c-Cbl Regulates Murine Subventricular Zone-Derived Neural Progenitor Cells in Dependence of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Mouse Lines
2.2.1. c-Cblfl/fl;Cbl-bKO;Cbl-3KO;Ascl1-CreERT2
2.2.2. c-Cblfl/fl;Cbl-bKO;Cbl-3KO;GLAST-CreERT2
2.3. Mouse Treatments
2.4. Tissue Preparation
2.5. Immunofluorescence (IF) Staining
2.6. Immunoperoxidase (IP) Staining
2.7. RNAscope
2.8. Flow Cytometry
2.9. RNA Extraction
2.10. Quantitative Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.11. Neurosphere Assays
2.12. Statistical Analysis of Anatomical and Biological Data
3. Results
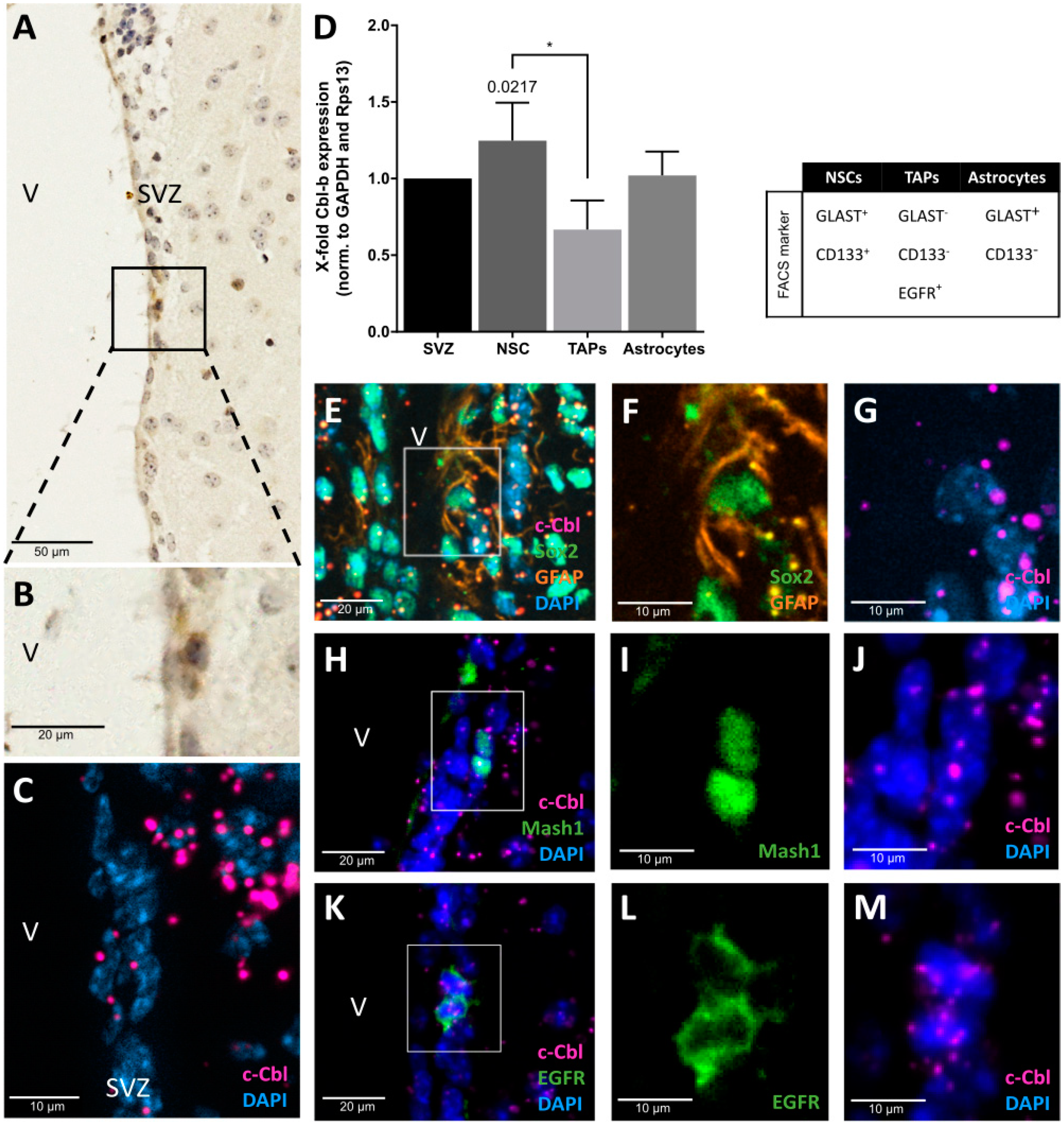
3.1. c-Cbl Is Localized in the SVZ and Expressed in NSCs and TAPs
3.2. c-Cbl Knock-Out in TAPs Increased Proliferation In Vitro
3.3. The Loss of c-Cbl in NSCs and TAPs Does Not Affect the Proliferation and Formation of Adult-Born Neurons in the SVZ In Vivo
3.4. c-Cbl Does Not Directly Affect Adult Neurogenesis in Hippocampal NSCs and TAPs
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, S.H.; Tanzi, R.E. Is Alzheimer’s Disease a Neurogenesis Disorder? Cell Stem Cell 2019, 25, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toda, T.; Parylak, S.L.; Linker, S.B.; Gage, F.H. The role of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in brain health and disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurkowski, M.P.; Bettio, L.; Woo, E.K.; Patten, A.; Yau, S.Y.; Gil-Mohapel, J. Beyond the Hippocampus and the SVZ: Adult Neurogenesis Throughout the Brain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 576444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.A.; Amruta, N.; Pinteaux, E.; Bix, G.J. Neurogenesis After Stroke: A Therapeutic Perspective. Transl. Stroke Res. 2021, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, M.; Demarais, N.J.; Faull, R.L.M.; Grey, A.C.; Curtis, M.A. Subventricular zone lipidomic architecture loss in Huntington’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2018, 146, 613–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Garrote, M.; Parga, J.A.; Labandeira, P.J.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L.; Rodriguez-Pallares, J. Dopamine regulates adult neurogenesis in the ventricular-subventricular zone via dopamine D3 angiotensin type 2 receptor interactions. Stem Cells 2021, 39, 1778–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenkoyan, K.; Margaryan, T.; Matinyan, S.; Chavushyan, V.; Danielyan, M.; Davtyan, T.; Aghajanov, M. Effects of beta-amyloid (1-42) Administration on the Main Neurogenic Niches of the Adult Brain: Amyloid-Induced Neurodegeneration Influences Neurogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, C.; Keller, S.; Schmidt, M.H.H. The Role of SVZ Stem Cells in Glioblastoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haughey, N.J.; Liu, D.; Nath, A.; Borchard, A.C.; Mattson, M.P. Disruption of neurogenesis in the subventricular zone of adult mice, and in human cortical neuronal precursor cells in culture, by amyloid beta-peptide: Implications for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuromolecular Med. 2002, 1, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Shin, S.M.; Kim, S.; Nam, Y.; Yoo, A.; Moon, M. Relationship between adult subventricular neurogenesis and Alzheimer’s disease: Pathologic roles and therapeutic implications. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 1002281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minger, S.L.; Ekonomou, A.; Carta, E.M.; Chinoy, A.; Perry, R.H.; Ballard, C.G. Endogenous neurogenesis in the human brain following cerebral infarction. Regen. Med. 2007, 2, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, Y.; Sawada, M.; Huang, S.H.; Ogino, T.; Ohata, S.; Kubo, A.; Sawamoto, K. Roles of Wnt Signaling in the Neurogenic Niche of the Adult Mouse Ventricular-Subventricular Zone. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyfeler, Y.; Kirch, R.D.; Mantei, N.; Leone, D.P.; Radtke, F.; Suter, U.; Taylor, V. Jagged1 signals in the postnatal subventricular zone are required for neural stem cell self-renewal. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 3504–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, R.; Bucci, C. Role of EGFR in the Nervous System. Cells 2020, 9, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Agoston, D.V. Vascular endothelial growth factor is involved in mediating increased de novo hippocampal neurogenesis in response to traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, F.; Tian, M.; Xu, Z.; Liang, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Tang, K.; He, M.; et al. Transcription factors COUP-TFI and COUP-TFII are required for the production of granule cells in the mouse olfactory bulb. Development 2015, 142, 1593–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, J.; Spits, M.; Neefjes, J.; Berlin, I. The EGFR odyssey—From activation to destruction in space and time. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 4087–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigismund, S.; Argenzio, E.; Tosoni, D.; Cavallaro, E.; Polo, S.; Di Fiore, P.P. Clathrin-mediated internalization is essential for sustained EGFR signaling but dispensable for degradation. Dev. Cell 2008, 15, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlandsson, A.; Enarsson, M.; Forsberg-Nilsson, K. Immature neurons from CNS stem cells proliferate in response to platelet-derived growth factor. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 3483–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigismund, S.; Algisi, V.; Nappo, G.; Conte, A.; Pascolutti, R.; Cuomo, A.; Bonaldi, T.; Argenzio, E.; Verhoef, L.G.; Maspero, E.; et al. Threshold-controlled ubiquitination of the EGFR directs receptor fate. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 2140–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.H.H.; Dikic, I. The Cbl interactome and its functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Tsygankov, A.Y. c-Cbl regulates glioma invasion through matrix metalloproteinase 2. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 111, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seong, M.W.; Park, J.H.; Yoo, H.M.; Yang, S.W.; Oh, K.H.; Ka, S.H.; Park, D.E.; Lee, S.T.; Chung, C.H. c-Cbl regulates alphaPix-mediated cell migration and invasion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 455, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehn, B.M.; Dittert, I.; Beyer, S.; von der Mark, K.; Bielke, W. c-Cbl binding and ubiquitin-dependent lysosomal degradation of membrane-associated Notch1. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 8033–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, Z.; Yu, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Sun, C.; Zhao, C.; et al. miR-22-3p enhances the intrinsic regenerative abilities of primary sensory neurons via the CBL/p-EGFR/p-STAT3/GAP43/p-GAP43 axis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 4605–4617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naramura, M.; Jang, I.K.; Kole, H.; Huang, F.; Haines, D.; Gu, H. c-Cbl and Cbl-b regulate T cell responsiveness by promoting ligand-induced TCR down-modulation. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.J.; Kole, H.K.; Brown, K.; Naramura, M.; Fukuhara, S.; Hu, R.J.; Jang, I.K.; Gutkind, J.S.; Shevach, E.; Gu, H. Cbl-b regulates the CD28 dependence of T-cell activation. Nature 2000, 403, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, E.K.; Sanchez, O.; Mill, P.; Krawczyk, C.; Hojilla, C.V.; Rubin, E.; Nau, M.M.; Khokha, R.; Lipkowitz, S.; Hui, C.C.; et al. Cbl-3-deficient mice exhibit normal epithelial development. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 7708–7718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Ables, J.L.; Dickel, L.K.; Eisch, A.J.; Johnson, J.E. Ascl1 (Mash1) defines cells with long-term neurogenic potential in subgranular and subventricular zones in adult mouse brain. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Tanaka, K.; Buffo, A.; Wurst, W.; Kuhn, R.; Gotz, M. Inducible gene deletion in astroglia and radial glia—A valuable tool for functional and lineage analysis. Glia 2006, 54, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Flanagan, J.; Su, N.; Wang, L.C.; Bui, S.; Nielson, A.; Wu, X.; Vo, H.T.; Ma, X.J.; Luo, Y. RNAscope: A novel in situ RNA analysis platform for formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. J. Mol. Diagn. 2012, 14, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llorens-Bobadilla, E.; Zhao, S.; Baser, A.; Saiz-Castro, G.; Zwadlo, K.; Martin-Villalba, A. Single-Cell Transcriptomics Reveals a Population of Dormant Neural Stem Cells that Become Activated upon Brain Injury. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 17, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, T.L.; Kempermann, G. One mouse, two cultures: Isolation and culture of adult neural stem cells from the two neurogenic zones of individual mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, e51225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankhead, P.; Loughrey, M.B.; Fernandez, J.A.; Dombrowski, Y.; McArt, D.G.; Dunne, P.D.; McQuaid, S.; Gray, R.T.; Murray, L.J.; Coleman, H.G.; et al. QuPath: Open source software for digital pathology image analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaker, Z.; Codega, P.; Doetsch, F. A mosaic world: Puzzles revealed by adult neural stem cell heterogeneity. Wiley Interdiscip Rev. Dev. Biol. 2016, 5, 640–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doetsch, F.; Caille, I.; Lim, D.A.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Subventricular zone astrocytes are neural stem cells in the adult mammalian brain. Cell 1999, 97, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlen, M.; Karlsson, M.J.; Hober, A.; Svensson, A.S.; Scheffel, J.; Kotol, D.; Zhong, W.; Tebani, A.; Strandberg, L.; Edfors, F.; et al. The human secretome. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, eaaz0274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codega, P.; Silva-Vargas, V.; Paul, A.; Maldonado-Soto, A.R.; Deleo, A.M.; Pastrana, E.; Doetsch, F. Prospective identification and purification of quiescent adult neural stem cells from their in vivo niche. Neuron 2014, 82, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques-Torrejon, M.A.; Porlan, E.; Banito, A.; Gomez-Ibarlucea, E.; Lopez-Contreras, A.J.; Fernandez-Capetillo, O.; Vidal, A.; Gil, J.; Torres, J.; Farinas, I. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 controls adult neural stem cell expansion by regulating Sox2 gene expression. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 12, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastrana, E.; Cheng, L.C.; Doetsch, F. Simultaneous prospective purification of adult subventricular zone neural stem cells and their progeny. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6387–6392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doetsch, F. The glial identity of neural stem cells. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathinam, C.; Thien, C.B.; Langdon, W.Y.; Gu, H.; Flavell, R.A. The E3 ubiquitin ligase c-Cbl restricts development and functions of hematopoietic stem cells. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 992–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crotchett, B.L.M.; Ceresa, B.P. Knockout of c-Cbl slows EGFR endocytic trafficking and enhances EGFR signaling despite incompletely blocking receptor ubiquitylation. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2021, 9, e00756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, B.; Zutshi, N.; An, W.; Goetz, B.; Arya, P.; Bielecki, T.A.; Mushtaq, I.; Storck, M.D.; Meza, J.L.; Band, V.; et al. An essential role of CBL and CBL-B ubiquitin ligases in mammary stem cell maintenance. Development 2017, 144, 1072–1086, Erratum in Development 2018, 145, dev172650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Kim, W.; Kim, L.K.; VanHouten, J.; Wysolmerski, J.J. HER2 signaling regulates HER2 localization and membrane retention. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, H.G.; Winkler, J.; Kempermann, G.; Thal, L.J.; Gage, F.H. Epidermal growth factor and fibroblast growth factor-2 have different effects on neural progenitors in the adult rat brain. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 5820–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakura, Y.; Nawa, H. ErbB1-4-dependent EGF/neuregulin signals and their cross talk in the central nervous system: Pathological implications in schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaborit, N.; Lindzen, M.; Yarden, Y. Emerging anti-cancer antibodies and combination therapies targeting HER3/ERBB3. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2016, 12, 576–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, S.M.; Sleumer, L.S.; Damen, E.; Meijer, I.M.; van Zoelen, E.J.; van Leeuwen, J.E. ErbB2 and ErbB4 Cbl binding sites can functionally replace the ErbB1 Cbl binding site. Cell. Signal. 2009, 21, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiuchi, T.; Ortiz-Zapater, E.; Monypenny, J.; Matthews, D.R.; Nguyen, L.K.; Barbeau, J.; Coban, O.; Lawler, K.; Burford, B.; Rolfe, D.J.; et al. The ErbB4 CYT2 variant protects EGFR from ligand-induced degradation to enhance cancer cell motility. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, ra78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rorsman, C.; Tsioumpekou, M.; Heldin, C.H.; Lennartsson, J. The Ubiquitin Ligases c-Cbl and Cbl-b Negatively Regulate Platelet-derived Growth Factor (PDGF) BB-induced Chemotaxis by Affecting PDGF Receptor beta (PDGFRbeta) Internalization and Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 11608–11618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funa, K.; Sasahara, M. The roles of PDGF in development and during neurogenesis in the normal and diseased nervous system. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014, 9, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimaschewski, L.; Claus, P. Fibroblast Growth Factor Signalling in the Diseased Nervous System. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 3884–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Langdon, W.Y.; Zhang, J. Negative regulation of receptor tyrosine kinases by ubiquitination: Key roles of the Cbl family of E3 ubiquitin ligases. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 971162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudo, G.; Bonomo, A.; Di Liberto, V.; Frinchi, M.; Fuxe, K.; Belluardo, N. The FGF-2/FGFRs neurotrophic system promotes neurogenesis in the adult brain. J. Neural Transm. 2009, 116, 995–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronska-Peski, M.; Goncalves, J.T.; Hebert, J.M. Enriched Environment Promotes Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis through FGFRs. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 2899–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Epitope | Species | Dilution | Company | Catalogue Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BrdU | Sheep | 1:400 | Biozol | GTX21893 |
| GFAP | Rabbit | 1:400 | DAKO | Z0334 |
| Ki-67 | Rat | 1:100 | Thermo Scientific | SolA15 |
| Mash1 | Rabbit | 1:200 | Abcam | ab211327 |
| Nestin | Mouse | 1:100 | Milipore | MAB353 |
| NeuN | Mouse | 1:100 | Milipore | MAB377 |
| c-Cbl | Rabbit | 1:200 | Invitrogen | PA5-82992 |
| Gene | PubMed (NM) | Forward (5′–3′) | Reverse (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rps 13 | NM_026533.3 | ttcaccgattggctcgatac | ttatgccactagagcagagg |
| Gapdh | NM_001289726.1 | tgaagcaggcatctgaggg | cgaaggtggaagagtgggag |
| c-Cbl | qMmuCID0023539, Bio-rad | ||
| Cbl-b | qMmuCID0023240, Biorad | ||
| Clb-3 | qMmuCED0039838, Bio-rad | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vogt, M.; Unnikrishnan, M.K.; Heinig, N.; Schumann, U.; Schmidt, M.H.H.; Barth, K. c-Cbl Regulates Murine Subventricular Zone-Derived Neural Progenitor Cells in Dependence of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. Cells 2023, 12, 2400. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12192400
Vogt M, Unnikrishnan MK, Heinig N, Schumann U, Schmidt MHH, Barth K. c-Cbl Regulates Murine Subventricular Zone-Derived Neural Progenitor Cells in Dependence of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. Cells. 2023; 12(19):2400. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12192400
Chicago/Turabian StyleVogt, Maximilian, Madhukrishna Kolothara Unnikrishnan, Nora Heinig, Ulrike Schumann, Mirko H. H. Schmidt, and Kathrin Barth. 2023. "c-Cbl Regulates Murine Subventricular Zone-Derived Neural Progenitor Cells in Dependence of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor" Cells 12, no. 19: 2400. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12192400
APA StyleVogt, M., Unnikrishnan, M. K., Heinig, N., Schumann, U., Schmidt, M. H. H., & Barth, K. (2023). c-Cbl Regulates Murine Subventricular Zone-Derived Neural Progenitor Cells in Dependence of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. Cells, 12(19), 2400. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12192400







