A YAP/TAZ–ARHGAP29–RhoA Signaling Axis Regulates Podocyte Protrusions and Integrin Adhesions
Abstract
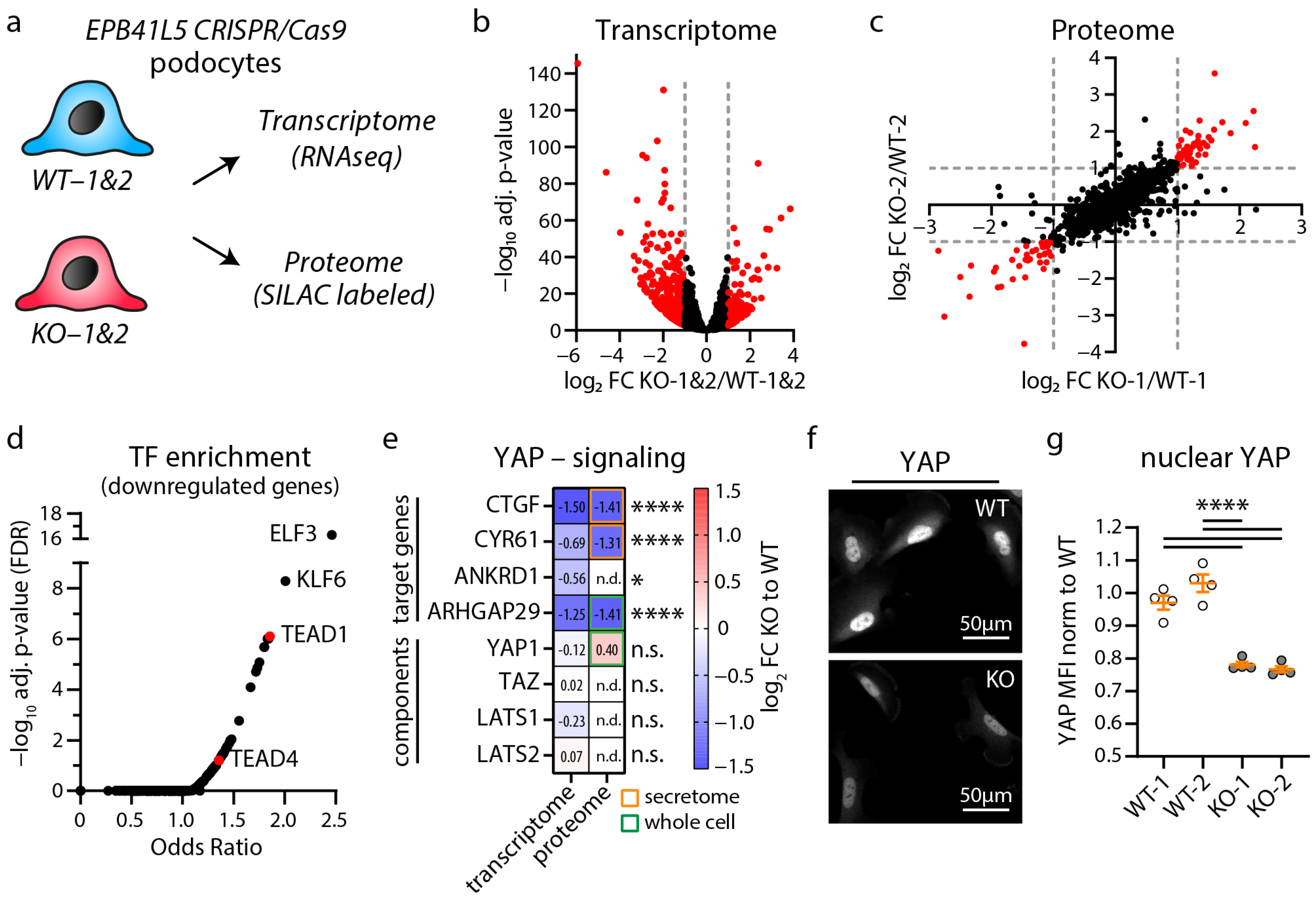
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Nephrocyte Analysis
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Expression Plasmids
2.4. Antibodies
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Analysis of Active RhoA
2.7. Immunofluorescence, Cell Spreading, and Integrin Adhesion Complex Analysis
2.8. Glomerular Disease Analysis
2.9. GlomAssay
2.10. RNA Sequencing
2.11. Proteomics
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Loss of EPB41L5 Impairs YAP/TAZ-TEAD Complex Mediated Transcriptional Signaling
3.2. Inhibition of YAP/TAZ-TEAD Complex Mediated Transcription Impairs Formation of Cell Protrusions, IACs and Expression of Podocyte Genes


3.3. ARHGAP29 Limits IAC Maturation and Promotes Cell Protrusion Formation


3.4. ARHGAP29 Expression Is Induced as a Consequence of Mild Podocyte Damage

4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Romagnani, P.; Remuzzi, G.; Glassock, R.; Levin, A.; Jager, K.J.; Tonelli, M.; Massy, Z.; Wanner, C.; Anders, H.J. Chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, J.B.; Anders, H.J.; Susztak, K.; Podesta, M.A.; Remuzzi, G.; Hildebrandt, F.; Romagnani, P. Podocytopathies. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collaboration, G.B.D.C.K.D. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet 2020, 395, 709–733. [Google Scholar]
- Benzing, T.; Salant, D. Insights into glomerular filtration and albuminuria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachs, N.; Sonnenberg, A. Cell-matrix adhesion of podocytes in physiology and disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2013, 9, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schell, C.; Huber, T.B. The evolving complexity of the podocyte cytoskeleton. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 3166–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuda, J.; Asano-Matsuda, K.; Kitzler, T.M.; Takano, T. Rho gtpase regulatory proteins in podocytes. Kidney Int. 2021, 99, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogg, M.; Maier, J.I.; Dotzauer, R.; Artelt, N.; Kretz, O.; Helmstadter, M.; Abed, A.; Sammarco, A.; Sigle, A.; Sellung, D.; et al. Srgap1 controls small rho gtpases to regulate podocyte foot process maintenance. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sever, S.; Schiffer, M. Actin dynamics at focal adhesions: A common endpoint and putative therapeutic target for proteinuric kidney diseases. Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kechagia, J.Z.; Ivaska, J.; Roca-Cusachs, P. Integrins as biomechanical sensors of the microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, J.D.; Dufresne, E.R.; Schwartz, M.A. Mechanotransduction and extracellular matrix homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogg, M.; Maier, J.I.; Van Wymersch, C.; Helmstadter, M.; Sammarco, A.; Lindenmeyer, M.; Zareba, P.; Montanez, E.; Walz, G.; Werner, M.; et al. Alpha-parvin defines a specific integrin adhesome to maintain the glomerular filtration barrier. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 33, 786–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lausecker, F.; Tian, X.; Inoue, K.; Wang, Z.; Pedigo, C.E.; Hassan, H.; Liu, C.; Zimmer, M.; Jinno, S.; Huckle, A.L.; et al. Vinculin is required to maintain glomerular barrier integrity. Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasuda-Yamahara, M.; Rogg, M.; Frimmel, J.; Trachte, P.; Helmstaedter, M.; Schroder, P.; Schiffer, M.; Schell, C.; Huber, T.B. Fermt2 links cortical actin structures, plasma membrane tension and focal adhesion function to stabilize podocyte morphology. Matrix Biol. 2018, 68–69, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Kim, J.J.; Monkley, S.M.; Gotoh, N.; Nandez, R.; Soda, K.; Inoue, K.; Balkin, D.M.; Hassan, H.; Son, S.H.; et al. Podocyte-associated talin1 is critical for glomerular filtration barrier maintenance. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 1098–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rinschen, M.M.; Godel, M.; Grahammer, F.; Zschiedrich, S.; Helmstadter, M.; Kretz, O.; Zarei, M.; Braun, D.A.; Dittrich, S.; Pahmeyer, C.; et al. A multi-layered quantitative in vivo expression atlas of the podocyte unravels kidney disease candidate genes. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 2495–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schell, C.; Rogg, M.; Suhm, M.; Helmstadter, M.; Sellung, D.; Yasuda-Yamahara, M.; Kretz, O.; Kuttner, V.; Suleiman, H.; Kollipara, L.; et al. The ferm protein epb41l5 regulates actomyosin contractility and focal adhesion formation to maintain the kidney filtration barrier. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E4621–E4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endlich, K.; Kliewe, F.; Endlich, N. Stressed podocytes-mechanical forces, sensors, signaling and response. Pflugers Arch. 2017, 469, 937–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suleiman, H.Y.; Roth, R.; Jain, S.; Heuser, J.E.; Shaw, A.S.; Miner, J.H. Injury-induced actin cytoskeleton reorganization in podocytes revealed by super-resolution microscopy. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e94137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hirano, M.; Hashimoto, S.; Yonemura, S.; Sabe, H.; Aizawa, S. Epb41l5 functions to post-transcriptionally regulate cadherin and integrin during epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 182, 1217–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakajima, H.; Tanoue, T. Epithelial cell shape is regulated by lulu proteins via myosin-ii. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maier, J.I.; Rogg, M.; Helmstadter, M.; Sammarco, A.; Schilling, O.; Sabass, B.; Miner, J.H.; Dengjel, J.; Walz, G.; Werner, M.; et al. Epb41l5 controls podocyte extracellular matrix assembly by adhesome-dependent force transmission. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.I.; Rogg, M.; Helmstadter, M.; Sammarco, A.; Walz, G.; Werner, M.; Schell, C. A novel model for nephrotic syndrome reveals associated dysbiosis of the gut microbiome and extramedullary hematopoiesis. Cells 2021, 10, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, S.; Morsut, L.; Aragona, M.; Enzo, E.; Giulitti, S.; Cordenonsi, M.; Zanconato, F.; Le Digabel, J.; Forcato, M.; Bicciato, S.; et al. Role of yap/taz in mechanotransduction. Nature 2011, 474, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Rio, A.; Perez-Jimenez, R.; Liu, R.; Roca-Cusachs, P.; Fernandez, J.M.; Sheetz, M.P. Stretching single talin rod molecules activates vinculin binding. Science 2009, 323, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhler, C.; Shivashankar, G.V. Regulation of genome organization and gene expression by nuclear mechanotransduction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Jiang, R.; Aoudjit, L.; Jones, N.; Takano, T. Activation of rhoa in podocytes induces focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1621–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Ellis, M.J.; Gomez, J.A.; Eisner, W.; Fennell, W.; Howell, D.N.; Ruiz, P.; Fields, T.A.; Spurney, R.F. Mechanisms of the proteinuria induced by rho gtpases. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwartzman, M.; Reginensi, A.; Wong, J.S.; Basgen, J.M.; Meliambro, K.; Nicholas, S.B.; D’Agati, V.; McNeill, H.; Campbell, K.N. Podocyte-specific deletion of yes-associated protein causes fsgs and progressive renal failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rinschen, M.M.; Grahammer, F.; Hoppe, A.K.; Kohli, P.; Hagmann, H.; Kretz, O.; Bertsch, S.; Hohne, M.; Gobel, H.; Bartram, M.P.; et al. Yap-mediated mechanotransduction determines the podocyte’s response to damage. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10, eaaf8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Wennmann, D.O.; Kremerskothen, J.; Weide, T.; Michgehl, U.; Pavenstadt, H.; Vollenbroker, B. Nuclear yap localization as a key regulator of podocyte function. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Wang, X.; He, Q.; Harris, R.C. Taz is important for maintenance of the integrity of podocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2022, 322, F419–F428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Chen, J.; Lim, Y.B.; Finch-Edmondson, M.L.; Seshachalam, V.P.; Qin, L.; Jiang, T.; Low, B.C.; Singh, H.; Lim, C.T.; et al. Yap regulates actin dynamics through arhgap29 and promotes metastasis. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, Y.; Park, J.; Feng, A.; Awasthi, P.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Iglesias-Bartolome, R. Yap1/taz-tead transcriptional networks maintain skin homeostasis by regulating cell proliferation and limiting klf4 activity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rogg, M.; Maier, J.I.; Ehle, M.; Sammarco, A.; Schilling, O.; Werner, M.; Schell, C. Nup133 controls nuclear pore assembly, transcriptome composition, and cytoskeleton regulation in podocytes. Cells 2022, 11, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankhead, P.; Loughrey, M.B.; Fernandez, J.A.; Dombrowski, Y.; McArt, D.G.; Dunne, P.D.; McQuaid, S.; Gray, R.T.; Murray, L.J.; Coleman, H.G.; et al. Qupath: Open source software for digital pathology image analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kindt, F.; Hammer, E.; Kemnitz, S.; Blumenthal, A.; Klemm, P.; Schluter, R.; Quaggin, S.E.; van den Brandt, J.; Fuellen, G.; Volker, U.; et al. A novel assay to assess the effect of pharmaceutical compounds on the differentiation of podocytes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kliewe, F.; Kuss, A.W.; Siegerist, F.; Schroder, S.; Schordan, S.; Artelt, N.; Kindt, F.; Amann, K.; Lindenmeyer, M.T.; Endlich, K.; et al. Studies on the role of the transcription factor tcf21 in the transdifferentiation of parietal epithelial cells into podocyte-like cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 55, 48–67. [Google Scholar]
- Keenan, A.B.; Torre, D.; Lachmann, A.; Leong, A.K.; Wojciechowicz, M.L.; Utti, V.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Kropiwnicki, E.; Wang, Z.; Ma’ayan, A. Chea3: Transcription factor enrichment analysis by orthogonal omics integration. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2019, 47, W212–W224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuttner, V.; Mack, C.; Rigbolt, K.T.; Kern, J.S.; Schilling, O.; Busch, H.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Dengjel, J. Global remodelling of cellular microenvironment due to loss of collagen vii. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2013, 9, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermle, T.; Braun, D.A.; Helmstadter, M.; Huber, T.B.; Hildebrandt, F. Modeling monogenic human nephrotic syndrome in the drosophila garland cell nephrocyte. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1521–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saras, J.; Franzen, P.; Aspenstrom, P.; Hellman, U.; Gonez, L.J.; Heldin, C.H. A novel gtpase-activating protein for rho interacts with a pdz domain of the protein-tyrosine phosphatase ptpl1. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 24333–24338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muller, P.M.; Rademacher, J.; Bagshaw, R.D.; Wortmann, C.; Barth, C.; van Unen, J.; Alp, K.M.; Giudice, G.; Eccles, R.L.; Heinrich, L.E.; et al. Systems analysis of rhogef and rhogap regulatory proteins reveals spatially organized rac1 signalling from integrin adhesions. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 498–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbediwy, A.; Vanyai, H.; Diaz-de-la-Loza, M.D.; Frith, D.; Snijders, A.P.; Thompson, B.J. Enigma proteins regulate yap mechanotransduction. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, jcs221788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wennmann, D.O.; Vollenbroker, B.; Eckart, A.K.; Bonse, J.; Erdmann, F.; Wolters, D.A.; Schenk, L.K.; Schulze, U.; Kremerskothen, J.; Weide, T.; et al. The hippo pathway is controlled by angiotensin ii signaling and its reactivation induces apoptosis in podocytes. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Randles, M.J.; Lausecker, F.; Humphries, J.D.; Byron, A.; Clark, S.J.; Miner, J.H.; Zent, R.; Humphries, M.J.; Lennon, R. Basement membrane ligands initiate distinct signalling networks to direct cell shape. Matrix Biol. 2020, 90, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, J.; Greenberg, D.; Ibrahim, S.; Maier, M.; Aoudjit, L.; Chapelle, J.; Baldwin, C.; He, Y.; Lamarche-Vane, N.; Takano, T. Cdgap maintains podocyte function and modulates focal adhesions in a src kinase-dependent manner. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.A.; Welsh, G.I. Podocyte rhogtpases: New therapeutic targets for nephrotic syndrome? F1000Res 2019, 8, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, C.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Li, R.; Ma, J.; et al. Rhoa deficiency disrupts podocyte cytoskeleton and induces podocyte apoptosis by inhibiting yap/dendrin signal. BMC Nephrol. 2016, 17, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Lin, K.C.; Kumar, A.; Placone, J.K.; Fang, C.; Wang, K.C.; Lu, S.; Pan, M.; Hong, A.W.; et al. Rap2 mediates mechanoresponses of the hippo pathway. Nature 2018, 560, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tagashira, T.; Fukuda, T.; Miyata, M.; Nakamura, K.; Fujita, H.; Takai, Y.; Hirata, K.I.; Rikitake, Y. Afadin facilitates vascular endothelial growth factor-induced network formation and migration of vascular endothelial cells by inactivating rho-associated kinase through arhgap29. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Post, A.; Pannekoek, W.J.; Ross, S.H.; Verlaan, I.; Brouwer, P.M.; Bos, J.L. Rasip1 mediates rap1 regulation of rho in endothelial barrier function through arhgap29. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11427–11432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, K.; Reimann, A.; Fritz, R.D.; Ryu, H.; Jeon, N.L.; Pertz, O. Spatio-temporal co-ordination of rhoa, rac1 and cdc42 activation during prototypical edge protrusion and retraction dynamics. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vega, F.M.; Fruhwirth, G.; Ng, T.; Ridley, A.J. Rhoa and rhoc have distinct roles in migration and invasion by acting through different targets. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 193, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.; Schlondorff, J.; Higgs, H.N.; Pollak, M.R. Inverted formin 2 regulates actin dynamics by antagonizing rho/diaphanous-related formin signaling. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vicente-Manzanares, M.; Ma, X.; Adelstein, R.S.; Horwitz, A.R. Non-muscle myosin ii takes centre stage in cell adhesion and migration. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, J.C.; Han, X.; Hsiao, C.T.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; Waterman, C.M. Analysis of the myosin-ii-responsive focal adhesion proteome reveals a role for beta-pix in negative regulation of focal adhesion maturation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mason, D.E.; Collins, J.M.; Dawahare, J.H.; Nguyen, T.D.; Lin, Y.; Voytik-Harbin, S.L.; Zorlutuna, P.; Yoder, M.C.; Boerckel, J.D. Yap and taz limit cytoskeletal and focal adhesion maturation to enable persistent cell motility. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 218, 1369–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanchanawong, P.; Calderwood, D.A. Organization, dynamics and mechanoregulation of integrin-mediated cell-ecm adhesions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 24, 142–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schell, C.; Sabass, B.; Helmstaedter, M.; Geist, F.; Abed, A.; Yasuda-Yamahara, M.; Sigle, A.; Maier, J.I.; Grahammer, F.; Siegerist, F.; et al. Arp3 controls the podocyte architecture at the kidney filtration barrier. Dev. Cell 2018, 47, 741–757.e748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beckham, Y.; Vasquez, R.J.; Stricker, J.; Sayegh, K.; Campillo, C.; Gardel, M.L. Arp2/3 inhibition induces amoeboid-like protrusions in mcf10a epithelial cells by reduced cytoskeletal-membrane coupling and focal adhesion assembly. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qu, C.; Roth, R.; Puapatanakul, P.; Loitman, C.; Hammad, D.; Genin, G.M.; Miner, J.H.; Suleiman, H.Y. Three-dimensional visualization of the podocyte actin network using integrated membrane extraction, electron microscopy, and machine learning. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 33, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.; Justus-Liebig-Universität, G. The role of the podocyte adhesion protein Epb41l5 for the composition and functionality of the glomerular basment membrane. In VVB Laufersweiler; Verlag: Giessen, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rogg, M.; Maier, J.I.; Helmstädter, M.; Sammarco, A.; Kliewe, F.; Kretz, O.; Weißer, L.; Van Wymersch, C.; Findeisen, K.; Koessinger, A.L.; et al. A YAP/TAZ–ARHGAP29–RhoA Signaling Axis Regulates Podocyte Protrusions and Integrin Adhesions. Cells 2023, 12, 1795. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12131795
Rogg M, Maier JI, Helmstädter M, Sammarco A, Kliewe F, Kretz O, Weißer L, Van Wymersch C, Findeisen K, Koessinger AL, et al. A YAP/TAZ–ARHGAP29–RhoA Signaling Axis Regulates Podocyte Protrusions and Integrin Adhesions. Cells. 2023; 12(13):1795. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12131795
Chicago/Turabian StyleRogg, Manuel, Jasmin I. Maier, Martin Helmstädter, Alena Sammarco, Felix Kliewe, Oliver Kretz, Lisa Weißer, Clara Van Wymersch, Karla Findeisen, Anna L. Koessinger, and et al. 2023. "A YAP/TAZ–ARHGAP29–RhoA Signaling Axis Regulates Podocyte Protrusions and Integrin Adhesions" Cells 12, no. 13: 1795. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12131795
APA StyleRogg, M., Maier, J. I., Helmstädter, M., Sammarco, A., Kliewe, F., Kretz, O., Weißer, L., Van Wymersch, C., Findeisen, K., Koessinger, A. L., Tsoy, O., Baumbach, J., Grabbert, M., Werner, M., Huber, T. B., Endlich, N., Schilling, O., & Schell, C. (2023). A YAP/TAZ–ARHGAP29–RhoA Signaling Axis Regulates Podocyte Protrusions and Integrin Adhesions. Cells, 12(13), 1795. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12131795







