LGR5 Expression Predicting Poor Prognosis Is Negatively Correlated with WNT5A in Colon Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Microarray (TMA) and Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.2. Cell Lines
2.3. Xenograft Colon Cancer Tissues
2.4. Real-Time qPCR
2.5. Clonogenic Assay
2.6. Colonosphere Formation
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Immunofluorescence Analysis
2.9. Acquisition of Gene Expression and Clinical Data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) Datasets
2.10. Identification of Independent Prognostic Parameters of Colon Cancer
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
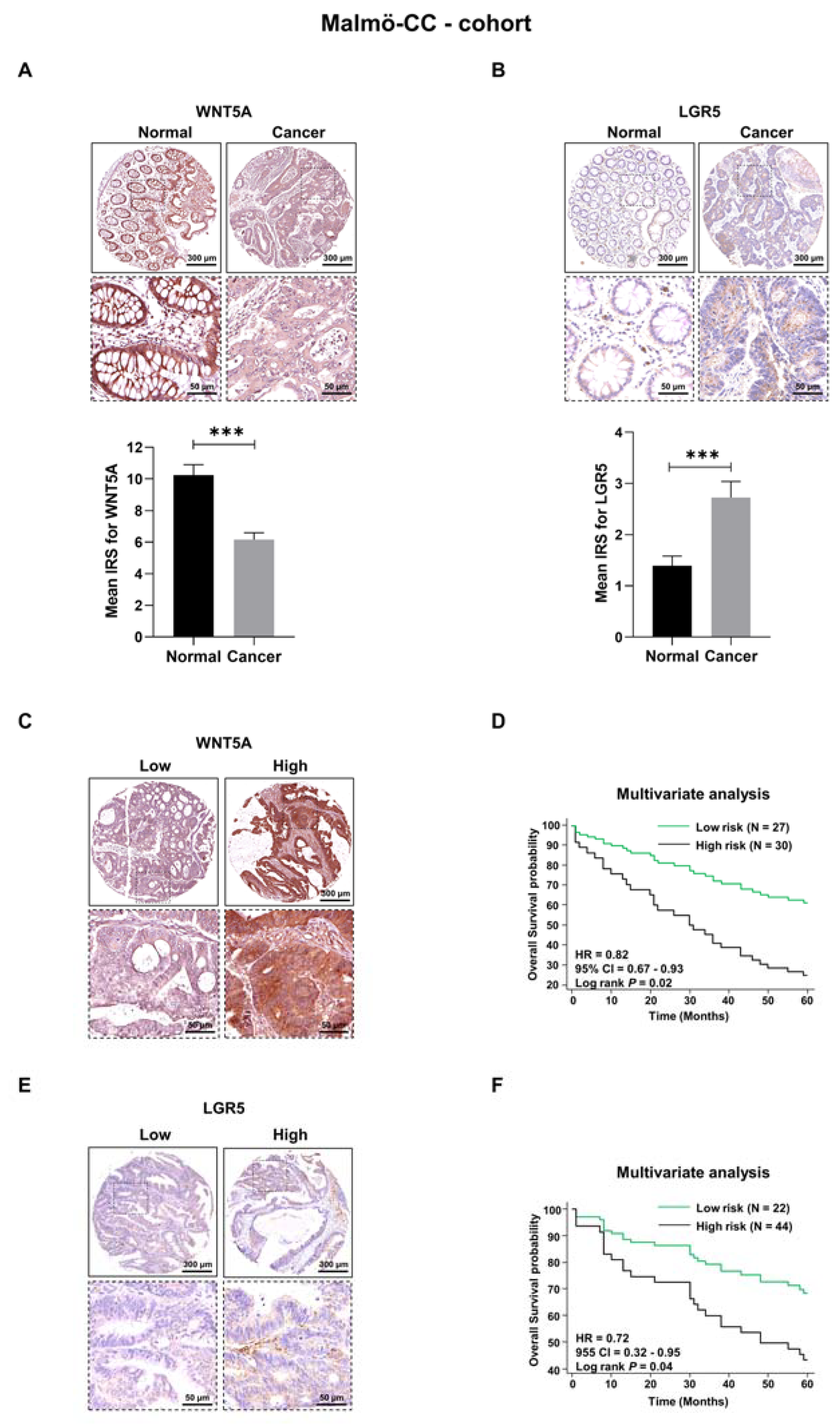
3.1. WNT5A and LGR5 Protein Expression in Colon Cancer Tissue
3.2. Evaluation of Survival Probabilities and Correlation between WNT5A and LGR5 Expression Based on Data from Publicly Available Colon Cancer Cohorts
3.3. WNT5A Signaling Decreases the Expression of LGR5 and the Growth of Colon Cancer Cells Both In Vitro and In Vivo
3.4. Parallel Analysis of Foxy5-Induced Effects on LGR5 Expression and β-Catenin Signaling
3.5. WNT5A Signaling Regulates the Expression of the LGR5 Ligand RSPO3
3.6. WNT5A Signaling Negatively Correlates with VEGFA Expression in Colon Cancer Tissues
3.7. Correlations between WNT5A and the Colon Cancer Stem Cell Marker DCLK1 in Colon Cancer Tissue from Different Cohorts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prasad, C.P.; Manchanda, M.; Mohapatra, P.; Andersson, T. WNT5A as a therapeutic target in breast cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018, 37, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, V.; Jobe, N.; Mehdawi, L.; Andersson, T. Targeting Oncogenic WNT Signalling with WNT Signalling-Derived Peptides. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2021, 269, 279–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumawat, K.; Gosens, R. WNT-5A: Signaling and functions in health and disease. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 567–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.D.; Chen, W.D. Emerging Roles of Wnt Ligands in Human Colorectal Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Hernández, E.; Velázquez, D.M.; Castañeda-Patlán, M.C.; Fuentes-García, G.; Fonseca-Camarillo, G.; Yamamoto-Furusho, J.K.; Romero-Avila, M.T.; García-Sáinz, J.A.; Robles-Flores, M. Canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling are simultaneously activated by Wnts in colon cancer cells. Cell Signal 2020, 72, 109636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejmek, J.; Dejmek, A.; Säfholm, A.; Sjölander, A.; Andersson, T. Wnt-5a protein expression in primary dukes B colon cancers identifies a subgroup of patients with good prognosis. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9142–9146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdawi, L.M.; Prasad, C.P.; Ehrnström, R.; Andersson, T.; Sjölander, A. Non-canonical WNT5A signaling up-regulates the expression of the tumor suppressor 15-PGDH and induces differentiation of colon cancer cells. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 1415–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakizaka, K.; Kamiyama, T.; Wakayama, K.; Orimo, T.; Shimada, S.; Nagatsu, A.; Kamachi, H.; Yokoo, H.; Fukai, M.; Kobayashi, N.; et al. Role of Wnt5a in suppressing invasiveness of hepatocellular carcinoma via epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, A.; Pagare, P.P.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. Drug discovery efforts toward inhibitors of canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in the treatment of cancer: A composition-of-matter review (2010–2020). Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, N.; Kurzrock, R. Targeting the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in cancer: Update on effectors and inhibitors. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 62, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.G.-; Kim, M.J.; Choi, W.J.; Moon, M.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.C.; Kang, S.G.; Seo, G.Y.; et al. Wnt3A induces GSK-3β phosphorylation and β-catenin accumulation through RhoA/ROCK. J. Cell Physiol. 2017, 232, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinzon-Daza, M.L.; Salaroglio, I.C.; Kopecka, J.; Garzon, R.; Couraud, P.O.; Ghigo, D.; Riganti, C. The cross-talk between canonical and non-canonical Wnt-dependent pathways regulates P-glycoprotein expression in human blood-brain barrier cells. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 1258–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackers, I.; Malgor, R. Interrelationship of canonical and non-canonical Wnt signalling pathways in chronic metabolic diseases. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2018, 15, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akoumianakis, I.; Polkinghorne, M.; Antoniades, C. Non-canonical WNT signalling in cardiovascular disease: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2022, 19, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, J.; Bellamkonda, K.; Liu, Q.; Andersson, T.; Sjölander, A. The WNT5A Agonist Foxy5 Reduces the Number of Colonic Cancer Stem Cells in a Xenograft Mouse Model of Human Colonic Cancer. Anticancer. Res. 2019, 39, 1719–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lau, W.; Barker, N.; Low, T.Y.; Koo, B.K.; Li, V.S.; Teunissen, H.; Kujala, P.; Haegebarth, A.; Peters, P.J.; van de Wetering, M.; et al. Lgr5 homologues associate with Wnt receptors and mediate R-spondin signalling. Nature 2011, 476, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ter Steege, E.J.; Bakker, E.R.M. The role of R-spondin proteins in cancer biology. Oncogene 2021, 40, 6469–6478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, F.; Zhang, H.H.; Odorizzi, A.; Burgess, A.W. LGR5 is a negative regulator of tumourigenicity, antagonizes Wnt signalling and regulates cell adhesion in colorectal cancer cell lines. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conboy, C.B.; Vélez-Reyes, G.L.; Rathe, S.K.; Abrahante, J.E.; Temiz, N.A.; Burns, M.B.; Harris, R.S.; Starr, T.K.; Largaespada, D.A. R-Spondins 2 and 3 Are Overexpressed in a Subset of Human Colon and Breast Cancers. DNA Cell Biol. 2021, 40, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satapathy, S.R.; Sjölander, A. Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1 promotes 5-fluorouracil resistance and resistance-derived stemness in colon cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2020, 488, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.G.; Mortensson, E.; Williams, A.C. Targeting LGR5 in Colorectal Cancer: Therapeutic gold or too plastic? Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Cao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Liu, X.; Geng, M. Expression of Wnt-5a and β-catenin in primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 3190–3195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dejmek, J.; Leandersson, K.; Manjer, J.; Bjartell, A.; Emdin, S.O.; Vogel, W.F.; Landberg, G.; Andersson, T. Expression and signaling activity of Wnt-5a/discoidin domain receptor-1 and Syk plays distinct but decisive roles in breast cancer patient survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ying, J.; Li, H.; Yu, J.; Ng, K.M.; Poon, F.F.; Wong, S.C.; Chan, A.T.; Sung, J.J.; Tao, Q. WNT5A exhibits tumor-suppressive activity through antagonizing the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling, and is frequently methylated in colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilkens, J.; Timmer, N.C.; Boer, M.; Ikink, G.J.; Schewe, M.; Sacchetti, A.; Koppens, M.A.J.; Song, J.Y.; Bakker, E.R.M. RSPO3 expands intestinal stem cell and niche compartments and drives tumorigenesis. Gut 2017, 66, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Y.; Xu, P. Global colorectal cancer burden in 2020 and projections to 2040. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 101174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elebiyo, T.C.; Rotimi, D.; Evbuomwan, I.O.; Maimako, R.F.; Iyobhebhe, M.; Ojo, O.A.; Oluba, O.M.; Adeyemi, O.S. Reassessing vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in anti-angiogenic cancer treatment. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2022, 32, 100620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Xu, J.; Zhu, Y. Self-renewal molecular mechanisms of colorectal cancer stem cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlos-Suárez, A.; Barriga, F.M.; Jung, P.; Iglesias, M.; Céspedes, M.V.; Rossell, D.; Sevillano, M.; Hernando-Momblona, X.; da Silva-Diz, V.; Muñoz, P.; et al. The intestinal stem cell signature identifies colorectal cancer stem cells and predicts disease relapse. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 8, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.K.; Islam, F.; Lam, A.K. The Roles of Cancer Stem Cells and Therapy Resistance in Colorectal Carcinoma. Cells 2020, 9, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ma, J.; Zhao, L.; Jin, X.; Li, H. R-spondin family biology and emerging linkages to cancer. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 428–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa, E.M.F.; Vermeulen, L. Wnt Signaling in Cancer Stem Cell Biology. Cancers 2016, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihemelandu, C.; Naeem, A.; Parasido, E.; Berry, D.; Chaldekas, K.; Harris, B.T.; Rodriguez, O.; Albanese, C. Clinicopathologic and prognostic significance of LGR5, a cancer stem cell marker in patients with colorectal cancer. Color. Cancer 2019, 8, CRC11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, Y.; Seno, H.; Fukuoka, A.; Ueo, T.; Yamaga, Y.; Maruno, T.; Nakanishi, N.; Kanda, K.; Komekado, H.; Kawada, M.; et al. Dclk1 distinguishes between tumor and normal stem cells in the intestine. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantari, E.; Razmi, M.; Tajik, F.; Asadi-Lari, M.; Ghods, R.; Madjd, Z. Oncogenic functions and clinical significances of DCLK1 isoforms in colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Tavoosidana, G.; Modarressi, M.H.; Rad, A.A.; Fazeli, M.S.; Shirkoohi, R.; Tavakoli-Yaraki, M.; Madjd, Z. Upregulation of circulating cancer stem cell marker, DCLK1 but not Lgr5, in chemoradiotherapy-treated colorectal cancer patients. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 4801–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.C.; Ahmed, I.; Stubbs, J.; Zhang, J.; Attard, T.; Septer, S.; Welch, D.; Anant, S.; Sampath, V.; Umar, S. DCLK1 isoforms and aberrant Notch signaling in the regulation of human and murine colitis. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumagalli, A.; Oost, K.C.; Kester, L.; Morgner, J.; Bornes, L.; Bruens, L.; Spaargaren, L.; Azkanaz, M.; Schelfhorst, T.; Beerling, E.; et al. Plasticity of Lgr5-Negative Cancer Cells Drives Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 26, 569–578.e567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, E.G.; Nasreddin, N.; Valbuena, G.N.; Mulholland, E.J.; Belnoue-Davis, H.L.; Eggington, H.R.; Schenck, R.O.; Wouters, V.M.; Wirapati, P.; Gilroy, K.; et al. Dynamic and adaptive cancer stem cell population admixture in colorectal neoplasia. Cell Stem Cell 2022, 29, 1213–1228.e1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari-Birgani, S.; Paranjothy, T.; Zuse, A.; Janikowski, T.; Cieslar-Pobuda, A.; Likus, W.; Urasinska, E.; Schweizer, F.; Ghavami, S.; Klonisch, T.; et al. Cancer stem cells, cancer-initiating cells and methods for their detection. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mehdawi, L.M.; Ghatak, S.; Chakraborty, P.; Sjölander, A.; Andersson, T. LGR5 Expression Predicting Poor Prognosis Is Negatively Correlated with WNT5A in Colon Cancer. Cells 2023, 12, 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12222658
Mehdawi LM, Ghatak S, Chakraborty P, Sjölander A, Andersson T. LGR5 Expression Predicting Poor Prognosis Is Negatively Correlated with WNT5A in Colon Cancer. Cells. 2023; 12(22):2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12222658
Chicago/Turabian StyleMehdawi, Lubna M., Souvik Ghatak, Payel Chakraborty, Anita Sjölander, and Tommy Andersson. 2023. "LGR5 Expression Predicting Poor Prognosis Is Negatively Correlated with WNT5A in Colon Cancer" Cells 12, no. 22: 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12222658
APA StyleMehdawi, L. M., Ghatak, S., Chakraborty, P., Sjölander, A., & Andersson, T. (2023). LGR5 Expression Predicting Poor Prognosis Is Negatively Correlated with WNT5A in Colon Cancer. Cells, 12(22), 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12222658





