Tumor Microenvironment and Microvascular Density in Human Glioblastoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. CD4, CD8, CD68, CD163, CD34, Ki67, Bcl6 and p53 Immunohistochemistry
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
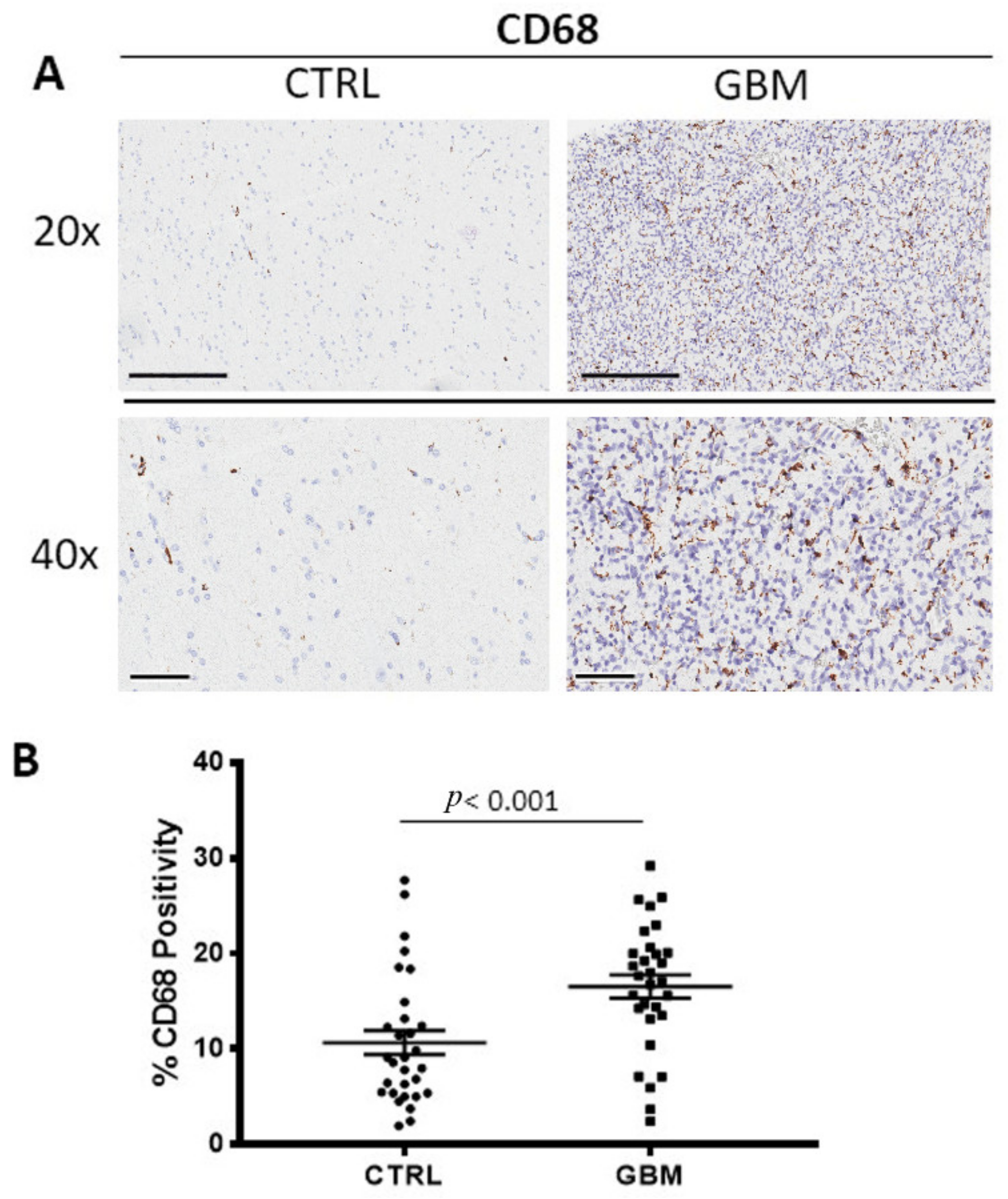
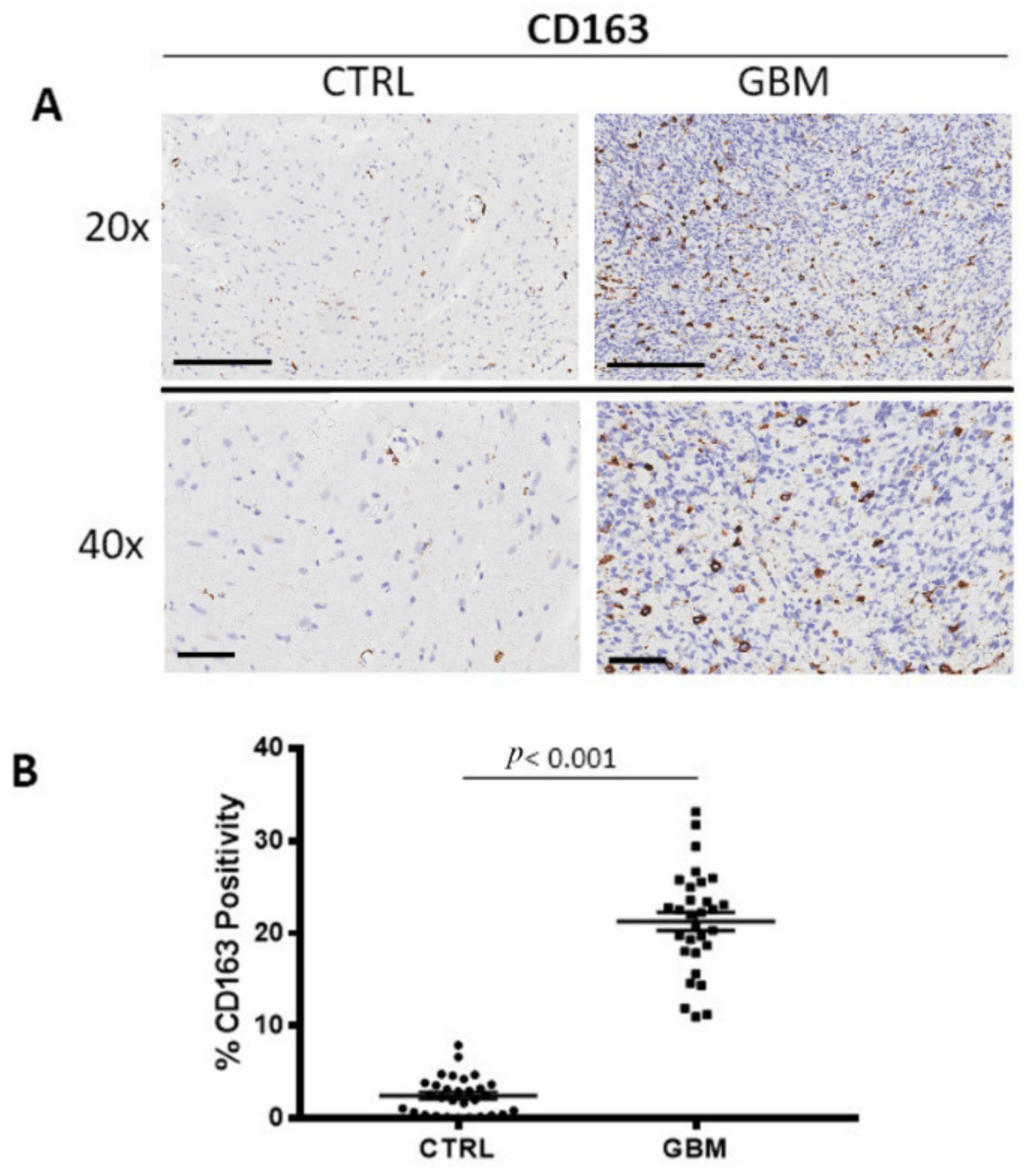
3.1. CD68 and CD163 Immunohistochemistry
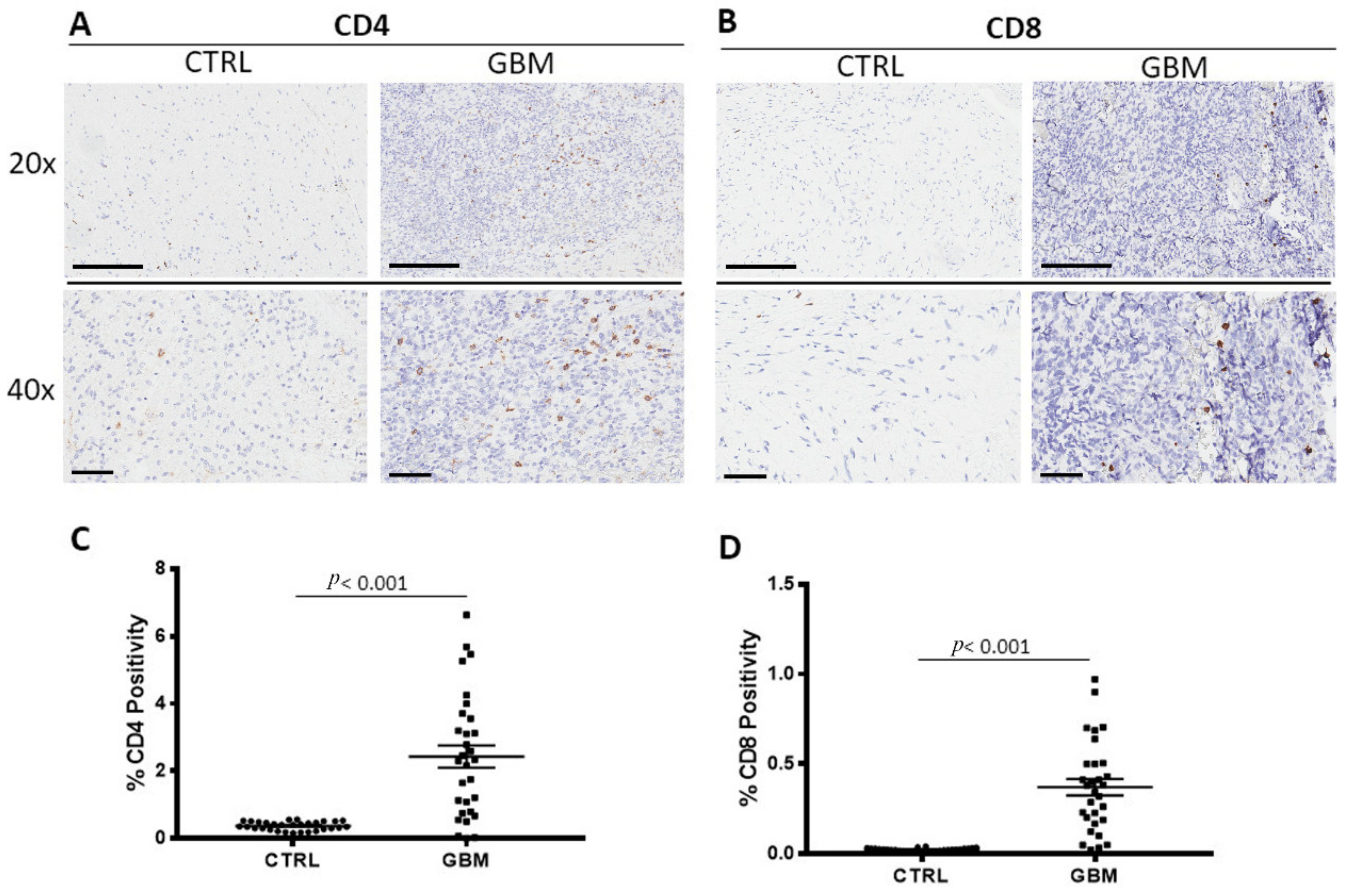
3.2. CD4 and CD8 Immunohistochemistry
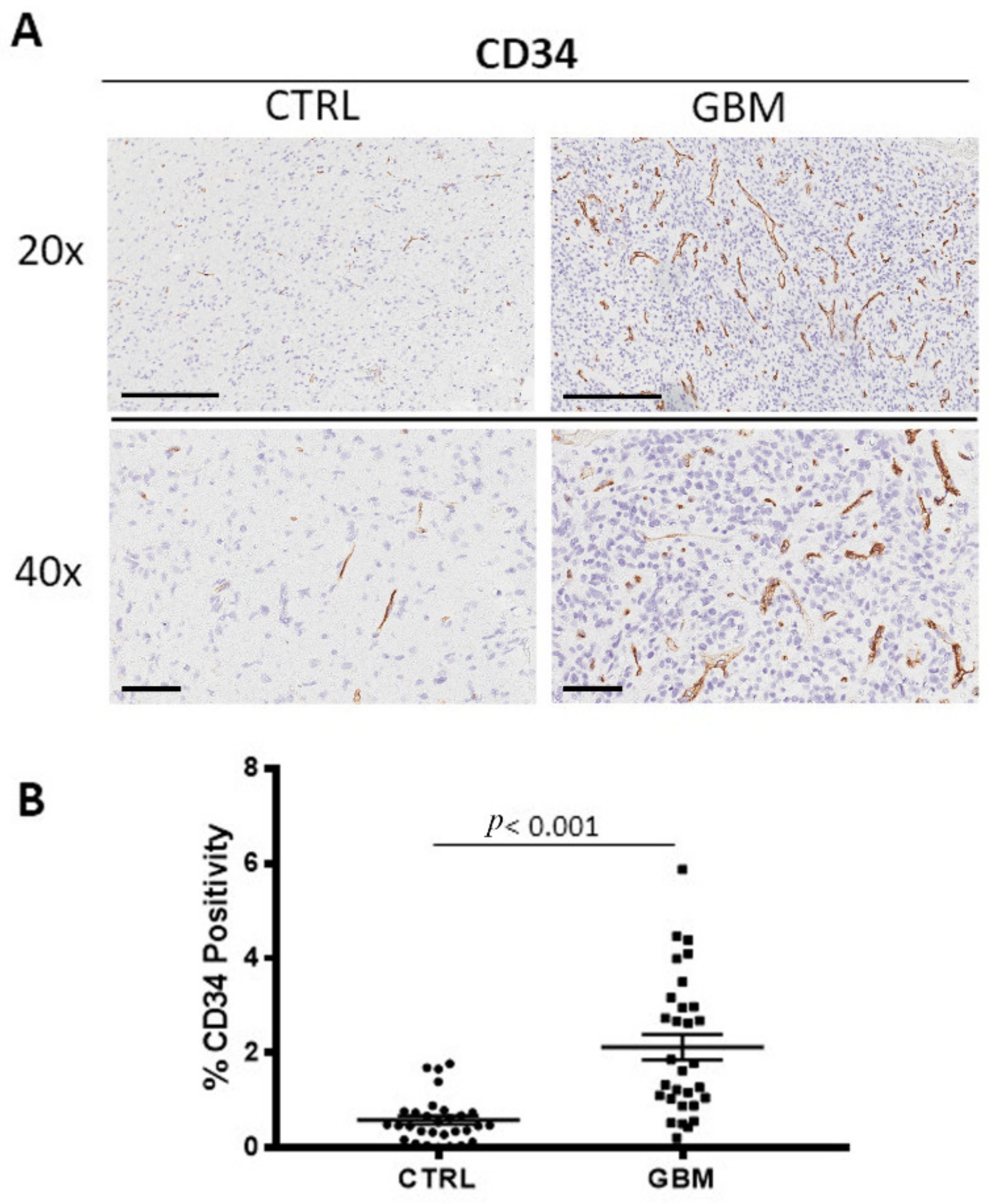
3.3. CD34 Immunohistochemistry
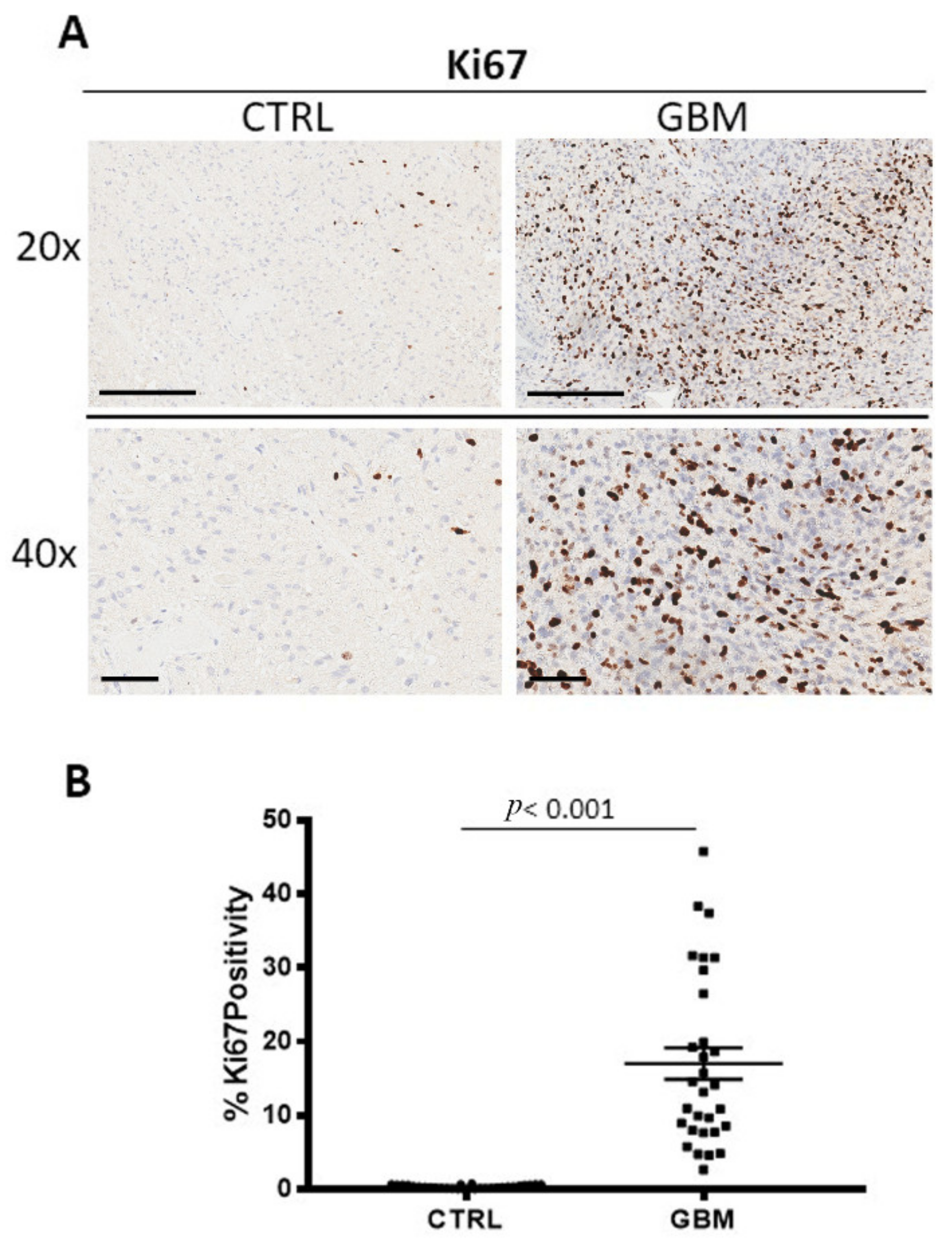
3.4. Ki67, Bcl6 and p53 Immunohistochemistry
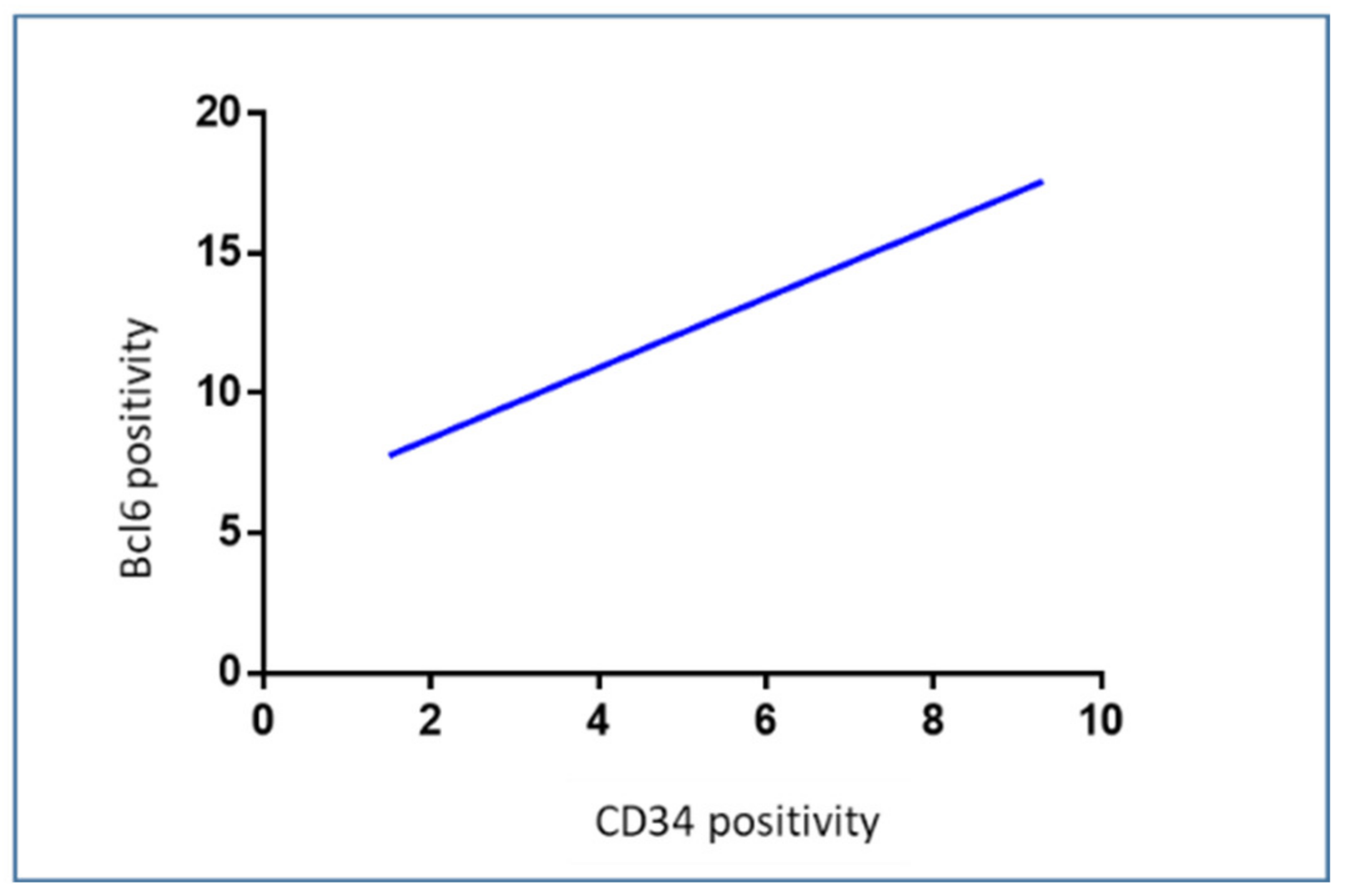
3.5. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2014–2018. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, iii1–iii105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Cui, Y.; Jiang, H.; Sui, D.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Lin, S. Circulating tumor cell is a common property of brain glioma and promotes the monitoring system. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 71330–71340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimura, T.; Neuchrist, C.; Kitz, K.; Budka, H.; Scheiner, O.; Kraft, D.; Lassmann, H. Monocyte subpopulations in human gliomas: Expression of Fc and complement receptors and correlation with tumor proliferation. Acta Neuropathol. 1990, 80, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skalli, O.; Wilhelmsson, U.; Orndahl, C.; Fekete, B.; Malmgren, K.; Rydenhag, B.; Pekny, M. Astrocytoma grade IV (glioblastoma multiforme) displays 3 subtypes with unique expression profiles of intermediate filament proteins. Hum. Pathol. 2013, 44, 2081–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Mittal, S.; Berens, M.E. Targeting adaptive glioblastoma: An overview of proliferation and invasion. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaiswal, J.; Shastry, A.H.; Ramesh, A.; Chickabasaviah, Y.T.; Arimappamagan, A.; Santosh, V. Spectrum of primary intracranial tumors at a tertiary care neurological institute: A hospital-based brain tumor registry. Neurol. India 2016, 64, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Janzer, R.C.; Ludwin, S.K.; Allgeier, A.; Fisher, B.; Belanger, K.; et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Taillibert, S.; Kanner, A.; Read, W.; Steinberg, D.; Lhermitte, B.; Toms, S.; Idbaih, A.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Fink, K.; et al. Effect of Tumor-Treating Fields Plus Maintenance Temozolomide vs Maintenance Temozolomide Alone on Survival in Patients with Glioblastoma: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 2306–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hambardzumyan, D.; Bergers, G. Glioblastoma: Defining Tumor Niches. Trends Cancer 2015, 1, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venkatesh, H.S.; Morishita, W.; Geraghty, A.C.; Silverbush, D.; Gillespie, S.M.; Arzt, M.; Tam, L.T.; Espenel, C.; Ponnuswami, A.; Ni, L.; et al. Electrical and synaptic integration of glioma into neural circuits. Nature 2019, 573, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eason, K.; Sadanandam, A. Molecular or Metabolic Reprograming: What Triggers Tumor Subtypes? Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 5195–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dauer, P.; Nomura, A.; Saluja, A.; Banerjee, S. Microenvironment in determining chemo-resistance in pancreatic cancer: Neighborhood matters. Pancreatology 2017, 17, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pitt, J.M.; Marabelle, A.; Eggermont, A.; Soria, J.C.; Kroemer, G.; Zitvogel, L. Targeting the tumor microenvironment: Removing obstruction to anticancer immune responses and immunotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1482–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, R.; Synowitz, M. CNS macrophages and peripheral myeloid cells in brain tumours. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 128, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruggieri, S.; De Giorgis, M.; Annese, T.; Tamma, R.; Notarangelo, A.; Marzullo, A.; Senetta, R.; Cassoni, P.; Notarangelo, M.; Ribatti, D.; et al. Dp71 Expression in Human Glioblastoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sica, A.; Larghi, P.; Mancino, A.; Rubino, L.; Porta, C.; Totaro, M.G.; Rimoldi, M.; Biswas, S.K.; Allavena, P.; Mantovani, A. Macrophage polarization in tumour progression. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2008, 18, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italiani, P.; Boraschi, D. From Monocytes to M1/M2 Macrophages: Phenotypical vs. Functional Differentiation. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, W.; Jackson-Cook, C.; Graf, M.R. Tumor-infiltrating, myeloid-derived suppressor cells inhibit T cell activity by nitric oxide production in an intracranial rat glioma + vaccination model. J. Neuroimmunol. 2010, 223, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, L.Y.; Wu, A.S.; Doucette, T.; Wei, J.; Priebe, W.; Fuller, G.N.; Qiao, W.; Sawaya, R.; Rao, G.; Heimberger, A.B. Intratumoral mediated immunosuppression is prognostic in genetically engineered murine models of glioma and correlates to immunotherapeutic responses. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 5722–5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umemura, N.; Saio, M.; Suwa, T.; Kitoh, Y.; Bai, J.; Nonaka, K.; Ouyang, G.F.; Okada, M.; Balazs, M.; Adany, R.; et al. Tumor-infiltrating myeloid-derived suppressor cells are pleiotropic-inflamed monocytes/macrophages that bear M1- and M2-type characteristics. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 83, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanachetty, S.; Cruz-Cruz, J.; Hoffmeyer, E.; Cole, A.P.; Mitra, S.S. New Insights into the Multifaceted Role of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells (MDSCs) in High-Grade Gliomas: From Metabolic Reprograming, Immunosuppression, and Therapeutic Resistance to Current Strategies for Targeting MDSCs. Cells 2021, 10, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostroumov, D.; Fekete-Drimusz, N.; Saborowski, M.; Kuhnel, F.; Woller, N. CD4 and CD8 T lymphocyte interplay in controlling tumor growth. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 689–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rutledge, W.C.; Kong, J.; Gao, J.; Gutman, D.A.; Cooper, L.A.; Appin, C.; Park, Y.; Scarpace, L.; Mikkelsen, T.; Cohen, M.L.; et al. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in glioblastoma are associated with specific genomic alterations and related to transcriptional class. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4951–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sayour, E.J.; McLendon, P.; McLendon, R.; De Leon, G.; Reynolds, R.; Kresak, J.; Sampson, J.H.; Mitchell, D.A. Increased proportion of FoxP3+ regulatory T cells in tumor infiltrating lymphocytes is associated with tumor recurrence and reduced survival in patients with glioblastoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2015, 64, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Ladomersky, E.; Lauing, K.L.; Wu, M.; Genet, M.; Gritsina, G.; Gyorffy, B.; Brastianos, P.K.; Binder, D.C.; Sosman, J.A.; et al. Infiltrating T Cells Increase IDO1 Expression in Glioblastoma and Contribute to Decreased Patient Survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 6650–6660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, P.M.; Prucca, C.G.; Caputto, B.L.; Guido, M.E. Adjusting the Molecular Clock: The Importance of Circadian Rhythms in the Development of Glioblastomas and Its Intervention as a Therapeutic Strategy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himes, B.T.; Geiger, P.A.; Ayasoufi, K.; Bhargav, A.G.; Brown, D.A.; Parney, I.F. Immunosuppression in Glioblastoma: Current Understanding and Therapeutic Implications. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 770561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.J.; Chen, J.S.; Jain, S.; Morshed, R.A.; Haddad, A.F.; Gill, S.; Beniwal, A.S.; Aghi, M.K. Immunotherapy Resistance in Glioblastoma. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 750675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topper, M.J.; Vaz, M.; Marrone, K.A.; Brahmer, J.R.; Baylin, S.B. The emerging role of epigenetic therapeutics in immuno-oncology. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Dutra-Clarke, M.; Mayakonda, A.; Hazawa, M.; Savinoff, S.E.; Doan, N.; Said, J.W.; Yong, W.H.; Watkins, A.; et al. BCL6 promotes glioma and serves as a therapeutic target. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 3981–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggieri, S.; Tamma, R.; Marzullo, A.; Annese, T.; Marinaccio, C.; Errede, M.; Susca, F.C.; Senetta, R.; Cassoni, P.; Vacca, A.; et al. Translocation of the proto-oncogene Bcl-6 in human glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Lett. 2014, 353, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perrin, S.L.; Samuel, M.S.; Koszyca, B.; Brown, M.P.; Ebert, L.M.; Oksdath, M.; Gomez, G.A. Glioblastoma heterogeneity and the tumour microenvironment: Implications for preclinical research and development of new treatments. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2019, 47, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drumm, M.R.; Dixit, K.S.; Grimm, S.; Kumthekar, P.; Lukas, R.V.; Raizer, J.J.; Stupp, R.; Chheda, M.G.; Kam, K.L.; McCord, M.; et al. Extensive brainstem infiltration, not mass effect, is a common feature of end-stage cerebral glioblastomas. Neuro-Oncology 2020, 22, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchbinder, E.I.; Desai, A. CTLA-4 and PD-1 Pathways: Similarities, Differences, and Implications of Their Inhibition. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 39, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Litak, J.; Mazurek, M.; Grochowski, C.; Kamieniak, P.; Rolinski, J. PD-L1/PD-1 Axis in Glioblastoma Multiforme. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lara-Velazquez, M.; Shireman, J.M.; Lehrer, E.J.; Bowman, K.M.; Ruiz-Garcia, H.; Paukner, M.J.; Chappell, R.J.; Dey, M. A Comparison Between Chemo-Radiotherapy Combined with Immunotherapy and Chemo-Radiotherapy Alone for the Treatment of Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 662302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, I.E.; Gabor Miklos, G.L. Bevacizumab for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.J.; Ali, S.; Qadir, M.G.; De La Fuente, M.I.; Ivan, M.E.; Komotar, R.J. The role of bevacizumab in the treatment of glioblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 133, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.E.; Alizadeh, D.; Starr, R.; Weng, L.; Wagner, J.R.; Naranjo, A.; Ostberg, J.R.; Blanchard, M.S.; Kilpatrick, J.; Simpson, J.; et al. Regression of Glioblastoma after Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2561–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omuro, A.; Vlahovic, G.; Lim, M.; Sahebjam, S.; Baehring, J.; Cloughesy, T.; Voloschin, A.; Ramkissoon, S.H.; Ligon, K.L.; Latek, R.; et al. Nivolumab with or without ipilimumab in patients with recurrent glioblastoma: Results from exploratory phase I cohorts of CheckMate 143. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Rourke, D.M.; Nasrallah, M.P.; Desai, A.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Mansfield, K.; Morrissette, J.J.D.; Martinez-Lage, M.; Brem, S.; Maloney, E.; Shen, A.; et al. A single dose of peripherally infused EGFRvIII-directed CAR T cells mediates antigen loss and induces adaptive resistance in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaaa0984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tamma, R.; Ranieri, G.; Ingravallo, G.; Annese, T.; Oranger, A.; Gaudio, F.; Musto, P.; Specchia, G.; Ribatti, D. Inflammatory Cells in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quail, D.F.; Joyce, J.A. The Microenvironmental Landscape of Brain Tumors. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Zhong, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, X.; Tong, A.; Zhou, L. Tumor-associated microglia and macrophages in glioblastoma: From basic insights to therapeutic opportunities. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 964898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, S.M.; Comba, A.; Varela, M.L.; Argento, A.E.; Brumley, E.; Abel, C., 2nd; Castro, M.G.; Lowenstein, P.R. The complex interactions between the cellular and non-cellular components of the brain tumor microenvironmental landscape and their therapeutic implications. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1005069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.; Heppner, F.L.; Tsirka, S.E. Microglia/macrophages promote glioma progression. Glia 2011, 59, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellert-Miklaszewska, A.; Dabrowski, M.; Lipko, M.; Sliwa, M.; Maleszewska, M.; Kaminska, B. Molecular definition of the pro-tumorigenic phenotype of glioma-activated microglia. Glia 2013, 61, 1178–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarneau, H.; Villeneuve, J.; Gowing, G.; Julien, J.P.; Vallieres, L. Increased glioma growth in mice depleted of macrophages. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 8874–8881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrego, E.; Castaneda, C.A.; Castillo, M.; Bernabe, L.A.; Casavilca, S.; Chakravarti, A.; Meng, W.; Garcia-Corrochano, P.; Villa-Robles, M.R.; Zevallos, R.; et al. Distribution of tumor-infiltrating immune cells in glioblastoma. CNS Oncol. 2018, 7, CNS21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinard, C.J.; International Immuno-Oncology Biomarker Working, G.; Lagree, A.; Lu, F.I.; Klein, J.; Oblak, M.L.; Salgado, R.; Cardenas, J.C.P.; Brunetti, B.; Muscatello, L.V.; et al. Comparative Evaluation of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Companion Animals: Immuno-Oncology as a Relevant Translational Model for Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensali, N.; Inderberg, E.M. Emerging Biomarkers for Immunotherapy in Glioblastoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munn, D.H.; Bronte, V. Immune suppressive mechanisms in the tumor microenvironment. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2016, 39, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mauldin, I.S.; Jo, J.; Wages, N.A.; Yogendran, L.V.; Mahmutovic, A.; Young, S.J.; Lopes, M.B.; Slingluff, C.L., Jr.; Erickson, L.D.; Fadul, C.E. Proliferating CD8(+) T Cell Infiltrates Are Associated with Improved Survival in Glioblastoma. Cells 2021, 10, 3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duy, C.; Yu, J.J.; Nahar, R.; Swaminathan, S.; Kweon, S.M.; Polo, J.M.; Valls, E.; Klemm, L.; Shojaee, S.; Cerchietti, L.; et al. BCL6 is critical for the development of a diverse primary B cell repertoire. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muschol-Steinmetz, C.; Jasmer, B.; Kreis, N.N.; Steinhauser, K.; Ritter, A.; Rolle, U.; Yuan, J.; Louwen, F. B-cell lymphoma 6 promotes proliferation and survival of trophoblastic cells. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamma, R.; Ruggieri, S.; Annese, T.; Simone, G.; Mangia, A.; Rega, S.; Zito, F.A.; Nico, B.; Ribatti, D. Bcl6/p53 expression, macrophages/mast cells infiltration and microvascular density in invasive breast carcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 22727–22740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardenas, M.G.; Oswald, E.; Yu, W.; Xue, F.; MacKerell, A.D., Jr.; Melnick, A.M. The Expanding Role of the BCL6 Oncoprotein as a Cancer Therapeutic Target. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Dube, C.; Gibert, M., Jr.; Cruickshanks, N.; Wang, B.; Coughlan, M.; Yang, Y.; Setiady, I.; Deveau, C.; Saoud, K.; et al. The p53 Pathway in Glioblastoma. Cancers 2018, 10, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastenhuber, E.R.; Lowe, S.W. Putting p53 in Context. Cell 2017, 170, 1062–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bieging, K.T.; Mello, S.S.; Attardi, L.D. Unravelling mechanisms of p53-mediated tumour suppression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tamma, R.; Ingravallo, G.; Annese, T.; d’Amati, A.; Lorusso, L.; Ribatti, D. Tumor Microenvironment and Microvascular Density in Human Glioblastoma. Cells 2023, 12, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12010011
Tamma R, Ingravallo G, Annese T, d’Amati A, Lorusso L, Ribatti D. Tumor Microenvironment and Microvascular Density in Human Glioblastoma. Cells. 2023; 12(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleTamma, Roberto, Giuseppe Ingravallo, Tiziana Annese, Antonio d’Amati, Loredana Lorusso, and Domenico Ribatti. 2023. "Tumor Microenvironment and Microvascular Density in Human Glioblastoma" Cells 12, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12010011
APA StyleTamma, R., Ingravallo, G., Annese, T., d’Amati, A., Lorusso, L., & Ribatti, D. (2023). Tumor Microenvironment and Microvascular Density in Human Glioblastoma. Cells, 12(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12010011








