Post-COVID Complications after Pressure Ulcer Surgery in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury Associate with Creatine Kinase Upregulation in Adipose Tissue
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Surgical Procedure
2.4. Biopsy Procedure
2.5. Blood Sera Collection
2.6. Protein Isolation
2.7. RNA Isolation
2.8. SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR, Immunohistochemistry, and Immunological and Proteomic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of the Patients
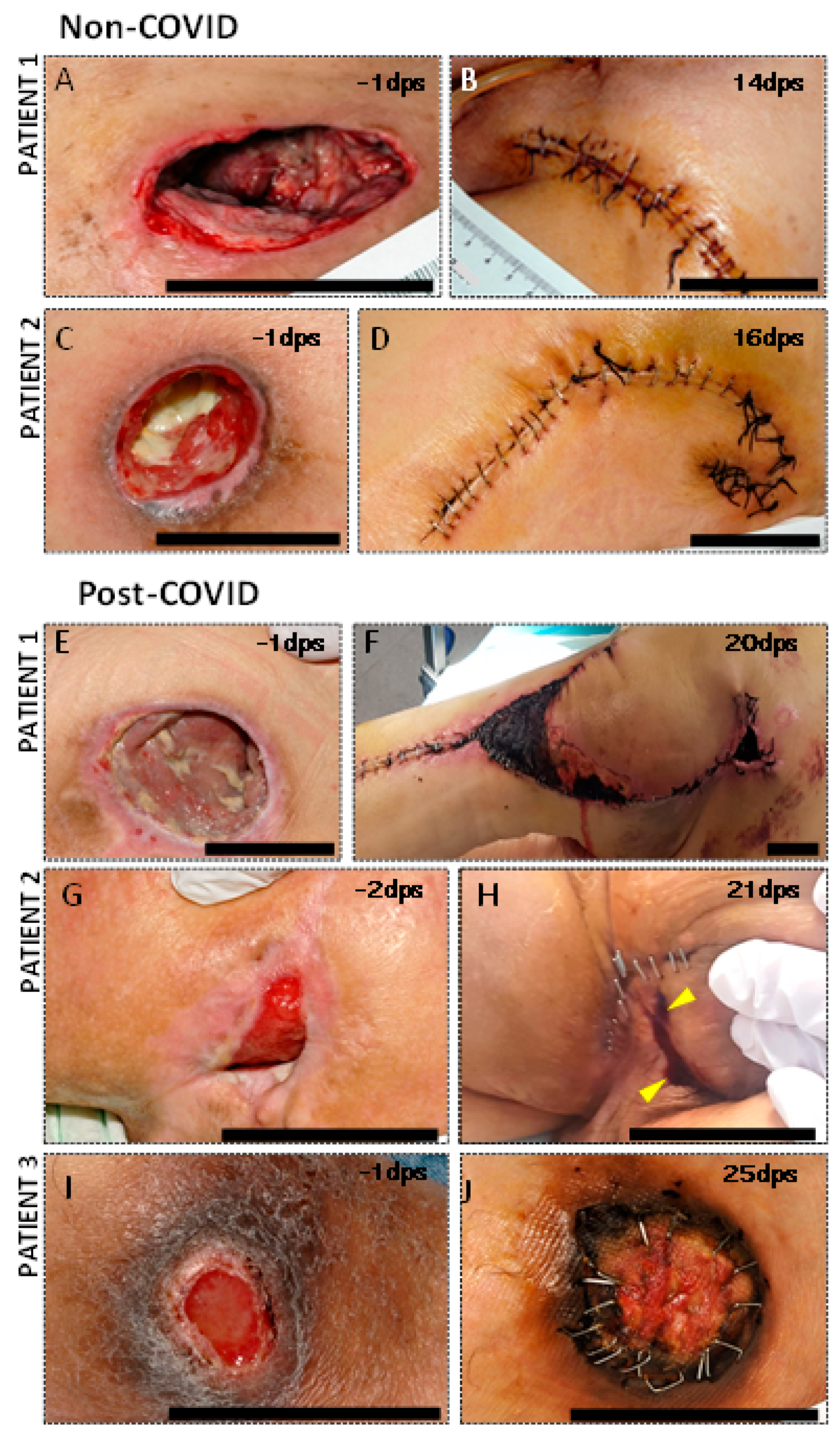
3.2. Clinical Complications in PU Postsurgical Recovery of SCI COVID Patients
3.3. The Subcutaneous White Adipose Tissue of Post-COVID Patients Does Not Show Presence of Viral Load
3.4. Proteomic Analysis Revealed an Increased Presence of Creatine Kinase Isoforms in s-WAT of COVID Patients
3.5. The Expression of CKM and CKMT2 in COVID s-WAT Is Found in Multinucleated Giant Cells
3.6. Antibodies against Post-COVID-Induced Proteins Can Be Found in the Serum of Post-COVID Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zakrasek, E.C.; Creasey, G.; Crew, J.D. Pressure ulcers in people with spinal cord injury in developing nations. Spinal Cord 2015, 53, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, R.A.; Cullum, N.A. Interventions for pressure ulcers: A summary of evidence for prevention and treatment. Spinal Cord 2018, 56, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uimonen, M.; Kuitunen, I.; Paloneva, J.; Launonen, A.P.; Ponkilainen, V.; Mattila, V.M. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on waiting times for elective surgery patients: A multicenter study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Lancet Rheumatology Too long to wait: The impact of COVID-19 on elective surgery. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021, 3, e83. [CrossRef]
- Bhangu, A.; Nepogodiev, D.; Glasbey, J.C.; Li, E.; Omar, O.M.; Gujjuri, R.R.; Morton, D.G.; Tsoulfas, G.; Keller, D.S.; Smart, N.J.; et al. Mortality and pulmonary complications in patients undergoing surgery with perioperative sars-cov-2 infection: An international cohort study. Lancet 2020, 396, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaborative, C.; Collaborative, G. Timing of surgery following SARS-CoV-2 infection: An international prospective cohort study. Anaesthesia 2021, 76, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.Z.; Chan, J.S.; Potter, A.L.; Chen, Y.-W.; Sandhu, H.S.; Panda, N.; Chang, D.C.; Yang, C.-F.J. The Risk of Postoperative Complications After Major Elective Surgery in Active or Resolved COVID-19 in the United States. Ann. Surg. 2022, 275, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.; Cuddigan, J.; Capasso, V.; Cox, J.; Delmore, B.M.N. Unavoidable Pressure Injury during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Position Paper from the National Pressure Injury Advisory Panel Previously the National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel (NPUAP) 1 ©NPIAP. 2020, pp. 1–8. Available online: https://cdn.ymaws.com/npiap.com/resource/resmgr/white_papers/Unavoidable_in_COVID_Pandemi.pdf (accessed on 3 April 2022).
- Tang, J.; Li, B.; Gong, J.; Li, W.; Yang, J. Challenges in the management of critical ill COVID-19 patients with pressure ulcer. Int. Wound J. 2020, 17, 1523–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuniavsky, M.; Vilenchik, E.; Lubanetz, A. Under (less) pressure—Facial pressure ulcer development in ventilated ICU patients: A prospective comparative study comparing two types of endotracheal tube fixations. Intensive Crit. Care Nurs. 2020, 58, 102804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ligt, M.; Hesselink, M.K.C.; Jorgensen, J.; Hoebers, N.; Blaak, E.E.; Goossens, G.H. Resveratrol supplementation reduces ACE2 expression in human adipose tissue. Adipocyte 2021, 10, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Benna, S. Association of high level gene expression of ACE2 in adipose tissue with mortality of COVID-19 infection in obese patients. Obes. Med. 2020, 19, 100283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheja, L.; Heeren, J. The endocrine function of adipose tissues in health and cardiometabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 507–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poma, A.M.; Bonuccelli, D.; Giannini, R.; Macerola, E.; Vignali, P.; Ugolini, C.; Torregrossa, L.; Proietti, A.; Pistello, M.; Basolo, A.; et al. COVID-19 autopsy cases: Detection of virus in endocrine tissues. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 45, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, M.; Cao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Long, X.; Liu, Z.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 not found in pressure injury exudates from COVID-19 patients. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, A.K.; Anderson, J.M. Macrophage fusion and multinucleated giant cells of inflammation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2011, 713, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, Y.; Ibata, I.; Ito, D.; Ohsawa, K.; Kohsaka, S. A Novel Geneiba1in the Major Histocompatibility Complex Class III Region Encoding an EF Hand Protein Expressed in a Monocytic Lineage. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 224, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knisely, A.; Zhou, Z.N.; Wu, J.; Huang, Y.; Holcomb, K.; Melamed, A.; Advincula, A.P.; Lalwani, A.; Khoury-Collado, F.; Tergas, A.I.; et al. Perioperative morbidity and mortality of patients with COVID-19 who undergo urgent and emergent surgical procedures. Ann. Surg. 2021, 273, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, H.E.; Deus, B.; Gerok, W. Mitochondrial creatine kinase from human heart muscle: Purification and characterization of the crystallized isoenzyme. J. Biochem. 1983, 94, 1247–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Jin, H.; Wang, M.; Hu, Y.; Chen, S.; He, Q.; Chang, J.; Hong, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, D.; et al. Neurologic Manifestations of Hospitalized Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akbar, M.R.; Pranata, R.; Wibowo, A.; Lim, M.A.; Sihite, T.A.; Martha, J.W. The prognostic value of elevated creatine kinase to predict poor outcome in patients with COVID-19—A systematic review and meta-analysis: Creatinine Kinase in COVID-19. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2021, 15, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsucci, D.; Trezzi, M.; Anichini, R.; Blanc, P.; Barontini, L.; Biagini, C.; Capitanini, A.; Comeglio, M.; Corsini, P.; Gemignani, F.; et al. Increased creatine kinase may predict a worse covid-19 outcome. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, T. Signaling—2000 and Beyond. Cell 2000, 100, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Besant, P.; Attwood, P.; Piggott, M. Focus on Phosphoarginine and Phospholysine. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2009, 10, 536–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, P.J.; Glogauer, M.; McCulloch, C.A. An Overview of the Derivation and Function of Multinucleated Giant Cells and Their Role in Pathologic Processes. Am. J. Pathol. 2019, 189, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lê, K.-A.; Mahurkar, S.; Alderete, T.L.; Hasson, R.E.; Adam, T.C.; Kim, J.S.; Beale, E.; Xie, C.; Greenberg, A.S.; Allayee, H.; et al. Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Macrophage Infiltration Is Associated with Hepatic and Visceral Fat Deposition, Hyperinsulinemia, and Stimulation of NF-κB Stress Pathway. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2802–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braune, J.; Lindhorst, A.; Fröba, J.; Hobusch, C.; Kovacs, P.; Blüher, M.; Eilers, J.; Bechmann, I.; Gericke, M. Multinucleated giant cells in adipose tissue are specialized in adipocyte degradation. Diabetes 2021, 70, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.H.; Manickam, B.; Ryvkin, V.; Zhou, X.J.; Fantuzzi, G.; Mazzone, T.; Sam, S. PCOS Is Associated with Increased CD11c Expression and Crown-Like Structures in Adipose Tissue and Increased Central Abdominal Fat Depots Independent of Obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E17–E24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Apovian, C.M.; Bigornia, S.; Mott, M.; Meyers, M.R.; Ulloor, J.; Gagua, M.; McDonnell, M.; Hess, D.; Joseph, L.; Gokce, N. Adipose Macrophage Infiltration Is Associated with Insulin Resistance and Vascular Endothelial Dysfunction in Obese Subjects. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 1654–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miron, R.J.; Bosshardt, D.D. Multinucleated Giant Cells: Good Guys or Bad Guys? Tissue Eng.-Part B Rev. 2018, 24, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suess, C.; Hausmann, R. Gross and histopathological pulmonary findings in a COVID-19 associated death during self-isolation. Int. J. Legal Med. 2020, 134, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernazza, A.; Mancini, M.; Rullo, E.; Bassi, M.; De Giacomo, T.; Della Rocca, C.; d’Amati, G. Early histologic findings of pulmonary SARS-CoV-2 infection detected in a surgical specimen. Virchows Arch. 2020, 477, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oprinca, G.C.; Muja, L.A. Postmortem examination of three SARS-CoV-2-positive autopsies including histopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis. Int. J. Legal Med. 2021, 135, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishwajeet, V.; Purohit, A.; Kumar, D.; Vijayvergia, P.; Tripathi, S.; Kanchan, T.; Kothari, N.; Dutt, N.; Elhence, P.A.; Bhatia, P.K.; et al. Evaluation of Liver Histopathological Findings of Coronavirus Disease 2019 by Minimally Invasive Autopsies. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2021, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhao, P.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L.; et al. Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, G.; Polling, S.; Pluk, H.; Venselaar, H.; Wijers, M.; Willemse, M.; Fransen, J.A.M.; Wieringa, B. Submembranous recruitment of creatine kinase B supports formation of dynamic actin-based protrusions of macrophages and relies on its C-terminal flexible loop. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 94, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loike, J.D.; Kozler, V.F.; Silverstein, S.C. Creatine kinase expression and creatine phosphate accumulation are developmentally regulated during differentiation of mouse and human monocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1984, 159, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gagiannis, D.; Steinestel, J.; Hackenbroch, C.; Schreiner, B.; Hannemann, M.; Bloch, W.; Umathum, V.G.; Gebauer, N.; Rother, C.; Stahl, M.; et al. Clinical, Serological, and Histopathological Similarities Between Severe COVID-19 and Acute Exacerbation of Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (CTD-ILD). Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 587517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.Y.; Mao, T.; Klein, J.; Dai, Y.; Huck, J.D.; Jaycox, J.R.; Liu, F.; Zhou, T.; Israelow, B.; Wong, P.; et al. Diverse functional autoantibodies in patients with COVID-19. Nature 2021, 595, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, A.; AlOtaiby, S.; Al Badarin, F.; Khraibi, A.; Hamdan, H.; Nader, M. Interaction of SARS-CoV-2 with cardiomyocytes: Insight into the underlying molecular mechanisms of cardiac injury and pharmacotherapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 146, 112518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchenko, A.; Wilm, M.; Vorm, O.; Mann, M. Mass spectrometric sequencing of proteins from silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, C.S.; Foehr, S.; Garfield, D.A.; Furlong, E.E.; Steinmetz, L.M.; Krijgsveld, J. Ultrasensitive proteome analysis using paramagnetic bead technology. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2014, 10, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shilov, I.V.; Seymour, S.L.; Patel, A.A.; Loboda, A.; Tang, W.H.; Keating, S.P.; Schaeffer, D.A. The paragon algorithm, a next generation search engine that uses sequence temperature values sequence temperature values and feature probabilities to identify peptides from tandem mass spectra. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2007, 6, 1638–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arevalo-Martin, A.; Grassner, L.; Garcia-Ovejero, D.; Paniagua-Torija, B.; Barroso-Garcia, G.; Arandilla, A.G.; Molina-Holgado, E. Elevated autoantibodies in subacute human spinal cord injury are naturally occurring antibodies. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Patients | Age | Sex | SCI | Grade PU | PU Localization | Comorbidity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-pandemic 2019 | 1 | 62 | M | P/C | IV | Ischium | Hypomagnesemia, diabetic peripheral vascular disease dyslipidemia |
| 2 | 56 | M | P/C | IV | Sacrum | Diabetic dyslipidemia | |
| 3 | 43 | M | P/I | IV | Heel | Arterial hypertension heart disease | |
| 4 | 48 | W | T/C | IV | Ischium | Respiratory insufficiency | |
| 5 | 54 | M | P/C | IV | Ischium | Arterial hypertension | |
| 6 | 58 | M | T/C | III | Trochanter | Respiratory insufficiency | |
| 7 | 64 | M | T/I | IV | Trochanter | Scoliosis pectus excavatum Respiratory insufficiency | |
| Pandemic 2020–2021 | 1 | 67 | M | P/C | IV | Trochanter | Diabetic obesity heart disease post-COVID-19 |
| 2 | 53 | M | P/C | IV | Ischium | Post-COVID-19 | |
| 3 | 39 | M | P/C | III | Heel | Post-COVID-19 | |
| 4 | 71 | W | P/C | IV | Ischium | Hypercholesterolemia | |
| 5 | 50 | M | P/C | IV | Trochanter | Osteoporosis | |
| 6 | 35 | M | P/C | IV | Ischium | Baclofen pump | |
| 7 | 67 | M | P/C | IV | Trochanter | Deep vein thrombosis OSAHS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Torija, M.; Esteban, P.F.; Espino-Rodríguez, F.J.; Paniagua-Torija, B.; Molina-Holgado, E.; Ceruelo, S.; Barroso-Garcia, G.; Arandilla, A.G.; Lopez-Almodovar, L.F.; Arevalo-Martin, A.; et al. Post-COVID Complications after Pressure Ulcer Surgery in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury Associate with Creatine Kinase Upregulation in Adipose Tissue. Cells 2022, 11, 1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11081282
Martínez-Torija M, Esteban PF, Espino-Rodríguez FJ, Paniagua-Torija B, Molina-Holgado E, Ceruelo S, Barroso-Garcia G, Arandilla AG, Lopez-Almodovar LF, Arevalo-Martin A, et al. Post-COVID Complications after Pressure Ulcer Surgery in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury Associate with Creatine Kinase Upregulation in Adipose Tissue. Cells. 2022; 11(8):1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11081282
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Torija, Mario, Pedro F. Esteban, Francisco Javier Espino-Rodríguez, Beatriz Paniagua-Torija, Eduardo Molina-Holgado, Silvia Ceruelo, Gemma Barroso-Garcia, Alba G. Arandilla, Luis F. Lopez-Almodovar, Angel Arevalo-Martin, and et al. 2022. "Post-COVID Complications after Pressure Ulcer Surgery in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury Associate with Creatine Kinase Upregulation in Adipose Tissue" Cells 11, no. 8: 1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11081282
APA StyleMartínez-Torija, M., Esteban, P. F., Espino-Rodríguez, F. J., Paniagua-Torija, B., Molina-Holgado, E., Ceruelo, S., Barroso-Garcia, G., Arandilla, A. G., Lopez-Almodovar, L. F., Arevalo-Martin, A., Moreno, J. A., Garcia-Ovejero, D., Durán-Ruiz, M. C., & Moreno-Luna, R. (2022). Post-COVID Complications after Pressure Ulcer Surgery in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury Associate with Creatine Kinase Upregulation in Adipose Tissue. Cells, 11(8), 1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11081282







