Astrocytosis, Inflammation, Axonal Damage and Myelin Impairment in the Internal Capsule following Striatal Ischemic Injury
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement and Experimental Groups
2.2. Induction of Striatal Focal Ischemia
2.3. Perfusion and Tissue Processing
2.3.1. Immunohistochemical Protocol
2.3.2. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
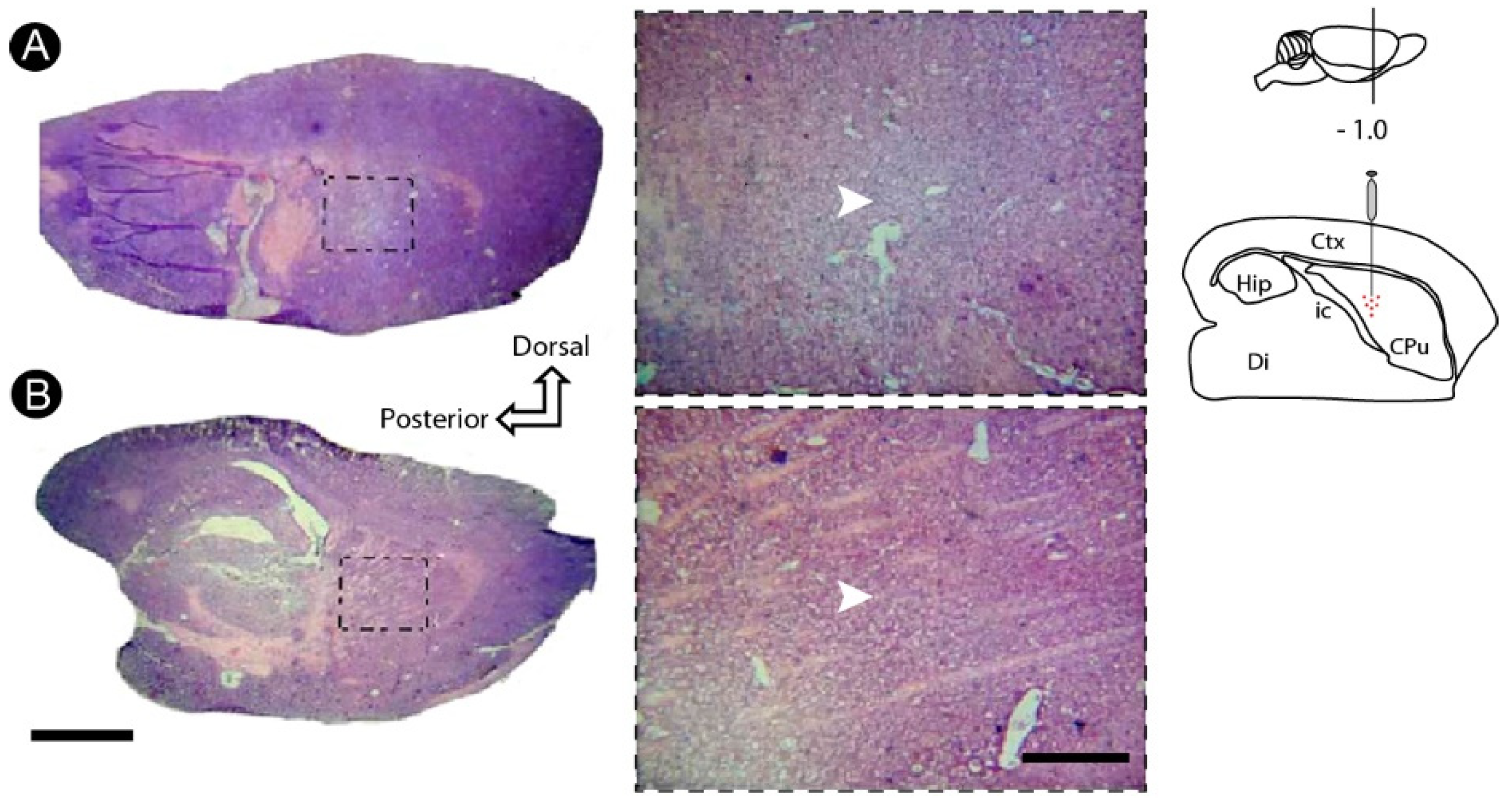
3.1. Basic Histology Reveals Cell Death Induced by ET-1 in the Striatum
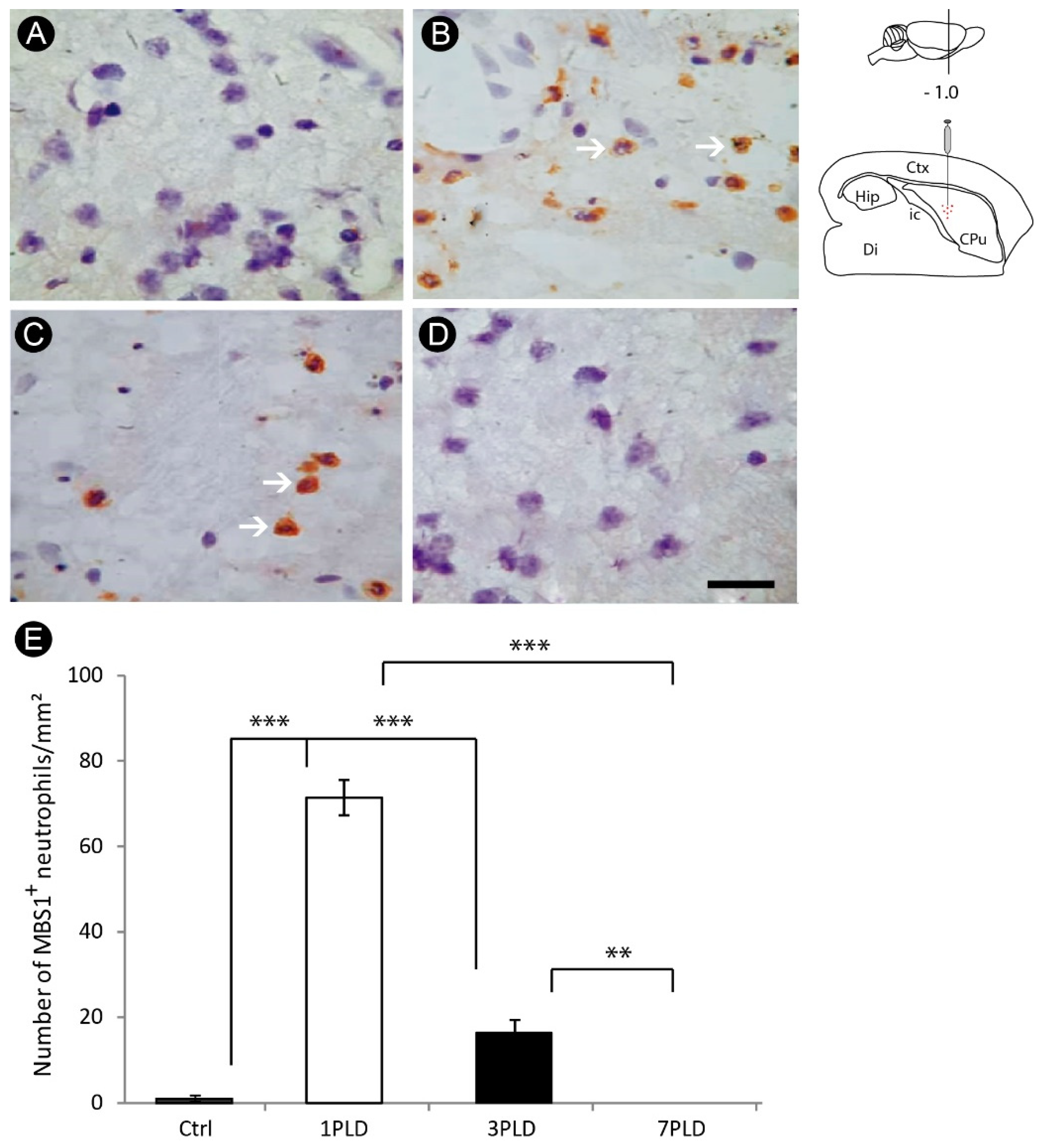
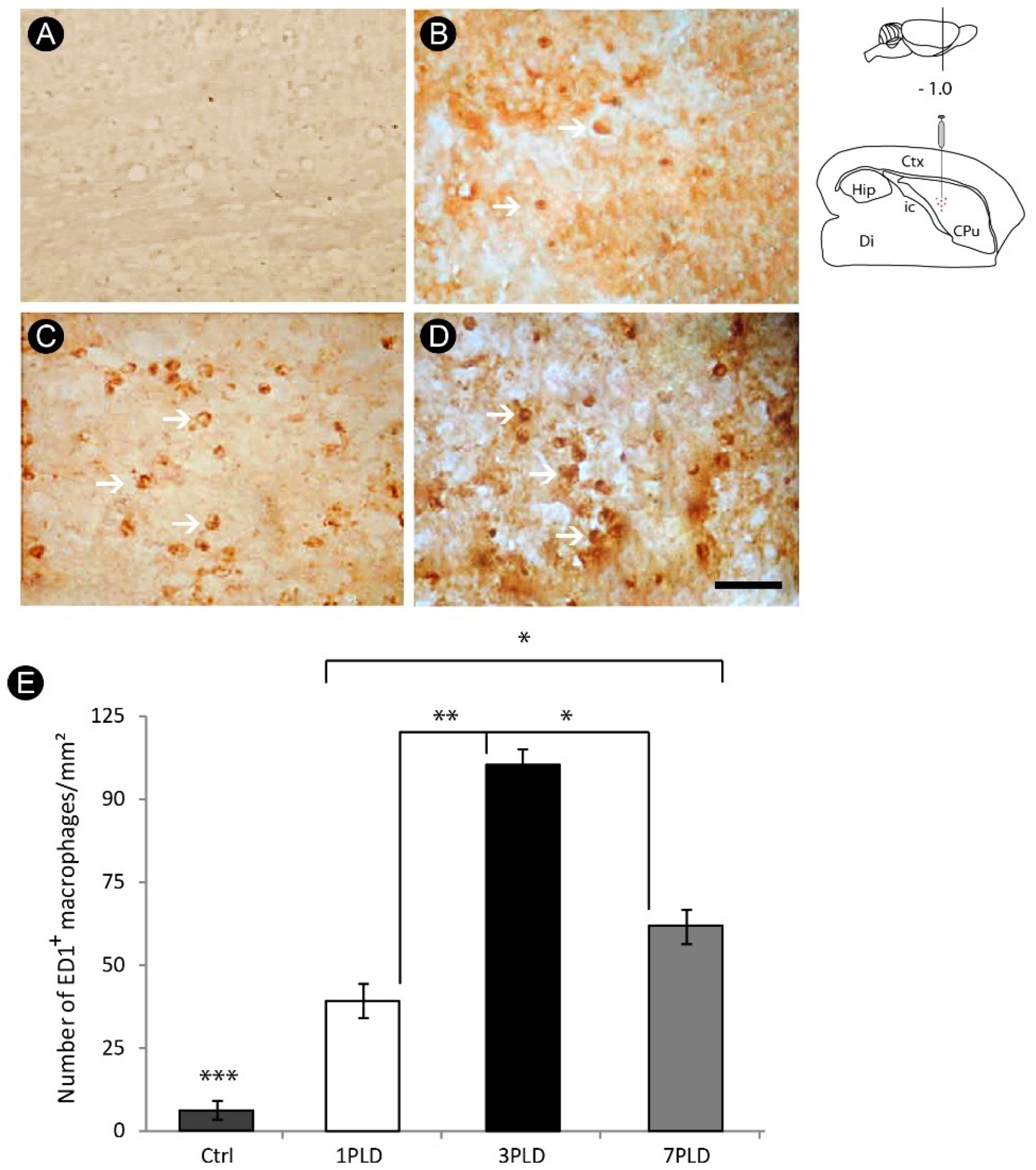
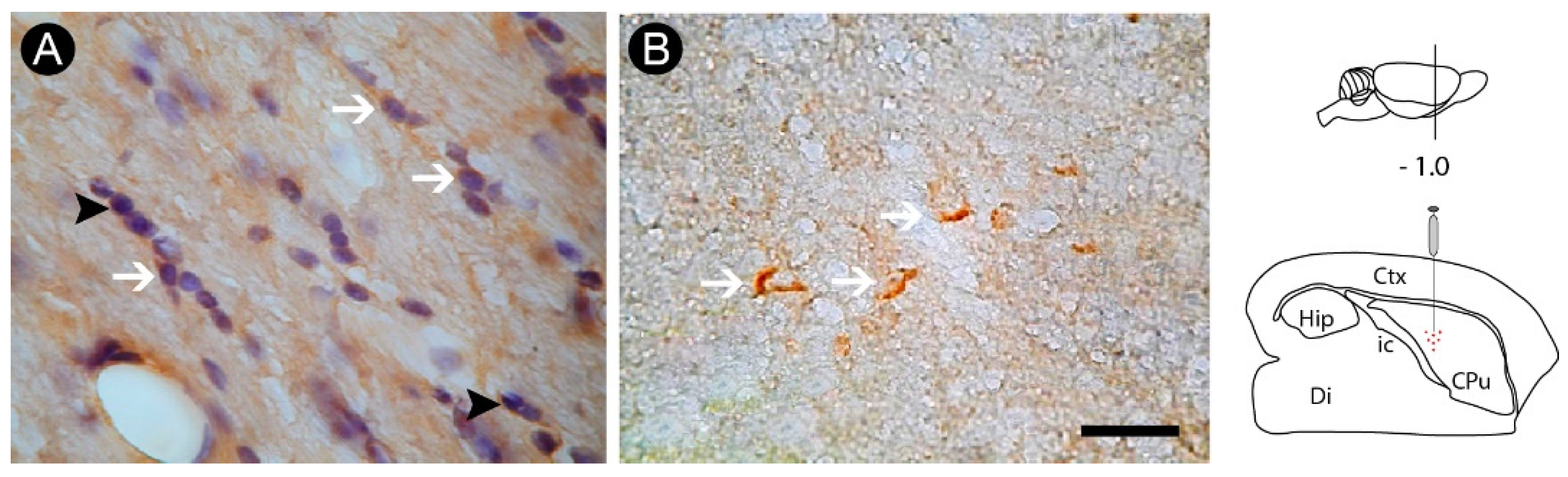
3.2. Inflammatory Response and Glial Activation in the Internal Capsule Induced by ET-1
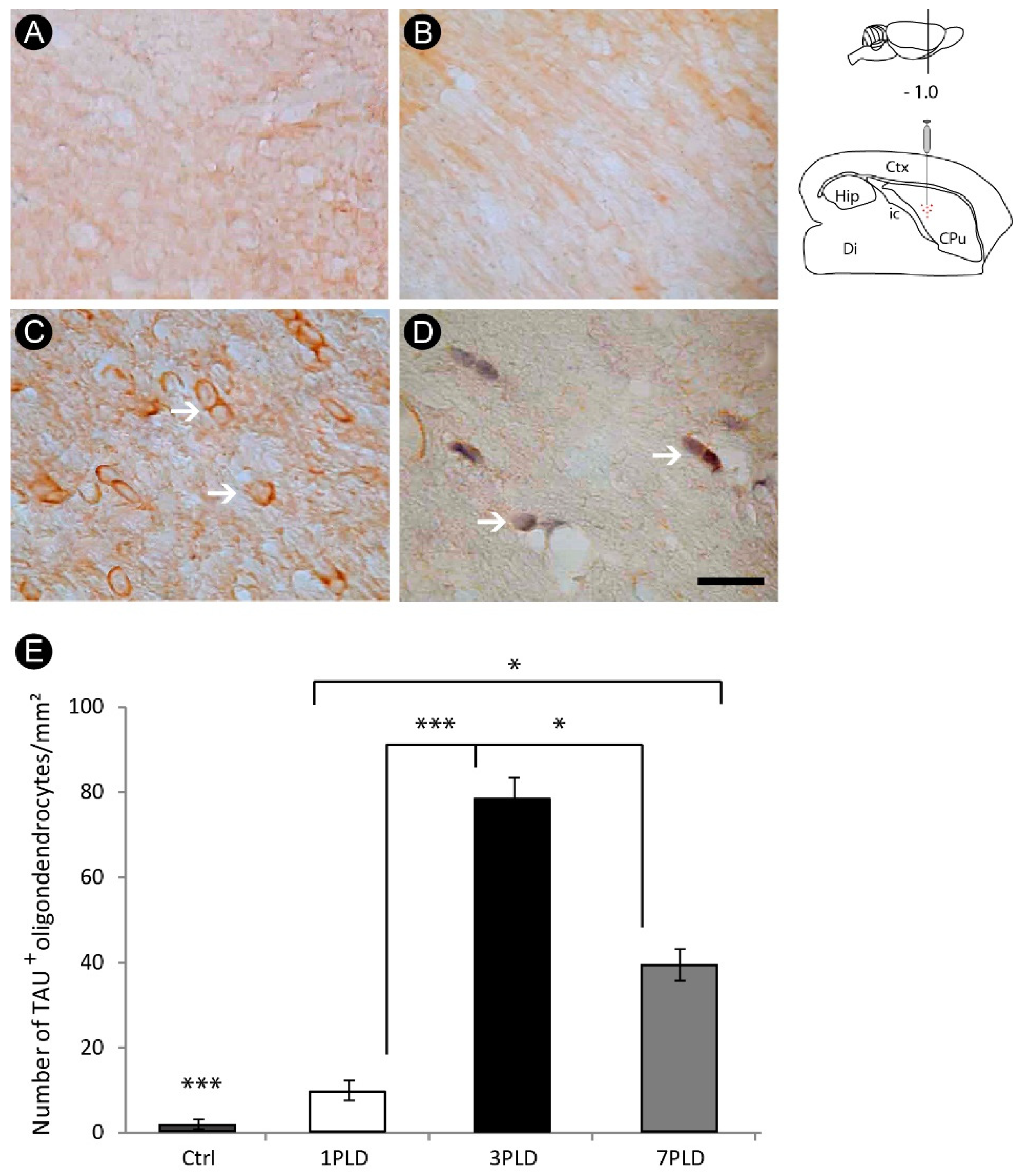
3.3. Oligodendrocyte Degeneration in the Internal Capsule Induced by ET-1 Injection
3.4. Axonal Lesion in the Internal Capsule Following ET-1 Injection
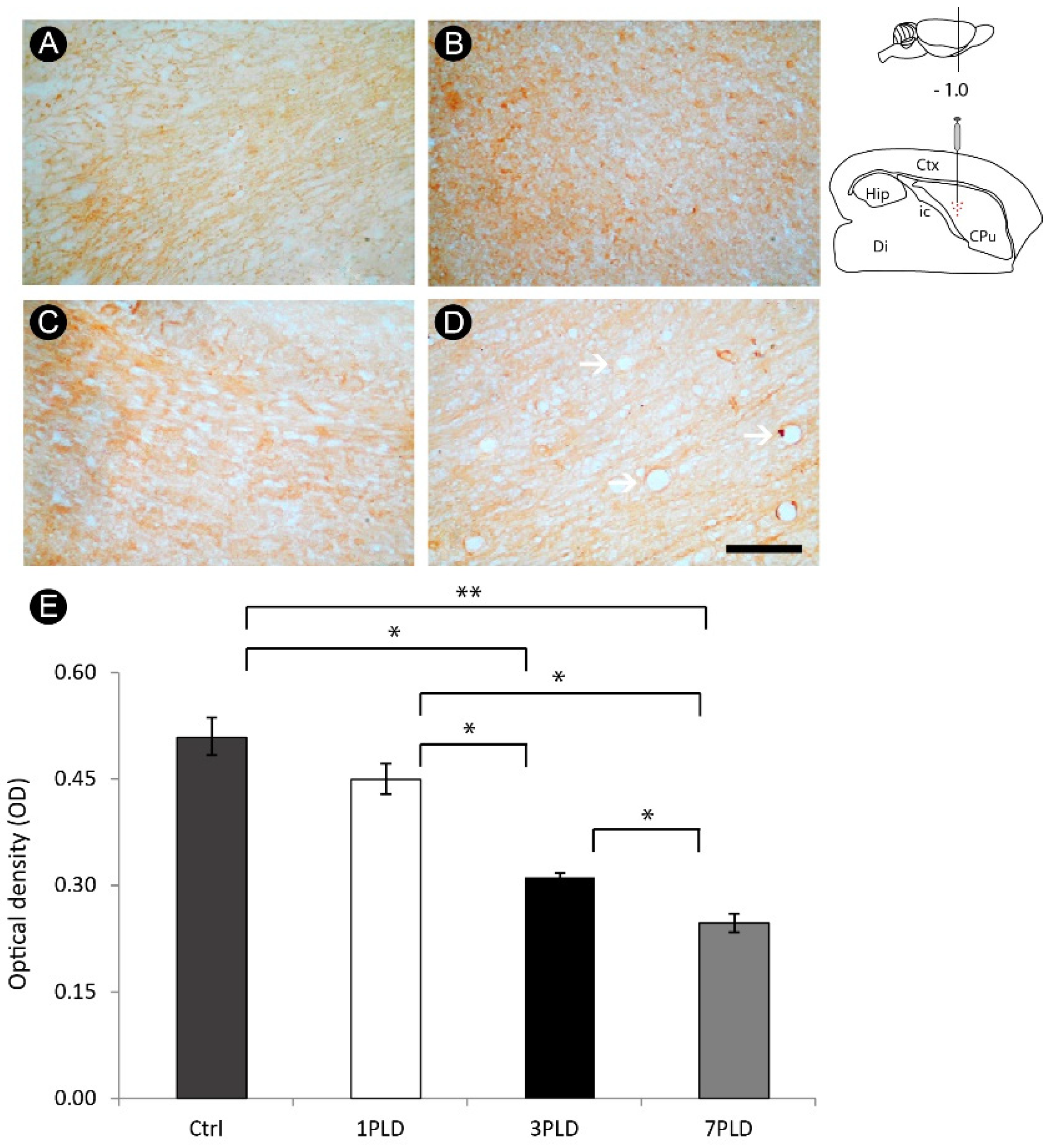
3.5. ET-1 Injection in Striatum Induced Progressive Impairment of Myelin in the Internal Capsule
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2016 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke, 1990-2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 48, 439–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coco, D.L.; Lopez, G.; Corrao, S. Cognitive impairment and stroke in elderly patients. Vasc. Health Risk. Manag. 2016, 12, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chohan, S.A.; Venkatesh, P.K.; How, C.H. Long-term complications of stroke and secondary prevention: An overview for primary care physicians. Singap. Med. J. 2019, 60, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajsic, S.; Gothe, H.; Borba, H.H.; Sroczynski, G.; Vujicic, J.; Toell, T.; Siebert, U. Economic burden of stroke: A systematic review on post-stroke care. Eur. J. Health Econ. 2019, 20, 107–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthi, R.V.; Feigin, V.L. Global Burden of Stroke. In Stroke: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management, 7th ed.; Grotta, J., Albers, G., Broderick, J., Kasner, S., Lo, E., Sacco, R., Wong, L., Day, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 163–178.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousufuddin, M.; Young, N. Aging and ischemic stroke. Aging 2019, 11, 2542–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, R.; Sutradhar, R.; Yao, Z.; Wodchis, W.P.; Rosella, L.C. Smoking, drinking, diet and physical activity-modifiable lifestyle risk factors and their associations with age to first chronic disease. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 49, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Custodio, A.D.; Morais Filho, A.B.; Gomes, A.T.N.; Lobato, I.A.F.; Cavalcanti, J.R.L.P.; Falcao, D.; Freire, M.A.M. Epidemiological characterization of stroke cases under rehabilitation on the Brazilian Unified Health System in Mossoró, Rio Grande do Norte. Health Sci. J. 2021, 11, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumral, E.; Erdoğan, C.E.; Arı, A.; Bayam, F.E.; Saruhan, G. Association of obesity with recurrent stroke and cardiovascular events. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 177, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aho, K.; Harmsen, P.; Hatano, S.; Marquardsen, J.; Smirnov, V.E.; Strasser, T. Cerebrovascular disease in the community: Results of a WHO collaborative study. Bull. World Health Organ. 1980, 58, 113–130. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2395897/pdf/bullwho00424-0120.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Donnan, G.A.; Fisher, M.; Macleod, M.; Davis, S.M. Stroke. Lancet 2008, 371, 1612–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzik, A.; Bushnell, C. Stroke epidemiology and risk factor management. Continuum 2017, 23, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshnam, S.E.; Winlow, W.; Farzaneh, M.; Farbood, Y.; Moghaddam, H.F. Pathogenic mechanisms following ischemic stroke. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 1167–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaraj, R.L.; Azimullah, S.; Beiram, R.; Jalal, F.Y.; Rosenberg, G.A. Neuroinflammation: Friend and foe for ischemic stroke. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, K.; Tian, D.C.; Li, Z.G.; Ducruet, A.F.; Lawton, M.T.; Shi, F.D. Global brain inflammation in stroke. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.A.M. Pathophysiology of neurodegeneration following traumatic brain injury. West Indian Med. J 2012, 61, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ng, S.Y.; Lee, A.Y.W. Traumatic Brain Injuries: Pathophysiology and potential therapeutic targets. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2019, 13, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, A.; Sarmah, D.; Kalia, K.; Borah, A.; Wang, X.; Dave, K.R.; Yavagal, D.R.; Bhattacharya, P. Advances in studies on stroke-induced secondary neurodegeneration (SND) and its treatment. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 1154–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Tang, X.; Xiao, H.; Hu, Z. Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Autophagy: Potential Targets of Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Based Therapies in Ischemic Stroke. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 641157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, R.R.; Santana, L.N.; Fernandes, R.M.; Nascimento, E.M.; Oliveira, A.C.; Fernandes, L.M.; Dos Santos, E.M.; Tavares, P.A.; Dos Santos, I.R.; Guimarães-Santos, A.; et al. Neurodegeneration and glial response after acute striatal stroke: Histological basis for neuroprotective studies. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 3173564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopes, R.S.; Cardoso, M.M.; Sampaio, A.O.; Barbosa, M.S., Jr.; Souza, C.C.; Silva, M.C.; Ferreira, E.M.; Freire, M.A.M.; Lima, R.R.; Gomes-Leal, W. Indomethacin treatment reduces microglia activation and increases numbers of neuroblasts in the subventricular zone and ischaemic striatum after focal ischaemia. J. Biosci. 2016, 41, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.A.M.; Santana, L.N.S.; Bittencourt, L.O.; Nascimento, P.C.; Fernandes, R.M.; Leão, L.K.R.; Fernandes, L.M.P.; Silva, M.C.F.; Amado, L.L.; Gomes-Leal, W.; et al. Methylmercury intoxication and cortical ischemia: Pre-clinical study of their comorbidity. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, R.R.; Oliveira, A.C.A.; Fernandes, R.M.; Nascimento, P.C.; Freire, M.A.M.; Gomes-Leal, W. Inflammatory response and secondary white matter damage to the corpus callosum after focal striatal stroke in rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 3rd ed.; Hard Cover Edition; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; p. 472. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, A.M.; Zurlo, J.; Rudacille, D. The three Rs and biomedical research. Science 1996, 272, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freire, M.A.M.; Faber, J.; Picanço-Diniz, C.W.; Franca, J.G.; Pereira, A. Morphometric variability of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate diaphorase neurons in the primary sensory areas of the rat. Neuroscience 2012, 205, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freire, M.A.M.; Franca, J.G.; Picanço-Diniz, C.W.; Pereira, A., Jr. Neuropil reactivity, distribution and morphology of NADPH diaphorase type I neurons in the barrel cortex of the adult mouse. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2005, 30, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A., Jr.; Freire, M.A.M.; Franca, J.G.; Picanço-Diniz, C.W. The barrel field of the adult mouse SmI cortex as revealed by NADPH-diaphorase histochemistry. Neuroreport 2000, 26, 1889–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.A.M.; Guimaraes, J.S.; Santos, J.R.; Simplicio, H.; Gomes-Leal, W. Morphometric analysis of NADPH diaphorase reactive neurons in a rat model of focal excitotoxic striatal injury. Neuropathology 2016, 36, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, F.; Haque, M.; Sarkar, M.; Ara, S.; Islam, M. White fiber dissection of brain; the internal capsule: A cadaveric study. Turk. Neurosurg. 2010, 20, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coizet, V.; Heilbronner, S.R.; Carcenac, C.; Mailly, P.; Lehman, J.F.; Savasta, M.; David, O.; Deniau, J.M.; Groenewegen, H.J.; Haber, S.N. Organization of the anterior limb of the internal capsule in the rat. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 2539–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boumpadre, M.C.; Arroyo, H.A.; Stroke Group. Basal ganglia and internal capsule stroke in childhood-risk factors, neuroimaging, and outcome in a series of 28 patients: A tertiary hospital experience. J. Child Neurol. 2009, 24, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatemichi, T.K.; Desmond, D.W.; Prohovnik, I.; Cross, D.T.; Gropen, T.I.; Mohr, J.P.; Stern, Y. Confusion and memory loss from capsular genu infarction: A thalamocortical disconnection syndrome? Neurology 1992, 42, 1966–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Zhou, G.; Zhuang, J.; Xu, C.; Zhou, H.; Peng, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zeng, H.; Li, J.; Yan, F.; et al. White Matter Injury After Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 562090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weishaupt, N.; Zhang, A.; Deziel, R.A.; Tasker, R.A.; Whitehead, S.N. Prefrontal Ischemia in the rat leads to secondary damage and inflammation in remote gray and white matter regions. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomes-Leal, W.; Corkill, D.J.; Freire, M.A.M.; Picanco-Diniz, C.W.; Perry, V.H. Astrocytosis, microglia activation, oligodendrocyte degeneration, and pyknosis following acute spinal cord injury. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 190, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimaraes, J.S.; Freire, M.A.M.; Lima, R.R.; Picanco-Diniz, C.W.; Pereira, A.; Gomes-Leal, W. Minocycline treatment reduces white matter damage after excitotoxic striatal injury. Brain Res. 2010, 6, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, S.M.; Rothwell, N.J. Inflammation in central nervous system injury. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 358, 1669–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morganti-Kossmann, M.C.; Rancan, M.; Stahel, P.F.; Kossmann, T. Inflammatory response in acute traumatic brain injury: A double-edged sword. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2002, 8, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morganti-Kossmann, M.C.; Semple, B.D.; Hellewell, S.C.; Bye, N.; Ziebell, J.M. The complexity of neuroinflammation consequent to traumatic brain injury: From research evidence to potential treatments. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 137, 731–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.A.M.; Faber, J.; Lemos, N.A.M.; Santos, J.R.; Cavalcanti, P.F.; Lima, R.H.; Morya, E. Distribution and morphology of calcium-binding proteins immunoreactive neurons following chronic tungsten multielectrode implants. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Marsh, S.E.; Stevens, B. Microglia and astrocytes in disease: Dynamic duo or partners in crime? Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 820–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irving, E.A.; Nicoll, J.; Graham, D.I.; Dewar, D. Increased tau immunoreactivity in oligodendrocytes following human stroke and head injury. Neurosci. Lett. 1996, 213, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irving, E.A.; Yatsushiro, K.; McCulloch, J.; Dewar, D. Rapid alteration of tau in oligodendrocytes after focal ischemic injury in the rat: Involvement of free radicals. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1997, 17, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza-Rodrigues, R.D.; Costa, A.M.; Lima, R.R.; Dos Santos, C.D.; Picanço-Diniz, C.W.; Gomes-Leal, W. Inflammatory response and white matter damage after microinjections of endothelin-1 into the rat striatum. Brain Res. 2008, 1200, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimaraes, J.S.; Freire, M.A.M.; Lima, R.R.; Souza-Rodrigues, R.D.; Costa, A.M.R.; Santos, C.D.; Picanço-Diniz, C.W.; Gomes-Leal, W. Mecanismos de degeneración secundaria en el sistema nervioso central durante los trastornos neuronales agudos y el daño en la sustancia blanca. Rev. Neurol. 2009, 48, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, I.M.; Lima, F.O.V.; Fernandes, L.C.B.; Norrara, B.; Neta, F.I.; Alves, R.D.; Cavalcanti, J.R.L.P.; Lucena, E.E.S.; Cavalcante, J.S.; Rego, A.C.M.; et al. Astragaloside IV supplementation promotes a neuroprotective effect in experimental models of neurological disorders: A systematic review. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019, 17, 648–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, I.M.; Freire, M.A.M.; Cavalcanti, J.R.L.P.; Araujo, D.P.; Norrara, B.; Rosa, I.M.M.M.; Azevedo, E.P.; Rego, A.C.M.; Filho, I.A.; Guzen, F.P. Supplementation with Curcuma longa reverses neurotoxic and behavioral damage in models of Alzheimer’s Disease: A systematic review. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019, 17, 406–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi Vastegani, S.; Hajipour, S.; Sarkaki, A.; Basir, Z.; Parisa Navabi, S.; Farbood, Y.; Khoshnam, S.E. Curcumin mitigates lipopolysaccharide-induced anxiety/depression-like behaviors, blood-brain barrier dysfunction and brain edema by decreasing cerebral oxidative stress in male rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2022, 782, 136697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglini, D.; Siwicka-Gieroba, D.; Rocco, P.R.; Cruz, F.F.; Silva, P.L.; Dabrowski, W.; Brunetti, I.; Patroniti, N.; Pelosi, P.; Robba, C. Novel Synthetic and Natural Therapies for Traumatic Brain Injury. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 1661–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Huang, C.; Ding, H.; Dong, J.; Gao, Z.; Yang, X.; Tang, Y.; Dong, Q. Aquaporin-4 and cerebrovascular diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitchen, P.; Salman, M.M.; Halsey, A.M.; Clarke-Bland, C.; MacDonald, J.A.; Ishida, H.; Vogel, H.J.; Almutiri, S.; Logan, A.; Kreida, S.; et al. Targeting Aquaporin-4 Subcellular Localization to Treat Central Nervous System Edema. Cell 2020, 181, 784–799.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvain, N.J.; Salman, M.M.; Pushie, M.J.; Hou, H.; Meher, V.; Herlo, R.; Peeling, L.; Kelly, M.E. The effects of trifluoperazine on brain edema, aquaporin-4 expression and metabolic markers during the acute phase of stroke using photothrombotic mouse model. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2021, 1863, 183573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman, M.M.; Kitchen, P.; Halsey, A.; Wang, M.X.; Törnroth-Horsefield, S.; Conner, A.C.; Badaut, J.; Iliff, J.J.; Bill, R.M. Emerging roles for dynamic aquaporin-4 subcellular relocalization in CNS water homeostasis. Brain 2022, 145, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman, M.M.; Kitchen, P.; Yool, A.J.; Bill, R.M. Recent breakthroughs and future directions in drugging aquaporins. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 43, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Primary Antibody | Secondary Antibody | Normal Serum | Labeling Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-MBS1 (1:2000, CNS Inflammation Group, Soton, UK) | Goat anti-rabbit (1:200, Vector Labs, Newark, CA, USA) | Goat | Neutrophils |
| Anti-ED1 (1:500, Serotec, Kidlington, UK) | Horse anti-mouse (1:200, Vector Labs, USA) | Horse | Activated microglia/macrophages |
| Anti-GFAP (1:1000, DAKO, UK) | Goat anti-rabbit (1:200, Vector Labs, USA) | Goat | Astrocytes |
| Anti-Tau-1 (1:500, Chemicon, USA) | Horse anti-mouse (1:200, Vector Labs, USA) | Horse | Pathological oligodendrocytes |
| Anti-MBP (1:100, Serotec, UK) | Horse anti-mouse (1:200, Vector Labs, USA) | Horse | Myelin |
| Anti-βapp (1:50, Chemicon, USA) | Horse anti-mouse (1:200, Vector Labs, USA) | Horse | Damaged axons |
| Anti-caspase-3 (1:250, Promega, Madison, WI, USA) | Goat anti-rabbit (1:200, Vector Labs, USA) | Goat | Apoptotic profiles |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Freire, M.A.M.; Lima, R.R.; Bittencourt, L.O.; Guimaraes, J.S.; Falcao, D.; Gomes-Leal, W. Astrocytosis, Inflammation, Axonal Damage and Myelin Impairment in the Internal Capsule following Striatal Ischemic Injury. Cells 2023, 12, 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030457
Freire MAM, Lima RR, Bittencourt LO, Guimaraes JS, Falcao D, Gomes-Leal W. Astrocytosis, Inflammation, Axonal Damage and Myelin Impairment in the Internal Capsule following Striatal Ischemic Injury. Cells. 2023; 12(3):457. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030457
Chicago/Turabian StyleFreire, Marco Aurelio M., Rafael Rodrigues Lima, Leonardo Oliveira Bittencourt, Joanilson S. Guimaraes, Daniel Falcao, and Walace Gomes-Leal. 2023. "Astrocytosis, Inflammation, Axonal Damage and Myelin Impairment in the Internal Capsule following Striatal Ischemic Injury" Cells 12, no. 3: 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030457
APA StyleFreire, M. A. M., Lima, R. R., Bittencourt, L. O., Guimaraes, J. S., Falcao, D., & Gomes-Leal, W. (2023). Astrocytosis, Inflammation, Axonal Damage and Myelin Impairment in the Internal Capsule following Striatal Ischemic Injury. Cells, 12(3), 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030457








