Mechanistic Insights into Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Therapies Targeting Pathophysiological Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
Literature Search
2. Pathogenesis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)
2.1. Genetic and Environmental Factors and Autoimmunity
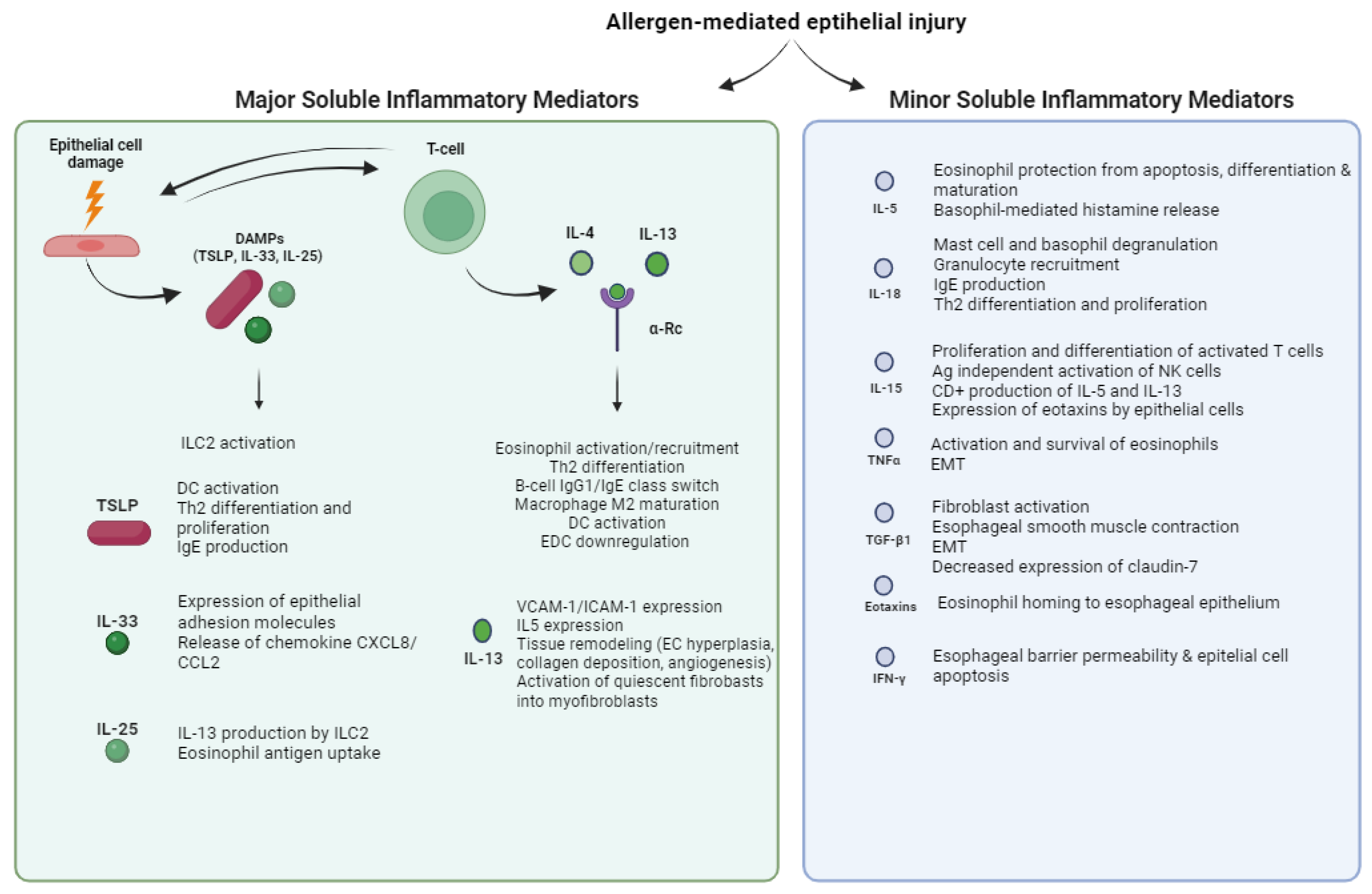
2.2. Soluble Inflammatory Mediators of EoE
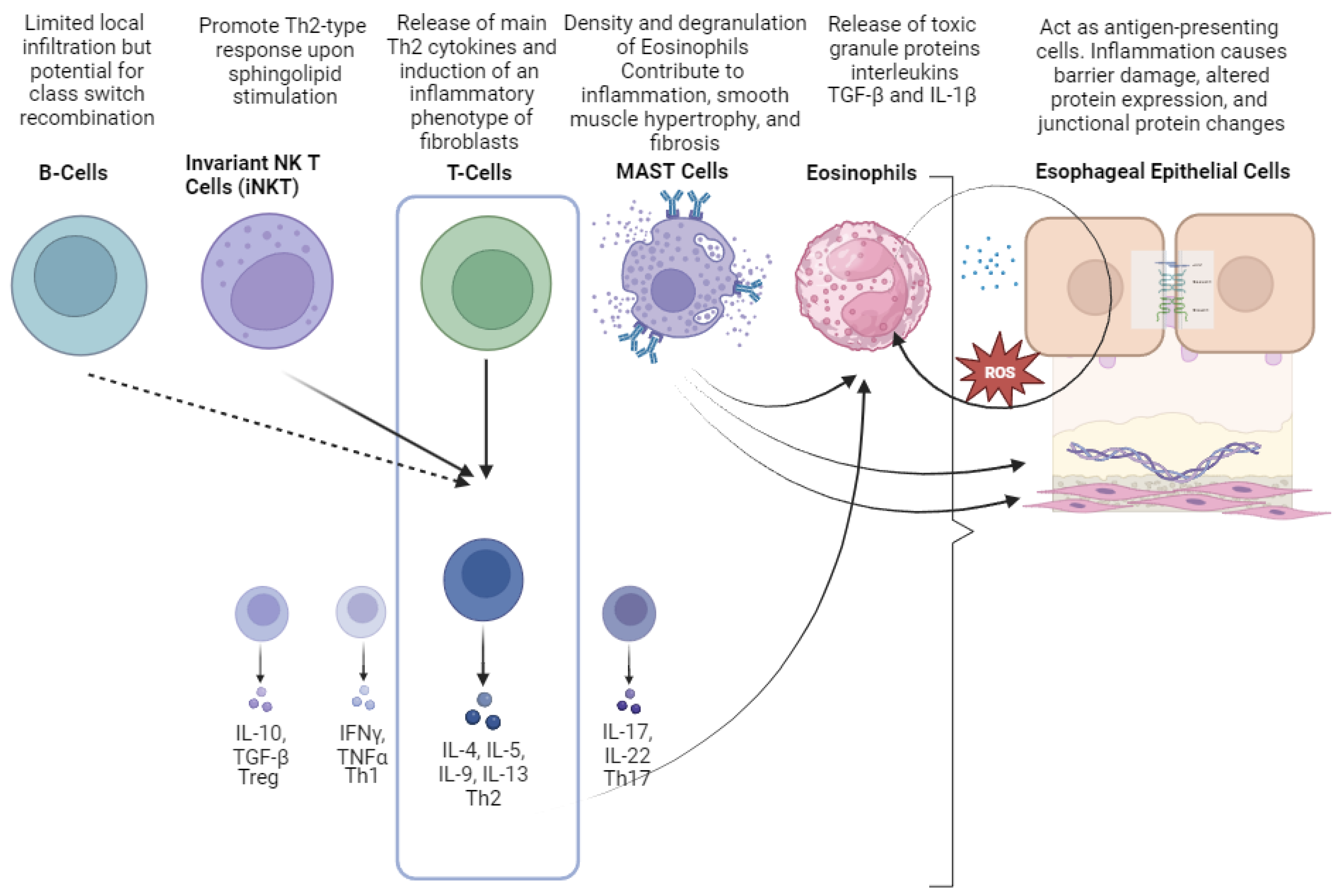
2.3. Cellular Mediators of EoE
3. Therapies Targeting Pathophysiological Mechanisms
3.1. Avoid Luminal Triggers
3.2. Targeting Epithelial Barrier
3.3. Targeting Soluble Mediators
3.3.1. Corticosteroids
3.3.2. Drugs Targeting Interleukin (IL)-4/IL-13
3.3.3. Drugs Targeting Other Interleukins (IL-5 and IL-15)
3.3.4. Drugs Targeting TGF-β and Prostaglandin Pathways
3.3.5. Drugs Targeting the IgE Pathway
3.3.6. Drugs Targeting Sphingosine-1-Phosphate (S1P), Integrin Pathways, and Sialic-Acid-Binding Ig-Like Lectins (Siglecs)
3.3.7. Drugs Targeting JAK-STAT6 Pathway
3.4. Targeting Cellular Mediators
3.4.1. Drugs Targeting Eosinophils
3.4.2. Drugs Targeting T Cells
3.4.3. Drugs Targeting Mast Cells
3.4.4. Immunotherapy for Environmental Allergens
4. Future Perspectives in EoE Targeted Therapy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muir, A.; Falk, G.W. Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Review. JAMA 2021, 326, 1310–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellon, E.S.; Hirano, I. Epidemiology and Natural History of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 319–332.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinowitz, S.S.; Yu, L.; Geraghty, P. EoE Behaves as a Unique Th2 Disease: A Narrative Review. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuta, G.T.; Katzka, D.A. Eosinophilic Esophagitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rank, M.A.; Sharaf, R.N.; Furuta, G.T.; Aceves, S.S.; Greenhawt, M.; Spergel, J.M.; Falck-Ytter, Y.T.; Dellon, E.S.; AGA Institute; Joint Task Force on Allergy-Immunology Practice Parameters Collaborators; et al. Technical Review on the Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Report from the AGA Institute and the Joint Task Force on Allergy-Immunology Practice Parameters. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1789–1810.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Infante, J.; Mata-Romero, P.; Martín-Holgado, D. New Approaches to Diet Therapy for Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2023, 39, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratacós Gómez, A.R.; Gómez Torrijos, E. Eosinophilic Esophagitis Due to Aeroallergens: A Systematic Review and Update. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 32, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, E.S.; Kim, H.P.; Sperry, S.L.W.; Rybnicek, D.A.; Woosley, J.T.; Shaheen, N.J. A Phenotypic Analysis Shows That Eosinophilic Esophagitis Is a Progressive Fibrostenotic Disease. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2014, 79, 577–585.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, K.M.; Aceves, S.S.; Dellon, E.S.; Gupta, S.K.; Spergel, J.M.; Furuta, G.T.; Rothenberg, M.E. Pathophysiology of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Santander, C.; Savarino, E.; Guagnozzi, D.; Pérez-Martínez, I.; Perelló, A.; Guardiola-Arévalo, A.; Barrio, J.; Elena Betoré-Glaria, M.; Gutiérrez-Junquera, C.; et al. EoE CONNECT, the European Registry of Clinical, Environmental, and Genetic Determinants in Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Rationale, Design, and Study Protocol of a Large-Scale Epidemiological Study in Europe. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2022, 15, 17562848221074204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Molina-Infante, J. Dietary Therapy for Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Chances and Limitations in the Clinical Practice. Expert. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 14, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biedermann, L.; Straumann, A. Mechanisms and Clinical Management of Eosinophilic Oesophagitis: An Overview. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumann, A.; Katzka, D.A. Diagnosis and Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, A.; Haboubi, H.N.; Attwood, S.E.; Auth, M.K.H.; Dunn, J.M.; Sweis, R.; Morris, D.; Epstein, J.; Novelli, M.R.; Hunter, H.; et al. British Society of Gastroenterology (BSG) and British Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (BSPGHAN) Joint Consensus Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Management of Eosinophilic Oesophagitis in Children and Adults. Gut 2022, 71, 1459–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franciosi, J.P.; Gordon, M.; Sinopoulou, V.; Dellon, E.S.; Gupta, S.K.; Reed, C.C.; Gutiérrez-Junquera, C.; Venkatesh, R.D.; Erwin, E.A.; Egiz, A.; et al. Medical Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 7, CD004065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franciosi, J.P.; Mougey, E.B.; Dellon, E.S.; Gutierrez-Junquera, C.; Fernandez-Fernandez, S.; Venkatesh, R.D.; Gupta, S.K. Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy for Eosinophilic Esophagitis: History, Mechanisms, Efficacy, and Future Directions. J. Asthma Allergy 2022, 15, 281–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottyan, L.C.; Parameswaran, S.; Weirauch, M.T.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Martin, L.J. The Genetic Etiology of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, E.S.; Martin, L.J.; Collins, M.H.; Kottyan, L.C.; Sucharew, H.; He, H.; Mukkada, V.A.; Succop, P.A.; Abonia, J.P.; Foote, H.; et al. Twin and Family Studies Reveal Strong Environmental and Weaker Genetic Cues Explaining Heritability of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 1084–1092.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenberg, M.E.; Spergel, J.M.; Sherrill, J.D.; Annaiah, K.; Martin, L.J.; Cianferoni, A.; Gober, L.; Kim, C.; Glessner, J.; Frackelton, E.; et al. Common Variants at 5q22 Associate with Pediatric Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleiman, P.M.A.; Wang, M.-L.; Cianferoni, A.; Aceves, S.; Gonsalves, N.; Nadeau, K.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Furuta, G.T.; Spergel, J.M.; Hakonarson, H. GWAS Identifies Four Novel Eosinophilic Esophagitis Loci. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrill, J.D.; Rothenberg, M.E. Genetic and Epigenetic Underpinnings of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterol. Clin. North. Am. 2014, 43, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, E.T.; Kuhl, J.T.; Martin, L.J.; Langefeld, C.D.; Dellon, E.S.; Rothenberg, M.E. Early-Life Environmental Exposures Interact with Genetic Susceptibility Variants in Pediatric Patients with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 632–637.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biedermann, L.; Straumann, A.; Greuter, T.; Schreiner, P. Eosinophilic Esophagitis-Established Facts and New Horizons. Semin. Immunopathol. 2021, 43, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massimino, L.; Barchi, A.; Mandarino, F.V.; Spanò, S.; Lamparelli, L.A.; Vespa, E.; Passaretti, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Savarino, E.V.; Jairath, V.; et al. A Multi-Omic Analysis Reveals the Esophageal Dysbiosis as the Predominant Trait of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angerami Almeida, K.; de Queiroz Andrade, E.; Burns, G.; Hoedt, E.C.; Mattes, J.; Keely, S.; Collison, A. The Microbiota in Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Systematic Review. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 37, 1673–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, A.J.; Hoffmann, C.; Muir, A.B.; Dods, K.K.; Spergel, J.M.; Bushman, F.D.; Wang, M.-L. Inflammation-Associated Microbiota in Pediatric Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Microbiome 2015, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.K.; Fang, R.; Wagner, B.D.; Choe, H.N.; Kelly, C.J.; Schroeder, S.; Moore, W.; Stevens, M.J.; Yeckes, A.; Amsden, K.; et al. Esophageal Microbiome in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laserna-Mendieta, E.J.; FitzGerald, J.A.; Arias-Gonzalez, L.; Ollala, J.M.; Bernardo, D.; Claesson, M.J.; Lucendo, A.J. Esophageal Microbiome in Active Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Changes Induced by Different Therapies. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, G.T.; Fillon, S.A.; Williamson, K.M.; Robertson, C.E.; Stevens, M.J.; Aceves, S.S.; Arva, N.C.; Chehade, M.; Collins, M.H.; Davis, C.M.; et al. Mucosal Microbiota Associated with Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Eosinophilic Gastritis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2023, 76, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Z. Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Esophageal Microbiota. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1206343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, Á.; Lucendo, A.J. Molecular Basis and Cellular Mechanisms of Eosinophilic Esophagitis for the Clinical Practice. Expert. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 13, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpathiou, G.; Papoudou-Bai, A.; Ferrand, E.; Dumollard, J.M.; Peoc’h, M. STAT6: A Review of a Signaling Pathway Implicated in Various Diseases with a Special Emphasis in Its Usefulness in Pathology. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2021, 223, 153477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Z.; Miller, T.L.; Abramson, L.; Thakkar, K.P.; Ketchem, C.J.; Reddy, S.; Greenberg, S.B.; Abichandani, S.; Chang, N.C.; Eluri, S.; et al. Association of Eosinophilic Esophagitis with Autoimmune and Connective Tissue Disorders, and the Impact on Treatment Response. Dis. Esophagus 2022, 36, doac043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellon, E.S.; Lin, L.; Beitia, R.; Moran, T.P.; Qian, Y. Serum Autoantibodies against Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecules as Disease Biomarkers of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodoun, M.V.; Tomar, S.; Tocker, J.E.; Wang, Y.H.; Finkelman, F.D. Prevention of Food Allergy Development and Suppression of Established Food Allergy by Neutralization of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin, IL-25, and IL-33. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 171–179.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-J. TSLP in Epithelial Cell and Dendritic Cell Cross Talk. Adv. Immunol. 2009, 101, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noti, M.; Wojno, E.D.T.; Kim, B.S.; Siracusa, M.C.; Giacomin, P.R.; Nair, M.G.; Benitez, A.J.; Ruymann, K.R.; Muir, A.B.; Hill, D.A.; et al. Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin-Elicited Basophil Responses Promote Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrill, J.D.; Gao, P.-S.; Stucke, E.M.; Blanchard, C.; Collins, M.H.; Putnam, P.E.; Franciosi, J.P.; Kushner, J.P.; Abonia, J.P.; Assa’ad, A.H.; et al. Variants of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin and Its Receptor Associate with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 160–165.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, S.F. The Role of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin (TSLP) in Allergic Disorders. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2010, 22, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omori, M.; Ziegler, S. Induction of IL-4 Expression in CD4(+) T Cells by Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, F.; Ruera, C.N.; Miculan, E.; Carasi, P.; Dubois-Camacho, K.; Garbi, L.; Guzman, L.; Hermoso, M.A.; Chirdo, F.G. IL-33 Alarmin and Its Active Proinflammatory Fragments Are Released in Small Intestine in Celiac Disease. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 581445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusilovsky, M.; Rochman, M.; Rochman, Y.; Caldwell, J.M.; Mack, L.E.; Felton, J.M.; Habel, J.E.; Porollo, A.; Pasare, C.; Rothenberg, M.E. Environmental Allergens Trigger Type 2 Inflammation through Ripoptosome Activation. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besnard, A.-G.; Togbe, D.; Guillou, N.; Erard, F.; Quesniaux, V.; Ryffel, B. IL-33-Activated Dendritic Cells Are Critical for Allergic Airway Inflammation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 1675–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rank, M.A.; Kobayashi, T.; Kozaki, H.; Bartemes, K.R.; Squillace, D.L.; Kita, H. IL-33-Activated Dendritic Cells Induce an Atypical TH2-Type Response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrill, J.D.; Rothenberg, M.E. Genetic Dissection of Eosinophilic Esophagitis Provides Insight into Disease Pathogenesis and Treatment Strategies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 23–32; quiz 33–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.Y.S.; Wong, C.K.; Cheung, P.F.Y.; Lam, C.W.K. Intracellular Signaling Mechanisms Regulating the Activation of Human Eosinophils by the Novel Th2 Cytokine IL-33: Implications for Allergic Inflammation. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2010, 7, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travers, J.; Rochman, M.; Caldwell, J.M.; Besse, J.A.; Miracle, C.E.; Rothenberg, M.E. IL-33 Is Induced in Undifferentiated, Non-Dividing Esophageal Epithelial Cells in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, L.M.; Heine, R.G.; Menheniott, T.R.; Buzzelli, J.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.; Pavlic, D.; O’Connor, L.; Al Gazali, K.; Hamilton, O.; Scurr, M.; et al. Elevated IL-33 expression is associated with pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis, and exogenous IL-33 promotes eosinophilic esophagitis development in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 310, G13–G25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwaha, A.K.; Laxer, R.; Liang, M.; Muise, A.M.; Eiwegger, T.; Immune Dysregulation Group. A Chromosomal Duplication Encompassing Interleukin-33 Causes a Novel Hyper IgE Phenotype Characterized by Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Generalized Autoimmunity. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 510–513.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturelli, N.; Lexmond, W.S.; Ohsaki, A.; Nurko, S.; Karasuyama, H.; Fiebiger, E.; Oyoshi, M.K. Allergic Skin Sensitization Promotes Eosinophilic Esophagitis through the IL-33-Basophil Axis in Mice. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1367–1380.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, L.K.; Hsu, C.-L.; Krier-Burris, R.A.; Chhiba, K.D.; Chien, K.B.; McKenzie, A.; Berdnikovs, S.; Bryce, P.J. IL-33 Precedes IL-5 in Regulating Eosinophil Commitment and Is Required for Eosinophil Homeostasis. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 3445–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Peng, N.; Xiao, F.; Shi, X.; Zhu, B.; Rui, K.; Tian, J.; Lu, L. New Insights into the Function of Interleukin-25 in Disease Pathogenesis. Biomark. Res. 2023, 11, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Guo, L.; Qiu, J.; Chen, X.; Hu-Li, J.; Siebenlist, U.; Williamson, P.R.; Urban, J.F.; Paul, W.E. IL-25-Responsive, Lineage-Negative KLRG1(Hi) Cells Are Multipotential “inflammatory” Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Smith, S.G.; Beaudin, S.; Dua, B.; Howie, K.; Gauvreau, G.; O’Byrne, P.M. IL-25 and IL-25 Receptor Expression on Eosinophils from Subjects with Allergic Asthma. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2014, 163, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D.; Radonjic-Hösli, S.; Straumann, A.; Yousefi, S.; Simon, H.-U. Active Eosinophilic Esophagitis Is Characterized by Epithelial Barrier Defects and Eosinophil Extracellular Trap Formation. Allergy 2015, 70, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junttila, I.S. Tuning the Cytokine Responses: An Update on Interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 Receptor Complexes. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchard, C.; Mingler, M.K.; Vicario, M.; Abonia, J.P.; Wu, Y.Y.; Lu, T.X.; Collins, M.H.; Putnam, P.E.; Wells, S.I.; Rothenberg, M.E. IL-13 Involvement in Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Transcriptome Analysis and Reversibility with Glucocorticoids. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 1292–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagalwalla, A.F.; Akhtar, N.; Woodruff, S.A.; Rea, B.A.; Masterson, J.C.; Mukkada, V.; Parashette, K.R.; Du, J.; Fillon, S.; Protheroe, C.A.; et al. Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition Contributes to Esophageal Remodeling and Reverses with Treatment. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 1387–1396.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klion, A.D.; Ackerman, S.J.; Bochner, B.S. Contributions of Eosinophils to Human Health and Disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2020, 15, 179–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Fulkerson, P.C.; Finkelman, F.D.; Mingler, M.; Fischetti, C.A.; Blanchard, C.; Rothenberg, M.E. IL-13 Induces Esophageal Remodeling and Gene Expression by an Eosinophil-Independent, IL-13R Alpha 2-Inhibited Pathway. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieder, F.; Nonevski, I.; Ma, J.; Ouyang, Z.; West, G.; Protheroe, C.; DePetris, G.; Schirbel, A.; Lapinski, J.; Goldblum, J.; et al. T-Helper 2 Cytokines, Transforming Growth Factor Β1, and Eosinophil Products Induce Fibrogenesis and Alter Muscle Motility in Patients with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1266–1277.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roufosse, F. Targeting the Interleukin-5 Pathway for Treatment of Eosinophilic Conditions Other than Asthma. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corren, J. Inhibition of Interleukin-5 for the Treatment of Eosinophilic Diseases. Discov. Med. 2012, 13, 305–312. [Google Scholar]
- Bullock, J.Z.; Villanueva, J.M.; Blanchard, C.; Filipovich, A.H.; Putnam, P.E.; Collins, M.H.; Risma, K.A.; Akers, R.M.; Kirby, C.L.; Buckmeier, B.K.; et al. Interplay of Adaptive Th2 Immunity with Eotaxin-3/c-C Chemokine Receptor 3 in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2007, 45, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Brunner, T.; De Weck, A.L.; Dahinden, C.A. Interleukin 5 Modifies Histamine Release and Leukotriene Generation by Human Basophils in Response to Diverse Agonists. J. Exp. Med. 1990, 172, 1577–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, N.L.; Mishra, A. Role of Interleukin-18 in the Pathophysiology of Allergic Diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2016, 32, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, D.; Hao, Y.; Zhou, W.; Ma, Y. The Relationship between Interleukin-18 Polymorphisms and Allergic Disease: A Meta-Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 290687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niranjan, R.; Rajavelu, P.; Ventateshaiah, S.U.; Shukla, J.S.; Zaidi, A.; Mariswamy, S.J.; Mattner, J.; Fortgang, I.; Kowalczyk, M.; Balart, L.; et al. Involvement of Interleukin-18 in the Pathogenesis of Human Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 157, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabstein, K.H.; Eisenman, J.; Shanebeck, K.; Rauch, C.; Srinivasan, S.; Fung, V.; Beers, C.; Richardson, J.; Schoenborn, M.A.; Ahdieh, M. Cloning of a T Cell Growth Factor That Interacts with the Beta Chain of the Interleukin-2 Receptor. Science 1994, 264, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, M.; Mavi, P.; Rayapudi, M.; Pandey, A.K.; Kaul, A.; Putnam, P.E.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Mishra, A. Interleukin-15 Expression Is Increased in Human Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Mediates Pathogenesis in Mice. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 182–193.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, C.; Wang, N.; Stringer, K.F.; Mishra, A.; Fulkerson, P.C.; Abonia, J.P.; Jameson, S.C.; Kirby, C.; Konikoff, M.R.; Collins, M.H.; et al. Eotaxin-3 and a Uniquely Conserved Gene-Expression Profile in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumann, A.; Bauer, M.; Fischer, B.; Blaser, K.; Simon, H.U. Idiopathic Eosinophilic Esophagitis Is Associated with a T(H)2-Type Allergic Inflammatory Response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 108, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muir, A.B.; Lim, D.M.; Benitez, A.J.; Modayur Chandramouleeswaran, P.; Lee, A.J.; Ruchelli, E.D.; Spergel, J.M.; Wang, M.-L. Esophageal Epithelial and Mesenchymal Cross-Talk Leads to Features of Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Vitro. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manresa, M.C.; Chiang, A.W.T.; Kurten, R.C.; Dohil, R.; Brickner, H.; Dohil, L.; Herro, R.; Akuthota, P.; Lewis, N.E.; Croft, M.; et al. Increased Production of LIGHT by T Cells in Eosinophilic Esophagitis Promotes Differentiation of Esophageal Fibroblasts Toward an Inflammatory Phenotype. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 1778–1792.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, E.; Souza, R.F.; Spechler, S.J. Tissue Remodeling in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 303, G1175–G1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, N.; Fernando, S.D.; Biette, K.A.; Hammer, J.A.; Capocelli, K.E.; Kitzenberg, D.A.; Glover, L.E.; Colgan, S.P.; Furuta, G.T.; Masterson, J.C. TGF-Β1 Alters Esophageal Epithelial Barrier Function by Attenuation of Claudin-7 in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Arias, A.; De Rezende, L.C.; Yagüe-Compadre, J.L.; Mota-Huertas, T.; González-Castillo, S.; Cuesta, R.A.; Tenias, J.M.; Bellón, T. Subepithelial Collagen Deposition, Profibrogenic Cytokine Gene Expression, and Changes after Prolonged Fluticasone Propionate Treatment in Adult Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Prospective Study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronio, A.; Covotta, F.; Pallotta, L.; Palma, R.; Badiali, D.; Sacchi, M.C.; Lamazza, A.; Severi, C. Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Cytokines Expression and Fibrotic Markers in Comparison to Celiac Disease. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, B.O.; Zanni, M.P.; Uguccioni, M.; Loetscher, M.; Mackay, C.R.; Pichler, W.J.; Yawalkar, N.; Baggiolini, M.; Moser, B. Functional Expression of the Eotaxin Receptor CCR3 in T Lymphocytes Co-Localizing with Eosinophils. Curr. Biol. 1997, 7, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, B.; Carlsten, J.; Sabo, E.; Kethu, S.; Meitner, P.; Tavares, R.; Jakate, S.; Mangray, S.; Aswad, B.; Resnick, M.B. Increased Expression of Eotaxin-3 Distinguishes between Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Hum. Pathol. 2007, 38, 1744–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, C.; Stucke, E.M.; Rodriguez-Jimenez, B.; Burwinkel, K.; Collins, M.H.; Ahrens, A.; Alexander, E.S.; Butz, B.K.B.; Jameson, S.C.; Kaul, A.; et al. A Striking Local Esophageal Cytokine Expression Profile in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 208–217e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Rothenberg, M.E. Intratracheal IL-13 Induces Eosinophilic Esophagitis by an IL-5, Eotaxin-1, and STAT6-Dependent Mechanism. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Hogan, S.P.; Brandt, E.B.; Rothenberg, M.E. An Etiological Role for Aeroallergens and Eosinophils in Experimental Esophagitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forssmann, U.; Uguccioni, M.; Loetscher, P.; Dahinden, C.A.; Langen, H.; Thelen, M.; Baggiolini, M. Eotaxin-2, a Novel CC Chemokine That Is Selective for the Chemokine Receptor CCR3, and Acts like Eotaxin on Human Eosinophil and Basophil Leukocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 2171–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holvoet, S.; Blanchard, C. Genetic and Molecular Mechanisms Leading to Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2014, 106, 276–280. [Google Scholar]
- Ruffner, M.A.; Hu, A.; Dilollo, J.; Benocek, K.; Shows, D.; Gluck, M.; Spergel, J.M.; Ziegler, S.F.; Hill, D.A.; Cerosaletti, K. Conserved IFN Signature between Adult and Pediatric Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffner, M.; Lal, M.; Gautam, R.; Muir, A.; Mrozek, Z.; Beers, J. Dysregulated Interferon Signaling in EoE Has Potential Implications for Esophageal Epithelial Cell Function. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, AB198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, B.L.; Kulis, M.; Guo, R.; Orgel, K.A.; Wolf, W.A.; Burks, A.W.; Vickery, B.P.; Dellon, E.S. Food-Specific IgG 4 Is Associated with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1190–1192.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuyler, A.J.; Wilson, J.M.; Tripathi, A.; Commins, S.P.; Ogbogu, P.U.; Kruzsewski, P.G.; Barnes, B.H.; McGowan, E.C.; Workman, L.J.; Lidholm, J.; et al. Specific IgG 4 Antibodies to Cow’s Milk Proteins in Pediatric Patients with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 139–148.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burk, C.M.; Dellon, E.S.; Steele, P.H.; Virkud, Y.V.; Kulis, M.; Burks, A.W.; Vickery, B.P. Eosinophilic Esophagitis during Peanut Oral Immunotherapy with Omalizumab. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 498–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumann, A.; Kristl, J.; Conus, S.; Vassina, E.; Spichtin, H.-P.; Beglinger, C.; Simon, H.-U. Cytokine Expression in Healthy and Inflamed Mucosa: Probing the Role of Eosinophils in the Digestive Tract. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2005, 11, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinit, C.; Dieme, A.; Courbage, S.; Dehaine, C.; Dufeu, C.M.; Jacquemot, S.; Lajus, M.; Montigny, L.; Payen, E.; Yang, D.D.; et al. Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management. Arch. Pediatr. 2019, 26, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Carlson, M.; Seki, S.; Abarbanel, D.; Quiros, A.; Cox, K.; Nadeau, K.C. Markers of Antigen Presentation and Activation on Eosinophils and T Cells in the Esophageal Tissue of Patients with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 56, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavi, P.; Rajavelu, P.; Rayapudi, M.; Paul, R.J.; Mishra, A. Esophageal Functional Impairments in Experimental Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G1347–G1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliewer, K.L.; Murray-Petzold, C.; Collins, M.H.; Abonia, J.P.; Bolton, S.M.; DiTommaso, L.A.; Martin, L.J.; Zhang, X.; Mukkada, V.A.; Putnam, P.E.; et al. Benralizumab for Eosinophilic Gastritis: A Single-Site, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, Á.; Lucendo, A.J.; Martínez-Fernández, P.; González-Castro, A.M.; Fortea, M.; González-Cervera, J.; Yagüe-Compadre, J.L.; Mota-Huertas, T.; Vicario, M. Dietary Treatment Modulates Mast Cell Phenotype, Density, and Activity in Adult Eosinophilic Oesophagitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2016, 46, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, D.J.; Mak, N.; Hurlbut, D.J.; Justinich, C.J. Atopic and Non-Atopic Eosinophilic Oesophagitis Are Distinguished by Immunoglobulin E-Bearing Intraepithelial Mast Cells. Histopathology 2012, 61, 810–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abonia, J.P.; Blanchard, C.; Butz, B.B.; Rainey, H.F.; Collins, M.H.; Stringer, K.; Putnam, P.E.; Rothenberg, M.E. Involvement of Mast Cells in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escourrou, P. Vasomotor activity and vascular geometry. Arch. Mal. Coeur Vaiss. 1991, 84, 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch, R.; Bokhary, R.; Marcon, M.A.; Cutz, E. Activated Mucosal Mast Cells Differentiate Eosinophilic (Allergic) Esophagitis from Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2007, 44, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niranjan, R.; Mavi, P.; Rayapudi, M.; Dynda, S.; Mishra, A. Pathogenic Role of Mast Cells in Experimental Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013, 304, G1087–G1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tappata, M.; Eluri, S.; Perjar, I.; Hollyfield, J.; Betancourt, R.; Randall, C.; Woosley, J.T.; Wechsler, J.B.; Dellon, E.S. Association of Mast Cells with Clinical, Endoscopic, and Histologic Findings in Adults with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Allergy 2018, 73, 2088–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, I.M.; Anilkumar, A.A.; Newbury, R.O.; Bhagat, M.; Beppu, L.Y.; Dohil, R.; Broide, D.H.; Aceves, S.S. Anti-IL-5 Therapy Reduces Mast Cell and IL-9 Cell Numbers in Pediatric Patients with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elieh Ali Komi, D.; Bjermer, L. Mast Cell-Mediated Orchestration of the Immune Responses in Human Allergic Asthma: Current Insights. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 56, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aceves, S.S.; Chen, D.; Newbury, R.O.; Dohil, R.; Bastian, J.F.; Broide, D.H. Mast Cells Infiltrate the Esophageal Smooth Muscle in Patients with Eosinophilic Esophagitis, Express TGF-Β1, and Increase Esophageal Smooth Muscle Contraction. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 1198–1204.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnani, P.; De Paulis, A.; Beltrame, C.; Annunziato, F.; Dente, V.; Maggi, E.; Romagnani, S.; Marone, G. Tryptase-Chymase Double-Positive Human Mast Cells Express the Eotaxin Receptor CCR3 and Are Attracted by CCR3-Binding Chemokines. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.; Zhang, X.; Pan, Z.; Spechler, S.J.; Souza, R.F. Mast Cell Effects on Esophageal Smooth Muscle and Their Potential Role in Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Achalasia. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2021, 320, G319–G327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehade, M.; Sampson, H.A.; Morotti, R.A.; Magid, M.S. Esophageal Subepithelial Fibrosis in Children with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2007, 45, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Navarro, M.; Comas, C.; Pascual, J.M.; Burgos, E.; Santamaría, L.; Larrauri, J. Immunophenotypic Characterization and Quantification of the Epithelial Inflammatory Infiltrate in Eosinophilic Esophagitis through Stereology: An Analysis of the Cellular Mechanisms of the Disease and the Immunologic Capacity of the Esophagus. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2007, 31, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavinasab, F.; Babaie, D.; Nilipour, Y.; Mansouri, M.; Imanzadeh, F.; Dara, N.; Rohani, P.; Khatami, K.; Sayyari, A.; Khoddami, M.; et al. Increased Number of Regulatory T Cells in Esophageal Tissue of Patients with Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Comparison to Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease and Control Groups. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2019, 47, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.A.; Luster, A.D. T Cell Homing to Epithelial Barriers in Allergic Disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitson-Salazar, A.; Yin, Y.; Wansley, D.L.; Young, M.; Bolan, H.; Arceo, S.; Ho, N.; Koh, C.; Milner, J.D.; Stone, K.D.; et al. Hematopoietic Prostaglandin D Synthase Defines a Proeosinophilic Pathogenic Effector Human T(H)2 Cell Subpopulation with Enhanced Function. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 907–918.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venuprasad, K.; Kong, Y.-C.M.; Farrar, M.A. Control of Th2-Mediated Inflammation by Regulatory T Cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuck, M.C.; Straumann, A.; Simon, H.-U. Relative Lack of T Regulatory Cells in Adult Eosinophilic Esophagitis—No Normalization after Corticosteroid Therapy. Allergy 2011, 66, 705–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantibhaedhyangkul, U.; Tatevian, N.; Gilger, M.A.; Major, A.M.; Davis, C.M. Increased Esophageal Regulatory T Cells and Eosinophil Characteristics in Children with Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2009, 39, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Jyonouchi, S.; Smith, C.L.; Saretta, F.; Abraham, V.; Ruymann, K.R.; Modayur-Chandramouleeswaran, P.; Wang, M.-L.; Spergel, J.M.; Cianferoni, A. Invariant Natural Killer T Cells in Children with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2014, 44, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayapudi, M.; Rajavelu, P.; Zhu, X.; Kaul, A.; Niranjan, R.; Dynda, S.; Mishra, A.; Mattner, J.; Zaidi, A.; Dutt, P.; et al. Invariant Natural Killer T-Cell Neutralization Is a Possible Novel Therapy for Human Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2014, 3, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.A.; McKenzie, A.N.J. Development and Function of Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, A.; Lo Presti, E.; Chini, R.; Gammeri, L.; Inchingolo, R.; Lohmeyer, F.M.; Nucera, E.; Gangemi, S. Emerging Role of Alarmins in Food Allergy: An Update on Pathophysiological Insights, Potential Use as Disease Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Implications. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, L.S.C.; Walker, J.A.; Jolin, H.E.; Scanlon, S.T.; Ishii, M.; Fallon, P.G.; McKenzie, A.N.J.; Clatworthy, M.R. Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells Exhibit Tissue-Specific Dynamic Behaviour During Type 2 Immune Responses. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 711907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, M.A.; Patel, G.; Hopp, R.; Yang, Q. Role of Innate Lymphoid Cells in Allergic Diseases. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2019, 40, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, T.A.; Baum, R.; Newbury, R.O.; Yang, T.; Dohil, R.; Aquino, M.; Doshi, A.; Walford, H.H.; Kurten, R.C.; Broide, D.H.; et al. Group 2 Innate Lymphocytes (ILC2) Are Enriched in Active Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 792–794.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, D.J.; Pooni, A.; Mak, N.; Hurlbut, D.J.; Basta, S.; Justinich, C.J. Antigen Presentation and MHC Class II Expression by Human Esophageal Epithelial Cells: Role in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochman, M.; Travers, J.; Abonia, J.P.; Caldwell, J.M.; Rothenberg, M.E. Synaptopodin Is Upregulated by IL-13 in Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Regulates Esophageal Epithelial Cell Motility and Barrier Integrity. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e96789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzka, D.A.; Tadi, R.; Smyrk, T.C.; Katarya, E.; Sharma, A.; Geno, D.M.; Camilleri, M.; Iyer, P.G.; Alexander, J.A.; Buttar, N.S. Effects of Topical Steroids on Tight Junction Proteins and Spongiosis in Esophageal Epithelia of Patients with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 1824–1829.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzka, D.A.; Geno, D.M.; Blair, H.E.; Lamsam, J.L.; Alexander, J.A.; Camilleri, M. Small Intestinal Permeability in Patients with Eosinophilic Oesophagitis during Active Phase and Remission. Gut 2015, 64, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravelli, A.; Villanacci, V.; Cadei, M.; Fuoti, M.; Gennati, G.; Salemme, M. Dilated Intercellular Spaces in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 59, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azouz, N.P.; Ynga-Durand, M.A.; Caldwell, J.M.; Jain, A.; Rochman, M.; Fischesser, D.M.; Ray, L.M.; Bedard, M.C.; Mingler, M.K.; Forney, C.; et al. The Antiprotease SPINK7 Serves as an Inhibitory Checkpoint for Esophageal Epithelial Inflammatory Responses. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaap9736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, K.J.; Lazenby, A.J.; Rowe, P.C.; Yardley, J.H.; Perman, J.A.; Sampson, H.A. Eosinophilic Esophagitis Attributed to Gastroesophageal Reflux: Improvement with an Amino Acid-Based Formula. Gastroenterology 1995, 109, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racca, F.; Pellegatta, G.; Cataldo, G.; Vespa, E.; Carlani, E.; Pelaia, C.; Paoletti, G.; Messina, M.R.; Nappi, E.; Canonica, G.W.; et al. Type 2 Inflammation in Eosinophilic Esophagitis: From Pathophysiology to Therapeutic Targets. Front. Physiol. 2022, 12, 815842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, Á.; González-Cervera, J.; Tenias, J.M.; Lucendo, A.J. Efficacy of Dietary Interventions for Inducing Histologic Remission in Patients with Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1639–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philpott, H.; Nandurkar, S.; Royce, S.G.; Thien, F.; Gibson, P.R. Allergy Tests Do Not Predict Food Triggers in Adult Patients with Eosinophilic Oesophagitis. A Comprehensive Prospective Study Using Five Modalities. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 44, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votto, M.; De Filippo, M.; Lenti, M.V.; Rossi, C.M.; Di Sabatino, A.; Marseglia, G.L.; Licari, A. Diet Therapy in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Focus on a Personalized Approach. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 9, 820192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Infante, J.; Gutierrez-Junquera, C.; Savarino, E.; Penagini, R.; Modolell, I.; Bartolo, O.; Prieto-García, A.; Mauro, A.; Alcedo, J.; Perelló, A.; et al. Helicobacter Pylori Infection Does Not Protect against Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Results from a Large Multicenter Case-Control Study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayerhofer, C.; Kavallar, A.M.; Aldrian, D.; Lindner, A.K.; Müller, T.; Vogel, G.F. Efficacy of Elimination Diets in Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 2197–2210.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spergel, J.M.; Elci, O.U.; Muir, A.B.; Liacouras, C.A.; Wilkins, B.J.; Burke, D.; Lewis, M.O.; Brown-Whitehorn, T.; Cianferoni, A. Efficacy of Epicutaneous Immunotherapy in Children with Milk-Induced Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 328–336.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, H.S.; Madara, J.L.; Stafford, R.J.; Grand, R.J.; Quinlan, J.-E.; Goldman, H. Intraepithelial Eosinophils: A New Diagnostic Criterion for Reflux Esophagitis. Gastroenterology 1982, 83, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, E.; Huo, X.; Yu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Pham, T.H.; Wang, D.H.; Spechler, S.J.; Souza, R.F. Omeprazole Blocks STAT6 Binding to the Eotaxin-3 Promoter in Eosinophilic Esophagitis Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spergel, J.M.; Dellon, E.S.; Liacouras, C.A.; Hirano, I.; Molina-Infante, J.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Furuta, G.T. Summary of the Updated International Consensus Diagnostic Criteria for Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 121, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warners, M.J.; Van Rhijn, B.D.; Verheij, J.; Smout, A.J.P.M.; Bredenoord, A.J. Disease Activity in Eosinophilic Esophagitis Is Associated with Impaired Esophageal Barrier Integrity. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 313, G230–G238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuelli, L.; Tumino, G.; Turriziani, M.; Modesti, A.; Bei, R. Topical Use of Sucralfate in Epithelial Wound Healing: Clinical Evidence and Molecular Mechanisms of Action. IAD 2010, 4, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamoorthy, S.; Cidlowski, J.A. Corticosteroids. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. A. 2016, 42, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.J.; Devlin, R.D.; Menaa, C.; Chung, H.; Roodman, G.D.; Reddy, S.V. Cloning and Identification of Human Sca as a Novel Inhibitor of Osteoclast Formation and Bone Resorption. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Infante, J.; Rivas, M.D.; Hernandez-Alonso, M.; Vinagre-Rodríguez, G.; Mateos-Rodríguez, J.M.; Dueñas-Sadornil, C.; Perez-Gallardo, B.; Ferrando-Lamana, L.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, N.; Bañares, R.; et al. Proton Pump Inhibitor-Responsive Oesophageal Eosinophilia Correlates with Downregulation of Eotaxin-3 and Th2 Cytokines Overexpression. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 40, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, E.S.; Sheikh, A.; Speck, O.; Woodward, K.; Whitlow, A.B.; Hores, J.M.; Ivanovic, M.; Chau, A.; Woosley, J.T.; Madanick, R.D.; et al. Viscous Topical Is More Effective Than Nebulized Steroid Therapy for Patients with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 321–324.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Miehlke, S.; Schlag, C.; Vieth, M.; Von Arnim, U.; Molina-Infante, J.; Hartmann, D.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Ciriza De Los Rios, C.; Schubert, S.; et al. Efficacy of Budesonide Orodispersible Tablets as Induction Therapy for Eosinophilic Esophagitis in a Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 74–86.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, I.; Dellon, E.S.; Hamilton, J.D.; Collins, M.H.; Peterson, K.; Chehade, M.; Schoepfer, A.M.; Safroneeva, E.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Falk, G.W.; et al. Efficacy of Dupilumab in a Phase 2 Randomized Trial of Adults with Active Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 111–122.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, E.S.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Collins, M.H.; Hirano, I.; Chehade, M.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Lucendo, A.J.; Spergel, J.M.; Aceves, S.; Sun, X.; et al. Dupilumab in Adults and Adolescents with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2317–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumann, A.; Conus, S.; Grzonka, P.; Kita, H.; Kephart, G.; Bussmann, C.; Beglinger, C.; Smith, D.A.; Patel, J.; Byrne, M.; et al. Anti-Interleukin-5 Antibody Treatment (Mepolizumab) in Active Eosinophilic Oesophagitis: A Randomised, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Trial. Gut 2010, 59, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assa’ad, A.H.; Gupta, S.K.; Collins, M.H.; Thomson, M.; Heath, A.T.; Smith, D.A.; Perschy, T.L.; Jurgensen, C.H.; Ortega, H.G.; Aceves, S.S. An Antibody Against IL-5 Reduces Numbers of Esophageal Intraepithelial Eosinophils in Children with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1593–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spergel, J.M.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Collins, M.H.; Furuta, G.T.; Markowitz, J.E.; Fuchs, G.; O’Gorman, M.A.; Abonia, J.P.; Young, J.; Henkel, T.; et al. Reslizumab in Children and Adolescents with Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Results of a Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 456–463.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumann, A.; Conus, S.; Degen, L.; Felder, S.; Kummer, M.; Engel, H.; Bussmann, C.; Beglinger, C.; Schoepfer, A.; Simon, H. Budesonide Is Effective in Adolescent and Adult Patients with Active Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 1526–1537.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, Z.A.; Sadek, A.; Abdelhady, A.M.; Darweesh, S.K.; Morsy, S.A.; Esmat, G. Losartan May Inhibit the Progression of Liver Fibrosis in Chronic HCV Patients. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2016, 5, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumann, A.; Hoesli, S.; Bussmann, C.; Stuck, M.; Perkins, M.; Collins, L.P.; Payton, M.; Pettipher, R.; Hunter, M.; Steiner, J.; et al. Anti-Eosinophil Activity and Clinical Efficacy of the CRTH2 Antagonist OC000459 in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Allergy 2013, 68, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.A.; Ravi, K.; Enders, F.T.; Geno, D.M.; Kryzer, L.A.; Mara, K.C.; Smyrk, T.C.; Katzka, D.A. Montelukast Does Not Maintain Symptom Remission After Topical Steroid Therapy for Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 214–221.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, A.T.; No, J.S.; Anderson, L.; Solomon, A.; Ciecierega, T.; Barfield, E.; Chien, K.; Schnoll-Sussman, F.; Reisacher, W.R. Esophageal IgE, IgG4, and Mucosal Eosinophilia in Individuals with Dysphagia. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicario, M.; Blanchard, C.; Stringer, K.F.; Collins, M.H.; Mingler, M.K.; Ahrens, A.; Putnam, P.E.; Abonia, J.P.; Santos, J.; Rothenberg, M.E. Local B Cells and IgE Production in the Oesophageal Mucosa in Eosinophilic Oesophagitis. Gut 2010, 59, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizou, D.; Enav, B.; Komlodi-Pasztor, E.; Hider, P.; Kim-Chang, J.; Noonan, L.; Taber, T.; Kaushal, S.; Limgala, R.; Brown, M.; et al. A Pilot Study of Omalizumab in Eosinophilic Esophagitis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0113483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, E.B.; Zimmermann, N.; Muntel, E.E.; Yamada, Y.; Pope, S.M.; Mishra, A.; Hogan, S.P.; Rothenberg, M.E. The Alpha4bbeta7-Integrin Is Dynamically Expressed on Murine Eosinophils and Involved in Eosinophil Trafficking to the Intestine. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2006, 36, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beales, I.L.P. Resolution of Refractory Eosinophilic Esophagitis with the Leukocyte-Trafficking Inhibitor Natalizumab. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 2688–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhu, Q.M.; Chiao, H.; Moawad, F.J.; Bao, F.; Konijeti, G.G. The Anti-A4β7 Integrin Therapeutic Antibody for Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Vedolizumab, Ameliorates Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Novel Clinical Observation. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 1261–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taft, T.H.; Mutlu, E.A. The Potential Role of Vedolizumab in Concomitant Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Crohn’s Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 1840–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiwamoto, T.; Kawasaki, N.; Paulson, J.C.; Bochner, B.S. Siglec-8 as a Drugable Target to Treat Eosinophil and Mast Cell-Associated Conditions. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 135, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellon, E.S.; Peterson, K.A.; Murray, J.A.; Falk, G.W.; Gonsalves, N.; Chehade, M.; Genta, R.M.; Leung, J.; Khoury, P.; Klion, A.D.; et al. Anti–Siglec-8 Antibody for Eosinophilic Gastritis and Duodenitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1624–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza Alvarez, L.B.; Liu, X.; Glover, S. Treatment-Resistant Eosinophilic Oesophagitis Successfully Managed with Tofacitinib. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e232558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netzer, P.; Gschossmann, J.M.; Straumann, A.; Sendensky, A.; Weimann, R.; Schoepfer, A.M. Corticosteroid-Dependent Eosinophilic Oesophagitis: Azathioprine and 6-Mercaptopurine Can Induce and Maintain Long-Term Remission. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 19, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leber, A.; Hontecillas, R.; Zoccoli-Rodriguez, V.; Ehrich, M.; Davis, J.; Chauhan, J.; Bassaganya-Riera, J. Nonclinical Toxicology and Toxicokinetic Profile of an Oral Lanthionine Synthetase C-Like 2 (LANCL2) Agonist, BT-11. Int. J. Toxicol. 2019, 38, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.M.D.C.E.; De Oliveira, E.E.; Ambrósio, M.G.E.; Ayupe, M.C.; De Souza, V.P.; Menegati, L.M.; Reis, D.R.D.L.; Machado, M.A.; Macedo, G.C.; Ferreira, A.P. Disodium Cromoglycate Treatment Reduces TH2 Immune Response and Immunohistopathological Features in a Murine Model of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 83, 106422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, J.A.; Zhang, J.; Whitworth, J.; Cavender, C. A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Study of the Use of Viscous Oral Cromolyn Sodium for the Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 120, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capucilli, P.; Cianferoni, A.; Grundmeier, R.W.; Spergel, J.M. Comparison of Comorbid Diagnoses in Children with and without Eosinophilic Esophagitis in a Large Population. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 121, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, C.C.; Iglesia, E.G.A.; Commins, S.P.; Dellon, E.S. Seasonal Exacerbation of Eosinophilic Esophagitis Histologic Activity in Adults and Children Implicates Role of Aeroallergens. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 122, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesia, E.G.A.; Commins, S.P.; Dellon, E.S. Complete Remission of Eosinophilic Esophagitis with Multi-Aeroallergen Subcutaneous Immunotherapy: A Case Report. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 2517–2519.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Swert, L.; Veereman, G.; Bublin, M.; Breiteneder, H.; Dilissen, E.; Bosmans, E.; Mattelaer, C.; Bullens, D. Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disease Suggestive of Pathogenesis-Related Class 10 (PR-10) Protein Allergy Resolved after Immunotherapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 600–602.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleuskens, M.T.A.; Haasnoot, M.L.; Herpers, B.M.; Ampting, M.T.J.V.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Garssen, J.; Redegeld, F.A.; Van Esch, B.C.A.M. Butyrate and Propionate Restore Interleukin 13-compromised Esophageal Epithelial Barrier Function. Allergy 2022, 77, 1510–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aich, J.; Mabalirajan, U.; Ahmad, T.; Agrawal, A.; Ghosh, B. Loss-of-Function of Inositol Polyphosphate-4-Phosphatase Reversibly Increases the Severity of Allergic Airway Inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, Y.-L.; Gutowska-Owsiak, D.; Hardman, C.S.; Westmoreland, M.; MacKenzie, T.; Cifuentes, L.; Waithe, D.; Lloyd-Lavery, A.; Marquette, A.; Londei, M.; et al. Proof-of-Concept Clinical Trial of Etokimab Shows a Key Role for IL-33 in Atopic Dermatitis Pathogenesis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaax2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsen, S.G.; Agache, I.O.; Soong, W.; Israel, E.; Chupp, G.L.; Cheung, D.S.; Theess, W.; Yang, X.; Staton, T.L.; Choy, D.F.; et al. Astegolimab (Anti-ST2) Efficacy and Safety in Adults with Severe Asthma: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, C.; Fautrel, B.; Rech, J.; Spertini, F.; Feist, E.; Kötter, I.; Hachulla, E.; Morel, J.; Schaeverbeke, T.; Hamidou, M.A.; et al. Open-Label, Multicentre, Dose-Escalating Phase II Clinical Trial on the Safety and Efficacy of Tadekinig Alfa (IL-18BP) in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wlodek, E.; Kirkpatrick, R.B.; Andrews, S.; Noble, R.; Schroyer, R.; Scott, J.; Watson, C.J.E.; Clatworthy, M.; Harrison, E.M.; Wigmore, S.J.; et al. A Pilot Study Evaluating GSK1070806 Inhibition of Interleukin-18 in Renal Transplant Delayed Graft Function. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corren, J.; Parnes, J.R.; Wang, L.; Mo, M.; Roseti, S.L.; Griffiths, J.M.; Van Der Merwe, R. Tezepelumab in Adults with Uncontrolled Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neighbour, H.; Boulet, L.-P.; Lemiere, C.; Sehmi, R.; Leigh, R.; Sousa, A.R.; Martin, J.; Dallow, N.; Gilbert, J.; Allen, A.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of an Oral CCR3 Antagonist in Patients with Asthma and Eosinophilic Bronchitis: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2014, 44, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grozdanovic, M.; Laffey, K.G.; Abdelkarim, H.; Hitchinson, B.; Harijith, A.; Moon, H.-G.; Park, G.Y.; Rousslang, L.K.; Masterson, J.C.; Furuta, G.T.; et al. Novel Peptide Nanoparticle–Biased Antagonist of CCR3 Blocks Eosinophil Recruitment and Airway Hyperresponsiveness. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 669–680.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, B.; Lee, A.I.; Choi, J. Treatment of Hypereosinophilic Syndrome with Cutaneous Involvement with the JAK Inhibitors Tofacitinib and Ruxolitinib. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 951–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, E.; Zhang, X.; Wilson, K.S.; Wang, D.H.; Park, J.Y.; Huo, X.; Yu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Spechler, S.J.; Souza, R.F. JAK-STAT6 Pathway Inhibitors Block Eotaxin-3 Secretion by Epithelial Cells and Fibroblasts from Esophageal Eosinophilia Patients: Promising Agents to Improve Inflammation and Prevent Fibrosis in EoE. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merves, J.; Chandramouleeswaran, P.M.; Benitez, A.J.; Muir, A.B.; Lee, A.J.; Lim, D.M.; Dods, K.; Mehta, I.; Ruchelli, E.D.; Nakagawa, H.; et al. Altered Esophageal Histamine Receptor Expression in Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE): Implications on Disease Pathogenesis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0114831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panch, S.R.; Bozik, M.E.; Brown, T.; Makiya, M.; Prussin, C.; Archibald, D.G.; Hebrank, G.T.; Sullivan, M.; Sun, X.; Wetzler, L.; et al. Dexpramipexole as an Oral Steroid-Sparing Agent in Hypereosinophilic Syndromes. Blood 2018, 132, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upparahalli Venkateshaiah, S.; Rayapudi, M.; Kandikattu, H.K.; Yadavalli, C.S.; Mishra, A. Blood mRNA Levels of T Cells and IgE Receptors Are Novel Non-Invasive Biomarkers for Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE). Clin. Immunol. 2021, 227, 108752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Jiménez, F.; Ugalde-Triviño, L.; Arias-González, L.; Relaño-Rupérez, C.; Casabona, S.; Pérez-Fernández, M.T.; Martín-Domínguez, V.; Fernández-Pacheco, J.; Laserna-Mendieta, E.J.; Muñoz-Hernández, P.; et al. Proteomic Analysis of the Esophageal Epithelium Reveals Key Features of Eosinophilic Esophagitis Pathophysiology. Allergy 2023, 78, 2732–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type of Therapy | Specific Therapeutic Intervention/Drug | Specific Pathophysiological Target Mechanism | Clinical Evidence and Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Avoiding luminal Triggers | Food elimination diet (FED)—eliminating from 1 up to 6 food allergens (from 1-FED to 6-FED) | Elimination of food antigens to reduce inflammation | Alternative second-line therapy [129] |
| Empirical allergen elimination | Elimination of common allergens to identify triggers | 50% proved efficacy—suggested sequential reintroduction [130] | |
| Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) | Inhibition of gastric acid secretion and esophageal barrier restoration | Established first-line therapy [129] | |
| Targeting epithelial barrier | Sucralfate | Enhancement of vascular flow, mucus production, and cytoprotective effects | Ongoing phase I trial (NCT0235307) |
| Targeting soluble mediators | Corticosteroids | Modulation of NF-kB cascade and reduction in eosinophil and cytokines recruitment | Swallowed topical steroids are agreed second-line therapy with proven efficacy [131] |
| Dupilumab, cendakimab, and dectrekumab | Inhibition of IL-4/IL-13 | Dupilumab approved by the FDA for >12-year-old and >40 kg EoE patients with proven efficacy [132]. Long-term phase III trials for dupilumab are ongoing (NCT03633617 and NCT04394351). Phase III trials for cendakimab are also ongoing (NCT04753697). | |
| Mepolizumab and reslizumab | Neutralization of IL-5 | Ongoing phase II trial for mepolizumab (NCT03656380). | |
| CALY-002 | Inhibition of IL-15 | Ongoing phase I trial (NCT04593251). | |
| Losartan | Indirect inhibition of TGF-β pathway | Ongoing phase II trial (NCT03029091). | |
| Timapiprant and montelukast | Inhibition of prostaglandins | Clinical efficacy but no histologic remission with timapiprant [133]; no clinical benefits of montelukast [134]. | |
| Omalizumab | Inhibition of IgE pathway | Disappointing results in pilot study [135]. | |
| S1P and integrin pathways | Modulation of S1P receptor and inhibition of α4β7 integrin | Ongoing phase II trials for S1P receptor modulator (NCT04682639). Proven efficacy of anti-α4β7 integrin [136,137]. | |
| Antolimab and lirentelimab | Siglec inhibition: reduction in the esophageal eosinophilic infiltrate and inhibition of eosinophil secretion of eotaxin | Ongoing phase II/III trial (NCT04322708). | |
| Tofacinib | JAK-STAT6 inhibition | Single case report [138]. | |
| Targeting cellular mediators | Benralizumab | Inhibition of IL-5 receptor | No clinical benefits: phase III trial (NCT04543409) prematurely terminated, but preliminary results of histological remission in an ongoing phase III trial (NCT03473977). |
| Azathioprine and BT-11 | T cells | BT-11 ongoing phase I trial (NCT04835168) | |
| Cromolyn sodium and barzolvolimab | Mast cells | Ongoing phase II trial of barzolvolimab (NCT05774184). | |
| Immunotherapy for environmental allergens | Subcutaneous immunotherapy for environmental allergens | Histologic remission in small case reports/small series [139,140]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Massironi, S.; Mulinacci, G.; Gallo, C.; Elvevi, A.; Danese, S.; Invernizzi, P.; Vespa, E. Mechanistic Insights into Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Therapies Targeting Pathophysiological Mechanisms. Cells 2023, 12, 2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12202473
Massironi S, Mulinacci G, Gallo C, Elvevi A, Danese S, Invernizzi P, Vespa E. Mechanistic Insights into Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Therapies Targeting Pathophysiological Mechanisms. Cells. 2023; 12(20):2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12202473
Chicago/Turabian StyleMassironi, Sara, Giacomo Mulinacci, Camilla Gallo, Alessandra Elvevi, Silvio Danese, Pietro Invernizzi, and Edoardo Vespa. 2023. "Mechanistic Insights into Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Therapies Targeting Pathophysiological Mechanisms" Cells 12, no. 20: 2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12202473
APA StyleMassironi, S., Mulinacci, G., Gallo, C., Elvevi, A., Danese, S., Invernizzi, P., & Vespa, E. (2023). Mechanistic Insights into Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Therapies Targeting Pathophysiological Mechanisms. Cells, 12(20), 2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12202473






