Natural Product Library Screens Identify Sanguinarine Chloride as a Potent Inhibitor of Telomerase Expression and Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Cell Culture and Transfection
2.3. Flow Cytometry Screening
2.4. Quantitative Telomeric Repeat Amplification Protocol (Q-TRAP) and IP-TRAP
2.5. Terminal Restriction Fragment (TRF)
2.6. SA-β-Gal Staining
2.7. GST Pull Down and Telomerase Activity Reconstitution In Vitro
2.8. Thioflavin T (ThT) Biochemical Assay
2.9. Microscale Thermophoresis (MST) Assay
2.10. Fluorescence Polarization Assay
2.11. Soft-Agar Colony Formation Assay
2.12. In Vivo Cell Derived Xenograft (CDX)
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
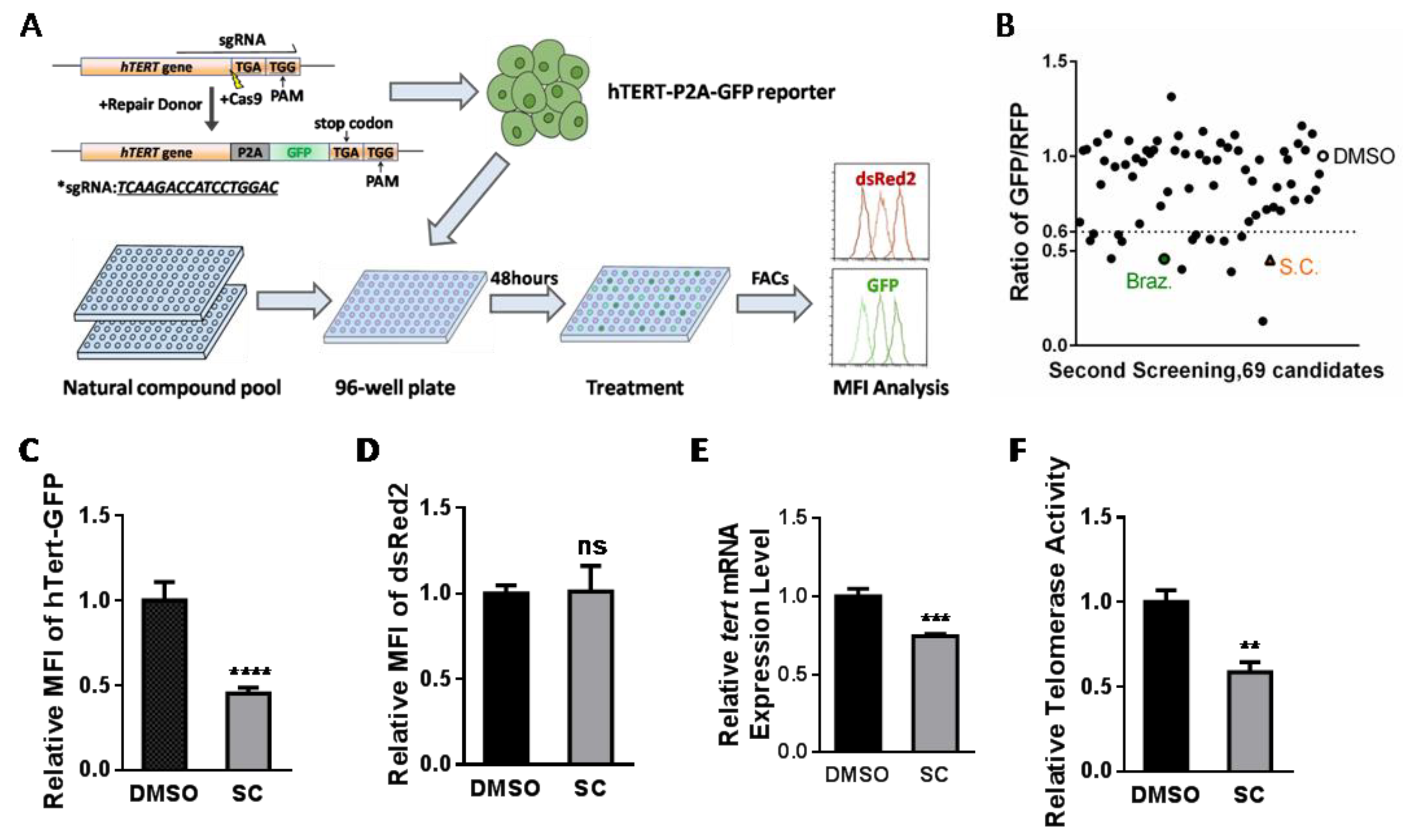
3.1. Natural Compound Screening in hTERT Promoter-Driven GFP Reporter Cell Line and Identification of Potential Inhibitor Candidates
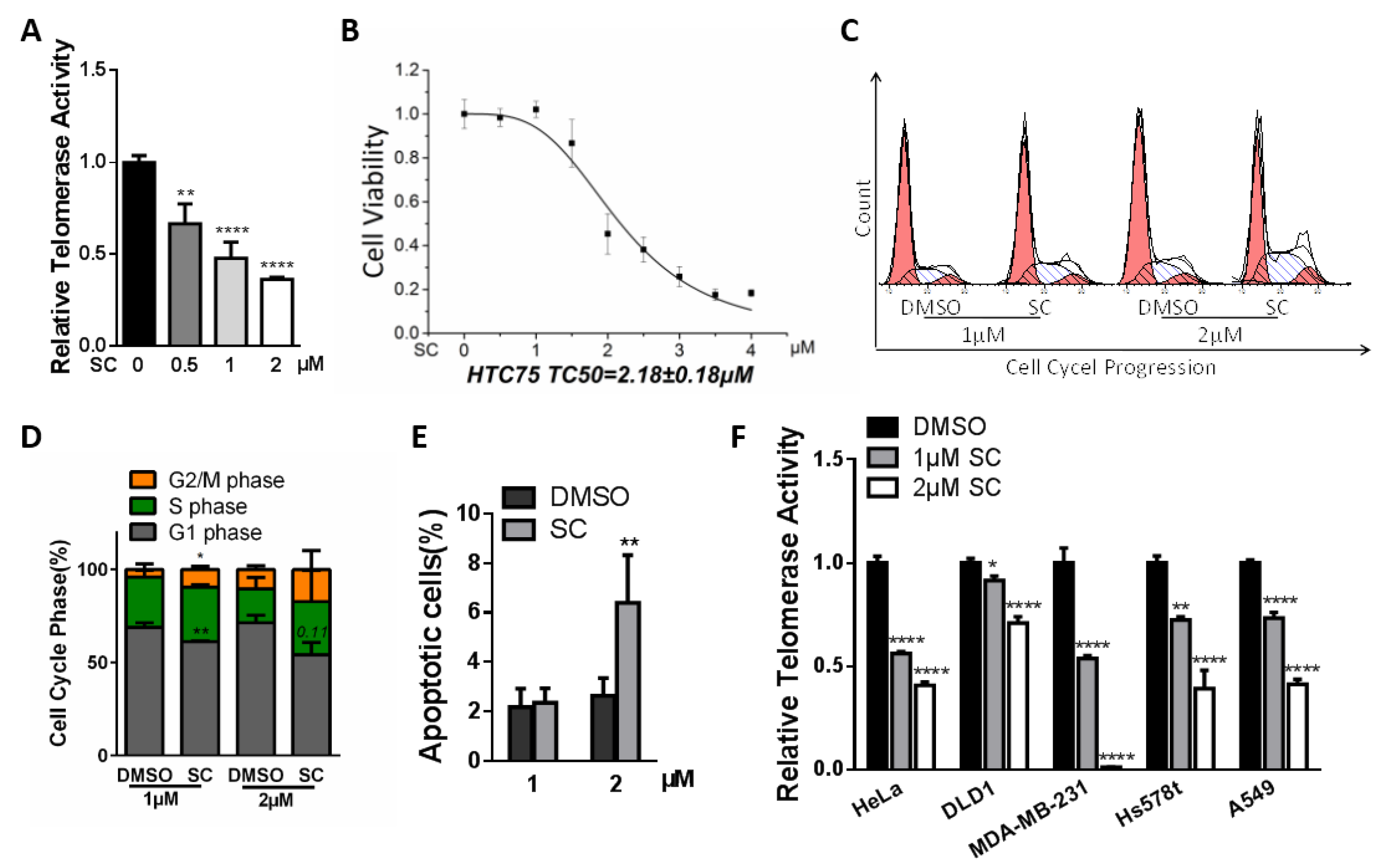
3.2. Inhibitory Effects of SC on Telomerase Activity in HTC75 Cancer Cells
3.3. Effects of SC on Cancer Cell Senescence and Telomere Length through Prolonged Treatment
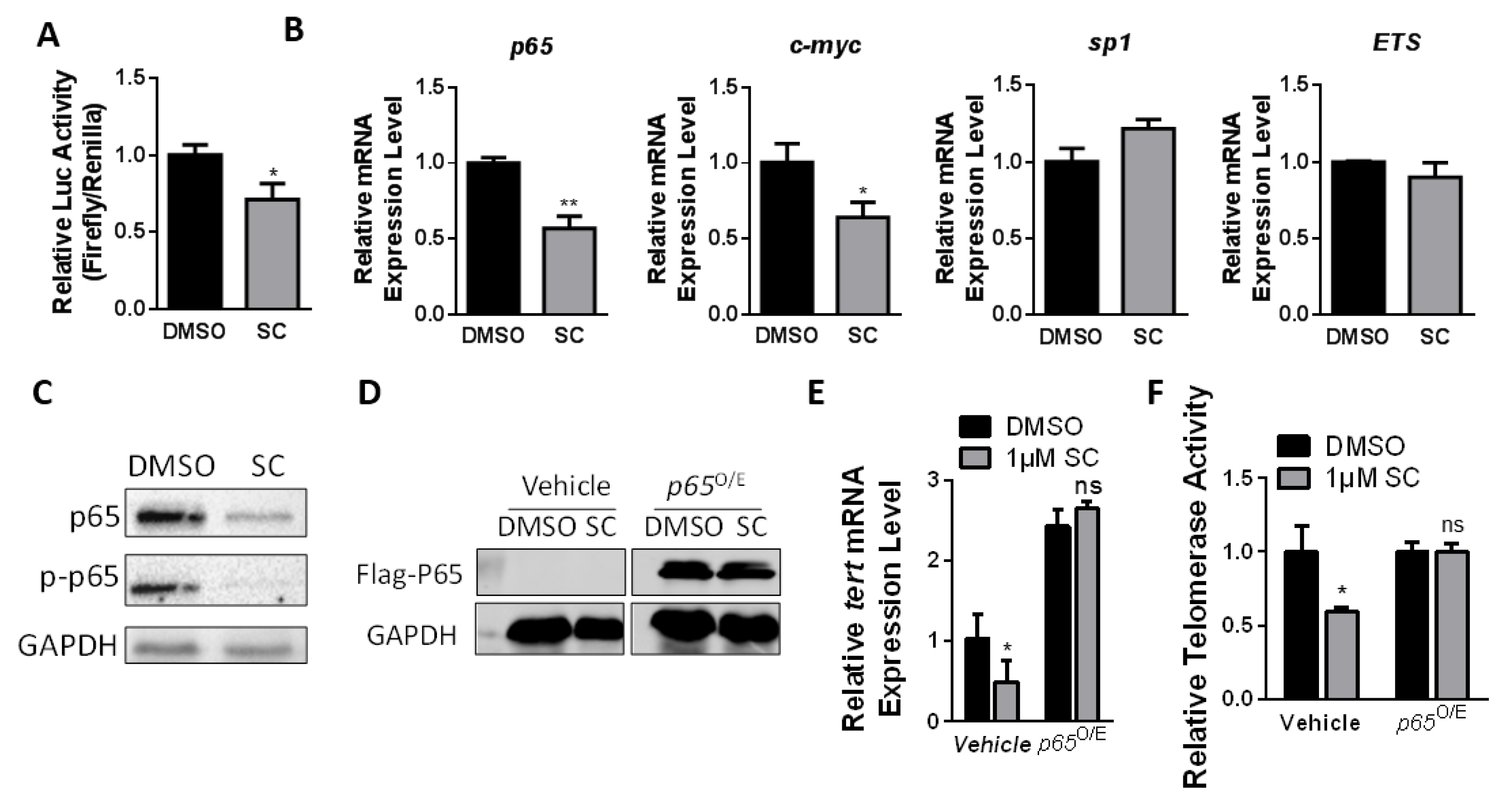
3.4. SC Inhibits Telomerase Depending on p65 Expression
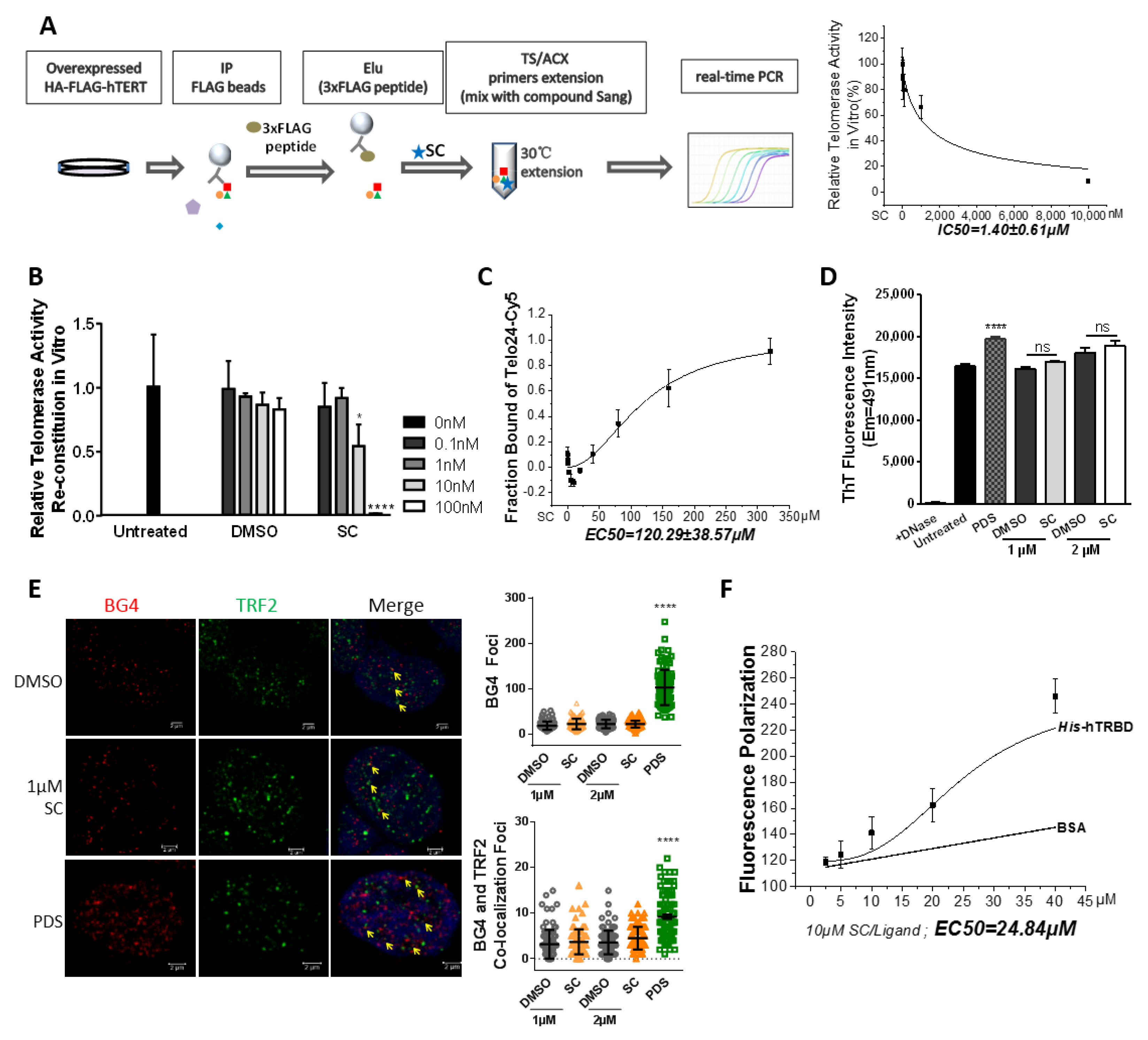
3.5. SC Directly Modulates Telomerase In Vitro
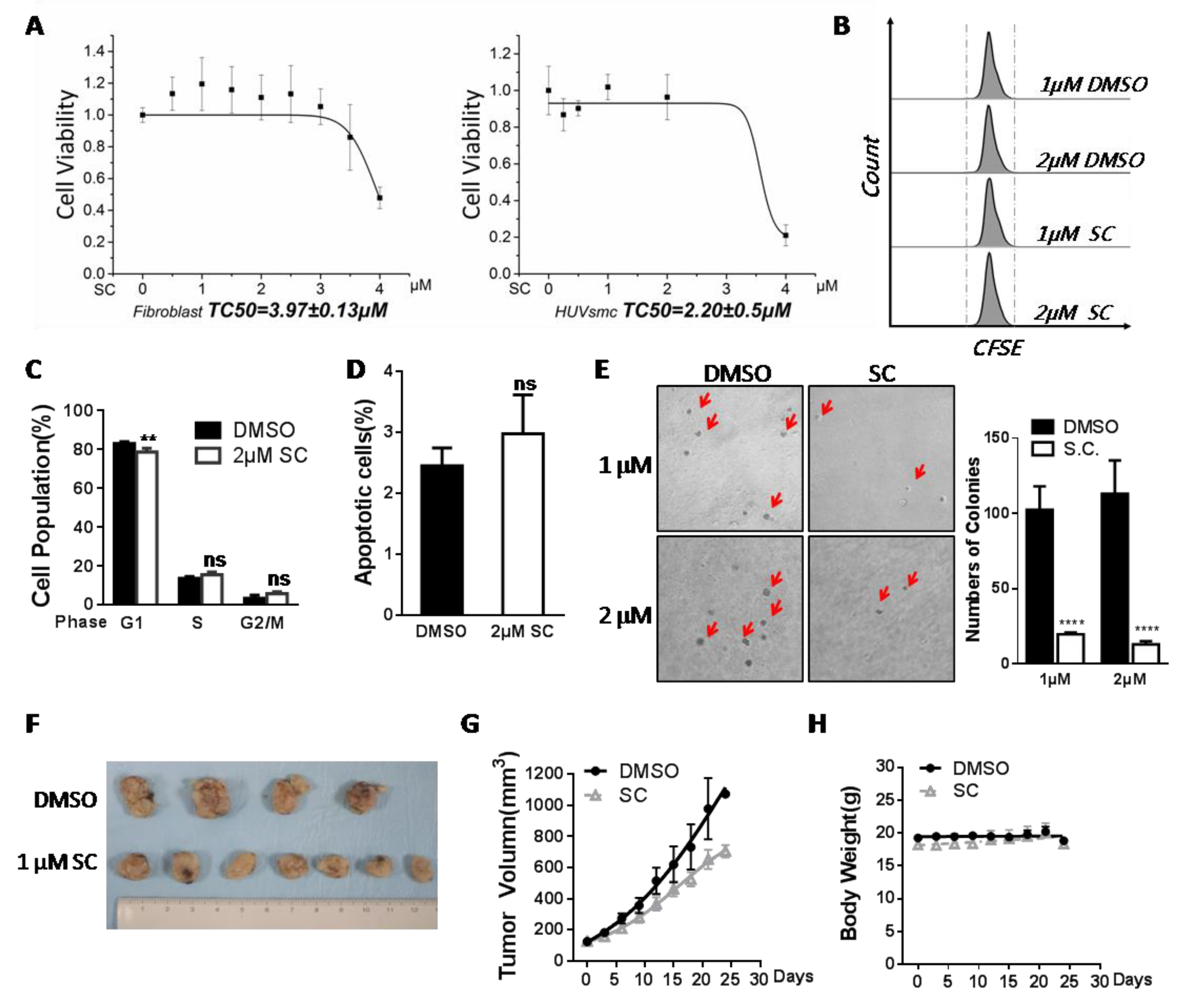
3.6. Assessment of Safety and Antitumor Efficacy of SC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blackburn, E.H. Switching and signaling at the telomere. Cell 2001, 106, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; O’Connor, M.S.; Qin, J.; Songyang, Z. Telosome, a mammalian telomere-associated complex formed by multiple telomeric proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 51338–51342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palm, W.; de Lange, T. How shelterin protects mammalian telomeres. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2008, 42, 301–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heaphy, C.M.; Subhawong, A.P.; Hong, S.-M.; Goggins, M.G.; Montgomery, E.A.; Gabrielson, E.; Netto, G.J.; Epstein, J.I.; Lotan, T.; Westra, W.H.; et al. Prevalence of the alternative lengthening of telomeres telomere maintenance mechanism in human cancer subtypes. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 1608–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.D.; Tam, J.; Wu, R.A.; Greber, B.J.; Toso, D.; Nogales, E.; Collins, K. Cryo-EM structure of substrate-bound human telomerase holoenzyme. Nature 2018, 557, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillis, J.A.; Schuller, A.P.; Skordalakes, E. Structure of the Tribolium castaneum telomerase catalytic subunit TERT. Nature 2008, 455, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.C.; Cech, T.R. Human telomerase: Biogenesis, trafficking, recruitment, and activation. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacKenzie, K.L.; Franco, S.; May, C.; Sadelain, M.; Moore, M.A. Mass cultured human fibroblasts overexpressing hTERT encounter a growth crisis following an extended period of proliferation. Exp. Cell Res. 2000, 259, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zheng, D.; Wang, M.; Cong, Y.-S. Telomerase reverse transcriptase activates the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor independent of telomerase activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 386, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.-J.; Grandori, C.; Amacker, M.; Simon-Vermot, N.; Polack, A.; Lingner, J.; Dalla-Favera, R. Direct activation of TERT transcription by c-MYC. Nat. Genet. 1999, 21, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, C.M.; Khattar, E.; Leow, S.C.; Liu, C.Y.; Muller, J.; Ang, W.X.; Li, Y.; Franzoso, G.; Li, S.; Guccione, E.; et al. Telomerase regulates MYC-driven oncogenesis independent of its reverse transcriptase activity. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 2109–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuo, Q.P.; Liu, S.K.; Li, Z.J.; Li, B.; Zhou, Y.L.; Guo, R.; Huang, L.H. NF-kappaB p65 modulates the telomerase reverse transcriptase in the HepG₂ hepatoma cell line. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 672, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, M.; Hideshima, T.; Hayashi, T.; Tai, Y.-T.; Mitsiades, C.S.; Mitsiades, N.; Chauhan, D.; Richardson, P.; Munshi, N.C.; Anderson, K.C. Nuclear factor-kappaB p65 mediates tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced nuclear translocation of telomerase reverse transcriptase protein. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, E.; Tedone, E.; O’Hara, R.; Cornelius, C.; Lai, T.-P.; Ludlow, A.; Wright, W.; Shay, J.W. The maintenance of telomere length in CD28+ T cells during T lymphocyte stimulation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, Y.; Cong, Y.S.; Zhou, J. Implications of telomerase reverse transcriptase in tumor metastasis. BMB Rep. 2020, 53, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, B.S.; Gellert, G.C.; Hochreiter, A.; Pongracz, K.; Wright, W.E.; Zielinska, D.; Chin, A.C.; Harley, C.B.; Shay, J.W.; Gryaznov, S.M. Lipid modification of GRN163, an N3’-->P5’ thio-phosphoramidate oligonucleotide, enhances the potency of telomerase inhibition. Oncogene 2005, 24, 5262–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bryan, C.; Rice, C.; Hoffman, H.; Harkisheimer, M.; Sweeney, M.; Skordalakes, E. Structural basis of telomerase inhibition by the highly specific BIBR1532. Structure 2015, 23, 1934–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doğan, F.; Özateş, N.P.; Bağca, B.G.; Abbaszadeh, Z.; Söğütlü, F.; Gasimli, R.; Gündüz, C.; Avcı Çığır, B. Investigation of the effect of telomerase inhibitor BIBR1532 on breast cancer and breast cancer stem cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 1282–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado, M.; Blasco, M.A.; Serrano, M. Cellular senescence in cancer and aging. Cell 2007, 130, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, B.D.; Broude, E.V.; Dokmanovic, M.; Zhu, H.; Ruth, A.; Xuan, Y.; Kandel, E.S.; Lausch, E.; Christov, K.; Roninson, I.B. A senescence-like phenotype distinguishes tumor cells that undergo terminal proliferation arrest after exposure to anticancer agents. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 3761–3767. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, C.; Guan, G.; Wang, H. The Anticancer Effect of Sanguinarine: A Review. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 2760–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, M.M.; Kumar, A.; Darnay, B.G.; Chainy, G.B.; Agarwal, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Sanguinarine (pseudochelerythrine) is a potent inhibitor of NF-kappaB activation, IkappaBalpha phosphorylation, and degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 30129–30134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adhami, V.M.; Aziz, M.H.; Reagan-Shaw, S.R.; Nihal, M.; Mukhtar, H.; Ahmad, N. Sanguinarine causes cell cycle blockade and apoptosis of human prostate carcinoma cells via modulation of cyclin kinase inhibitor-cyclin-cyclin-dependent kinase machinery. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.-Y.; Meng, Q.-H.; Chong, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Rosen, E.M.; Fan, S. Sanguinarine is a novel VEGF inhibitor involved in the suppression of angiogenesis and cell migration. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 1, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mackraj, I.; Govender, T.; Gathiram, P. Sanguinarine. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2008, 26, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Damm, D.D.; Curran, A.; White, D.K.; Drummond, J.F. Leukoplakia of the maxillary vestibule--an association with Viadent? Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 1999, 87, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas, A.K.; Allen, C.M.; Loudon, J. The association between Viadent use and oral leukoplakia. Epidemiology 2001, 12, 741–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Huang, Y.; Weng, K.; Lin, S.; Li, Y.; Shi, G.; Chen, Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, D.; Ma, W.; et al. TOE1 acts as a 3′ exonuclease for telomerase RNA and regulates telomere maintenance. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Liu, D.; Wan, M.; Safari, A.; Kim, H.; Sun, W.; O’Connor, M.S.; Zhou, S. TPP1 is a homologue of ciliate TEBP-beta and interacts with POT1 to recruit telomerase. Nature 2007, 445, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Yuan, B.; Ying, S.; Niu, C.; Mai, H.; Guan, X.; Yang, X.; Teng, Y.; Lin, J.; Huang, J.; et al. PES1 is a critical component of telomerase assembly and regulates cellular senescence. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chin, R.L.; Tolman, A.C. Telomerase Inhibitors and Methods of Their Use. WO Patent 0,193,864, 13 December 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Van Steensel, B.; De Lange, T. Control of telomere length by the human telomeric protein TRF1. Nature 1997, 385, 740–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.Y.; Kim, G.-Y.; Lee, W.H.; Choi, Y.H. Sanguinarine, a benzophenanthridine alkaloid, induces apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 human breast carcinoma cells through a reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial pathway. Chemotherapy 2008, 54, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Lee, T.-J.; Leem, J.; Choi, K.S.; Park, J.-W.; Kwon, T.K. Sanguinarine-induced apoptosis: Generation of ROS, down-regulation of Bcl-2, c-FLIP, and synergy with TRAIL. J. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 104, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eitsuka, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Kato, S.; Ito, J.; Otoki, Y.; Takasu, S.; Shimizu, N.; Takahashi, T.; Miyazawa, T. Modulation of telomerase activity in cancer cells by dietary compounds: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, S.; Pradhan, S.K.; Kar, A.; Chowdhury, S.; Dasgupta, D. Molecular basis of recognition of quadruplexes human telomere and c-myc promoter by the putative anticancer agent sanguinarine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA—Gen. Subj. 2013, 1830, 4189–4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureini, S.K.; Esmaeili, H.; Abachi, F.; Khiali, S.; Islam, B.; Kuta, M.; Saboury, A.A.; Hoffmann, M.; Sponer, J.; Parkinson, G.; et al. Selectivity of major isoquinoline alkaloids from Chelidonium majus towards telomeric G-quadruplex: A study using a transition-FRET (t-FRET) assay. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA—Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 2020–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddiqui-Jain, A.; Grand, C.L.; Bearss, D.J.; Hurley, L.H. Direct evidence for a G-quadruplex in a promoter region and its targeting with a small molecule to repress c-MYC transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11593–11598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohanty, J.; Barooah, N.; Dhamodharan, V.; Harikrishna, S.; Pradeepkumar, P.I.; Bhasikuttan, A.C. Thioflavin T as an efficient inducer and selective fluorescent sensor for the human telomeric G-quadruplex DNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pica, F.; Balestrieri, E.; Serafino, A.; Sorrentino, R.; Gaziano, R.; Moroni, G.; Moroni, N.; Palmieri, G.; Mattei, M.; Garaci, E.; et al. Antitumor effects of the benzophenanthridine alkaloid sanguinarine in a rat syngeneic model of colorectal cancer. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2012, 23, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Xu, Y.; Peng, T.; Yan, J.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Z. Sanguinarine exhibits antitumor activity via up-regulation of Fas-associated factor 1 in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2017, 31, e21914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, N.-I.; Jeon, S.G.; Ahn, E.-M.; Hahn, J.-T.; Bahn, J.H.; Jang, J.S.; Cho, S.-W.; Park, J.K.; Choi, S.Y. Anticonvulsant compounds from the wood of Caesalpinia sappan L. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2000, 23, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Kim, S.H.; Jeong, S.J.; Sohn, E.J.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, S.H. Brazilin induces apoptosis and G2/M arrest via inactivation of histone deacetylase in multiple myeloma U266 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9882–9889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gizard, F.; Heywood, E.B.; Findeisen, H.M.; Zhao, Y.; Jones, K.L.; Cudejko, C.; Post, G.R.; Staels, B.; Bruemmer, D. Telomerase activation in atherosclerosis and induction of telomerase reverse transcriptase expression by inflammatory stimuli in macrophages. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Basu, P.; Kumar, G.S. Sanguinarine and Its Role in Chronic Diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 928, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahsan, H.; Reagan-Shaw, S.; Breur, J.; Ahmad, N. Sanguinarine induces apoptosis of human pancreatic carcinoma AsPC-1 and BxPC-3 cells via modulations in Bcl-2 family proteins. Cancer Lett. 2007, 249, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Jin, M.L.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, S.-J.; Park, G. Sanguinarine inhibits invasiveness and the MMP-9 and COX-2 expression in TPA-induced breast cancer cells by inducing HO-1 expression. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eun, J.-P.; Koh, G.Y. Suppression of angiogenesis by the plant alkaloid, sanguinarine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 317, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basini, G.; Bussolati, S.; Santini, S.E.; Grasselli, F. Sanguinarine inhibits VEGF-induced angiogenesis in a fibrin gel matrix. Biofactors 2007, 29, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefano, I.; Raspaglio, G.; Zannoni, G.F.; Travaglia, D.; Prisco, M.G.; Mosca, M.; Ferlini, C.; Scambia, G.; Gallo, D. Antiproliferative and antiangiogenic effects of the benzophenanthridine alkaloid sanguinarine in melanoma. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 1374–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eid, S.Y.; El-Readi, M.Z.; Wink, M. Synergism of three-drug combinations of sanguinarine and other plant secondary metabolites with digitonin and doxorubicin in multi-drug resistant cancer cells. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 1288–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaziano, R.; Moroni, G.; Buè, C.; Miele, M.T.; Sinibaldi-Vallebona, P.; Pica, F. Antitumor effects of the benzophenanthridine alkaloid sanguinarine: Evidence and perspectives. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2016, 8, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achkar, I.W.; Mraiche, F.; Mohammad, R.M.; Uddin, S. Anticancer potential of sanguinarine for various human malignancies. Future Med. Chem. 2017, 9, 933–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.N.; Chen, W.; Peng, S.Q.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhang, R.; Liang, R.; Liu, H.; Zhu, J.-S.; Zhang, J. Sanguinarine inhibits the tumorigenesis of gastric cancer by regulating the TOX/DNA-PKcs/ KU70/80 pathway. Pathol.-Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 152677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, S.A.; Alter, B.P. Dyskeratosis congenita. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 23, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, S.; Lin, S.; Chen, K.; Yin, S.; Peng, H.; Cai, N.; Ma, W.; Songyang, Z.; Huang, Y. Natural Product Library Screens Identify Sanguinarine Chloride as a Potent Inhibitor of Telomerase Expression and Activity. Cells 2022, 11, 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11091485
Yan S, Lin S, Chen K, Yin S, Peng H, Cai N, Ma W, Songyang Z, Huang Y. Natural Product Library Screens Identify Sanguinarine Chloride as a Potent Inhibitor of Telomerase Expression and Activity. Cells. 2022; 11(9):1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11091485
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Siyu, Song Lin, Kexin Chen, Shanshan Yin, Haoyue Peng, Nanshuo Cai, Wenbin Ma, Zhou Songyang, and Yan Huang. 2022. "Natural Product Library Screens Identify Sanguinarine Chloride as a Potent Inhibitor of Telomerase Expression and Activity" Cells 11, no. 9: 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11091485
APA StyleYan, S., Lin, S., Chen, K., Yin, S., Peng, H., Cai, N., Ma, W., Songyang, Z., & Huang, Y. (2022). Natural Product Library Screens Identify Sanguinarine Chloride as a Potent Inhibitor of Telomerase Expression and Activity. Cells, 11(9), 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11091485





