Peptidyl Arginine Deiminases in Chronic Diseases: A Focus on Rheumatoid Arthritis and Interstitial Lung Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. PAD Enzyme
2.1. Peptidyl Arginine Deiminases “PADs”
2.2. Biological Function
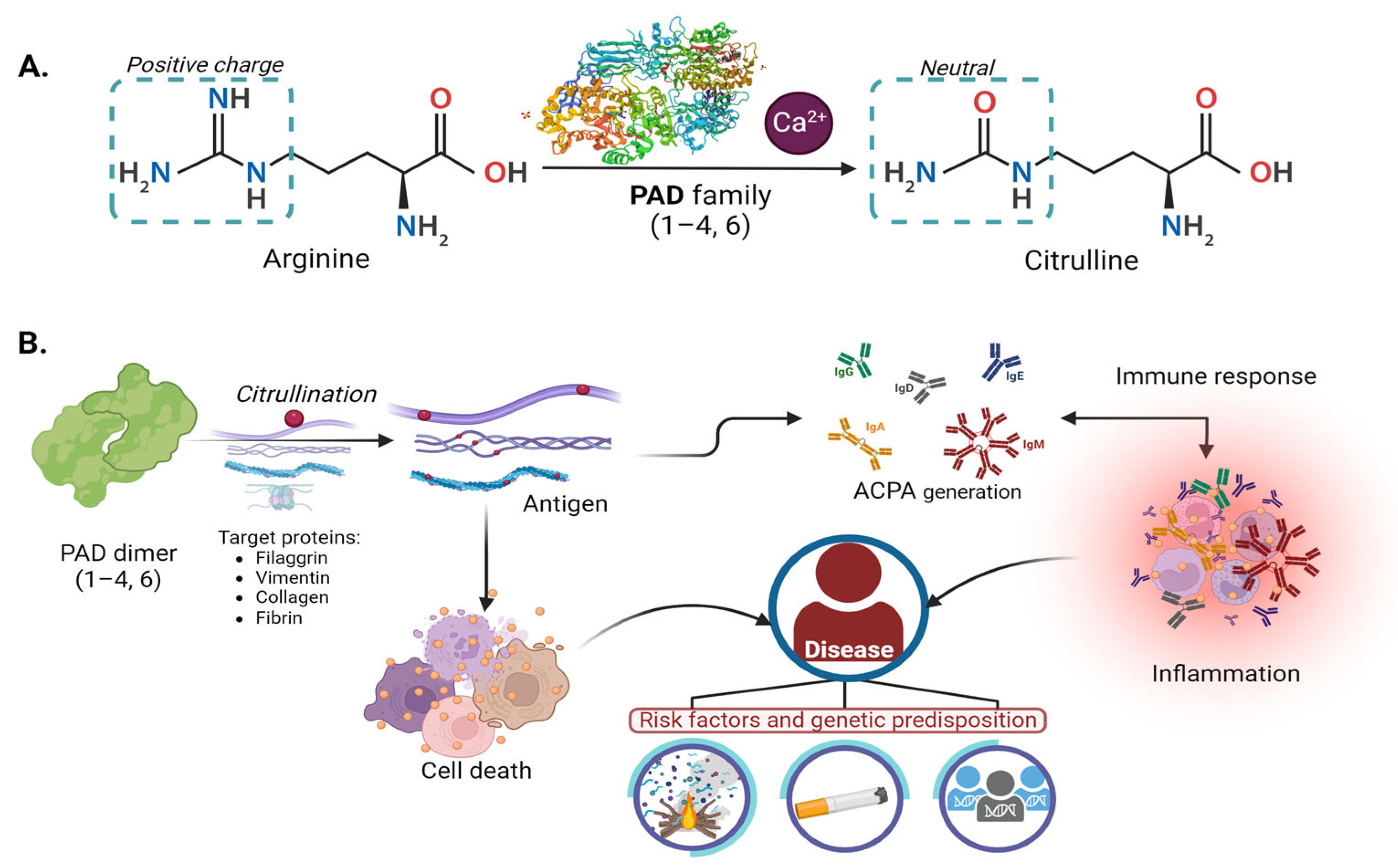
2.3. Enzyme Mechanism
2.4. Enzyme Regulation
3. Genes
3.1. Localization and Structure of the Gene
3.2. Genetic Variants
4. Citrullination, PAD, and Physiopathology
4.1. Rheumatoid Arthritis
4.1.1. Molecular Mechanisms and Role of PADs in RA
4.1.2. Genetic Associations: Variations in PAD Genes and Their Potential Contribution to RA Susceptibility and Severity
4.2. Lung Diseases
4.2.1. Role of PADs in Lung Diseases
| Protein | Lung Disease | Evaluation | Clinical Finding | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAD4 | Cystic fibrosis | Autoantibody anti-PAD4 levels | Elevated levels compared with the control group. Negative correlation with pulmonary function. | [110] |
| PAD4 | Cystic fibrosis | Autoantibody anti-PAD4 levels | Increased levels were observed, compared to patients with rheumatoid arthritis. A negative correlation was found between lung function and increased P. aeruginosa lung infection. | [111] |
| PAD2 PAD4 | COPD | LL-37 Citrullination | Infiltration of airway cells with PAD4 and Neutrophils. PADI2 in bronchial epithelial cells and leukocytes. PADI2 and PADI4 citrullinated LL-37 at three arginine sites (7, 29, and 34). This led to changes in the production of proinflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α. | [112] |
| PAD2 | IPF | Fibrosis | Citrullinated vimentin in lung macrophages, a significant increase in IPF and IPF-smokers. | [113] |
| PAD4 | IPF RA-ILD | Protein expression in granulocytes and macrophages | Citrullinated peptide increased in IPF and ILD | [114] |
| PAD4 | IPF RA-ILD | Autoantibody production | Anti-PAD4- patients have a higher DTA Fibrosis Score (fibrosis on HRCT was quantified using a data-driven texture analysis DTA fibrosis score). Anti-PAD4+ better lung function (FVC%) | [115] |
| CEP-1 | RA-ILD | Autoantibody production | The presence of anti-CCP/CEP-1+ is associated with ILD and erosive disease. | [116] |
| ACPA | RA-ILD | Reactivity of peptides Citrullinated proteins | >3-fold increase in reactivity. | [117] |
| PAD2 PAD4 | RA-ILD | Protein levels and SNV in gene PADI | Increased protein PAD4 levels in RA-ILD patients and PADI4 SNV risk genotype carriers. | [118] |
4.2.2. NET-PAD in Lung Diseases
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dreyton, C.J.; Knuckley, B.; Jones, J.E.; Lewallen, D.M.; Thompson, P.R. Mechanistic Studies of Protein Arginine Deiminase 2: Evidence for a Substrate-Assisted Mechanism. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 4426–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzilotti, C.; Pratesi, F.; Tommasi, C.; Migliorini, P. Peptidylarginine Deiminase 4 and Citrullination in Health and Disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2010, 9, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vossenaar, E.R.; Zendman, A.J.W.; van Venrooij, W.J.; Pruijn, G.J.M. PAD, a Growing Family of Citrullinating Enzymes: Genes, Features and Involvement in Disease. Bioessays 2003, 25, 1106–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Gaalen, F.A.; Linn-Rasker, S.P.; van Venrooij, W.J.; de Jong, B.A.; Breedveld, F.C.; Verweij, C.L.; Toes, R.E.; Huizinga, T.W. Autoantibodies to Cyclic Citrullinated Peptides Predict Progression to Rheumatoid Arthritis in Patients with Undifferentiated Arthritis: A Prospective Cohort Study. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavanas, S.; Adoue, V.; Méchin, M.-C.; Ying, S.; Dong, S.; Duplan, H.; Charveron, M.; Takahara, H.; Serre, G.; Simon, M. Long-Range Enhancer Associated with Chromatin Looping Allows AP-1 Regulation of the Peptidylarginine Deiminase 3 Gene in Differentiated Keratinocyte. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méchin, M.C.; Enji, M.; Nachat, R.; Chavanas, S.; Charveron, M.; Ishida-Yamamoto, a.; Serre, G.; Takahara, H.; Simon, M. The Peptidylarginine Deiminases Expressed in Human Epidermis Differ in Their Substrate Specificities and Subcellular Locations. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 1984–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachat, R.; Méchin, M.C.; Takahara, H.; Chavanas, S.; Charveron, M.; Serre, G.; Simon, M. Peptidylarginine Deiminase Isoforms 1-3 Are Expressed in the Epidermis and Involved in the Deimination of K1 and Filaggrin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 124, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Kanno, T.; Yamaki, A.; Kojima, T.; Shiraiwa, M.; Kawada, A.; Méchin, M.-C.; Chavanas, S.; Serre, G.; Simon, M.; et al. NF-Y and Sp1/Sp3 Are Involved in the Transcriptional Regulation of the Peptidylarginine Deiminase Type III Gene (PADI3) in Human Keratinocytes. Biochem. J. 2006, 397, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X. Jinxiang Han Expression of Peptidylarginine Deiminase Type 4 (PAD4) in Various Tumors. Mol. Carcinog. 2006, 45, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baka, Z.; György, B.; Géher, P.; Buzás, E.I.; Falus, A.; Nagy, G. Citrullination under Physiological and Pathological Conditions. Jt. Bone Spine 2012, 79, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Kan, R.; Anguish, L.; Nelson, L.M.; Coonrod, S.A. Potential Role for MATER in Cytoplasmic Lattice Formation in Murine Oocytes. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanno, T.; Kawada, A.; Yamanouchi, J.; Yosida-Noro, C.; Yoshiki, A.; Shiraiwa, M.; Kusakabe, M.; Manabe, M.; Tezuka, T.; Takahara, H. Human Peptidylarginine Deiminase Type III: Molecular Cloning and Nucleotide Sequence of the CDNA, Properties of the Recombinant Enzyme, and Immunohistochemical Localization in Human Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 115, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, B.; Ishigami, A.; Maruyama, N.; Carp, R.I.; Kim, Y.-S.; Choi, E.-K. Peptidylarginine Deiminase and Protein Citrullination in Prion Diseases: Strong Evidence of Neurodegeneration. Prion 2013, 7, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, S.; Rocha-Ferreira, E.; Thei, L.; Mawjee, P.; Bennett, K.; Thompson, P.R.; Subramanian, V.; Nicholas, A.P.; Peebles, D.; Hristova, M.; et al. Peptidylarginine Deiminases: Novel Drug Targets for Prevention of Neuronal Damage Following Hypoxic Ischemic Insult (HI) in Neonates. J. Neurochem. 2014, 130, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Stadler, S.; Correll, S.; Li, P.; Wang, D.; Hayama, R.; Leonelli, L.; Han, H.; Grigoryev, S.A.; et al. Histone Hypercitrullination Mediates Chromatin Decondensation and Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 184, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, F.; Darrah, E.; Gucek, M.; Cole, R.N.; Rosen, A.; Zhu, X. Autocitrullination of Human Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase Type 4 Regulates Protein Citrullination during Cell Activation. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1630–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arandjelovic, S.; McKenney, K.R.; Leming, S.S.; Mowen, K.A. ATP Induces Protein Arginine Deiminase 2-Dependent Citrullination in Mast Cells through the P2X7 Purinergic Receptor. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 4112–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarcsa, E.; Marekov, L.N.; Mei, G.; Melino, G.; Lee, S.C.; Steinert, P.M. Protein Unfolding by Peptidylarginine Deiminase: Substrate Specificity and Structural Relationships of the Natural Substrates Trichohyalin and Filaggrin. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 30709–30716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Venrooij, W.J.; Pruijn, G.J. Citrullination: A Small Change for a Protein with Great Consequences for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Res. 2000, 2, 249–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, C.Y.; Shave, S.; Chor, A.L.T.; Salleh, A.B.; Rahman, M.B.B.A.; Walkinshaw, M.D.; Tejo, B.A. Discovery of a New Class of Inhibitors for the Protein Arginine Deiminase Type 4 (PAD4) by Structure-Based Virtual Screening. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13 (Suppl. S1), S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-L.; Tsai, I.-C.; Chang, C.-W.; Liao, Y.-F.; Liu, G.-Y.; Hung, H.-C. Functional Roles of the Non-Catalytic Calcium-Binding Sites in the N-Terminal Domain of Human Peptidylarginine Deiminase 4. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e51660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Ying, S.; Kojima, T.; Shiraiwa, M.; Kawada, A.; Méchin, M.-C.; Adoue, V.; Chavanas, S.; Serre, G.; Simon, M.; et al. Crucial Roles of MZF1 and Sp1 in the Transcriptional Regulation of the Peptidylarginine Deiminase Type I Gene (PADI1) in Human Keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, K.; Hagiwara, T.; Yamada, M. Nuclear Localization of Peptidylarginine Deiminase V and Histone Deimination in Granulocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 49562–49568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama-Hamada, M.; Suzuki, A.; Kubota, K.; Takazawa, T.; Ohsaka, M.; Kawaida, R.; Ono, M.; Kasuya, A.; Furukawa, H.; Yamada, R.; et al. Comparison of Enzymatic Properties between HPADI2 and HPADI4. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 327, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- György, B.; Tóth, E.; Tarcsa, E.; Falus, A.; Buzás, E.I. Citrullination: A Posttranslational Modification in Health and Disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 38, 1662–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knuckley, B.; Bhatia, M.; Thompson, P.R. Protein Arginine Deiminase 4: Evidence for a Reverse Protonation Mechamism. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 6578–6587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, S.B.; Stitt, B.L.; Ash, D.E. Cysteine 351 Is an Essential Nucleophile in Catalysis by Porphyromonas Gingivalis Peptidylarginine Deiminase. Arc. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 504, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.E.; Causey, C.P.; Knuckley, B.; Slack-Noyes, J.L.; Thompson, P.R. Protein Arginine Deiminase 4 (PAD4): Current Understanding and Future Therapeutic Potential. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Devel. 2009, 12, 616–627. [Google Scholar]
- Leitman, D.C.; Paruthiyil, S.; Vivar, O.I.; Saunier, E.F.; Herber, C.B.; Cohen, I.; Tagliaferri, M.; Speed, T.P. Regulation of Specific Target Genes and Biological Responses by Estrogen Receptor Subtype Agonists. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2011, 10, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vossenaar, E.R.; Després, N.; Lapointe, E.; van der Heijden, A.; Lora, M.; Senshu, T.; van Venrooij, W.J.; Ménard, H.A. Rheumatoid Arthritis Specific Anti-Sa Antibodies Target Citrullinated Vimentin. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2004, 6, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, K.; Arai, S.; Suzuki, A.; Nariai, Y.; Urano, T.; Nakayama, M.; Ohara, O.; Yamamura, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Miyazaki, T. PAD4 Regulates Proliferation of Multipotent Haematopoietic Cells by Controlling C-Myc Expression. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Too, C.L.; Murad, S.; Dhaliwal, J.S.; Larsson, P.T.; Jiang, X.; Ding, B.; Alfredsson, L.; Klareskog, L.; Padyukov, L. Polymorphisms in Peptidylarginine Deiminase (PADI) Associate with Rheumatoid Arthritis in Diverse Asian Populations: Evidence from MyEIRA Study and Meta-Analysis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, R250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iida, A.; Nakamura, Y. Identification of 45 Novel SNPs in the 83-Kb Region Containing Peptidylarginine Deiminase Types 1 and 3 Loci on Chromosomal Band 1p36.13. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 49, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerbino, D.R.; Achuthan, P.; Akanni, W.; Amode, M.R.; Barrell, D.; Bhai, J.; Billis, K.; Cummins, C.; Gall, A.; Girón, C.G.; et al. Ensembl 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 46, D754–D761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Bello, J.; Vargas-Alarcón, G.; Tovilla-Zárate, C.; Fragoso, J.M. Polimorfismos de Un Solo Nucleótido (SNP): Implicaciones Funcionales de Los SNP Reguladores (RSNP) y de Los SNP-ARN Estructurales (SrSNP) En Enfermedades Complejas. Gac. Med. Mex. 2013, 149, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lim, M.-K.; Shim, T.S.; Park, M.; Lee, S.-K.; Sohn, Y.-H.; Sheen, D.-H.; Shim, S.-C. Heterozygote Genotypes for PADI4_89 Were Protectively Associated with Susceptibility to Tuberculosis in Koreans. Rheumatol. Int. 2014, 35, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moscarello, M.A.; Wood, D.D.; Ackerley, C.; Boulias, C. Myelin in Multiple Sclerosis Is Developmentally Immature. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 94, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscarello, M.A.; Mastronardi, F.G.; Wood, D.D. The Role of Citrullinated Proteins Suggests a Novel Mechanism in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Sclerosis. Neurochem. Res. 2007, 32, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastronardi, F.G.; Wood, D.D.; Mei, J.; Raijmakers, R.; Tseveleki, V.; Dosch, H.-M.; Probert, L.; Casaccia-Bonnefil, P.; Moscarello, M.A. Increased Citrullination of Histone H3 in Multiple Sclerosis Brain and Animal Models of Demyelination: A Role for Tumor Necrosis Factor-Induced Peptidylarginine Deiminase 4 Translocation. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 11387–11396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaga, H.; Ishigami, A. Protein Deimination in the Rat Brain after Kainate Administration: Citrulline-Containing Proteins as a Novel Marker of Neurodegeneration. Neurosci. Lett. 2001, 299, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, S.; Gögel, S.; Leung, K.-Y.; Vernay, B.; Nicholas, A.P.; Causey, C.P.; Thompson, P.R.; Greene, N.D.E.; Ferretti, P. Protein Deiminases: New Players in the Developmentally Regulated Loss of Neural Regenerative Ability. Dev. Biol. 2011, 355, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishigami, A.; Ohsawa, T.; Hiratsuka, M.; Taguchi, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Saito, Y.; Murayama, S.; Asaga, H.; Toda, T.; Kimura, N.; et al. Abnormal Accumulation of Citrullinated Proteins Catalyzed by Peptidylarginine Deiminase in Hippocampal Extracts from Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 80, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, Y.; Nunokawa, A.; Kaneko, N.; Arinami, T.; Ujike, H.; Inada, T.; Iwata, N.; Kunugi, H.; Itokawa, M.; Otowa, T.; et al. A Two-Stage Case-Control Association Study of PADI2 with Schizophrenia. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 54, 430–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Ji, H.J.; Sun, N.B.; Chang, X.T.; Xu, B.; Wang, Y.; Cao, M.; Zhu, Q.; Zang, Q.I.; Jiang, Z.M. B-Cell Specific Moloney Leukemia Virus Insert Site 1 and Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase IV Positively Regulate Carcinogenesis and Progression of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 4349–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.; Han, J.; Pang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shen, Z. Increased PADI4 Expression in Blood and Tissues of Patients with Malignant Tumors. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baka, Z.; Barta, P.; Losonczy, G.; Krenács, T.; Pápay, J.; Szarka, E.; Sármay, G.; Babos, F.; Magyar, A.; Géher, P.; et al. Specific Expression of PAD4 and Citrullinated Proteins in Lung Cancer Is Not Associated with Anti-CCP Antibody Production. Int. Immunol. 2011, 23, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherrington, B.D.; Zhang, X.; McElwee, J.L.; Morency, E.; Anguish, L.J.; Coonrod, S.A. Potential Role for PAD2 in Gene Regulation in Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElwee, J.L.; Mohanan, S.; Griffith, O.L.; Breuer, H.C.; Anguish, L.J.; Cherrington, B.D.; Palmer, A.M.; Howe, L.R.; Subramanian, V.; Causey, C.P.; et al. Identification of PADI2 as a Potential Breast Cancer Biomarker and Therapeutic Target. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gamble, M.J.; Stadler, S.; Cherrington, B.D.; Causey, C.P.; Thompson, P.R.; Roberson, M.S.; Kraus, W.L.; Coonrod, S.A. Genome-Wide Analysis Reveals PADI4 Cooperates with Elk-1 to Activate c-Fos Expression in Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNee, G.; Eales, K.L.; Wei, W.; Williams, D.S.; Barkhuizen, A.; Bartlett, D.B.; Essex, S.; Anandram, S.; Filer, A.; Moss, P.A.H.; et al. Citrullination of Histone H3 Drives IL-6 Production by Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells in MGUS and Multiple Myeloma. Leukemia 2017, 31, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Cui, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, S.; Chang, X. Investigating Citrullinated Proteins in Tumour Cell Lines. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 11, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O.; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 Rheumatoid Arthritis Classification Criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Collaborative Initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebbag, M.; Simon, M.; Vincent, C.; Masson-Bessière, C.; Girbal, E.; Durieux, J.-J.; Serre, G. The Antiperinuclear Factor and the So-Called Antikeratin Antibodies Are the Same Rheumatoid Arthritis-Specific Autoantibodies. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 2672–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firestein, G.S. Evolving Concepts of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nature 2003, 423, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vossenaar, E.R.; Radstake, T.R.D.; Van Der Heijden, A.; Van Mansum, M.A.M.; Dieteren, C.; De Rooij, D.J.; Barrera, P.; Zendman, A.J.W.; Van Venrooij, W.J. Expression and Activity of Citrullinating Peptidylarginine Deiminase Enzymes in Monocytes and Macrophages. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2004, 63, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.; Li, S.; Chen, B.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, L.; Li, F. Serum Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibodies and Rheumatoid Factor Increase the Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis–Related Interstitial Lung Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 4533–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoda, H.; Fujio, K.; Shibuya, M.; Okamura, T.; Sumitomo, S.; Okamoto, A.; Sawada, T.; Yamamoto, K. Detection of Autoantibodies to Citrullinated BiP in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients and Pro-Inflammatory Role of Citrullinated BiP in Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, A.; Kochi, Y.; Shoda, H.; Seri, Y.; Fujio, K.; Sawada, T.; Yamada, R.; Yamamoto, K. Decreased Severity of Experimental Autoimmune Arthritis in Peptidylarginine Deiminase Type 4 Knockout Mice. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016, 17, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damgaard, D.; Senolt, L.; Nielsen, M.F.; Pruijn, G.J.; Nielsen, C.H. Demonstration of Extracellular Peptidylarginine Deiminase (PAD) Activity in Synovial Fluid of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Using a Novel Assay for Citrullination of Fibrinogen. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikari, K.; Kuwahara, M.; Nakamura, T.; Momohara, S.; Hara, M.; Yamanaka, H.; Tomatsu, T.; Kamatani, N. Association between PADI4 and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Replication Study. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 3054–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.P.; Lee, H.S.; Ju, H.; Cho, H.; Kang, C.; Bae, S.C. A Functional Haplotype of the PADI4 Gene Associated with Increased Rheumatoid Arthritis Susceptibility in Koreans. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badillo-Soto, M.A.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, M.; Pérez-Pérez, M.E.; Daza-Benitez, L.; Bollain-y-Goytia, J.J.; Carrillo-Jiménez, M.A.; Avalos-Díaz, E.; Herrera-Esparza, R. Potential Protein Targets of the Peptidylarginine Deiminase 2 and Peptidylarginine Deiminase 4 Enzymes in Rheumatoid Synovial Tissue and Its Possible Meaning. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 3, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damgaard, D.; Senolt, L.; Nielsen, C.H. Increased Levels of Peptidylarginine Deiminase 2 in Synovial Fluid from Anti-CCP-Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: Association with Disease Activity and Inflammatory Markers. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 918–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelli, L.C.; Konig, M.F.; Gelber, A.C.; Iii, C.O.B.; Darrah, E. Smoking Is Not Linked to the Development of Anti-Peptidylarginine Deiminase 4 Autoantibodies in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolfenbach, J.R.; Deane, K.D.; Derber, L.A.; Colin, I.; Donnell, O.; Gilliland, W.R.; Edison, J.D.; Rosen, A.; Darrah, E.; Norris, J.M.; et al. Autoimmunity to Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase Type 4 Precedes Clinical Onset of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2633–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, M.K.; Kantyka, T.; Falkowski, K.; Aliko, A.; Aga, A.B.; Lillegraven, S.; Sexton, J.; Fevang, B.T.; Mydel, P.; Haavardsholm, E.A. Peptidylarginine Deiminase 4 (PAD4) Activity in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 49, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darrah, E.; Giles, J.T.; Davis, R.L.; Naik, P.; Wang, H.; Konig, M.F.; Cappelli, L.C.; Bingham, C.O.; Danoff, S.K.; Andrade, F. Autoantibodies to Peptidylarginine Deiminase 2 Are Associated with Less Severe Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, L.; Pratesi, F.; Brink, M.; Ärlestig, L.; Amato, C.D.; Bartaloni, D.; Migliorini, P.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S. Antibodies Directed against Endogenous and Exogenous Citrullinated Antigens Pre-Date the Onset of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auger, I.; Balandraud, N.; Massy, E.; Hemon, M.F.; Peen, E.; Arnoux, F.; Mariot, C.; Martin, M.; Lafforgue, P.; Busnel, J.M.; et al. Peptidylarginine Deiminase Autoimmunity and the Development of Anti–Citrullinated Protein Antibody in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Hapten–Carrier Model. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnoux, F.; Mariot, C.; Peen, E.; Lambert, N.C.; Balandraud, N.; Roudier, J.; Isabelle, A. Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase Immunization Induces Anticitrullinated Protein Antibodies in Mice with Particular MHC Types. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E10169–E10177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelf, M.A.; Sokolove, J.; Lahey, L.J.; Wagner, C.A.; Wang, Y.; Beebe, D.J.; Robinson, W.H.; Huttenlocher, A. Peptidylarginine Deiminase 4 Contributes to Tumor Necrosis Factor α–Induced Inflammatory Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 1482–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandpur, R.; Carmona-Rivera, C.; Vivekanandan-Giri, A.; Gizinski, A.; Yalavarthi, S.; Knight, J.S.; Friday, S.; Li, S.; Patel, R.M.; Subramanian, V.; et al. NETs Are a Source of Citrullinated Autoantigens and Stimulate Inflammatory Responses in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 178ra40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirugnanasambandham, I.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Kuppusamy, G.; Kumar Singh, S.; Dua, K. Peptidylarginine Deiminase-4: Medico-Formulative Strategy towards Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 200, 115040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Pedrera, C.; Barbarroja, N.; Patiño-Trives, A.M.; Luque-Tévar, M.; Collantes-Estevez, E.; Escudero-Contreras, A.; Pérez-Sánchez, C. Molecular Sciences Effects of Biological Therapies on Molecular Features of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparks, J.A.; Costenbader, K.H. Genetics, Environment, and Gene-Environment Interactions in the Development of Systemic Rheumatic Diseases. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. 2015, 40, 637–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronzer, V.L.; Sparks, J.A. Occupational Inhalants, Genetics and the Respiratory Mucosal Paradigm for ACPA-Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, E.; Kelly, C.; Eggleton, P.; De Soyza, A.; Hutchinson, D. The Lung in ACPA-Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Initiating Site of Injury? Rheumatology 2014, 53, 1940–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costenbader, K.H.; Karlson, E.W. Cigarette Smoking and Autoimmune Disease: What Can We Learn from Epidemiology? Lupus 2006, 15, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsalahy, M.M.; Nasser, H.S.; Hashem, M.M.; Elsayed, S.M. Effect of Tobacco Smoking on Tissue Protein Citrullination and Disease Progression in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Saudi Pharm. J. 2010, 18, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klareskog, L.; Stolt, P.; Lundberg, K.; Källberg, H.; Bengtsson, C.; Grunewald, J.; Rönnelid, J.; Erlandsson Harris, H.; Ulfgren, A.-K.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S.; et al. A New Model for an Etiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Smoking May Trigger HLA–DR (Shared Epitope)–Restricted Immune Reactions to Autoantigens Modified by Citrullination. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makrygiannakis, D.; Hermansson, M.; Ulfgren, A.-K.; Nicholas, A.P.; Zendman, A.J.W.; Eklund, A.; Grunewald, J.; Skold, C.M.; Klareskog, L.; Catrina, A.I. Smoking Increases Peptidylarginine Deiminase 2 Enzyme Expression in Human Lungs and Increases Citrullination in BAL Cells. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 1488–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, K.; Shimizu, T.; Hashimoto, H.; Hidaka, Y.; Yamada, M.; Sato, M. Structural Basis for Histone N-Terminal Recognition by Human Peptidylarginine Deiminase 4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5291–5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, S.-Y.; Han, T.-U.; Choi, C.-B.; Sung, Y.-K.; Bae, S.-C.; Kang, C. Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase Type IV (PADI4) Haplotypes Interact with Shared Epitope Regardless of Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide Antibody or Erosive Joint Status in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Case Control Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.; Xia, Y.; Pan, J.; Meng, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, X. PADI2 Is Significantly Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochi, Y.; Thabet, M.M.; Suzuki, A.; Okada, Y.; Daha, N.A.; Toes, R.E.M.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Myouzen, K.; Kubo, M.; Yamada, R.; et al. PADI4 Polymorphism Predisposes Male Smokers to Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 512–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, A.; Yamada, R.; Chang, X.; Tokuhiro, S.; Sawada, T.; Suzuki, M.; Nagasaki, M.; Nakayama-Hamada, M.; Kawaida, R.; Ono, M.; et al. Functional Haplotypes of PADI4, Encoding Citrullinating Enzyme Peptidylarginine Deiminase 4, Are Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesla, M.; Kolarz, B.; Darmochwal-Kolarz, D. The Lack of Association between PADI4_94 or PADI4_104 Polymorphisms and RF, ACPA and Anti-PAD4 in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panati, K.; Pal, S.; Rao, K.V.; Reddy, V.D. Association of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) of PADI4 Gene with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) in Indian Population. Genes Genet. Syst. 2012, 87, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, A.; Bowes, J.; Eyre, S.; Spreckley, K.; Hinks, A.; John, S.; Worthington, J. A Functional Haplotype of ThePADI4 Gene Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis in a Japanese Population Is Not Associated in a United Kingdom Population. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 1117–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harney, S.M.J.; Meisel, C.; Sims, A.-M.; Woon, P.Y.; Wordsworth, B.P.; Brown, M.A. Genetic and Genomic Studies of PADI4 in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology 2005, 44, 869–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plenge, R.M.; Padyukov, L.; Remmers, E.F.; Purcell, S.; Lee, A.T.; Karlson, E.W.; Wolfe, F.; Kastner, D.L.; Alfredsson, L.; Altshuler, D.; et al. Replication of Putative Candidate-Gene Associations with Rheumatoid Arthritis in >4000 Samples from North America and Sweden: Association of Susceptibility with PTPN22, CTLA4, and PADI4. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 77, 1044–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoppe, B.; Häupl, T.; Gruber, R.; Kiesewetter, H.; Burmester, G.R.; Salama, A.; Dörner, T. Detailed Analysis of the Variability of Peptidylarginine Deiminase Type 4 in German Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Case-Control Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandjbakhch, F.; Fajardy, I.; Ferré, B.; Dubucquoi, S.; Flipo, R.-M.; Roger, N.; Solau-Gervais, E. A Functional Haplotype of PADI4 Gene in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Positive Correlation in a French Population. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 36, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, M.; Zakeri, Z.; Taheri, H.; Bahari, G.; Taheri, M. Association between Peptidylarginine Deiminase Type 4 Rs1748033 Polymorphism and Susceptibility to Rheumatoid Arthritis in Zahedan, Southeast Iran. Iran. J. Allergy. Asthma. Immunol. 2015, 14, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zavala-Cerna, M.G.; Gonzalez-Montoya, N.G.; Nava, A.; Gamez-Nava, J.I.; Moran-Moguel, M.C.; Rosales-Gomez, R.C.; Gutierrez-Rubio, S.A.; Sanchez-Corona, J.; Gonzalez-Lopez, L.; Davalos-Rodriguez, I.P.; et al. PADI4 Haplotypes in Association with RA Mexican Patients, a New Prospect for Antigen Modulation. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 383681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verea Hernando, H.; Otero González, I. Neumopatías Por Fármacos; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturbe Fernández, D.; Peris Sánchez, R.; Ferreira Moreno, A.; Fernández, F.E. Aspectos Relevantes En El Manejo de La Enfermedad Pulmonar Intersticial Difusa. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2009, 45, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Disdier, C.; Pérez-Negrín, L.; Morales, P.; Cordovilla, R. Revista Del Año 2009 En Neumología Intervencionista, Enfermedades Intersticiales y Trasplante. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2010, 46, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Jiménez, E.; Molina-Molina, M.; Ramírez, J.; Aliaga, J.L.; Sánchez, M.; Xaubet, A. Diffuse Interstitial Lung Disease Related to Peribronchiolar Metaplasia. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2009, 45, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, H.; Oka, S.; Shimada, K.; Masuo, K.; Nakajima, F.; Funano, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Komiya, A.; Fukui, N.; Sawasaki, T.; et al. Autoantibody Profiles in Collagen Disease Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD): Antibodies to Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I-Related Chain A (MICA) as Markers of ILD. Biomark. Insights 2015, 10, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, D.A. Lung Disease Related to Collagen Vascular Disease. J. Thorac. Imaging 2009, 24, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, H.P.; Dong, S.K.; Park, I.N.; Se, J.J.; Kitaichi, M.; Nicholson, A.G.; Colby, T.V. Prognosis of Fibrotic Interstitial Pneumonia: Idiopathic versus Collagen Vascular Disease-Related Subtypes. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 175, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Elicker, B.M.; Maldonado, F.; Webb, W.R.; Ryu, J.H.; Van Uden, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; King, T.E.; Collard, H.R. Usual Interstitial Pneumonia in Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 35, 1322–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulin, F.; Doyle, T.J.; Fletcher, E.A.; Ascherman, D.P.; Rosas, I.O. Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Shared Mechanistic and Phenotypic Traits Suggest Overlapping Disease Mechanisms. Rev. Investig. Clin. 2015, 67, 280–286. [Google Scholar]
- Klareskog, L.; Catrina, A.I.; Paget, S. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Lancet 2009, 373, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, M.; Collins, B.F.; Ho, L.A.; Raghu, G. Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Lung Disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2015, 24, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harlow, L.; Gochuico, B.R.; Rosas, I.O.; Doyle, T.J.; Osorio, J.C.; Travers, T.S.; Camacho, C.C.; Oddis, C.V.; Ascherman, D.P.; Immunol, C. Anti-Citrullinated Heat Shock Protein 90 Antibodies Identified in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Are a Marker of Lung-Specific Immune Responses. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 155, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugli, E.B.; Correia, R.E.S.M.; Fischer, R.; Lundberg, K.; Bracke, K.R.; Montgomery, A.B.; Kessler, B.M.; Brusselle, G.G.; Venables, P.J. Expression of Citrulline and Homocitrulline Residues in the Lungs of Non-Smokers and Smokers: Implications for Autoimmunity in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damgaard, D.; Nielsen, M.F.B.; Quisgaard Gaunsbaek, M.; Palarasah, Y.; Svane-Knudsen, V.; Nielsen, C.H.; Friberg, M.; Gaunsbaek, M.Q.; Palarasah, Y.; Svane-Knudsen, V.; et al. Smoking Is Associated with Increased Levels of Extra- Cellular Peptidylarginine Deiminase 2 (PAD2) in the Lungs. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33, 405–408. [Google Scholar]
- Linnemann, R.W.; Yadav, R.; Zhang, C.; Sarr, D.; Rada, B.; Stecenko, A.A. Serum Anti-PAD4 Autoantibodies Are Present in Cystic Fibrosis Children and Increase with Age and Lung Disease Severity. Autoimmunity 2022, 55, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Yoo, D.G.; Kahlenberg, J.M.; Bridges, S.L.; Oni, O.; Huang, H.; Stecenko, A.; Rada, B. Systemic Levels of Anti-PAD4 Autoantibodies Correlate with Airway Obstruction in Cystic Fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2019, 18, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilsgård, O.; Andersson, P.; Malmsten, M.; Nordin, S.L.; Linge, H.M.; Eliasson, M.; Sörenson, E.; Erjefält, J.S.; Bylund, J.; Olin, A.I.; et al. Peptidylarginine Deiminases Present in the Airways during Tobacco Smoking and Inflammation Can Citrullinate the Host Defense Peptide LL-37, Resulting in Altered Activities. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 46, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, F.; Surolia, R.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G.; Kulkarni, T.; Massicano, A.V.F.; Mobley, J.A.; Mondal, S.; De Andrade, J.A.; et al. Citrullinated Vimentin Mediates Development and Progression of Lung Fibrosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eaba2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samara, K.D.; Trachalaki, A.; Tsitoura, E.; Koutsopoulos, A.V.; Lagoudaki, E.D.; Lasithiotaki, I.; Margaritopoulos, G.; Pantelidis, P.; Bibaki, E.; Siafakas, N.M.; et al. Upregulation of Citrullination Pathway: From Autoimmune to Idiopathic Lung Fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, T.M.; Solomon, J.J.; Humphries, S.M.; Swigris, J.J.; Ahmed, F.; Wang, H.; Darrah, E.; Demoruelle, M.K. Serum Antibodies to Peptidylarginine Deiminase-4 in Rheumatoid Arthritis Associated-Interstitial Lung Disease Are Associated with Decreased Lung Fibrosis and Improved Survival. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 365, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alunno, A.; Bistoni, O.; Pratesi, F.; La Paglia, G.M.C.; Puxeddu, I.; Migliorini, P.; Gerli, R. Anti-Citrullinated Alpha Enolase Antibodies, Interstitial Lung Disease and Bone Erosion in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, J.T.; Danoff, S.K.; Sokolove, J.; Wagner, C.A.; Winchester, R.; Pappas, D.A.; Siegelman, S.; Connors, G.; Robinson, W.H.; Bathon, J.M. Association of Fine Specificity and Repertoire Expansion of Anticitrullinated Peptide Antibodies with Rheumatoid Arthritis Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nava-Quiroz, K.J.; Rojas-Serrano, J.; Perez-Rubio, G.; Buendia-Roldan, I.; Mejía, M.; Fernández-López, J.C.; Rodríguez-Henriquez, P.; Ayala-Alcantar, N.; Ramos-Martínez, E.; López-Flores, L.A.; et al. Molecular Factors in PAD2 (PADI2) and PAD4 (PADI4) Are Associated with Interstitial Lung Disease Susceptibility in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Cells 2023, 12, 2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, L.; Ugarte-Berzal, E.; Martens, E.; Fiten, P.; Vandooren, J.; Janssens, R.; Blanter, M.; Yu, K.; Boon, M.; Struyf, S.; et al. Citrullination as a Novel Posttranslational Modification of Matrix Metalloproteinases. Matrix Biol. 2021, 95, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulvinskiene, I.; Raudoniute, J.; Bagdonas, E.; Ciuzas, D.; Poliakovaite, K.; Stasiulaitiene, I.; Zabulyte, D.; Bironaite, D.; Rimantas Venskutonis, P.; Martuzevicius, D.; et al. Lung Alveolar Tissue Destruction and Protein Citrullination in Diesel Exhaust-Exposed Mouse Lungs. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 125, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabcanovic-Musija, F.; Obermayer, A.; Stoiber, W.; Krautgartner, W.D.; Steinbacher, P.; Winterberg, N.; Bathke, C.A.; Klappacher, M.; Studnicka, M. Neutrophil Extracellular Trap (NET) Formation Characterises Stable and Exacerbated COPD and Correlates with Airflow Limitation. Respir. Res. 2015, 16, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Tomita, B.; Salinger, A.; Tilvawala, R.R.; Li, L.; Hakami, H.; Liu, T.; Tsoyi, K.; Rosas, I.O.; Reinhardt, D.P.; et al. PAD2-Mediated Citrullination of Fibulin-5 Promotes Elastogenesis. Matrix Biol. 2021, 102, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, A.M.; De Pablo, P.; Buckley, C.D.; Ahmad, A.; Stockley, R.A. Smoke Exposure as a Determinant of Autoantibody Titre in A1-Antitrypsin Deficiency and COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 37, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, D.; Müller, J.; McCarthy, J.E.; Gun’ko, Y.K.; Verma, N.K.; Bi, X.; Di Cristo, L.; Kickham, L.; Movia, D.; Prina-Mello, A.; et al. Cadmium Nanoparticles Citrullinate Cytokeratins within Lung Epithelial Cells: Cadmium as a Potential Cause of Citrullination in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2018, 13, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigari, N.; Moghimi, N.; Shahraki, F.S.; Mohammadi, S.; Roshani, D. Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide (CCP) Antibody in Patients with Wood-Smoke-Induced Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) without Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2015, 35, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, J.T.; Darrah, E.; Danoff, S.; Johnson, C.; Andrade, F.; Rosen, A.; Bathon, J.M. Association of Cross-Reactive Antibodies Targeting Peptidyl-Arginine Deiminase 3 and 4 with Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiersma, V.R.; Clarke, A.; Pouwels, S.D.; Perry, E.; Abdullah, T.M.; Kelly, C.; De Soyza, A.; Hutchinson, D.; Eggleton, P.; Bremer, E. Galectin-9 Is a Possible Promoter of Immunopathology in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Activation of Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase 4 (PAD-4) in Granulocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palterer, B.; Vitiello, G.; Del Carria, M.; D’Onofrio, B.; Martinez-Prat, L.; Mahler, M.; Cammelli, D.; Parronchi, P. Anti-Protein Arginine Deiminase Antibodies Are Distinctly Associated with Joint and Lung Involvement in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology 2023, 62, 2410–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, A.; Khan, M.A.; Bade, G.; Talwar, A. Orchestration of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (Nets), a Unique Innate Immune Function during Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Development. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Ikari, J.; Anazawa, R.; Tanaka, N.; Katsumata, Y.; Shimada, A.; Suzuki, E.; Tatsumi, K. PAD4 Deficiency Improves Bleomycin-Induced Neutrophil Extracellular Traps and Fibrosis in Mouse Lung. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 63, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawaja, A.A.; Chong, D.L.W.; Sahota, J.; Mikolasch, T.A.; Pericleous, C.; Ripoll, V.M.; Booth, H.L.; Khan, S.; Rodriguez-Justo, M.; Giles, I.P.; et al. Identification of a Novel HIF-1α-AMβ2 Integrin-NET Axis in Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Disease. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Enzymes | Intracellular Localization | Main Distribution in Tissues/Organs | Physiological Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAD1 | Cytosol | Dermis and uterus. | Citrullination of simple keratin, differentiation of keratinocytes. | [3,4,5] |
| PAD2 | Cytosol | Skeletal muscle, spleen, brain, salivary glands, uterus. | In the plasticity of the central nervous system. It interacts with the inhibitor of κB kinase, suppresses the activity of NF-κB and stimulation through lipopolysaccharides. | [3,6,7] |
| PAD3 | Cytosol | Hair follicles and epidermis. | Differentiation of epidermis in terminal stages of cells. | [3,6,7,8] |
| PAD4/5 | Nucleus | Hematopoietic system. | p53 regulation and estrogen pathway. | [3,9,10] |
| PAD6 | Cytosol | Ovaries, testes, and peripheral blood leukocytes. | Activation of embryonic genome. Movement (kinesis) of oocytes by microtubules. | [3,8,11,12] |
| Gene | Variant Total * | Total SNP n (%) | SNP | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| srSNP | cSNP | |||||||
| 3′UTR n (%) | 5′UTR n (%) | Intronic n (%) | Synonymous n (%) | Non-Synonymous n (%) | ||||
| PADI1 | ENSG00000142623 | 12,075 | 11,231 (93.01) | 231 (1.91) | 23 (0.19) | 4927 (40.80) | 155 (1.28) | 375 (3.11) |
| PADI2 | ENSG00000117115 | 21,526 | 19,288 (89.60) | 298 (1.38) | 20 (0.09) | 10,220 (47.48) | 293 (1.36) | 539 (2.50) |
| PADI3 | ENSG00000142619 | 6150 | 5638 (91.67) | 160 (2.60) | 17 (0.28) | 3668 (59.64) | 151 (2.46) | 347 (5.64) |
| PADI4 | ENSG00000159339 | 21,122 | 19,324 (91.49) | 93 (0.44) | 20 (0.09) | 9417 (44.58) | 167 (0.79) | 421 (1.99) |
| PADI6 | ENSG00000276747 | 6998 | 6214 (88.80) | 42 (0.60) | 21 (0.30) | 4239 (60.57) | 200 (2.86) | 292 (4.17) |
| SNV Tested | Former Nomenclature | Country | n (Cases/Controls) | p | OR (CI 95%) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PADI1 | ||||||
| rs2977310 | China | 429 (266/163) | [84] | |||
| PADI2 | ||||||
| rs2235926 rs2057094 rs2076616 | China | 429 (266/163) | <0.01 <0.05 NS | 1.70 (1.57–1.86) 1.36 (1.06–1.86) 1.33 (1.00–1.77) | [84] | |
| rs1005753 | China | 461 (255/206) | <0.05 | 0.77 (0.51–1.15) | [32] | |
| rs1005753 | Malaysia | 1502 (516/986) | <0.05 | 0.97 (0.81–1.17) | ||
| rs1005753 | India | 664 (379/285) | <0.05 | 0.78 (0.62–1.00) | ||
| PADI4 | ||||||
| rs11203368 | China | 429 (266/163) | <0.01 | 0.59 (0.44–0.78) | [84] | |
| rs11203367 | PADI4_104 | Japan | 1926 (1019/907) | <0.05 | 1.14 (1.0–1.29) | [85] |
| rs874881 rs2240340 rs2240339 rs1748033 | PADI4_92 PADI4_94 PADI4_95 PADI4_97 PADI4_99 PADI4_100 PADI4_101 PADI4_104 | Japan | 1566 (830/736) | <0.01 | 1.66 (1.23–2.25) 1.97 (1.44–2.69) 1.89 (1.35–2.66) 1.92 (1.35–2.7) 1.82 (1.33–2.44) 1.75 (1.3–2.38) 1.82 (1.33–2.5) 2.0 (1.41–2.86) | [86] |
| rs2240340 rs2240337 rs1748033 | PADI4_94 PADI4_102 PADI4_104 | Japan | 2096 (1170/926) | ≤0.01 | 1.23 (1.09–1.39) 1.33 (1.07–1.73) 1.21 (1.07–1.38) | [60] |
| rs2240340 rs1748033 | PADI4_94 PADI4_104 | Poland | 147(122/25) | NS | [87] | |
| rs11203366 rs11203367 rs874881 rs1748033 | PADI4_89 PADI4_90 PADI4_92 PADI4_104 | Korea | 937 (545/392) | <0.05 | 1.7 (1.3–2.2) 1.7 (1.3–2.2) 1.7 (1.2–2.4) 1.8 (1.2–1.9) | [61] |
| rs11203366 | PADI4_89 | Korea | 133 (50/83) | <0.05 | 2.22 (0.72–6.86) | [36] |
| rs1748033 | PADI4_104 | India | 151 (95/56) | <0.001 | 2.27 (1.28–4.011) | [88] |
| rs11203366 rs11203367 rs874881 rs1748033 | PADI4_89 PADI4_90 PADI4_92 PADI4_104 | UK | 1320 (839/481) | NS | [89] | |
| rs874881 rs2240340 rs2240339 rs1748033 | PADI4_92 PADI4_94 PADI4_97, 99 PADI4_100 PADI4_103 PADI4_104 | UK | 222 (111/111) | NS | [90] | |
| rs2240340 | PADI4_94 | Sweden | 1031 (1530/881) | NS | [91] | |
| rs2240340 | PADI4_94 | USA | 1716 (840/876) | ≤0.001 | 1.24 (1.08–1.42) | [91] |
| rs11203366 rs11203367 rs2240340 | PADI4_89 PADI4_90 PADI4_94 | Germany | 204 (102/102) | <0.05 | 1.6 (1.1–2.3) 1.6 (1.1–2.3) 1.6 (1.1–2.3) | [92] |
| rs11203366 rs11203367 | PADI4_89 PADI4_90 | France | 680 (405/275) | >0.05 <0.05 | [93] | |
| rs1748033 | PADI4_104 | Iran | 300 (150/150) | ≤0.01 | 1.63 (1.16–2.29) | [94] |
| rs1748033 | PADI4_104 | Netherlands | 1026 (635/391) | <0.05 | 1.32 (1.02–1.72) | [85] |
| rs11203366 rs11203367 | PADI4_89 PADI4_90 | Mexico | 184 (86/98) | <0.05 | 2.51 (1.19–5.32) 2.64 (1.21–5.75) | [95] |
| PADI6 | ||||||
| rs10788668 rs2526839 rs6695849 rs7538876 | China | 429 (266/163) | NS | [84] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nava-Quiroz, K.J.; López-Flores, L.A.; Pérez-Rubio, G.; Rojas-Serrano, J.; Falfán-Valencia, R. Peptidyl Arginine Deiminases in Chronic Diseases: A Focus on Rheumatoid Arthritis and Interstitial Lung Disease. Cells 2023, 12, 2829. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12242829
Nava-Quiroz KJ, López-Flores LA, Pérez-Rubio G, Rojas-Serrano J, Falfán-Valencia R. Peptidyl Arginine Deiminases in Chronic Diseases: A Focus on Rheumatoid Arthritis and Interstitial Lung Disease. Cells. 2023; 12(24):2829. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12242829
Chicago/Turabian StyleNava-Quiroz, Karol J., Luis A. López-Flores, Gloria Pérez-Rubio, Jorge Rojas-Serrano, and Ramcés Falfán-Valencia. 2023. "Peptidyl Arginine Deiminases in Chronic Diseases: A Focus on Rheumatoid Arthritis and Interstitial Lung Disease" Cells 12, no. 24: 2829. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12242829
APA StyleNava-Quiroz, K. J., López-Flores, L. A., Pérez-Rubio, G., Rojas-Serrano, J., & Falfán-Valencia, R. (2023). Peptidyl Arginine Deiminases in Chronic Diseases: A Focus on Rheumatoid Arthritis and Interstitial Lung Disease. Cells, 12(24), 2829. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12242829








