Bronchoalveolar-Lavage-Derived Fibroblast Cell Line (B-LSDM7) as a New Protocol for Investigating the Mechanisms of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Characteristics
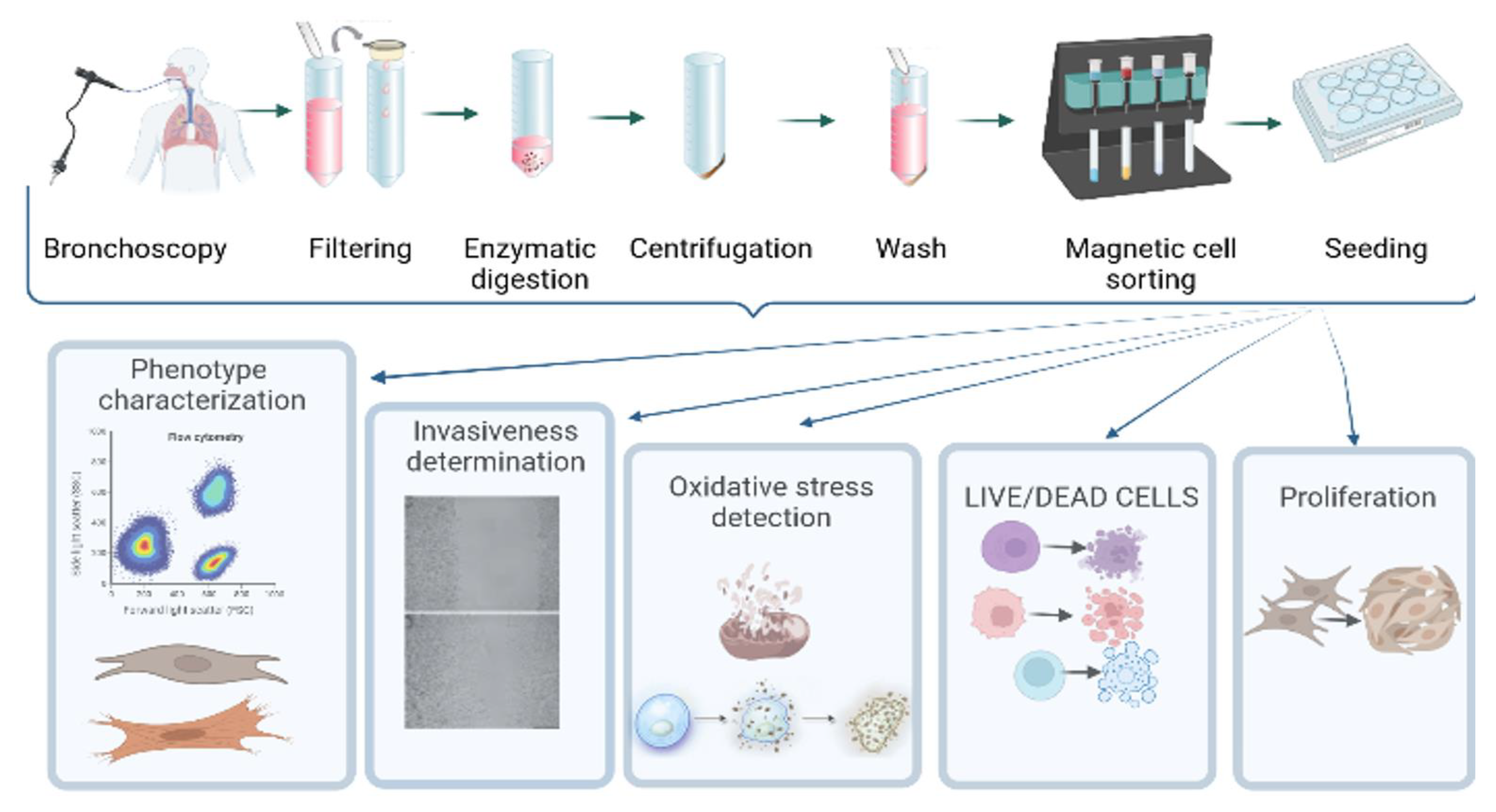
2.2. Collection and Processing of BAL
2.3. Isolation of Adhering Cells
2.4. Fibroblast-Like Cell Culture Derived from BAL
2.5. Fibroblast Cell Culture
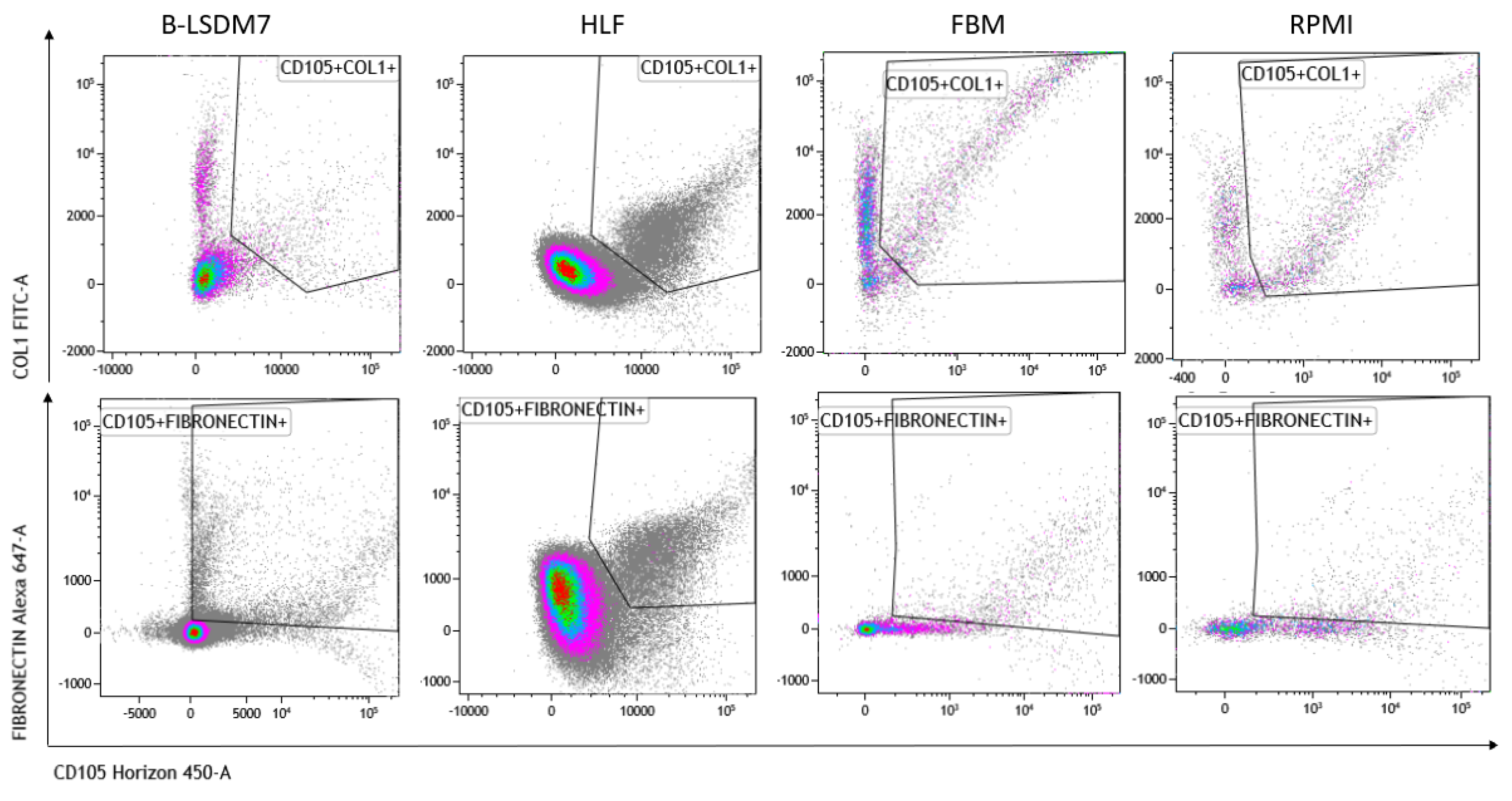
2.6. Characterization of Phenotype
2.7. Wound Scratch Test
2.8. Cell Sorting with Anti-Fibroblast Microbeads
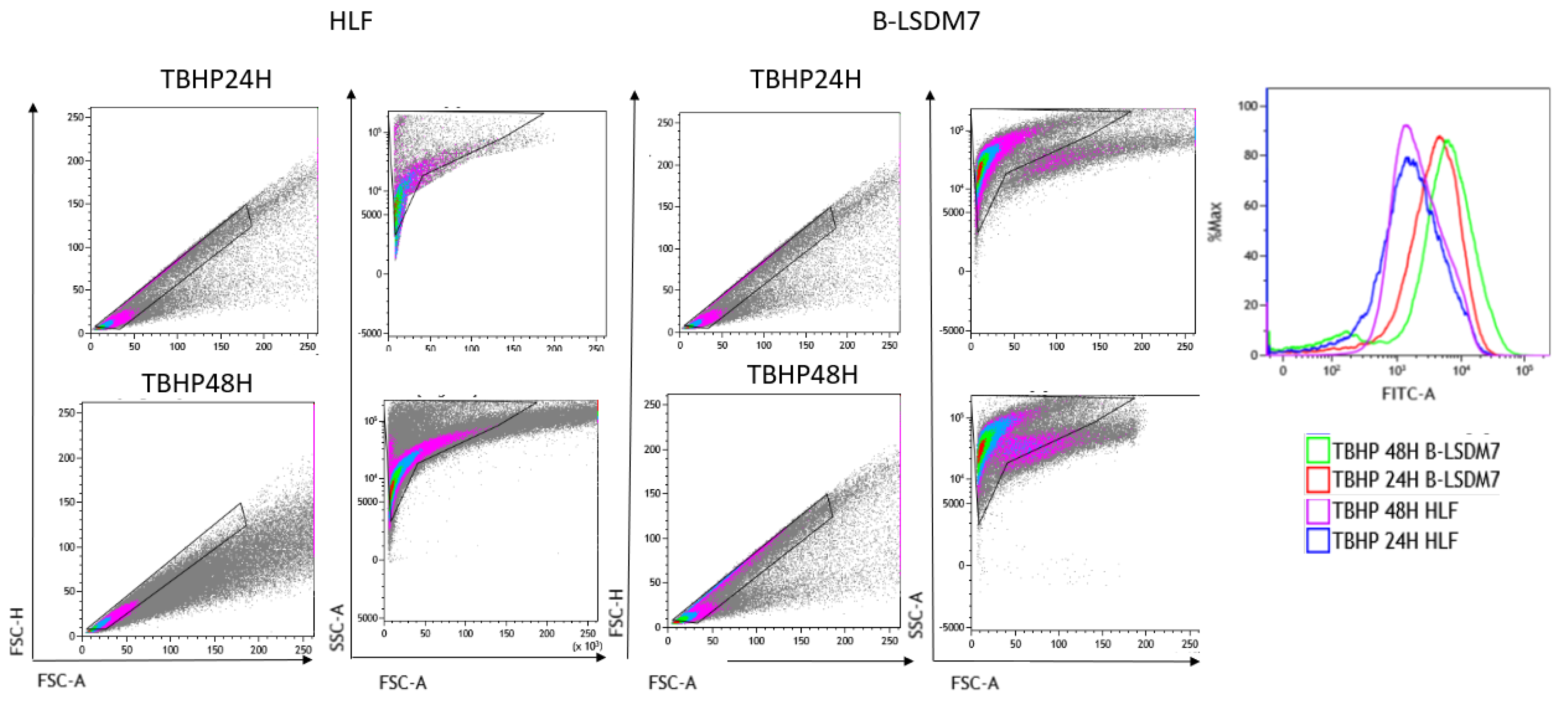
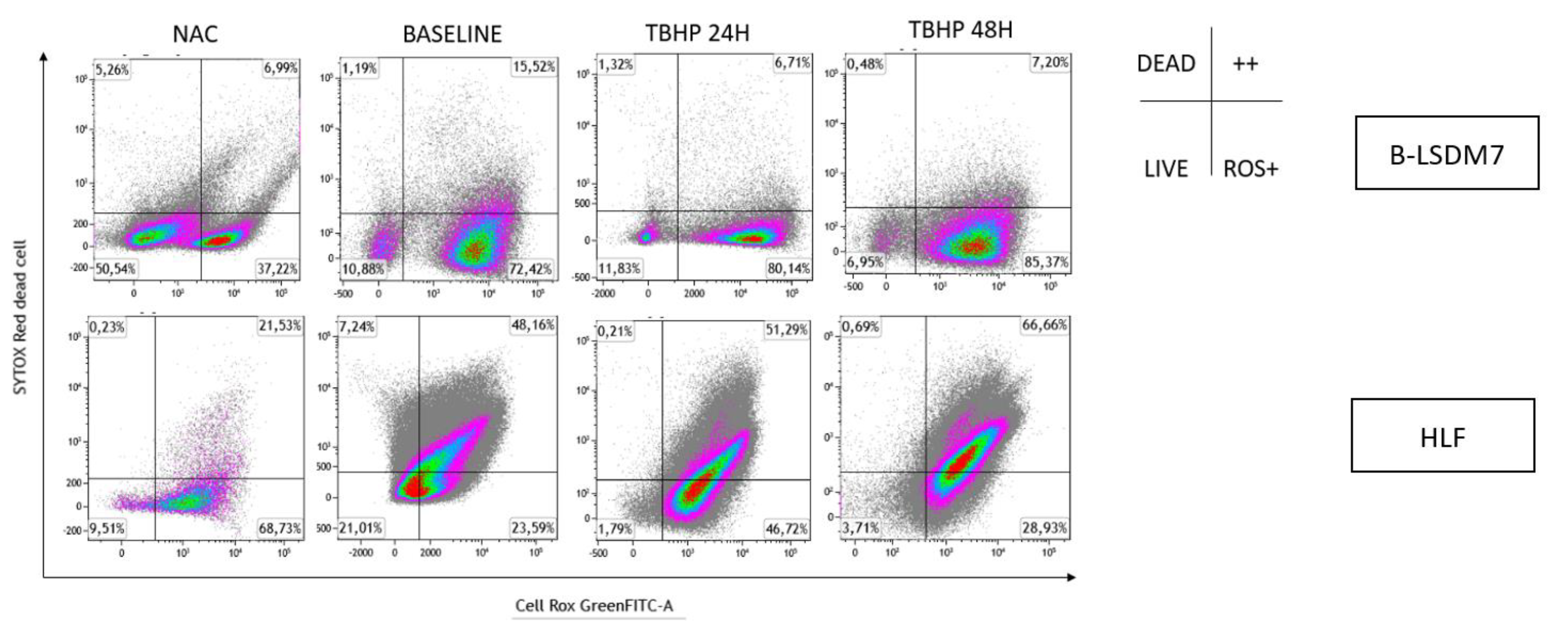
2.9. Detection of Oxidative Stress
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient’s Clinical and Diagnostic Features
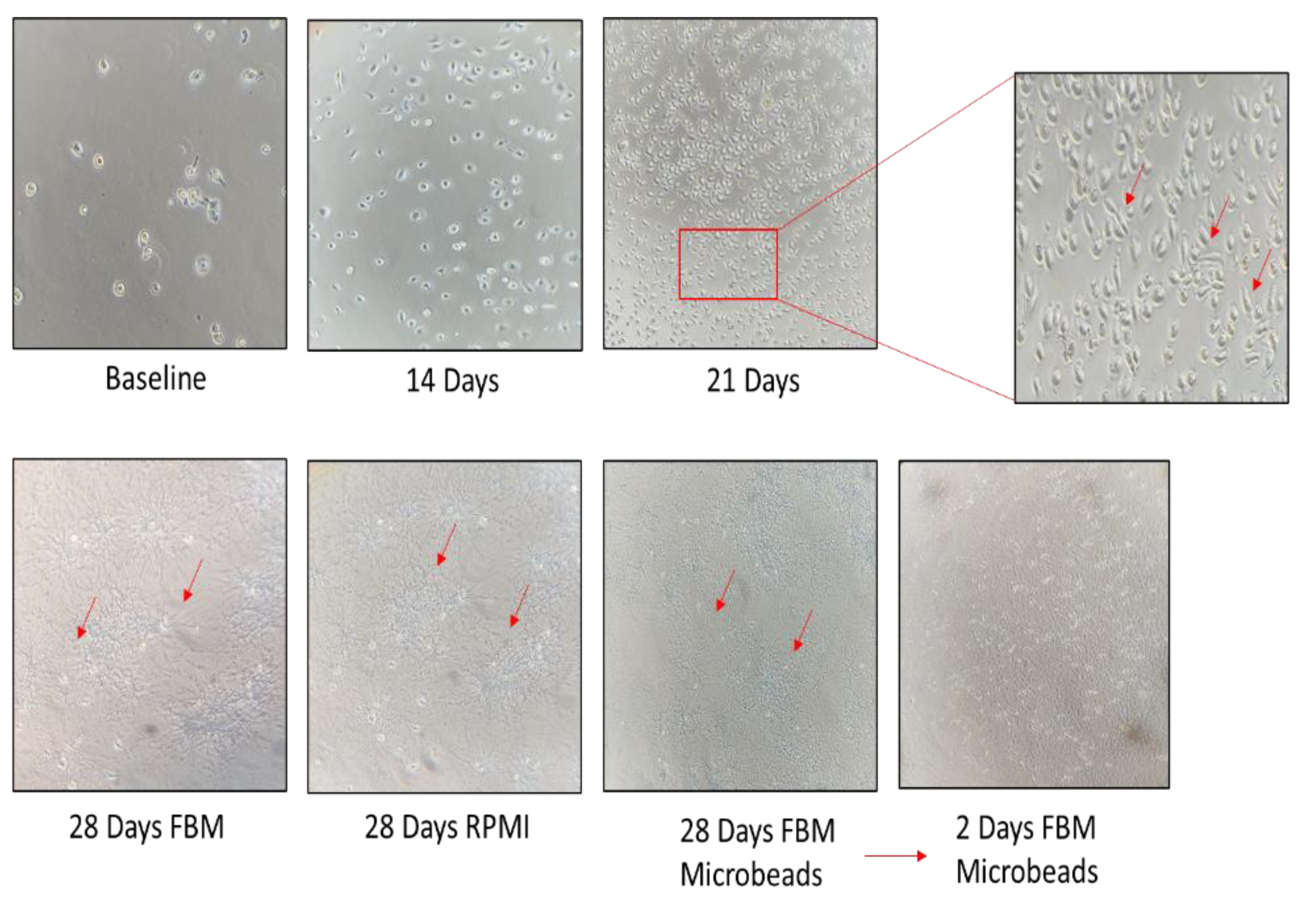
3.2. Establishment of a Morphologically Unique Fibroblast Cell Line (B-LSDM7) from IPF
3.3. Comparison of B-LSDM7 with Human Lung Fibroblast Tissue from IPF Patient
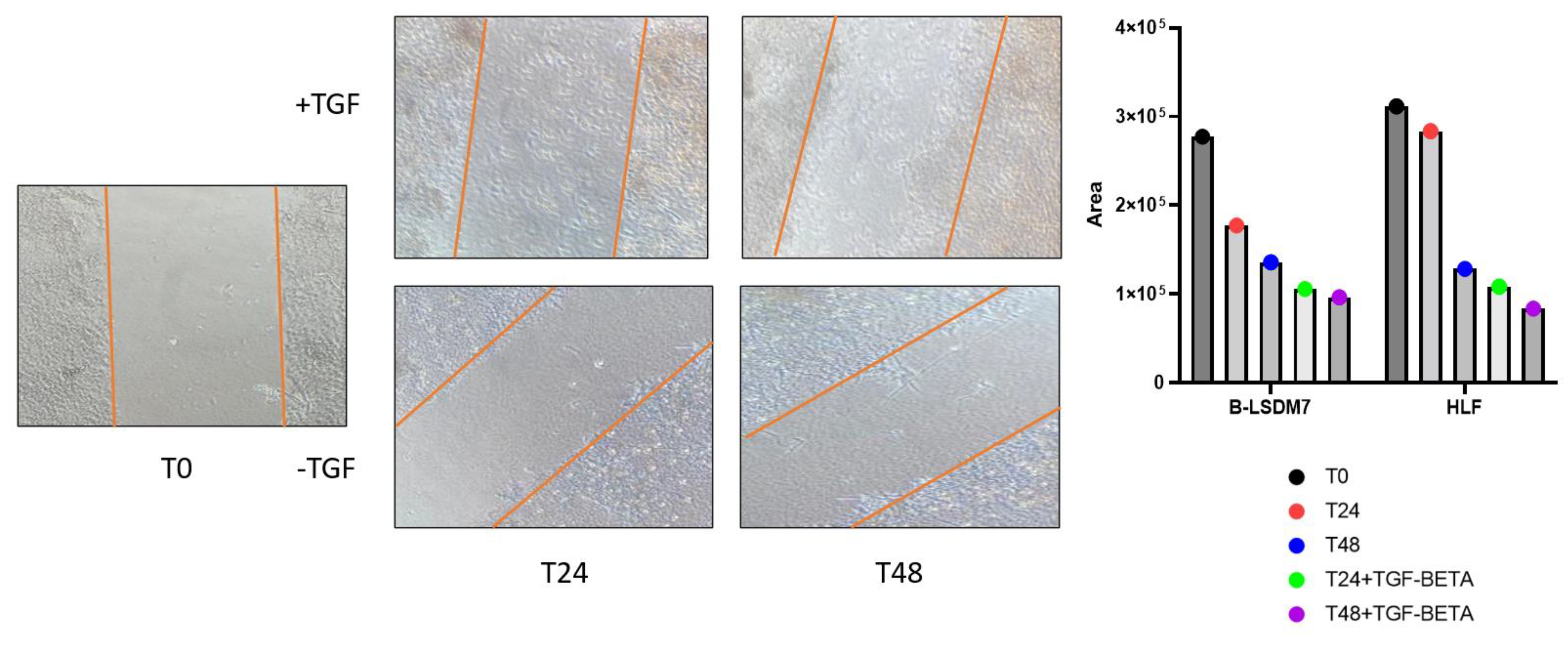
3.4. Tgf-β Administration and Scratch Test
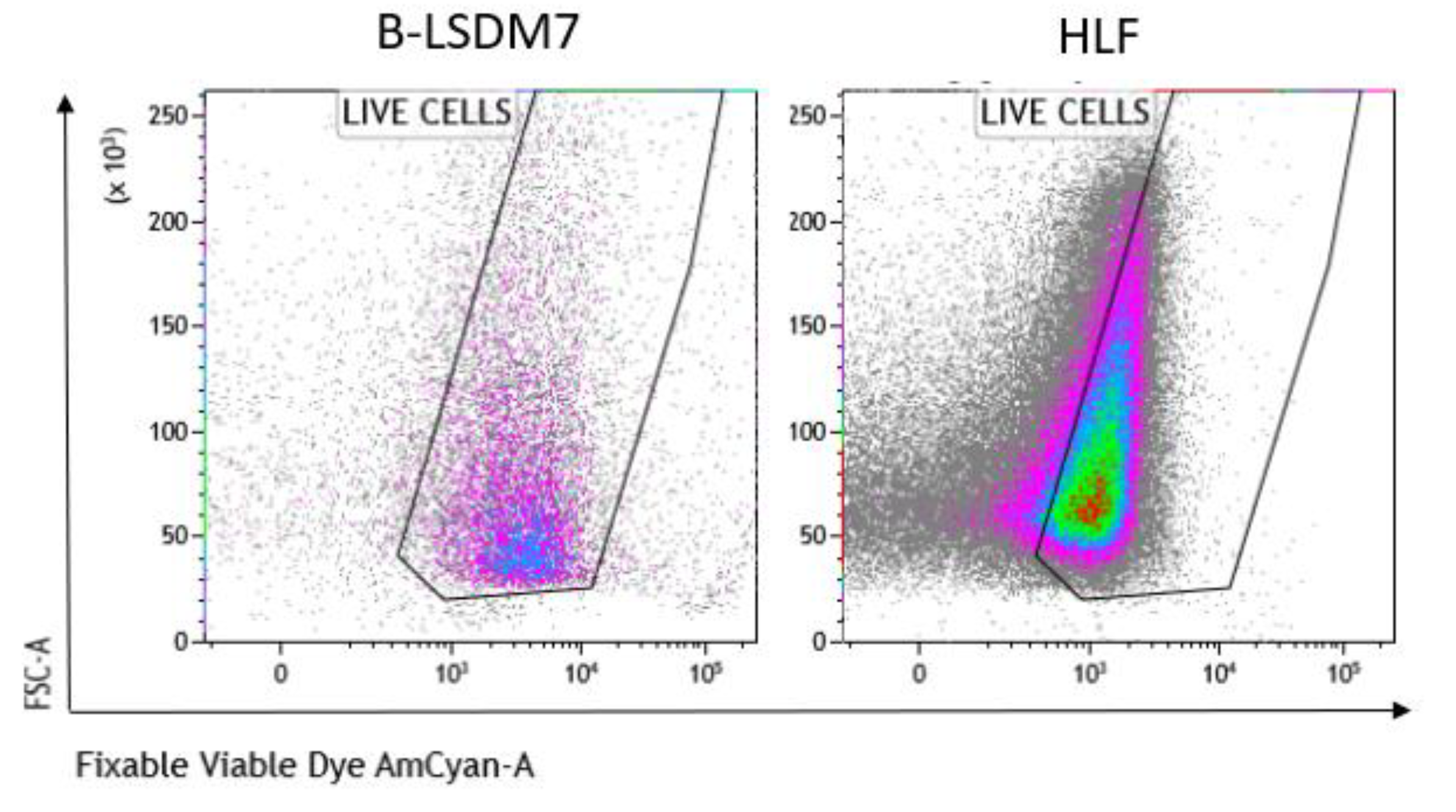
3.5. Characterization of Phenotype
3.6. Detection of ROS
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Availability of Data and Material
Abbreviations
References
- Chen, X.; Guo, J.; Yu, D.; Jie, B.; Zhou, Y. Predictors of Mortality in Progressive Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 754851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Myers, J.L.; Richeldi, L.; Ryerson, C.J.; Lederer, D.J.; Behr, J.; Cottin, V.; Danoff, S.K.; Morell, F.; et al. Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, e44–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Alessandro, M.; Bergantini, L.; Cameli, P.; Fanetti, M.; Alderighi, L.; Armati, M.; Refini, R.M.; Alonzi, V.; Sestini, P.; Bargagli, E. Immunologic responses to antifibrotic treatment in IPF patients. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 95, 107525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameli, P.; Refini, R.M.; Bergantini, L.; d’Alessandro, M.; Alonzi, V.; Magnoni, C.; Rottoli, P.; Sestini, P.; Bargagli, E. Long-Term Follow-Up of Patients With Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Treated With Pirfenidone or Nintedanib: A Real-Life Comparison Study. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 581828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargagli, E.; Refini, R.M.; d’Alessandro, M.; Bergantini, L.; Cameli, P.; Vantaggiato, L.; Bini, L.; Landi, C. Metabolic Dysregulation in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgalla, G.; Iovene, B.; Calvello, M.; Ori, M.; Varone, F.; Richeldi, L. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Pathogenesis and management. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, R.T.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.A. Fibroblasts in fibrosis: Novel roles and mediators. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.K.; Sheppard, D.; Chapman, H.A. TGF-β1 Signaling and Tissue Fibrosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a022293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sisto, M.; Ribatti, D.; Lisi, S. Organ Fibrosis and Autoimmunity: The Role of Inflammation in TGFβ-Dependent EMT. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Zhuang, S. New Insights Into the Role and Mechanism of Partial Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Kidney Fibrosis. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 569322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Urso, M.; Kurniawan, N.A. Mechanical and Physical Regulation of Fibroblast–Myofibroblast Transition: From Cellular Mechanoresponse to Tissue Pathology. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman, M.; Pardo, A. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: An epithelial/fibroblastic cross-talk disorder. Respir. Res. 2002, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schildge, J.; Frank, J.; Klar, B. The Role of Bronchoalveolar Lavage in the Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: An Investigation of the Relevance of the Protein Content. Pneumologie 2016, 70, 435–441. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, K.C.; Raghu, G. Bronchoalveolar lavage for the evaluation of interstitial lung disease: Is it clinically useful? Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergantini, L.; d’Alessandro, M.; Cameli, P.; Otranto, A.; Finco, T.; Curatola, G.; Sestini, P.; Bargagli, E. Prognostic role of NK cell percentages in bronchoalveolar lavage from patients with different fibrotic interstitial lung diseases. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 230, 108827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergantini, L.; d’Alessandro, M.; Cameli, P.; Perrone, A.; Cekorja, B.; Boncompagni, B.; Mazzei, M.A.; Sestini, P.; Bargagli, E. Integrated approach to bronchoalveolar lavage cytology to distinguish interstitial lung diseases. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 89, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Alessandro, M.; Soccio, P.; Bergantini, L.; Cameli, P.; Scioscia, G.; Foschino Barbaro, M.P.; Lacedonia, D.; Bargagli, E. Extracellular Vesicle Surface Signatures in IPF Patients: A Multiplex Bead-Based Flow Cytometry Approach. Cells 2021, 10, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, J.; Rubio, G.A.; Limper, A.H.; Williams, K.; Elliot, S.J.; Ninou, I.; Aidinis, V.; Tzouvelekis, A.; Glassberg, M.K. Exploring Animal Models That Resemble Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maher, T.M.; Nambiar, A.M.; Wells, A.U. The role of precision medicine in interstitial lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 102146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.C.; Raghu, G.; Baughman, R.P.; Brown, K.K.; Costabel, U.; du Bois, R.M.; Drent, M.; Haslam, P.L.; Kim, D.S.; Nagai, S.; et al. An Official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice Guideline: The Clinical Utility of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Cellular Analysis in Interstitial Lung Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 1004–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonsatti, E.; Sigalotti, L.; Arslan, P.; Altomonte, M.; Maio, M. Emerging role of endoglin (CD105) as a marker of angiogenesis with clinical potential in human malignancies. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2003, 3, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Issa, R.; Kumar, P.; Hampson, I.N.; Lopez-Novoa, J.M.; Bernabeu, C.; Kumar, S. CD105 prevents apoptosis in hypoxic endothelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 2677–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hutton, C.; Heider, F.; Blanco-Gomez, A.; Banyard, A.; Kononov, A.; Zhang, X.; Karim, S.; Paulus-Hock, V.; Watt, D.; Steele, N.; et al. Single-cell analysis defines a pancreatic fibroblast lineage that supports anti-tumor immunity. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1227–1244.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannoni, P.; Grosso, M.; Fugazza, G.; Nizzari, M.; Capra, M.C.; Bianchi, R.; Fiocca, R.; Salvi, S.; Montecucco, F.; Bertolotto, M.; et al. Establishment and Characterization of a Novel Fibroblastic Cell Line (SCI13D) Derived from the Broncho-Alveolar Lavage of a Patient with Fibrotic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denu, R.A.; Nemcek, S.; Bloom, D.D.; Goodrich, A.D.; Kim, J.; Mosher, D.F.; Hematti, P. Fibroblasts and Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells Are Phenotypically Indistinguishable. Acta Haematol. 2016, 136, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bradbury, P.; Nader, C.P.; Cidem, A.; Rutting, S.; Sylvester, D.; He, P.; Rezcallah, M.C.; O’Neill, G.M.; Ammit, A.J. Tropomyosin 2.1 collaborates with fibronectin to promote TGF-β1-induced contraction of human lung fibroblasts. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Masta, S.; Meyers, D.; Narayanan, A.S. Collagen Synthesis by Normal and Fibrotic Human Lung Fibroblasts and the Effect of Transforming Growth Factor-β. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1989, 140, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, B.C.; Liebler, J.M.; Luby-Phelps, K.; Nicholson, A.G.; Crandall, E.D.; du Bois, R.M.; Borok, Z. Induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in alveolar epithelial cells by transforming growth factor-beta1: Potential role in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 1321–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, S.H. Genesis of the myofibroblast in lung injury and fibrosis. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2012, 9, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, S. Identification, Friend or Foe: Vimentin and α-Smooth Muscle Actin in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 4191–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Origin of Myofibroblasts in Lung Fibrosis | SpringerLink. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s43152-020-00022 (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- dos Santos, G.; Rogel, M.R.; Baker, M.A.; Troken, J.R.; Urich, D.; Morales-Nebreda, L.; Sennello, J.A.; Kutuzov, M.A.; Sitikov, A.; Davis, J.M.; et al. Vimentin regulates activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quesnel, C.; Nardelli, L.; Piednoir, P.; Leçon, V.; Marchal-Somme, J.; Lasocki, S.; Bouadma, L.; Philip, I.; Soler, P.; Crestani, B.; et al. Alveolar fibroblasts in acute lung injury: Biological behaviour and clinical relevance. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 35, 1312–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larson-Casey, J.L.; Carter, A.B. Assay to evaluate BAL Fluid regulation of Fibroblast α-SMA Expression. Bio-Protocal 2016, 6, e2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watson, W.H.; Ritzenthaler, J.D.; Roman, J. Lung extracellular matrix and redox regulation. Redox Biol. 2016, 8, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bocchino, M.; Agnese, S.; Fagone, E.; Svegliati, S.; Grieco, D.; Vancheri, C.; Gabrielli, A.; Sanduzzi, A.; Avvedimento, E.V. Reactive Oxygen Species Are Required for Maintenance and Differentiation of Primary Lung Fibroblasts in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guzy, R.D.; Stoilov, I.; Elton, T.J.; Mecham, R.P.; Ornitz, D.M. Fibroblast growth factor 2 is required for epithelial recovery, but not for pulmonary fibrosis, in response to bleomycin. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 52, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koo, H.Y.; El-Baz, L.M.; House, S.; Cilvik, S.N.; Dorry, S.J.; Shoukry, N.M.; Salem, M.L.; Hafez, H.S.; Dulin, N.O.; Ornitz, D.M.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 2 decreases bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis and inhibits fibroblast collagen production and myofibroblast differentiation. J. Pathol. 2018, 246, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Du, Y.; Shen, Y.; He, Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, Z. TGF-beta 1 induced fibroblast proliferation is mediated by the FGF-2/ERK pathway. Front. Biosci. 2012, 17, 2667–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bergantini, L.; d’Alessandro, M.; Gangi, S.; Cavallaro, D.; Campiani, G.; Butini, S.; Landi, C.; Bini, L.; Cameli, P.; Bargagli, E. Bronchoalveolar-Lavage-Derived Fibroblast Cell Line (B-LSDM7) as a New Protocol for Investigating the Mechanisms of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Cells 2022, 11, 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11091441
Bergantini L, d’Alessandro M, Gangi S, Cavallaro D, Campiani G, Butini S, Landi C, Bini L, Cameli P, Bargagli E. Bronchoalveolar-Lavage-Derived Fibroblast Cell Line (B-LSDM7) as a New Protocol for Investigating the Mechanisms of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Cells. 2022; 11(9):1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11091441
Chicago/Turabian StyleBergantini, Laura, Miriana d’Alessandro, Sara Gangi, Dalila Cavallaro, Giuseppe Campiani, Stefania Butini, Claudia Landi, Luca Bini, Paolo Cameli, and Elena Bargagli. 2022. "Bronchoalveolar-Lavage-Derived Fibroblast Cell Line (B-LSDM7) as a New Protocol for Investigating the Mechanisms of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis" Cells 11, no. 9: 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11091441
APA StyleBergantini, L., d’Alessandro, M., Gangi, S., Cavallaro, D., Campiani, G., Butini, S., Landi, C., Bini, L., Cameli, P., & Bargagli, E. (2022). Bronchoalveolar-Lavage-Derived Fibroblast Cell Line (B-LSDM7) as a New Protocol for Investigating the Mechanisms of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Cells, 11(9), 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11091441












