Cellular Distribution of Secreted Phospholipase A2 in Lungs of IPF Patients and Its Inhibition in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice
Abstract
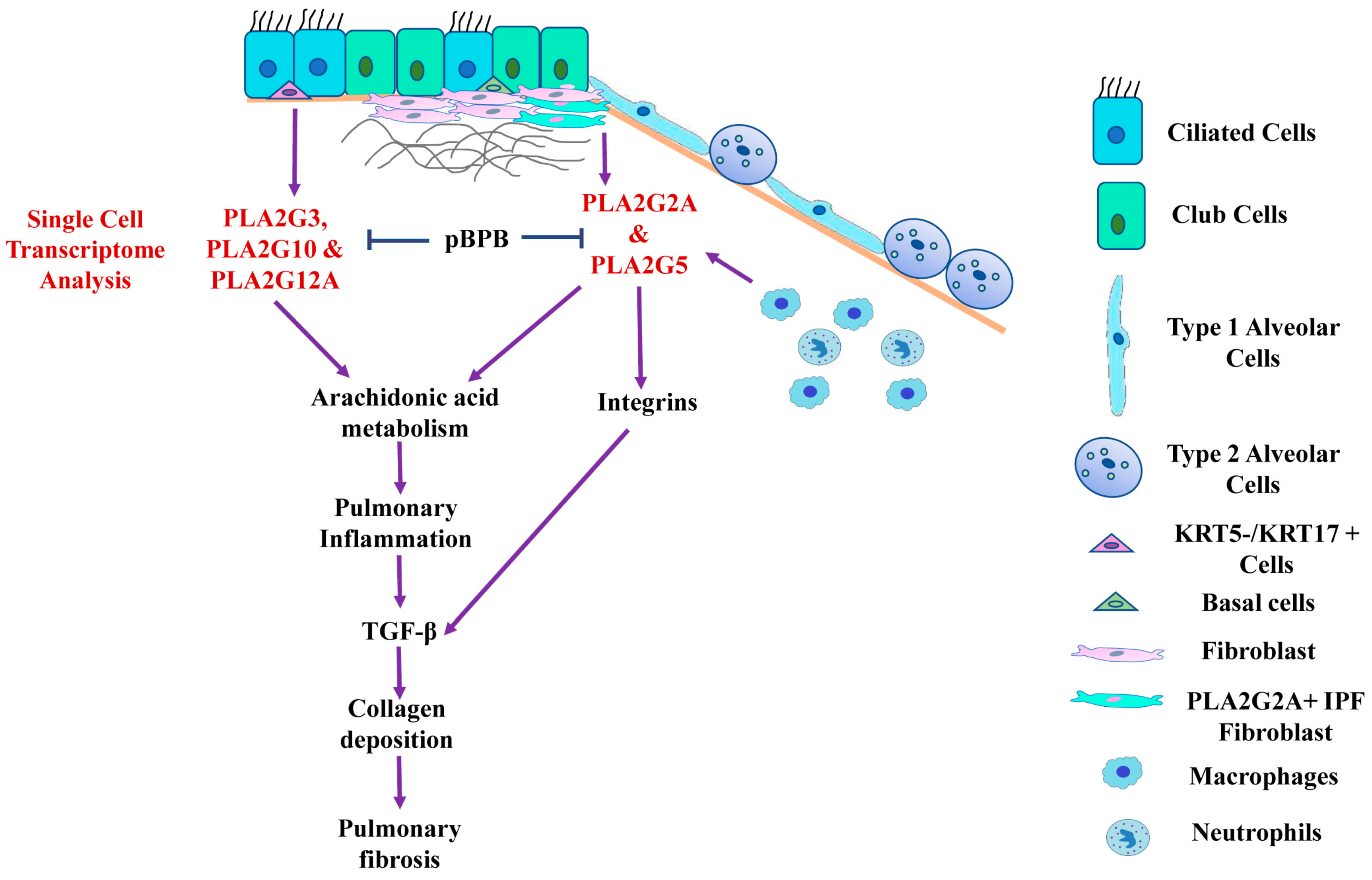
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Single-Cell RNA-Sequencing Data Acquisition
2.2. Single-Cell RNA-Sequencing Data Analysis
2.3. Pathway Enrichment Analysis
2.4. Patient Samples and Animals
2.5. Mice Model of Pulmonary Fibrosis
2.6. Treatment with pBPB
2.7. BAL Fluid Analysis
2.8. Lung Histopathology and Morphometry
2.9. Elastin Measurement in Lung Lysate
2.10. sPLA2 Activity Assay
2.11. ELISA
2.12. Statistics
3. Results
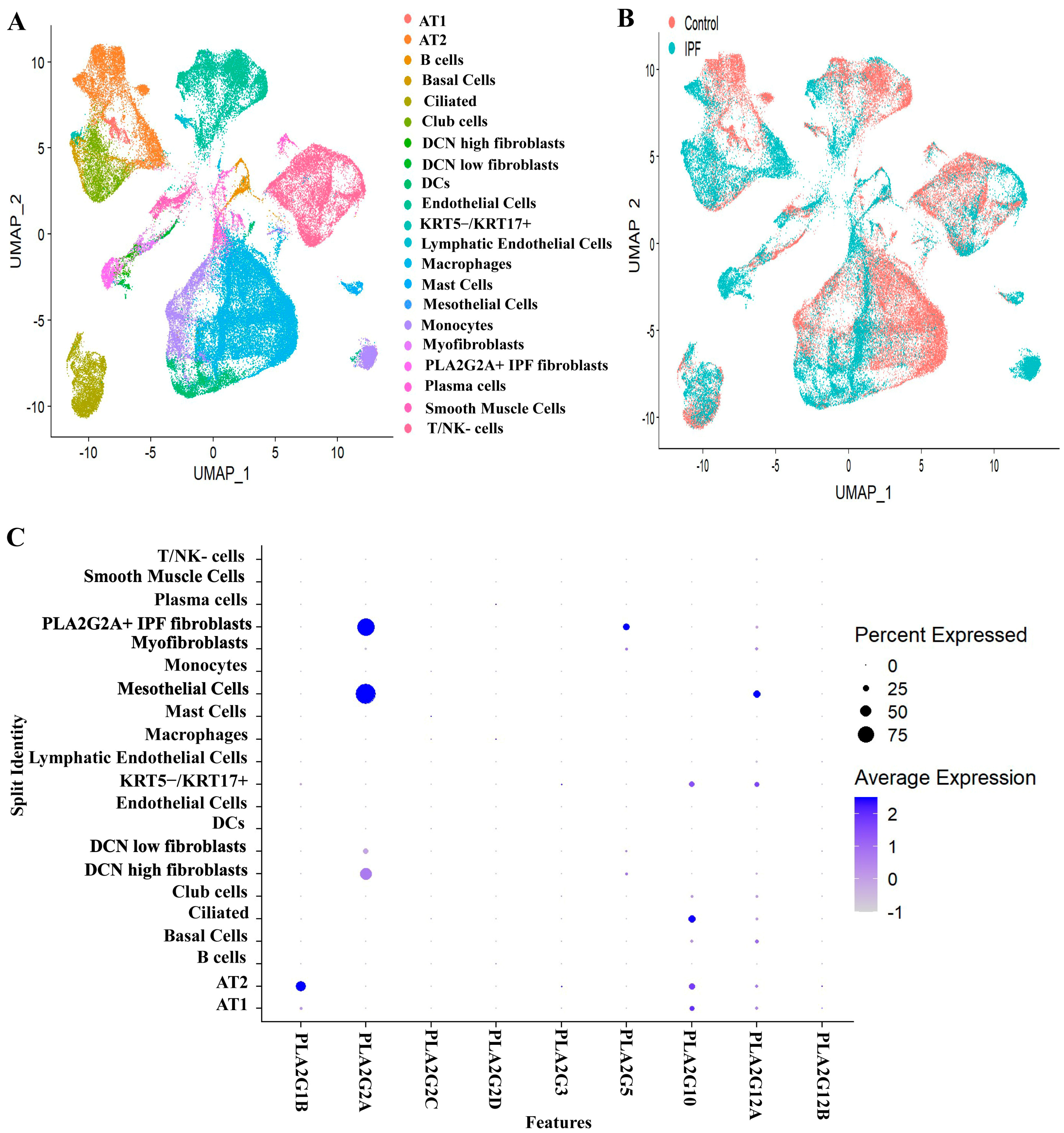
3.1. Expression Profiles of Various Secretory Phospholipase A2 Isoforms in IPF Patients and Controls
- (a)
- EPCAM+ epithelial cells (clusters 1 and 4),
- (b)
- PTPRC+ immune cells (clusters 0, 2, 6 and 7),
- (c)
- PECAM1+ and EPAS1+ endothelial cells (cluster 3) and
- (d)
- EPCAM- PTPRC- and PECAM1- mesenchymal cells (cluster 5).
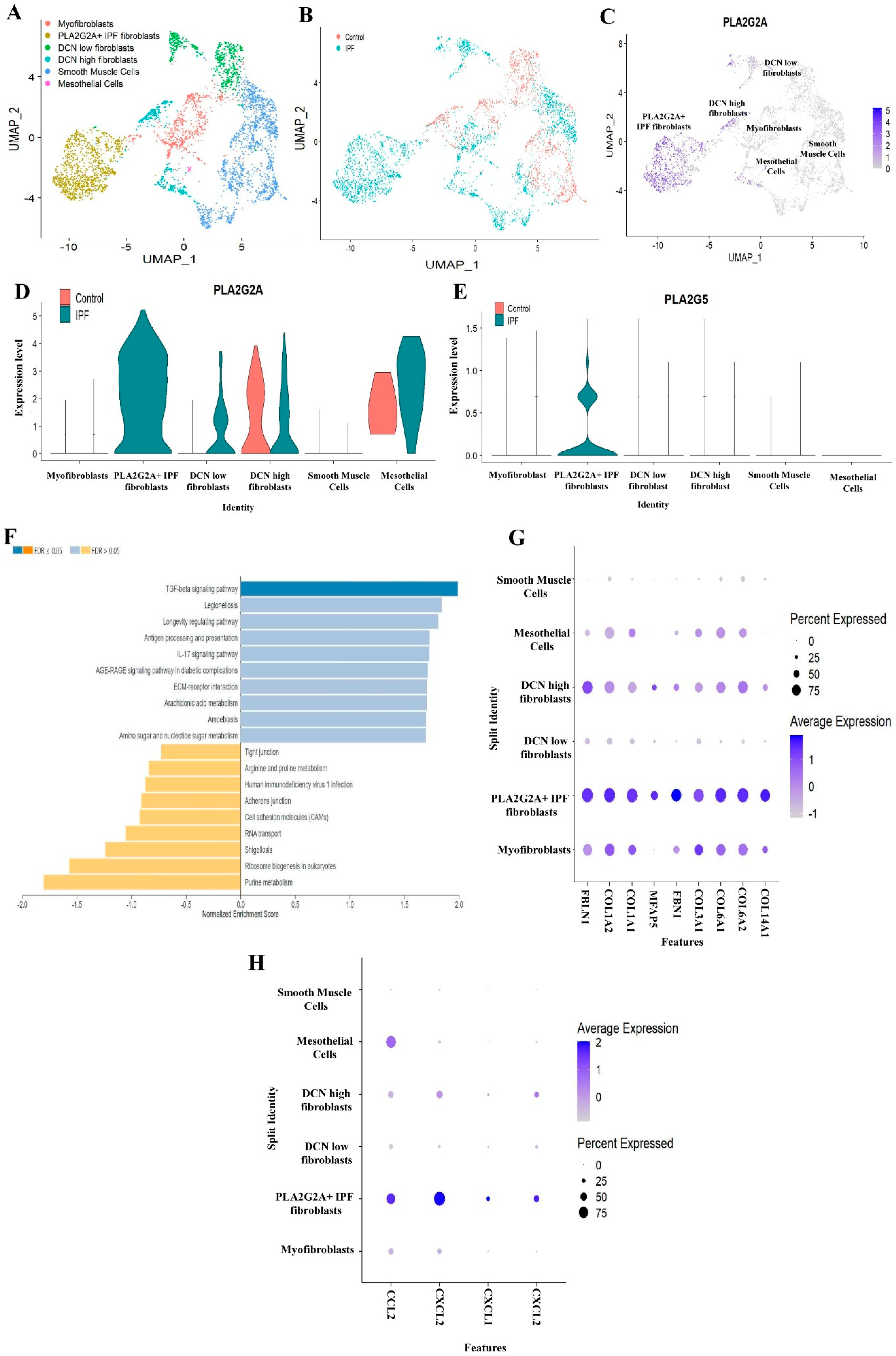
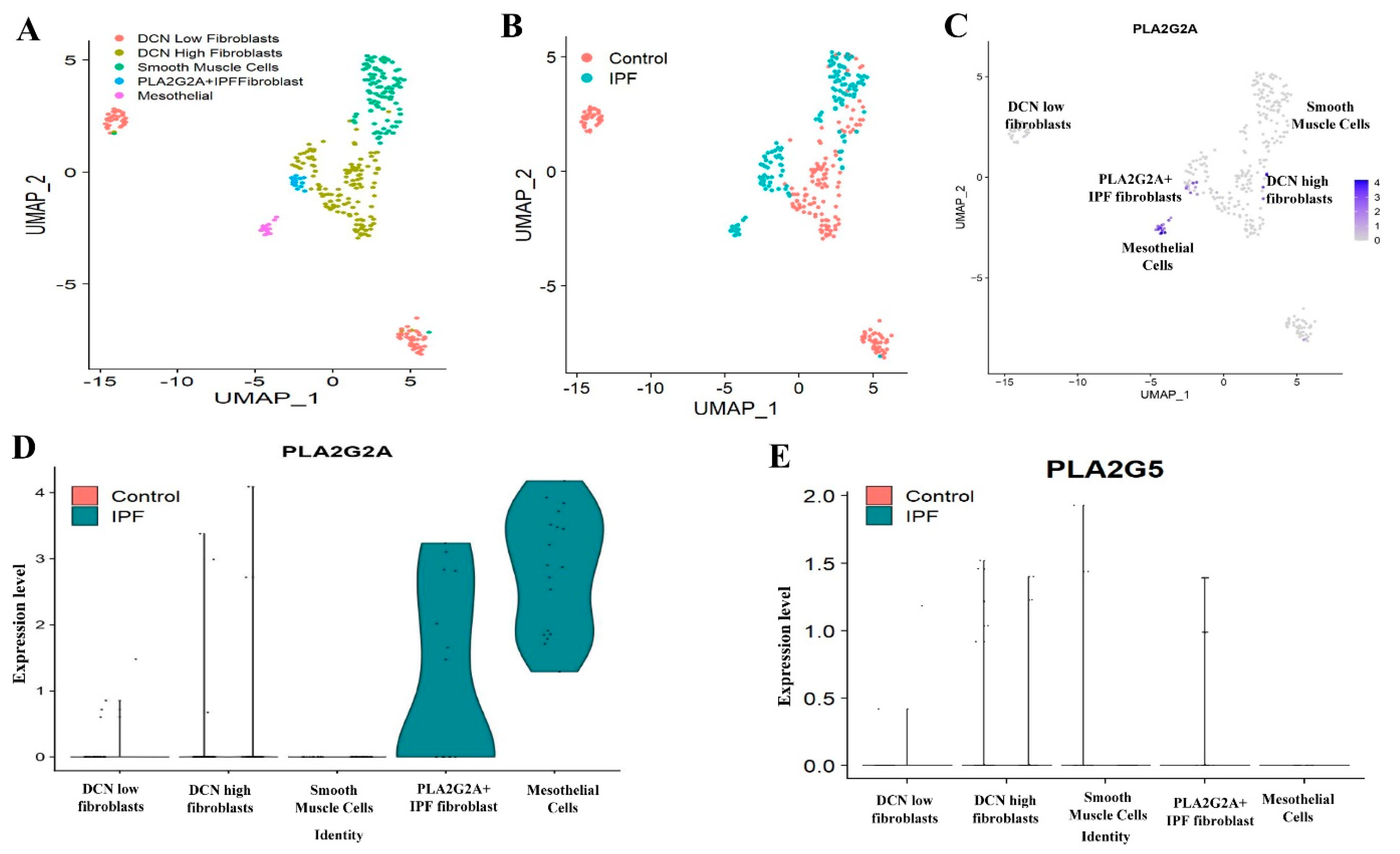
3.2. Single Cell RNA-seq Analysis of Mesecnymal Cells Reveals PLA2G2A High Fibroblast in IPF Petients
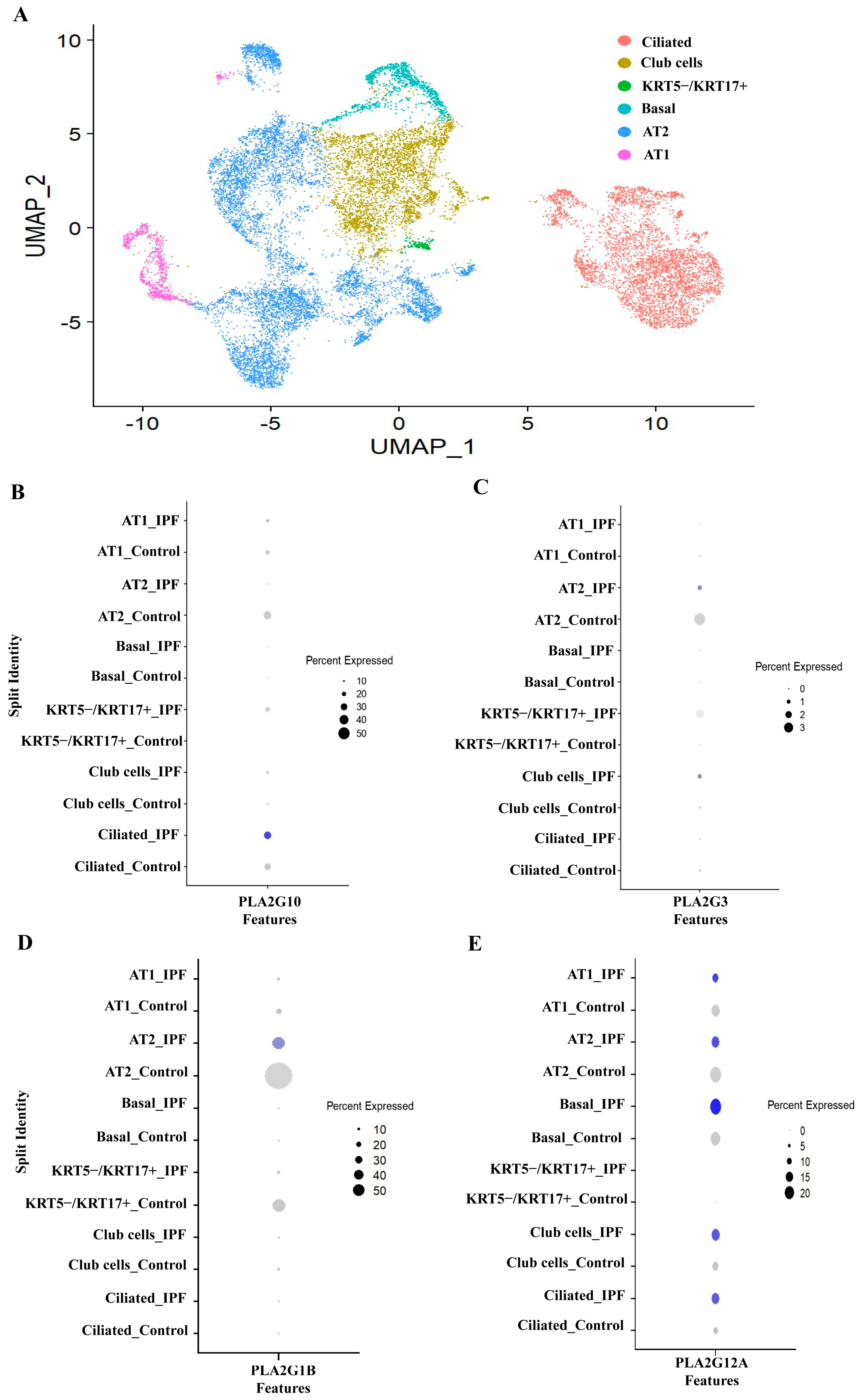
3.3. PLA2G1B, PLA2G3 PLA2G10 and PLA2G12A Isoforms Have Shown Differential Expression in IPF Patients
3.4. Expression of sPLA2-IIA Increased in the Plasma Samples of IPF Patients
3.5. Development of Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis with Time Kinetics
3.6. pBPB Attenuates Pulmonary Fibrosis in Bleomycin-Induced Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selman, M.; Pardo, A. The Leading Role of Epithelial Cells in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Cell. Signal. 2020, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman, M.; Pardo, A. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: An Epithelial/Fibroblastic Cross-Talk Disorder. Respir. Res. 2002, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancil, I.T.; Michalski, J.E.; Davis-Hall, D.; Chu, H.W.; Park, J.A.; Magin, C.M.; Yang, I.V.; Smith, B.J.; Dobrinskikh, E.; Schwartz, D.A. Pulmonary Fibrosis Distal Airway Epithelia Are Dynamically and Structurally Dysfunctional. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shea, B.S.; Tager, A.M. Role of the Lysophospholipid Mediators Lysophosphatidic Acid and Sphingosine 1-Phosphate in Lung Fibrosis. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2012, 9, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tager, A.M.; LaCamera, P.; Shea, B.S.; Campanella, G.S.; Selman, M.; Zhao, Z.; Polosukhin, V.; Wain, J.; Karimi-Shah, B.A.; Kim, N.D.; et al. The Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor LPA1 Links Pulmonary Fibrosis to Lung Injury by Mediating Fibroblast Recruitment and Vascular Leak. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballester, B.; Milara, J.; Cortijo, J. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer: Mechanisms and Molecular Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Letsiou, E.; Htwe, Y.M.; Dudek, S.M. Secretory Phospholipase A2 Enzymes in Acute Lung Injury. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 79, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pniewska, E.; Pawliczak, R. The Involvement of Phospholipases A2 in Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagase, T.; Uozumi, N.; Ishii, S.; Kita, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Ohga, E.; Ouchi, Y.; Shimizu, T. A Pivotal Role of Cytosolic Phospholipase A(2) in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, C.C. Cytosolic Phospholipase A2: Physiological Function and Role in Disease. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 1386–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, R.; Gutierrez, B.; Cordova, C.; Roman, A.S.; Alvarez, Y.; Hernandez, M.; Cachofeiro, V.; Nieto, M.L. Secreted Phospholipase A2-IIA Modulates Transdifferentiation of Cardiac Fibroblast through EGFR Transactivation: An Inflammation–Fibrosis Link. Cells 2020, 9, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doré, E.; Joly-Beauparlant, C.; Morozumi, S.; Mathieu, A.; Lévesque, T.; Allaeys, I.; Duchez, A.C.; Cloutier, N.; Leclercq, M.; Bodein, A.; et al. The Interaction of Secreted Phospholipase A2-IIA with the Microbiota Alters Its Lipidome and Promotes Inflammation. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e152638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, M.; Taketomi, Y.; Girard, C.; Yamamoto, K.; Lambeau, G. Emerging Roles of Secreted Phospholipase A2 Enzymes: Lessons from Transgenic and Knockout Mice. Biochimie 2010, 92, 561–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, J.P. Molecular Determinants of Bacterial Sensitivity and Resistance to Mammalian Group IIA Phospholipase A2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1848, 3072–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wijkander, J.; O’Flaherty, J.T.; Nixon, A.B.; Wykle, R.L. 5-Lipoxygenase Products Modulate the Activity of the 85-KDa Phospholipase A2 in Human Neutrophils. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 26543–26549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernández, M.; Burillo, S.L.; Crespo, M.S.; Nieto, M.L. Secretory Phospholipase A2 Activates the Cascade of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases and Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 in the Human Astrocytoma Cell Line 1321N1. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anthonsen, M.W.; Solhaug, A.; Johansen, B. Functional Coupling between Secretory and Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 Modulates Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha- and Interleukin-1beta-Induced NF-Kappa B Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 30527–30536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Habermann, A.C.; Gutierrez, A.J.; Bui, L.T.; Yahn, S.L.; Winters, N.I.; Calvi, C.L.; Peter, L.; Chung, M.I.; Taylor, C.J.; Jetter, C.; et al. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals Profibrotic Roles of Distinct Epithelial and Mesenchymal Lineages in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukui, T.; Sun, K.H.; Wetter, J.B.; Wilson-Kanamori, J.R.; Hazelwood, L.A.; Henderson, N.C.; Adams, T.S.; Schupp, J.C.; Poli, S.D.; Rosas, I.O.; et al. Collagen-Producing Lung Cell Atlas Identifies Multiple Subsets with Distinct Localization and Relevance to Fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reyfman, P.A.; Walter, J.M.; Joshi, N.; Anekalla, K.R.; McQuattie-Pimentel, A.C.; Chiu, S.; Fernandez, R.; Akbarpour, M.; Chen, C.I.; Ren, Z.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis of Human Lung Provides Insights into the Pathobiology of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 1517–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, A.; Mabalirajan, U.; Jaiswal, A.; Rehman, R.; Singh, V.P.; Ghosh, B. Parabromophenacyl Bromide Inhibits Subepithelial Fibrosis by Reducing TGF-Β1 in a Chronic Mouse Model of Allergic Asthma. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2015, 167, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ram, A.; Das, M.; Gangal, S.V.; Ghosh, B. Para-Bromophenacyl Bromide Alleviates Airway Hyperresponsiveness and Modulates Cytokines, IgE and Eosinophil Levels in Ovalbumin-Sensitized and -Challenged Mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2004, 4, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satija, R.; Farrell, J.A.; Gennert, D.; Schier, A.F.; Regev, A. Spatial Reconstruction of Single-Cell Gene Expression Data. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stuart, T.; Butler, A.; Hoffman, P.; Hafemeister, C.; Papalexi, E.; Mauck, W.M.; Hao, Y.; Stoeckius, M.; Smibert, P.; Satija, R. Comprehensive Integration of Single-Cell Data. Cell 2019, 177, 1888–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Hao, S.; Andersen-Nissen, E.; Mauck, W.M.; Zheng, S.; Butler, A.; Lee, M.J.; Wilk, A.J.; Darby, C.; Zager, M.; et al. Integrated Analysis of Multimodal Single-Cell Data. Cell 2021, 184, 3573–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A.; Hoffman, P.; Smibert, P.; Papalexi, E.; Satija, R. Integrating Single-Cell Transcriptomic Data across Different Conditions, Technologies, and Species. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafemeister, C.; Satija, R. Normalization and Variance Stabilization of Single-Cell RNA-Seq Data Using Regularized Negative Binomial Regression. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jaehnig, E.J.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, B. WebGestalt 2019: Gene Set Analysis Toolkit with Revamped UIs and APIs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W199–W205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruscitti, F.; Ravanetti, F.; Bertani, V.; Ragionieri, L.; Mecozzi, L.; Sverzellati, N.; Silva, M.; Ruffini, L.; Menozzi, V.; Civelli, M.; et al. Quantification of Lung Fibrosis in IPF-Like Mouse Model and Pharmacological Response to Treatment by Micro-Computed Tomography. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeller, A.; Ask, K.; Warburton, D.; Gauldie, J.; Kolb, M. The Bleomycin Animal Model: A Useful Tool to Investigate Treatment Options for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis? Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walters, D.M.; Kleeberger, S.R. Mouse Models of Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2008, 5, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, S.; Reddy, J.R.; Rajesh, N.; Jaiswal, A.; Mabalirajan, U.; Palakodety, R.K.; Mukherjee, P.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Novel Benzoxazinone Derivative as Potent Human Neutrophil Elastase Inhibitor: Potential Implications in Lung Injury. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 931, 175187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabalirajan, U.; Rehman, R.; Ahmad, T.; Kumar, S.; Singh, S.; Leishangthem, G.D.; Aich, J.; Kumar, M.; Khanna, K.; Singh, V.P.; et al. Linoleic Acid Metabolite Drives Severe Asthma by Causing Airway Epithelial Injury. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hübner, R.H.; Gitter, W.; El Mokhtari, N.E.; Mathiak, M.; Both, M.; Bolte, H.; Freitag-Wolf, S.; Bewig, B. Standardized Quantification of Pulmonary Fibrosis in Histological Samples. Biotechniques 2008, 44, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, R.; Jaiswal, A.; Agrawal, A.; Mabalirajan, U. Ku70 Modulation Alleviates Murine Allergic Asthma Features and Restores Mitochondrial Function in Lungs. Mitochondrion 2021, 57, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, S.; Breuer, R.; Lossos, I.S.; Berkman, N.; Christensen, T.G.; Connor, M.W.; Goldstein, R.H.; Or, R. Effect of Immunomodulators on Bleomycin-Induced Lung Injury. Respiration 1999, 66, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laxer, U.; Lossos, I.S.; Gillis, S.; Or, R.; Christensen, T.G.; Goldstein, R.H.; Breuer, R. The Effect of Enoxaparin on Bleomycin-Induced Lung Injury in Mice. Exp. Lung Res. 1999, 25, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izbicki, G.; Segel, M.J.; Christensen, T.G.; Conner, M.W.; Breuer, R. Time Course of Bleomycin-Induced Lung Fibrosis. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2002, 83, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Sato, H.; Miki, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Taketomi, Y. A New Era of Secreted Phospholipase A2. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 1248–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, P.; Fytianos, K.; Blumer, S.; Roux, J.; Gazdhar, A.; Savic, S.; Knudsen, L.; Jonigk, D.; Kuehnel, M.P.; Mykoniati, S.; et al. Basal-Like Cell-Conditioned Medium Exerts Anti-Fibrotic Effects In Vitro and In Vivo. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 844119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, E.L.; Janssen, W.J.; Riches, D.W.H.; Moss, M.; Downey, G.P. The Fibroproliferative Response in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Mechanisms and Clinical Significance. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michalski, J.E.; Kurche, J.S.; Schwartz, D.A. From ARDS to Pulmonary Fibrosis: The next Phase of the COVID-19 Pandemic? Transl. Res. 2022, 241, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringardner, B.D.; Baran, C.P.; Eubank, T.D.; Marsh, C.B. The Role of Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2008, 10, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boudreau, L.H.; Duchez, A.C.; Cloutier, N.; Soulet, D.; Martin, N.; Bollinger, J.; Paré, A.; Rousseau, M.; Naika, G.S.; Lévesque, T.; et al. Platelets Release Mitochondria Serving as Substrate for Bactericidal Group IIA-Secreted Phospholipase A2 to Promote Inflammation. Blood 2014, 124, 2173–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Gao, P. Neutrophils Modulate Fibrogenesis in Chronic Pulmonary Diseases. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snider, J.M.; You, J.K.; Wang, X.; Snider, A.J.; Hallmark, B.; Zec, M.M.; Seeds, M.C.; Sergeant, S.; Johnstone, L.; Wang, Q.; et al. Group IIA Secreted Phospholipase A2 Is Associated with the Pathobiology Leading to COVID-19 Mortality. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e149236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesur, O.; Bernard, A.; Arsalane, K.; Lauwerys, R.; Bégin, R.; Cantin, A.; Lane, D. Clara Cell Protein (CC-16) Induces a Phospholipase A2-Mediated Inhibition of Fibroblast Migration In Vitro. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 152, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuschner, G.; Reiter, F.; Stocker, F.; Crispin, A.; Kneidinger, N.; Veit, T.; Klenner, F.; Ceelen, F.; Zimmermann, G.; Leuchte, H.; et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Among Young Patients: Challenges in Diagnosis and Management. Lung 2018, 196, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meltzer, E.B.; Noble, P.W. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2008, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nadrous, H.F.; Myers, J.L.; Decker, P.A.; Ryu, J.H. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in Patients Younger than 50 Years. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2005, 80, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Chen, S.Y.; Hou, Q.; Yeh, W.S.; Collard, H.R. Incidence and Prevalence of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in US Adults 18–64 Years Old. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sritharan, S.S.; Gajewska, M.E.; Skytte, A.B.S.; Madsen, L.B.; Bendstrup, E. Familial Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in a Young Female. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2018, 24, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidgood, M.J.; Jamal, O.S.; Cunningham, A.M.; Brooks, P.M.; Scott, K.F. Type IIA Secretory Phospholipase A2 Up-Regulates Cyclooxygenase-2 and Amplifies Cytokine-Mediated Prostaglandin Production in Human Rheumatoid Synoviocytes. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 2790–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ibeas, E.; Fuentes, L.; Martín, R.; Hernández, M.; Nieto, M.L. Secreted Phospholipase A2 Type IIA as a Mediator Connecting Innate and Adaptive Immunity: New Role in Atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 81, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, R.; Rockel, J.S.; Kapoor, M.; Hinz, B. The Inflammatory Speech of Fibroblasts. Immunol. Rev. 2021, 302, 126–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Zhu, K.; Fujita, C.K.; Zhao, M.; Lam, K.S.; Kurth, M.J.; Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. Proinflammatory Secreted Phospholipase A2 Type IIA (SPLA-IIA) Induces Integrin Activation through Direct Binding to a Newly Identified Binding Site (Site 2) in Integrins Avβ3, A4β1, and A5β1. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takada, Y.; Fujita, M. Secreted Phospholipase A2 Type IIA (SPLA2-IIA) Activates Integrins in an Allosteric Manner. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 925, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saegusa, J.; Akakura, N.; Wu, C.Y.; Hoogland, C.; Ma, Z.; Lam, K.S.; Liu, F.T.; Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. Pro-Inflammatory Secretory Phospholipase A2 Type IIA Binds to Integrins Avβ3 and A4β1 and Induces Proliferation of Monocytic Cells in an Integrin-Dependent Manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 26107–26115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munger, J.S.; Huang, X.; Kawakatsu, H.; Griffiths, M.J.D.; Dalton, S.L.; Wu, J.; Pittet, J.F.; Kaminski, N.; Garat, C.; Matthay, M.A.; et al. The Integrin Alpha v Beta 6 Binds and Activates Latent TGF Beta 1: A Mechanism for Regulating Pulmonary Inflammation and Fibrosis. Cell 1999, 96, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henderson, N.C.; Sheppard, D. Integrin-Mediated Regulation of TGFβ in Fibrosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1832, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheppard, D. The Role of Integrins in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2008, 17, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goodwin, A.; Jenkins, G. Role of Integrin-Mediated TGFbeta Activation in the Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2009, 37, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milad, N.; Morissette, M.C. Revisiting the Role of Pulmonary Surfactant in Chronic Inflammatory Lung Diseases and Environmental Exposure. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2021, 30, 210077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.L.; Rostami, M.R.; LeBlanc, M.; Kaner, R.J.; O’Beirne, S.L.; Mezey, J.G.; Leopold, P.L.; Quast, K.; Visvanathan, S.; Fine, J.S.; et al. Dysregulation of Club Cell Biology in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, T.; Yanagihara, T.; Suzuki, K.; Hamada, N.; Tsubouchi, K.; Ogata-Suetsugu, S.; Mikumo, H.; Ikeda-Harada, C.; Maeyama, T.; Kuwano, K.; et al. Depletion of Club Cells Attenuates Bleomycin-Induced Lung Injury and Fibrosis in Mice. J. Inflamm. 2017, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, I.V.; Coldren, C.D.; Leach, S.M.; Seibold, M.A.; Murphy, E.; Lin, J.; Rosen, R.; Neidermyer, A.J.; McKean, D.F.; Groshong, S.D.; et al. Expression of Cilium-Associated Genes Defines Novel Molecular Subtypes of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Thorax 2013, 68, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duncan Hite, R.; Grier, B.L.; Moseley Waite, B.; Veldhuizen, R.A.; Possmayer, F.; Yao, L.J.; Seeds, M.C. Surfactant Protein B Inhibits Secretory Phospholipase A2 Hydrolysis of Surfactant Phospholipids. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2012, 302, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Curfs, D.M.J.; Ghesquiere, S.A.I.; Vergouwe, M.N.; Van Der Made, I.; Gijbels, M.J.J.; Greaves, D.R.; Verbeek, J.S.; Hofker, M.H.; De Winther, M.P.J. Macrophage Secretory Phospholipase A2 Group X Enhances Anti-Inflammatory Responses, Promotes Lipid Accumulation, and Contributes to Aberrant Lung Pathology. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 21640–21648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mak, T.W.; Saunders, M.E.; Jett, B.D. (Eds.) Innate Immunity. In Primer to the Immune Response; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 55–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Oslund, R.C.; Bollinger, J.G.; Henderson, W.R.; Santana, L.F.; Altemeier, W.A.; Gelb, M.H.; Hallstrand, T.S. Eosinophil Cysteinyl Leukotriene Synthesis Mediated by Exogenous Secreted Phospholipase A2 Group X. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 41491–41500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kikawada, E.; Bonventre, J.V.; Arm, J.P. Group V Secretory PLA2 Regulates TLR2-Dependent Eicosanoid Generation in Mouse Mast Cells through Amplification of ERK and CPLA2α Activation. Blood 2007, 110, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruipérez, V.; Astudillo, A.M.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Coordinate Regulation of TLR-Mediated Arachidonic Acid Mobilization in Macrophages by Group IVA and Group V Phospholipase A2s. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 3877–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajkumar, R.; Konishi, K.; Richards, T.J.; Ishizawar, D.C.; Wiechert, A.C.; Kaminski, N.; Ahmad, F. Genomewide RNA Expression Profiling in Lung Identifies Distinct Signatures in Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Secondary Pulmonary Hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2010, 298, H1235–H1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruscitti, F.; Ravanetti, F.; Essers, J.; Ridwan, Y.; Belenkov, S.; Vos, W.; Ferreira, F.; KleinJan, A.; Van Heijningen, P.; Van Holsbeke, C.; et al. Longitudinal Assessment of Bleomycin-Induced Lung Fibrosis by Micro-CT Correlates with Histological Evaluation in Mice. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2017, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, N.; Hayashi, H.; Shimamura, M.; Baba, S.; Yoshida, S.; Morishita, R.; Rakugi, H.; Nakagami, H. Prevention of Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis by a RANKL Peptide in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Rhee, C.K.; Kim, T.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, S.H.; Yoon, H.K.; Kim, S.C.; Lee, S.Y.; Kwon, S.S.; Kim, K.H.; et al. Effect of Pravastatin on Bleomycin-Induced Acute Lung Injury and Pulmonary Fibrosis. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2010, 37, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sul, O.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, T.; Seo, K.W.; Cha, H.J.; Kwon, B.; Ahn, J.J.; Cho, Y.S.; Oh, Y.M.; Jegal, Y.; et al. GSPE Protects against Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice via Ameliorating Epithelial Apoptosis through Inhibition of Oxidative Stress. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 8200189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatomi, M.; Hisada, T.; Ishizuka, T.; Koga, Y.; Ono, A.; Kamide, Y.; Seki, K.; Aoki-Saito, H.; Tsurumaki, H.; Sunaga, N.; et al. 17(R)-Resolvin D1 Ameliorates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice. Physiol. Rep. 2015, 3, e12628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharaee-Kermani, M.; Hatano, K.; Nozaki, Y.; Phan, S.H. Gender-Based Differences in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 1593–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bauer, Y.; Tedrow, J.; De Bernard, S.; Birker-Robaczewska, M.; Gibson, K.F.; Guardela, B.J.; Hess, P.; Klenk, A.; Lindell, K.O.; Poirey, S.; et al. A Novel Genomic Signature with Translational Significance for Human Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 52, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewin, M.; Samuel, S.; Merkel, J.; Bickler, P. Varespladib (LY315920) Appears to Be a Potent, Broad-Spectrum, Inhibitor of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 and a Possible Pre-Referral Treatment for Envenomation. Toxins 2016, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lewin, M.R.; Williams, D.J.; Lomonte, B. Varespladib (LY315920) and Methyl Varespladib (LY333013) Abrogate or Delay Lethality Induced by Presynaptically Acting Neurotoxic Snake Venoms. Toxins 2020, 12, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volwerk, J.J.; Pieterson, W.A.; de Haas, G.H. Histidine at the Active Site of Phospholipase A2. Biochemistry 1974, 13, 1446–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, Y.; Kaminski, N.E. Phospholipase A2 Inhibitors P-Bromophenacyl Bromide and Arachidonyl Trifluoromethyl Ketone Suppressed Interleukin-2 (IL-2) Expression in Murine Primary Splenocytes. Arch. Toxicol. 1999, 73, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baarsma, H.A.; Engelbertink, L.H.J.M.; Van Hees, L.J.; Menzen, M.H.; Meurs, H.; Timens, W.; Postma, D.S.; Kerstjens, H.A.M.; Gosens, R. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK-3) Regulates TGF-Β1-Induced Differentiation of Pulmonary Fibroblasts. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 169, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurrieri, C.; Piazza, F.; Gnoato, M.; Montini, B.; Biasutto, L.; Gattazzo, C.; Brunetta, E.; Cabrelle, A.; Cinetto, F.; Niero, R.; et al. 3-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-4-(1-Methyl-1H-Indol-3-Yl)-1H-Pyrrole-2,5-Dione (SB216763), a Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Inhibitor, Displays Therapeutic Properties in a Mouse Model of Pulmonary Inflammation and Fibrosis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 332, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| S. No. | Pathway | Normalized Enrichment Score | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | TGF-beta signaling pathway | 1.9917 | <2.2 ×10−16 |
| 2. | Longevity regulating pathway | 1.8124 | <2.2 × 10−16 |
| 3. | Legionellosis | 1.8419 | 0.0011287 |
| 4. | AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications | 1.7161 | 0.0063559 |
| 5. | IL-17 signaling pathway | 1.7311 | 0.0066445 |
| 6. | Antigen processing and presentation | 1.7329 | 0.0081112 |
| 7. | ECM-receptor interaction | 1.7329 | 0.0086674 |
| 8. | Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism | 1.6986 | 0.0093085 |
| 9. | Arachidonic acid metabolism | 1.7057 | 0.010127 |
| 10. | Amoebiasis | 1.7010 | 0.011737 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaiswal, A.; Rehman, R.; Dutta, J.; Singh, S.; Ray, A.; Shridhar, M.; Jaisankar, J.; Bhatt, M.; Khandelwal, D.; Sahoo, B.; et al. Cellular Distribution of Secreted Phospholipase A2 in Lungs of IPF Patients and Its Inhibition in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice. Cells 2023, 12, 1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12071044
Jaiswal A, Rehman R, Dutta J, Singh S, Ray A, Shridhar M, Jaisankar J, Bhatt M, Khandelwal D, Sahoo B, et al. Cellular Distribution of Secreted Phospholipase A2 in Lungs of IPF Patients and Its Inhibition in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice. Cells. 2023; 12(7):1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12071044
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaiswal, Ashish, Rakhshinda Rehman, Joytri Dutta, Sabita Singh, Archita Ray, Malathy Shridhar, Jaswant Jaisankar, Manas Bhatt, Dikshit Khandelwal, Bandya Sahoo, and et al. 2023. "Cellular Distribution of Secreted Phospholipase A2 in Lungs of IPF Patients and Its Inhibition in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice" Cells 12, no. 7: 1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12071044
APA StyleJaiswal, A., Rehman, R., Dutta, J., Singh, S., Ray, A., Shridhar, M., Jaisankar, J., Bhatt, M., Khandelwal, D., Sahoo, B., Ram, A., & Mabalirajan, U. (2023). Cellular Distribution of Secreted Phospholipase A2 in Lungs of IPF Patients and Its Inhibition in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice. Cells, 12(7), 1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12071044






