Unravelling the Gastroprotective Potential of Kefir: Exploring Antioxidant Effects in Preventing Gastric Ulcers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Kefir Preparation, Administration, and Microbiological Composition
2.4. Induction of Gastric Ulcer
2.5. Analysis of Gastric Juice
2.6. Gross Morphology, Ulcer Score, and Protective Index
2.7. Isolation of Gastric Cells
2.8. Reactive Oxygen Species Production
2.9. Cell Viability and Apoptosis
2.10. DNA Fragmentation
2.11. Plasma Levels of IL-10 and TNF-α
2.12. Myeloperoxidase Activity
2.13. Histopathological Evaluation of Gastric Damage
2.14. Gastric Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.15. Construction of PDB Structure of NADPH Oxidase 2
2.16. Molecular Docking
2.17. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
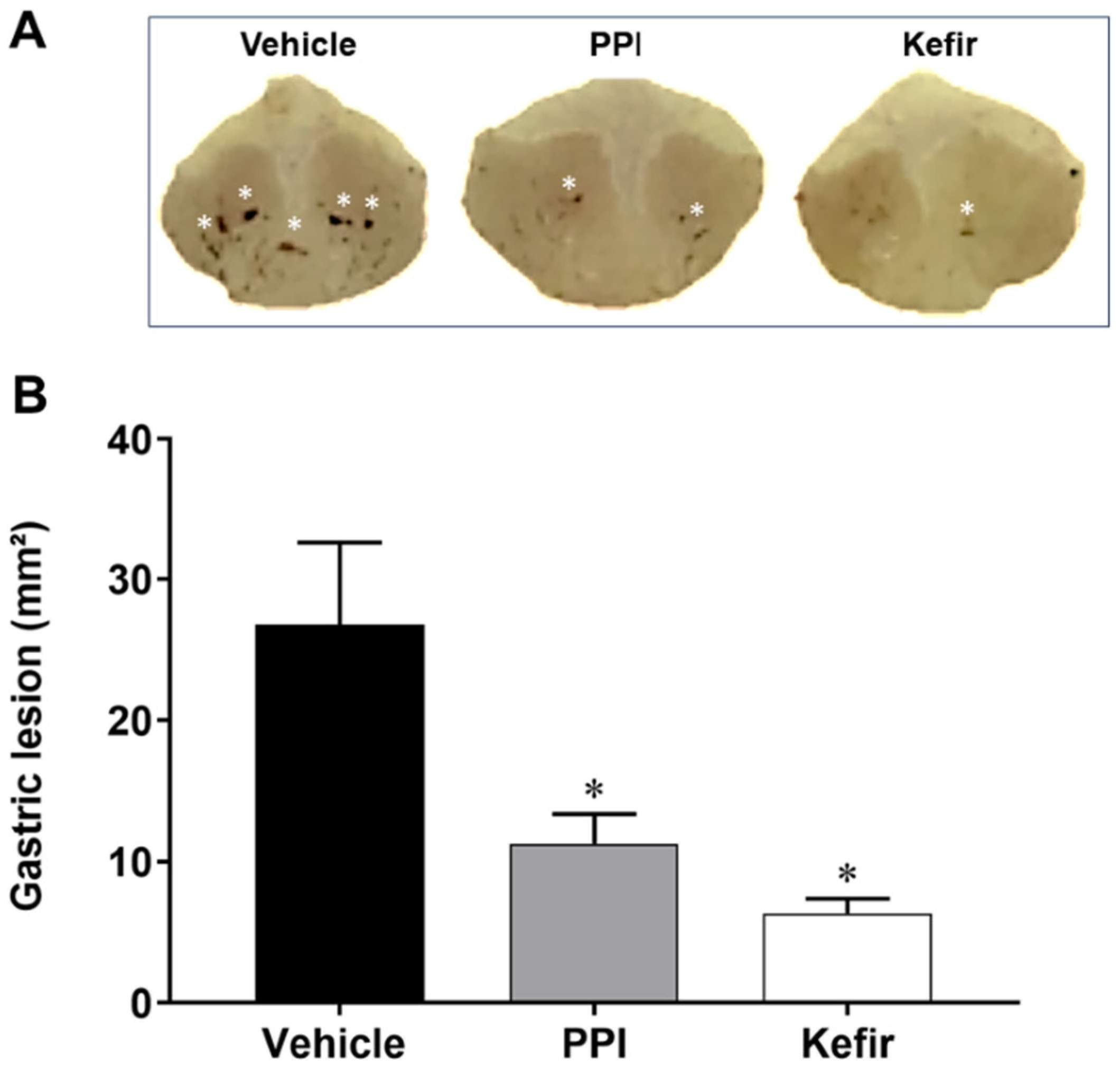
3.1. Effect of Kefir on Gross Morphology in Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Ulcer in Mice
3.2. Effects of Kefir on Ulcer and Protection Indexes
3.3. Effects of Kefir on ROS Production in Gastric cells of Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Ulcer in Mice
3.4. Effects of Kefir on Cell Apoptosis and DNA Fragmentation in Gastric Cells of Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Ulcer in Mice
3.5. Effects of Kefir on Systemic Cytokine Levels and Myeloperoxidase Activity in Plasma of Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Ulcer in Mice
3.6. Kefir Effects on Gastric Mucus and Histopathological Alterations in Gastric Tissue of Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Ulcer in Mice
3.7. Bioprospection of Antioxidant Peptides from Kefir and the Favorable Interaction with NADPH Oxidase 2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bindu, S.; Mazumder, S.; Bandyopadhyay, U. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and organ damage: A current perspective. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 180, 114147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongrakpanich, S.; Wongrakpanich, A.; Melhado, K.; Rangaswami, J. A Comprehensive Review of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug Use in The Elderly. Aging Dis. 2018, 9, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, F.W.D.; McAlindon, M.E. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and the gastrointestinal tract. Clin. Med. 2021, 21, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yegen, B.C. Lifestyle and Peptic Ulcer Disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 2034–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavitt, R.T.; Lipowska, A.M.; Anyane-Yeboa, A.; Gralnek, I.M. Diagnosis and Treatment of Peptic Ulcer Disease. Am. J. Med. 2019, 132, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Park, H.J.; Kim, H.; Song, J.; Lee, D. Gastroprotective Effects of Paeonia Extract Mixture HT074 against Experimental Gastric Ulcers in Rats. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 3546258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.; Chiranthanut, N.; Chansakaow, S.; Sireeratawong, S.; Khonsung, P.; Nimlamool, W.; Takuathung, M.N.; Lertprasertsuke, N. Gastroprotective effects of Pikad Tri-phol-sa-mut-than herbal remedy on multiple gastric ulcer models in rats. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, Z.; Li, M.; Xu, J.; Howell, D.C.; Li, Z.; Chen, F.E. Recent development on COX-2 inhibitors as promising anti-inflammatory agents: The past 10 years. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 2790–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faki, Y.; Er, A. Different Chemical Structures and Physiological/Pathological Roles of Cyclooxygenases. Rambam Maimonides Med. J. 2021, 12, e0003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkey, C.J.; Rampton, D.S. Prostaglandins and the gastrointestinal mucosa: Are they important in its function, disease, or treatment? Gastroenterology 1985, 89, 1162–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Mendoza, M.E.; López-Lorenzo, Y.; Cruz-Antonio, L.; Cruz-Oseguera, A.; García-Machorro, J.; Arrieta, J. Gastroprotective Effect of Juanislamin on Ethanol-Induced Gastric Lesions in Rats: Role of Prostaglandins, Nitric Oxide and Sulfhydryl Groups in the Mechanism of Action. Molecules 2020, 25, 2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Huang, H.; Guo, Z.; Chang, Y.; Li, Z. Role of prostaglandin E2 in tissue repair and regeneration. Theranostics 2021, 11, 8836–8854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, G.M.; Aires, R.; Santos, S.V.; Côco, L.Z.; Peters, B.; de Leone, E.M.A.; Ramos, A.B.; Amorim, G.F.; Nogueira, B.V.; de Ribeiro, G.R.C.; et al. Sildenafil attenuates nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory-induced gastric ulceration in mice via antioxidant and antigenotoxic mechanisms. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2021, 48, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barboza, K.R.M.; Coco, L.Z.; Alves, G.M.; Peters, B.; Vasquez, E.C.; Pereira, T.M.C.; Meyrelles, S.S.; Campagnaro, B.P. Gastroprotective effect of oral kefir on indomethacin-induced acute gastric lesions in mice: Impact on oxidative stress. Life Sci. 2018, 209, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.M.; Sachs, G. Pharmacology of proton pump inhibitors. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2008, 10, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fossmark, R.; Martinsen, T.C.; Waldum, H.L. Adverse Effects of Proton Pump Inhibitors—Evidence and Plausibility. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yibirin, M.; De Oliveira, D.; Valera, R.; Plitt, A.E.; Lutgen, S. Adverse Effects Associated with Proton Pump Inhibitor Use. Cureus 2021, 13, e12759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmy, H.A.; Ismail, A.F. Gastroprotective effect of kefir on ulcer induced in irradiated rats. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2015, 144, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowiak, P.; Śliżewska, K. Effects of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics on Human Health. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, Y.I.; Abd El-Ghffar, E.A. Spirulina ameliorates aspirin-induced gastric ulcer in albino mice by alleviating oxidative stress and inflammation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluzio, M.D.C.G.; Dias, M.M.E.; Martinezm, J.Á.; Milagrom, F.I. Kefir and Intestinal Microbiota Modulation: Implications in Human Health. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 638740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farag, M.A.; Jomaa, S.A.; El-Wahed, A.A.; El-Seedi, A.H.R. The Many Faces of Kefir Fermented Dairy Products: Quality Characteristics, Flavour Chemistry, Nutritional Value, Health Benefits, and Safety. Nutrients 2020, 12, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, X.; Jiang, H.; Dong, M. Analysis of the microflora in Tibetan kefir grains using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Food Microbiol. 2009, 26, 770–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friques, A.G.; Arpini, C.M.; Kalil, I.C.; Gava, A.L.; Leal, M.A.; Porto, M.L.; Nogueira, B.V.; Dias, A.T.; Andrade, T.U.; Pereira, T.M.C.; et al. Chronic administration of the probiotic kefir improves the endothelial function in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, K.T.; de Melo Pereira, G.V.; Campos, C.R.; Dragone, G.; Schwan, R.F. Brazilian kefir: Structure, microbial communities and chemical composition. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Zhang, L. Comparative analysis of the microbial community composition between Tibetan kefir grains and milks. Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamba, R.R.; Yamamoto, S.; Abdel-Hamid, M.; Sasaki, T.; Michihata, T.; Koyanagi, T.; Enomoto, T. Chemical, Microbiological, and Functional Characterization of Kefir Produced from Cow’s Milk and Soy Milk. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 7019286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenab, A.; Roghanian, R.; Ghorbani, N.; Ghaedi, K.; Emtiazi, G. The Efficacy of Electrospun PAN/Kefiran Nanofiber and Kefir in Mammalian Cell Culture: Promotion of PC12 Cell Growth, Anti-MCF7 Breast Cancer Cells Activities, and Cytokine Production of PBMC. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.J.; Huang, W.C.; Lin, J.S.; Chen, Y.M.; Ho, S.T.; Huang, C.C.; Tung, Y.T. Kefir Supplementation Modifies Gut Microbiota Composition, Reduces Physical Fatigue, and Improves Exercise Performance in Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, M.R.; Blandón, L.M.; Vandenberghe, L.P.; Rodrigues, C.; Castro, G.R.; Thomaz-Soccol, V.; Soccol, C.R. Milk kefir: Composition, microbial cultures, biological activities, and related products. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klippel, B.F.; Duemke, L.B.; Leal, M.A.; Friques, A.G.; Dantas, E.M.; Dalvi, R.F.; Gava, A.L.; Pereira, T.M.C.; Andrade, T.U.; Meyrelles, S.S.; et al. Effects of Kefir on the Cardiac Autonomic Tones and Baroreflex Sensitivity in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aires, R.; Amorim, F.G.; Côco, L.Z.; da Conceição, A.P.; Zanardo, T.É.C.; Taufner, G.H.; Nogueira, B.V.; Vasquez, E.C.; Pereira, T.M.C.; Campagnaro, B.P.; et al. Use of kefir peptide (Kef-1) as an emerging approach for the treatment of oxidative stress and inflammation in 2K1C mice. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 1965–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.W.; Kang, H.W.; Lim, W.C.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, I.Y.; Cho, H.Y. Kefir prevented excess fat accumulation in diet-induced obese mice. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2017, 81, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santanna, A.F.; Filete, P.F.; Lima, E.M.; Porto, M.L.; Meyrelles, S.S.; Vasquez, E.C.; Endringer, D.C.; Lenz, D.; Abdalla, D.S.P.; Pereira, T.M.C.; et al. Chronic administration of the soluble, nonbacterial fraction of kefir attenuates lipid deposition in LDLr−/− mice. Nutrition 2017, 35, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.L.; Tsai, T.C.; Tsai, Y.C.; Liao, J.W.; Yen, C.C.; Chen, C.M. Kefir peptides prevent high-fructose corn syrup-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in a murine model by modulation of inflammation and the JAK2 signaling pathway. Nutr. Diabetes 2016, 6, e237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohseni, S.; Bayani, M.; Bahmani, F.; Tajabadi-Ebrahimi, M.; Bayani, M.A.; Jafari, P.; Asemi, Z. The beneficial effects of probiotic administration on wound healing and metabolic status in patients with diabetic foot ulcer: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2018, 34, e2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, N.; El-Hayek, S.; Tarras, O.; El-Sabban, M.; El-Sibai, M.; Rizk, S. Kefir exhibits anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects on colon adenocarcinoma cells with no significant effects on cell migration and invasion. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 2117–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi, M.; Moridnia, A.; Mortazavi, D.; Salehi, M.; Bagheri, M.; Sheikhi, A. Kefir: A powerful probiotics with anticancer properties. Med. Oncol. 2017, 34, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senol, A.; Isler, M.; Sutcu, R.; Akin, M.; Cakir, E.; Ceyhan, B.M.; Kockar, M.C. Kefir treatment ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 13020–13029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, İ.; Dolar, M.E.; Özpınar, H. Effect of administering kefir on the changes in fecal microbiota and symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease: A randomized controlled trial. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 30, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ton, A.M.M.; Campagnaro, B.P.; Alves, G.A.; Aires, R.; Côco, L.Z.; Arpini, C.M.; Guerra E Oliveira, T.; Campos-Toimil, M.; Meyrelles, S.S.; Pereira, T.M.C.; et al. Oxidative Stress and Dementia in Alzheimer’s Patients: Effects of Synbiotic Supplementation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 2638703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos, V.R.; Aires, R.; Côco, L.Z.; Domingues, R.B.; Meyrelles, S.S.; Vasquez, E.C.; Pereira, T.M.C.; Campagnaro, B.P. Benefits of multi-day supplementation with probiotic kefir in Rasmussen encephalitis: The first case report. Nutr. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 2390–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellikci-Koyu, E.; Sarer-Yurekli, B.P.; Akyon, Y.; Aydin-Kose, F.; Karagozlu, C.; Ozgen, A.G.; Brinkmann, A.; Nitsche, A.; Ergunay, K.; Yilmaz, E.; et al. Effects of Regular Kefir Consumption on Gut Microbiota in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome: A Parallel-Group, Randomized, Controlled Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, K.N.; Fávero, A.G.; Ribeiro, W.; Ferreira, C.M.; Sartorelli, P.; Cardili, L.; Bogsan, C.S.; Bertaglia Pereira, J.N.; Sinigaglia, R.C.; Malinverni, A.C.M.; et al. Effects of kefir fermented milk beverage on sodium dextran sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis in rats. Heliyon 2022, 9, e12707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, C.P.; Rosario, A.I.L.S.; Lelis, C.A.; Rekowsky, B.S.S.; Carvalho, A.P.A.; Rosário, D.K.A.; Elias, T.A.; Costa, M.P.; Foguel, D.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Bioactive Compounds from Kefir and Their Potential Benefits on Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 9081738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabiu, S.; Garuba, T.; Sunmonu, T.O.; Sulyman, A.O.; Ismail, N.O. Indomethacin-induced gastric ulceration in rats: Ameliorative roles of Spondias mombin and Ficus exasperata. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamaddonfard, E.; Erfanparast, A.; Farshid, A.A.; Imani, M.; Mirzakhani, N.; Salighedar, R.; Tamaddonfard, S. Safranal, a constituent of saffron, exerts gastro-protective effects against indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer. Life Sci. 2019, 224, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, S.M.; White, K.L.; Schorah, C.J.; Calvert, R.J.; Skinner, C.; Miller, D.; Axon, A.T. In vivo DNA damage in gastric epithelial cells. Mutat. Res. 2000, 468, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, M.L.; Lírio, L.M.; Dias, A.T.; Batista, A.T.; Campagnaro, B.P.; Mill, J.G.; Meyrelles, S.S.; Baldo, M.P. Increased oxidative stress and apoptosis in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of fructose-fed rats. Toxicol. In Vitro 2015, 29, 1977–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagnaro, B.P.; Tonini, C.L.; Nogueira, B.V.; Casarini, D.E.; Vasquez, E.C.; Meyrelles, S.S. DNA damage and augmented oxidative stress in bone marrow mononuclear cells from Angiotensin-dependent hypertensive mice. Int. J. Hypertens. 2013, 2013, 305202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minozzo, B.R.; Lemes, B.M.; Justo, A.D.S.; Lara, J.E.; Petry, V.E.K.; Fernandes, D.; Belló, C.; Vellosa, J.C.R.; Campagnoli, E.B.; Nunes, O.C.; et al. Anti-ulcer mechanisms of polyphenols extract of Euphorbia umbellata (Pax) Bruyns (Euphorbiaceae). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 191, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amorim, F.G.; Coitinho, L.B.; Dias, A.T.; Friques, A.G.F.; Monteiro, B.L.; Rezende, L.C.D.; Pereira, T.M.C.; Campagnaro, B.P.; De Pauw, E.; Vasquez, E.C.; et al. Identification of new bioactive peptides from Kefir milk through proteopeptidomics: Bioprospection of antihypertensive molecules. Food Chem. 2019, 282, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinegger, M.; Meier, M.; Mirdita, M.; Vöhringer, H.; Haunsberger, S.J.; Söding, J. HH-suite3 for fast remote homology detection and deep protein annotation. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirdita, M.; von den Driesch, L.; Galiez, C.; Martin, M.J.; Söding, J.; Steinegger, M. Uniclust databases of clustered and deeply annotated protein sequences and alignments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D170–D176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guex, N.; Peitsch, M.C.; Schwede, T. Automated comparative protein structure modeling with SWISS-MODEL and Swiss-PdbViewer: A historical perspective. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studer, G.; Rempfer, C.; Waterhouse, A.M.; Gumienny, R.; Haas, J.; Schwede, T. QMEANDisCo—Distance constraints applied on model quality estimation. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 1765–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Jin, B.; Li, H.; Huang, S.Y. HPEPDOCK: A web server for blind peptide-protein docking based on a hierarchical algorithm. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piovesan, D.; Minervini, G.; Tosatto, S.C. The RING 2.0 web server for high quality residue interaction networks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Pan, S. Sources of superoxide radicals involved in the pathogenesis of diethyldithiocarbamate-induced gastric antral ulcer in rats. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 1998, 97, 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Cui, J.; Song, C.J.; Bian, J.S.; Sparatore, A.; Soldato, P.D.; Wang, X.Y.; Yan, C.D. H(2)S-releasing aspirin protects against aspirin-induced gastric injury via reducing oxidative stress. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Naga, R.N. Apocynin protects against ethanol-induced gastric ulcer in rats by attenuating the upregulation of NADPH oxidases 1 and 4. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2015, 242, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Li, X.; Xu, R.; Yao, K.; Yang, W.; Zhu, H.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J. DUOX2, a common modulator in preventive effects of monoamine-based antidepressants on water immersion restraint stress- and indomethacin- induced gastric mucosal damage. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 876, 173058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, L.; Gordon, M.; Baines, P.A.; Iheozor-Ejiofor, Z.; Sinopoulou, V.; Akobeng, A.K. Probiotics for induction of remission in ulcerative colitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 3, CD005573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milner, E.; Stevens, B.; An, M.; Lam, V.; Ainsworth, M.; Dihle, P.; Stearns, J.; Dombrowski, A.; Rego, D.; Segars, K. Utilizing Probiotics for the Prevention and Treatment of Gastrointestinal Diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 689958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgari, B.; Kermanian, F.; Hedayat Yaghoobi, M.; Vaezi, A.; Soleimanifar, F.; Yaslianifard, S. The Anti-Helicobacter pylori Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus, L. plantarum, and L. rhamnosus in Stomach Tissue of C57BL/6 Mice. Visc. Med. 2020, 36, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isik, M.; Ozbayer, C.; Donmez, D.B.; Colak, E.; Ustuner, M.C.; Erol, K.; Degirmenci, I. Effects of the probiotic, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, on ulcer pathogenesis, HSP70 stress protein and nitric oxide levels in stress induced ulcer. Biotech. Histochem. 2022, 97, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotteland, M.; Cruchet, S.; Verbeke, S. Effect of Lactobacillus ingestion on the gastrointestinal mucosal barrier alterations induced by indometacin in humans. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 15, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, E.K.; Yu, L.; Wong, H.P.; Wu, W.K.; Shin, V.Y.; Tai, E.K.; So, W.H.; Woo, P.C.; Cho, C.H. Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG enhances gastric ulcer healing in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 565, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friques, A.G.F.; Santos, F.D.N.; Angeli, D.B.; Silva, F.A.C.; Dias, A.T.; Aires, R.; Leal, M.A.S.; Nogueira, B.V.; Amorim, F.G.; Campagnaro, B.P.; et al. Bisphenol A contamination in infant rats: Molecular, structural, and physiological cardiovascular changes and the protective role of kefir. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 75, 108254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, B.L.; Dias, A.T.; Wanderkoke, S.C.; Yokota, R.; Casarini, D.E.; Leal, M.A.S.; Nogueira, B.V.; Meyrelles, S.S.; Campos-Toimil, M.; Campagnaro, B.P.; et al. Protective effects of kefir in the angiotensin II-dependent hypertension. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 75, 104260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, N.F.; Kumar, M.R.; Yeap, S.K.; Abdullah, J.O.; Khalid, M.; Omar, A.R.; Osman, M.A.; Mortadza, S.A.S.; Alitheen, N.B. Kefir and Its Biological Activities. Foods 2021, 10, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellatif, S.A.; Abdel Razik, E.S.; Abu-Serie, M.M.; Mahfouz, A.; Shater, A.F.; Saleh, F.M.; Hassan, M.M.; Alsanie, W.F.; Altalhi, A.; Daigham, G.E.; et al. Immunomodulatory Efficacy-Mediated Anti-HCV and Anti-HBV Potential of Kefir Grains; Unveiling the In Vitro Antibacterial, Antifungal, and Wound Healing Activities. Molecules 2022, 27, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Tang, G.; Zhang, C.; Wang, N.; Feng, Y. Gallic Acid and Diabetes Mellitus: Its Association with Oxidative Stress. Molecules 2021, 26, 7115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Deng, X.; Jian, S.; Zhang, M.; Wen, C.; Xin, Z.; Zhang, L.; Tong, A.; Ye, S.; Liao, P.; et al. Gallic Acid Alleviates Gut Dysfunction and Boosts Immune and Antioxidant Activities in Puppies Under Environmental Stress Based on Microbiome-Metabolomics Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 813890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, C.; Bindu, S.; Dey, S.; Alam, A.; Goyal, M.; Iqbal, M.S.; Sarkar, S.; Kumar, R.; Halder, K.K.; Debnath, M.C.; et al. Tryptamine-gallic acid hybrid prevents non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastropathy: Correction of mitochondrial dysfunction and inhibition of apoptosis in gastric mucosal cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 3495–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelwahab, S.I. Protective mechanism of gallic acid and its novel derivative against ethanol-induced gastric ulcerogenesis: Involvement of immunomodulation markers, Hsp70 and Bcl-2-associated X protein. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 16, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Asokkumar, K.; Umamaheswari, M.; Sivashanmugam, A.T.; Subhadradevi, V. Antiulcerogenic effect of gallic Acid in rats and its effect on oxidant and antioxidant parameters in stomach tissue. Indian. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 75, 149–155. [Google Scholar]
- Mard, S.A.; Mojadami, S.; Farbood, Y.; Gharib Naseri, M.K. The anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects of gallic acid against mucosal inflammation- and erosions-induced by gastric ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Vet. Res. Forum 2015, 6, 305–311. [Google Scholar]
- Fanaei, H.; Mard, S.A.; Sarkaki, A.; Goudarzi, G.; Khorsandi, L. Gallic acid treats dust-induced NAFLD in rats by improving the liver’s anti-oxidant capacity and inhibiting ROS/NFκβ/TNFα inflammatory pathway. Iran. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2021, 24, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengoa, A.A.; Dardis, C.; Gagliarini, N.; Garrote, G.L.; Abraham, A.G. Exopolysaccharides From Lactobacillus paracasei Isolated From Kefir as Potential Bioactive Compounds for Microbiota Modulation. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 583254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Nishizawa, T.; Tsugawa, H.; Mogami, S.; Hibi, T. Roles of oxidative stress in stomach disorders. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2012, 50, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yao, L.; Chu, L.; Du, H.; Fu, F. Protective effects of escin against indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer in mice. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2014, 24, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdogan, F.S.; Ozarslan, S.; Guzel-Seydim, Z.B.; Kök Taş, T. The effect of kefir produced from natural kefir grains on the intestinal microbial populations and antioxidant capacities of Balb/c mice. Food Res. Int. 2019, 115, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoneum, M.; Abdulmalek, S.; Pan, D. Reversal of age-associated oxidative stress in mice by PFT, a novel kefir product. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2020, 34, 2058738420950149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, O.S.M.; Amin, N.E.; Abdel Fattah, S.M.; Abd El-Rahman, O. Ameliorative effect of kefir against γ-irradiation induced liver injury in male rats: Impact on oxidative stress and inflammation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 35161–35173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badr, A.M.; El-Orabi, N.F.; Mahran, Y.F.; Badr, A.M.; Bayoumy, N.M.; Hagar, H.; Elmongy, E.I.; Atawia, R.T. In vivo and In silico evidence of the protective properties of carvacrol against experimentally-induced gastric ulcer: Implication of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiapoptotic mechanisms. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2023, 382, 110649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lima, M.D.S.F.; da Silva, R.A.; da Silva, M.F.; da Silva, P.A.B.; Costa, R.M.P.B.; Teixeira, J.A.C.; Porto, A.L.F.; Cavalcanti, M.T.H. Brazilian Kefir-Fermented Sheep’s Milk, a Source of Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Peptides. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2018, 10, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malta, S.M.; Batista, L.L.; Silva, H.C.G.; Franco, R.R.; Silva, M.H.; Rodrigues, T.S.; Correia, L.I.V.; Martins, M.M.; Venturini, G.; Espindola, F.S.; et al. Identification of bioactive peptides from a Brazilian kefir sample, and their anti-Alzheimer potential in Drosophila melanogaster. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejban, P.; Eslami, F.; Rahimi, N.; Takzare, N.; Jahansouz, M.; Dehpour, A.R. Involvement of nitric oxide pathway in the anti-inflammatory effect of modafinil on indomethacin-, stress-, and ethanol -induced gastric mucosal injury in rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 887, 173579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vona, R.; Pallotta, L.; Cappelletti, M.; Severi, C.; Matarrese, P. The Impact of Oxidative Stress in Human Pathology: Focus on Gastrointestinal Disorders. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Dou, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, H.; Wu, J.; Huang, Q.; Luo, D.; Yi, T.; Liu, Y.; Su, Z.; et al. Prophylactic efficacy of patchoulene epoxide against ethanol-induced gastric ulcer in rats: Influence on oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 283, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Wu, H.Q.; Cui, H.L.; Li, Y.Y.; Li, C.Z. Gastroprotective and anti-ulcer effects of oxymatrine against several gastric ulcer models in rats: Possible roles of antioxidant, antiinflammatory, and prosurvival mechanisms. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 2047–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miri, S.T.; Sotoodehnejadnematalahi, F.; Amiri, M.M.; Pourshafie, M.R.; Rohani, M. The impact of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium probiotic cocktail on modulation of gene expression of gap junctions dysregulated by intestinal pathogens. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venema, K.; Verhoeven, J.; Verbruggen, S.; Espinosa, L.; Courau, S. Probiotic survival during a multi-layered tablet development as tested in a dynamic, computer-controlled in vitro model of the stomach and small intestine (TIM-1). Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tompkins, T.A.; Mainville, I.; Arcand, Y. The impact of meals on a probiotic during transit through a model of the human upper gastrointestinal tract. Benef. Microbes 2011, 2, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.Y.; Liu, J.M.; Luo, H.H.; Liu, A.H.; Jiang, Y. Potential protective effects of Clostridium butyricum on experimental gastric ulcers in mice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8340–8351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobyliak, N.; Falalyeyeva, T.; Virchenko, O.; Mykhalchyshyn, G.; Bodnar, P.; Spivak, M.; Yankovsky, D.; Beregova, T.; Ostapchenko, L. Comparative experimental investigation on the efficacy of mono- and multiprobiotic strains in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease prevention. BMC Gastroenterol. 2016, 16, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeesi, M.; Eskandari-Roozbahani, N.; Shomali, T. Gastro-protective effect of Biebersteinia multifida root hydro-methanolic extract in rats with ethanol-induced peptic ulcer. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2019, 9, 410–418. [Google Scholar]
- Mennigen, R.; Nolte, K.; Rijcken, E.; Utech, M.; Loeffler, B.; Senninger, N.; Bruewer, M. Probiotic mixture VSL#3 protects the epithelial barrier by maintaining tight junction protein expression and preventing apoptosis in a murine model of colitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 296, G1140–G1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, E.K.; Tai, E.K.K.; Koo, M.W.L.; Wong, H.P.S.; Wu, W.K.K.; Yu, L.; So, W.H.L.; Woo, P.C.Y.; Cho, C.H. Enhancement of gastric mucosal integrity by Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 2128–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado Galdeano, C.; Cazorla, S.I.; Lemme Dumit, J.M.; Vélez, E.; Perdigón, G. Beneficial Effects of Probiotic Consumption on the Immune System. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 74, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinderola, G.; Perdigón, G.; Duarte, J.; Farnworth, E.; Matar, C. Effects of the oral administration of the exopolysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens on the gut mucosal immunity. Cytokine 2006, 36, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhouani, H.; Gonçalves, C.; Maia, F.R.; Oliveira, J.M.; Reis, R.L. Biological performance of a promising Kefiran-biopolymer with potential in regenerative medicine applications: A comparative study with hyaluronic acid. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virchenko, O.V.; Falalyeyeva, T.M.; Beregova, T.V.; Maryana, S.Y. The multistrain probiotic enhances the healing process of stress-induced lesions of the gastric mucosa of rats. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 249–259. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, S.; Yadav, S.K.; Saha, B.; Tyagi, M.; Singh Rathee, J.; Chattopadhyay, S. A bis-resorcinol resveratrol congener prevents indomethacin-induced gastric ulceration by inhibiting TNF-α as well as NF-κB and JNK pathways. Free Radic. Res. 2019, 53, 596–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaeishahmirzadi, M.; Motamedi Rad, N.; Kalantar, M.; Ayatollahi, H.; Shakeri, S.; Sheikhi, M.; Shekari, M. The Association of Gastritis and Peptic Ulcer With Polymorphisms in the Inflammatory-related Genes IL-4 and IL-10 in Iranian Population. Iran. J. Pathol. 2018, 13, 229–236. [Google Scholar]
- Gomi, A.; Harima-Mizusawa, N.; Shibahara-Sone, H.; Kano, M.; Miyazaki, K.; Ishikawa, F. Effect of Bifidobacterium bifidum BF-1 on gastric protection and mucin production in an acute gastric injury rat model. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, Y.; Yoshikawa, T. Oxidative stress involvement and gene expression in indomethacin-induced gastropathy. Redox Rep. 2006, 11, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornick, S.; Tawiah, A.; Chadee, K. Roles and regulation of the mucus barrier in the gut. Tissue Barriers 2015, 3, e982426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovarik, J.J.; Hölzl, M.A.; Hofer, J.; Waidhofer-Söllner, P.; Sobanov, Y.; Koeffel, R.; Saemann, M.D.; Mechtcheriakova, D.; Zlabinger, G.J. Eicosanoid modulation by the short-chain fatty acid n-butyrate in human monocytes. Immunology 2013, 139, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoder, G.; Al-Menhali, A.A.; Al-Yassir, F.; Karam, S.M. Potential role of probiotics in the management of gastric ulcer. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasaly, N.; Hermoso, M.A.; Gotteland, M. Butyrate and the Fine-Tuning of Colonic Homeostasis: Implication for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolte, M.; Meining, A.; Seifert, E.; Alexandridis, T. Treatment with lansoprazole also induces hypertrophy of the parietal cells of the stomach. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2000, 196, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.H. Proton Pump Inhibitor-Related Gastric Mucosal Changes. Gut Liver 2021, 15, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, K.L.; Araújo, T.H.; Schneedorf, J.M.; de Souza Ferreira, C.; Moraes, G.D.O.I.; Coimbra, R.S.; Rodrigues, M.R. A novel beer fermented by kefir enhances anti-inflammatory and anti-ulcerogenic activities found isolated in its constituents. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 21, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Groups | Gastric Index | Ulcer Protection (%) | Gastric Juice (pH) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle | 4.0 ± 0.3 | - | 4.91 ± 0.42 |
| PPI | 3.0 ± 0.2 | 64.33 ± 6.31 * | 4.35 ± 0.37 |
| Kefir | 3.0 ± 0.3 | 69.39 ± 4.90 * | 4.55 ± 0.25 |
| Groups | IL-10 (pg/mL) | TNF-α (pg/mL) | MPO Activity (a.u. mg Protein) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle | 24.9 ± 2.0 | 56.2 ± 5.5 pg/mL | 0.042 ± 0.012 |
| PPI | 23.5 ± 2.4 * | 38.8 ± 3.0 pg/mL * | 0.050 ± 0.011 |
| Kefir | 33.8 ± 2.6 *# | 34.7 ± 4.9 pg/mL * | 0.040 ± 0.010 |
| # | Peptide Sequence | Dock Scoring (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | AVPYPQR | −179.717 |
| 2 | CGLVPVLAENR | −211.662 |
| 3 | DFGHIQYVAAYR | −236.526 |
| 4 | DMPIQAFLLY | −202.306 |
| 5 | EINQFYQK | −195.413 |
| 6 | EMPFPKYPVEPF | −208.377 |
| 7 | FLLYQEPVLGPVRGPFPIIV | −261.937 |
| 8 | FVAPFPEVFG | −215.28 |
| 9 | GLFQINNK | −165.179 |
| 10 | GTWYSLAMAASDISLLDAQSAPLR | −215.777 |
| 11 | IHPFAQTQSLVYPFPGP | −236.735 |
| 12 | IHPFAQTQSLVYPFPGPIPNSLPQN | −245.583 |
| 13 | IPPLTQTPVVVPPFLQPEVMGVSK | −278.492 |
| 14 | KLDQWLCEK | −182.732 |
| 15 | KVGINYWLAHK | −221.75 |
| 16 | LACQCLVR | −172.099 |
| 17 | LLDDDLTDDIMCVK | −141.894 |
| 18 | LLYQEPVLGPVRGPFPIIV | −242.36 |
| 19 | LVYPFPGPIHNSLPQ | −231.785 |
| 20 | LVYPFPGPIPN | −212.428 |
| 21 | LYQEPVLGPVRGPFPII | −217.374 |
| 22 | LYQEPVLGPVRGPFPIIV | −220.833 |
| 23 | NLHLPLPLLQ | −228.763 |
| 24 | NLHLPLPLLQS | −194.289 |
| 25 | PFPEVFGK | −210.473 |
| 26 | QFLPYPYYAKPA | −233.97 |
| 27 | RFFVAPFPEVFGK | −252.026 |
| 28 | SLVYPFPGPIH | −228.771 |
| 29 | SLVYPFPGPIHNSLPQ | −241.852 |
| 30 | SQSLTLTDVENLHLPLP | −196.224 |
| 31 | TDLLNVCMDAK | −166.611 |
| 32 | VAPFPEVFGK | −195.564 |
| 33 | WCTISQPEWFK | −217.273 |
| 34 | YPFPGPIPN | −223.244 |
| 35 | YPVEPFTESQSL | −189.741 |
| Rank | NADPH Oxidase 2 | Peptide 13 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | W18 | I1 |
| 2 | L21 | F14 |
| 3 | W272 | P2 |
| 4 | F62 | P12 |
| 5 | L66 | V10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Côco, L.Z.; Aires, R.; Carvalho, G.R.; Belisário, E.d.S.; Yap, M.K.K.; Amorim, F.G.; Conde-Aranda, J.; Nogueira, B.V.; Vasquez, E.C.; Pereira, T.d.M.C.; et al. Unravelling the Gastroprotective Potential of Kefir: Exploring Antioxidant Effects in Preventing Gastric Ulcers. Cells 2023, 12, 2799. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12242799
Côco LZ, Aires R, Carvalho GR, Belisário EdS, Yap MKK, Amorim FG, Conde-Aranda J, Nogueira BV, Vasquez EC, Pereira TdMC, et al. Unravelling the Gastroprotective Potential of Kefir: Exploring Antioxidant Effects in Preventing Gastric Ulcers. Cells. 2023; 12(24):2799. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12242799
Chicago/Turabian StyleCôco, Larissa Zambom, Rafaela Aires, Glaucimeire Rocha Carvalho, Eduarda de Souza Belisário, Michelle Khai Khun Yap, Fernanda Gobbi Amorim, Javier Conde-Aranda, Breno Valentim Nogueira, Elisardo Corral Vasquez, Thiago de Melo Costa Pereira, and et al. 2023. "Unravelling the Gastroprotective Potential of Kefir: Exploring Antioxidant Effects in Preventing Gastric Ulcers" Cells 12, no. 24: 2799. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12242799
APA StyleCôco, L. Z., Aires, R., Carvalho, G. R., Belisário, E. d. S., Yap, M. K. K., Amorim, F. G., Conde-Aranda, J., Nogueira, B. V., Vasquez, E. C., Pereira, T. d. M. C., & Campagnaro, B. P. (2023). Unravelling the Gastroprotective Potential of Kefir: Exploring Antioxidant Effects in Preventing Gastric Ulcers. Cells, 12(24), 2799. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12242799






