Macrophage Implication in IPF: Updates on Immune, Epigenetic, and Metabolic Pathways
Abstract
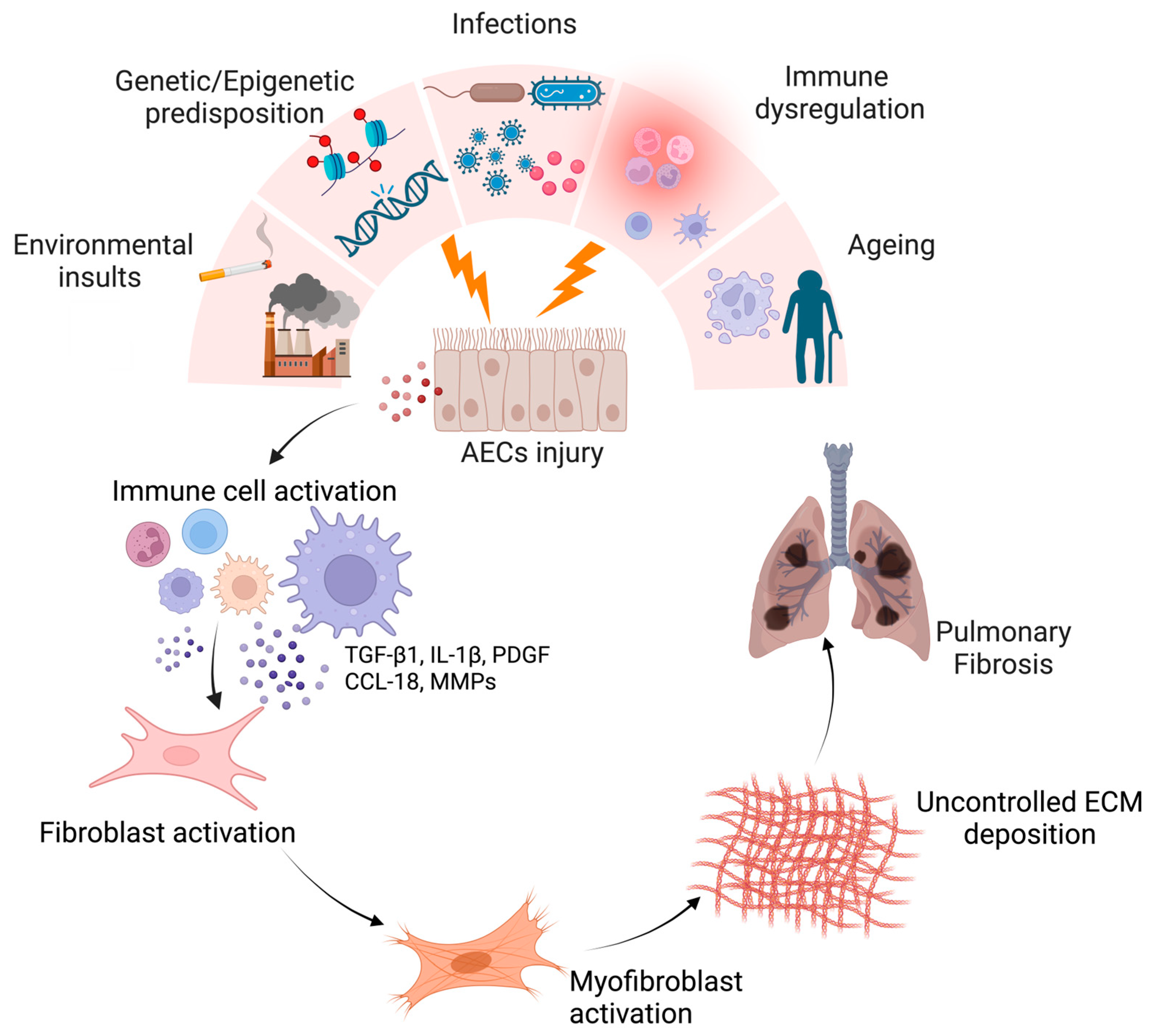
:1. Introduction
1.1. Generalities about IPF
1.2. Main Immune Players in IPF
2. Macrophages in Lung Fibrosis
2.1. Main Macrophage Populations in the Lungs
2.2. Macrophage Polarization in IPF
3. Macrophage-Related Mechanisms in IPF
3.1. Surface Receptor-Dependent Mechanisms
3.2. Metabolism-Related Mechanisms
3.3. Transcriptional and Epigenetic Mechanisms
3.4. Macrophage Subsets and Cytokines/Chemokines
3.4.1. Subsets
3.4.2. Cytokines/Chemokines
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maher, T.M.; Bendstrup, E.; Dron, L.; Langley, J.; Smith, G.; Khalid, J.M.; Patel, H.; Kreuter, M. Global Incidence and Prevalence of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.J.; Collard, H.R.; Pardo, A.; Raghu, G.; Richeldi, L.; Selman, M.; Swigris, J.J.; Taniguchi, H.; Wells, A.U. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesé, L.; Nunes, H.; Cottin, V.; Israel-Biet, D.; Crestani, B.; Guillot-Dudoret, S.; Cadranel, J.; Wallaert, B.; Tazi, A.; Maître, B.; et al. Gender Differences in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Are Men and Women Equal? Front. Med. 2021, 8, 713698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, D.S.; Grossfeld, D.; Renna, H.A.; Agarwala, P.; Spiegler, P.; DeLeon, J.; Reiss, A.B. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Current and Future Treatment. Clin. Respir. J. 2022, 16, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, L.; Guo, X.; Fan, H.; Shi, J.; Hou, S.; Lv, Q. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Microenvironment Targeted Delivery. Cells 2022, 11, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Richeldi, L.; Thomson, C.C.; Inoue, Y.; Johkoh, T.; Kreuter, M.; Lynch, D.A.; Maher, T.M.; Martinez, F.J.; et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (an Update) and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Adults: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, e18–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeganathan, N.; Cleland, D.; Sathananthan, M. The Association of Lung Cancer with Pulmonary Fibrosis. ERJ Open Res. 2022, 8, 505–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, K.M.; Castells, E.; Dixon, K.; Mason, S.; Elliott, G.; Marshall, H.; Poblocka, M.A.; Macip, S.; Richardson, M.; Khalfaoui, L.; et al. Evaluation of Pirfenidone and Nintedanib in a Human Lung Model of Fibrogenesis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 679388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, S.L.; Creamer, A.; Hayton, C.; Chaudhuri, N. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF): An Overview. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heukels, P.; Moor, C.C.; von der Thüsen, J.H.; Wijsenbeek, M.S.; Kool, M. Inflammation and Immunity in IPF Pathogenesis and Treatment. Respir. Med. 2019, 147, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behr, J.; Costabel, U.; Worth, H. Comments of the DGP on the press release dated 21.10.2011 of the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute about the PANTHER Study on IPF patients. Pneumologie 2011, 65, 724–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prednisone, Azathioprine, and N-Acetylcysteine for Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1968–1977. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; De Los Santos, F.G.; Phan, S.H. The Bleomycin Model of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1627, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, G.; Xiong, W.; Gu, W.; Wang, C.-Y. Macrophages: Friend or Foe in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis? Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysanthopoulou, A.; Mitroulis, I.; Apostolidou, E.; Arelaki, S.; Mikroulis, D.; Konstantinidis, T.; Sivridis, E.; Koffa, M.; Giatromanolaki, A.; Boumpas, D.T.; et al. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promote Differentiation and Function of Fibroblasts. J. Pathol. 2014, 233, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, A.D.; Kliment, C.R.; Metz, H.E.; Kim, K.-H.; Kargl, J.; Agostini, B.A.; Crum, L.T.; Oczypok, E.A.; Oury, T.A.; Houghton, A.M. Neutrophil Elastase Promotes Myofibroblast Differentiation in Lung Fibrosis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 98, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.A.; Eksteen, B.; Reid, D.; Paine, H.V.; Alansary, A.; Johannson, K.; Gwozd, C.; Goring, K.-A.R.; Vo, T.; Proud, D.; et al. Role of IL-17A and Neutrophils in Fibrosis in Experimental Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 1663–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jegal, Y. The Role of Neutrophils in the Pathogenesis of IPF. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2022, 37, 945–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinder, B.W.; Brown, K.K.; Schwarz, M.I.; Ix, J.H.; Kervitsky, A.; King, T.E. Baseline BAL Neutrophilia Predicts Early Mortality in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Chest 2008, 133, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Li, M.; Liu, B.; Ma, Z.; Yang, Q. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps and Pulmonary Fibrosis: An Update. J. Inflamm. 2023, 20, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tang, J.; Shuai, W.; Meng, J.; Feng, J.; Han, Z. Macrophage Polarization and Its Role in the Pathogenesis of Acute Lung Injury/Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 69, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsi, E.; Kamng’ona, R.; Rylance, J.; Solórzano, C.; Jesus Reiné, J.; Mwandumba, H.C.; Ferreira, D.M.; Jambo, K.C. Human Alveolar Macrophages Predominately Express Combined Classical M1 and M2 Surface Markers in Steady State. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.J. Macrophage Polarization. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017, 79, 541–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rőszer, T. Understanding the Mysterious M2 Macrophage through Activation Markers and Effector Mechanisms. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 816460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.M.; Mo, Y.; Bang, J.-Y.; Ko, Y.G.; Ahn, Y.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Koh, J.; Yim, J.-J.; Kang, H.-R. Classical Monocyte-Derived Macrophages as Therapeutic Targets of Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Comparison of Intratracheal and Intravenous Administration in a Mouse Model of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2023, 24, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, O.; Winkler, J.; Minasyan, M.; Herzog, E.L. The Role of Immune and Inflammatory Cells in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, G.; Liu, A.; Herzog, E.L. Evolving Perspectives on Innate Immune Mechanisms of IPF. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 676569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, J.W.; Breuer, C.K. Fibrocytes: A Critical Review and Practical Guide. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 784401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoso, A.; Mazza, E.M.C.; Bicciato, S.; Mandruzzato, S.; Bronte, V.; Serafini, P.; Inverardi, L. Human Fibrocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Express IDO and Promote Tolerance via Treg-Cell Expansion. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 3307–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsburgh, S.; Todryk, S.; Ramming, A.; Distler, J.H.W.; O’Reilly, S. Innate Lymphoid Cells and Fibrotic Regulation. Immunol. Lett. 2018, 195, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquelot, N.; Seillet, C.; Vivier, E.; Belz, G.T. Innate Lymphoid Cells and Cancer. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messing, M.; Jan-Abu, S.C.; McNagny, K. Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells: Central Players in a Recurring Theme of Repair and Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Jakubzick, C.; Osterburg, A.R.; Nelson, R.L.; Gupta, N.; McCormack, F.X.; Borchers, M.T. Dendritic Cell Trafficking and Function in Rare Lung Diseases. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 57, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, N.W.; Scheraga, R.G.; Galvin, J.R.; Iacono, A.T.; Britt, E.J.; Luzina, I.G.; Burke, A.P.; Atamas, S.P. Lymphocyte Aggregates Persist and Accumulate in the Lungs of Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Inflamm. Res. 2013, 6, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.F.; Egan, A.M.; Shaughnessy, G.F.; Anderson, D.K.; Kottom, T.J.; Dasari, H.; Van Keulen, V.P.; Aubry, M.-C.; Yi, E.S.; Limper, A.H.; et al. Antifibrotics Modify B-Cell-Induced Fibroblast Migration and Activation in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 64, 722–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellamri, N.; Viel, R.; Morzadec, C.; Lecureur, V.; Joannes, A.; de Latour, B.; Llamas-Gutierrez, F.; Wollin, L.; Jouneau, S.; Vernhet, L. TNF-α and IL-10 Control CXCL13 Expression in Human Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havenar-Daughton, C.; Lindqvist, M.; Heit, A.; Wu, J.E.; Reiss, S.M.; Kendric, K.; Bélanger, S.; Kasturi, S.P.; Landais, E.; Akondy, R.S.; et al. CXCL13 Is a Plasma Biomarker of Germinal Center Activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2702–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenderov, K.; Collins, S.L.; Powell, J.D.; Horton, M.R. Immune Dysregulation as a Driver of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e143226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Huang, T.; Zhang, L. T Cells in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Crucial but Controversial. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, L.-Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, F.-X.; Chen, L.-M.; Sun, F.; Jia, S.; Zhang, S.; et al. IL-24 Deficiency Protects Mice against Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis by Repressing IL-4-Induced M2 Program in Macrophages. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 1270–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.M.; Yang, X.S.; Luo, Q.; She, Y.X.; Yu, Q.Y.; Tang, X.X. Deleterious Role of Th9 Cells in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Cells 2021, 10, 3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, R.; Shapoori, S.; Rezaeepoor, M.; Sanaei, R.; Ganjalikhani-Hakemi, M.; Azizi, G.; Rae, W.; Aghamohammadi, A.; Rezaei, N. Features and Roles of T Helper 9 Cells and Interleukin 9 in Immunological Diseases. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2019, 47, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, L.; Zhao, C.; Qin, F.; He, Z.-Y.; Wang, X.; Zhong, X.-N. Th17 Cells and IL-17 Promote the Skin and Lung Inflammation and Fibrosis Process in a Bleomycin-Induced Murine Model of Systemic Sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2016, 34 (Suppl. 100), 14–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boveda-Ruiz, D.; D’Alessandro-Gabazza, C.N.; Toda, M.; Takagi, T.; Naito, M.; Matsushima, Y.; Matsumoto, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Gil-Bernabe, P.; Chelakkot-Govindalayathil, A.-L.; et al. Differential Role of Regulatory T Cells in Early and Late Stages of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Immunobiology 2013, 218, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galati, D.; De Martino, M.; Trotta, A.; Rea, G.; Bruzzese, D.; Cicchitto, G.; Stanziola, A.A.; Napolitano, M.; Sanduzzi, A.; Bocchino, M. Peripheral Depletion of NK Cells and Imbalance of the Treg/Th17 Axis in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Patients. Cytokine 2014, 66, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.W.; Herzog, E.L. Regulatory T Cells in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 1978–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, D.; Chow, A.; Noizat, C.; Teo, P.; Beasley, M.B.; Leboeuf, M.; Becker, C.D.; See, P.; Price, J.; Lucas, D.; et al. Tissue-Resident Macrophages Self-Maintain Locally throughout Adult Life with Minimal Contribution from Circulating Monocytes. Immunity 2013, 38, 792–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parimon, T.; Yao, C.; Stripp, B.R.; Noble, P.W.; Chen, P. Alveolar Epithelial Type II Cells as Drivers of Lung Fibrosis in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez-Galan, L.; Becerril, C.; Ruiz, A.; Ramon-Luing, L.A.; Cisneros, J.; Montaño, M.; Salgado, A.; Ramos, C.; Buendía-Roldán, I.; Pardo, A.; et al. Fibroblasts From Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Induce Apoptosis and Reduce the Migration Capacity of T Lymphocytes. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 820347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharat, A.; Bhorade, S.M.; Morales-Nebreda, L.; McQuattie-Pimentel, A.C.; Soberanes, S.; Ridge, K.; DeCamp, M.M.; Mestan, K.K.; Perlman, H.; Budinger, G.R.S.; et al. Flow Cytometry Reveals Similarities Between Lung Macrophages in Humans and Mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 54, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, Y.D.; Jeong, D.; Chung, D.H. Development and Functions of Alveolar Macrophages. Mol. Cells 2021, 44, 292–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allden, S.J.; Ogger, P.P.; Ghai, P.; McErlean, P.; Hewitt, R.; Toshner, R.; Walker, S.A.; Saunders, P.; Kingston, S.; Molyneaux, P.L.; et al. The Transferrin Receptor CD71 Delineates Functionally Distinct Airway Macrophage Subsets during Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuma, T.; Terasaki, Y.; Kaikita, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Kuziel, W.A.; Kawasuji, M.; Takeya, M. C-C Chemokine Receptor 2 (CCR2) Deficiency Improves Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis by Attenuation of Both Macrophage Infiltration and Production of Macrophage-Derived Matrix Metalloproteinases. J. Pathol. 2004, 204, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyfman, P.A.; Walter, J.M.; Joshi, N.; Anekalla, K.R.; McQuattie-Pimentel, A.C.; Chiu, S.; Fernandez, R.; Akbarpour, M.; Chen, C.-I.; Ren, Z.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis of Human Lung Provides Insights into the Pathobiology of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 1517–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Bossche, J.; Malissen, B.; Mantovani, A.; De Baetselier, P.; Van Ginderachter, J.A. Regulation and Function of the E-Cadherin/Catenin Complex in Cells of the Monocyte-Macrophage Lineage and DCs. Blood 2012, 119, 1623–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.M.; Chiu, S.F.; Misharin, A.V.; Ridge, K.M. Lung Interstitial Macrophages: Establishing Identity and Uncovering Heterogeneity. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 57, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isshiki, T.; Vierhout, M.; Naiel, S.; Ali, P.; Yazdanshenas, P.; Kumaran, V.; Yang, Z.; Dvorkin-Gheva, A.; Rullo, A.F.; Kolb, M.R.J.; et al. Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Pro-Fibrotic Macrophages in Interstitial Lung Disease. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2023, 211, 115501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morse, C.; Tabib, T.; Sembrat, J.; Buschur, K.; Bittar, H.T.; Valenzi, E.; Jiang, Y.; Kass, D.J.; Gibson, K.; Chen, W.; et al. Proliferating SPP1/MERTK-Expressing Macrophages in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1802441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbi, N.; Lambrecht, B.N. Location, Function, and Ontogeny of Pulmonary Macrophages during the Steady State. Pflug. Arch. 2017, 469, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S.; Plüddemann, A.; Martinez Estrada, F. Macrophage Heterogeneity in Tissues: Phenotypic Diversity and Functions. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 262, 36–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Biswas, S.K.; Galdiero, M.R.; Sica, A.; Locati, M. Macrophage Plasticity and Polarization in Tissue Repair and Remodelling. J. Pathol. 2013, 229, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Levin, M.; Kaplan, D.L. Bioelectric Modulation of Macrophage Polarization. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Filardi, E.; Vega, M.A.; Sánchez-Mateos, P.; Corbí, A.L.; Puig-Kröger, A. Heme Oxygenase-1 Expression in M-CSF-Polarized M2 Macrophages Contributes to LPS-Induced IL-10 Release. Immunobiology 2010, 215, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toshchakov, V.; Jones, B.W.; Lentschat, A.; Silva, A.; Perera, P.-Y.; Thomas, K.; Cody, M.J.; Zhang, S.; Williams, B.R.G.; Major, J.; et al. TLR2 and TLR4 Agonists Stimulate Unique Repertoires of Host Resistance Genes in Murine Macrophages: Interferon-Beta-Dependent Signaling in TLR4-Mediated Responses. J. Endotoxin. Res. 2003, 9, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunna, C.; Mengru, H.; Lei, W.; Weidong, C. Macrophage M1/M2 Polarization. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 877, 173090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechkovsky, D.V.; Prasse, A.; Kollert, F.; Engel, K.M.Y.; Dentler, J.; Luttmann, W.; Friedrich, K.; Müller-Quernheim, J.; Zissel, G. Alternatively Activated Alveolar Macrophages in Pulmonary Fibrosis-Mediator Production and Intracellular Signal Transduction. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 137, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronte, V.; Zanovello, P. Regulation of Immune Responses by L-Arginine Metabolism. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, M.G.; Guild, K.J.; Artis, D. Novel Effector Molecules in Type 2 Inflammation: Lessons Drawn from Helminth Infection and Allergy. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, T.A.; Barron, L.; Thompson, R.W.; Madala, S.K.; Wilson, M.S.; Cheever, A.W.; Ramalingam, T. Quantitative Assessment of Macrophage Functions in Repair and Fibrosis. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2011, 14, Unit14.22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Sica, A.; Sozzani, S.; Allavena, P.; Vecchi, A.; Locati, M. The Chemokine System in Diverse Forms of Macrophage Activation and Polarization. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapouri-Moghaddam, A.; Mohammadian, S.; Vazini, H.; Taghadosi, M.; Esmaeili, S.-A.; Mardani, F.; Seifi, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Afshari, J.T.; Sahebkar, A. Macrophage Plasticity, Polarization, and Function in Health and Disease. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 6425–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Ni, H.; Lan, L.; Wei, X.; Xiang, R.; Wang, Y. Fra-1 Protooncogene Regulates IL-6 Expression in Macrophages and Promotes the Generation of M2d Macrophages. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyken, S.J.; Locksley, R.M. Interleukin-4- and Interleukin-13-Mediated Alternatively Activated Macrophages: Roles in Homeostasis and Disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 317–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, T.A.; Vannella, K.M. Macrophages in Tissue Repair, Regeneration, and Fibrosis. Immunity 2016, 44, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonniaud, P.; Kolb, M.; Galt, T.; Robertson, J.; Robbins, C.; Stampfli, M.; Lavery, C.; Margetts, P.J.; Roberts, A.B.; Gauldie, J. Smad3 Null Mice Develop Airspace Enlargement and Are Resistant to TGF-Beta-Mediated Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 2099–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arizmendi, N.; Puttagunta, L.; Chung, K.L.; Davidson, C.; Rey-Parra, J.; Chao, D.V.; Thebaud, B.; Lacy, P.; Vliagoftis, H. Rac2 Is Involved in Bleomycin-Induced Lung Inflammation Leading to Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2014, 15, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, S.; Singh, A.R.; Wong, S.S.; Zulcic, M.; Jiang, M.; Pardo, A.; Selman, M.; Hagood, J.S.; Durden, D.L. Rac2 Is Required for Alternative Macrophage Activation and Bleomycin Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis; a Macrophage Autonomous Phenotype. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucero, A.C.; Bakiri, L.; Roediger, B.; Suzuki, M.; Jimenez, M.; Mandal, P.; Braghetta, P.; Bonaldo, P.; Paz-Ares, L.; Fustero-Torre, C.; et al. Fra-2–Expressing Macrophages Promote Lung Fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3293–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ohno, S.; Steer, B.; Klee, S.; Staab-Weijnitz, C.A.; Wagner, D.; Lehmann, M.; Stoeger, T.; Königshoff, M.; Adler, H. S100a4 Is Secreted by Alternatively Activated Alveolar Macrophages and Promotes Activation of Lung Fibroblasts in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Lu, Y.-T.; Chen, S.-Y.; Hsu, C.-F.; Lu, Y.-C.; Wang, C.-Y.; Huang, K.-L. Targeting Pathogenic Macrophages by the Application of SHP-1 Agonists Reduces Inflammation and Alleviates Pulmonary Fibrosis. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, J.; Han, Y.; Feng, D.; Yue, S.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, Z. Two-Pore-Domain Potassium Channel TREK–1 Mediates Pulmonary Fibrosis through Macrophage M2 Polarization and by Direct Promotion of Fibroblast Differentiation. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Deng, D.; Li, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhao, J.; Qian, Q.; Wang, W.; Cai, J.; Yu, W.; Liu, J. TREM2 Insufficiency Protects against Pulmonary Fibrosis by Inhibiting M2 Macrophage Polarization. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 118, 110070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Xian, H.; Nian-yu, Z.; Jia-cui, S.; Dong, W.; Hui-ping, L. C-Type Lectin Mincle Initiates IL-17-Mediated Inflammation in Acute Exacerbations of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 159, 114253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Rudrakshala, J.; Williams, R.; Rodriguez, S.; Sorkhdini, P.; Yang, A.X.; Mundy, M.; Yang, D.; Palmisciano, A.; Walsh, T.; et al. CRTH2 Mediates Profibrotic Macrophage Differentiation and Promotes Lung Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2022, 67, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wen, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.; Guan, J.; Xie, S.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; et al. DDR1 Activation in Macrophage Promotes IPF by Regulating NLRP3 Inflammasome and Macrophage Reaction. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 113, 109294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElTanbouly, M.A.; Zhao, Y.; Schaafsma, E.; Burns, C.M.; Mabaera, R.; Cheng, C.; Noelle, R.J. VISTA: A Target to Manage the Innate Cytokine Storm. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 595950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-H.; Adams, T.S.; Hu, Q.; Shin, H.J.; Chae, G.; Lee, S.E.; Sharma, L.; Kwon, H.-K.; Lee, F.Y.; Park, H.-J.; et al. VISTA (PD-1H) Is a Crucial Immune Regulator to Limit Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2022, 69, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kuai, Q.; Gao, F.; Wang, Y.; He, M.; Zhou, H.; Han, G.; Jiang, X.; Ren, S.; Yu, Q. Overexpression of TIM-3 in Macrophages Aggravates Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 61, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, D.; Roksandic Milenkovic, M.; Kotur Stevuljevic, J.; Markovic, J.; Ceriman, V.; Kontic, M.; Skodric Trifunovic, V. Membrane PD-L1 Expression and Soluble PD-L1 Plasma Levels in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis—A Pilot Study. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 6660–6669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Liu, Y.; Dai, H.; Wang, C. Fatty Acid Metabolism and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Physiol. 2022, 12, 794629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, D.A.; Lottes, R.G.; Ryan, R.M.; Spyropoulos, D.D.; Baatz, J.E. Dysfunctional Lactate Metabolism in Human Alveolar Type II Cells from Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Lung Explant Tissue. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamanaka, R.B.; Mutlu, G.M. Metabolic Requirements of Pulmonary Fibrosis: Role of Fibroblast Metabolism. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 6331–6352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahangari, F.; Price, N.L.; Malik, S.; Chioccioli, M.; Bärnthaler, T.; Adams, T.S.; Kim, J.; Pradeep, S.P.; Ding, S.; Cosmos, C.; et al. MicroRNA-33 Deficiency in Macrophages Enhances Autophagy, Improves Mitochondrial Homeostasis, and Protects against Lung Fibrosis. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e158100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, G.; Qiu, L.; Liu, X.; Zhou, S.; Wu, J. Contribution of Adiponectin/Carnitine Palmityl Transferase 1A-Mediated Fatty Acid Metabolism during the Development of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 5265616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Nie, Y.; Duan, S.; Zhang, T.; Wang, W.; Ye, R.D.; Hou, S.; Qian, F. Protein Kinase C δ (PKCδ) Attenuates Bleomycin Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis via Inhibiting NF-ΚB Signaling Pathway. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson-Casey, J.L.; Vaid, M.; Gu, L.; He, C.; Cai, G.-Q.; Ding, Q.; Davis, D.; Berryhill, T.F.; Wilson, L.S.; Barnes, S.; et al. Increased Flux through the Mevalonate Pathway Mediates Fibrotic Repair without Injury. J. Clin. Invest 2019, 129, 4962–4978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson-Casey, J.L.; Gu, L.; Davis, D.; Cai, G.-Q.; Ding, Q.; He, C.; Carter, A.B. Post-Translational Regulation of PGC-1α Modulates Fibrotic Repair. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogger, P.P.; Albers, G.J.; Hewitt, R.J.; O’Sullivan, B.J.; Powell, J.E.; Calamita, E.; Ghai, P.; Walker, S.A.; McErlean, P.; Saunders, P.; et al. Itaconate Controls the Severity of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabc1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannikou, M.; Barbayianni, I.; Fanidis, D.; Grigorakaki, T.; Vlachopoulou, E.; Konstantopoulos, D.; Fousteri, M.; Nikitopoulou, I.; Kotanidou, A.; Kaffe, E.; et al. MAP3K8 Regulates Cox-2–Mediated Prostaglandin E2 Production in the Lung and Suppresses Pulmonary Inflammation and Fibrosis. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitoura, E.; Vasarmidi, E.; Bibaki, E.; Trachalaki, A.; Koutoulaki, C.; Papastratigakis, G.; Papadogiorgaki, S.; Chalepakis, G.; Tzanakis, N.; Antoniou, K.M. Accumulation of Damaged Mitochondria in Alveolar Macrophages with Reduced OXPHOS Related Gene Expression in IPF. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaka, T.; Kido, T.; Noguchi, S.; Yamada, S.; Noguchi, H.; Guo, X.; Nawata, A.; Wang, K.-Y.; Oda, K.; Takaki, T.; et al. The Overexpression of Peroxiredoxin-4 Affects the Progression of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helou, D.G.; Martin, S.F.; Pallardy, M.; Chollet-Martin, S.; Kerdine-Römer, S. Nrf2 Involvement in Chemical-Induced Skin Innate Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Yang, L.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Q.; Ran, H.; Li, P.; Wang, Z. ROS-Responsive Liposomes as an Inhaled Drug Delivery Nanoplatform for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Treatment via Nrf2 Signaling. J. Nanobiotechnology 2022, 20, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Ye, L.; Du, F.; Ye, M.; Li, C.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, H.; Liu, Z.; Ma, J.; et al. Iron Metabolism Regulation of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.K.; Kim, R.Y.; Brown, A.C.; Donovan, C.; Vanka, K.S.; Mayall, J.R.; Liu, G.; Pillar, A.L.; Jones-Freeman, B.; Xenaki, D.; et al. Critical Role for Iron Accumulation in the Pathogenesis of Fibrotic Lung Disease. J. Pathol. 2020, 251, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Arisi, I.; Puxeddu, E.; Mramba, L.K.; Amicosante, M.; Swaisgood, C.M.; Pallante, M.; Brantly, M.L.; Sköld, C.M.; Saltini, C. Bronchoalveolar Lavage (BAL) Cells in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Express a Complex pro-Inflammatory, pro-Repair, Angiogenic Activation Pattern, Likely Associated with Macrophage Iron Accumulation. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmann, J.; Thompson, P.R. Protein Arginine Methylation and Citrullination in Epigenetic Regulation. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 654–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velagacherla, V.; Mehta, C.H.; Nayak, Y.; Nayak, U.Y. Molecular Pathways and Role of Epigenetics in the Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Life Sci. 2022, 291, 120283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Spek, C.A.; Scicluna, B.P.; van der Poll, T.; Duitman, J. Myeloid DNA Methyltransferase3b Deficiency Aggravates Pulmonary Fibrosis by Enhancing Profibrotic Macrophage Activation. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, G.-R.; Zhou, Q.; Yue, H.; Rao, L.-Z.; Yuan, T.; Mo, B.; Wang, F.-X.; Chen, L.-M.; et al. MBD2 Serves as a Viable Target against Pulmonary Fibrosis by Inhibiting Macrophage M2 Program. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabb6075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Y.; Wu, G.-R.; Wang, Q.; Pan, T.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Xiong, W.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Y. Macrophage-Targeted Delivery of SiRNA to Silence Mecp2 Gene Expression Attenuates Pulmonary Fibrosis. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2022, 7, e10280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskari, K.; Sabu, S.; Distler, O.; Neidhart, M.; Karouzakis, E. Pos0368 Citrullination Induces Epigenetic Memory of the Innate Immune System. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.J.; Surolia, R.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G.; Kulkarni, T.; Massicano, A.V.F.; Mobley, J.A.; Mondal, S.; de Andrade, J.A.; et al. Citrullinated Vimentin Mediates Development and Progression of Lung Fibrosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eaba2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McErlean, P.; Bell, C.G.; Hewitt, R.J.; Busharat, Z.; Ogger, P.P.; Ghai, P.; Albers, G.J.; Calamita, E.; Kingston, S.; Molyneaux, P.L.; et al. DNA Methylome Alterations Are Associated with Airway Macrophage Differentiation and Phenotype during Lung Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 204, 954–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutanquoi, P.-M.; Burgy, O.; Beltramo, G.; Bellaye, P.-S.; Dondaine, L.; Marcion, G.; Pommerolle, L.; Vadel, A.; Spanjaard, M.; Demidov, O.; et al. TRIM33 Prevents Pulmonary Fibrosis by Impairing TGF-Β1 Signalling. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1901346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Du, Y.; Li, G.; Xiao, P.; Sun, X.; Song, W.; Lai, L.; Xia, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q. Myeloid Fbxw7 Prevents Pulmonary Fibrosis by Suppressing TGF-β Production. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 760138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.J.; Hong, K.S.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, M.; Choi, A.M.K.; Stout-Delgado, H.W.; Moon, J.-S. DROSHA-Dependent AIM2 Inflammasome Activation Contributes to Lung Inflammation during Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Cells 2019, 8, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiot, J.; Cambier, M.; Boeckx, A.; Henket, M.; Nivelles, O.; Gester, F.; Louis, E.; Malaise, M.; Dequiedt, F.; Louis, R.; et al. Macrophage-Derived Exosomes Attenuate Fibrosis in Airway Epithelial Cells through Delivery of Antifibrotic MiR-142-3p. Thorax 2020, 75, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balli, D.; Ustiyan, V.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, I.-C.; Masino, A.J.; Ren, X.; Whitsett, J.A.; Kalinichenko, V.V.; Kalin, T.V. Foxm1 Transcription Factor Is Required for Lung Fibrosis and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penke, L.R.; Speth, J.M.; Dommeti, V.L.; White, E.S.; Bergin, I.L.; Peters-Golden, M. FOXM1 Is a Critical Driver of Lung Fibroblast Activation and Fibrogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2389–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goda, C.; Balli, D.; Black, M.; Milewski, D.; Le, T.; Ustiyan, V.; Ren, X.; Kalinichenko, V.V.; Kalin, T.V. Loss of FOXM1 in Macrophages Promotes Pulmonary Fibrosis by Activating P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1008692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birnhuber, A.; Biasin, V.; Schnoegl, D.; Marsh, L.M.; Kwapiszewska, G. Transcription Factor Fra-2 and Its Emerging Role in Matrix Deposition, Proliferation and Inflammation in Chronic Lung Diseases. Cell Signal. 2019, 64, 109408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eferl, R.; Hasselblatt, P.; Rath, M.; Popper, H.; Zenz, R.; Komnenovic, V.; Idarraga, M.-H.; Kenner, L.; Wagner, E.F. Development of Pulmonary Fibrosis through a Pathway Involving the Transcription Factor Fra-2/AP-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10525–10530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-M.; Cho, S.J.; Cho, W.-K.; Park, J.W.; Lee, J.-H.; Choi, A.M.; Rosas, I.O.; Zheng, M.; Peltz, G.; Lee, C.G.; et al. Laminin A1 Is a Genetic Modifier of TGF-Β1–Stimulated Pulmonary Fibrosis. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e99574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Xiao, Y.; Tian, X.; Lu, Y.; Chu, H. Selective Depletion of CD11b-Positive Monocytes/Macrophages Potently Suppresses Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 114, 109570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deletion of C-FLIP from CD11bhi Macrophages Prevents Development of Bleomycin-Induced Lung Fibrosis-PMC. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5941310/ (accessed on 18 May 2023).
- Nouno, T.; Okamoto, M.; Ohnishi, K.; Kaieda, S.; Tominaga, M.; Zaizen, Y.; Ichiki, M.; Momosaki, S.; Nakamura, M.; Fujimoto, K.; et al. Elevation of Pulmonary CD163+ and CD204+ Macrophages Is Associated with the Clinical Course of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Patients. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 4005–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bao, J.; Bian, Y.; Erben, U.; Wang, P.; Song, K.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Gao, Z.; Qin, Z. S100A4+ Macrophages Are Necessary for Pulmonary Fibrosis by Activating Lung Fibroblasts. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, N.; Suzukawa, M.; Nagase, H.; Koizumi, Y.; Ro, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Yoshihara, H.; Kojima, Y.; Kamiyama-Hara, A.; Hebisawa, A.; et al. IL-9 Blockade Suppresses Silica-Induced Lung Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 60, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortekaas, R.K.; Geillinger-Kästle, K.E.; Borghuis, T.; Belharch, K.; Webster, M.; Timens, W.; Burgess, J.K.; Gosens, R. Interleukin-11 Disrupts Alveolar Epithelial Progenitor Function. ERJ Open Res. 2023, 9, 00679–02022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Baek, A.R.; Lee, J.H.; Jang, A.S.; Kim, D.J.; Chin, S.S.; Park, S.W. IL-37 Attenuates Lung Fibrosis by Inducing Autophagy and Regulating TGF-Β1 Production in Mice. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 2265–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.-R.; Liu, S.-S.; Min, J.-L.; Yin, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.-N.; Li, X.; Liu, S.-S. CCL17 Drives Fibroblast Activation in the Progression of Pulmonary Fibrosis by Enhancing the TGF-β/Smad Signaling. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2023, 210, 115475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Innate Immune Cells | Role in IPF | References |
|---|---|---|
| Neutrophils | Neutrophil elastase (NE) promotes fibrosis and tissue remodeling. Forced vital capacity values and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) neutrophil counts have an inverse relationship. Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) are found to be associated with fibrosis. | [15,16,17,18,19,20] |
| Macrophages | Pro-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic properties associated with M1 macrophages. Anti-inflammatory, pro-fibrotic, and tissue-regenerating properties are associated with M2 macrophages. | [14,21,22,23,24] |
| Monocytes | Progenitor cells for pro-fibrotic macrophages and fibrocytes. Release (pro-fibrotic) inflammatory cytokines. Increased monocyte count is correlated with poorer survival. | [10,25,26,27] |
| Fibrocytes | Fibrocytes contribute to fibroblast-mediated tissue remodeling. | [27,28] |
| Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) | Increased MDSC numbers are associated with poor lung functions, severe pulmonary hypertension, and increased regulatory T cells. Involved in pro-fibrotic and immune-dysregulated environments. | [26,27,29] |
| Type-2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) | Increased ILC2 count in IPF patients’ BAL associated with an enhanced type-2 immune environment. ILC2s potentiate ECM synthesis and tissue remodeling via IL-13 production. | [27,30,31,32] |
| Dendritic cells (DCs) | Immature DCs accumulate in regions of epithelial hyperplasia and fibrotic lesions. Mature DCs are concentrated in lymphoid follicles along with T and B cells in IPF patients. Possibly involved in ongoing inflammation in IPF lungs. | [10,33,34] |
| Adaptive Immune Cells | ||
| B cells | Increased number of IgA+ memory B cells and plasmablasts in the blood and lungs of IPF patients. High levels of B cell activation factor (BAFF) and CXCL13 in the serum of IPF patients. CpG and β-glucan stimulation of B cells promotes inflammatory and fibrotic changes in IPF patients. | [35,36,37,38] |
| Th1 cells | Attenuate fibrosis via the production of IFN-γ. | [26,38,39] |
| Th2 cells | Dominant in IPF and antagonizes Th1 cells. Enhance fibrosis through the production of type 2 cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13. IL-4 and IL-13 stimulate (myo) fibroblast activation and proliferation while predisposing macrophages to a pro-fibrotic phenotype. | [26,38,39,40] |
| Th9 cells | Unclear role in IPF etiology contradictory effects of Th9 cells and IL-9 have been observed in the development of fibrosis. | [10,41,42] |
| Th17 cells | Pro-fibrotic function via the production of IL-17, which stimulates fibroblast proliferation and collagen secretion. | [17,38,39,41,43] |
| Regulatory T cells (Tregs) | Tregs have opposing roles in the progression of IPF. Promotion or inhibition depends on the disease stage. | [38,44,45,46] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pokhreal, D.; Crestani, B.; Helou, D.G. Macrophage Implication in IPF: Updates on Immune, Epigenetic, and Metabolic Pathways. Cells 2023, 12, 2193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12172193
Pokhreal D, Crestani B, Helou DG. Macrophage Implication in IPF: Updates on Immune, Epigenetic, and Metabolic Pathways. Cells. 2023; 12(17):2193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12172193
Chicago/Turabian StylePokhreal, Deepak, Bruno Crestani, and Doumet Georges Helou. 2023. "Macrophage Implication in IPF: Updates on Immune, Epigenetic, and Metabolic Pathways" Cells 12, no. 17: 2193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12172193
APA StylePokhreal, D., Crestani, B., & Helou, D. G. (2023). Macrophage Implication in IPF: Updates on Immune, Epigenetic, and Metabolic Pathways. Cells, 12(17), 2193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12172193






