The Role of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors in Preeclampsia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
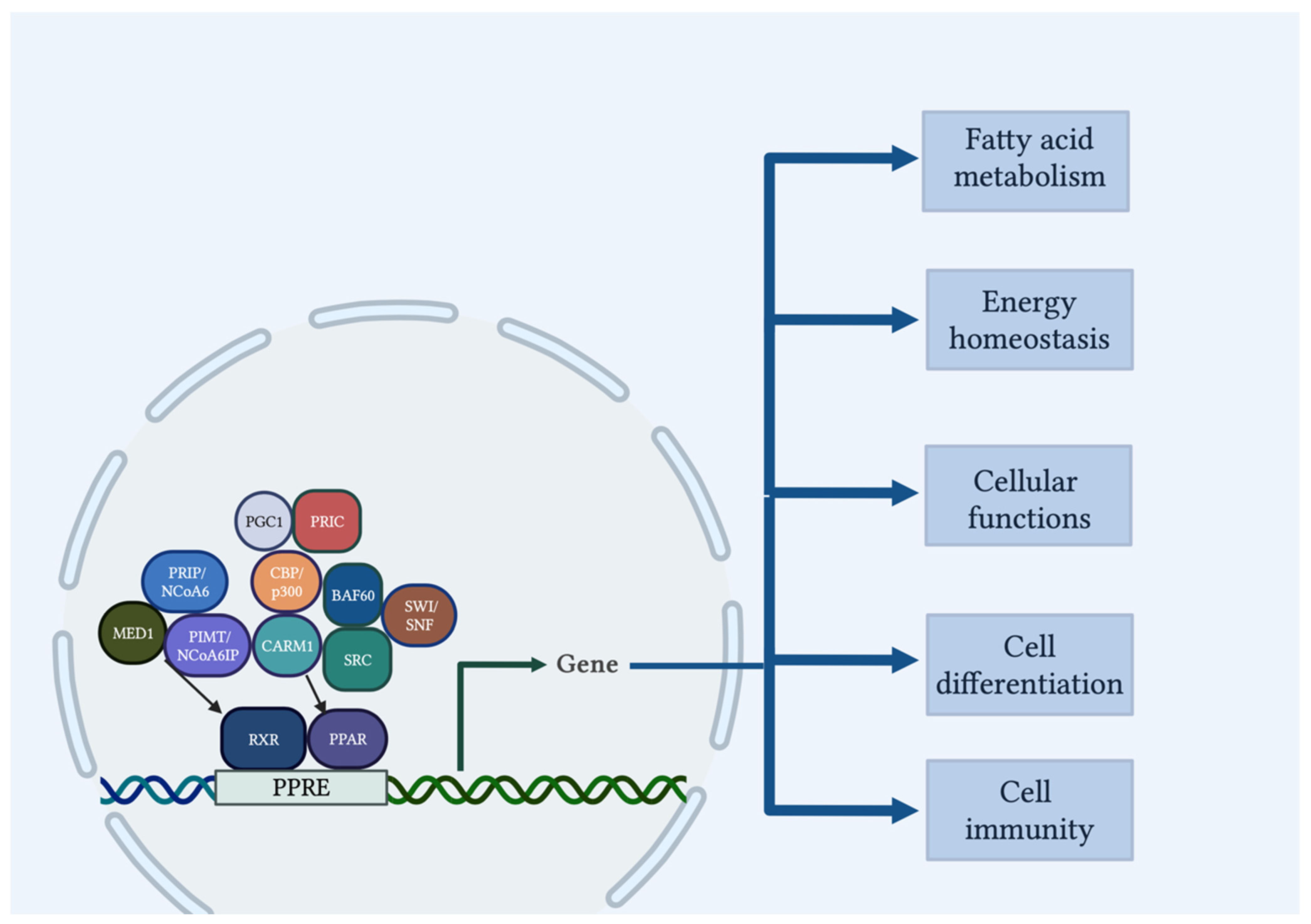
2. PPAR Structure and Mechanism of Action
3. The Role of PPARs in Hypertension
4. The Role of PPARs in Trophoblast Functions and Fetal Origins
5. The Role of PPARs in Uterine and Placental Angiogenesis
6. The Role of PPARα in Preeclampsia
7. The Role of PPARβ/δ in Preeclampsia
8. The Role of PPARγ in Preeclampsia
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wojczakowski, W.; Kimber-Trojnar, Z.; Dziwisz, F.; Slodzinska, M.; Slodzinski, H.; Leszczynska-Gorzelak, B. Preeclampsia and Cardiovascular Risk for Offspring. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steegers, E.A.; von Dadelszen, P.; Duvekot, J.J.; Pijnenborg, R. Pre-eclampsia. Lancet 2010, 376, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gestational Hypertension and Preeclampsia: ACOG Practice Bulletin, Number 222. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 135, e237–e260. [CrossRef]
- Sibai, B.M. Maternal and uteroplacental hemodynamics for the classification and prediction of preeclampsia. Hypertension 2008, 52, 805–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karrar, S.A.; Hong, P.L. Preeclampsia; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ives, C.W.; Sinkey, R.; Rajapreyar, I.; Tita, A.T.N.; Oparil, S. Preeclampsia-Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentations: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 1690–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auwerx, J.; Baulieu, E.; Beato, M.; Becker-Andre, M.; Burbach, P.H.; Camerino, G.; Chambon, P.; Cooney, A.; Dejean, A.; Dreyer, C.; et al. Nuclear Receptors Nomenclature C. A unified nomenclature system for the nuclear receptor superfamily. Cell 1999, 97, 161–163. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Shen, W.J.; Bittner, S.; Kraemer, F.B.; Azhar, S. PPARs: Regulators of metabolism and as therapeutic targets in cardiovascular disease. Part II: PPAR-beta/delta and PPAR-gamma. Future Cardiol. 2017, 13, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.D.; Wagner, N. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor beta/delta (PPARbeta/delta) acts as regulator of metabolism linked to multiple cellular functions. Pharm. Ther. 2010, 125, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunmeir, R.; Xu, F. Functional Regulation of PPARs through Post-Translational Modifications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bensinger, S.J.; Tontonoz, P. Integration of metabolism and inflammation by lipid-activated nuclear receptors. Nature 2008, 454, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.S.; Papreddy, K.; Musunuri, S.; Okonkwo, A. Prevention/reversal of choline deficiency-induced steatohepatitis by a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha ligand in rats. In Vivo 2002, 16, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Szilagyi, J.T.; Avula, V.; Fry, R.C. Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Their Effects on the Placenta, Pregnancy, and Child Development: A Potential Mechanistic Role for Placental Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors (PPARs). Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2020, 7, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Yang, H.; Ye, Y.; Ma, Z.; Kuhn, C.; Rahmeh, M.; Mahner, S.; Makrigiannakis, A.; Jeschke, U.; von Schönfeldt, V. Role of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors (PPARs) in Trophoblast Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaginis, C.; Spanopoulou, E.; Theocharis, S. PPAR-gamma signaling pathway in placental development and function: A potential therapeutic target in the treatment of gestational diseases. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2008, 12, 1049–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christofides, A.; Konstantinidou, E.; Jani, C.; Boussiotis, V.A. The role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR) in immune responses. Metabolism 2021, 114, 154338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grygiel-Gorniak, B. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and their ligands: Nutritional and clinical implications—A review. Nutr. J. 2014, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berger, J.; Moller, D.E. The mechanisms of action of PPARs. Annu. Rev. Med. 2002, 53, 409–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viswakarma, N.; Jia, Y.; Bai, L.; Vluggens, A.; Borensztajn, J.; Xu, J.; Reddy, J.K. Coactivators in PPAR-Regulated Gene Expression. PPAR Res. 2010, 2010, 250126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.; Reddy, J.K. Transcription coactivators for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2007, 1771, 936–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaginis, C.; Giagini, A.; Theocharis, S. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPAR-gamma) ligands as potential therapeutic agents to treat arthritis. Pharm. Res. 2009, 60, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaginis, C.; Tsantili-Kakoulidou, A.; Theocharis, S. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma ligands as bone turnover modulators. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2007, 16, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaginis, C.; Theocharis, S.; Tsantili-Kakoulidou, A. A consideration of PPAR-gamma ligands with respect to lipophilicity: Current trends and perspectives. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2007, 16, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margeli, A.; Kouraklis, G.; Theocharis, S. Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-gamma (PPAR-gamma) ligands and angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 2003, 6, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaginis, C.; Theocharis, S.; Tsantili-Kakoulidou, A. Structural basis for the design of PPAR-gamma ligands: A survey on quantitative structure- activity relationships. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaginis, C.; Margeli, A.; Theocharis, S. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma ligands as investigational modulators of angiogenesis. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2007, 16, 1561–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaginis, C.; Tsourouflis, G.; Theocharis, S. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPAR-gamma) ligands: Novel pharmacological agents in the treatment of ischemia reperfusion injury. Curr. Mol. Med. 2008, 8, 562–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaginis, C.; Theocharis, S.; Tsantili-Kakoulidou, A. Investigation of the lipophilic behaviour of some thiazolidinediones. Relationships with PPAR-gamma activity. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 857, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaginis, C.; Theocharis, S.; Tsantili-Kakoulidou, A. Quantitative structure-activity relationships for PPAR-gamma binding and gene transactivation of tyrosine-based agonists using multivariate statistics. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2008, 72, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaginis, C.; Tsantili-Kakoulidou, A.; Theocharis, S. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-gamma Ligands: Potential Pharmacological Agents for Targeting the Angiogenesis Signaling Cascade in Cancer. PPAR Res. 2008, 2008, 431763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feige, J.N.; Gelman, L.; Michalik, L.; Desvergne, B.; Wahli, W. From molecular action to physiological outputs: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors are nuclear receptors at the crossroads of key cellular functions. Prog. Lipid Res. 2006, 45, 120–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefipour, Z.; Newaz, M. PPARalpha ligand clofibrate ameliorates blood pressure and vascular reactivity in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2014, 35, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koh, K.K.; Quon, M.J.; Han, S.H.; Chung, W.J.; Ahn, J.Y.; Kim, J.A.; Lee, Y.; Shin, E.K. Additive beneficial effects of fenofibrate combined with candesartan in the treatment of hypertriglyceridemic hypertensive patients. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goya, K.; Sumitani, S.; Xu, X.; Kitamura, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Kurebayashi, S.; Saito, H.; Kouhara, H.; Kasayama, S.; Kawase, I. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha agonists increase nitric oxide synthase expression in vascular endothelial cells. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delerive, P.; Martin-Nizard, F.; Chinetti, G.; Trottein, F.; Fruchart, J.C.; Najib, J.; Duriez, P.; Staels, B. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor activators inhibit thrombin-induced endothelin-1 production in human vascular endothelial cells by inhibiting the activator protein-1 signaling pathway. Circ. Res. 1999, 85, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guan, J.; Zhao, M.; He, C.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, W.; Cui, Y.L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, B.Y.; et al. Anti-Hypertensive Action of Fenofibrate via UCP2 Upregulation Mediated by PPAR Activation in Baroreflex Afferent Pathway. Neurosci. Bull. 2019, 35, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, E.; Frkanec, J.T.; Cunard, R. Fibrates upregulate TRB3 in lymphocytes independent of PPAR alpha by augmenting CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta (C/EBP beta) expression. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 1218–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toral, M.; Romero, M.; Perez-Vizcaino, F.; Duarte, J.; Jimenez, R. Antihypertensive effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-beta/delta activation. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2017, 312, H189–H200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirkby, N.S.; Sampaio, W.; Etelvino, G.; Alves, D.T.; Anders, K.L.; Temponi, R.; Shala, F.; Nair, A.S.; Ahmetaj-Shala, B.; Jiao, J.; et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 Selectively Controls Renal Blood Flow Through a Novel PPARbeta/delta-Dependent Vasodilator Pathway. Hypertension 2018, 71, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, M.; Toral, M.; Robles-Vera, I.; Sánchez, M.; Jiménez, R.; O’Valle, F.; Rodriguez-Nogales, A.; Pérez-Vizcaino, F.; Gálvez, J.; Duarte, J. Activation of Peroxisome Proliferator Activator Receptor beta/delta Improves Endothelial Dysfunction and Protects Kidney in Murine Lupus. Hypertension 2017, 69, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, I.; Gurnell, M.; Crowley, V.E.F.; Agostini, M.; Schwabe, J.W.; Soos, M.A.; Maslen, G.L.; Williams, T.D.M.; Lewis, H.; Schafer, A.J.; et al. Dominant negative mutations in human PPARgamma associated with severe insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Nature 1999, 402, 880–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelou, E.; Warren, H.R.; Mosen-Ansorena, D.; Mifsud, B.; Pazoki, R.; Gao, H.; Ntritsos, G.; Dimou, N.; Cabrera, C.P.; Karaman, I.; et al. Publisher Correction: Genetic analysis of over 1 million people identifies 535 new loci associated with blood pressure traits. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullert, S.; Schneider, F.; Haak, E.; Rau, H.; Badenhoop, K.; Lubben, G.; Usadel, K.H.; Konrad, T. Effects of pioglitazone in nondiabetic patients with arterial hypertension: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 5503–5506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogihara, T.; Rakugi, H.; Ikegami, H.; Mikami, H.; Masuo, K. Enhancement of insulin sensitivity by troglitazone lowers blood pressure in diabetic hypertensives. Am. J. Hypertens. 1995, 8, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dormandy, J.A.; Charbonnel, B.; Eckland, D.J.A.; Erdmann, E.; Massi-Benedetti, M.; Moules, I.K.; Skene, A.M.; Tan, M.H.; Lefèbvre, P.J.; Murray, G.D.; et al. Secondary prevention of macrovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes in the PROactive Study (PROspective pioglitAzone Clinical Trial In macroVascular Events): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2005, 366, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komajda, M.; Curtis, P.; Hanefeld, M.; Beck-Nielsen, H.; Pocock, S.J.; Zambanini, A.; Jones, N.P.; Gomis, R.; Home, P.D. Effect of the addition of rosiglitazone to metformin or sulfonylureas versus metformin/sulfonylurea combination therapy on ambulatory blood pressure in people with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial (the RECORD study). Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2008, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, S.; Livergood, M.C.; Nakagawa, P.; Wu, J.; Sigmund, C.D. Role of the Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptors in Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 1021–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, E.B.; Eykholt, R.; Helliwell, R.J.; Gilmour, R.S.; Mitchell, M.D.; Marvin, K.W. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor isoform expression changes in human gestational tissues with labor at term. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 64, 1586–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadra, K.; Anghel, S.I.; Joye, E.; Tan, N.S.; Basu-Modak, S.; Trono, D.; Wahli, W.; Desvergne, B. Differentiation of trophoblast giant cells and their metabolic functions are dependent on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor beta/delta. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 3266–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Handschuh, K.; Guibourdenche, J.; Tsatsaris, V.; Guesnon, M.; Laurendeau, I.; Evain-Brion, D.; Fournier, T. Human chorionic gonadotropin produced by the invasive trophoblast but not the villous trophoblast promotes cell invasion and is down-regulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 5011–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, M.; Lei, Z.M.; Rao Ch, V. The central role of human chorionic gonadotropin in the formation of human placental syncytium. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 1108–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fournier, T.; Guibourdenche, J.; Handschuh, K.; Tsatsaris, V.; Rauwel, B.; Davrinche, C.; Evain-Brion, D. PPARgamma and human trophoblast differentiation. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2011, 90, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handschuh, K.; Guibourdenche, J.; Cocquebert, M.; Tsatsaris, V.; Vidaud, M.; Evain-Brion, D.; Fournier, T. Expression and regulation by PPARgamma of hCG alpha- and beta-subunits: Comparison between villous and invasive extravillous trophoblastic cells. Placenta 2009, 30, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalom-Barak, T.; Zhang, X.; Chu, T.; Schaiff, W.T.; Reddy, J.K.; Xu, J.; Sadovsky, Y.; Barak, Y. Placental PPARgamma regulates spatiotemporally diverse genes and a unique metabolic network. Dev. Biol. 2012, 372, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muralimanoharan, S.; Kwak, Y.T.; Mendelson, C.R. Redox-Sensitive Transcription Factor NRF2 Enhances Trophoblast Differentiation via Induction of miR-1246 and Aromatase. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 2022–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tache, V.; Ciric, A.; Moretto-Zita, M.; Li, Y.; Peng, J.; Maltepe, E.; Milstone, D.S.; Parast, M.M. Hypoxia and trophoblast differentiation: A key role for PPARgamma. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 2815–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blitek, A.; Szymanska, M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor beta/delta and gamma agonists differentially affect prostaglandin E2 and cytokine synthesis and nutrient transporter expression in porcine trophoblast cells during implantation. Theriogenology 2020, 152, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruebner, M.; Langbein, M.; Strissel, P.L.; Henke, C.; Schmidt, D.; Goecke, T.W.; Faschingbauer, F.; Schild, R.L.; Beckmann, M.W.; Strick, R. Regulation of the human endogenous retroviral Syncytin-1 and cell-cell fusion by the nuclear hormone receptors PPARgamma/RXRalpha in placentogenesis. J. Cell Biochem. 2012, 113, 2383–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Yuan, H.; Qu, J.; Shen, R. Activation of peroxisome proliferator activator receptor delta in mouse impacts lipid composition and placental development at early stage of gestation. Biol Reprod. 2014, 91, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handschuh, K.; Guibourdenche, J.; Guesnon, M.; Laurendeau, I.; Evain-Brion, D.; Fournier, T. Modulation of PAPP-A expression by PPARgamma in human first trimester trophoblast. Placenta 2006, 27 (Suppl. SA), S127–S134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bildirici, I.; Roh, C.R.; Schaiff, W.T.; Lewkowski, B.M.; Nelson, D.M.; Sadovsky, Y. The lipid droplet-associated protein adipophilin is expressed in human trophoblasts and is regulated by peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor-gamma/retinoid X receptor. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 6056–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cawyer, C.R.; Horvat, D.; Leonard, D.; Allen, S.R.; Jones, R.O.; Zawieja, D.C.; Kuehl, T.J.; Uddin, M.N. Hyperglycemia impairs cytotrophoblast function via stress signaling. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 211, 541.e1–541.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huin, C.; Corriveau, L.; Bianchi, A.; Keller, J.M.; Collet, P.; Krémarik-Bouillaud, P.; Domenjoud, L.; Bécuwe, P.; Schohn, H.; Ménard, D.; et al. Differential expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) in the developing human fetal digestive tract. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2000, 48, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wieser, F.; Waite, L.; Depoix, C.; Taylor, R.N. PPAR Action in Human Placental Development and Pregnancy and Its Complications. PPAR Res. 2008, 2008, 527048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindegaard, M.L.; Nielsen, L.B. Maternal diabetes causes coordinated down-regulation of genes involved with lipid metabolism in the murine fetal heart. Metabolism 2008, 57, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringseis, R.; Gutgesell, A.; Dathe, C.; Brandsch, C.; Eder, K. Feeding oxidized fat during pregnancy up-regulates expression of PPARalpha-responsive genes in the liver of rat fetuses. Lipids Health Dis. 2007, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Braissant, O.; Wahli, W. Differential expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha, -beta, and -gamma during rat embryonic development. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 2748–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higa, R.; Gonzalez, E.; Pustovrh, M.C.; White, V.; Capobianco, E.; Martinez, N.; Jawerbaum, A. PPARdelta and its activator PGI2 are reduced in diabetic embryopathy: Involvement of PPARdelta activation in lipid metabolic and signalling pathways in rat embryo early organogenesis. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2007, 13, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pustovrh, M.C.; Capobianco, E.; Martinez, N.; Higa, R.; White, V.; Jawerbaum, A. MMP/TIMP balance is modulated in vitro by 15dPGJ(2) in fetuses and placentas from diabetic rats. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 39, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M.R.; Fontes, A.M.; Barbieri, M.A.; Saraiva, M.D.C.P.; Simões, V.M.F.; da Silva, A.A.M.; Abraham, K.J.; Bettiol, H. Effects of FTO and PPARgamma variants on intrauterine growth restriction in a Brazilian birth cohort. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2021, 54, e10465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lendvai, A.; Deutsch, M.J.; Plosch, T.; Ensenauer, R. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors under epigenetic control in placental metabolism and fetal development. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 310, E797–E810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, N.; Wagner, K.D. PPARs and Angiogenesis-Implications in Pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, D.J.; Polverini, P.J.; Rastinejad, F.; Le Beau, M.M.; Lemons, R.S.; Frazier, W.A.; Bouck, N.P. A tumor suppressor-dependent inhibitor of angiogenesis is immunologically and functionally indistinguishable from a fragment of thrombospondin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 6624–6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gizard, F.; Amant, C.; Barbier, O.; Bellosta, S.; Robillard, R.; Percevault, F.; Sevestre, H.; Krimpenfort, P.; Corsini, A.; Rochette, J.; et al. PPAR alpha inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation underlying intimal hyperplasia by inducing the tumor suppressor p16INK4a. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 3228–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, T.; Lu, T.; d’Uscio, L.V.; Lam, C.F.; Lee, H.C.; Katusic, Z.S. Angiogenic function of prostacyclin biosynthesis in human endothelial progenitor cells. Circ. Res. 2008, 103, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, J.K.; Kim, H.L.; Jeon, K.H.; Choi, Y.E.; Lee, H.S.; Kwon, Y.W.; Jang, J.J.; Cho, H.J.; Kang, H.J.; Oh, B.H.; et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-delta activates endothelial progenitor cells to induce angio-myogenesis through matrix metallo-proteinase-9-mediated insulin-like growth factor-1 paracrine networks. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 1755–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nadra, K.; Quignodon, L.; Sardella, C.; Joye, E.; Mucciolo, A.; Chrast, R.; Desvergne, B. PPARgamma in placental angiogenesis. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 4969–4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nenicu, A.; Korbel, C.; Gu, Y.; Menger, M.D.; Laschke, M.W. Combined blockade of angiotensin II type 1 receptor and activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma by telmisartan effectively inhibits vascularization and growth of murine endometriosis-like lesions. Hum. Reprod. 2014, 29, 1011–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Xue, L.; Nie, A.; Yang, Q.; Peng, X.; Chen, Z.; Yang, L.; Xie, Y.; Yuan, A.; Xu, J. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of PPARgamma expression in porcine uteroplacenta for regulating of placental angiogenesis through VEGF-mediated signalling. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2020, 55, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.T.; Shyu, M.K.; Huang, M.C.; Hsu, C.C.; Yeh, S.Y.; Chen, M.R.; Lin, C.J. Hypoxia-mediated down-regulation of OCTN2 and PPARalpha expression in human placentas and in BeWo cells. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker Nitert, M.; Scholz-Romero, K.; Kubala, M.H.; McIntyre, H.D.; Callaway, L.K.; Barrett, H.L. Placental fibroblast growth factor 21 is not altered in late-onset preeclampsia. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2015, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, P.; Chen, Z.; Sun, Q.; Li, Y.; Gu, H.; Ni, X. Reduced expression of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 in preeclamptic placentas is associated with decreased PPARgamma but increased PPARalpha expression. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holdsworth-Carson, S.; Lim, R.; Mitton, A.; Whitehead, C.; Rice, G.; Permezel, M.; Lappas, M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors are altered in pathologies of the human placenta: Gestational diabetes mellitus, intrauterine growth restriction and preeclampsia. Placenta 2010, 31, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana-Garrido, A.; Reyes-Goya, C.; Espinosa-Martín, P.; Sobrevia, L.; Beltrán, L.M.; Vázquez, C.M.; Mate, A. Oxidative and Inflammatory Imbalance in Placenta and Kidney of sFlt1-Induced Early-Onset Preeclampsia Rat Model. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodie, V.A.; Young, A.; Jordan, F.; Sattar, N.; Greer, I.A.; Freeman, D.J. Human placental peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta and gamma expression in healthy pregnancy and in preeclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction. J. Soc. Gynecol. Investig. 2005, 12, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Song, W.; Yang, Y. Inhibition of ALKBH5-mediated m(6) A modification of PPARG mRNA alleviates H/R-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in placenta trophoblast. Environ. Toxicol. 2022, 37, 910–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Ma, Y.; Chen, L.; Chang, J.; Zhong, M.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X.; Sun, F.; Xiao, L.; et al. Maternal RND3/RhoE deficiency impairs placental mitochondrial function in preeclampsia by modulating the PPARgamma-UCP2 cascade. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasture, V.; Sundrani, D.; Dalvi, S.; Swamy, M.; Kale, A.; Joshi, S. Maternal omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin E improve placental angiogenesis in late-onset but not early-onset preeclampsia. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2019, 461, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zhuang, X.; Jiang, M.; Guan, F.; Fu, Q.; Lin, J. ANGPTL4 mediates the protective role of PPARgamma activators in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahendra, J.; Parthiban, P.S.; Mahendra, L.; Balakrishnan, A.; Shanmugam, S.; Junaid, M.; Romanos, G.E. Evidence Linking the Role of Placental Expressions of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-gamma and Nuclear Factor-Kappa B in the Pathogenesis of Preeclampsia Associated with Periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 2016, 87, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meister, S.; Hahn, L.; Beyer, S.; Paul, C.; Mitter, S.; Kuhn, C.; von Schönfeldt, V.; Corradini, S.; Sudan, K.; Schulz, C.; et al. Regulation of Epigenetic Modifications in the Placenta during Preeclampsia: PPARgamma Influences H3K4me3 and H3K9ac in Extravillous Trophoblast Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahardjo, B.; Widjajanto, E.; Sujuti, H.; Keman, K. Different levels of IL-1alpha, IL-6, TNF-alpha, NF-kappaB and PPAR-gamma in monocyte cultures exposed by plasma preeclampsia and normotensive pregnancy. Pregnancy Hypertens 2014, 4, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waite, L.L.; Louie, R.E.; Taylor, R.N. Circulating activators of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors are reduced in preeclamptic pregnancy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Tang, F.; Zhao, X. miR-27b-3p is Highly Expressed in Serum of Patients with Preeclampsia and has Clinical Significance. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2022, 22, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hastie, R.; Brownfoot, F.C.; Pritchard, N.; Hannan, N.J.; Cannon, P.; Nguyen, V.; Palmer, K.; Beard, S.; Tong, S.; Kaitu’U-Lino, T.J. EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) Signaling and the Mitochondria Regulate sFlt-1 (Soluble FMS-Like Tyrosine Kinase-1) Secretion. Hypertension 2019, 73, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.P.; Wu, J.H.; Hu, J.R. Correlations of MMP-9 and PPARgamma gene polymorphisms with occurrence of preeclampsia. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 771–778. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Rouault, C.; Clément, K.; Zhu, W.; Degrelle, S.A.; Charles, M.A.; Heude, B.; Fournier, T. C1431T Variant of PPARgamma Is Associated with Preeclampsia in Pregnant Women. Life 2021, 11, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permadi, W.; Mantilidewi, K.I.; Khairani, A.F.; Lantika, U.A.; Ronosulistyo, A.R.; Bayuaji, H. Differences in expression of Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor-gamma in early-onset preeclampsia and late-onset preeclampsia. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laasanen, J.; Heinonen, S.; Hiltunen, M.; Mannermaa, A.; Laakso, M. Polymorphism in the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma gene in women with preeclampsia. Early Hum. Dev. 2002, 69, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, Z.; Shakiba, M.; Rezavand, N.; Rahimi, Z.; Vaisi-Raygani, A.; Rahimi, Z.; Shakiba, E. Gene variants and haplotypes of Vitamin D biosynthesis, transport, and function in preeclampsia. Hypertens Pregnancy 2021, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armistead, B.; Kadam, L.; Siegwald, E.; McCarthy, F.P.; Kingdom, J.C.; Kohan-Ghadr, H.R.; Drewlo, S. Induction of the PPARgamma (Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor gamma)-GCM1 (Glial Cell Missing 1) Syncytialization Axis Reduces sFLT1 (Soluble fms-Like Tyrosine Kinase 1) in the Preeclamptic Placenta. Hypertension 2021, 78, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohan-Ghadr, H.R.; Kilburn, B.A.; Kadam, L.; Johnson, E.; Kolb, B.L.; Rodriguez-Kovacs, J.; Hertz, M.; Armant, D.R.; Drewlo, S. Rosiglitazone augments antioxidant response in the human trophoblast and prevents apoptosisdagger. Biol. Reprod. 2019, 100, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, B.; Kohan-Ghadr, H.R.; Drewlo, S. The Potential for Placental Activation of PPARgamma to Improve the Angiogenic Profile in Preeclampsia. Cells 2022, 11, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, R.; Xu, R.; Chu, Y.; Gu, W. Procyanidin B2 ameliorates endothelial dysfunction and impaired angiogenesis via the Nrf2/PPARgamma/sFlt-1 axis in preeclampsia. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 177, 106127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saka, M.H.; Madi, N.M.; Ibrahim, R.R.; Alghazaly, G.M.; Elshwaikh, S.; El-Bermawy, M. The ameliorative effect of angiotensin 1-7 on experimentally induced-preeclampsia in rats: Targeting the role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors gamma expression & asymmetric dimethylarginine. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 671, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nema, J.; Randhir, K.; Wadhwani, N.; Sundrani, D.; Joshi, S. Maternal vitamin D deficiency reduces docosahexaenoic acid, placental growth factor and peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma levels in the pup brain in a rat model of preeclampsia. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fat. Acids 2021, 175, 102364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueki, N.; Kanasaki, K.; Kanasaki, M.; Takeda, S.; Koya, D. Catechol-O-Methyltransferase Deficiency Leads to Hypersensitivity of the Pressor Response Against Angiotensin II. Hypertension 2017, 69, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, H.I.G.; Masri, A.A.A. The Potential Therapeutic Role of Peroxisome ProliferatorActivated Receptors Agonist in Preeclamptic Pregnant Rats. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2018, 28, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, F.P.; Drewlo, S.; Kingdom, J.; Johns, E.J.; Walsh, S.K.; Kenny, L.C. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma as a potential therapeutic target in the treatment of preeclampsia. Hypertension 2011, 58, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCarthy, F.P.; Drewlo, S.; English, F.A.; Kingdom, J.; Johns, E.J.; Kenny, L.C.; Walsh, S.K. Evidence implicating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Hypertension 2011, 58, 882–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zuo, C. Aspirin Ameliorates Preeclampsia Induced by a Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Antagonist. Reprod. Sci. 2018, 25, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yang, H. The preventive effect of low-dose aspirin in a PPAR-gamma antagonist treated mouse model of preeclampsia. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2022, 22, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holobotovskyy, V.; Chong, Y.S.; Burchell, J.; He, B.; Phillips, M.; Leader, L.; Murphy, T.V.; Sandow, S.L.; McKitrick, D.J.; Charles, A.K.; et al. Regulator of G protein signaling 5 is a determinant of gestational hypertension and preeclampsia. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 290ra88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pham, J.; Arul Nambi Rajan, K.; Li, P.; Parast, M.M. The role of Sirtuin1-PPARgamma axis in placental development and function. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 60, R201–R212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| PPARs | Expression Sites | Functions | Natural Ligands | Synthetic Ligands |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPARα | Liver, Heart, Intestine, Kidneys, Skeletal muscles, Brown adipose tissue | Fatty acid metabolism | Unsaturated fatty acids Leukotrienes Eicosatetraenoic acids | Fibrates |
| PPARβ/δ | Ubiquitously | Fatty acid oxidation, Blood cholesterol and glucose level regulation | Unsaturated fatty acids Prostacyclins Very low-density lipoproteins | GW501516 |
| PPARγ | Adipocytes | Adipogenesis, Lipid biosynthesis, Lipoprotein metabolism, Insulin sensitivity | Unsaturated fatty acids Eicosatetraenoic acids Octadecadienoic acids Prostaglandins | (Non-)Thiazolidinedioneinsulin sensitizers Angiotensin II receptor antagonists Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs Synthetic cannabinoids |
| PPARs | Models | Expression Levels | Treatment Agents | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPARα | Rat, Human | ↓ | None | [80,81,84] |
| Human | ↑ | [82,83] | ||
| PPARβ/δ | Human | ↔ | None | [85] |
| Human | ↑ | [82] | ||
| PPARγ | Mouse, Rat, Human | ↓ | Rosiglitazone, Troglitazone, Angiotensin 1–7, Tinprotoporphyrin IX, Aspirin, Omega-3 fatty acid, Vitamin D, Procyanidin B2 | [58,82,84,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113] |
| Human | ↑ | None | [83,96,98] | |
| Human | ↔ | [81,85,99,100] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Psilopatis, I.; Vrettou, K.; Fleckenstein, F.N.; Theocharis, S. The Role of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors in Preeclampsia. Cells 2023, 12, 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12040647
Psilopatis I, Vrettou K, Fleckenstein FN, Theocharis S. The Role of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors in Preeclampsia. Cells. 2023; 12(4):647. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12040647
Chicago/Turabian StylePsilopatis, Iason, Kleio Vrettou, Florian Nima Fleckenstein, and Stamatios Theocharis. 2023. "The Role of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors in Preeclampsia" Cells 12, no. 4: 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12040647
APA StylePsilopatis, I., Vrettou, K., Fleckenstein, F. N., & Theocharis, S. (2023). The Role of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors in Preeclampsia. Cells, 12(4), 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12040647








