Assessing Cannabidiol as a Therapeutic Agent for Preventing and Alleviating Alzheimer’s Disease Neurodegeneration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
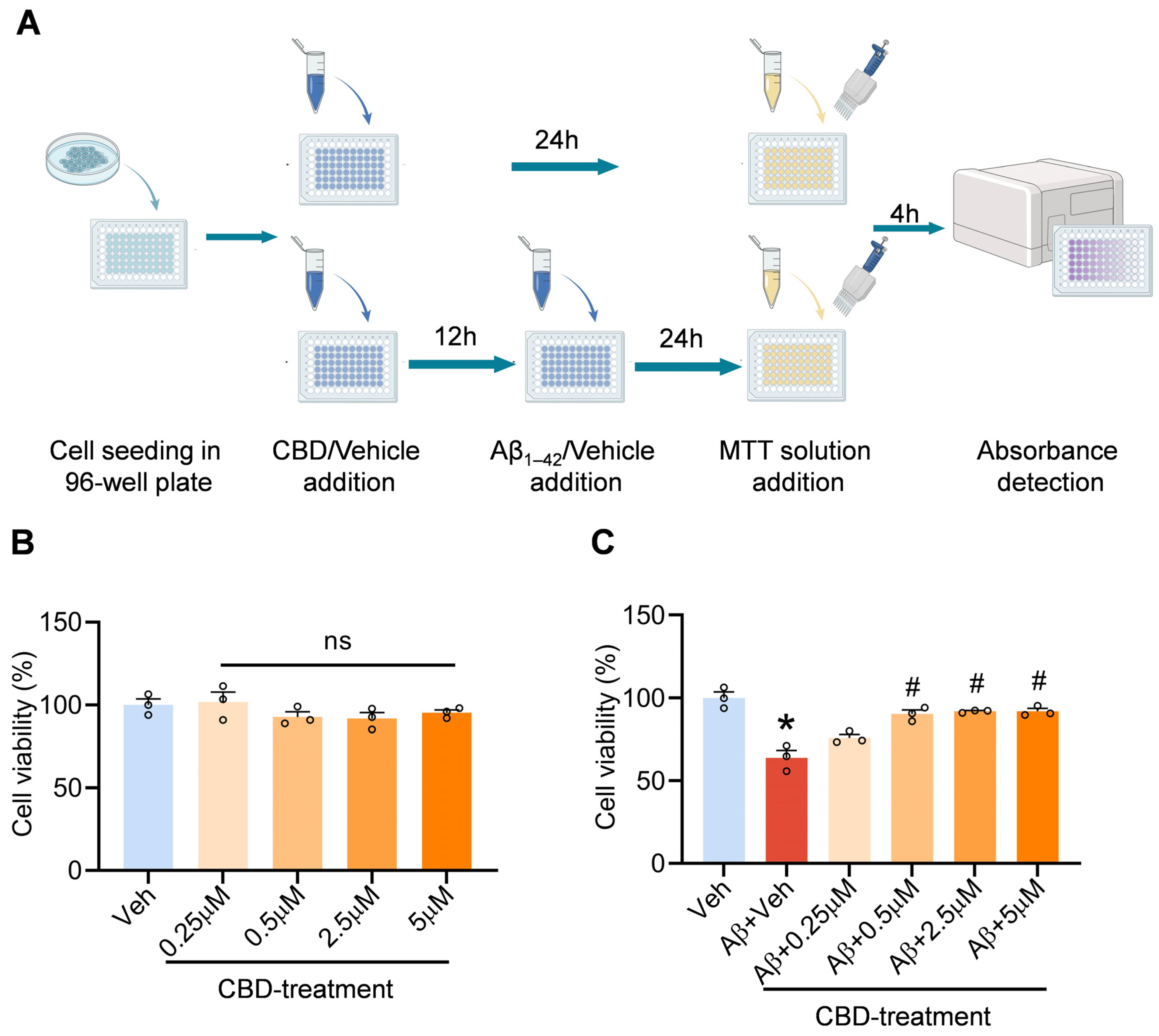
2.1. Cell Culture and Cytotoxicity Test In Vitro
2.2. Animals and Drug Administration
2.3. Morris Water Maze
2.4. RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR
2.5. Immunofluorescence
2.6. RNA-Seq Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. CBD’s Neuroprotective Impact on Aβ-Induced Neuronal Cytotoxicity
3.2. CBD’s Ameliorative Effects on Cognitive Deficits in Aβ1–42-Induced Mice
3.3. Synaptic and Neurotrophic Modulation by CBD in Aβ1–42-Induced Mice
3.4. CBD’s Attenuation of Neuroinflammation and Glial Reactivity in Aβ1–42-Induced Mice
3.5. CBD’s Modulation of Inflammatory Pathways and Synaptic Restoration in AD Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knopman, D.S.; Amieva, H.; Petersen, R.C.; Chételat, G.; Holtzman, D.M.; Hyman, B.T.; Nixon, R.A.; Jones, D.T. Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winblad, B.; Amouyel, P.; Andrieu, S.; Ballard, C.; Brayne, C.; Brodaty, H.; Cedazo-Minguez, A.; Dubois, B.; Edvardsson, D.; Feldman, H.; et al. Defeating Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias: A priority for European science and society. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 455–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheltens, P.; De Strooper, B.; Kivipelto, M.; Holstege, H.; Chételat, G.; Teunissen, C.E.; Cummings, J.; van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurd, M.D.; Martorell, P.; Delavande, A.; Mullen, K.J.; Langa, K.M. Monetary costs of dementia in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klyucherev, T.O.; Olszewski, P.; Shalimova, A.A.; Chubarev, V.N.; Tarasov, V.V.; Attwood, M.M.; Syvänen, S.; Schiöth, H.B. Advances in the development of new biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Neurodegener. 2022, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansokho, C.; Heneka, M.T. Neuroinflammatory responses in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neural. Transm. 2018, 125, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.; Yang, L.; Cole, A.; Sun, L.; Chiang, A.C.; Fowler, S.W.; Shim, D.J.; Rodriguez-Rivera, J.; Taglialatela, G.; Jankowsky, J.L.; et al. NFκB-activated astroglial release of complement C3 compromises neuronal morphology and function associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 2015, 85, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Guttenplan, K.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Bennett, F.C.; Bohlen, C.J.; Schirmer, L.; Bennett, M.L.; Münch, A.E.; Chung, W.S.; Peterson, T.C.; et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 2017, 541, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyman, M.; Lloyd, D.G.; Ji, X.; Vizcaychipi, M.P.; Ma, D. Neuroinflammation: The role and consequences. Neurosci. Res. 2014, 79, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Beja-Glasser, V.F.; Nfonoyim, B.M.; Frouin, A.; Li, S.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Merry, K.M.; Shi, Q.; Rosenthal, A.; Barres, B.A.; et al. Complement and microglia mediate early synapse loss in Alzheimer mouse models. Science 2016, 352, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, E.B. History of cannabis and its preparations in saga, science, and sobriquet. Chem. Biodivers. 2007, 4, 1614–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devinsky, O.; Marsh, E.; Friedman, D.; Thiele, E.; Laux, L.; Sullivan, J.; Miller, I.; Flamini, R.; Wilfong, A.; Filloux, F.; et al. Cannabidiol in patients with treatment-resistant epilepsy: An open-label interventional trial. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, R. The Path to the First FDA-Approved Cannabis-Derived Treatment and What Comes Next. JAMA 2018, 320, 1227–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compton, W.M.; Einstein, E.B. The Need for Evidence Regarding Cannabidiol. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2021067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozela, E.; Juknat, A.; Gao, F.; Kaushansky, N.; Coppola, G.; Vogel, Z. Pathways and gene networks mediating the regulatory effects of cannabidiol, a nonpsychoactive cannabinoid, in autoimmune T cells. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lin, C.; Jin, S.; Wang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wang, X. Cannabidiol alleviates neuroinflammation and attenuates neuropathic pain via targeting FKBP5. Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 111, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallée, A.; Lecarpentier, Y.; Vallée, J.N. Possible actions of cannabidiol in obsessive-compulsive disorder by targeting the WNT/β-catenin pathway. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 230–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, E.; Bonato, J.M.; Mori, M.A.; Mattos, B.A.; Guimarães, F.S.; Milani, H.; de Campos, A.C.; de Oliveira, R.M.W. Cannabidiol Confers Neuroprotection in Rats in a Model of Transient Global Cerebral Ischemia: Impact of Hippocampal Synaptic Neuroplasticity. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 5338–5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neniskyte, U.; Neher, J.J.; Brown, G.C. Neuronal death induced by nanomolar amyloid β is mediated by primary phagocytosis of neurons by microglia. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 39904–39913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardura-Fabregat, A.; Boddeke, E.; Boza-Serrano, A.; Brioschi, S.; Castro-Gomez, S.; Ceyzériat, K.; Dansokho, C.; Dierkes, T.; Gelders, G.; Heneka, M.T.; et al. Targeting Neuroinflammation to Treat Alzheimer’s Disease. CNS Drugs 2017, 31, 1057–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obulesu, M.; Jhansilakshmi, M. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: An understanding of physiology and pathology. Int. J. Neurosci. 2014, 124, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, F.; Edison, P. Neuroinflammation and microglial activation in Alzheimer disease: Where do we go from here? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Li, X. Asiaticoside Mitigates Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology by Attenuating Inflammation and Enhancing Synaptic Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, C.; Ettcheto, M.; Bicker, J.; Fernandes, M.J.; Falcão, A.; Camins, A.; Fortuna, A. Under the umbrella of depression and Alzheimer’s disease physiopathology: Can cannabinoids be a dual-pleiotropic therapy? Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 90, 101998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watt, G.; Karl, T. In vivo Evidence for Therapeutic Properties of Cannabidiol (CBD) for Alzheimer’s Disease. Front Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shen, D.; Zhu, Z.; Lyu, D.; He, C.; Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, Q.; Wang, G. Dual roles of demethylation in cancer treatment and cardio-function recovery. Redox Biol. 2023, 64, 102785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oveisgharan, S.; Wilson, R.S.; Yu, L.; Schneider, J.A.; Bennett, D.A. Association of Early-Life Cognitive Enrichment with Alzheimer Disease Pathological Changes and Cognitive Decline. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henstridge, C.M.; Hyman, B.T.; Spires-Jones, T.L. Beyond the neuron-cellular interactions early in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 20, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobili, A.; Latagliata, E.C.; Viscomi, M.T.; Cavallucci, V.; Cutuli, D.; Giacovazzo, G.; Krashia, P.; Rizzo, F.R.; Marino, R.; Federici, M.; et al. Dopamine neuronal loss contributes to memory and reward dysfunction in a model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thambisetty, M.; Howard, R.; Glymour, M.M.; Schneider, L.S. Alzheimer’s drugs: Does reducing amyloid work? Science 2021, 374, 544–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Bestard-Lorigados, I.; Song, W. The synapse as a treatment avenue for Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 2940–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canter, R.G.; Penney, J.; Tsai, L.H. The road to restoring neural circuits for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2016, 539, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salpietro, V.; Dixon, C.L.; Guo, H.; Bello, O.D.; Vandrovcova, J.; Efthymiou, S.; Maroofian, R.; Heimer, G.; Burglen, L.; Valence, S.; et al. AMPA receptor GluA2 subunit defects are a cause of neurodevelopmental disorders. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, R.; Hayashi, Y.; Hell, J.W. CaMKII: A central molecular organizer of synaptic plasticity, learning and memory. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2022, 23, 666–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Q.; Xie, W.; Liu, Z.; Geng, D.; Wang, L. Circ-Vps41 positively modulates Syp and its overexpression improves memory ability in aging mice. Front Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 1037912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustos, F.J.; Ampuero, E.; Jury, N.; Aguilar, R.; Falahi, F.; Toledo, J.; Ahumada, J.; Lata, J.; Cubillos, P.; Henríquez, B.; et al. Epigenetic editing of the Dlg4/PSD95 gene improves cognition in aged and Alzheimer’s disease mice. Brain 2017, 140, 3252–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.J.; Watson, J.J.; Shoemark, D.K.; Barua, N.U.; Patel, N.K. GDNF, NGF and BDNF as therapeutic options for neurodegeneration. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 138, 155–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Liu, G.; Peng, W.; He, J.; Cai, C.; Xiong, W.; Chen, S.; Yang, M.; Dong, Z. Combined deficiency of SLAMF8 and SLAMF9 prevents endotoxin-induced liver inflammation by downregulating TLR4 expression on macrophages. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paushter, D.H.; Du, H.; Feng, T.; Hu, F. The lysosomal function of progranulin, a guardian against neurodegeneration. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 136, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Chen, J.; Keep, R.F.; Xi, G.; Hua, Y. Prx2 (Peroxiredoxin 2) as a Cause of Hydrocephalus After Intraventricular Hemorrhage. Stroke 2020, 51, 1578–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, R.; van der Lee, S.J.; Naj, A.C.; Bellenguez, C.; Badarinarayan, N.; Jakobsdottir, J.; Kunkle, B.W.; Boland, A.; Raybould, R.; Bis, J.C.; et al. Rare coding variants in PLCG2, ABI3, and TREM2 implicate microglial-mediated innate immunity in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreone, B.J.; Przybyla, L.; Llapashtica, C.; Rana, A.; Davis, S.S.; van Lengerich, B.; Lin, K.; Shi, J.; Mei, Y.; Astarita, G.; et al. Alzheimer’s-associated PLCγ2 is a signaling node required for both TREM2 function and the inflammatory response in human microglia. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, G.; Shimizu, T.; Ikenaka, K.; Fan, K.; Ma, J. Cathepsin C promotes microglia M1 polarization and aggravates neuroinflammation via activation of Ca(2+)-dependent PKC/p38MAPK/NF-κB pathway. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Wu, X.; Fan, B.; Li, N.; Lin, Y.; Yao, Y.; Ma, J. Up-regulation of microglial cathepsin C expression and activity in lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, A.S.; Jenkins, M.A.; Banke, T.G.; Schousboe, A.; Makino, Y.; Johnson, R.C.; Huganir, R.; Traynelis, S.F. Mechanism of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II regulation of AMPA receptor gating. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Yuan, B.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Cui, R.; Yang, W.; Li, B. Emerging role of AMPA receptor subunit GluA1 in synaptic plasticity: Implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Prolif. 2021, 54, e12959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagahara, A.H.; Merrill, D.A.; Coppola, G.; Tsukada, S.; Schroeder, B.E.; Shaked, G.M.; Wang, L.; Blesch, A.; Kim, A.; Conner, J.M.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rodent and primate models of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla, S.; Suñol, C.; García-Mesa, Y.; Giménez-Llort, L.; Sanfeliu, C.; Cristòfol, R. Physical exercise improves synaptic dysfunction and recovers the loss of survival factors in 3xTg-AD mouse brain. Neuropharmacology 2014, 81, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla, S.; Ursulet, S.; Álvarez-López, M.J.; Castro-Freire, M.; Perpiñá, U.; García-Mesa, Y.; Bortolozzi, A.; Giménez-Llort, L.; Kaliman, P.; Cristòfol, R.; et al. Lenti-GDNF gene therapy protects against Alzheimer’s disease-like neuropathology in 3xTg-AD mice and MC65 cells. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2014, 20, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budni, J.; Bellettini-Santos, T.; Mina, F.; Garcez, M.L.; Zugno, A.I. The involvement of BDNF, NGF and GDNF in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Aging Dis. 2015, 6, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberlin, L.E.; Erickson, K.I.; Mackey, R.; Klunk, W.E.; Aizenstein, H.; Lopresti, B.J.; Kuller, L.H.; Lopez, O.L.; Snitz, B.E. Peripheral inflammatory biomarkers predict the deposition and progression of amyloid-β in cognitively unimpaired older adults. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 95, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rego, S.; Sanchez, G.; Da Mesquita, S. Current views on meningeal lymphatics and immunity in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2023, 18, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesworth, R.; Cheng, D.; Staub, C.; Karl, T. Effect of long-term cannabidiol on learning and anxiety in a female Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 931384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, A.J.; Downey, L.A.; Manning, B.; Hayley, A.C. Cannabinoid treatments for anxiety: A systematic review and consideration of the impact of sleep disturbance. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 143, 104941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Wang, S.; Yu, D.; Lu, X.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Z.; Yan, C. Cannabidiol prevents depressive-like behaviors through the modulation of neural stem cell differentiation. Front. Med. 2022, 16, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadoon, K.A.; Ratcliffe, S.H.; Barrett, D.A.; Thomas, E.L.; Stott, C.; Bell, J.D.; O’Sullivan, S.E.; Tan, G.D. Efficacy and Safety of Cannabidiol and Tetrahydrocannabivarin on Glycemic and Lipid Parameters in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel Group Pilot Study. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1777–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, M.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Bátkai, S.; Patel, V.; Saito, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Kashiwaya, Y.; Horváth, B.; Mukhopadhyay, B.; Becker, L.; et al. Cannabidiol attenuates cardiac dysfunction, oxidative stress, fibrosis, and inflammatory and cell death signaling pathways in diabetic cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 2115–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, G.; Scuderi, C.; Valenza, M.; Togna, G.I.; Latina, V.; De Filippis, D.; Cipriano, M.; Carratù, M.R.; Iuvone, T.; Steardo, L. Cannabidiol reduces Aβ-induced neuroinflammation and promotes hippocampal neurogenesis through PPARγ involvement. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Gene | Primer Forward (3′ → 5′) | Primer Reverse (3′ → 5′) |
|---|---|---|
| Bdnf | TCATACTTCGGTTGCATGAAGG | AGACCTCTCGAACCTGCCC |
| Camk2α | ACCTGCACCCGATTCACAG | TGGCAGCATACTCCTGACCA |
| Camk2β | TCACCGACGAGTACCAGCTA | GGCAGATCCGAGCTTCTCTC |
| Ctsc | CCAACTGCACCTATCTTGACC | AAGGCAAACCACTTGTAGTCATT |
| Dlg4 | TGAGATCAGTCATAGCAGCTACT | CTTCCTCCCCTAGCAGGTCC |
| Dusp10 | CCATCTCCTTTAGACGACAGGG | GCTACCACTACCTGGGCTG |
| Gapdh | TGGCCTTCCGTGTTCCTAC | GAGTTGCTGTTGAAGTCGCA |
| Gdnf | TCCAACTGGGGGTCTACGG | GCCACGACATCCCATAACTTCAT |
| Glua1 | TCCCCAACAATATCCAGATAGGG | AAGCCGCATGTTCCTGTGATT |
| Glua2 | TTCTCCTGTTTTATGGGGACTGA | CTACCCGAAATGCACTGTATTCT |
| Grn | ATGTGGGTCCTGATGAGCTG | GCTCGTTATTCTAGGCCATGTG |
| Lbp | GATCACCGACAAGGGCCTG | GGCTATGAAACTCGTACTGCC |
| Lrrk2 | GATCTCTGCACTCAGCTGTTTA | GCTTCTCACTGTCTTCCTCTTC |
| Mcp-1 | GCATCCACGTGTTGGCTC | CTCCAGCCTACTCATTGGGATCA |
| Mmp8 | CCAAGGAGTGTCCAAGCCAT | CCTGCAGGAAAACTGCATCG |
| Ncf1 | ACACCTTCATTCGCCATATTGC | TCGGTGAATTTTCTGTAGACCAC |
| Nupr1 | TCAACAGATGTCGGGGGAGA | TCTGCAGTGTGGGGCTTATG |
| Plcg2 | CCGACTCTTACGCCATCA | GGGTAGCGAAGCCTCATC |
| Prdx2 | GGTAACGCGCAAATCGGAAAG | TCCAGTGGGTAGAAAAAGAGGT |
| Rps19 | CAGCAGGAGTTCGTCAGAGC | CACCCATTCGGGGACTTTCA |
| Slamf8 | TCTCCTTCCCGTTGTGGTTG | CCAGATAGCCTCACGCACTTG |
| Stap1 | CGGTCAGGATACCGGGAGTA | GCTCAGTAAGGCATGTGAGGT |
| Syp | GAGAGAACAACAAAGGGCCAA | GCGGATGAGCTAACTAGCCAC |
| Tnf-α | CCCTCACACTCAGATCATCTTCT | GCTACGACGTGGGCTACAG |
| Ttbk1 | ATCCTGGAGTCCATTGAAGC | GCTAGCCCAAAGTCCAACAT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Ding, H.; Wang, G.; Li, X. Assessing Cannabidiol as a Therapeutic Agent for Preventing and Alleviating Alzheimer’s Disease Neurodegeneration. Cells 2023, 12, 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12232672
Chen L, Sun Y, Li J, Liu S, Ding H, Wang G, Li X. Assessing Cannabidiol as a Therapeutic Agent for Preventing and Alleviating Alzheimer’s Disease Neurodegeneration. Cells. 2023; 12(23):2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12232672
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Long, Yuan Sun, Jinran Li, Sai Liu, Hancheng Ding, Guangji Wang, and Xinuo Li. 2023. "Assessing Cannabidiol as a Therapeutic Agent for Preventing and Alleviating Alzheimer’s Disease Neurodegeneration" Cells 12, no. 23: 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12232672
APA StyleChen, L., Sun, Y., Li, J., Liu, S., Ding, H., Wang, G., & Li, X. (2023). Assessing Cannabidiol as a Therapeutic Agent for Preventing and Alleviating Alzheimer’s Disease Neurodegeneration. Cells, 12(23), 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12232672






