refractory acute respiratory distress syndrome. Ann. Intensive Care 2017, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlebowski, M.M.; Baltagi, S.; Carlson, M.; Levy, J.H.; Spinella, P.C. Clinical controversies in anticoagulation monitoring and antithrombin supplementation for ECMO. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lukito, P.; Wong, A.; Jing, J.; Arthur, J.F.; Marasco, S.F.; Murphy, D.A.; Bergin, P.J.; Shaw, J.A.; Collecutt, M.; Andrews, R.K.; et al. Mechanical circulatory support is associated with loss of platelet receptors glycoprotein Ibα and glycoprotein VI. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 2253–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalbhenn, J.; Schlagenhauf, A.; Rosenfelder, S.; Schmutz, A.; Zieger, B. Acquired von Willebrand syndrome and impaired platelet function during venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: Rapid onset and fast recovery. J. Hear. Lung Transplant. 2018, 37, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, P.M.; Chalupsky, J.; Olivier, C.B.; Bojti, I.; Pooth, J.-S.; Trummer, G.; Bode, C.; Diehl, P. Early platelet dysfunction in patients receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation is associated with mortality. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiegele, M.; Infanger, L.; Lacom, C.; Koch, S.; Baierl, A.; Schaden, E. Thrombin Generation and Platelet Function in ICU Patients Undergoing CVVHD Using Regional Citrate Anticoagulation. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wand, S.; Schneider, S.; Meybohm, P.; Zacharowski, K.; Weber, C.F. Assessment of hemo-static changes after initiation of con-tinuous venovenous hemodialysis. Clin. Lab. 2015, 61, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidance from the Expert Haematology Panel (EHP) on Covid-19 Vaccineinduced Immune Thrombocytopenia and Thrombosis (VITT). Available online: https://b-s-h.org.uk/about-us/news/guidance-produced-by-the-expert-haematology-panel-ehp-focussed-on-vaccine-induced-thrombosis-and-thrombocytopenia-vitt/ (accessed on 5 December 2021).
- Greinacher, A.; Thiele, T.; Warkentin, T.E.; Weisser, K.; Kyrle, P.A.; Eichinger, S. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 nCov-19 Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2092–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, D.; Liu, Y.; Shayakhmetov, D.; Li, Z.-Y.; Ni, S.; Lieber, A. Adenovirus-Platelet Interaction in Blood Causes Virus Sequestration to the Reticuloendothelial System of the Liver. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 4866–4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, Z.; Greene, M.I.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, H. Structural Features and PF4 Functions that Occur in Heparin-Induced Thrombocy-topenia (HIT) Complicated by COVID- 19. Antibodies 2020, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semple, J.W. Platelets play a direct role in sepsis-associated endothelial cell death. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 99, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semple, J.W.; Italiano, J.E., Jr.; Freedman, J. Platelets and the immune continuum. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewitte, A.; Lepreux, S.; Villeneuve, J.; Rigothier, C.; Combe, C.; Ouattara, A.; Ripoche, J.; Dewitte, A.; Lepreux, S.; Villeneuve, J.; et al. Blood platelets and sepsis pathophysiology: A new therapeutic prospect in critical ill patients? Ann. Intensive Care 2017, 7, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Venkata, C.; Kashyap, R.; Farmer, J.C.; Afessa, B. Thrombocytopenia in adult patients with sepsis: Incidence, risk factors, and its association with clinical outcome. J. Intensive Care 2013, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bounes, V.F.; Mémier, V.; Marcaud, M.; Jacquemin, A.; Hamzeh-Cognasse, H.; Garcia, C.; Series, J.; Sié, P.; Minville, V.; Gratacap, M.P.; et al. Platelet activation and prothrombotic properties in a mouse model of peritoneal sepsis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, A.; Rana, A.; Westein, E.; Westein, E.; Niego, B.; Niego, B.; Hagemeyer, C.E.; Hagemeyer, C.E.; Rana, A.; Rana, A.; et al. Shear-Dependent Platelet Aggregation: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 6, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakariassen, K.S.; Orning, L.; Turitto, V.T. The impact of blood shear rate on arterial thrombus formation. Futur. Sci. OA 2015, 1, FSO30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finsterbusch, M.; Schrottmaier, W.C.; Kral-Pointner, J.B.; Salzmann, M.; Assingerm, A. Measuring and interpreting platelet-leukocyte aggregates. Platelets 2018, 29, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.K.; Brown, P.D.N.; Lund, B.V.; Nielsen, O.J.; Hasselbalch, H. Increased circulating platelet-leukocyte aggregates in myeloproliferative disorders is correlated to previous thrombosis, platelet activation and platelet count. Eur. J. Haematol. 2001, 66, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, Y.; Du, L.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, J. Platelet-leukocyte aggregate is associated with adverse events after surgical intervention for rheumatic heart disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawaz, M.; Fateh-Moghadam, S.; Pilz, G.; Gurland, H.J.; Werdan, K. Platelet activation and interaction with leucocytes in pa-tients with sepsis or multiple organ failure. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 25, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, S.M.; Lutay, N.; Holmqvist, B.; Shannon, O. The Dynamics of Platelet Activation during the Progression of Strepto-coccal Sepsis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarbock, A.; Singbartl, K.; Ley, K. Complete reversal of acid-induced acute lung injury by blocking of platelet-neutrophil aggregation. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 3211–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lupu, F.; Kinasewitz, G.; Dormer, K. The role of endothelial shear stress on haemodynamics, inflammation, coagulation and glycocalyx during sepsis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 12258–12271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehamzeh-Cognasse, H.; Edamien, P.; Echabert, A.; Pozzetto, B.; Ecognasse, F.; Egarraud, O. Platelets and Infections – Complex Interactions with Bacteria. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greco, E.; Lupia, E.; Bosco, O.; Vizio, B.; Montrucchio, G. Platelets and Multi-Organ Failure in Sepsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDonald, B.; Davis, R.P.; Kim, S.-J.; Tse, M.; Esmon, C.T.; Kolaczkowska, E.; Jenne, C.N. Platelets and neutrophil extracellular traps collaborate to promote intravascular coagulation during sepsis in mice. Blood 2017, 129, 1357–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van den Boogaard, F.E.; Schouten, M.; de Stoppelaar, S.F.; Roelofs, J.J.; Brands, X.; Schultz, M.J.; van’t Veer, C.; van der Poll, T. Throm-bocytopenia impairs host defense during murine Streptococcus pneumoniae pneumonia. Crit Care Med. 2015, 43, e75–e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Stoppelaar, S.F.; van ‘t Veer, C.; Claushuis, T.A.; Albersen, B.J.; Roelofs, J.J.; van der Poll, T. Thrombocytopenia impairs host defense in gram-negative pneumonia-derived sepsis in mice. Blood 2014, 124, 3781–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birnie, E.; Claushuis, T.A.M.; Koh, G.C.K.W.; Limmathurotsakul, D.; Day, N.P.J.; Roelofs, J.J.T.H.; Ware, J.; Hou, B.; de Vos, A.F.; van der Poll, T.; et al. Thrombocytopenia Impairs Host Defense Against Burkholderia pseudomallei (Meli-oidosis). J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 219, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Claushuis, T.A.M.; Van Vught, L.A.; Scicluna, B.; Wiewel, M.A.; Klouwenberg, P.M.C.K.; Hoogendijk, A.J.; Ong, D.; Cremer, O.; Horn, J.; Franitza, M.; et al. Thrombocytopenia is associated with a dysregulated host response in critically ill sepsis patients. Blood 2016, 127, 3062–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kor, D.J.; Erlich, J.; Gong, M.N.; Malinchoc, M.; Carter, R.E.; Gajic, O.; Talmor, D.S. Association of prehospitalization aspirin therapy and acute lung injury: Results of a multicenter international observational study of at-risk patients. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 39, 2393–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valerio-Rojas, J.C.; Jaffer, I.J.; Kor, D.J.; Gajic, O.; Cartin-Ceba, R. Outcomes of Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock Patients on Chronic Antiplatelet Treatment: A Historical Cohort Study. Crit. Care Res. Pr. 2013, 2013, 782573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, A.K.; Dunn, S.P.; Feola, D.J.; Martin, C.A.; Charnigo, R.; Li, Z.; Abdel-Latif, A.; Smyth, S.S. Clopidogrel treatment and the in-cidence and severity of community acquired pneumonia in a cohort study and meta-analysis of antiplatelet therapy in pneumonia and critical illness. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2013, 35, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kor, D.J.; Carter, R.E.; Park, P.K.; Festic, E.; Banner-Goodspeed, V.M.; Hinds, R.; Talmor, D.; Gajic, O.; Ware, L.B.; Gong, M.N.; et al. Effect of Aspirin on Development of ARDS in At-Risk Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department: The LIPS-A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 315, 2406–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eisen, D.P.; Leder, K.; Woods, R.L.; Lockery, J.E.; McGuinness, S.L.; Wolfe, R.; Pilcher, D.; Moore, E.M.; Shastry, A.; Nelson, M.R.; et al. Effect of aspirin on deaths associated with sepsis in healthy older people (ANTISEPSIS): A ran-domised, double-blind, placebo-controlled primary prevention trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2021, 9, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Technique | Function | Strengths | Pitfalls |
|---|---|---|---|
| LTA | Evaluation of changes in transmission of light through a sample of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) or platelet suspensions in buffer in response to the addition of a platelet agonist | Less influenced by platelet count Available guidelines on how to interpret LTA results | Time-consuming and technically challenging technique High cost of reagents and consumables |
| IA | Calculation of the increase in electrical resistance between two electrodes immersed in a diluted sample of whole blood, PRP, or platelet suspension | Shortening of the time window to surgery following P2Y12 inhibitor discontinuation | Misdiagnose of dense granule secretion defects Inferior to LTA for the detection and discrimination of mild platelet function disorders |
| lumi-aggregometer | Different version of LTA, quantifying the ATP secretion with a luciferin/luciferase assay in parallel with platelet aggregation measures | Information on platelet secretion in addition to platelet aggregation measures | Few reports in the literature on its performance and validation Affected by several variables (concentration of luciferin/luciferase, agonists and ATP standard, volume of PPP and PRP, duration of incubation and measurement, adjustment of platelet count of the PRP). |
| PFA-200 | Assessment of platelet deposition and thrombus growth by microscopy requiring blood to flow over a surface coated with a thrombogenic substrate | Comprehension of the behavior of platelets under physiological and pathological flow, as it occurs within a vessel | Fairly insensitive for the detection of mild platelet function defects |
| Flow cytometry | Analysis of the expression of activation markers on platelets surface | A smaller volume of blood is needed without platelet-rich plasma preparation | Further validation and standardization tests are required before its application in diagnostic laboratories |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fogagnolo, A.; Campo, G.C.; Mari, M.; Pompei, G.; Pavasini, R.; Volta, C.A.; Spadaro, S. The Underestimated Role of Platelets in Severe Infection a Narrative Review. Cells 2022, 11, 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030424
Fogagnolo A, Campo GC, Mari M, Pompei G, Pavasini R, Volta CA, Spadaro S. The Underestimated Role of Platelets in Severe Infection a Narrative Review. Cells. 2022; 11(3):424. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030424
Chicago/Turabian StyleFogagnolo, Alberto, Gianluca Calogero Campo, Matilde Mari, Graziella Pompei, Rita Pavasini, Carlo Alberto Volta, and Savino Spadaro. 2022. "The Underestimated Role of Platelets in Severe Infection a Narrative Review" Cells 11, no. 3: 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030424
APA StyleFogagnolo, A., Campo, G. C., Mari, M., Pompei, G., Pavasini, R., Volta, C. A., & Spadaro, S. (2022). The Underestimated Role of Platelets in Severe Infection a Narrative Review. Cells, 11(3), 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030424