Abstract
Gabapentin (GBP), a GABA analogue, is primarily used as an anticonvulsant for the treatment of partial seizures and neuropathic pain. Whereas a majority of the side effects are associated with the nervous system, emerging evidence suggests there is a high risk of heart diseases in patients taking GBP. In the present study, we first used a preclinical model of rats to investigate, firstly, the acute cardiovascular responses to GBP (bolus i.v. injection, 50 mg/kg) and secondly the effects of chronic GBP treatment (i.p. 100 mg/kg/day × 7 days) on cardiovascular function and the myocardial proteome. Under isoflurane anesthesia, rat blood pressure (BP), heart rate (HR), and left ventricular (LV) hemodynamics were measured using Millar pressure transducers. The LV myocardium and brain cortex were analyzed by proteomics, bioinformatics, and western blot to explore the molecular mechanisms underlying GBP-induced cardiac dysfunction. In the first experiment, we found that i.v. GBP significantly decreased BP, HR, maximal LV pressure, and maximal and minimal dP/dt, whereas it increased IRP-AdP/dt, Tau, systolic, diastolic, and cycle durations (* p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 vs. baseline; n = 4). In the second experiment, we found that chronic GBP treatment resulted in hypotension, bradycardia, and LV systolic dysfunction, with no change in plasma norepinephrine. In the myocardium, we identified 109 differentially expressed proteins involved in calcium pathways, cholesterol metabolism, and galactose metabolism. Notably, we found that calmodulin, a key protein of intracellular calcium signaling, was significantly upregulated by GBP in the heart but not in the brain. In summary, we found that acute and chronic GBP treatments suppressed cardiovascular function in rats, which is attributed to abnormal calcium signaling in cardiomyocytes. These data reveal a novel side effect of GBP independent of the nervous system, providing important translational evidence to suggest that GBP can evoke adverse cardiovascular events by depression of myocardial function.
1. Introduction
Gabapentin (GBP) is a 3,3-disubstituted derivative of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). It is recommended as a first-line treatment for chronic neuropathic pain, particularly in diabetic neuropathy and post-herpetic neuralgia [1], and as an anticonvulsant to help control partial seizures in the treatment of epilepsy [2]. GBP is also used to treat an array of other central nervous system-associated disorders, including insomnia, drug and alcohol addiction, anxiety, bipolar disorder, borderline personality disorder, menopausal conditions, vertigo, pruritic disorders, and migraines [3]. However, increasing evidence indicates that GBP is misused and abused, with various side effects such as central hypoventilation, deficits in visual field, suicidal behavior, somnolence, dizziness, mood changes, and tiredness [4].
Although most GBP therapeutic side effects are evoked by alterations in neural function, clinical and animal studies increasingly suggest there are non-neural effects that directly act on peripheral tissues and organs, particularly the cardiovascular system. Designed as an analog of GABA, GBP binds with high affinity to the α2δ subunits of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels (VGCCs) [5] and reduces the high-threshold Ca2+ currents of presynaptic membranes. This leads to the inhibition of the release of the excitatory amino acids glutamate and aspartate [1]. Since the α2δ subunits are expressed in all subtypes of VGCCs [6], which are present not only in neurons but also in all other excitable cells (including skeletal muscle, vascular smooth muscle, and ventricular myocytes) [7], the influence that GBP has on the functioning of non-nervous systems and its relevant side effects should not be ignored.
Indeed, a retrospective cohort study revealed a significantly increased risk of adverse cardiovascular events, including heart failure, myocardial infarction, peripheral vascular disease, stroke, deep venous thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism in patients with diabetic neuropathy following long-term use of GBP [8]. Furthermore, several clinical cases of GBP-induced atrial fibrillation [9], acute heart failure [10,11], cardiomyopathy [12], and intraoperative hypotension [13] have been reported recently. Thus, we postulate that these events may be attributed, in part, to the effects of GBP on Ca2+ currents in cardiomyocytes or vascular smooth muscles.
Evidence from animal studies suggest that GBP can impact cardiovascular function by both central and peripheral mechanisms. Chen et al. [14] found that microinjecting GBP into the nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) of the brainstem induced prominent dose-related depressor and bradycardic responses in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) via nitric oxide (NO)-dependent mechanisms. Behuliak et al. [15] demonstrated that acute intravenous injections of GBP lowered blood pressure and heart rate by a sympatho-inhibitory mechanism in both SHR and normotensive rats (WKY), with more pronounced effects observed in the former. Interestingly, by utilizing pressure arteriography and whole-cell voltage-clamp techniques, Largeau et al. [16] found that GBP dramatically decreased the myogenic tone of isolated mesenteric arteries and evoked weak vasodilation in endothelium-denuded vessels, but it had no significant effect on Cav1.2 currents in ventricular cardiomyocytes. These studies suggest that GBP-induced peripheral edema and acute heart failure may be due to the effects of GBP on heart and blood vessels. However, to the best of our knowledge, no studies have investigated GBP’s influence on left ventricular (LV) function in intact animals. In the present study, we evaluated the effects of acute and chronic administration of GBP on hemodynamics in isoflurane-anesthetized rats to address the hypothesis that GBP can suppress cardiac function. In addition, we performed label-free mass spectrometry-based proteomics of the LV myocardium followed by bioinformatic analysis to explore the molecular mechanisms and intracellular pathways underlying the GBP effects on cardiomyocytes.
2. Materials and Methods
All animal procedures were conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and conformed to ARRIVE Guidelines (https://www.nc3rs.org.uk/arrive-guidelines, accessed on 9 May 2023), as approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of Nebraska Medical Centre (UNMC-IACUC Protocol #17-080-09).
Eighteen Fisher 344 rats (3–4 months old), which included both sexes, were assigned to two groups. Group 1 (4 rats) was used to determine the acute cardiovascular responses to a bolus intravenous injection (i.v.) of GBP (50 mg/kg; Gabapentin, PHR1049-1G, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). Group 2 (10 rats) was used to determine the effects of 7 days of intraperitoneal injections (i.p.) of GBP (100 mg/kg) on cardiovascular function and, in addition, determine the proteomic profile of the myocardium.
2.1. Arterial Blood Pressure (AP), Heart Rate (HR), and Left Ventricular (LV) Hemodynamics Measurements
Rats were anesthetized with 3% isoflurane delivered in 100% oxygen, lying on an electric heating pad to maintain body temperature at 37 °C. A PE10 catheter was inserted into the superior vena cava through the right jugular for vein saline supplementation and i.v. injection of GBP. A catheter-tipped transducer (SPR-407, Millar Instruments, Houston, TX, USA) was advanced via the right femoral artery into the abdominal aorta to measure BP and HR, whereas another catheter-tipped transducer (SPR-320NR, Millar Instruments, Houston, TX, USA) was advanced via the right carotid artery into the LV chamber to measure cardiac function. The transducer signals were input into a PowerLab data-acquisition system with sampling rate at 2 k/s, from which the data were monitored, recorded, and saved in a computer by the LabChart 8 software and analyzed using the Blood Pressure Module software v1 (AD Instruments, Colorado Springs, CO, USA) with an average of 50–100 cycles.
2.2. Plasma Norepinephrine Assay
A volume of 300 μL of plasma was used to measure norepinephrine (NE) concentration employing a Norepinephrine Enzyme Immunoassay kit (Labor Diagnostika Nord KG, Nordhorn, Germany), based on the manufacturer’s instructions and performed in duplicates for each sample.
2.3. Proteomics Analysis
(1) Sample preparation for mass spectrometry
The protein concentration was estimated in each sample using a BCA Protein Assay Kit (Pierce). An amount of 100 μg of protein from each sample was diluted to a 100 μL volume with 100 mM of ammonium bicarbonate (ambic). Proteins were reduced with 5 μL of 200 mM tris(2-carboxyethyl) phosphine (TCEP) (1 h incubation, 55 °C) and alkylated with 5 μL of 375 mM iodoacetamide (IAA) (30 min incubation in the dark, room temperature). The reduced and alkylated proteins were purified with acetone precipitation at −20 °C overnight. The next day, protein precipitates were collected by centrifugation at 8000× g for 10 min at 4 °C and pellets were briefly air-dried and resuspended in 100 μL of 50 mM ambic. The protein digestion was carried out using 2.5 μg of trypsin per sample (16 h incubation, 37 °C). The samples were dried out using a speed vacuum and then desalted with C18 spin columns (Pierce). Clean peptides were dried out again with a speed vacuum and resuspended in 100 mM TEAB. The TMT label reagents were equilibrated at room temperature for 10–15 min with the lid sealed, followed by the addition of 42 μL of anhydrous acetonitrile to each of the 0.8 mg TMT label reagents, which was vortexed briefly to make sure the reagents were fully dissolved. The peptides were labeled by adding 42 μL of TMT label reagent to every 100 μL of resuspended peptides and incubated for 1 h at room temperature. Quenching of the reaction was then performed by adding 8 μL of quench buffer to the reaction and incubating for 15 min at room temperature. All labeled peptide samples from the two treatment groups were combined for comparison with the experimental sets containing different tags. The pooled peptide sample was then desalted using high pH reverse-phase HPLC, and the eluted peptides were collected and dried using a speed vac. The dried peptides were finally dissolved in 40 μL 0.1% (v/v) aqueous FA and analyzed using a high-resolution mass spectrometry nano-LC-MS/MS Orbitrap Exploris 480 coupled with a UltiMate 3000 HPLC system (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
(2) LC-MS/MS
An amount of 1.5 μg of each sample was loaded onto a trap column Acclaim PepMap 100 (75 μm × 2 cm C18 LC Columns, Thermo Fisher Scientific) at a flow rate of 4 μL/min, and then separated with a Thermo RSLC Ultimate 3000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific) on a Thermo Easy-Spray PepMap RSLC C18 column (75 μm × 50 cm C-18 2 μm, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) at a flow rate 0.3 μL/min and 50 °C, with a step gradient of 9–25% solvent B (0.1% FA in 80% acetonitrile) for 10–20 min and 25–40% solvent B for 15–120 min, with a 155 min total run time. The MS scan was completed using a detector: Orbitrap resolution 120,000; scan range 350–1800 m/z; RF lens 30%; AGC target 4.0 × 105; maximum injection time 100 ms. The most intense ions with charge states of 2–6 isolated in 3 s cycles were selected in the MS scan for further fragmentation. The MS2 scan parameters set were: activation HCD with 35% normalized collision energy, detected at a mass resolution of 30,000, the AGC target for MS/MS was set at 5.0 × 104, and the ion filling time was set to 60 ms.
(3) Data Analysis
Protein identification was performed by searching MS/MS data against the UniProt database (Rat) in Proteome Discoverer (Thermo Fisher Sci, Waltham, MA, USA, vs. 3.0.), assuming the digestion enzyme trypsin and the 10plex TMT reporter ion MS2 mode as the searching mode. The parameters for Sequest HT were set as follows: enzyme: trypsin, max missed cleavage: 2, precursor mass tolerance: 10 ppm, peptide tolerance: ±0.02 Da, fixed modifications: carbamidomethyl (C); dynamic modifications: oxidation (M), acetyl (N-term) and TMT (K)—229.163 Da. The parameters for the precursor ions quantifier was set as follows: peptides to use unique + razor, precursor abundance based on intensity; normalization mode: total peptide amount; scaling mode: on all average.
2.4. Bioinformatics Analysis
Proteins were recognized as differentially expressed if the p-value of the t-test was ≤0.05 and the absolute fold change was ≥1.5. A gene ontology (GO) analysis of the differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) was conducted using the Cytoscape plug-in, ClueGO [17]. Biological processes and molecular functions were included for the GO enrichment analysis. A canonical pathway analysis was performed using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) software (Ingenuity Systems, Redwood City, CA, USA, www.ingenuity.com, accessed on 8 August 2023) by comparing the DEPs against known canonical pathways (signaling and metabolic) within the IPA knowledgebase. For further analysis, enriched pathways with a Benjamini–Hochberg false discovery rate (FDR) p-value ≤ 0.05 were considered.
2.5. Western Blotting Analysis
Protein isolation from the LV myocardium and brain cortex of saline- and GBP- treated animals was isolated using RIPA buffer (50 mM TrisHCl, 195 mM NaCl, 2 mM EDTA, 1% NP-40, 0.1% SDS) with 1% protease inhibitor cocktail (ab65621 Abcam, Cambridge, UK) and then centrifuged at 20,000× g × 20 min at 4 °C. The protein concentration was estimated using the Pierce bicinchoninic acid assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). An amount of 10 μg and 5 μg of proteins from the LV myocardium and brain cortex of each animal were loaded separately onto a 10% Bis-Tris wells (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) under reducing conditions, then transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane using iBlot2 (Invitrogen). Post transfer, the membranes were stained with Ponceau S stain (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) to assess for equal protein loading detection and quantification. The membranes were treated on a rocker for 1 h at room temperature with 5% fat free milk to block nonspecific antibody binding. After blocking, the membranes were incubated overnight at 4 °C with 1:1000 calmodulin (CaM) antibody (A4885; ABclonal, Woburn, MA, USA). The next day, the membranes were washed and treated with 1:2500 HRP conjugated anti-rabbit IgG for 1 h followed by additional washes. Blots were developed with 1:1 solution of Radiance Chemiluminescent Substrate and Luminol/Enhancer (Azure Biosystems, Dublin, CA, USA). G:BOX CHEMI XRQ imaging system (Syngene, Frederick, MD, USA) was used to visualize the blots, and the images acquired were quantified using the Image-J software version 1.52a.
2.6. Statistical Analyses
All data are expressed as mean ± SD. Student’s t-test was used to compare the difference between the 2 groups, with the aid of Prism 8 software. A p value of <0.05 was taken as indicative of statistical significance.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Acute Bolus Intravenous Injection of GBP on Cardiovascular Function
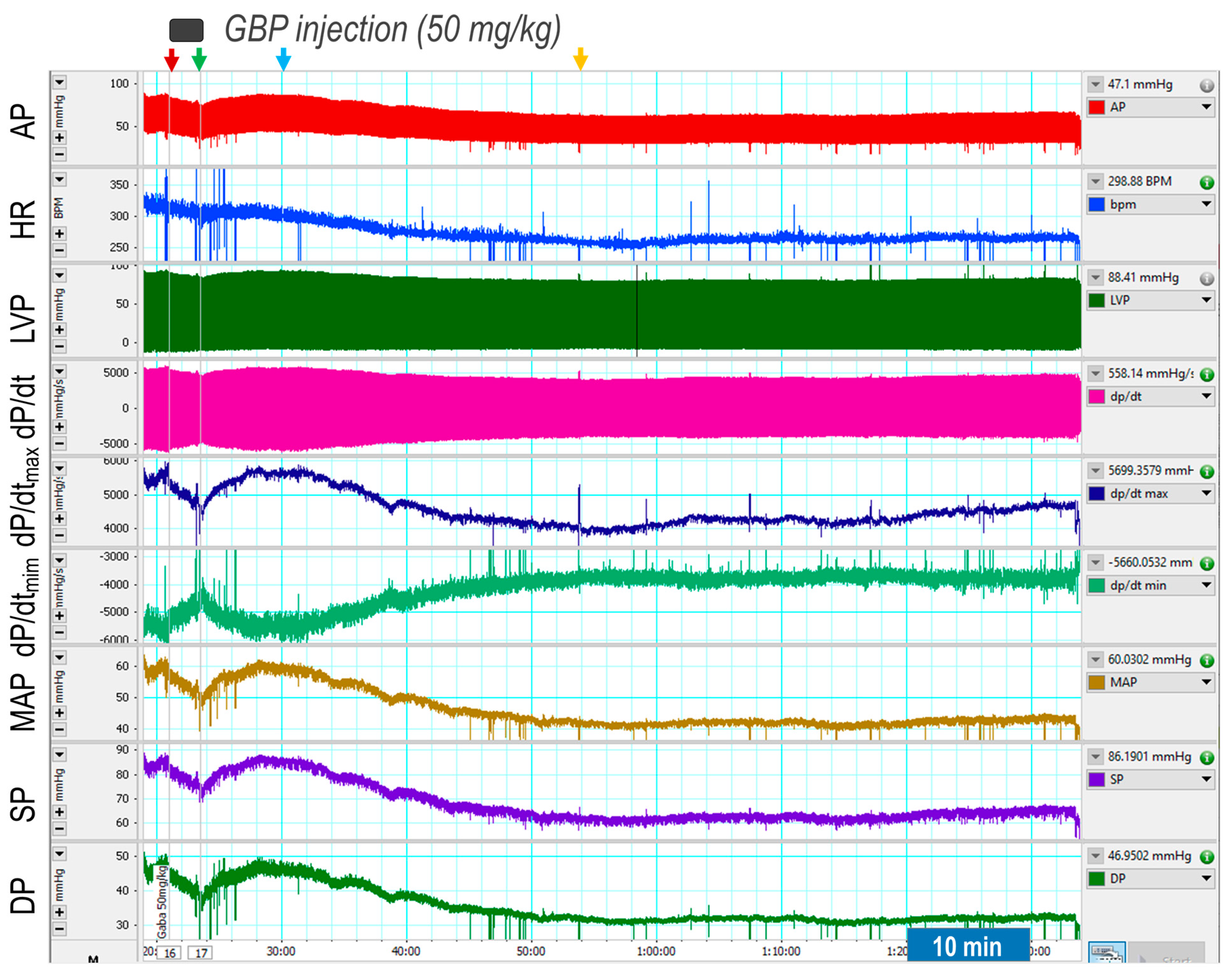
First, we determined the acute responses of BP, HR, and LV hemodynamics to an intravenous injection of GBP (50 mg/kg; 100 mg/mL × 0.1 mL in 3 min). The results are shown in Figure 1, representative of an original recording and the Table 1), the combined summary data.
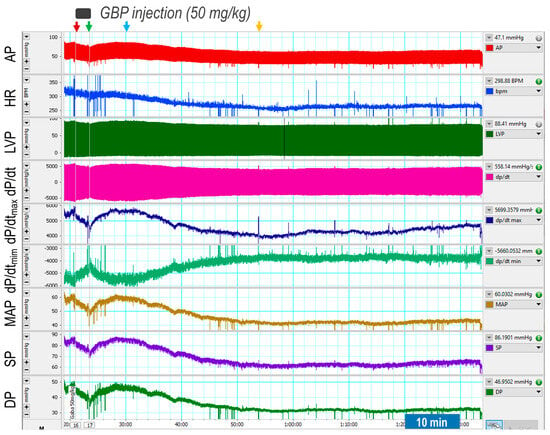
Figure 1.
Representative of an original recording showing effects of a bolus i.v. injection of GBP on cardiovascular function. The red and green arrows indicate the start and end of a GBP injection, respectively. The yellow arrow indicates the maximal effect of GBP.

Table 1.
Combined data showing effects of a bolus i.v. injection of GBP on cardiovascular function.
The recording shows that GBP administration evoked a transient and slight suppression of most hemodynamic parameters, followed by a prolonged and significant inhibition, showing a biphasic effect. Since the i.v. catheter tip was placed into the superior vena cava, we believe the inhibitory effect of the 1st phase was induced directly by the outflow of GBP solution from the catheter tip going through the heart chamber and the vessel system. Accordingly, when the injection was completed (indicated by the green arrow), this effect disappears. At approximately 7 min post injection (indicated by the blue arrow) when the GBP solution was completely mixed with circulating blood and the GBP concentration in the blood reached a steady state, we observed the inhibitory effect of the second phase, which lasted at least 60 min with a maximal effect appearing at 30 min post injection (indicated by the yellow arrow). Since the half-life of GBP is 5–7 h, we speculate that i.v. GBP-induced cardiovascular inhibition could potentially last longer than one hour.
Table 1 shows that BP, HR, and most LV hemodynamic parameters are significantly reduced after GBP treatment (the values were calculated at 30 min post injection indicated by the yellow arrow) as compared with the baseline (before GBP treatment). The decreased systolic pressure (SP) and pulse pressure (PP) represent impaired cardiac function and reduced cardiac output, whereas the decreased diastolic pressure suggests vasodilation. The lower maximal and minimal dP/dt values suggest depressed myocardial contractility and impaired LV relaxation, which are further confirmed by a significantly decreased IRP-AdP/dt, the slope of a straight line fit to the pressure over the isovolumic relaxation period, in addition to a significantly increased Tau, the exponential time constant of relaxation. However, there was no significant difference in LVEDP between pre- and post-GBP, suggesting that acute GBP-induced depression of cardiac function did not develop into heart failure. It should be noted that an i.v. injection of 0.1 mL of saline (vehicle) did not evoke significant changes in BP, HR, and LV hemodynamics over the same time period as rats that underwent GBP injections (data not shown).
3.2. Effect of Chronic i.p. Treatment of GBP on Cardiovascular Function
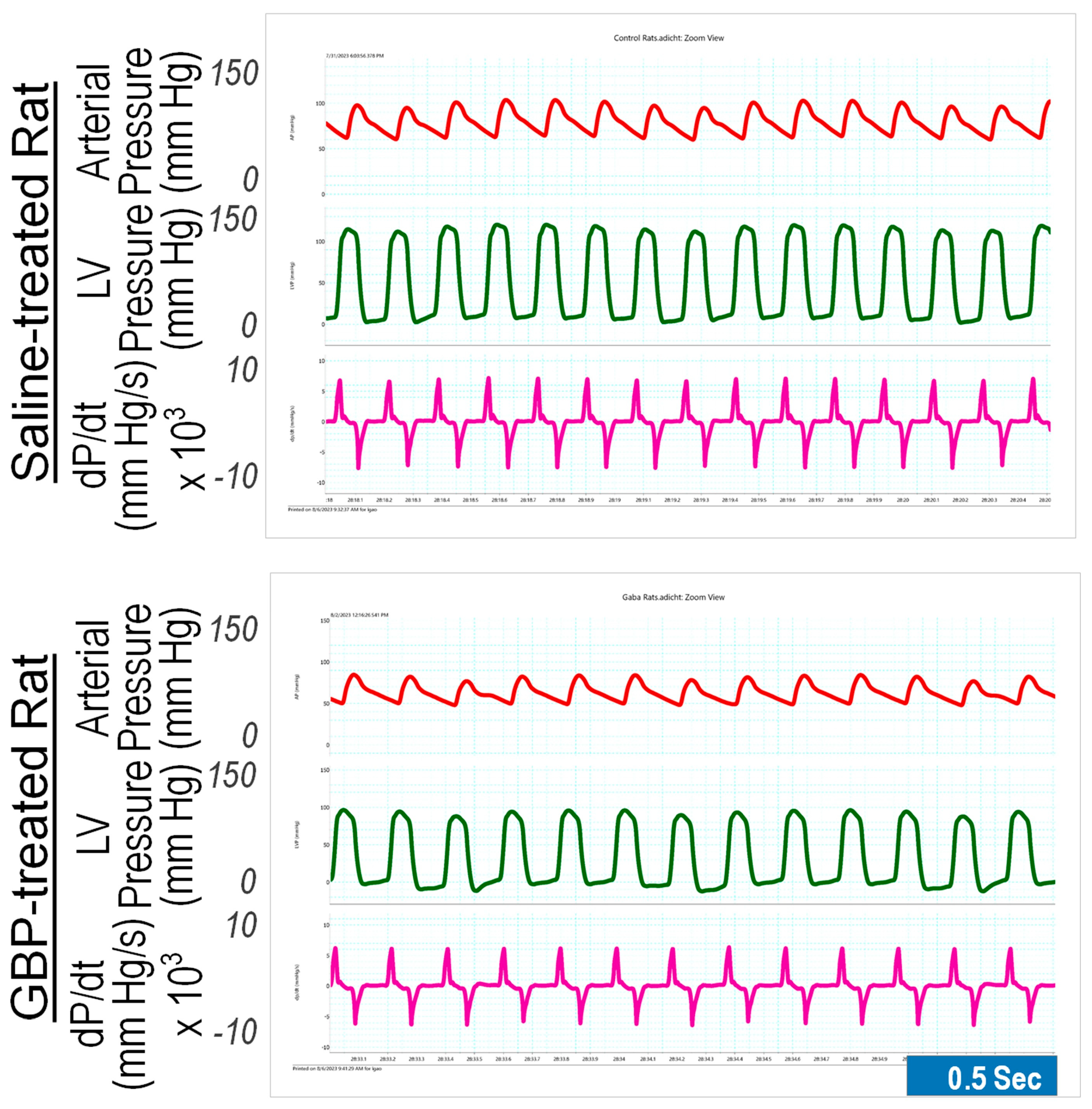
We determined the chronic effects of GBP administration (i.p. 100 mg/kg/day for seven consecutive days) on cardiovascular function compared with saline as the control vehicle. The measurements were carried out 6 h after last GBP administration on day 7. The results are shown in Figure 2, in which the left panel is representative of the original recordings and the right panel shows the combined data (Table 2). GBP-treated rats exhibited significantly lower BP, HR, and LV hemodynamics compared to the rats receiving i.p. saline, suggesting that the inhibitory effects of chronic GBP treatment on cardiovascular function was similar to those induced by acute GBP-treatment. However, some parameters, which were significantly reduced in the acute GBP-treated rats (Table 1), did not display a significant change in chronic GBP-treated rats (Table 2), such as PP, dP/dtmin, IRP-Average dP/dt, Tau, DD, and CD, suggesting a different cardiovascular response to acute- and chronic- GBP administration. However, this difference could also be attributed to the different time points the two groups chose for calculating the parameters, since we evaluated the acute response after 30 min post GBP treatment (Table 1) but evaluated the chronic response at 6 h after GBP administration (Table 2).
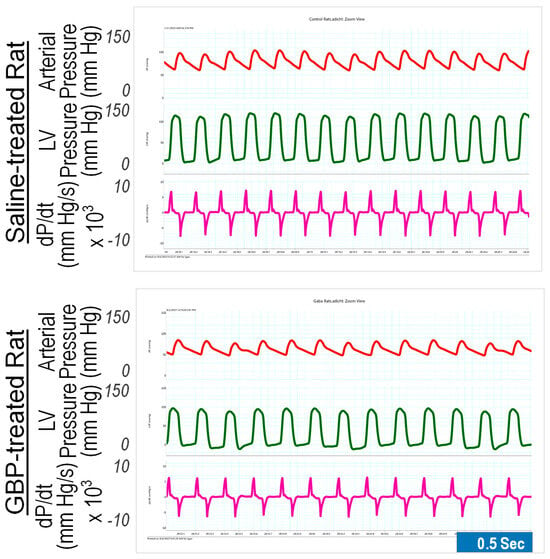
Figure 2.
Representative of original recordings showing effects of the 7-day i.p. injection treatment of GBP on cardiovascular function. Top panel: a saline-treated rat; Bottom panel: a GBP-treated rat.

Table 2.
Combined data showing effects of the 7-day i.p. injection treatment of GBP on cardiovascular function.
3.3. Plasma NE Concentration
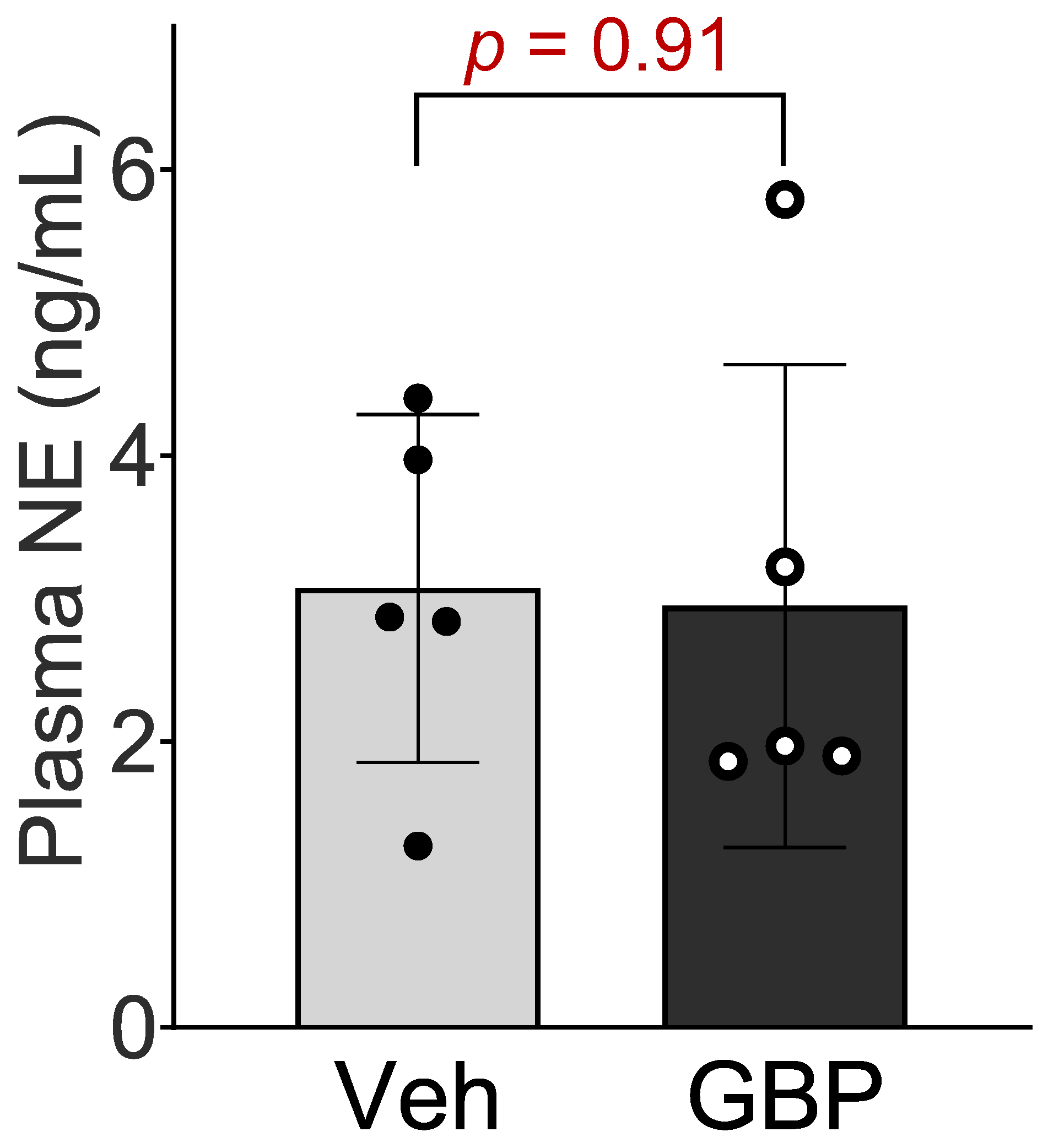
To determine whether the sympathetic system is involved in GBP-induced cardiovascular dysfunction, we next measured the plasma NE concentration in the rats receiving chronic GPB treatment. No significant differences in plasma NE concentration were observed between the two groups (Figure 3), which suggests that the 7-day i.p. treatment of GBP in a dose of 100 mg/kg does not change circulating catecholamine and sympathetic tone.
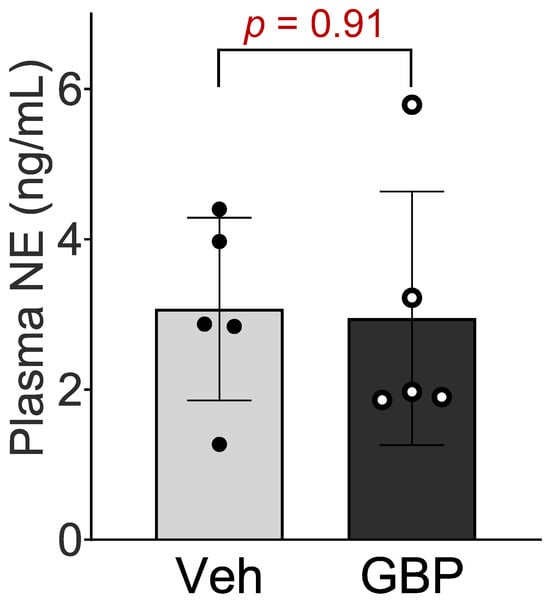
Figure 3.
Plasma norepinephrine concentration of the rats receiving the 7-day saline or GBP treatment. n = 5/group. NE: norepinephrine; Veh: vehicle; GBP: gabapentin.
3.4. Proteomics and Bioinformatics Analyses
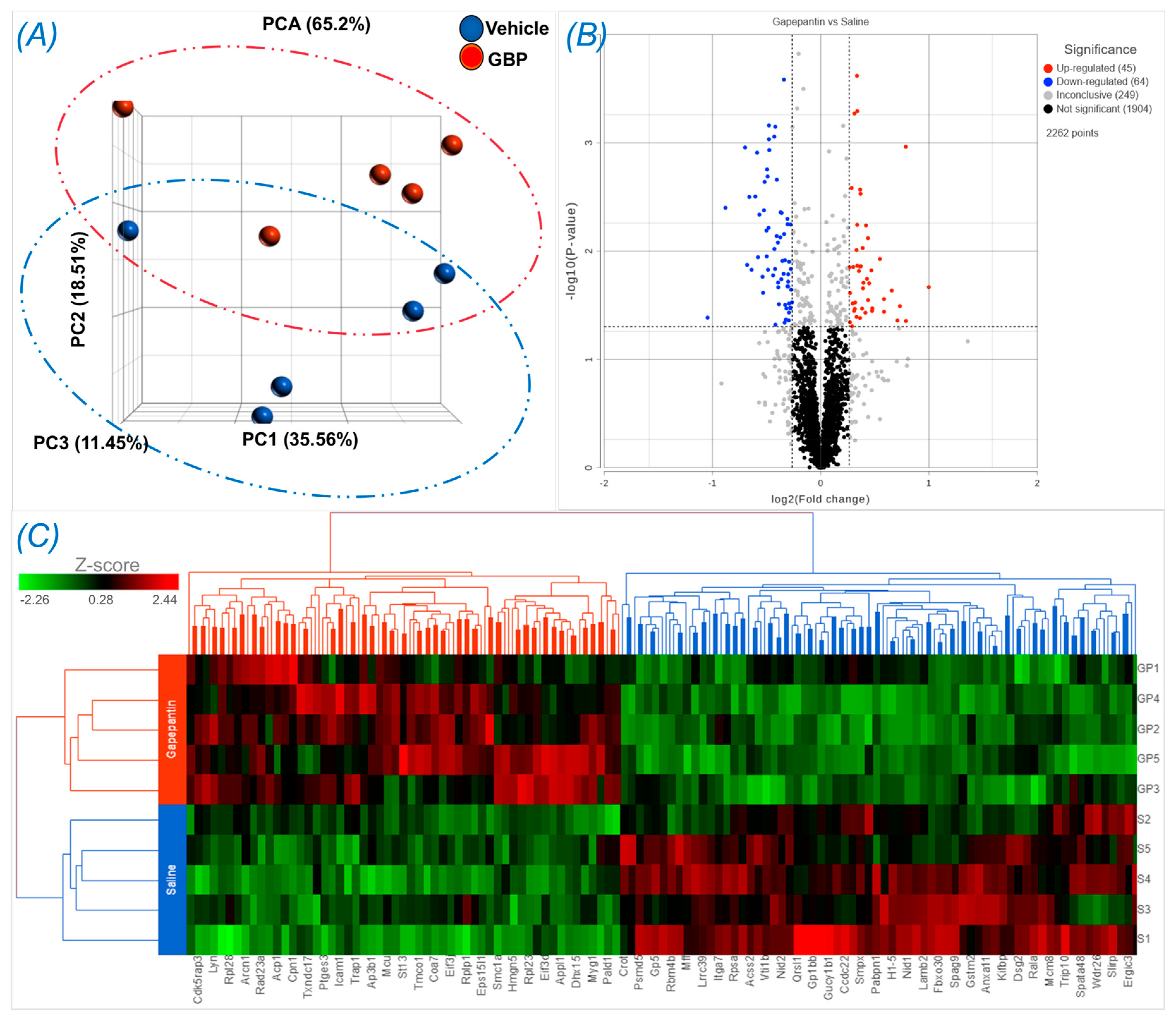
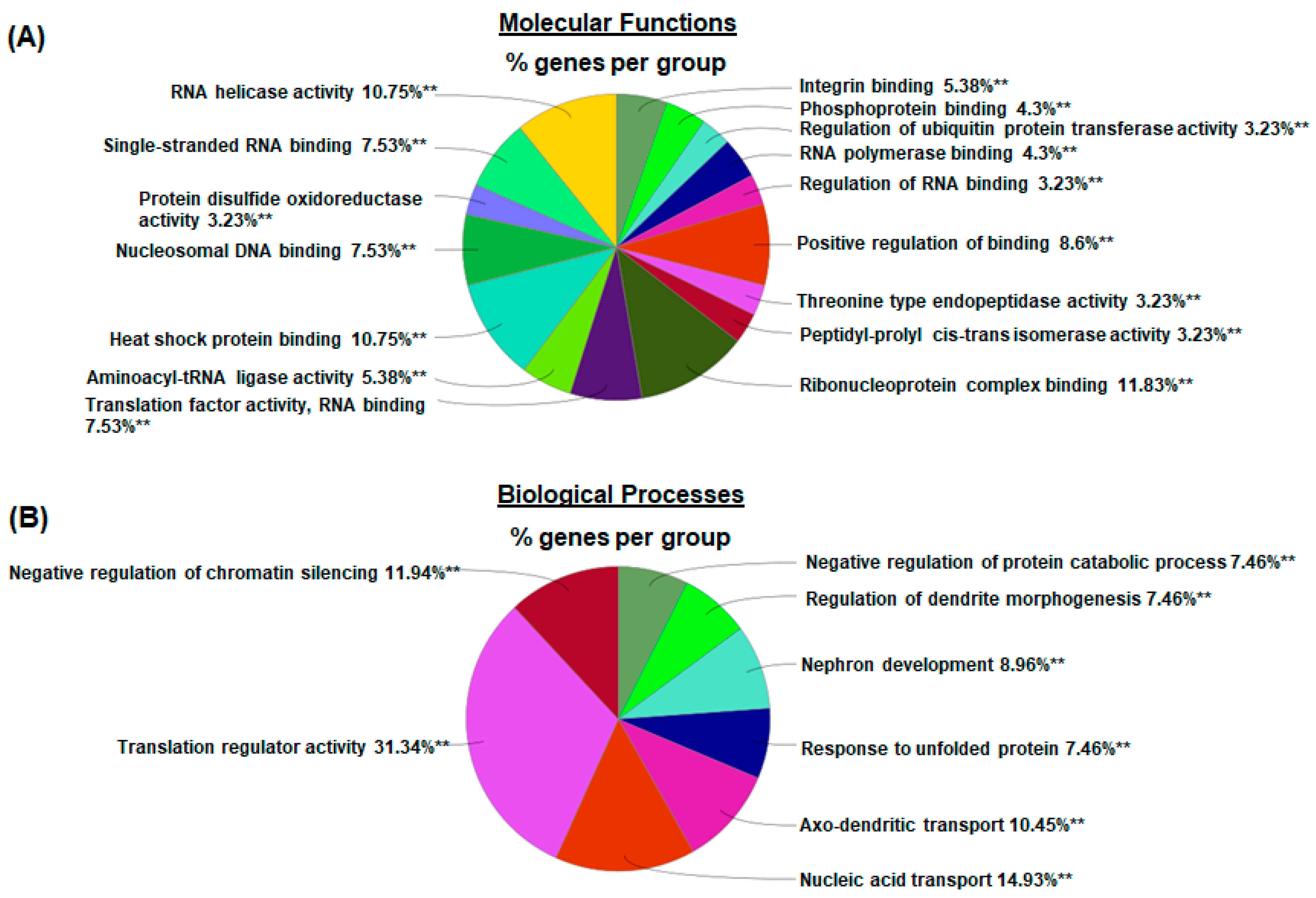
To explore the molecular mechanisms underlying chronic GBP treatment-induced cardiac dysfunction, we employed Tandem Mass Tag (TMT) multiplexing coupled to liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry based quantitative proteomics to analyze LV myocardium. A total of 2262 proteins with a minimum of two plus unique peptides were identified, of which 109 proteins were found to be differentially expressed between the groups (Supplemental Table S1). Panel A of Figure 4 shows the principal component analysis (PCA), which represents an overall separation and reproducibility amongst the biological replicates that occurred between GBP- and saline-treated rats with 65.2% of variation. Panel B of Figure 4 is a volcano plot indicating significantly upregulated (red dots, n = 45) or downregulated (blue dots, n = 64) proteins in GBP rats compared to saline rats. Panel C of Figure 4 is a heatmap analysis of the top 121 proteins, revealing a favorable consistency of protein profiles between the groups. Next, using ClueGO, a user friendly cytoscape plug in, we analyzed both the molecular and biological processes enriched within the differentially expressed proteins. Amongst the molecular functions, we found enrichment of ribonucleoprotein complex (11.8%), heat shock binding (10.75%), and RNA helicase activity (10.75%). Similarly, in the biological functions, we found enrichment in the translation regulator activity (31.34%), followed by nucleic acid transport (14.93%), and negative regulation of chromatin silencing (11.94%). These data are presented in Figure 5.
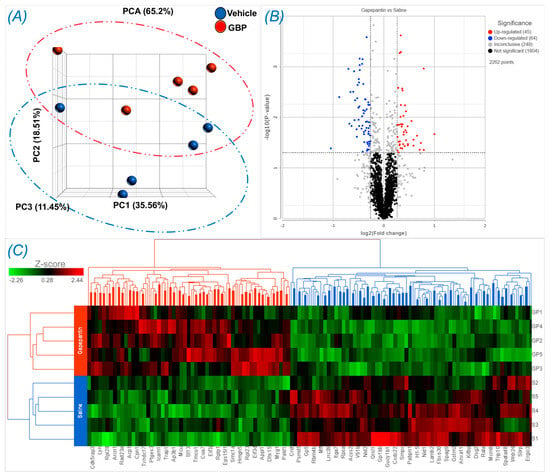
Figure 4.
Differentially expressed proteins in the LV myocardium of rats receiving GBP or saline treatment for 7 days. (A) Principal component analysis (PCA) showing a separation occurred between the groups. (B) Volcano plot showing the log2 fold change plotted against the −log10 p value; (C) Heatmap showing the log2 of the top 121 differentially expressed proteins with 55 up- and 66 down-regulation. n = 5/group.
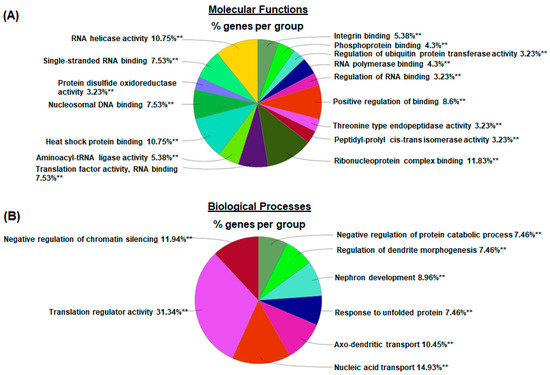
Figure 5.
Pie chart representing the distribution of differentially expressed proteins identified in the LV myocardium of GBP-rats compared to saline-rats, according to the proteins’ molecular functions (A) and biological processes (B) by using ClueGO analysis. ** p < 0.001 as compared with saline groups, n = 5/groups.
3.5. Western Blotting Analysis
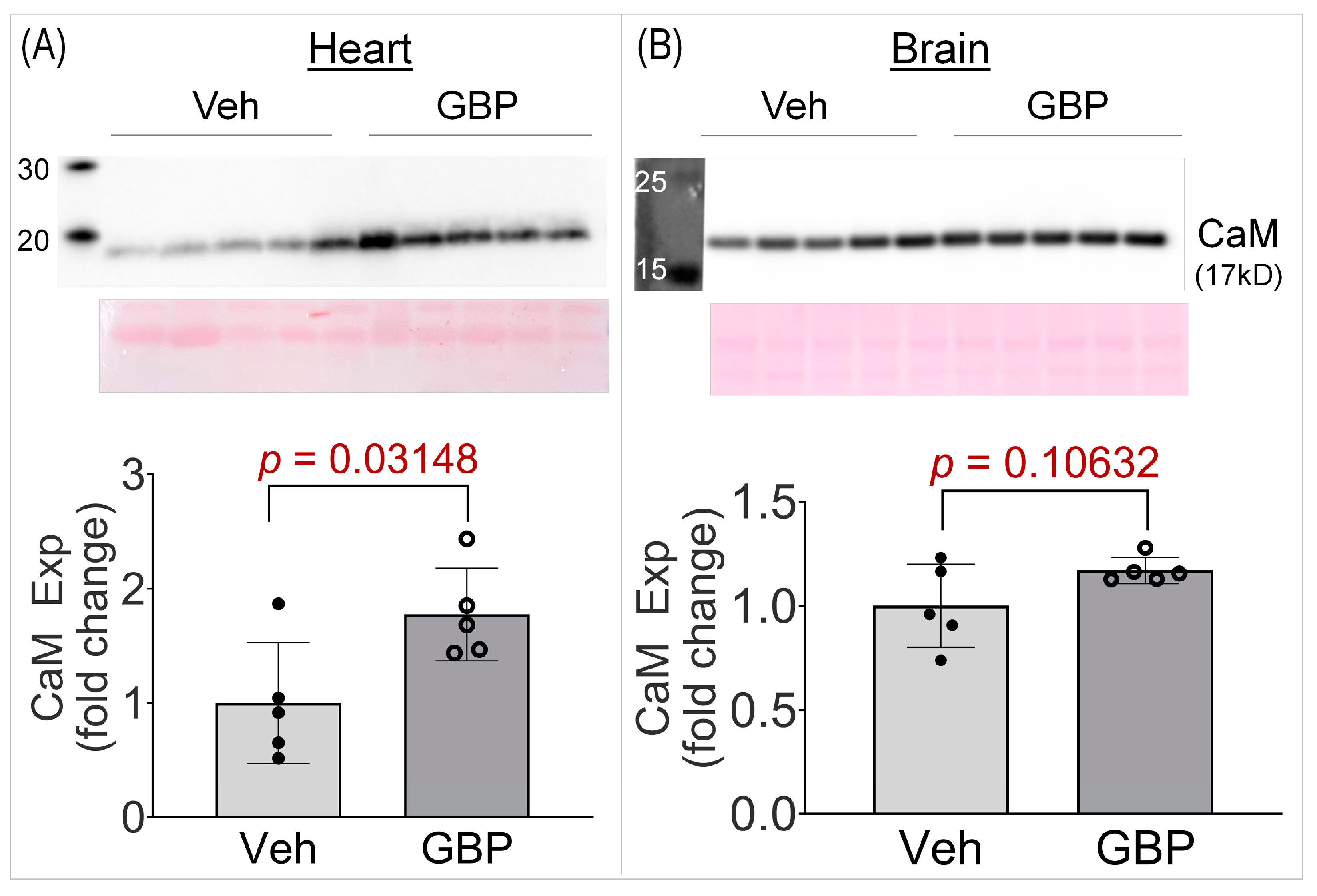
High throughput studies generate vast amounts of data and initially identify potential hits, thus there is the need for further validation. One such protein hit we identified from the proteomics screen was calmodulin (CaM), which was +1.52 fold upregulated in the GBP group. To further validate its upregulation, we performed a western blot on the heart lysates from the two groups. As seen in Figure 6, CaM expression was significantly elevated (+1.77 fold) in the heart lysates of the GBP-treated animals, thus validating our proteomics screen data. To further ascertain whether the upregulation of CaM is heart specific, we also examined its expression in the brain cortical lysates of the two groups. Notably, there was no change in CaM expression in the brain lysates of the GBP animals. This suggests that the 7-day i.p. treatment of GBP with a dose of 100 mg/kg/day significantly upregulates CaM in the myocardium specifically, which may contribute to the subsequent cardiac dysfunction.
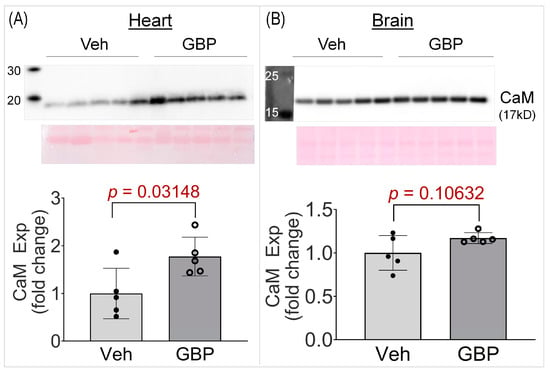
Figure 6.
Western blot data showing CaM expression in the LV myocardium (A) and brain cortex (B) of rats receiving the 7-day Veh or GBP treatment. n = 5/group. Veh: vehicle (saline); GBP: gabapentin; CaM: calmodulin; Exp: expression.
4. Discussion
Although GBP has long been used in a neurosetting, its cardiovascular side effects have recently attracted attention in human medicine, veterinary medicine, and basic medical science areas [8,18]. However, the exact actions and underlying mechanisms of GBP on the heart, blood vessels, and autonomic regulation remain to be completely elucidated. The novel findings of the present study are that both acute and chronic systemic administration of GBP in rats evoked a significant inhibition of cardiac function. This included bradycardia, depressed myocardial contractility, and LV systolic/diastolic dysfunction, which were accompanied by a decrease in BP without a change in plasma norepinephrine concentration. These data imply a direct effect of GBP on the heart. In addition, when using mass spectrometry-based proteomics, we identified 109 differentially expressed proteins in heart samples of rats receiving chronic GBP treatment. Bioinformatics analysis further suggests that these proteins are involved in calcium signaling pathways, cholesterol metabolism, galactose metabolism, and other biological processes associated with cardiac function. One of the most important pathways that we identified using proteomics and validated by western blot in this study was CaM, a highly conserved protein that senses intracellular Ca2+ and relays signals to various Ca2+-sensitive enzymes, ion channels, and other proteins [19]. We found that CaM was markedly upregulated in the myocardium, but not in the brain cortices of the rats receiving chronic GBP treatment. This finding strongly suggests an association of the observed cardiac dysfunction with impaired regulation of cardiomyocyte Ca2+ signaling. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to provide physiological and molecular evidence suggesting a direct effect of GBP on cardiac function and protein profiles by combining whole animal experiments with omics techniques and molecular validation. Consistent with our findings in normal rats, a recent study by Allen et al. [20] demonstrated that a single dose of oral GBP in healthy cats produced a modest decrease in LV systolic function, displaying a significant decrease in two-dimensional fractional shortening and a significant increase in both LV internal diameter in systole and left atrial volume.
The effects of GBP on cardiovascular function in normotensive and hypertensive rats has been investigated recently by several studies. In conscious spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) and Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) rats, Behuliak et al. [15] found that acute intravenous injection of GBP significantly reduced BP and HR, with greater effects in SHR than WKY. They further demonstrated that the hypotension and bradycardia were mediated by attenuating sympathetic nerve transmission and modulating the arterial baroreceptor-HR reflex. To explore the central mechanisms of GBP-evoked cardiovascular depression, Chen et al. [14] found that microinjection of GBP into the nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) of SHR rats induced a dose-dependent decrease in BP and HR, which was completely abolished by pretreatment with L-NAME, a NOS inhibitor. These data suggest a critical role of GBP in central autonomic regulation via a NO-dependent pathway. In contrast, to explore the peripheral mechanisms of GBP-induced edema and acute heart failure, Largeau et al. [16] utilized pressure arteriography and whole-cell patch clamp to study the direct effects of GBP on vasomotor capacity of third-order mesenteric arteries and L-type calcium current in LV cardiomyocytes isolated from adult male Wistar rats. They found that GBP evoked a marked decrease in myogenic tone and weak vasodilation but there were no effects on cellular Ca2+ current. These data are the first pieces of evidence demonstrating how GBP can modulate cardiovascular function through a direct effect on non-nervous tissues. In the present study, by simultaneously measuring BP, HR, and LV hemodynamics in anesthetized rats, we found an immediate hypotension, bradycardia, and impaired LV contractility/relaxation in response to intravenous injection of GBP, further confirming the direct effects of GBP on the heart and blood vessels.
There are no clinical studies to have investigated the side effects or toxicity of GBP on cardiovascular function, however, several case reports describe adverse cardiovascular events induced by GBP or its structurally similar compound, pregabalin. These include the development of new onset congestive heart failure [10,11], decompensation of pre-existing CHF [21,22,23], cardiac conduction disturbances [24,25], atrial fibrillation [9], and hypotension [13,26]. In an analysis of a large-scale nation-wide database of de-identified patients (TriNetZ EHRs), Pan et al. [8] recently found a significant increase in the risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart failure, myocardial infarction, peripheral vascular disease, stroke, deep venous thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism in patients with diabetic neuropathy following long-term use of GBP and pregabalin. Furthermore, they found that there were significant associations between short-term (3 month) GBP use and heart failure, myocardial infarction, peripheral vascular disease, deep venous thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism. The data in the present study provides animal-based experimental evidence to support the cardiovascular dysfunction described by these clinical case reports and the high risk of cardiovascular diseases found by the retrospective cohort study.
Although autonomic dysfunction has been proposed to explain the negative influence of GBP on the cardiovascular system [14,15], the exact mechanisms remain to be explored. A decreased peripheral sympathetic nerve transmission [15] and suppressed central sympathetic nerve outflow [14] can explain GBP-induced hypotension and bradycardia, however this not likely the cause of GBP-evoked new onset congestive heart failure [10,11], decompensation of pre-existing heart failure [21,22,23], or an increase in the risk of heart failure [8], since sympatho-inhibition is generally believed to ameliorate, rather than exacerbate, the cardiac dysfunction in the heart failure state. Based on our data showing acute cardiac dysfunction by GBP and marked upregulation of CaM in the myocardium of rats receiving chronic GBP, we hypothesize that GBP-induced cardiovascular pathological consequences may be attributed to a direct effect of GBP on myocardial contractility induced by abnormal Ca2+ signaling in cardiomyocytes.
Despite its structural similarity to GABA, GBP cannot bind to GABA receptors or affect the neuronal uptake or degradation of GABA, suggesting that the effects of GBP are not mediated by interacting directly with GABA receptors or with high-affinity Na+-dependent GABA transporters [27]. Instead, GBP directly inhibits the voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs) of neurons, leading to a reduction in presynaptic Ca2+ influx, a decrease in the release of excitatory neurotransmitters, and a relief of neuropathic pain [28]. VGCCs are composed of a complex, consisting of an α1 and associated β and α2δ subunits, to which the α1 subunit constitutes the channel pore and allows calcium influx from the extracellular space into the cells. The β and α2δ subunits support channel trafficking and tune the kinetic properties of Ca2+ currents [29,30]. By binding to the α2δ subunits of the VGCC complex, GBP blocks neuronal Ca2+ influx, exerting its analgesic efficacy [28,31]. In addition to the nervous system, VGCCs are also found in other excitable tissues, such as cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and endocrine cells, playing a critical role in the regulation of muscle contraction and hormone secretion [30]. In the present study, we propose that the cardiac dysfunction observed in rats (and in other studies with cats) [20] is related to a blockade by GBP on cardiomyocytes L-type Ca2+ current by binding to the α2δ subunit of the CaV1.2 channel, a cardiac subtype of VGCCs. Moreover, by employing a [3H]GBP binding assay and α2δ-null mice, Fuller-Bicer et al. [32] demonstrated a binding capacity of GBP with VGCCs in cardiomyocytes. Furthermore, they found that α2δ-deficient hearts display a significantly lower basal contractility and relaxation (+dP/dt and -dP/dt) as compared with the wild type [32]. Actually, VGCCs participate in and are critical for almost all aspects of cardiac physiology, pathology, and pharmacology, through regulating extracellular Ca2+ influx and subsequent intracellular signaling transduction [33,34].
Cardiomyocyte VGCCs, the CaV1.2 channel subunit, mediates excitation-contraction coupling (ECC), a highly coordinated process whereby membrane depolarization leads to contraction [35]. During the period of action potential generation, small amounts of extracellular Ca2+ ions enter the cytosol via the CaV1.2 and trigger the release of massive amounts of intracellular Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) into the cytosol via the ryanodine receptor (RyR, a Ca2+ release channels resided in SR), known as Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release (CICR) [36]. These Ca2+ ions released from SR bind to troponin-C and enable actin-myosin cross-bridging and sliding of the myofilaments, resulting in sarcomere shortening and myocardial contraction [37]. CICR is a complex process critical for ECC, not only involving in CaV1.2 and RyR but also CaM. CaM is a Ca2+ binding protein, which crosstalks with both CaV1.2 and RyR, forming a triangular interaction to regulate Ca2+ behavior and kinetics [38]. On one hand, the functional communications between the RyR and CaV1.2 are believed to be reciprocal. CaV1.2 opens RyR, defined as orthograde signaling, and RyR can prevent CaV1.2 inactivation, defined as retrograde signaling [39,40]. On the other hand, CaM in both Ca2+-bound and Ca2+-free states can bind and regulate both RyR and CaV1.2. RyR activity is increased by CaM at low Ca2+ concentrations (nM; Ca2+-free CaM) but inhibited by CaM at high Ca2+ concentrations (μM; Ca2+-bound CaM), whereas CaV1.2 can be inactivated and facilitated by CaM via its binding to channel’s C-terminal domain as a Ca2+ sensor [38]. One of the important findings from the present study is a marked upregulation of CaM in the hearts of rats receiving the 7-day GBP treatment, suggesting an impact of GBP on cardiomyocyte Ca2+ signaling which we believe underlies the subsequent cardiac dysfunction. Indeed, it has been found that hyper-activated Ca2+/CaM signaling contributed to pathology in several cardiac diseases, including heart failure, cardiac hypertrophy, and arrhythmia [41,42]. Although the exact mechanisms by which GBP upregulates CaM and the resulting functional consequences by the upregulated CaM remain unclear, though our data does suggest the involvement of intracellular Ca2+ signaling dysfunction in GBP-induced cardiac side effects and will open novel avenues for treating in the future.
In conclusion, the present study revealed that both acute and chronic treatments with GBP in normal adult rats had a significant adverse effect on global cardiovascular function, including hypotension, bradycardia, and reduced LV systolic/diastolic function. This is the first study to provide direct evidence demonstrating inhibition of GBP on cardiac contractility. Given the observed substantial increase in myocardial CaM protein expression in the GBP-treated rats, we speculate that a disruption in Ca2+ signaling pathways within cardiac myocytes plays a pivotal role in these effects.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cells12232705/s1, Table S1: Raw data of proteomics.
Author Contributions
L.G. and V.V.P. conceived the project and co-wrote the article; L.G. and S.P. carried out cardiovascular experiments and generated Figure 1 and Figure 2; V.S. made the preclinical rat model; K.S. performed proteomic analysis and generated Figure 4 under the guidance of V.K.; S.J. performed bioinformatics analysis and generated Figure 5 under the guidance of C.G.; Western blot analyses were performed by V.V.P. and V.S; and L.Y. measured the plasma norepinephrine concentration. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant R01HL160820 awarded to L.G. The Bioinformatics and Systems Biology Core is partially supported by NIH awards to C.G. (5P20GM103427, 5P30CA036727, 5U54GM115458).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of the University of Nebraska Medical Center (protocol code 17-080-09-FC approved on 9 January 2023).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are contained within the article and supplementary materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Baillie, J.K.; Power, I. The mechanism of action of gabapentin in neuropathic pain. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2006, 7, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ziganshina, L.E.; Abakumova, T.; Hoyle, C.H. Gabapentin monotherapy for epilepsy: A review. Int. J. Risk Saf. Med. 2023, 34, 243–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.V.; Havens, J.R.; Walsh, S.L. Gabapentin misuse, abuse and diversion: A systematic review. Addiction 2016, 111, 1160–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintero, G.C. Review about gabapentin misuse, interactions, contraindications and side effects. J. Exp. Pharmacol. 2017, 9, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calandre, E.P.; Rico-Villademoros, F.; Slim, M. Alpha2delta ligands, gabapentin, pregabalin and mirogabalin: A review of their clinical pharmacology and therapeutic use. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2016, 16, 1263–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isom, L.L.; De Jongh, K.S.; Catterall, W.A. Auxiliary subunits of voltage-gated ion channels. Neuron 1994, 12, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catterall, W.A. Structure and regulation of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2000, 16, 521–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Davis, P.B.; Kaebler, D.C.; Blankfield, R.P.; Xu, R. Cardiovascular risk of gabapentin and pregabalin in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Hunter, K.; Berry, H.; Martins, Y.C. Atrial fibrillation induced by gabapentin: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2023, 17, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-bast, B.; Deshpande, R.; Hu, Y.Y.; Siddique, M. Gabapentin induced heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barold, S.; Barold, D.; Hon, R. Gabapentin-Induced Congestive Heart Failure. Case Rep. Clin. Cardiol. J. 2023, 3, 130. [Google Scholar]
- Tellor, K.B.; Ngo-Lam, R.; Badran, D.; Armbruster, A.L.; Schwarze, M.W. A rare case of a gabapentin-induced cardiomyopathy. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2019, 44, 644–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, J.H.; Tobias, J.D. Gabapentin and intraoperative hypotension. Pediatr. Anesth. Crit. Care J. 2021, 9, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.-H.; Li, Y.-D.; Cheng, P.-W.; Fang, Y.-C.; Lai, C.-C.; Tseng, C.-J.; Pan, J.-Y.; Yeh, T.-C. Gabapentin reduces blood pressure and heart rate through the nucleus tractus solitarii. Acta Cardiol. Sin. 2019, 35, 627–633. [Google Scholar]
- Behuliak, M.; Bencze, M.; Polgárová, K.; Kuneš, J.; Vaněčková, I.; Zicha, J. Hemodynamic Response to Gabapentin in Conscious Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Role Sympathetic Nerv. Syst. 2018, 72, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Largeau, B.; Bordy, R.; Pasqualin, C.; Bredeloux, P.; Cracowski, J.-L.; Lengellé, C.; Gras-Champel, V.; Auffret, M.; Maupoil, V.; Jonville-Béra, A.-P. Gabapentinoid-induced peripheral edema and acute heart failure: A translational study combining pharmacovigilance data and in vitro animal experiments. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 149, 112807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindea, G.; Mlecnik, B.; Hackl, H.; Charoentong, P.; Tosolini, M.; Kirilovsky, A.; Fridman, W.-H.; Pagès, F.; Trajanoski, Z.; Galon, J. ClueGO: A Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1091–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronezi, T.M.; Lopes, D.J.; Zardo, I.L.; Ferronatto, J.V.; Trojan, M.M.; Franck, K.R.; de Azevedo, A.F.; Spiering, A.G.; Nunes, L.N.; Fadel, L.; et al. Evaluation of the effects of gabapentin on the physiologic and echocardiographic variables of healthy cats: A prospective, randomized and blinded study. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2022, 24, e498–e504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, S.W.; Leclerc, E. Novel aspects of CaM target recognition and activation. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.E.; LeBlanc, N.L.; Scollan, K.F. Hemodynamic, echocardiographic, and sedative effects of oral gabapentin in healthy Cats. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2021, 57, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, R.L.; Cantu, M.; Lindenfeld, J.; Hergott, L.J.; Lowes, B.D. Possible heart failure exacerbation associated with pregabalin: Case discussion and literature review. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2008, 9, 922–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Smedt, R.H.; Jaarsma, T.; Van Den Broek, S.A.; Haaijer-Ruskamp, F.M. Decompensation of chronic heart failure associated with pregabalin in a 73-year-old patient with postherpetic neuralgia: A case report. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 66, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, N.; Mockler, M.; Ryder, M.; Ledwidge, M.; McDonald, K. Decompensation of chronic heart failure associated with pregabalin in patients with neuropathic pain. J. Card. Fail. 2007, 13, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasimas, J.J.; Burkhart, K.K. Cardiac conduction disturbances after an overdose of nefazodone and gabapentin. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2006, 24, 886–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksakal, E.; Bakirci, E.M.; Emet, M.; Uzkeser, M. Complete atrioventricular block due to overdose of pregabalin. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2012, 30, 2101.e1–2101.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein-Schwartz, W.; Shepherd, J.G.; Gorman, S.; Dahl, B. Characterization of gabapentin overdose using a poison center case series. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.P.; Gee, N.S.; Su, T.-Z.; Kocsis, J.D.; Welty, D.F.; Brown, J.P.; Dooley, D.J.; Boden, P.; Singh, L. A summary of mechanistic hypotheses of gabapentin pharmacology. Epilepsy Res. 1998, 29, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, W.; Wu, H.; Yu, X.; Song, T.; Xu, X.; Xu, F. The calcium channel α2δ1 subunit: Interactional targets in primary sensory neurons and role in neuropathic pain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 699731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzetti, S.; Di Biase, V. Small molecules as modulators of voltage-gated calcium channels in neurological disorders: State of the art and perspectives. Molecules 2022, 27, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, W.A. Voltage-gated calcium channels. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a003947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chincholkar, M. Analgesic mechanisms of gabapentinoids and effects in experimental pain models: A narrative review. Br. J. Anaesth. 2018, 120, 1315–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller-Bicer, G.A.; Varadi, G.; Koch, S.E.; Ishii, M.; Bodi, I.; Kadeer, N.; Muth, J.N.; Mikala, G.; Petrashevskaya, N.N.; Jordan, M.A.; et al. Targeted disruption of the voltage-dependent calcium channel alpha2/delta-1-subunit. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2009, 297, H117–H124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roden, D.M.; Balser, J.R.; George, A.L., Jr.; Anderson, M.E. Cardiac ion channels. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2002, 64, 431–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisner, D. Calcium in the heart: From physiology to disease. Exp. Physiol. 2014, 99, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, L.S.; Bers, D.M. Role of Ca2+/CaM-dependent protein kinase (CaMK) in excitation-contraction coupling in the heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 73, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabiato, A. Calcium-induced release of calcium from the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Am. J. Physiol. 1983, 245, C1–C14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, M.; Ebashi, F.; Imai, S. Cardiac Myosin B and Calcium Ions. J. Biochem. 1964, 55, 192–194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Sencer, S.; Hamilton, S.L. CaM modulation of proteins involved in excitation-contraction coupling. Front. Biosci.-Landmark 2002, 7, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, J.; Sekiguchi, N.; Rando, T.A.; Allen, P.D.; Beam, K.G. Two regions of the ryanodine receptor involved in coupling with L-type Ca2+ channels. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 13403–13406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, J.; Dirksen, R.T.; Nguyen, H.T.; Pessah, I.N.; Beam, K.G.; Allen, P.D. Enhanced dihydropyridine receptor channel activity in the presence of ryanodine receptor. Nature 1996, 380, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Brown, J.H. Role of Ca2+/CaM-dependent protein kinase II in cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 63, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulman, H.; Anderson, M.E. Ca/CaM-dependent Protein Kinase II in Heart Failure. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Mech. 2010, 7, e117–e122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).