Inward Operation of Sodium-Bicarbonate Cotransporter 1 Promotes Astrocytic Na+ Loading and Loss of ATP in Mouse Neocortex during Brief Chemical Ischemia
Abstract
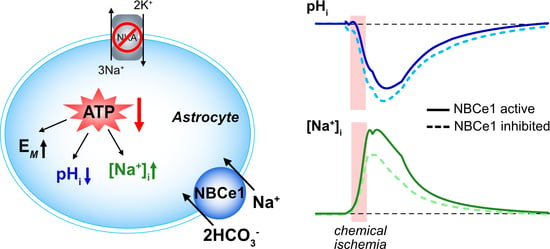
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Organotypic Slice Cultures
2.2. Imaging of Intracellular pH and Na+
2.3. FRET-Based Imaging of Intracellular ATP
2.4. Measurement of Extracellular K+, pH, and Na+
2.5. Patch-Clamp Recordings
2.6. Modeling NBCe1 Activity
2.7. Numerical Methods
2.8. Data Analysis and Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Probing NBCe1 Activity in Organotypic Slice Cultures
3.2. Role of NBCe1 Activity in Astrocytic Ion Changes during Brief Chemical Ischemia
3.3. Modeling Ion Dynamics and NBCe1 Activity during Transient Energy Deprivation
3.4. NBCe1 Activity and ATP Consumption in Astrocytes
4. Discussion
4.1. NBCe1 Activity Influences Astrocytic pHi and [Na+]i
4.2. Operation of NBCe1 during Brief Chemical Ischemia
4.3. Possible Consequences of NBCe1 Activity in the Ischemic Brain
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Model Equations and Parameters

| Parameter | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| γv | Scaling factor for membrane potential | 1970 mV μM−1 |
| VRsa | Volume ratio between the ECS and astrocyte | 3 |
| VT | Voltage constant in Nernst equation | 26.7 mV |
| GK | Peak conductance of K+ channels | 2072.3 μM mV−1 s−1 |
| GNa | Peak conductance of Na+ channels | 68.08 μM mV−1 s−1 |
| GNBCe1 | Peak conductance of NBCe1 | 392.22 μM mV−1 s−1 |
| GNHE | Peak conductance of NHE | GNBCe1 |
| JNaKmax | Maximum flux through NKA | 4.26 × 104 µM s−1 |
| KNa | Association constant for Na+ to NKA | 10 × 103 µM |
| KKo | Association constant for K+ to NKA | 1.5 × 103 µM |
| diff | Diffusion constant of Na+, K+, and pH | 0.5 s−1 |
| βi | Intracellular intrinsic buffering capacity | 25 mM/pH unit |
| βo | Extracellular intrinsic buffering capacity | 10.5 mM/pH unit |
| pKa | Negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant of carbonic acid | 6.1 |
| s | Solubility of CO2 | 2.25 × 10−4 mM Pa−1 |
| PCO2 | Partial pressure of CO2 | 5332.9 Pa |
| Kh | Dissociation constant of CO2 | 800 nmol L−1 |
| Parameter | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| [Na+]o | Extracellular Na+ concentration | 157 mM |
| [Na+]i | Intracellular Na+ concentration | 12 mM |
| [K+]o | Extracellular K+ concentration | 2.5 mM |
| [K+]i | Intracellular K+ concentration | 146 mM |
| Vi | Intracellular membrane potential | −83 mV |
| pHo | Extracellular pH value | 7.35 |
| pHi | Intracellular pH value | 7.32 |
| Parameter | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline value of [K+]bath | 2.5 mM | |
| k1 | −0.002675 s−1 | |
| k2 | −2 | |
| k3 | −0.0052 s−1 | |
| k4 | 1.350 | |
| k5 | 0.73 | |
| k6 | −0.00169 | |
| k7 | 7.6 | |
| k8 | −1.02 | |
| Baseline value of [Na+]bath | 157 mM | |
| p1 | −1.1906 × 10−26 s−1 | |
| p2 | 5.045 × 10−23 s−1 | |
| p3 | −8.122 × 10−20 s−1 | |
| p4 | 5.6637 × 10−17 s−1 | |
| p5 | −7.006 × 10−15 s−1 | |
| p6 | −1.3156 × 10−11 s−1 | |
| p7 | 7.521 × 10−9 s−1 | |
| p8 | −1.326 × 10−6 s−1 | |
| p9 | 3.51 × 10−6 s−1 | |
| p10 | 1.0005 | |
| Baseline value of | 7.35 − 5.4275 × 10−19 s−1 | |
| p1 | −4.7273 × 10−26 s−1 | |
| p2 | 2.47264 × 10−22 s−1 | |
| p3 | −5.4275 × 10−19 s−1 | |
| p4 | 6.4515 × 10−16 s−1 | |
| p5 | −4.4486 × 10−13 s−1 | |
| p6 | 1/7487 s−10 | |
| p7 | −3.4571 s−8 | |
| p8 | 2.0687 × 10−6 s−1 | |
| p9 | 1.0069 × 10−4 s−1 | |
| p10 | 0.9999 |
| Parameter | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| a1 | Parameter in sigmoidal function | 1000 |
| b1 | Parameter in sigmoidal function | 0.0022134 s−1 |
| c1 | Parameter in sigmoidal function | 0 |
| t0 | Beginning of pump inhibition | 300 s |
| a2 | Parameter in sigmoidal function | 1.52 |
| b2 | Parameter in sigmoidal function | −0.02014 s−1 |
| c2 | Parameter in sigmoidal function | 5.738 |
| d | Intercept parameter in sigmoidal functions | 1.13 |
References
- Kofuji, P.; Newman, E.A. Potassium buffering in the central nervous system. Neuroscience 2004, 129, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, B.R.; Stoica, A.; MacAulay, N. Managing Brain Extracellular K+ during Neuronal Activity: The Physiological Role of the Na+/K+-ATPase Subunit Isoforms. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, I.A.; Erecinska, M. Energetic demands of the Na+/K+ ATPase in mammalian astrocytes. Glia 1997, 21, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, C.R.; Verkhratsky, A. Principles of sodium homeostasis and sodium signalling in astroglia. Glia 2016, 64, 1611–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danbolt, N.C. Glutamate uptake. Prog. Neurobiol. 2001, 65, 1–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schousboe, A.; Sarup, A.; Bak, L.K.; Waagepetersen, H.S.; Larsson, O.M. Role of astrocytic transport processes in glutamatergic and GABAergic neurotransmission. Neurochem. Int. 2004, 45, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somjen, G.G. Ions in the Brain: Normal Function, Seizures, and Stroke; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dirnagl, U.; Iadecola, C.; Moskowitz, M.A. Pathobiology of ischaemic stroke: An integrated view. Trends Neurosci. 1999, 22, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Putten, M.J.A.M.; Fahlke, C.; Kafitz, K.W.; Hofmeijer, J.; Rose, C.R. Dysregulation of astrocyte ion homeostasis and its relevance for stroke-induced brain damage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerkau, N.J.; Rakers, C.; Durry, S.; Petzold, G.C.; Rose, C.R. Reverse NCX Attenuates Cellular Sodium Loading in Metabolically Compromised Cortex. Cereb. Cortex 2018, 28, 4264–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrobon, D.; Moskowitz, M.A. Chaos and commotion in the wake of cortical spreading depression and spreading depolarizations. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.J.; Oshima, T.; Attwell, D. Glutamate release in severe brain ischaemia is mainly by reversed uptake. Nature 2000, 403, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karus, C.; Mondragao, M.A.; Ziemens, D.; Rose, C.R. Astrocytes restrict discharge duration and neuronal sodium loads during recurrent network activity. Glia 2015, 63, 936–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, T.; Kafitz, K.W.; Roderigo, C.; Rose, C.R. Ammonium-evoked alterations in intracellular sodium and pH reduce glial glutamate transport activity. Glia 2009, 57, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemens, D.; Oschmann, F.; Gerkau, N.J.; Rose, C.R. Heterogeneity of activity-induced sodium transients between astrocytes of the mouse hippocampus and neocortex: Mechanisms and consequences. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 2620–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, C.R.; Ziemens, D.; Verkhratsky, A. On the special role of NCX in astrocytes: Translating Na+-transients into intracellular Ca2+ signals. Cell Calcium 2020, 86, 102154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziato, L.; Boscia, F.; Pignataro, G. Ionic transporter activity in astrocytes, microglia, and oligodendrocytes during brain ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Luo, L.; Sun, B.; Sun, D. Roles of glial ion transporters in brain diseases. Glia 2020, 68, 472–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, M.D.; Boron, W.F. The divergence, actions, roles, and relatives of sodium-coupled bicarbonate transporters. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 803–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevensee, M.O.; Boron, W.F. Effects of acute hypoxia on intracellular-pH regulation in astrocytes cultured from rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 2008, 1193, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deitmer, J.W.; Rose, C.R. Ion changes and signalling in perisynaptic glia. Brain Res. Rev. 2010, 63, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesler, M. Regulation and modulation of pH in the brain. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 1183–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatton, J.Y.; Magistretti, P.J.; Barros, L.F. Sodium signaling and astrocyte energy metabolism. Glia 2016, 64, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deitmer, J.W.; Theparambil, S.M.; Ruminot, I.; Noor, S.I.; Becker, H.M. Energy Dynamics in the Brain: Contributions of Astrocytes to Metabolism and pH Homeostasis. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, L.F.; Ruminot, I.; Sotelo-Hitschfeld, T.; Lerchundi, R.; Fernandez-Moncada, I. Metabolic Recruitment in Brain Tissue. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2023, 85, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaman, I.; Belanger, M.; Magistretti, P.J. Astrocyte-neuron metabolic relationships: For better and for worse. Trends Neurosci. 2011, 34, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, C.R.; Ransom, B.R. Intracellular sodium homeostasis in rat hippocampal astrocytes. J. Physiol. 1996, 491, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, Z.N.; Deitmer, J.W.; Theparambil, S.M. Cytosolic sodium regulation in mouse cortical astrocytes and its dependence on potassium and bicarbonate. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 234, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornell, I.M.; Bevensee, M.O. Regulators of Slc4 bicarbonate transporter activity. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theparambil, S.M.; Hosford, P.S.; Ruminot, I.; Kopach, O.; Reynolds, J.R.; Sandoval, P.Y.; Rusakov, D.A.; Barros, L.F.; Gourine, A.V. Astrocytes regulate brain extracellular pH via a neuronal activity-dependent bicarbonate shuttle. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraig, R.P.; Pulsinelli, W.A.; Plum, F. Carbonic acid buffer changes during complete brain ischemia. Am. J. Physiol. 1986, 250, R348–R357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menyhart, A.; Zolei-Szenasi, D.; Puskas, T.; Makra, P.; Orsolya, M.T.; Szepes, B.E.; Toth, R.; Ivankovits-Kiss, O.; Obrenovitch, T.P.; Bari, F.; et al. Spreading depolarization remarkably exacerbates ischemia-induced tissue acidosis in the young and aged rat brain. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, H.; Huynh Nhat, K.P.; Togawa, H.; Saito, K.; Iino, R.; Kato-Yamada, Y.; Nagai, T.; Noji, H. Visualization of ATP levels inside single living cells with fluorescence resonance energy transfer-based genetically encoded indicators. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 15651–15656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawenis, L.R.; Bradford, E.M.; Prasad, V.; Lorenz, J.N.; Simpson, J.E.; Clarke, L.L.; Woo, A.L.; Grisham, C.; Sanford, L.P.; Doetschman, T.; et al. Colonic anion secretory defects and metabolic acidosis in mice lacking the NBC1 Na+/HCO3− cotransporter. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 9042–9052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, J.; Rose, C.R. Synaptically induced sodium signals in hippocampal astrocytes in situ. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 5859–5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoppini, L.; Buchs, P.A.; Muller, D. A simple method for organotypic cultures of nervous tissue. J. Neurosci. Methods 1991, 37, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerchundi, R.; Kafitz, K.W.; Farfers, M.; Beyer, F.; Huang, N.; Rose, C.R. Imaging of intracellular ATP in organotypic tissue slices of the mouse brain using the FRET-based sensor ATeam1.03YEMK. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2019, 154, e60294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, R.; Heinemann, U. Synaptic reorganization in explanted cultures of rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 1999, 815, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, S.D.; Kovalchuk, Y.; Rose, C.R. Properties of the new fluorescent Na+ indicator CoroNa Green: Comparison with SBFI and confocal Na+ imaging. J. Neurosci. Methods 2006, 155, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, T.; Rose, C.R. Ammonium influx pathways into astrocytes and neurones of hippocampal slices. J. Neurochem. 2010, 115, 1123–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eitelmann, S.; Stephan, J.; Everaerts, K.; Durry, S.; Pape, N.; Gerkau, N.J.; Rose, C.R. Changes in Astroglial K+ upon Brief Periods of Energy Deprivation in the Mouse Neocortex. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerchundi, R.; Kafitz, K.W.; Winkler, U.; Farfers, M.; Hirrlinger, J.; Rose, C.R. FRET-based imaging of intracellular ATP in organotypic brain slices. J. Neurosci. Res. 2019, 97, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haack, N.; Rose, C.R. Preparation, calibration and application of potassium-selective microelectrodes. In Microelectrodes; Lei, K.F., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 87–105. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, K.L. Cell-attached voltage-clamp and current-clamp recording and stimulation techniques in brain slices. J. Neurosci. Methods 2006, 154, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapaliya, P.; Pape, N.; Rose, C.R.; Ullah, A. Modeling the heterogeneity of sodium and calcium homeostasis between cortical and hippocampal astrocytes and its impact on bioenergetics. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1035553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, A.; Plank, M.J.; David, T. Macro scale modelling of cortical spreading depression and the role of astrocytic gap junctions. J. Theor. Biol. 2018, 458, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salameh, A.I.; Hubner, C.A.; Boron, W.F. Role of Cl−–HCO3− exchanger AE3 in intracellular pH homeostasis in cultured murine hippocampal neurons, and in crosstalk to adjacent astrocytes. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 93–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, N.J.; Agarwal, A.K. Metabolic Acidosis and Metabolic Alkalosis. In Textbook of Nephrology, 3rd ed.; Mandal, A.K., Prakash, J., Eds.; Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers: New Delhi, India, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebens, A.W.; Boron, W.F. Depolarization-induced alkalinization in proximal tubules. I. Characteristics and dependence on Na+. Am. J. Physiol. 1989, 256, F342–F353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, C.A.; Ransom, B.R. Depolarization-induced alkalinization (DIA) in rat hippocampal astrocytes. J. Neurophysiol. 1994, 72, 2816–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ch’en, F.F.; Villafuerte, F.C.; Swietach, P.; Cobden, P.M.; Vaughan-Jones, R.D. S0859, an N-cyanosulphonamide inhibitor of sodium-bicarbonate cotransport in the heart. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 972–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.; Gerkau, N.J.; Kafitz, K.W.; Patting, M.; Jolmes, F.; Henneberger, C.; Rose, C.R. Rapid Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Reveals That TRPV4 Channels Promote Dysregulation of Neuronal Na+ in Ischemia. J. Neurosci. 2022, 42, 552–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, T.; Shi, Y.; Xiong, Z.G.; Sun, D. Proton-sensitive cation channels and ion exchangers in ischemic brain injury: New therapeutic targets for stroke? Prog. Neurobiol. 2014, 115, 189–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesler, M. Failure and function of intracellular pH regulation in acute hypoxic-ischemic injury of astrocytes. Glia 2005, 50, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, C.R.; Ransom, B.R. Mechanisms of H+ and Na+ changes induced by glutamate, kainate, and D-Aspartate in rat hippocampal astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 5393–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theparambil, S.M.; Ruminot, I.; Schneider, H.P.; Shull, G.E.; Deitmer, J.W. The electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter NBCe1 is a high-affinity bicarbonate carrier in cortical astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 1148–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, D.; Bevensee, M.O. Na-coupled bicarbonate transporters of the solute carrier 4 family in the nervous system: Function, localization, and relevance to neurologic function. Neuroscience 2010, 171, 951–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickmann, M.; Orlowski, B.; Heupel, K.; Roussa, E. Distinct expression and subcellular localization patterns of Na+/HCO3− cotransporter (SLC 4A4) variants NBCe1-A and NBCe1-B in mouse brain. Neuroscience 2007, 146, 1220–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintner, D.B.; Su, G.; Lenart, B.; Ballard, A.J.; Meyer, J.W.; Ng, L.L.; Shull, G.E.; Sun, D. Increased tolerance to oxygen and glucose deprivation in astrocytes from Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 1 null mice. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2004, 287, C12–C21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, G.; Song, S.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H.; Bhuiyan, M.I.H.; Li, E.; Nepomuceno, R.; Ye, Q.; Sun, M.; Calderon, M.J.; et al. Selective knockout of astrocytic Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 1 reduces astrogliosis, BBB damage, infarction, and improves neurological function after ischemic stroke. Glia 2018, 66, 126–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevensee, M.O.; Apkon, M.; Boron, W.F. Intracellular pH regulation in cultured astrocytes from rat hippocampus. II. Electrogenic Na/HCO3 cotransport. J. Gen. Physiol. 1997, 110, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brune, T.; Fetzer, S.; Backus, K.H.; Deitmer, J.W. Evidence for electrogenic sodium-bicarbonate cotransport in cultured rat cerebellar astrocytes. Pflügers Arch. 1994, 429, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, S.; Su, P.; Xie, Z.D.; Gui, T.X.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.M. Molecular insight into coordination sites for substrates and their coupling kinetics in Na+/HCO3− cotransporter NBCe1. J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 3083–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, M.F. Who’s on first … Na+, HCO3− or CO32−? J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 3005–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turovsky, E.; Theparambil, S.M.; Kasymov, V.; Deitmer, J.W.; Del Arroyo, A.G.; Ackland, G.L.; Corneveaux, J.J.; Allen, A.N.; Huentelman, M.J.; Kasparov, S.; et al. Mechanisms of CO2/H+ Sensitivity of Astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 10750–10758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourine, A.V.; Dale, N. Brain H+/CO2 sensing and control by glial cells. Glia 2022, 70, 1520–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grichtchenko, I.I.; Chesler, M. Depolarization-induced alkalinization of astrocytes in gliotic hippocampal slices. Neuroscience 1994, 62, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theparambil, S.M.; Naoshin, Z.; Thyssen, A.; Deitmer, J.W. Reversed electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter 1 is the major acid loader during recovery from cytosolic alkalosis in mouse cortical astrocytes. J. Physiol. 2015, 593, 3533–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidtmann, H.; Ruminot, I.; Becker, H.M.; Deitmer, J.W. Inhibition of monocarboxylate transporter by N-cyanosulphonamide S0859. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 762, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio, J.A.; Heimrich, B.; Soriano, E.; Schwegler, H.; Frotscher, M. Proliferation and differentiation of glial fibrillary acidic protein-immunoreactive glial cells in organotypic slice cultures of rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 1991, 43, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frotscher, M.; Zafirov, S.; Heimrich, B. Development of identified neuronal types and of specific synaptic connections in slice cultures of rat hippocampus. Prog. Neurobiol. 1995, 45, 143–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benediktsson, A.M.; Schachtele, S.J.; Green, S.H.; Dailey, M.E. Ballistic labeling and dynamic imaging of astrocytes in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. J. Neurosci. Methods 2005, 141, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, M.A.; Lo, E.H.; Iadecola, C. The science of stroke: Mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron 2010, 67, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniele, S.G.; Trummer, G.; Hossmann, K.A.; Vrselja, Z.; Benk, C.; Gobeske, K.T.; Damjanovic, D.; Andrijevic, D.; Pooth, J.S.; Dellal, D.; et al. Brain vulnerability and viability after ischaemia. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2021, 22, 553–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erecinska, M.; Silver, I.A. Ions and energy in mammalian brain. Prog. Neurobiol. 1994, 43, 37–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartings, J.A.; Shuttleworth, C.W.; Kirov, S.A.; Ayata, C.; Hinzman, J.M.; Foreman, B.; Andrew, R.D.; Boutelle, M.G.; Brennan, K.C.; Carlson, A.P.; et al. The continuum of spreading depolarizations in acute cortical lesion development: Examining Leao’s legacy. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2017, 37, 1571–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mies, G.; Paschen, W. Regional changes of blood flow, glucose, and ATP content determined on brain sections during a single passage of spreading depression in rat brain cortex. Exp. Neurol. 1984, 84, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.J.; Brady, J.D.; Mohr, C. Astrocyte metabolism and signaling during brain ischemia. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraig, R.P.; Chesler, M. Astrocytic acidosis in hyperglycemic and complete ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1990, 10, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutch, W.A.; Hansen, A.J. Extracellular pH changes during spreading depression and cerebral ischemia: Mechanisms of brain pH regulation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1984, 4, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, A.J. Effect of anoxia on ion distribution in the brain. Physiol. Rev. 1985, 65, 101–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Azad, P.; Zhao, H.W.; Wang, J.; Poulsen, O.; Freitas, B.C.; Muotri, A.R.; Haddad, G.G. The Na+/HCO3− co-transporter is protective during ischemia in astrocytes. Neuroscience 2016, 339, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarenko, A.; Chesler, M. Rapid astrocyte death induced by transient hypoxia, acidosis, and extracellular ion shifts. Glia 2001, 34, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Jia, M.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Li, C.; Ren, B.; Qian, F.; Wu, J. The electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter and its roles in the myocardial ischemia-reperfusion induced cardiac diseases. Life Sci. 2021, 270, 119153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giffard, R.G.; Papadopoulos, M.C.; van Hooft, J.A.; Xu, L.; Giuffrida, R.; Monyer, H. The electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter: Developmental expression in rat brain and possible role in acid vulnerability. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa-Gonzalez, M.; Martin-Lopez, G.; Perez-Alvarez, M.J. Dysregulation of mTOR Signaling after Brain Ischemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakipoor, S.; Giannaki, M.; Theparambil, S.M.; Zecha, J.; Kuster, B.; Heermann, S.; Deitmer, J.W.; Roussa, E. Functional expression of electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter 1 (NBCe1) in mouse cortical astrocytes is dependent on S255–257 and regulated by mTOR. Glia 2019, 67, 2264–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannaki, M.; Ludwig, C.; Heermann, S.; Roussa, E. Regulation of electrogenic Na+/HCO3− cotransporter 1 (NBCe1) function and its dependence on m-TOR mediated phosphorylation of Ser(245). J. Cell. Physiol. 2022, 237, 1372–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.W.; Choi, I.J.; Kwon, T.H. Altered expression of sodium transporters in ischemic penumbra after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 59, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, Y.; Yoo, K.Y.; Park, O.K.; Kwon, S.H.; Lee, C.H.; Choi, J.H.; Hwang, I.K.; Seo, J.Y.; Cho, J.H.; Won, M.H. Na+/HCO3− cotransporter immunoreactivity changes in neurons and expresses in astrocytes in the gerbil hippocampal CA1 region after ischemia/reperfusion. Neurochem. Res. 2011, 36, 2459–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Jo, J.; Wang, C.-Y.; Oh, H.; Choy, T.J.; Kim, K.; D’Alessandro, A.; Reshetnyak, Y.K.; Jung, S.Y.; Chen, Z.; et al. Astrocytic Slc4a4 regulates blood-brain barrier integrity in healthy and stroke brains via a NO-CCL2-CCR2 pathway. bioRxiv 2023. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, M.O.; Menyhart, A.; Frank, R.; Hantosi, D.; Farkas, E.; Bari, F. Tissue Acidosis Associated with Ischemic Stroke to Guide Neuroprotective Drug Delivery. Biology 2020, 9, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, R.P. Acidotoxicity trumps excitotoxicity in ischemic brain. Arch. Neurol. 2006, 63, 1368–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shono, Y.; Kamouchi, M.; Kitazono, T.; Kuroda, J.; Nakamura, K.; Hagiwara, N.; Ooboshi, H.; Ibayashi, S.; Iida, M. Change in intracellular pH causes the toxic Ca2+ entry via NCX1 in neuron- and glia-derived cells. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2010, 30, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beppu, K.; Sasaki, T.; Tanaka, K.F.; Yamanaka, A.; Fukazawa, Y.; Shigemoto, R.; Matsui, K. Optogenetic countering of glial acidosis suppresses glial glutamate release and ischemic brain damage. Neuron 2014, 81, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, S.A.; Barres, B.A. The Detrimental Role of Glial Acidification during Ischemia. Neuron 2014, 81, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Van Paesschen, W.; Stalmans, I.; Horita, S.; Yamada, H.; Bergmans, B.A.; Legius, E.; Riant, F.; De Jonghe, P.; Li, Y.; et al. Defective membrane expression of the Na+–HCO3− cotransporter NBCe1 is associated with familial migraine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15963–15968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, B.R.; MacAulay, N. Activity-dependent astrocyte swelling is mediated by pH-regulating mechanisms. Glia 2017, 65, 1668–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostby, I.; Oyehaug, L.; Einevoll, G.T.; Nagelhus, E.A.; Plahte, E.; Zeuthen, T.; Lloyd, C.M.; Ottersen, O.P.; Omholt, S.W. Astrocytic mechanisms explaining neural-activity-induced shrinkage of extraneuronal space. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florence, C.M.; Baillie, L.D.; Mulligan, S.J. Dynamic volume changes in astrocytes are an intrinsic phenomenon mediated by bicarbonate ion flux. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacAulay, N. Molecular mechanisms of K+ clearance and extracellular space shrinkage-Glia cells as the stars. Glia 2020, 68, 2192–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Close, B.; Banister, K.; Baumans, V.; Bernoth, E.M.; Bromage, N.; Bunyan, J.; Erhardt, W.; Flecknell, P.; Gregory, N.; Hackbarth, H.; et al. Recommendations for euthanasia of experimental animals: Part 2. DGXT of the European Commission. Lab. Anim. 1997, 31, 137–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Everaerts, K.; Thapaliya, P.; Pape, N.; Durry, S.; Eitelmann, S.; Roussa, E.; Ullah, G.; Rose, C.R. Inward Operation of Sodium-Bicarbonate Cotransporter 1 Promotes Astrocytic Na+ Loading and Loss of ATP in Mouse Neocortex during Brief Chemical Ischemia. Cells 2023, 12, 2675. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12232675
Everaerts K, Thapaliya P, Pape N, Durry S, Eitelmann S, Roussa E, Ullah G, Rose CR. Inward Operation of Sodium-Bicarbonate Cotransporter 1 Promotes Astrocytic Na+ Loading and Loss of ATP in Mouse Neocortex during Brief Chemical Ischemia. Cells. 2023; 12(23):2675. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12232675
Chicago/Turabian StyleEveraerts, Katharina, Pawan Thapaliya, Nils Pape, Simone Durry, Sara Eitelmann, Eleni Roussa, Ghanim Ullah, and Christine R. Rose. 2023. "Inward Operation of Sodium-Bicarbonate Cotransporter 1 Promotes Astrocytic Na+ Loading and Loss of ATP in Mouse Neocortex during Brief Chemical Ischemia" Cells 12, no. 23: 2675. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12232675
APA StyleEveraerts, K., Thapaliya, P., Pape, N., Durry, S., Eitelmann, S., Roussa, E., Ullah, G., & Rose, C. R. (2023). Inward Operation of Sodium-Bicarbonate Cotransporter 1 Promotes Astrocytic Na+ Loading and Loss of ATP in Mouse Neocortex during Brief Chemical Ischemia. Cells, 12(23), 2675. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12232675