A Live Cell Protein Complementation Assay for ORFeome-Wide Probing of Human HOX Interactomes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
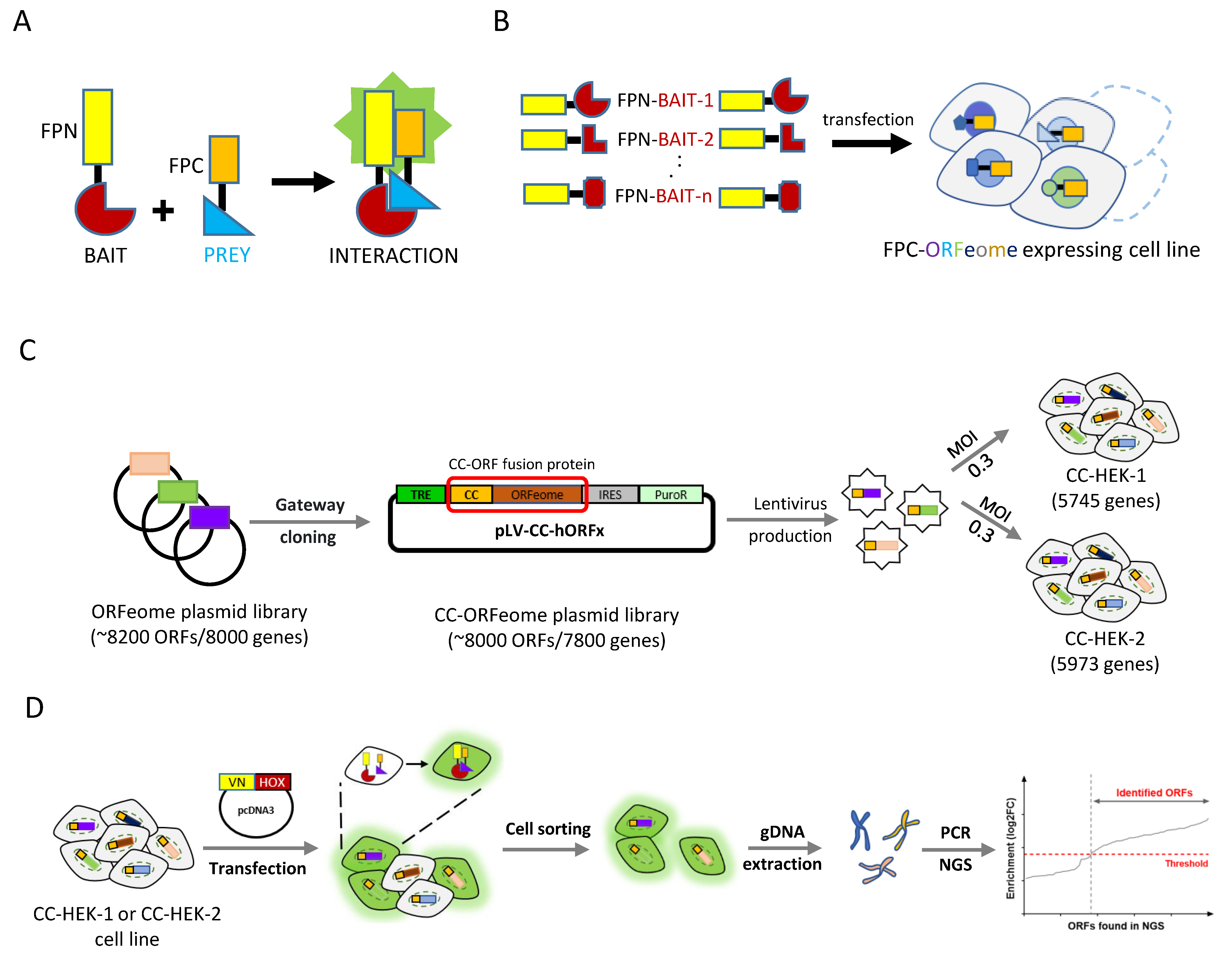
2.1. Cell-PCA Screen Design
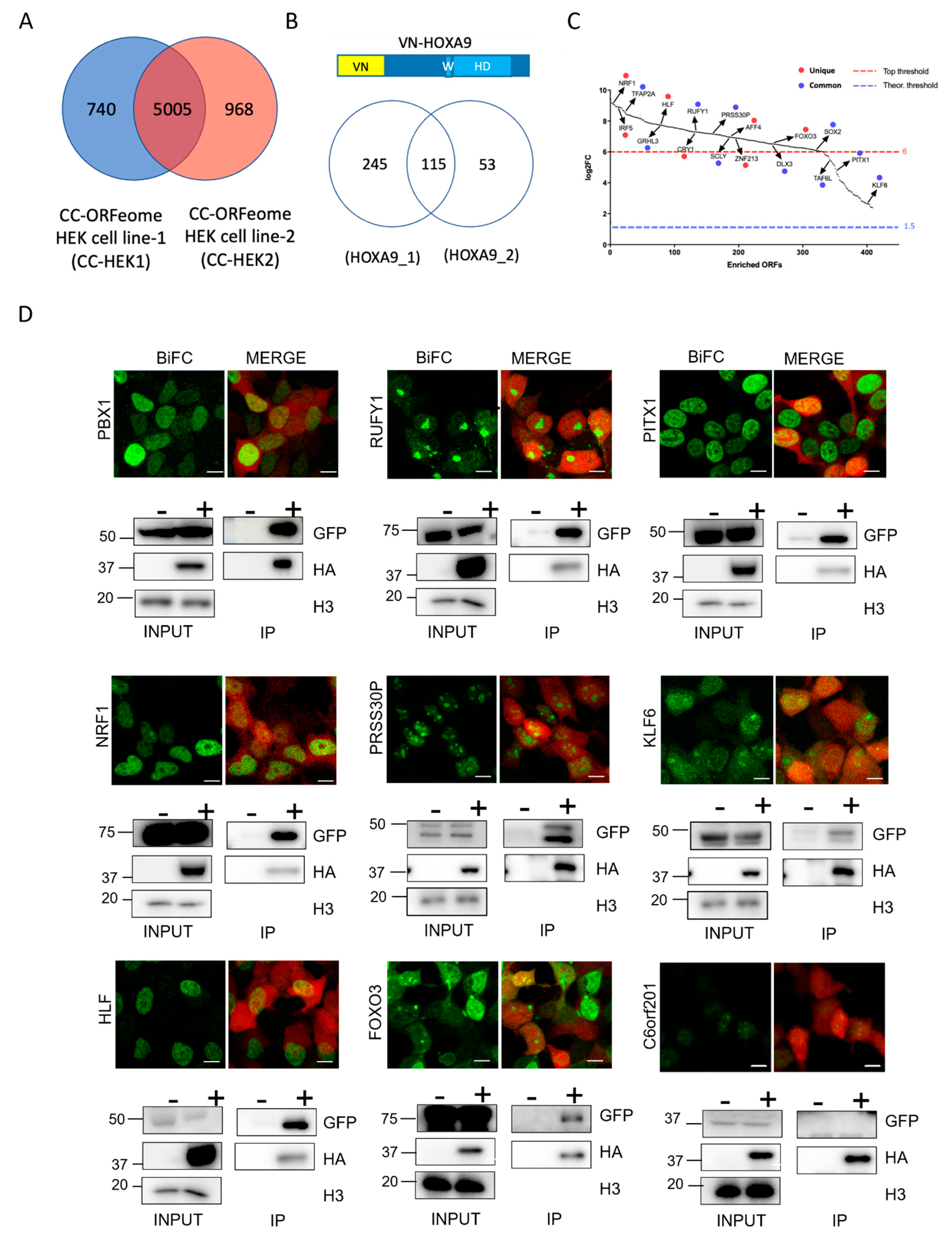
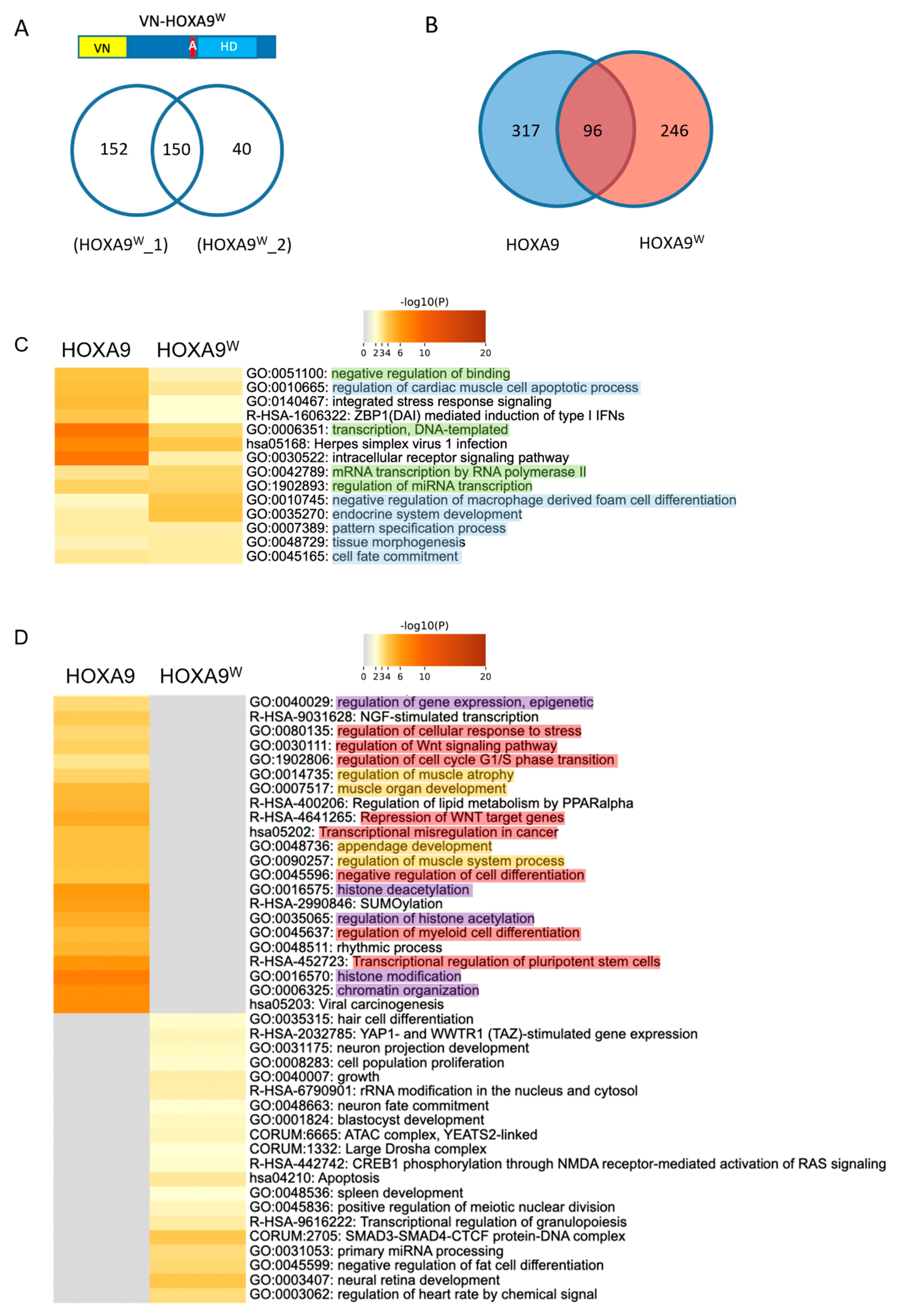
2.2. Proof-of-Concept Cell-PCA Screen for HOXA9 Interactomes
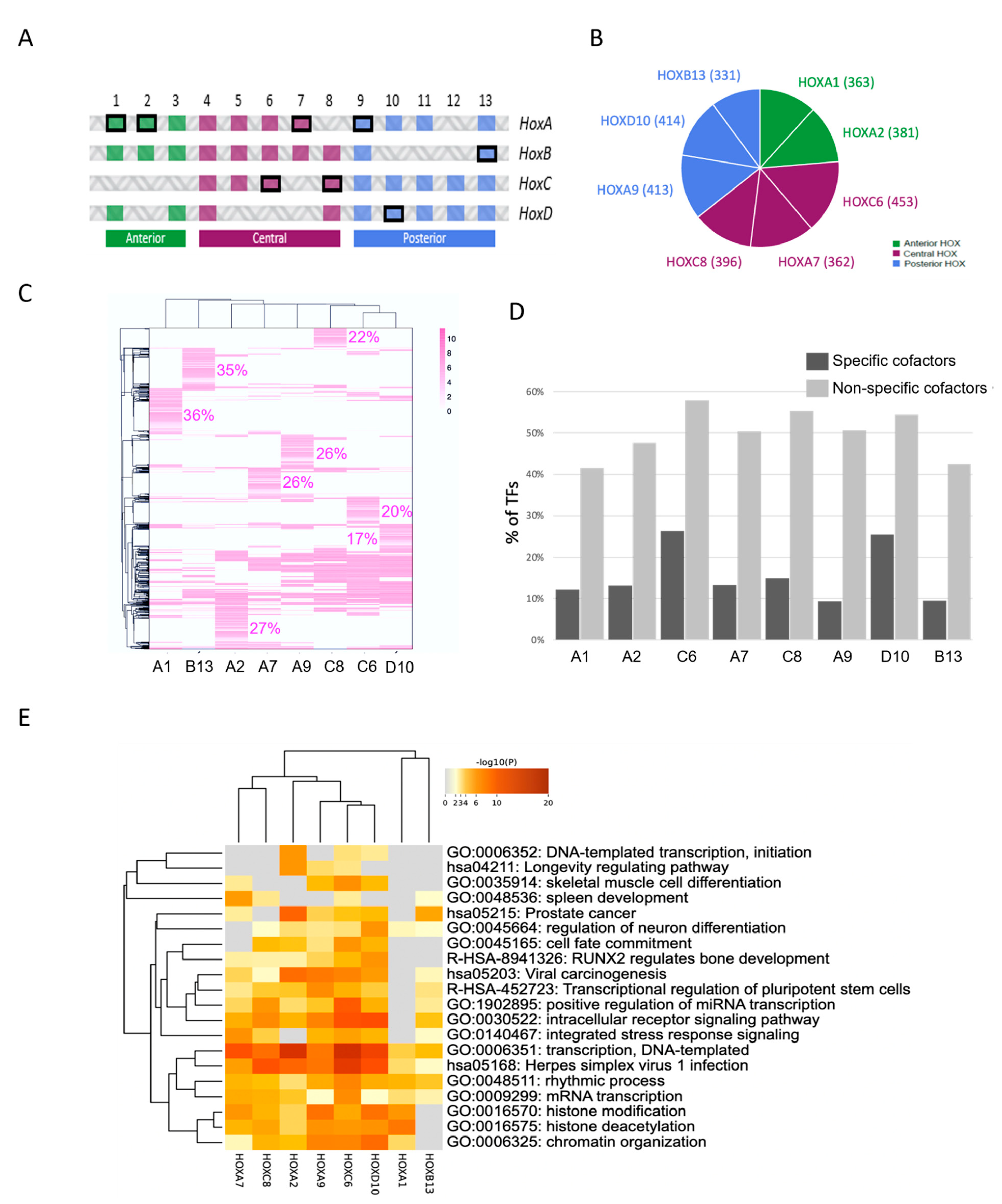
2.3. Using Cell-PCA for a Global Comparison of HOX Interactomes
2.4. CREB3L4 Interacted with HOXB13 and Promoted Its Proliferative Activity in a Prostate Cancer Cell Context
3. Discussion
3.1. Cell-PCA Allowed Interactomes to Be Captured and Compared in the Same Live Cell Context
3.2. HOX Interactomes Were Revealed with Cell-PCA: Molecular Properties and Comparison with Existing Databases
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines
4.2. Plasmids
4.3. Lentivirus Preparation and Infection
4.4. Immunostaining of CC-ORF Transduced HEK Cells
4.5. Cell-PCA Screen
4.6. Next Generation Sequencing and Identification of the Positive hORFs
4.7. Identification of HOX-Interacting ORF Candidates
4.8. Individual BiFC Validation in Live Cells
4.9. Individual Co-Immunoprecipitation (IP) Validation
4.10. Functional Enrichment and Interactome Analysis
4.11. xCELLigence Assays
4.12. siRNAs Used in This Study Were from Eurogentec
4.13. siRNAs and RT-QPCRs
4.14. Sequences of the Primers Used in This Study
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paiano, A.; Margiotta, A.; De Luca, M.; Bucci, C. Yeast Two-Hybrid Assay to Identify Interacting Proteins. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2019, 95, e70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Varnaitė, R.; MacNeill, S.A. Meet the neighbours: Mapping local protein interactomes by proximity-dependent labelling with BioID. Proteomics 2016, 16, 2503–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carnesecchi, J.; Sigismondo, G.; Domsch, K.; Baader, C.E.P.; Rafiee, M.R.; Krijgsveld, J.; Lohmann, I. Multi-Level and Lineage-Specific Interactomes of the Hox Transcription Factor Ubx Contribute to Its Functional Specificity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, K.E.; Kim, Y.; Huh, W.K.; Park, H.O. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) analysis: Advances and recent applications for Genome-Wide interaction studies. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 2039–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Remy, I.; Campbell-Valois, F.X.; Michnick, S.W. Detection of Protein–Protein Interactions Using a Simple Survival Protein-Fragment Complementation Assay (PCA) Based on the Enzyme Dihydrofolate Reductase. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2120–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendzen, K.W.; Böhmer, M.; Wallmeroth, N.; Peter, S.; Vesić, M.; Zhou, Y.; Tiesler, F.K.E.; Schleifenbaum, F.; Harter, K. Screening for in Planta Protein-Protein Interactions Combining Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation with Flow Cytometry. Plant Methods 2012, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, Z.; Liang, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Songyang, Z.; Lin, S.-Y.; Mills, G.B. A retrovirus-based protein complementation assay screen reveals functional AKT1-binding partners. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15014–15019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, O.-H.; Kim, H.; He, Q.; Baek, H.J.; Yang, D.; Chen, L.-Y.; Liang, J.; Chae, H.K.; Safari, A.; Liu, D.; et al. Genome-Wide YFP Fluorescence Complementation Screen Identifies New Regulators for Telomere Signaling in Human Cells. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2011, 10, M110.001628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, S.E.; Hodimont, E.; Green, C.M. A fluorescent bimolecular complementation screen reveals MAF1, RNF7 and SETD3 as PCNA-associated proteins in human cells. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 2509–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pearson, J.C.; Lemons, D.; McGinnis, W. Modulating Hox gene functions during animal body patterning. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallo, M. Reassessing the Role of Hox Genes during Vertebrate Development and Evolution. Trends Genet. 2018, 34, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seifert, A.; Werheid, D.F.; Knapp, S.M.; Tobiasch, E. Role of Hox Genes in Stem Cell Differentiation. World J. Stem Cells 2015, 7, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, B.; Vandeputte, J.; Remacle, S.; Bergiers, I.; Simonis, N.; Twizere, J.-C.; Vidal, M.; Rezsohazy, R. Protein Interactions of the Transcription Factor Hoxa1. BMC Dev. Biol. 2012, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baeëza, M.; Viala, S.; Heim, M.; Dard, A.; Hudry, B.; Duffraisse, M.; Rogulja-Ortmann, A.; Brun, C.; Merabet, S. Inhibitory Activities of Short Linear Motifs Underlie Hox Interactome Specificity in Vivo. eLife 2015, 4, e06034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischof, J.; Duffraisse, M.; Furger, E.; Ajuria, L.; Giraud, G.; Vanderperre, S.; Paul, R.; Björklund, M.; Ahr, D.; Ahmed, A.W.; et al. Generation of a Versatile Bifc Orfeome Library for Analyzing Protein–Protein Interactions in Live Drosophila. eLife 2018, 7, e38853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dard, A.; Reboulet, J.; Jia, Y.; Bleicher, F.; Duffraisse, M.; Vanaker, J.-M.; Forcet, C.; Merabet, S. Human HOX Proteins Use Diverse and Context-Dependent Motifs to Interact with TALE Class Cofactors. Cell Rep. 2018, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, C.-D.; Kerppola, T.K. Simultaneous Visualization of Multiple Protein Interactions in Living Cells Using Multicolor Fluorescence Complementation Analysis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hudry, B.; Viala, S.; Graba, Y.; Merabet, S. Visualization of Protein Interactions in Living Drosophila Embryos by the Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation Assay. BMC Biol. 2011, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dard, A.; Jia, Y.; Reboulet, J.; Bleicher, F.; Lavau, C.; Merabet, S. The Human HOXA9 Protein Uses Paralog-Specific Residues of the Homeodomain to Interact with TALE-Class Cofactors. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LaRonde-LeBlanc, N.A.; Wolberger, C. Structure of HoxA9 and Pbx1 Bound to DNA: Hox Hexapeptide and DNA Recognition Anterior to Posterior. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 2060–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, G.J.; Liberante, F.G.; Kettyle, L.M.; O’Hagan, K.A.; Finnegan, D.P.J.; Bullinger, L.; Geerts, D.; McMullin, M.F.; Lappin, T.R.J.; Mills, K.I.; et al. HOXA/PBX3 Knockdown Impairs Growth and Sensitizes Cytogenetically Normal Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells to Chemotherapy. Haematologica 2013, 98, 1216–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ando, H.; Natsume, A.; Senga, T.; Watanabe, R.; Ito, I.; Ohno, M.; Iwami, K.; Ohka, F.; Motomura, K.; Kinjo, S.; et al. Peptide-Based Inhibition of the HOXA9/PBX Interaction Retards the Growth of Human Meningioma. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2014, 73, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merabet, S.; Saadaoui, M.; Sambrani, N.; Hudry, B.; Pradel, J.; Affolter, M.; Graba, Y. A Unique Extradenticle Recruitment Mode in the Drosophila Hox Protein Ultrabithorax. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16946–16951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, P.; Xia, J.H.; Sipeky, C.; Dong, X.M.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Cruz, S.P.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, J.; et al. Biology and Clinical Implications of the 19q13 Aggressive Prostate Cancer Susceptibility Locus. Cell 2018, 174, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, J.H.; Wei, G.H. Oncogenic regulatory circuits driven by 19q13 rs11672691 underlies prostate cancer aggressiveness. Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2018, 5, e1516451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.P.; Xian, P.; Luo, H.; Dai, J.Y.; Bai, Y.; Li, Y.; Tang, X.L. Comprehensive Landscape of HOXA2, HOXA9, and HOXA10 as Potential Biomarkers for Predicting Progression and Prognosis in Prostate Cancer. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 24, 5740971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonkers, J.; Pai, P.; Sukumar, S. Multiple roles of HOX proteins in Metastasis: Let me count the ways. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 661–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Xie, M.; Ji, X.; Luo, X.; Huang, W.; Xia, L. Homeobox Genes in Cancers: From Carcinogenesis to Recent Therapeutic Intervention. Front. Oncol. 2021, 14, 4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Li, J.; Kiriluk, K.J.; Rosen, A.M.; Paner, G.P.; Antic, T.; Lussier, Y.A.; Vander Griend, D.J. Deregulation of a Hox Protein Regulatory Network Spanning Prostate Cancer Initiation and Progression. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4291–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgan, R.; Boxall, A.; Harrington, K.J.; Simpson, G.R.; Michael, A.; Pandha, H.S. Targeting HOX Transcription Factors in Prostate Cancer. BMC Urol. 2014, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Whitington, T.; Gao, P.; Lindberg, J.F.; Yang, Y.; Sun, J.; Väisänen, M.R.; Szulkin, R.; Annala, M.; Yan, J.; et al. A Prostate Cancer Susceptibility Allele at 6q22 Increases RFX6 Expression by Modulating HOXB13 Chromatin Binding. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanOpstall, C.; Perike, S.; Brechka, H.; Gillard, M.; Lamperis, S.; Zhu, B.; Brown, R.; Bhanvadia, R.; Vander Griend, D.J. MEIS-mediated suppression of human prostate cancer growth and metastasis through HOXB13-dependent regulation of proteoglycans. Elife 2020, 9, e53600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.R.; Kim, I.J.; Kang, T.W.; Choi, C.; Kim, K.K.; Kim, M.S.; Nam, K.I.; Jung, C. HOXB13 downregulates intracellular zinc and increases NF-kB signaling to promote prostate cancer metastasis. Oncogene 2014, 33, 4558–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.J.; Kang, T.W.; Jeong, T.; Kim, Y.R.; Jung, C. HOXB13 Regulates the Prostate-Derived Ets Factor: Implications for Prostate Cancer Cell Invasion. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Misawa, A.; Kondo, Y.; Takei, H.; Takizawa, T. Long Noncoding RNA HOXA11-AS and Transcription Factor HOXB13 Modulate the Expression of Bone Metastasis-Related Genes in Prostate Cancer. Gene 2021, 12, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, U.; Fuessel, S.; Koch, R.; Gustavo; Baretton, B.; Lohse, A.; Tomasetti, S.; Unversucht, S.; Froehner, M.; Wirth, M.P.; et al. QuantitativeMulti-Gene Expression Profiling of Primary ProstateCancer. Prostate 2006, 66, 1521–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly Accurate Protein Structure Prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadi, M.; Anyango, S.; Deshpande, M.; Nair, S.; Natassia, C.; Yordanova, G.; Yuan, D.; Stroe, O.; Wood, G.; Laydon, A.; et al. AlphaFold Protein Structure Database: Massively Expanding the Structural Coverage of Protein-Sequence Space with High-Accuracy Models. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D439–D444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerignoli, F.; Abassi, Y.A.; Lamarche, B.J.; Guenther, G.; Santa Ana, S.; Guimet, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Xi, B. In vitro immunotherapy potency assays using real-time cell analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Şimşek, S.; Şüküroğlu, A.A.; Yetkin, D.; Özbek, B.; Battal, D.; Genç, R. DNA-damage and cell cycle arrest initiated anti-cancer potency of super tiny carbon dots on MCF7 cell line. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribollet, V.; Cerutti, C.; Géloën, A.; Berger, E.; De Mets, R.; Balland, M.; Courchet, J.; Vanacker, J.M.; Forcet, C. ERRα coordinates actin and focal adhesion dynamics. Cancer Gene Therapy. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022, 29, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remy, I.; Michnick, S.W. Regulation of Apoptosis by the Ft1 Protein, a New Modulator of Protein Kinase B/Akt. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 1493–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Von Mering, C.; Krause, R.; Snel, B.; Cornell, M.; Oliver, S.G.; Fields, S.B.P. Comparative assessment of large-scale data sets of protein-protein interactions. Nature 2002, 417, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brückner, A.; Polge, C.; Lentze, N.; Auerbach, D.S.U. Yeast two-hybrid, a powerful tool for systems biology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 2763–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chi, X.; Zheng, Q.; Jiang, R.; Chen-Tsai, R.Y.; Kong, L.J. A System for Site-Specific Integration of Transgenes in Mammalian Cells. PLoS ONE 2019, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, M.K.; Lim, G.; Yi, D.G.; Chang, Y.J.; Yang, E.B.; Lee, K.Y.; Huh, W.K. Genome-Wide Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation Analysis of SUMO Interactome in Yeast. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taminiau, A.; Draime, A.; Tys, J.; Lambert, B.; Vandeputte, J.; Nguyen, N.; Renard, P.; Geerts, D.; Rezsöhazy, R. HOXA1 Binds RBCK1/HOIL-1 and TRAF2 and Modulates the TNF/NF-ΚB Pathway in a Transcription-Independent Manner. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 7331–7349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yea, K.; Zhang, H.; Xie, J.; Jones, T.M.; Yang, G.; Song, B.D.; Lerner, R.A. Converting Stem Cells to Dendritic Cells by Agonist Antibodies from Unbiased Morphogenic Selections. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 14966–14971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afgan, E.; Baker, D.; Batut, B.; van den Beek, M.; Bouvier, D.; Cech, M.; Chilton, J.; Clements, D.; Coraor, N.; Grüning, B.A.; et al. The Galaxy Platform for Accessible, Reproducible and Collaborative Biomedical Analyses: 2018 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W537–W544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt Removes Adapter Sequences from High-Throughput Sequencing Reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cock, P.J.A.; Chilton, J.M.; Grüning, B.; Johnson, J.E.; Soranzo, N. NCBI BLAST+ Integrated into Galaxy. GigaScience 2015, 4, s13742-015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape Provides a Biologist-Oriented Resource for the Analysis of Systems-Level Datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader, G.D.; Hogue, C.W. An Automated Method for Finding Molecular Complexes in Large Protein Interaction Networks. BMC Bioinform. 2003, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, Y.; Reboulet, J.; Gillet, B.; Hughes, S.; Forcet, C.; Tribollet, V.; Hajj Sleiman, N.; Kundlacz, C.; Vanacker, J.-M.; Bleicher, F.; et al. A Live Cell Protein Complementation Assay for ORFeome-Wide Probing of Human HOX Interactomes. Cells 2023, 12, 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12010200
Jia Y, Reboulet J, Gillet B, Hughes S, Forcet C, Tribollet V, Hajj Sleiman N, Kundlacz C, Vanacker J-M, Bleicher F, et al. A Live Cell Protein Complementation Assay for ORFeome-Wide Probing of Human HOX Interactomes. Cells. 2023; 12(1):200. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12010200
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Yunlong, Jonathan Reboulet, Benjamin Gillet, Sandrine Hughes, Christelle Forcet, Violaine Tribollet, Nawal Hajj Sleiman, Cindy Kundlacz, Jean-Marc Vanacker, Françoise Bleicher, and et al. 2023. "A Live Cell Protein Complementation Assay for ORFeome-Wide Probing of Human HOX Interactomes" Cells 12, no. 1: 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12010200
APA StyleJia, Y., Reboulet, J., Gillet, B., Hughes, S., Forcet, C., Tribollet, V., Hajj Sleiman, N., Kundlacz, C., Vanacker, J.-M., Bleicher, F., & Merabet, S. (2023). A Live Cell Protein Complementation Assay for ORFeome-Wide Probing of Human HOX Interactomes. Cells, 12(1), 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12010200







