HLA-B*57:01/Carbamazepine-10,11-Epoxide Association Triggers Upregulation of the NFκB and JAK/STAT Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Detection of CBZ and EPX Bound to sHLA-B*57:01 Molecules
2.2. Detection of CBZ- or EPX-Induced Modifications of the LCL721.221/HLA-B*57:01 Proteome
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
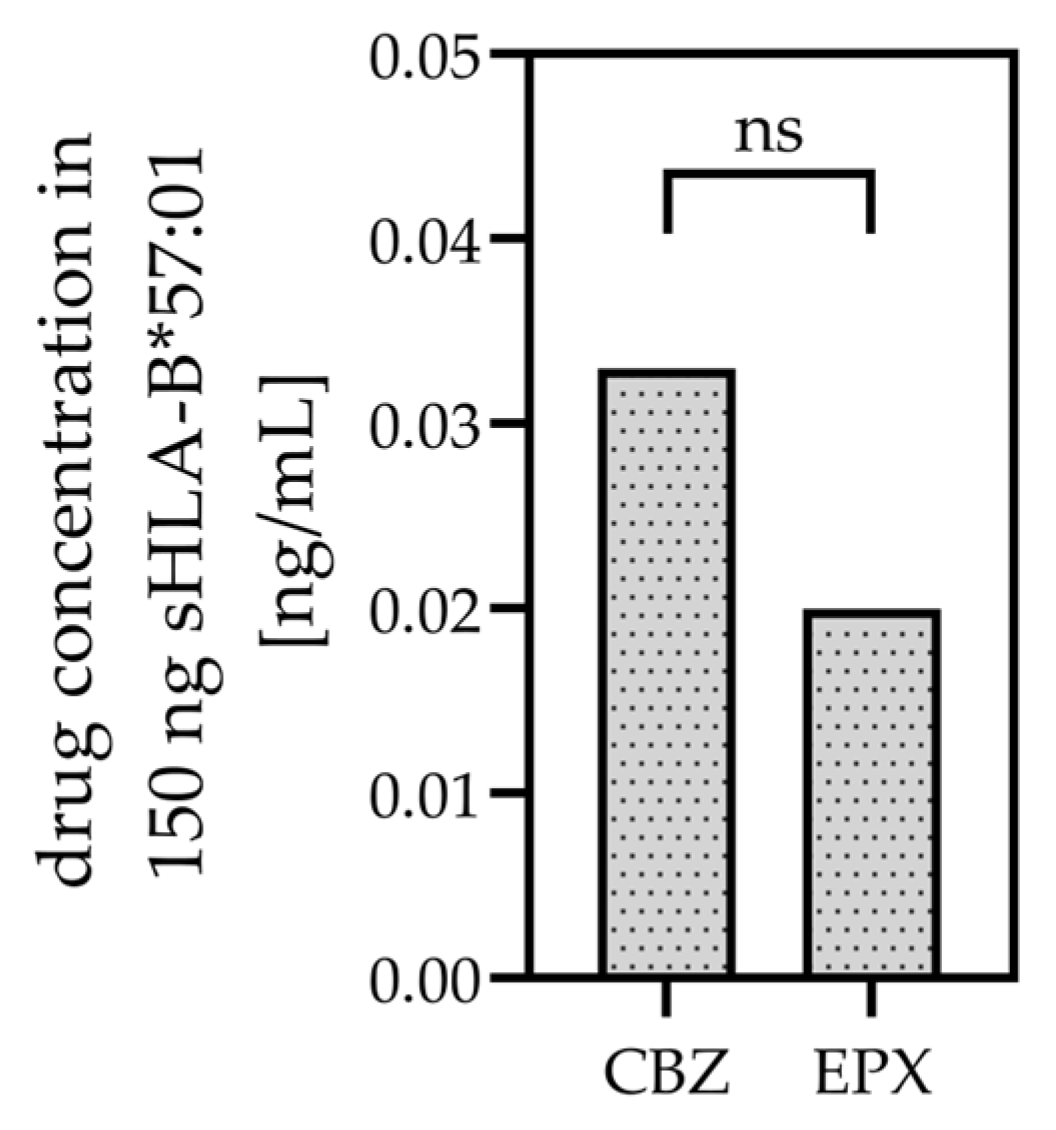
3.1. CBZ and EPX Bind to sHLA-B*57:01
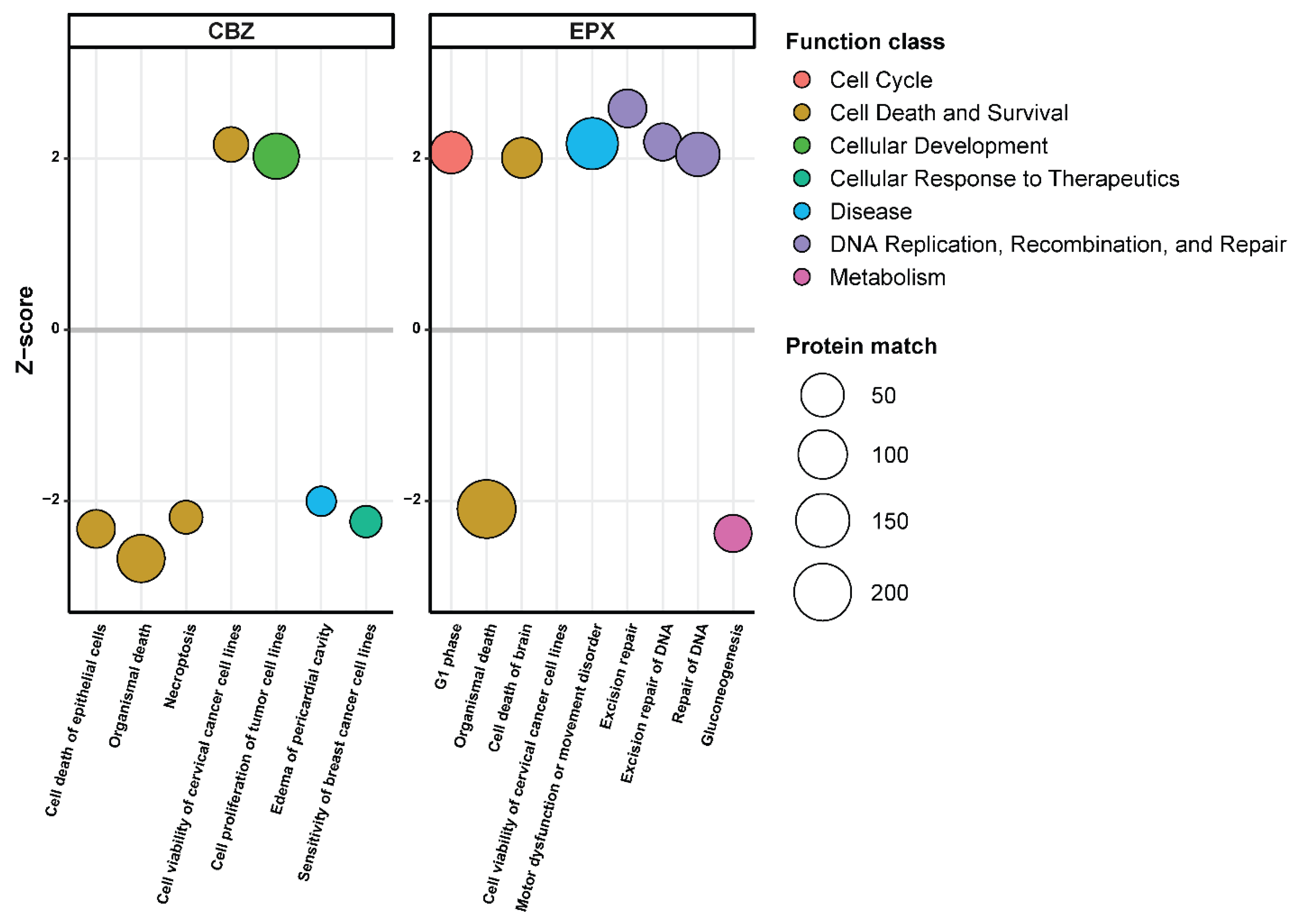
3.2. Quantitative Proteomic Analysis after CBZ and EPX Treatment
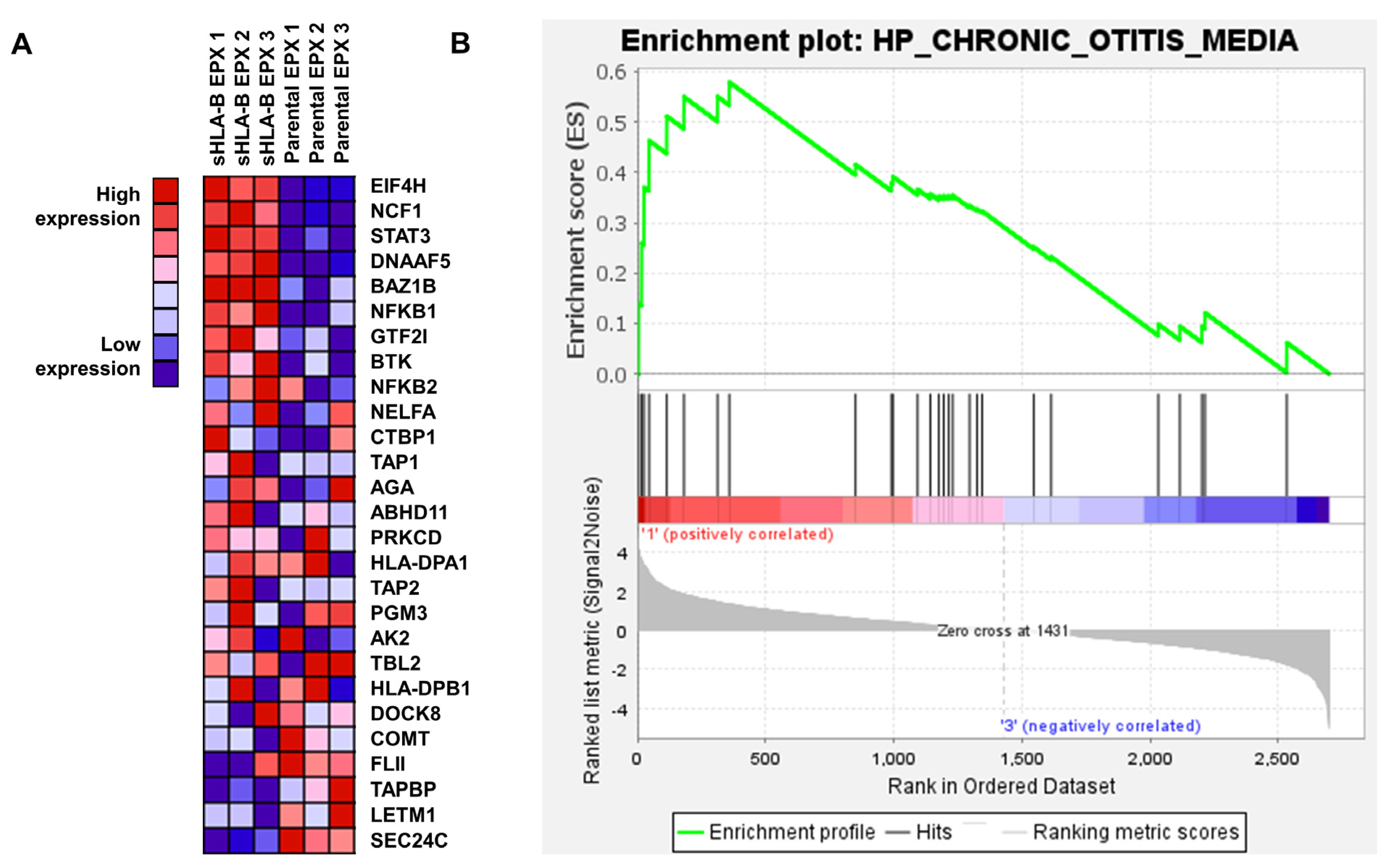
3.3. EPX Treatment Induced a Strong Reaction in the Proteome of LCL721.221/sHLA-B*57:01 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simper, G.; Celik, A.A.; Kunze-Schumacher, R.B.H.; Blasczyk, R.; Bade-Döding, C. Physiology and Pathology of Drug Hypersensitivity: Role of Human Leukocyte Antigens; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hò, G.-G.T.; Hiemisch, W.; Pich, A.; Matern, M.; Gräser, L.S.; Blasczyk, R.; Bade-Doeding, C.; Simper, G.S. Small Molecule/HLA Complexes Alter the Cellular Proteomic Content; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nebeker, J.R.; Barach, P.; Samore, M. Clarifying adverse drug events: A clinician’s guide to terminology, documentation, and reporting. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 140, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurwitz, J.H.; Field, T.S.; Avorn, J.; McCormick, D.; Jain, S.; Eckler, M.; Benser, M.; Edmondson, A.C.; Bates, D.W. Incidence and preventability of adverse drug events in nursing homes. Am. J. Med. 2000, 109, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.W.; Cullen, D.J.; Laird, N.; Petersen, L.A.; Small, S.D.; Servi, D.; Laffel, G.; Sweitzer, B.; Shea, B.F.; Hallisey, R.; et al. Incidence of adverse drug events and potential adverse drug events. Implications for prevention. ADE Prevention Study Group. JAMA 1995, 274, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, I.R.; Aronson, J.K. Adverse drug reactions: Definitions, diagnosis, and management. Lancet 2000, 356, 1255–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawlins, M.D. Clinical pharmacology. Adverse reactions to drugs. Br. Med. J. (Clin. Res. Ed.) 1981, 282, 974–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pichler, W.J.; Hausmann, O. Classification of Drug Hypersensitivity into Allergic, p-i, and Pseudo-Allergic Forms. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 171, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetherington, S.; Hughes, A.R.; Mosteller, M.; Shortino, D.; Baker, K.L.; Spreen, W.; Lai, E.; Davies, K.; Handley, A.; Dow, D.J.; et al. Genetic variations in HLA-B region and hypersensitivity reactions to abacavir. Lancet 2002, 359, 1121–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallal, S.; Nolan, D.; Witt, C.; Masel, G.; Martin, A.; Moore, C.; Sayer, D.; Castley, A.; Mamotte, C.; Maxwell, D.; et al. Association between presence of HLA-B*5701, HLA-DR7, and HLA-DQ3 and hypersensitivity to HIV-1 reverse-transcriptase inhibitor abacavir. Lancet 2002, 359, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.H.; Hung, S.-I.; Hong, H.-S.; Hsih, M.-S.; Yang, L.-C.; Ho, H.-C.; Wu, J.-Y.; Chen, Y.-T. Medical genetics: A marker for Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Nature 2004, 428, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, P.; Hertzman, R.J.; Palubinsky, A.M.; Giles, J.B.; Karnes, J.H.; Gibson, A.; Phillips, E.J. Immunopharmacogenomics: Mechanisms of HLA-Associated Drug Reactions. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 110, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinkernagel, R.M.; Doherty, P.C. Restriction of in vitro T cell-mediated cytotoxicity in lymphocytic choriomeningitis within a syngeneic or semiallogeneic system. Nature 1974, 248, 701–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neefjes, J.; Jongsma, M.L.M.; Paul, P.; Bakke, O. Towards a systems understanding of MHC class I and MHC class II antigen presentation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, K.; Rötzschke, O.; Stevanović, S.; Jung, G.; Rammensee, H.-G. Allele-specific motifs revealed by sequencing of self-peptides eluted from MHC molecules. 1991. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 2741–2747. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wieczorek, M.; Abualrous, E.T.; Sticht, J.; Álvaro-Benito, M.; Stolzenberg, S.; Noé, F.; Freund, C. Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) Class I and MHC Class II Proteins: Conformational Plasticity in Antigen Presentation. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCormack, M.; Alfirevic, A.; Bourgeois, S.; Farrell, J.J.; Kasperavičiūtė, D.; Carrington, M.; Sills, G.J.; Marson, T.; Jia, X.; De Bakker, P.I.; et al. HLA-A*3101 and Carbamazepine-Induced Hypersensitivity Reactions in Europeans. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1134–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hari, Y.; Frutig-Schnyder, K.; Hurni, M.; Yawalkar, N.; Zanni, M.P.; Schnyder, B.; Kappeler, A.; Von Greyerz, S.; Braathen, L.R.; Pichler, W.J. T cell involvement in cutaneous drug eruptions. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2001, 31, 1398–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassif, A.; Bensussan, A.; Boumsell, L.; Deniaud, A.; Moslehi, H.; Wolkenstein, P.; Bagot, M.; Roujeau, J.-C. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: Effector cells are drug-specific cytotoxic T cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, V.L.M.; Pirmohamed, M. The HLA-A*31:01 allele: Influence on carbamazepine treatment. Pharm. Pers. Med. 2017, 10, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Deshpande, P.; Hertzman, R.J.; Palubinsky, A.M.; Gibson, A.; Phillips, E.J. Genomic Risk Factors Driving Immune-Mediated Delayed Drug Hypersensitivity Reactions. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 641905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertzman, R.J.; Deshpande, P.; Gibson, A.; Phillips, E.J. Role of pharmacogenomics in T-cell hypersensitivity drug reactions. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 21, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simper, G.S.; Gräser, L.S.; Celik, A.A.; Kuhn, J.; Kunze-Schumacher, H.; Hò, G.-G.T.; Blasczyk, R.; Pich, A.; Bade-Doeding, C. The Mechanistic Differences in HLA-Associated Carbamazepine Hypersensitivity. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mockenhaupt, M.; Wang, C.; Hung, S.; Sekula, P.; Schmidt, A.H.; Pan, R.; Chen, C.; Dunant, A.; Le Gouvello, S.; Schumacher, M.; et al. HLA-B*57:01 confers genetic susceptibility to carbamazepine-induced SJS/TEN in Europeans. Allergy 2019, 74, 2227–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassolas, B.; Haddad, C.; Mockenhaupt, M.; Dunant, A.; Liss, Y.; Bork, K.; Haustein, U.F.; Vieluf, D.; Roujeau, J.C.; Le Louet, H. ALDEN, an Algorithm for Assessment of Drug Causality in Stevens–Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: Comparison With Case–Control Analysis. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 88, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetherington, S.; McGuirk, S.; Powell, G.; Cutrell, A.; Naderer, O.; Spreen, B.; Lafon, S.; Pearce, G.; Steel, H. Hypersensitivity reactions during therapy with the nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor abacavir. Clin. Ther. 2001, 23, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallal, S.; Phillips, E.; Carosi, G.; Molina, J.-M.; Workman, C.; Tomažič, J.; Jägel-Guedes, E.; Rugina, S.; Kozyrev, O.; Cid, J.F.; et al. HLA-B*5701 Screening for Hypersensitivity to Abacavir. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chessman, D.; Kostenko, L.; Lethborg, T.; Purcell, A.W.; Williamson, N.A.; Chen, Z.; Kjer-Nielsen, L.; Mifsud, N.A.; Tait, B.D.; Holdsworth, R.; et al. Human Leukocyte Antigen Class I-Restricted Activation of CD8+ T Cells Provides the Immunogenetic Basis of a Systemic Drug Hypersensitivity. Immunity 2008, 28, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Illing, P.T.; Vivian, J.P.; Dudek, N.L.; Kostenko, L.; Chen, Z.; Bharadwaj, M.; Miles, J.J.; Kjer-Nielsen, L.; Gras, S.; Williamson, N.A.; et al. Immune self-reactivity triggered by drug-modified HLA-peptide repertoire. Nature 2012, 486, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saag, M.; Balu, R.; Phillips, E.; Brachman, P.; Martorell, C.; Burman, W.; Stancil, B.; Mosteller, M.; Brothers, C.; Wannamaker, P.; et al. High Sensitivity of Human Leukocyte Antigen–B*5701 as a Marker for Immunologically Confirmed Abacavir Hypersensitivity in White and Black Patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Genin, E.; Chen, D.-P.; Hung, S.-I.; Sekula, P.; Schumacher, M.A.; Chang, P.-Y.; Tsai, S.-H.; Wu, T.-L.; Bellón, T.; Tamouza, R.; et al. HLA-A*31:01 and different types of carbamazepine-induced severe cutaneous adverse reactions: An international study and meta-analysis. Pharm. J. 2013, 14, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simper, G.S.; Hò, G.-G.; Celik, A.; Huyton, T.; Kuhn, J.; Kunze-Schumacher, H.; Blasczyk, R.; Bade-Döding, C. Carbamazepine-Mediated Adverse Drug Reactions: CBZ-10,11-epoxide but Not Carbamazepine Induces the Alteration of Peptides Presented by HLA-B *15:02. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 5086503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haukamp, F.J.; Gall, E.; Hò, G.-G.T.; Hiemisch, W.; Stieglitz, F.; Kuhn, J.; Blasczyk, R.; Pich, A.; Bade-Döding, C. Unravelling the Proteomics of HLA-B*57:01+ Antigen Presenting Cells during Abacavir Medication. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hò, G.-G.T.; Heinen, F.J.; Huyton, T.; Blasczyk, R.; Bade-Döding, C. HLA-F*01:01 presents peptides with N-terminal flexibility and a preferred length of 16 residues. Immunogenetics 2019, 71, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gall, E.; Stieglitz, F.; Pich, A.; Behrens, G.M.N.; Kuhn, J.; Blasczyk, R.; Haukamp, F.J.; Bade-Döding, C. Proteomic Profiling and T Cell Receptor Usage of Abacavir Susceptible Subjects. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.; Mann, M. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UniProt, C. UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D480–D489. [Google Scholar]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Sinitcyn, P.; Carlson, A.; Hein, M.Y.; Geiger, T.; Mann, M.; Cox, J. The Perseus computational platform for comprehensive analysis of (prote)omics data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- Gu, Z.; Eils, R.; Schlesner, M. Complex heatmaps reveal patterns and correlations in multidimensional genomic data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2847–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mootha, V.K.; Lindgren, C.M.; Eriksson, K.-F.; Subramanian, A.; Sihag, S.; Lehar, J.; Puigserver, P.; Carlsson, E.; Ridderstråle, M.; Laurila, E.; et al. PGC-1α-responsive genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately downregulated in human diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griss, J.; Perez-Riverol, Y.; Lewis, S.; Tabb, D.L.; Dianes, J.A.; Del-Toro, N.; Rurik, M.; Walzer, M.; Kohlbacher, O.; Hermjakob, H.; et al. Recognizing millions of consistently unidentified spectra across hundreds of shotgun proteomics datasets. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunze-Schumacher, H.; Blasczyk, R.; Bade-Doeding, C. Soluble HLA Technology as a Strategy to Evaluate the Impact of HLA Mismatches. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlton, O.A.; Harris, V.R.; Phan, K.; Mewton, M.E.; Jackson, C.J.; Cooper, A. Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis and Steven–Johnson Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review. Adv. Wound Care 2020, 9, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phase 0 trials: A platform for drug development? Lancet 2009, 374, 176. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Tourneau, C.; Lee, J.; Siu, L. Dose escalation methods in phase I cancer clinical trials. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 708–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kerr, B.M.; Thummel, K.E.; Wurden, C.J.; Klein, S.M.; Kroetz, D.L.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Levy, R. Human liver carbamazepine metabolism: Role of CYP3A4 and CYP2C8 in 10,11-epoxide formation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1994, 47, 1969–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madson, J.G.; Lynch, D.T.; Tinkum, K.L.; Putta, S.K.; Hansen, L.A. Erbb2 Regulates Inflammation and Proliferation in the Skin after Ultraviolet Irradiation. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 169, 1402–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardinez, C.; Miraghazadeh, B.; Tanita, K.; Da Silva, E.; Hoshino, A.; Okada, S.; Chand, R.; Asano, T.; Tsumura, M.; Yoshida, K.; et al. Gain-of-function IKBKB mutation causes human combined immune deficiency. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 2715–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snyder, M.; He, W.; Zhang, J.J. The DNA replication factor MCM5 is essential for Stat1-mediated transcriptional activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14539–14544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banerjee, S.; Biehl, A.; Gadina, M.; Hasni, S.; Schwartz, D.M. JAK–STAT Signaling as a Target for Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases: Current and Future Prospects. Drugs 2017, 77, 521–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, J.; Cheblal, A.; Gasser, S. Underappreciated Roles of DNA Polymerase delta in Replication Stress Survival. Trends Genet. 2021, 37, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. POLD2 is activated by E2F1 to promote triple-negative breast cancer proliferation. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 981329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, F.; Long, J.; Liu, J.; Deng, Z.; Yan, B.; Liang, C.; Huang, X.; Liu, J.; Tang, W. An integrative analysis revealing POLD2 as a tumor suppressive immune protein and prognostic biomarker in pan-cancer. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 877468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, A.; Ferlosio, A.; Arcuri, G.; Scioli, M.G.; De Falco, S.; Spagnoli, L.G. Flt-1 expression influences apoptotic susceptibility of vascular smooth muscle cells through the NF-kappaB/IAP-1 pathway. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 85, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jackson, N.M.; Ceresa, B.P. EGFR-mediated apoptosis via STAT3. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 356, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, I.P. FLT1: A potential therapeutic target in sepsis-associated ARDS? Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 219–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbah, D.A.; Hajjo, R.; Sweidan, K. Review on Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Structure, Signaling Pathways, Interactions, and Recent Updates of EGFR Inhibitors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 815–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, C.; Wolkenstein, P.; Adle, H.; Wechsler, J.; Garchon, H.; Revuz, J.; Roujeau, J. Apoptosis as a mechanism of keratinocyte death in toxic epidermal necrolysis. Br. J. Dermatol. 1996, 134, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, G.; Yang, T.; Song, W. INSR mediated by transcription factor KLF4 and DNA methylation ameliorates osteoarthritis progression via inactivation of JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 7953–7967. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, M.; Hakem, R.; Furlonger, C.; Hakem, A.; Duncan, G.S.; Sasaki, T.; Bouchard, D.; Lu, L.; Wu, G.E.; Paige, C.J.; et al. Caspase-3 regulates cell cycle in B cells: A consequence of substrate specificity. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Nam, Y.W.; Kim, S.; Oh, D.-B.; Song, J. Necroptosis molecular mechanisms: Recent findings regarding novel necroptosis regulators. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertheloot, D.; Latz, E.; Franklin, B.S. Necroptosis, pyroptosis and apoptosis: An intricate game of cell death. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1106–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Lim, J.M.E.; Chia, C.; Ren, E.C. CD39+ regulatory T cells modulate the immune response to carbamazepine in HLA-B*15:02 carriers. Immunobiology 2019, 225, 151868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haukamp, F.J.; Hartmann, Z.M.; Pich, A.; Kuhn, J.; Blasczyk, R.; Stieglitz, F.; Bade-Döding, C. HLA-B*57:01/Carbamazepine-10,11-Epoxide Association Triggers Upregulation of the NFκB and JAK/STAT Pathways. Cells 2023, 12, 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12050676
Haukamp FJ, Hartmann ZM, Pich A, Kuhn J, Blasczyk R, Stieglitz F, Bade-Döding C. HLA-B*57:01/Carbamazepine-10,11-Epoxide Association Triggers Upregulation of the NFκB and JAK/STAT Pathways. Cells. 2023; 12(5):676. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12050676
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaukamp, Funmilola Josephine, Zoe Maria Hartmann, Andreas Pich, Joachim Kuhn, Rainer Blasczyk, Florian Stieglitz, and Christina Bade-Döding. 2023. "HLA-B*57:01/Carbamazepine-10,11-Epoxide Association Triggers Upregulation of the NFκB and JAK/STAT Pathways" Cells 12, no. 5: 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12050676
APA StyleHaukamp, F. J., Hartmann, Z. M., Pich, A., Kuhn, J., Blasczyk, R., Stieglitz, F., & Bade-Döding, C. (2023). HLA-B*57:01/Carbamazepine-10,11-Epoxide Association Triggers Upregulation of the NFκB and JAK/STAT Pathways. Cells, 12(5), 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12050676






