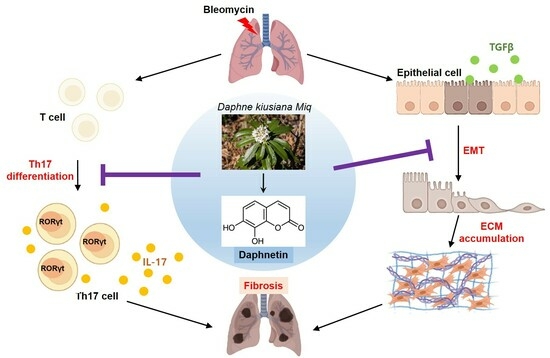
Daphnetin Alleviates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis through Inhibition of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and IL-17A
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Daphnetin
2.2. Mice
2.3. Splenocyte Culture and Compounds Treatment
2.4. Cell Culture
2.5. Cell Viability Assay
2.6. BLM-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Mouse Model
2.7. Pulmonary Mechanical Function Test
2.8. Staining for Histopathological Analysis
2.9. Hydroxyproline Assay
2.10. Quantitative PCR Analysis
2.11. Western Blot Analysis
2.12. Measurement of Cytokines by ELISA
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Daphnetin Inhibits Th17 Differentiation by Suppressing Transcription Factor RORγt
3.2. Daphnetin Reduces TGF-β-Induced EMT by Inhibiting AKT Signaling Pathway in BEAS-2B Cells
3.3. Daphnetin Improves Mechanical Function of Lung in BLM-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis
3.4. Daphnetin Attenuates BLM-Induced Fibrotic Changes in Lung Tissue
3.5. Daphnetin Suppresses IL-17A Production and Th17 Differentiation in BLM-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moss, B.J.; Ryter, S.W.; Rosas, I.O. Pathogenic Mechanisms Underlying Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2022, 17, 515–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Confalonieri, P.; Volpe, M.C.; Jacob, J.; Maiocchi, S.; Salton, F.; Ruaro, B.; Confalonieri, M.; Braga, L. Regeneration or Repair? The Role of Alveolar Epithelial Cells in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF). Cells 2022, 11, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeldi, L.; Collard, H.R.; Jones, M.G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhreal, D.; Crestani, B.; Helou, D.G. Macrophage Implication in IPF: Updates on Immune, Epigenetic, and Metabolic Pathways. Cells 2023, 12, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, S.; Idell, S. Caveolin-1-Related Intervention for Fibrotic Lung Diseases. Cells 2023, 12, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratella, E.; Ruaro, B.; Giudici, F.; Wade, B.; Santagiuliana, M.; Salton, F.; Confalonieri, P.; Simbolo, M.; Scarpa, A.; Tollot, S.; et al. Evaluation of Correlations between Genetic Variants and High-Resolution Computed Tomography Patterns in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, P.M.; Patterson, C.M.; Reed, A.K.; Thillai, M. Lung transplantation for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Chen, F.; Fang, H.; Mi, J.; Qi, Q.; Yang, M. Daphnetin inhibits proliferation and inflammatory response in human HaCaT keratinocytes and ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin lesion in mice. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.W.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, M.O.; Lee, R.W.; Kang, M.J.; Kim, S.M.; Min, J.H.; Oh, E.S.; Song, Y.N.; Jung, S.; et al. Daphnodorin C isolated from the stems of Daphne kiusiana Miquel attenuates airway inflammation in a mouse model of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Phytomedicine 2022, 96, 153848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, M.; Saleem, A.; Xaveria, A.; Akhtar, M.F. Daphnetin: A bioactive natural coumarin with diverse therapeutic potentials. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 993562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.W.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Kang, Y.H.; Mao, Y.; Wang, H.H.; Ge, W.H.; Shi, L.Y. Anti-inflammatory and protective properties of daphnetin in endotoxin-induced lung injury. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 12315–12325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Li, D. Daphnetin activates the Nrf2-dependent antioxidant response to prevent arsenic-induced oxidative insult in human lung epithelial cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 302, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Song, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Duan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Bi, X.; Geng, Y.; Chen, S.; et al. Daphnetin ameliorates acute lung injury in mice with severe acute pancreatitis by inhibiting the JAK2-STAT3 pathway. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Ge, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, B.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Shan, J.; Cheng, H.; Shi, L. Daphnetin ameliorates experimental colitis by modulating microbiota composition and T(reg)/T(h)17 balance. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 9308–9322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, K.; Kang, M.A.; Jang, H.J.; Ryu, H.W.; Oh, S.R.; Lee, H.J. Kurarinone Attenuates BLM-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis via Inhibiting TGF-β Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Hahn, H.J.; Oh, S.R.; Lee, H.J. Theophylline Attenuates BLM-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis by Inhibiting Th17 Differentiation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.-J.; Kim, W.J.; Lee, S.U.; Kim, M.-O.; Park, M.H.; Song, S.; Kim, D.-Y.; Lee, S.M.; Yuk, H.J.; Lee, D.Y.; et al. Optimization of chiisanoside and chiisanogenin isolation from Eleutherococcus sessiliflorus (Rupr. & Maxim.) leaves for industrial application: A pilot study. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 185, 115099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Lee, K.; Kang, M.A.; Kim, T.H.; Jang, H.J.; Ryu, H.W.; Oh, S.R.; Lee, H.J. Tilianin attenuates HDM-induced allergic asthma by suppressing Th2-immune responses via downregulation of IRF4 in dendritic cells. Phytomedicine 2021, 80, 153392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girtsman, T.; Jaffar, Z.; Ferrini, M.; Shaw, P.; Roberts, K. Natural Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells inhibit Th2 polarization but are biased toward suppression of Th17-driven lung inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 88, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoya, S.K.; Wilson, T.D.; Collins, E.L.; Lau, K.; Larkin, J., 3rd. Isolation and th17 differentiation of naïve CD4 T lymphocytes. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 26, e50765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciofani, M.; Madar, A.; Galan, C.; Sellars, M.; Mace, K.; Pauli, F.; Agarwal, A.; Huang, W.; Parkhurst, C.N.; Muratet, M.; et al. A validated regulatory network for Th17 cell specification. Cell 2012, 151, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, B.C.; Borok, Z. TGF-beta-induced EMT: Mechanisms and implications for fibrotic lung disease. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2007, 293, L525–L534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. The role of transforming growth factor β in T helper 17 differentiation. Immunology 2018, 155, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, Y.X.; Yu, Q.Y.; Tang, X.X. Role of interleukins in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Qu, L.; Sun, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zeng, J.; He, L.; Li, X.; Gu, W.; Nie, J.; Yu, X.; et al. Daphnetin contributes to allergen-induced Th2 cytokine expression and type 2-immune responses in atopic dermatitis and asthma. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 12383–12399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Q.; Hu, P.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Yang, T.; Liu, R. Daphnetin exerts an anticancer effect by attenuating the pro-inflammatory cytokines. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Zhou, T.; Wang, J.; Sang, X.; Lan, L.; Luo, L.; Yin, Z. Daphnetin reduces endotoxin lethality in mice and decreases LPS-induced inflammation in Raw264.7 cells via suppressing JAK/STATs activation and ROS production. Inflamm. Res. 2017, 66, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rex, D.A.B.; Dagamajalu, S.; Gouda, M.M.; Suchitha, G.P.; Chanderasekaran, J.; Raju, R.; Prasad, T.S.K.; Bhandary, Y.P. A comprehensive network map of IL-17A signaling pathway. J. Cell Commun. Signal 2023, 17, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouda, M.M.; Rex, D.A.B.; Es, S.P.; Modi, P.K.; Chanderasekaran, J.; Bhandary, Y.P. Proteomics Analysis Revealed the Importance of Inflammation-Mediated Downstream Pathways and the Protective Role of Curcumin in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in C57BL/6 Mice. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 2950–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Roden, A.C.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Prakash, Y.S.; Matteson, E.L.; Tschumperlin, D.J.; et al. Profibrotic effect of IL-17A and elevated IL-17RA in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and rheumatoid arthritis-associated lung disease support a direct role for IL-17A/IL-17RA in human fibrotic interstitial lung disease. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2019, 316, L487–L497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakura, Y.; Ishigame, H.; Saijo, S.; Nakae, S. Functional specialization of interleukin-17 family members. Immunity 2011, 34, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, A.; Gombault, A.; Villeret, B.; Alsaleh, G.; Fanny, M.; Gasse, P.; Adam, S.M.; Crestani, B.; Sibilia, J.; Schneider, P.; et al. B cell activating factor is central to bleomycin- and IL-17-mediated experimental pulmonary fibrosis. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 56, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margadant, C.; Sonnenberg, A. Integrin-TGF-beta crosstalk in fibrosis, cancer and wound healing. EMBO Rep. 2010, 11, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, R.T.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.A. Fibroblasts in fibrosis: Novel roles and mediators. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kliment, C.R.; Englert, J.M.; Crum, L.P.; Oury, T.D. A novel method for accurate collagen and biochemical assessment of pulmonary tissue utilizing one animal. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2011, 4, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tashiro, J.; Rubio, G.A.; Limper, A.H.; Williams, K.; Elliot, S.J.; Ninou, I.; Aidinis, V.; Tzouvelekis, A.; Glassberg, M.K. Exploring Animal Models That Resemble Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, L.; Wang, B.; Yuan, M.; Zhu, R. Drugs and Targets in Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.-J.; Ryu, H.W.; Kim, J.-H.; Hahn, H.-J.; Jang, H.-J.; Ko, S.-K.; Oh, S.-R.; Lee, H.-J. Daphnetin Alleviates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis through Inhibition of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and IL-17A. Cells 2023, 12, 2795. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12242795
Park S-J, Ryu HW, Kim J-H, Hahn H-J, Jang H-J, Ko S-K, Oh S-R, Lee H-J. Daphnetin Alleviates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis through Inhibition of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and IL-17A. Cells. 2023; 12(24):2795. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12242795
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Soo-Jin, Hyung Won Ryu, Ji-Hyeong Kim, Hwa-Jeong Hahn, Hyun-Jae Jang, Sung-Kyun Ko, Sei-Ryang Oh, and Hyun-Jun Lee. 2023. "Daphnetin Alleviates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis through Inhibition of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and IL-17A" Cells 12, no. 24: 2795. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12242795
APA StylePark, S. -J., Ryu, H. W., Kim, J. -H., Hahn, H. -J., Jang, H. -J., Ko, S. -K., Oh, S. -R., & Lee, H. -J. (2023). Daphnetin Alleviates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis through Inhibition of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and IL-17A. Cells, 12(24), 2795. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12242795